Cleft Palate and Voice Disorders Study Guide
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Fluency
Effortless, rhythmical, evenly flowing speech.
Voice
Sound produced by vocal folds.
Cleft Palate
Congenital split in the roof of the mouth.
Oral-Facial Cleft Stats
1 in 750 live births among European Americans.
fourth most frequent birth defect
50% have clefts on both the lip and palate
25% of affected individuals have clefts involving either one side (unilateral) or both sides (bilateral) of the lip
25% of affected individuals have clefts of the palate only
50% have clefts on both the lip and palate
Pitch
Perceived highness or lowness of a voice.
Loudness
Perceived strength of a sound, from quiet to loud
Disfluency
Speech marked by phrase repetitions, interjections, pauses, and revisions
Atypical Disfluencies
Single syllable, syllable, or sound repetitions.
Quality
Sound characteristics of a person's voice, which is a combination of the long-term characteristics of their speech patterns and the auditory coloring of their voice
Palate Development
Formation of the palate between 6-9 weeks.
the premaxilla (housing for 4 front teeth) joins with the palatine processes, which then fuse with each other front to back to form the palate
Types of Cleft Lip
Partial/incomplete: no alveolar ridge involvement
complete: alveolar ridge involved
Types of Cleft Palate
Complete cleft: affects the hard and soft palate
incomplete cleft: affects only the soft palate
submucous: notch in the hard palate
occult clefts: malformation of palatal musculature
Voice Quality Characteristics
Breathy: sound of air is apparent
strained: effort apparent
harsh: excessive muscle tension
tough: uneven, harsh
aphonia: loss of voice
dysphonia: voice disorder
Surgical Care Timeline
cleft Lip repaired by 3 months; cleft palate by 12 months.
Prolongations
Holding a sound longer than normal.
Voice Disorder Causes
edema: vocal folds tissues swollen
atrophy: reduction in tissue
hyperfunction: increased muscle
hypofunction: decrease in muslcle activity
abuse/misuse: screaming, excessive use
medical: nervous system damage, cancer, virus
psychogenic: emotional stress, unresolved psychological issues
Stuttering
Most common form of fluency impairment.
Contact Ulcers
Ulcers on vocal processes of arytenoid cartilages.
Papillomas
Wart-like growths from human papilloma virus.
Nodules
Most common vocal fold abnormality.
Secondary Behaviors
Counterproductive actions to avoid stuttering.
Assessment Team
Includes SLPs, surgeons, and dentists.
Psychological Stuttering
Stuttering related to psychological factors.
Acquired Stuttering
Neurogenic stuttering due to brain injury.
Developmental Stuttering
Common speech fluency issue in children.
Voice Problems
Affects 20% of patients with voice issues.
Neurologist
Specialist involved in voice problem assessment.
Prosthodontist
Dental specialist who may assist with voice issues.
Vocal Fold Abuse
Can lead to voice disorders over time.
Speech-Language Pathologist (SLP)
Provides intensive therapy post-surgery for voice issues.
Polyps
Softer, pliable growths on vocal folds.
Voice Quality
Describes breathy or hoarse vocal characteristics.
Carcinoma
Cancer affecting the larynx.
Stuttering Incidence
Percentage of people who stuttered in life.
Cluttering
Rapid, unintelligible bursts of speech.
Spasmodic Dysphonia
Voice disorder from basal ganglia disturbances.
Adductor SD
Most common type, causes strain-strangle voice.
Abductor SD
Involves inappropriate contraction of abductor muscles.
Mixed SD
Least common spasmodic dysphonia type.
Aphonia
Total loss of voice without organic cause.
Dysphonia
Abnormal voice quality without identifiable cause.
Assessment Process
Includes case history and speech sample evaluation.
MIDVAS
Stuttering modification process: motivation to stabilization.
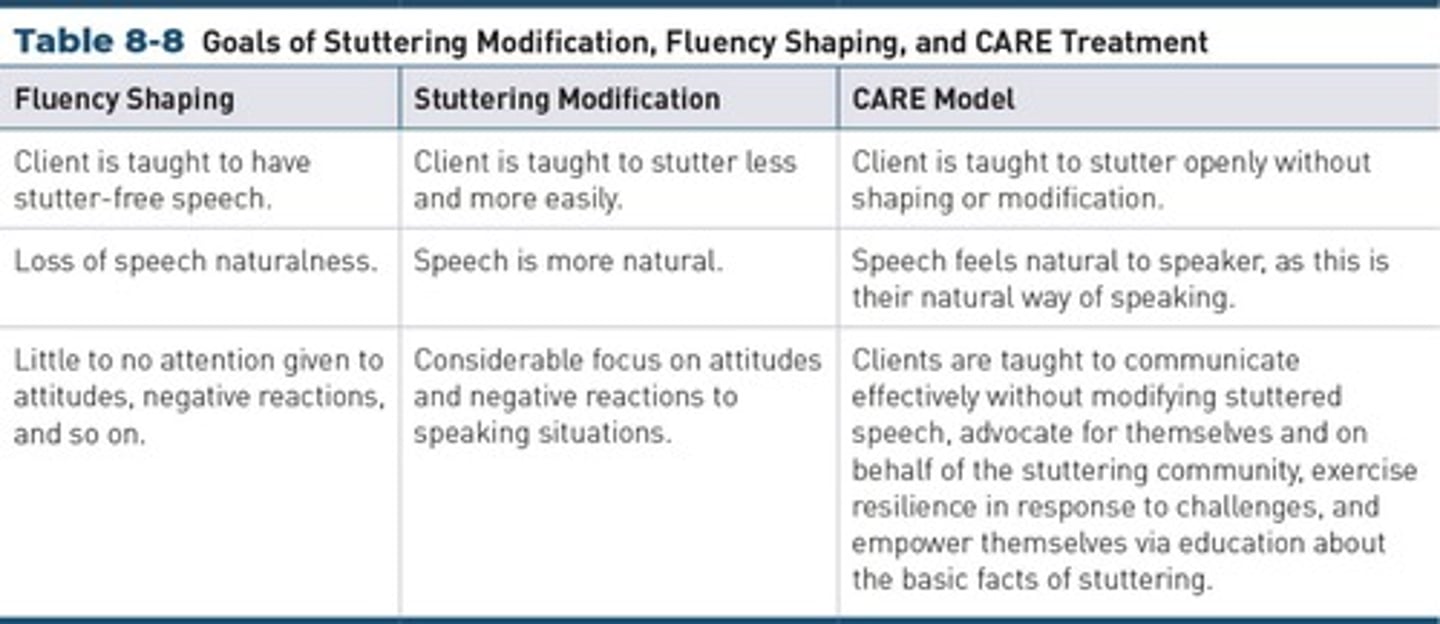
Fluency Shaping
Aims for stutter-free speech through controlled techniques.
GILCU
Gradual increase in utterance length and complexity.
Voice Therapy
Tailored to specific voice disorder types.
Listener Responsibilities
Guidelines for interacting with individuals who stutter.
Disfluency Count
Measurement of speech interruptions during assessment.
Eye Blinks
Non-verbal cues that may accompany speech issues.
Laryngeal Removal
May require alternative voice sources post-surgery.