CLRS 205 - Cardiovascular & Interventional Radiology
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Primary purpose of cardiovascular imaging?
Anatomical detail
Primary purpose of interventional radiology/angiography?
Diagnose and Treatment
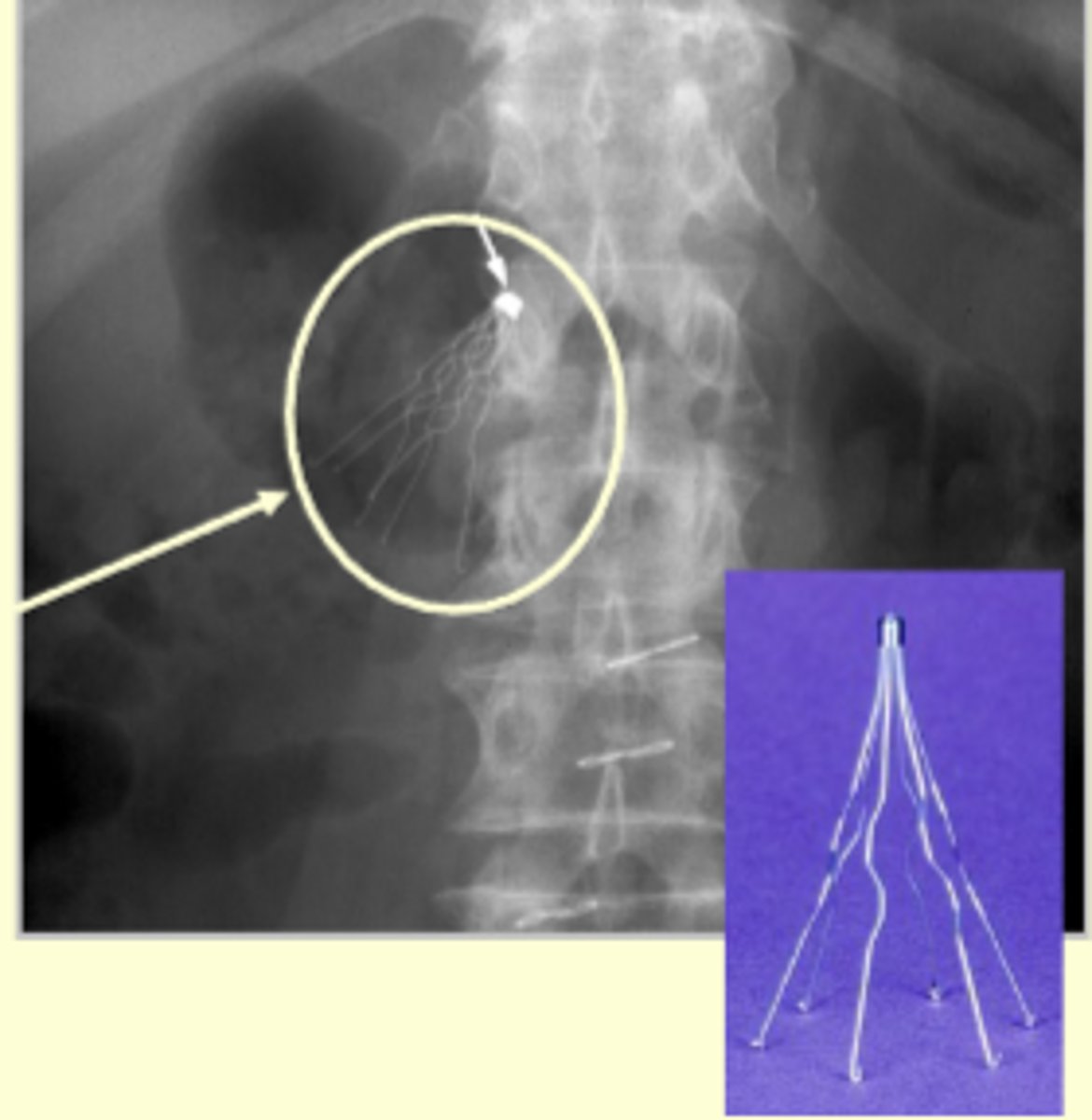
What is angiography?
