UC Davis PSC 001 - Midterm 1
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
Critical Thinking
systematically questions and evaluates information using well-supported evidence: weighs facts, considers source, uses logic and reasoning to see whether information makes sense, considers alternate explanations
Dualism
(Descartes) the presumption that mind and body are two distinct entities that interact with one another, and in some cases are intertwined
Structuralism
(Wundt) an approach to psychology based on the idea that conscious experience can be broken down into its basic underlying components
Functionalism
(James) an approach to psychology concerned with the purpose/function of behavior
Gestalt
(Koffka) the whole of personal experience is different from the sum of its parts
Psychoanalysis
(Freud) a method that attempts to bring the content of the unconscious into conscious awareness so that conflicts can be revealed
Behaviorism
(Watson) a psychological approach that emphasizes the role of environmental forces in producing observable behavior
Cognitive Psychology
the study of mental functions such as intelligence, thinking, language, memory, and decision making
Cognitive Neuroscience
the study of neural mechanisms underlying thought, learning, perception, language, and memory
Social Psychology
the study of how people influence other people's thoughts, feelings, and actions
Evolutionary Psychology
this field attempts to explain mental traits as products of natural selection
The Case Study of Genie
A girl who suffered extreme privation, her parents left her in a basement, gave her food and prevented her from making any form of attachment. She was beaten for making sounds. Didn't have toys or any other children to interact with.
Although she received extensive teaching, she had trouble speaking clearly at an adult-level, showing the consequences of extreme social isolation on language development and an existence of the critical period for language.
Stages of Prenatal Development
conception-birth
1. zygote: conception-2 weeks
2. embryo: 2 weeks-2 months (forming organs)
3. fetus: 2 months-birth (organs formed, heart beats)
Teratogens
agents from the environment that can reach the embryo or fetus during prenatal development and cause harm
