dermatology basics (skin, hair, nails) exam
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
83 Terms
why do we care about skin, hair and nails?
it is the largest organ, indicator of internal health
what are skin functions?
protection from the environment, containment of tissues, organs, and vital substances (H2O), heat regulation, sensation, vitamin D, storage (energy adipose tissue)
what are the layers of the skin?
epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis
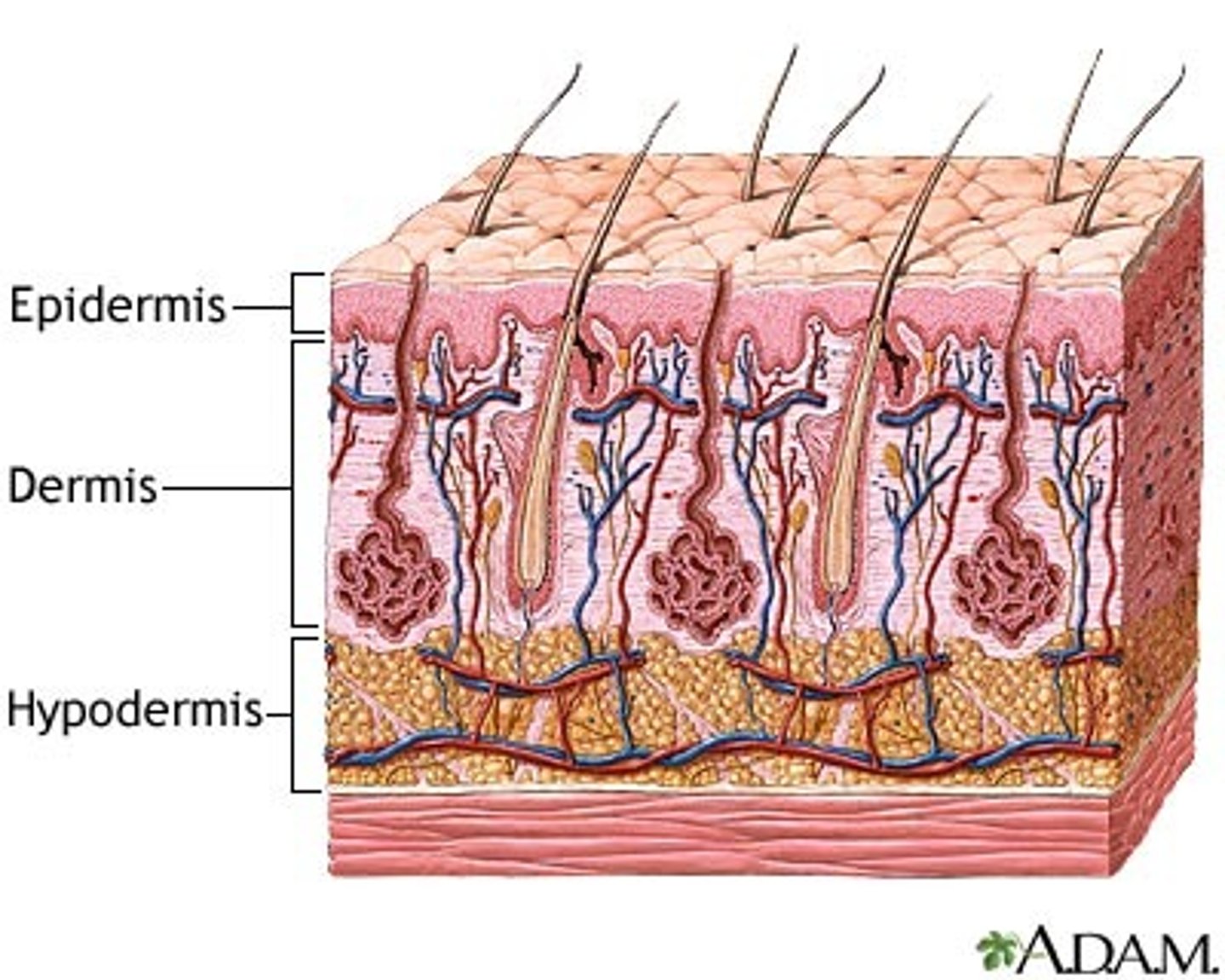
epidermis
stratified (layered) epithelium with tough outer surface composed of keratin
dermis
dense layer of collagen and elastic fibers that give skin its strength, living layer, with blood vessels
hypodermis
subcutaneous tissue, adipose- skin ligaments, determines mobility over underlying fascia
OLDCARTS
Onset, location, duration, C (itch, burn, pain, warmth), Alleviating/aggrevating, radiation (rash spread), treatment/travel, S - how bad is it, limiting function?