The radiographic exam of blood vessels and a method of opening obstructed blood vessels.
How is angiography performed?
A long, thin tube (catheter) is threaded through the vascular system to the area of interest, which then injects contrast in the vessels.
What type of contrast media is used in angiography?
A water-soluble, iodinated contrast media.
What conditions are required during the angiography procedure?
The procedure is performed under sterile conditions, similar to a surgical suite.
Where is the catheter typically inserted?
In the femoral artery or vein, called Seldinger technique
What imaging technique is used to observe the movement of the catheter?
Fluoroscopy.
What is the purpose of injecting contrast media during catheterization?
To absorb more x-rays than surrounding tissue, providing visualization of the filled vessels.
How are the images of the vessels recorded during the procedure?
As a series of images, which may include still images, videotape, or motion filming (cine).
What does the series of images demonstrate during catheterization?
The initial filling of the vessels through their emptying.
What is cardiac catheterization?
A medical procedure that examines the vessels and chambers of the heart.
How is cardiac catheterization similar to angiography?
Both procedures involve the introduction and placement of a catheter, iodinated contrast media, and performed in sterile environment.
What pathologies can interventional procedures treat?
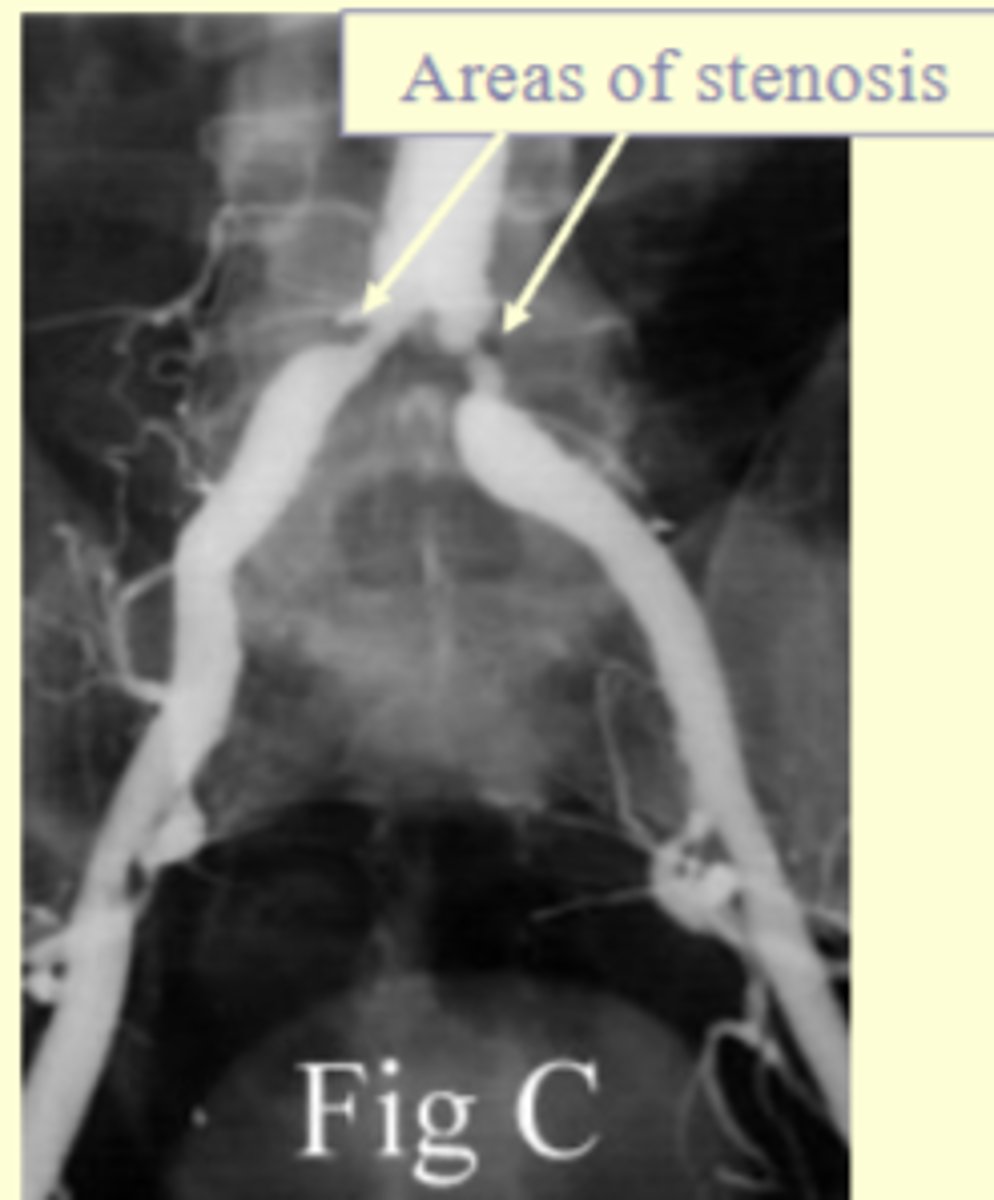
- stenosis (abnormal narrowing) of a vessel
- aneurysm (ballooning of a vessel)
- arteriovenous malformation (AVM) (an overgrown tangle of blood vessels