Brain Development
by age 4, the human _____ has grown to about 80% of adult size
Development of Frontal Cortex and Limbic Systems in Adolescents
the _______ ______ of the brain is not fully developed until the early 20s, so adolescents have a difficult time thinking critically about the consequences of their actions or planning; the _______ ______ is associated with higher order thinking, problem solving, and planning
the ______ ______ matures more quickly than the former; the ______ ______ is the neural basis for mood, emotion, and drives
this disconnect results in teenagers being more likely to act on their impulses.
Puberty
the period of sexual maturation, during which a person becomes capable of reproducing; timing varies depending on biological and environmental influences
Erikson's Theory of Psychosocial Development
throughout every stage of life, an individual must face a crisis that they must overcome; for adolescents, they must develop an adult identity (gender/ ethnic) or risk role confusion
Effects of Aging on Cognition
steady decline in overall health, memory, and mental processing, as the frontal lobes of the brain shrink throughout adulthood, but intelligence is unchanged
people who engage in physical, social, and mental activities tend to show less cognitive decline as they age
Nature and Nurture
genetics and environment; they influence one another and are inseparable; these two factors have a hand in the development of individuals
Genotype
the genetic material we inherit from our parents
Phenotype
the observable expression of the genotype, including bodily characteristics and behavior
Environment
every aspect of the individual and his or her surroundings (including prenatal experience) other than the genes
Epigenetics
how genes are expressed depending on environment
Mendelian Inheritance
a sort of gene inheritance
dominant gene: expressed whenever it is present in either parent
recessive gene: expressed only when it is matched with a similar gene from other parent
Polygenic Inheritance
inheritance in which traits are governed by more than one gene
Sensory Neurons
these neurons detect information from the physical world and pass that information to the brain
Motor Neurons