dermatologic history includes
PMH, FH, medications, allergies, SH
documentation is important because
it describes the location relative to a common anatomic landmark with appropriate medical terminology for future reference
proximal
close to origin
distal
further away from origin
describe a skin lesion using categories:
primary and secondary morphology, size, border/demarcation, color, shape, distribution
primary morphology
general size and shape
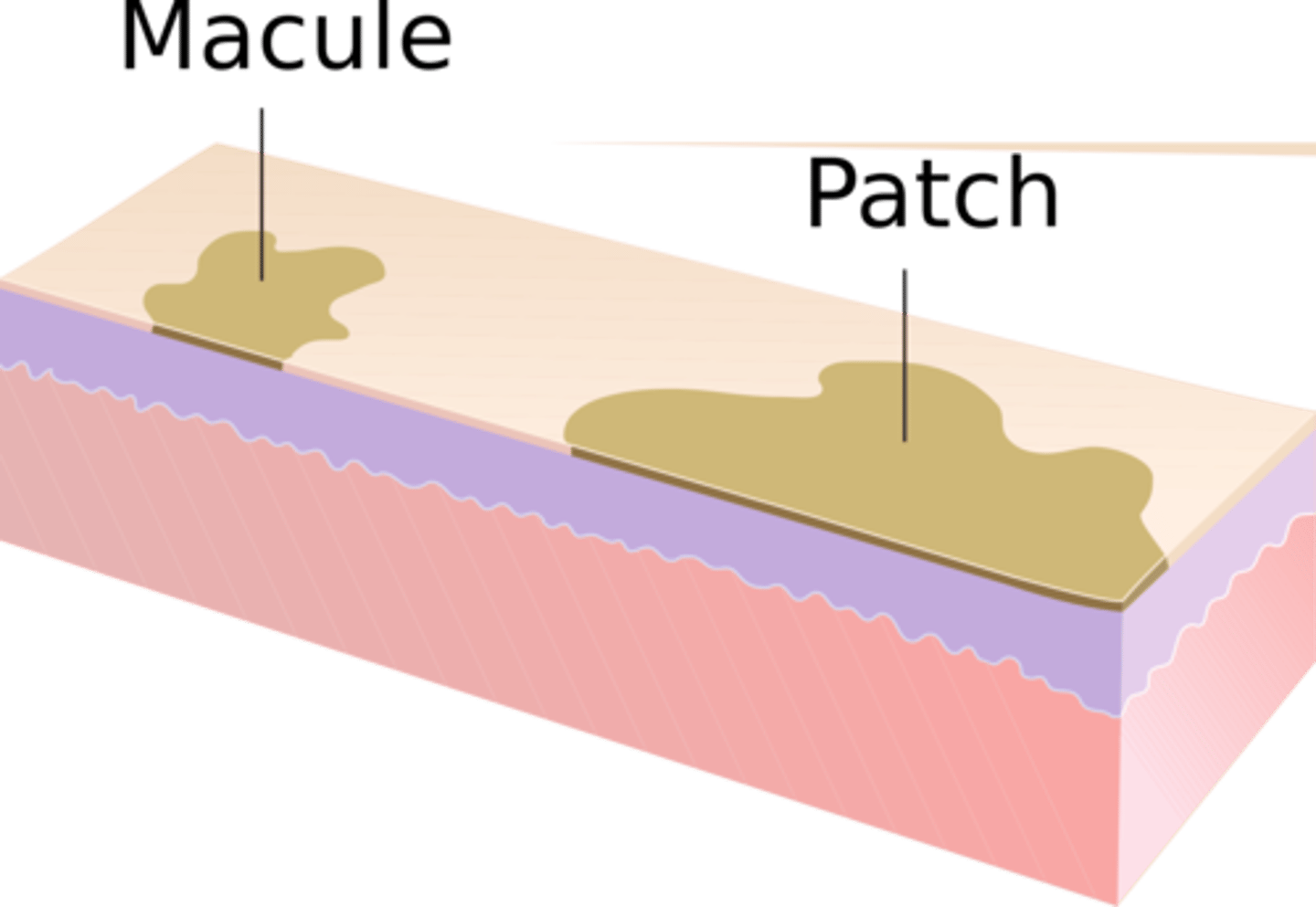
macule