- thrombolysis (clotting)
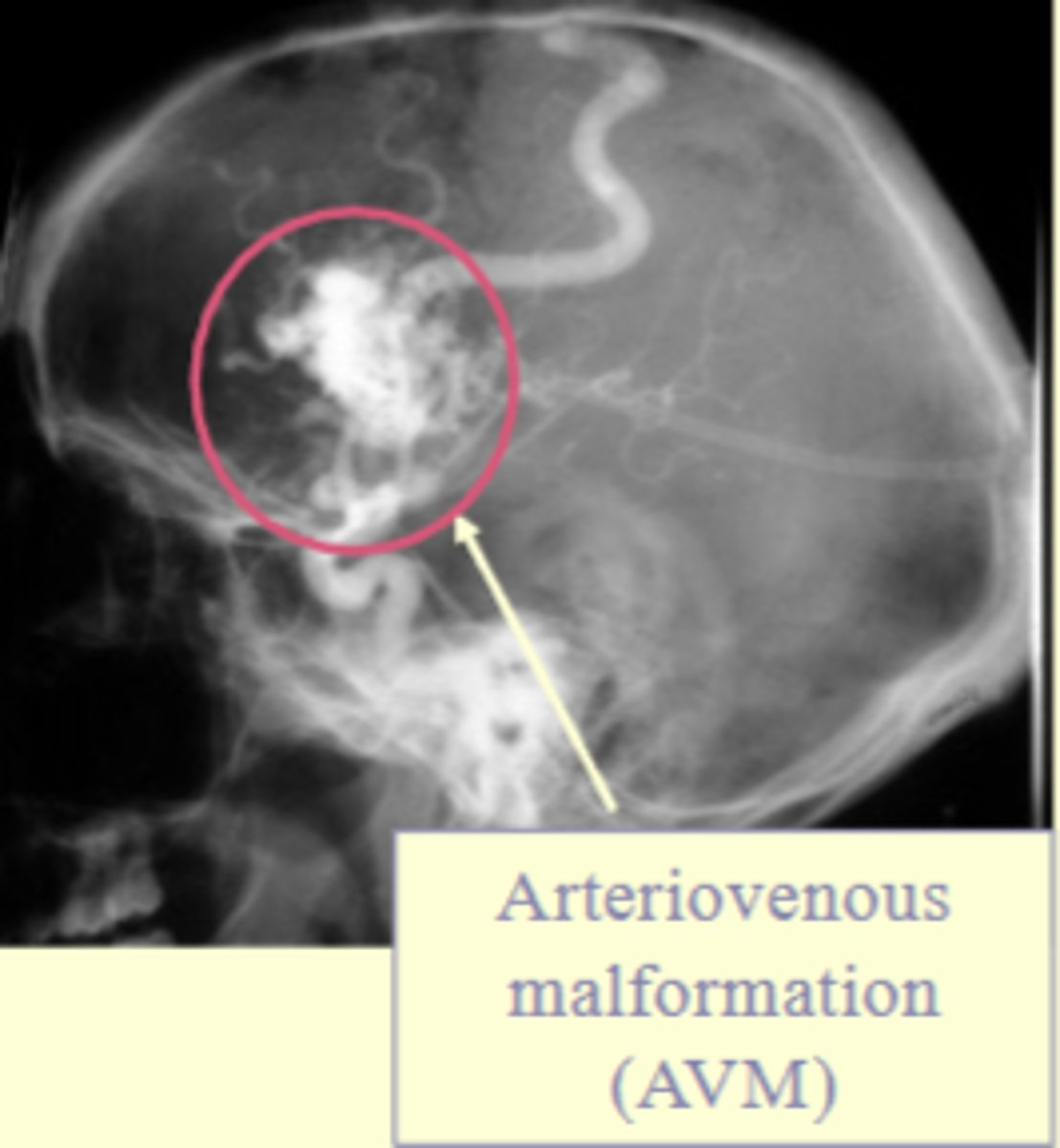
What is the benefit of interventional procedures in angiography?
They allow the patient to avoid or delay surgical procedures.
What is the most common interventional procedure?
Balloon Angioplasty
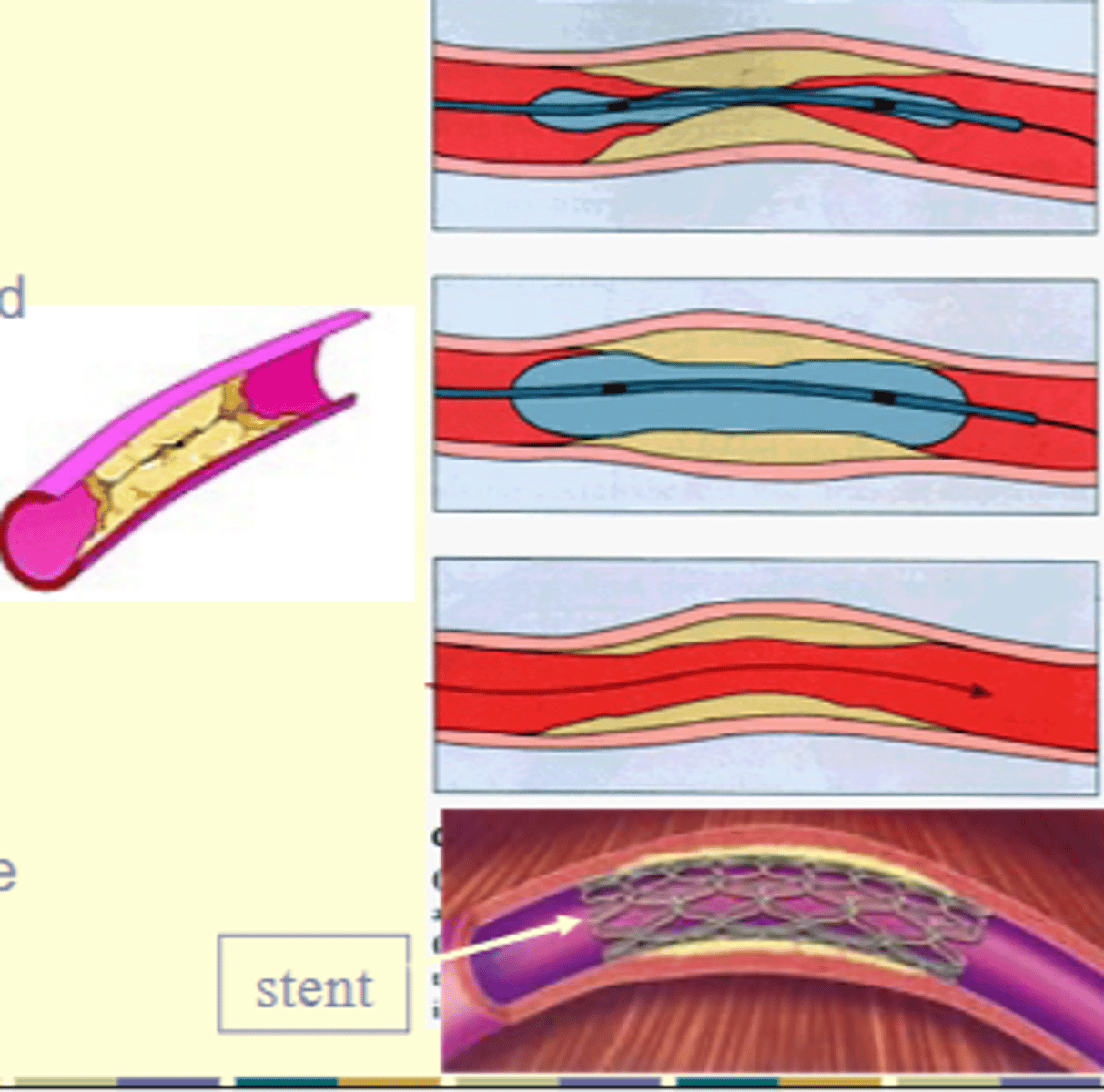
What condition does balloon angioplasty primarily address?
Stenosis due to atherosclerosis (fatty deposits in the artery); alleviates stenosis and restores blood flow
How is balloon angioplasty performed?
A deflated catheter is threaded into the stenotic area, inflated to open the vessel, and then removed after deflation.
What is often placed in the vessel after balloon angioplasty to prevent closure?
A stent (a mesh tube)
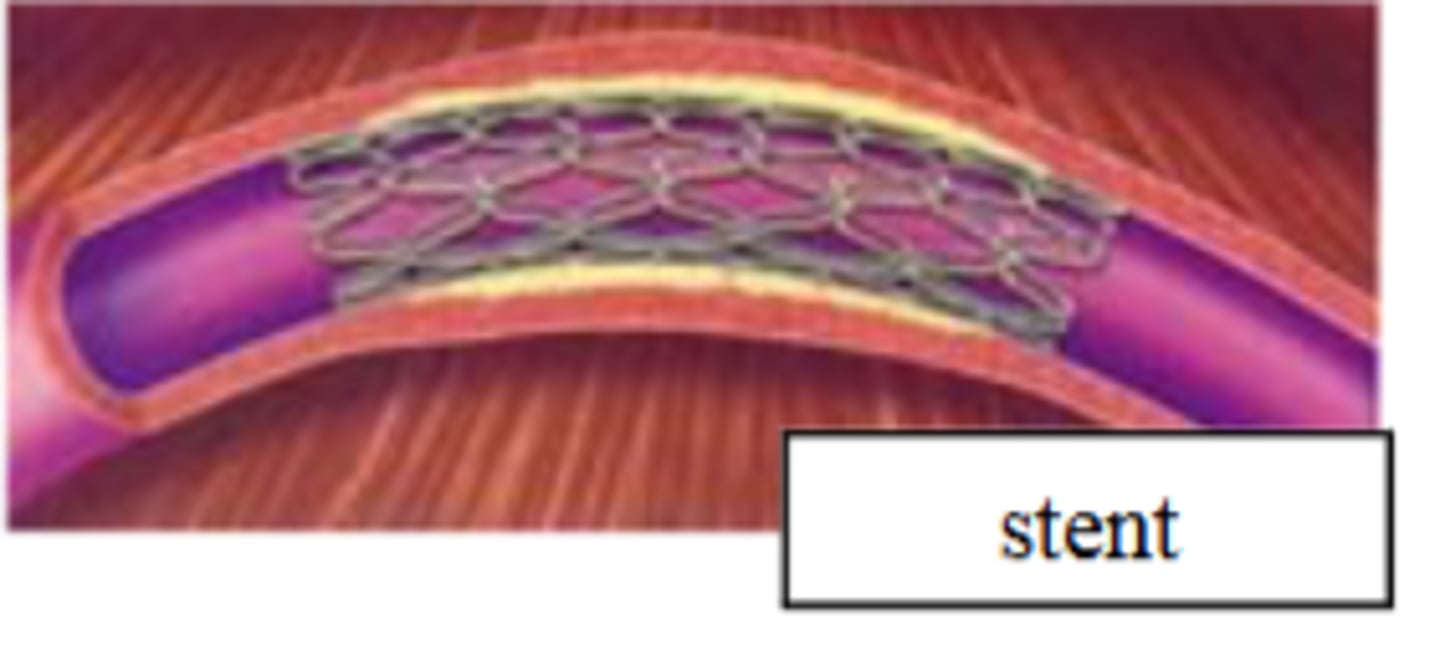
