SNAB TOPIC 1- Lifestyle, health and risk
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
1.1 Understand why many animals have a heart and circulation
Mass transport to overcome limitations of diffusion in meeting the requirements of organisms.
limitations of diffusion: for organisms with low SA:V ratio, it is slow as diffusion distance is large. takes time for all cells to receive required chemicals
1.2 Understand the importance of water as a solvent in transport, including its dipole nature.
Water is a polar molecule
Because of its dipole nature it is polar (uneven distribution of charge)
Cohesion (hydrogen bonds with other h2o molecules.)
Adhesion (hydrogen bonds with other molecules)
Good solvent (it can surround charged/polar molecules)
High specific heat capacity- large amount of energy needed to break many hydrogen bonds
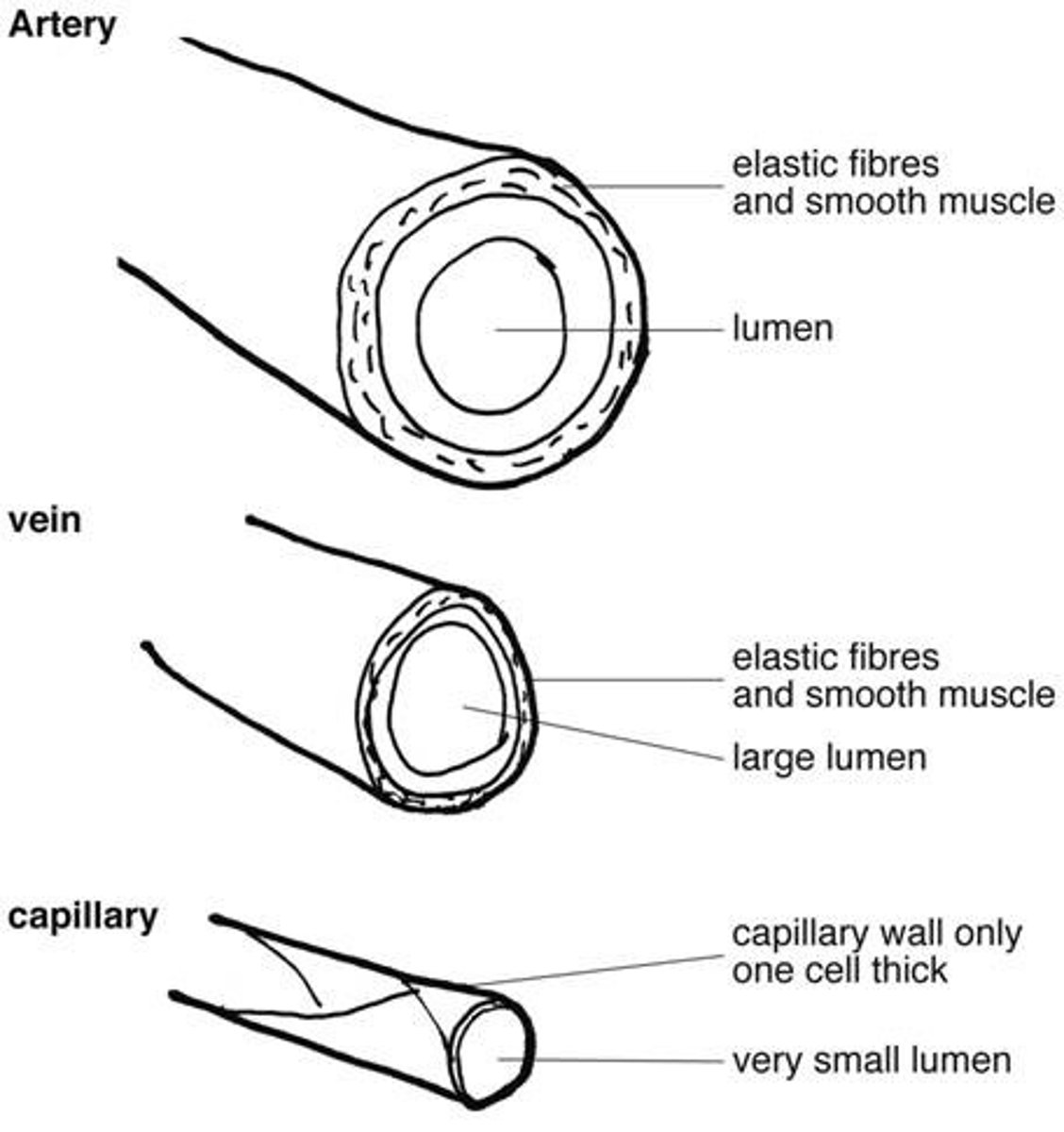
1.3 Understand how the structures of blood vessels (capillaries, arteries and veins) relate to their functions.
Arteries
•Small lumen -maintain high blood pressure
•Smooth endothelial lining - less resistance
•Thick layer of smooth muscle - contracts and relaxes to constrict/dilate blood vessels
•More Elastic fibres- stretch and recoil
•More Collagen fibres - strength and support
Function:
Carries oxygenated blood to body tissues
Veins