non-palpable, lesion less than 1 cm, different color than surrounding skin, petechiae
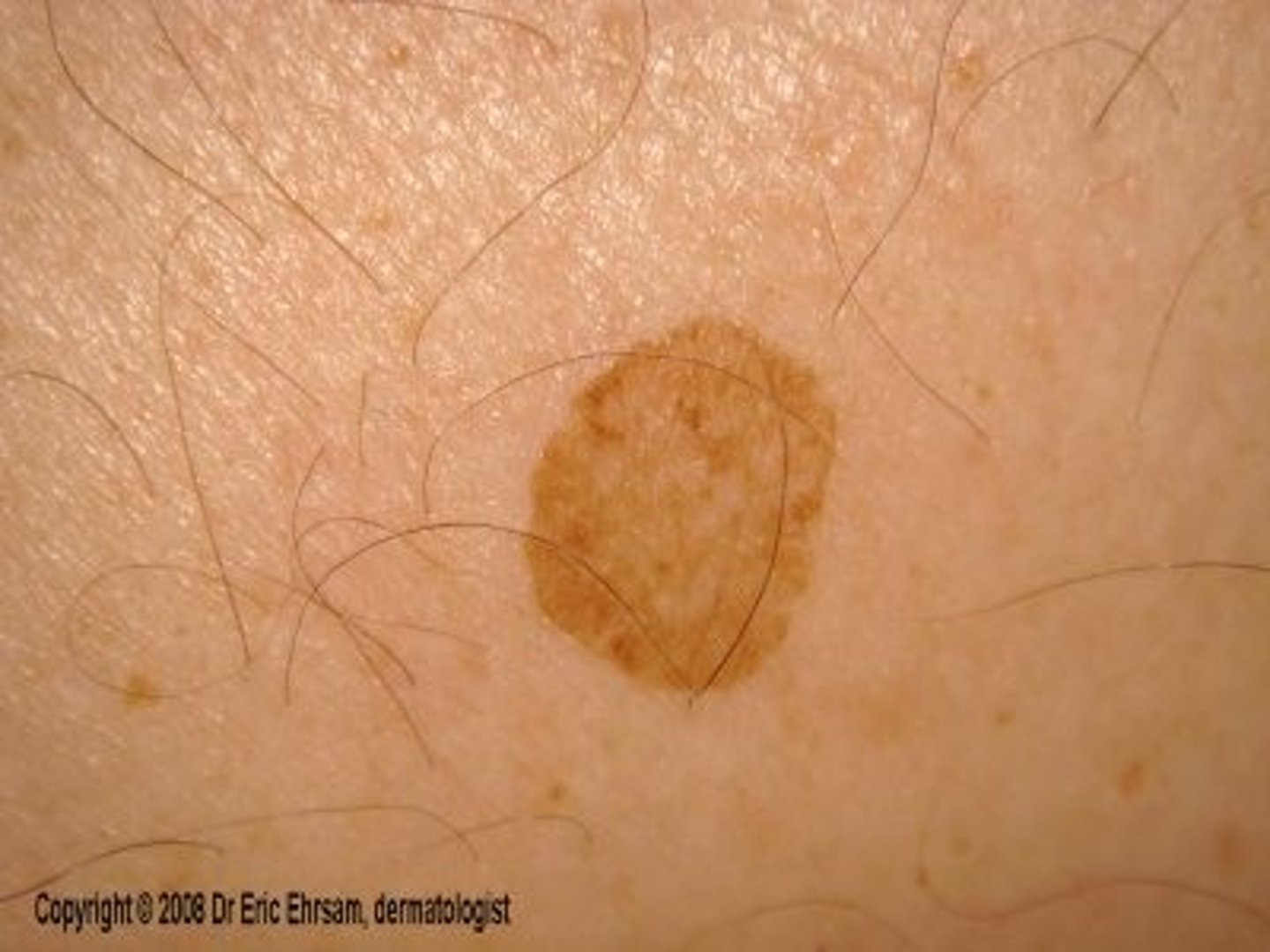
patch
non-palpable lesion greater than 1 cm, different color than surrounding skin, eg. cafe au laid spot
papule