In which arteries is balloon angioplasty frequently performed?
Coronary arteries, especially after a heart attack
What other procedures can be performed alongside angiography and cardiac catheterization?
Many interventional procedures can be performed in conjunction with them.
What major equipment is used for interventional radiology/cardiovascular imaging?
Fluoroscopy, C-arm, needles and hammers, catheters, guide wires, computer, and heart monitoring/oximetry equipment
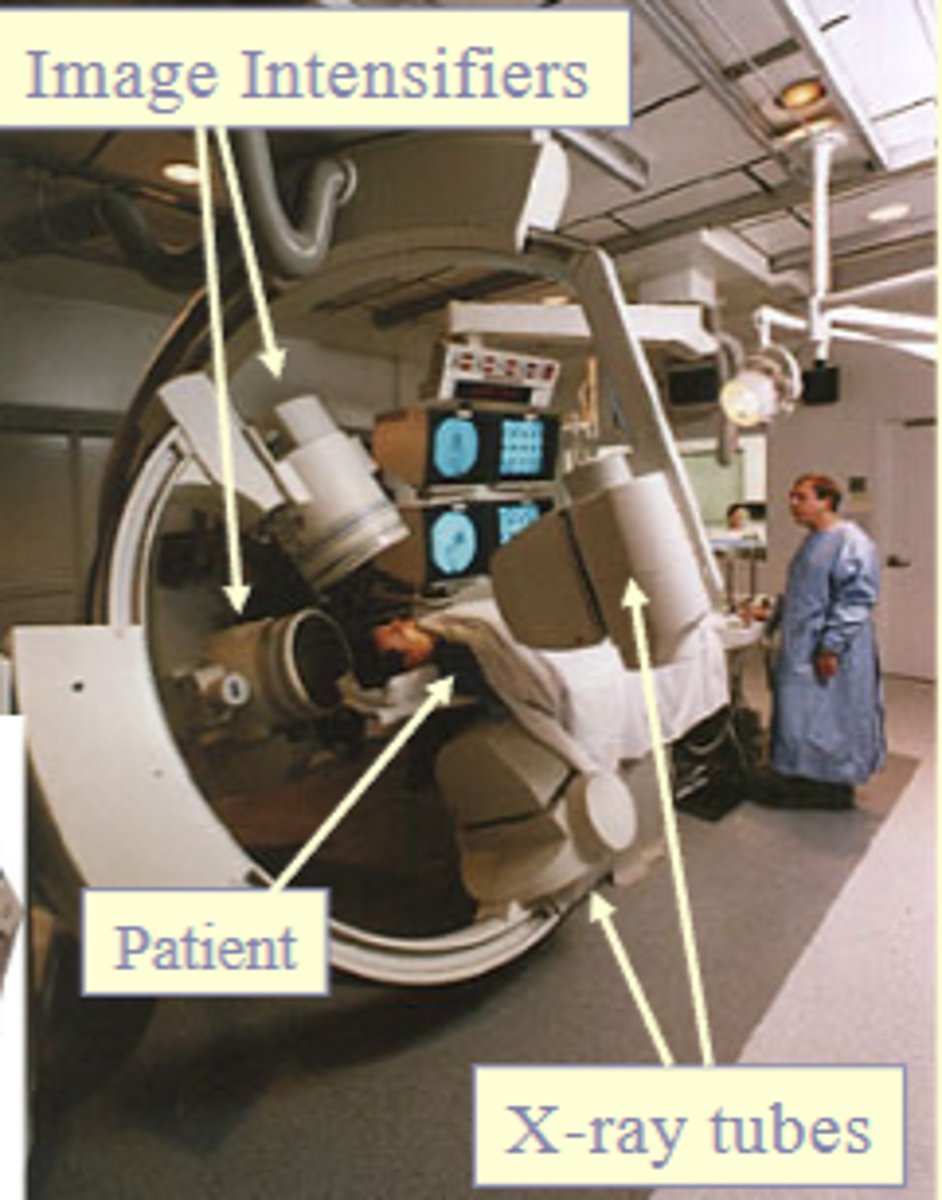
What type of fluoroscopy is commonly used in cardiovascular imaging?
Digital fluoroscopy.
What technology does digital fluoroscopy utilize for image processing?
A fast, powerful computer to store and manipulate images.
What is Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA)?