•Large lumen- Minimal resistance to flow
•Thinner layer of smooth muscle - blood is instead pushed by skeletal muscle contractions & passively by blood pressure
•Thinner elastic fibre layers- for larger lumen and so that blood can be pushed by skeletal muscle contraction
•Reduced collagen fibres- same as above
•Valves- Prevents backflow of blood
Function:
Carries deoxygenated blood back to the heart (except the pulmonary vein carrying oxygenated blood FROM the lungs)
Capillaries
•One cell-thin endothelium - allows easy gas exchange
•Narrow lumen - slows blood flow so that gaseous exchange happens over an even distribution.
•Very small - can fit in between cells
Function:
Allow gas exchange between cells
1.3 Structure of capillaries, arteries and veins [IMAGE]
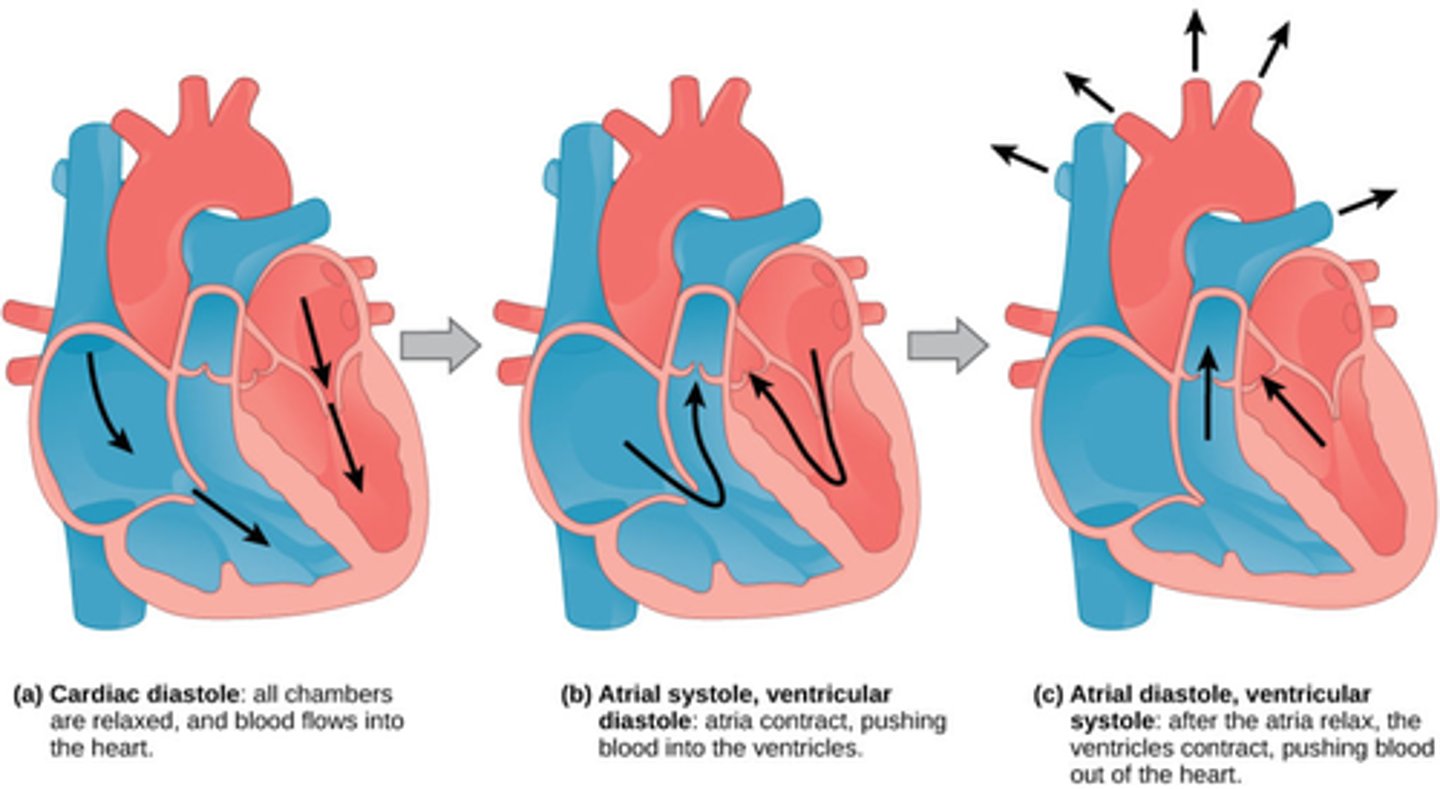
1.4 i) Know the cardiac cycle (atrial systole, ventricular systole and cardiac
diastole)
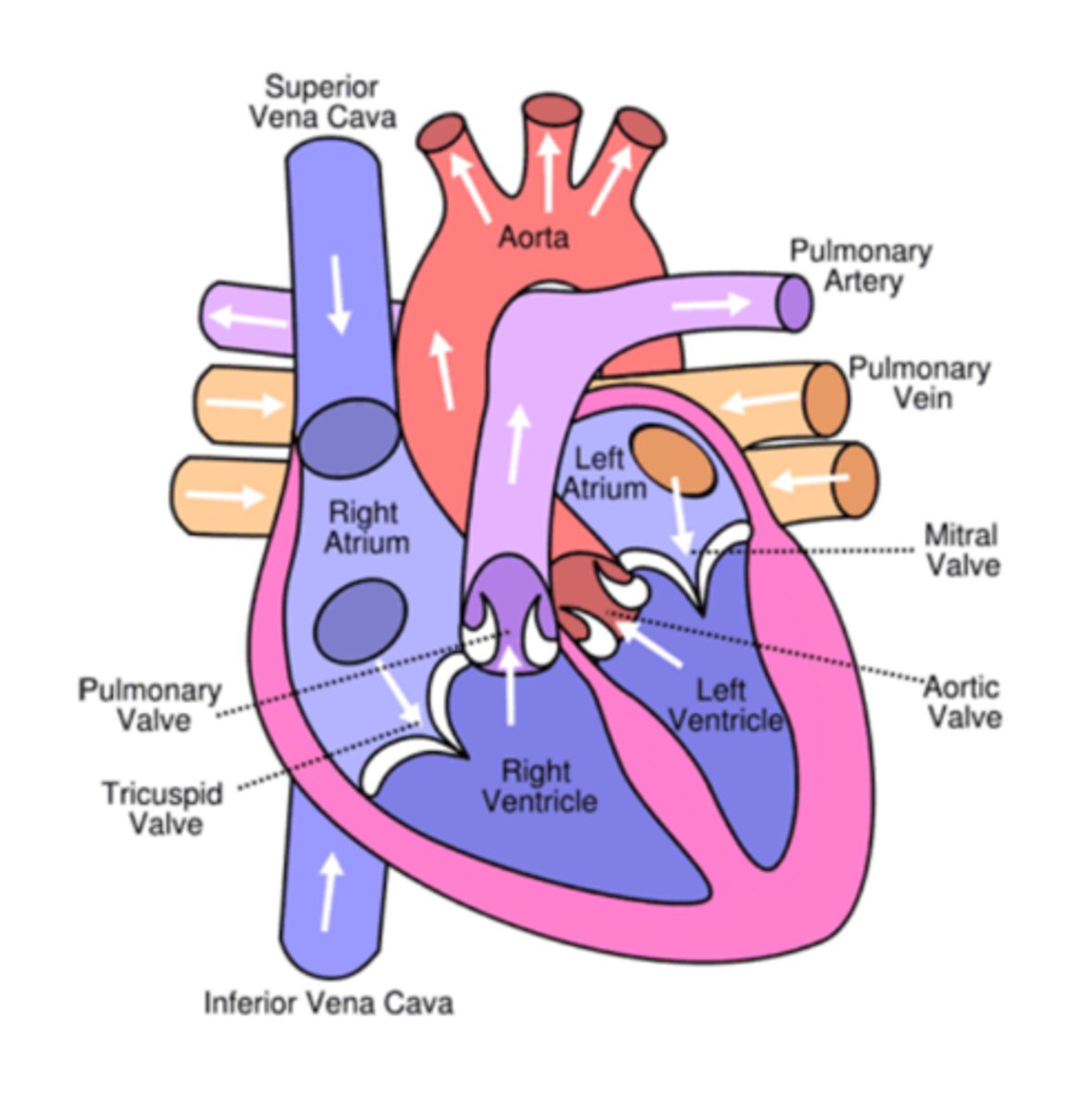
1.4 i) (IMAGE) The structure and operation of the mammalian heart
Bicuspid valve= Semilunar valve
Tricuspid valve= AV valve
1.4 i) Know the cardiac cycle (atrial systole, ventricular systole and cardiac diastole) and relate the structure and operation of the mammalian heart, including the major blood vessels, to its function.
Atrial systole
1) Low pressure blood flows in both atria from pulmonary/vena cava veins