elevated solid lesion less than 1 cm ie. verruca (wart)
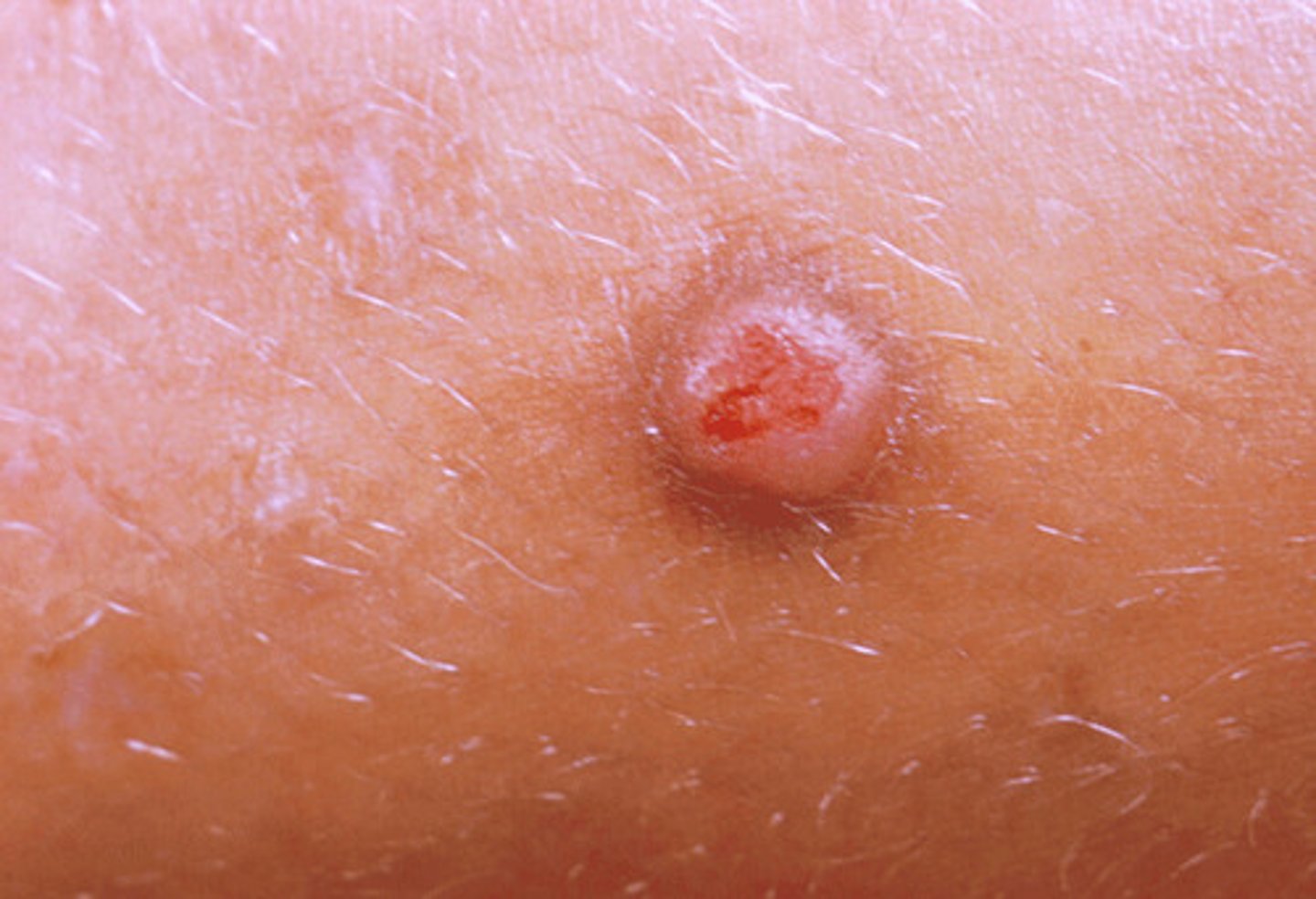
plaque
elevated flat/plateau like solid lesion greater than 1 cm (ie. Psoriasis)
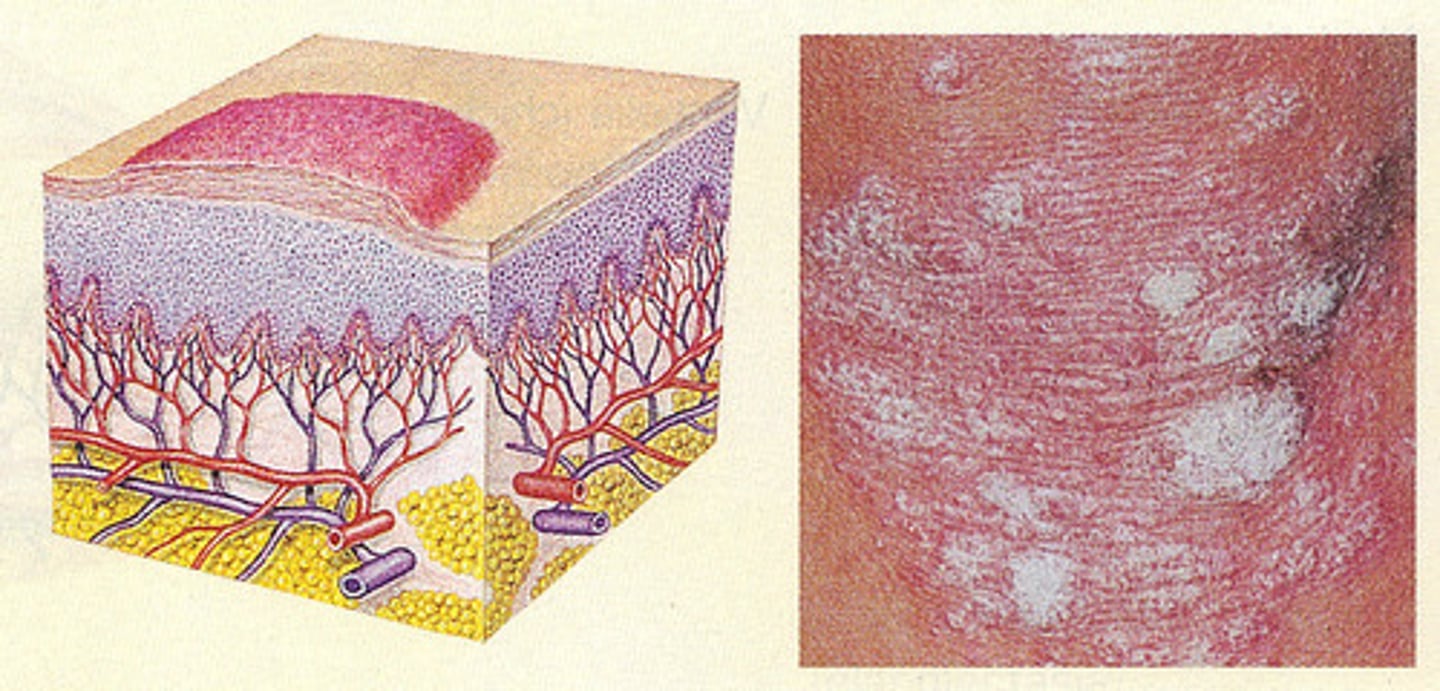
nodule