these neurons direct muscles to contract or relax, thereby producing movement
Neuron Structure
dendrite → cell body → axon → myelin sheath → terminal buttons → synapse
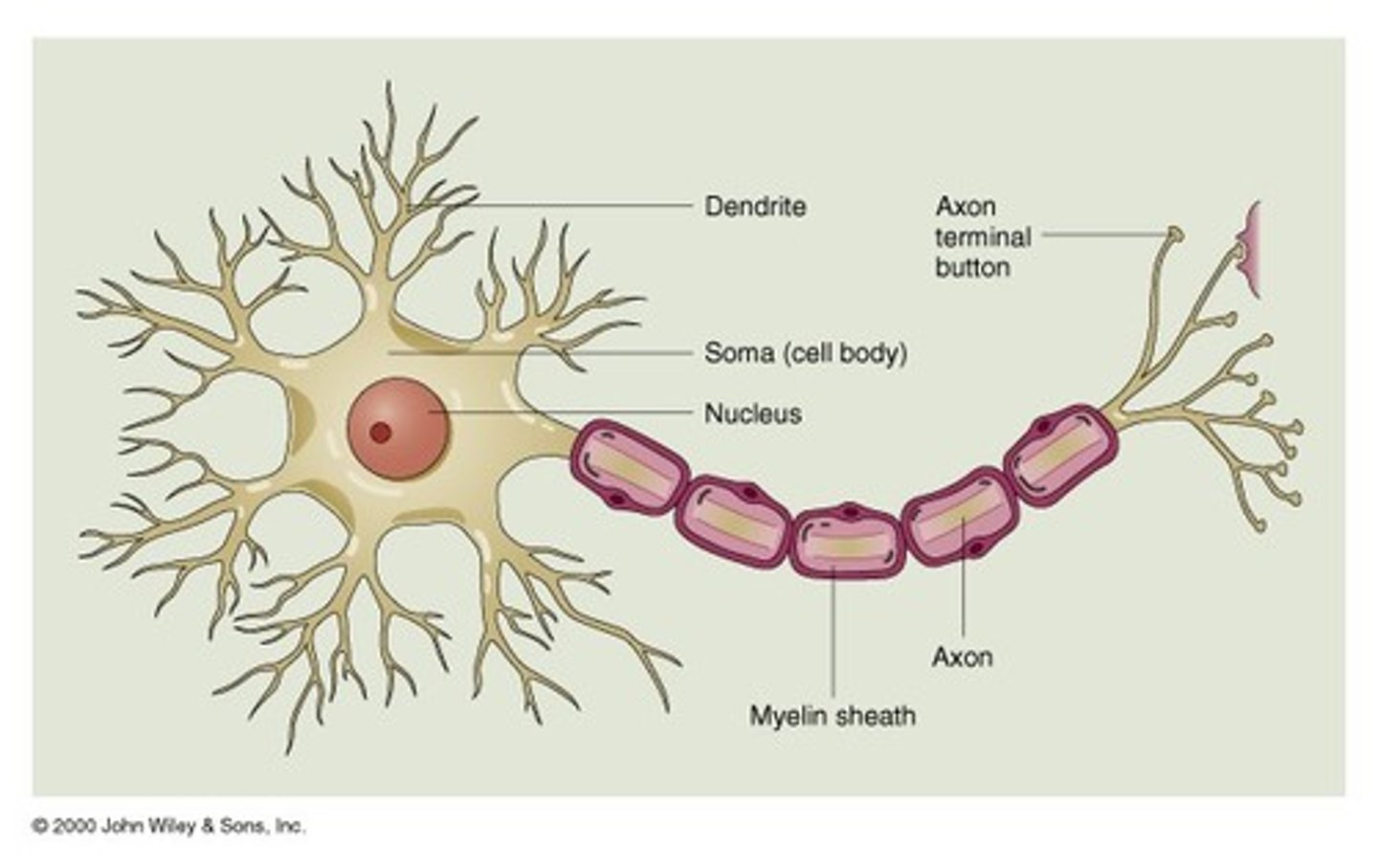
Neural Communication
neurons are powered by electrical impulses & communicate with other neurons via chemical signals (neurotransmitters)
Myelination
the process by which axons become coated with ______, a fatty substance that speeds the transmission of nerve impulses from neuron to neuron; made up of glial cells; encases and insulates certain axons
Synaptic Transmission
1. action potentials cause neurotransmitters to be released by the presynaptic neuron
2. travel across the synapse
3. bind to specific receptors on the postsynaptic neurons' dendrites
4. continues to have an effect until somehow deactivated
Serotonin
a type of neurotransmitter that plays an important role in our experience of different moods
Dopamine
a type of neurotransmitter that plays an important role in our experience of rewards
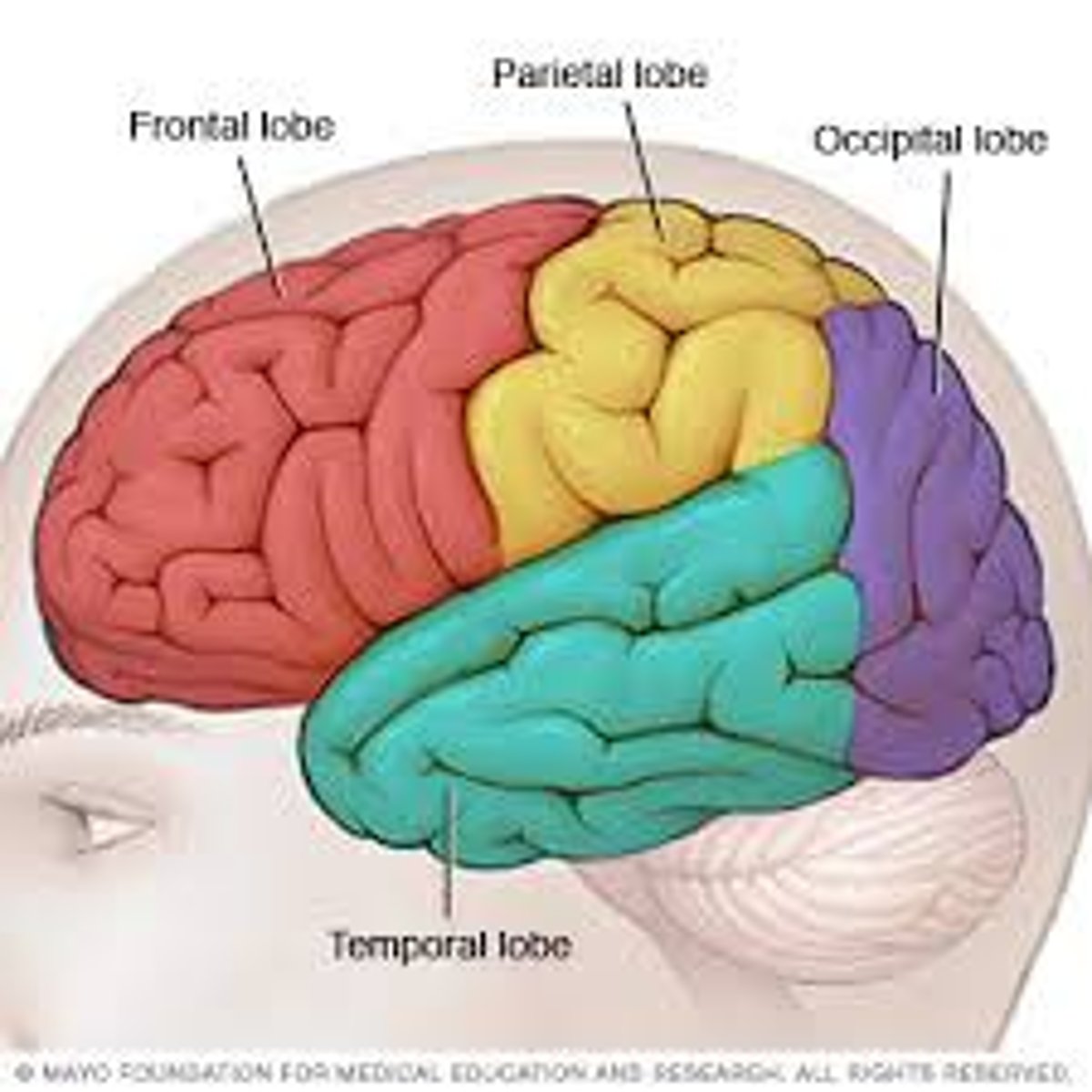
Cerebral Cortex
occipital lobe: vision (eyes on the back of your head)
temporal lobe: hearing, memory (right next to your ears)
frontal lobe: thought, planning, movement (will face any challenge head on)
parietal lobe: touch, spatial relations (presence and proximity to stimulus)
Corpus Callosum
this section of the brain connects the right and left hemispheres and allows information to flow between them
Autonomic Nervous System
a part of the peripheral nervous system that regulates the body's internal environment through the sympathetic division and parasympathetic division
stimulates glands and maintains internal organs; carries signals from glands and organs to central nervous system
Sympathetic Division
the part of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body to deal with perceived threats; fight or flight
Parasympathetic Division
the part of the autonomic nervous system that generally conserves bodily resources; resting, peaceful
Plasticity
the brain's capacity for modification, as evident in brain reorganization following damage (especially in children) and in experiments on the effects of experience on brain development
What Makes a Good Theory?