2) Atria fill, blood volume increases, blood pressure increases, AV valves slightly open, blood leaks into ventricles
3) Atrial walls contract, reducing volume and increasing blood pressure
4) Blood is forced into ventricles
Ventricular systole
1)Ventricles fill up
2)Ventricular walls contract
3) Volume decreases, pressure increases
4)Pressure of blood shuts AV valves & prevents backflow
5) Pressure of blood opens semilunar valves
6) Blood flows out of aorta/pulmonary artery
Diastole
1) Atrial/ventricular walls relax
2) Elastic recoil of walls increase volume
3)Increased volume=lower pressure
4)Pressure is higher in arteries than in ventricles, semilunar valves close
5)Coronary arteries fill
6) Lower pressure in atria, blood flows in
1.4 ii) Know how the relationship between heart structure and function can be
investigated practically.
Heart can be investigated practically in a dissection
•examine externally
•identify vessels
•flow water in pulmonary vein
•cut open ventricles, examine differences between both sides
•atria cut open
•semilunar/atrioventricular valves can be seen as well as tendons that attach to prevent inversion
Bicuspid valve= Semilunar valve
Tricuspid valve= AV valve
1.5 Understand the course of events that leads to atherosclerosis (endothelial dysfunction, inflammatory response, plaque formation, raised blood pressure).
1) endothelial dysfunction
2) Inflammatory response, white blood cells move
3) Atheroma is formed when cholesterol builds up
4) Calcium and fibrous tissue form a plaque
5) Arterial elasticity is reduced and artery lumen is narrowed
6) Blood pressure is raised
7) Positive feedback loop
( Increased risk of blood clot )
1.6 Understand the blood-clotting process (thromboplastin release, conversion of prothrombin to thrombin and fibrinogen to fibrin) and its role in cardiovascular disease (CVD).
Sticky platelets--> exposed collagen
Thromboplatin released
Thromboplastin is an enzyme
Thromboplastin helps convert the inactive protein prothrombin, into the active enzyme thrombin
(in the presence of calcium and vitamin K)
Thrombin catalyses soluble fibrinogen conversion into insoluble fibrin.
Fibrin forms a mesh, trapping blood cells/platelets.
How do blood clots cause CVD?
If a blood clot forms in the coronary artery:
1) Blood flow to cardiac muscle is reduced
2) Reduces aerobic respiration in heart
3) Lactic acid build-up from anaerobic respiration damages the heart
1.7 Know how factors such as genetics, diet, age, gender, high blood pressure, smoking and inactivity increase the risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD).