A technique that requires a digital system to subtract bony and soft tissue anatomy from images, leaving only contrast-filled vessels.
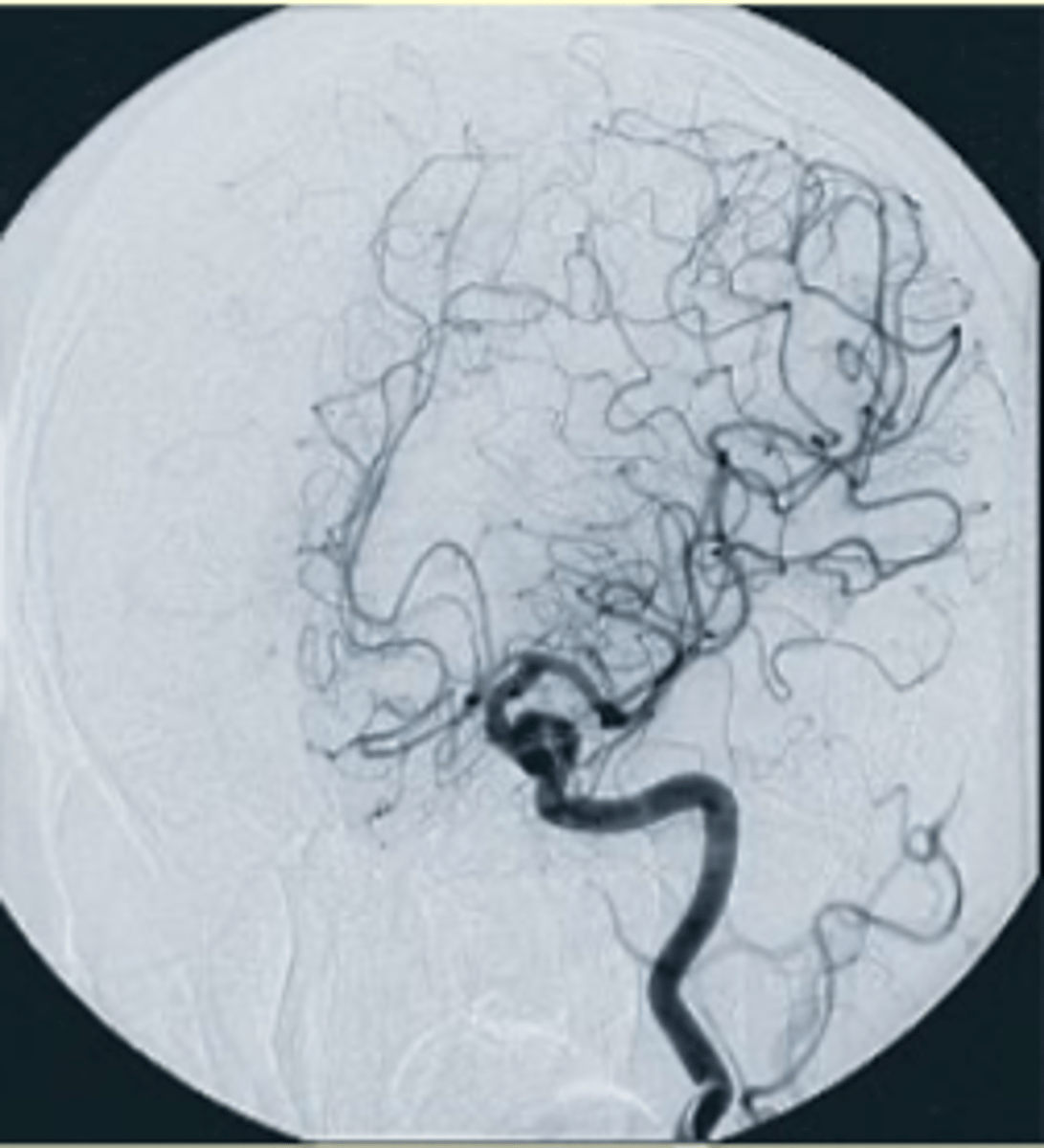
What are catheters used for during angiographic and cardiac catheterization procedures?
They are used to visualize blood vessels and perform interventions, with types and sizes depending on the vessel and patient size.
What is the purpose of a guide wire in catheterization procedures?
The guide wire helps the physician thread the catheter through the patient's vasculature by providing support and flexibility.
When is the guide wire removed during the catheterization process?
The guide wire is removed prior to the injection of contrast material.
What is monitored during cardiac catheterization?
The patient's ECG, pressure in the vessels, and oxygen level of the blood.