supported by data, falsifiable, parsimonious, experiment is stable over numerous trials, leading back to the theory
Scientific Method
systematic procedure for observing & measuring phenomena to answer empirical questions
1. theory: an explanation or model of how a phenomenon works
2. hypothesis: a specific, testable prediction about the outcome that would best support the theory
3. research: the systematic and careful collection of data
Descriptive Studies
aka observational studies; involve observing & noting the behavior of people or other animals to provide a systematic & objective analysis of the behavior
Correlational Studies
examine how variables are naturally related in the real world, without any attempt by the researcher to alter them; researchers cannot draw causal conclusions from correlational studies; correlation≠causation
Experimental Studies
study that tests causal hypotheses by measuring (dependent variable) and manipulating (independent variable) variables
Confound
a factor other than the independent variable that may influence the results
Reliability
extent to which a measure is stable & consistent over time
Validity
extent to which study actually measures what it intends to measure
Internal Validity
the degree to which the effects observed in an experiment are due to the manipulation
External Validity
the degree to which the findings of a study generalize to the real world
Correlations
how two variables relate to each other
positive ___________: both variables either increase or decrease together
negative ___________: as one variable increases, the other decreases
___________ coefficient: a number between −1 and +1 calculated so as to represent the linear dependence of two variables
Observer Bias
systematic errors in observation that occur because of an observer's expectations; the observer seeks to find data that fits their theory
Random Assignment