Genetics:
Predisposition
Age
Reduced elasticity of arteries, more prone to damage.
Plaque build up over the years
Gender
Females less at risk (estrogen increases HDL cholesterol)
High blood pressure
Increased risk of endothelial damage--> atheroma formation
Physical inactivity
Increases obesity risk, raises high blood pressure
Being more active means energy going in is closer to energy being used
Smoking
CO has more affinity for haemoglobin
Less oxygen in blood
Heart rate increases to compensate
Diet
High saturated fats -->high cholesterol-->increased atheroma risk
High salt= water retention= high blood pressure
1.8 Be able to analyse and interpret quantitative data on illness and mortality rates to determine health risks, including distinguishing between correlation and causation and recognising conflicting evidence.
Correlation: A relationship between two variables where if one increases/decreases the other will increase/decrease
Causation: When two variables are causally linked. One is consequential of the other
1.9 Be able to evaluate the design of studies used to determine health risk factors, including sample selection and sample size used to collect data that is both valid and reliable.
Sample size: the sample size being larger increases the likelihood of statistical significance
Sample selection: Valid sample selection ensures that any results are not skewed by a factor such as bias.
Cohort study:
Follows large number of people over extended period
They are monitored and divided.
The exposure to risk factors is recorded.
Any correlation is identified
Case control study:
A "Case" group compared with a "control" group.
•Case group has disease, control group does not.
•Group exposure to risk factors is recorded.
•Risk factors contributing to disease development are identified
1.10 Understand why people's perceptions of risks are often different from the actual risks, including underestimating and overestimating the risks due to diet and other lifestyle factors in the development of heart disease.
Overestimating risk
•If the risk is out of their own control/involuntary
•If the risk is very small but portrayed as disastrous (e.g. plane crash)
Underestimating risk
If it has a long term effect that is ignored
If they are underinformed
1.11 i) Be able to analyse data on energy budgets and diet.
1.11 ii) Understand the consequences of energy imbalance, including weight loss, weight gain, and development of obesity.
ENERGY IMBALANCE
Weight loss: if energy in is lower than energy used
Weight gain: if energy in is higher than energy used
Obesity development: BMI above 30, leads to increased CVD risk
1.12 i) Know the difference between monosaccharides, disaccharides and
polysaccharides, including glycogen and starch (amylose and amylopectin).
Monosaccharides
e.g. glucose, fructose, galactose
Rapid energy absorption
1 sugar unit
Disaccharides
2 sugar units joined by glycosidic bond in a condensation reaction
e.g. maltose, sucrose and lactose
Polysaccharides
glycogen: long, heavily branched molecule with an overall spherical shape.
Linearly adjacent glucose molecules joined together by alpha-1,4 glycosidic bonds
Branched glucose molecules joined together by alpha-1,6 glycosidic bonds.
mostly soluble in water, but does not affect water potential in the body
starch: composes of amylose and amylopectin
amylose: joined by alpha-1,4 glycosidic bonds, straight coiled chain
amylopectin: branched molecule, joined together by alpha 1-4 bonds between the straight chain, and 1-6 glycosidic bonds at the branches
insoluble in water
1.12 ii) Be able to relate the structures of monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides to their roles in providing and storing energy (β-glucose and cellulose are not required in this topic).
Monosaccharides:
Small, can easily be transported and used/broken down.
Polysaccharides:
Long sugar chain polymer, joined by glycosidic bonds
1.13 Know how monosaccharides join to form disaccharides (sucrose, lactose and maltose) and polysaccharides (glycogen and amylose) through condensation reactions forming glycosidic bonds, and how these can be split through hydrolysis reactions.
Monosaccharides
•Glucose
•Fructose
•Galactose
Disaccharides
•Lactose (+H2O)<=> glucose+galactose
•Sucrose (+H2O)<=> glucose+fructose
•Maltose (+H2O) <=> glucose+glucose
1.14 i) Know how a triglyceride is synthesised by the formation of ester bonds during condensation reactions between glycerol and three fatty acids.