What is the purpose of monitoring during cardiac catheterization?
To help diagnose the patient's condition.
What areas of the body can angiography be performed on?
Most major and minor blood vessels in the head, neck, chest, abdomen, pelvis, and extremities. Lymphatic, urinary, and biliary systems.
What procedure is used to image the heart and associated vessels?
Cardiac catheterization.
What age groups benefit from cardiovascular and interventional studies?
Patients of all ages, including newborn infants and adults.
What procedure is often performed on newborn infants with cardiac abnormalities?
Cardiac catheterizations.
What conditions do most adults have when undergoing cardiac catheterizations?
Angina (chest or heart pain) or a history of heart attack.
What type of patients might undergo angiographic procedures?
Injured patients to assess if blood vessels have been damaged.
What conditions might prompt patients to have studies done for AVM?
Patients who have suffered strokes or have symptoms indicating an AVM.
Role of cardiovascular technologist
- Scrub in and assist physician
- Circulate in room during procedure
- Position patient and adjust imaging variables
- Maintain radiation safety
- Work closely with doctors and nurses as a multidisciplinary team
- Operate highly technical equipment under stressful conditions
- Monitor patient condition
- Prepare contrast media
What contrast media should be used if patient is allergic to iodine contrast?
CO2 Carbon dioxide
(T/F) The patient is sedated under general anesthesia during angioplasty
True
(T/F) Interventional radiology only uses CT and MRI
False, it uses all radiologic modalities