each participant has an equal chance of being assigned to any level of the independent variable, to ensure preexisting differences are randomly distributed between conditions (during experiment)
Random Sampling
everyone in the population has an equal chance of being chosen to participate (before the experiment)
Significance Testing
how likely differences between groups and relationships between variables occur by chance
Sensation
the sense organs' detection of external stimulus, their response, & the transmission of these responses to the brain
Perception
the brain's processing, organization, & interpretation of sensory signals; results in internal representations of the stimuli that form a conscious experience of the world
Perception Pathway
sensory receptors detect specific physical or chemical stimulation → connecting neurons → thalamus → primary sensory cortex, where impulse is interpreted
exception: smell has the most direct route to the brain—doesn't go through the thalamus
Absolute Threshold
the minimum intensity of stimulation that must occur before you experience a sensation (stimuli correctly detected 50% of the time)
Signal Detection Theory
detection of a faint stimulus requires a judgment based on a subjective interpretation of ambiguous information
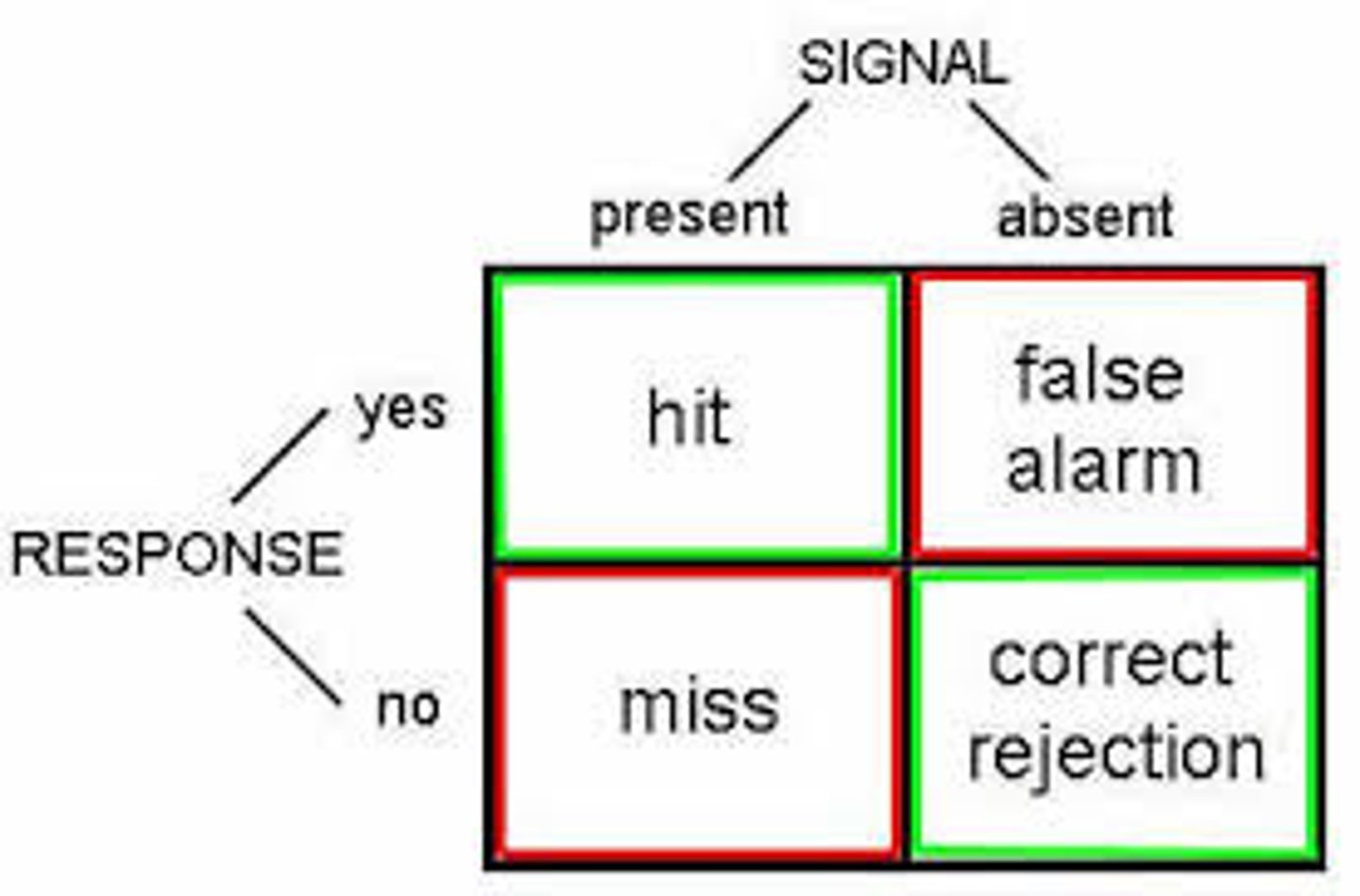
Bottom-up Processing
perception based on the physical features of the stimulus
Top-down Processing
how knowledge, expectations, or past experiences shape the interpretation of sensory information
Visual Pathway
light → cornea → lens → retina → photoreceptors (rods, cones, ganglion cells)
Hearing
hair cells are the sensory receptors for...
Taste
taste buds are the sensory receptors for...
Smell
olfactory epitheliums are the sensory receptors for...
Touch
skin is the sensory receptor for...
Vision
photoreceptors (rods and cones) found in the retina are the sensory receptor for...
Fast Pain Fibers
sharp, fast pain; useful for immediate protection
Slow Pain Fibers
chronic, dull, steady pain; useful for recuperation and spinal cord processing