3 fatty acids + 1 glycerol --> Triglyceride + H2O
This is another condensation reaction
3 ester bonds are formed between each of the triglycerides and the glycerol
Glycerol is hydrophilic, fatty acids are hydrophobic
1.14 ii) Know the differences between saturated and unsaturated lipids.
Saturated lipids
Straight chain, no double bonds
(is saturated with hydrogens)
Strong I.M forces, holds sat.fats together, they are solid at RTP
Unsaturated lipids
Has a carbon=carbon double bond.
It is bent at the point of double bonding
They cannot pack together tightly so are liquid at RTP
1.15 i) Be able to analyse and interpret data on the possible significance for health of blood cholesterol levels and levels of high-density lipoproteins (HDLs) and low-density lipoproteins (LDLs).
LDL = bad cholesterol
HDL = good cholesterol
HDLs carry lipids to liver to break them down
LDLs cause the release of lipids into the blood
Healthy LDL:HDL ratio in blood is around 3:1
Above 5:1 increases risk of heart disease
1.15 ii) Know the evidence for a causal relationship between blood cholesterol levels (total cholesterol and LDL cholesterol) and cardiovascular disease (CVD).
1.16 Understand how people use scientific knowledge about the effects of diet, including obesity indicators, body mass index and waist-to-hip ratio, exercise and smoking to reduce their risk of coronary heart disease.
BMI= Mass(kg)/Height² (m²)
30+ obese
Affected by muscle mass however, which is denser than fat
Waist to hip ratio
Men should not be over 0.9
Women should not be over 0.85
CORE PRACTICAL 1:
Investigate the effect of caffeine on heart rate in Daphnia.
Method
1) Remove Daphnia with pipette,
2) Add to cotton wool with distilled water
3) Let it acclimatise for 2 minutes
4) Add a drop of a known conc. of caffeine solution
5) Record the number of heartbeats seen through a microscope in 60 seconds, time with stopwatch
6) Do repeats at varying caffeine concentrations
Control variables
•Temperature
•Volume of solutions
•Stress of daphnia
•Size of daphnia
•Location daphnia come from
Calculation
•Mean
•Standard deviation
Considerations
Ethics:
Why use Daphnia?
•Not endangered
•Produce asexually as clones
•they are transparent, can see their heart
•Less developed nervous system, reduced sense of pain
1.17 Be able discuss the potential ethical issues regarding the use of invertebrates in research.
Discussion
•they may not endangered
•they may produce asexually as clones
•Less developed nervous system, reduced sense of pain
•they did not get to consent
•research does not prioritise animal welfare of science
CORE PRACTICAL 2:
Investigate the vitamin C content of food and drink.
Method
Pipette 1cm3 of 1% blue DCPIP into conical flask
Fill burette with chosen fruit juice
Find volume of fruit juice needed to decolourise DCPIP
Repeat with each fruit juice
Calibration: Use known concentrations of vitamin C and titrate against 1cm3 1% DCPIP. Plot a graph of the volume of solution used to decolourise DCPIP, against the concentrations of vitamin C used. The results with the fruit juice can be compared with this graph, finding out the %content of vitamin C within the juice.
Calculation
By comparing with the calibration curve, % of vitamin C can be worked out.
1% vitamin C=10mg, so apply this with the juice values to get the mass.
1.18 Know the benefits and risks of treatments for cardiovascular disease (CVD) (antihypertensives, statins, anticoagulants and platelet inhibitors).
Antihypertensives: reduce blood pressure Includes diuretics (reduces water retention), beta blockers (reduces heart rate) & ACE inhibitors (reduces arterial blood pressure)
Statins: Reduce blood cholesterol levels
Platelet inhibitors: Reduces risks of clot formation
Anticoagulants: Reduce risk of clot formation
[SIDE EFFECTS]:
Anticoagulants=uncontrolled bleeding
Platelet inhibs= stomach bleeding
Diuretics=Nausea, muscle cramps and dizziness
ACE inhibitors= dizziness, heart arrhythmia
Statins=nausea, inflammation, diarrhoea
Beta blockers=Diabetes
Most of them cause nausea/dizziness as a side effect