elevated domed solid lesion greater than 1 cm example: lipoma, sebaceous cyst
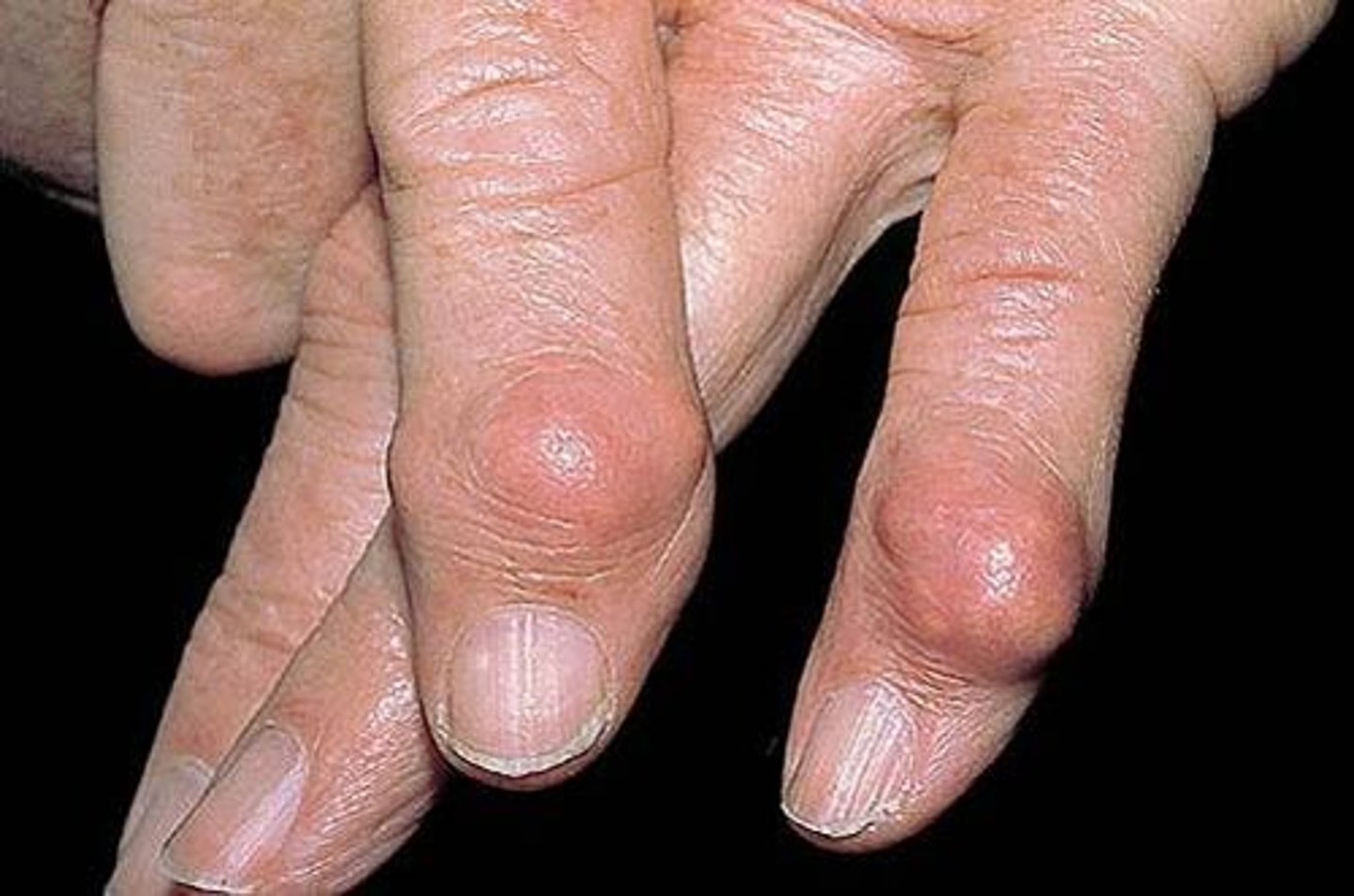
vesicle
elevated fluid filled lesions less than 1 cm ie. chicken pox
bulla
elevated fluid filled lesion, greater than 1 cm ie. diabetic bullae (bullosis diabeticorum)
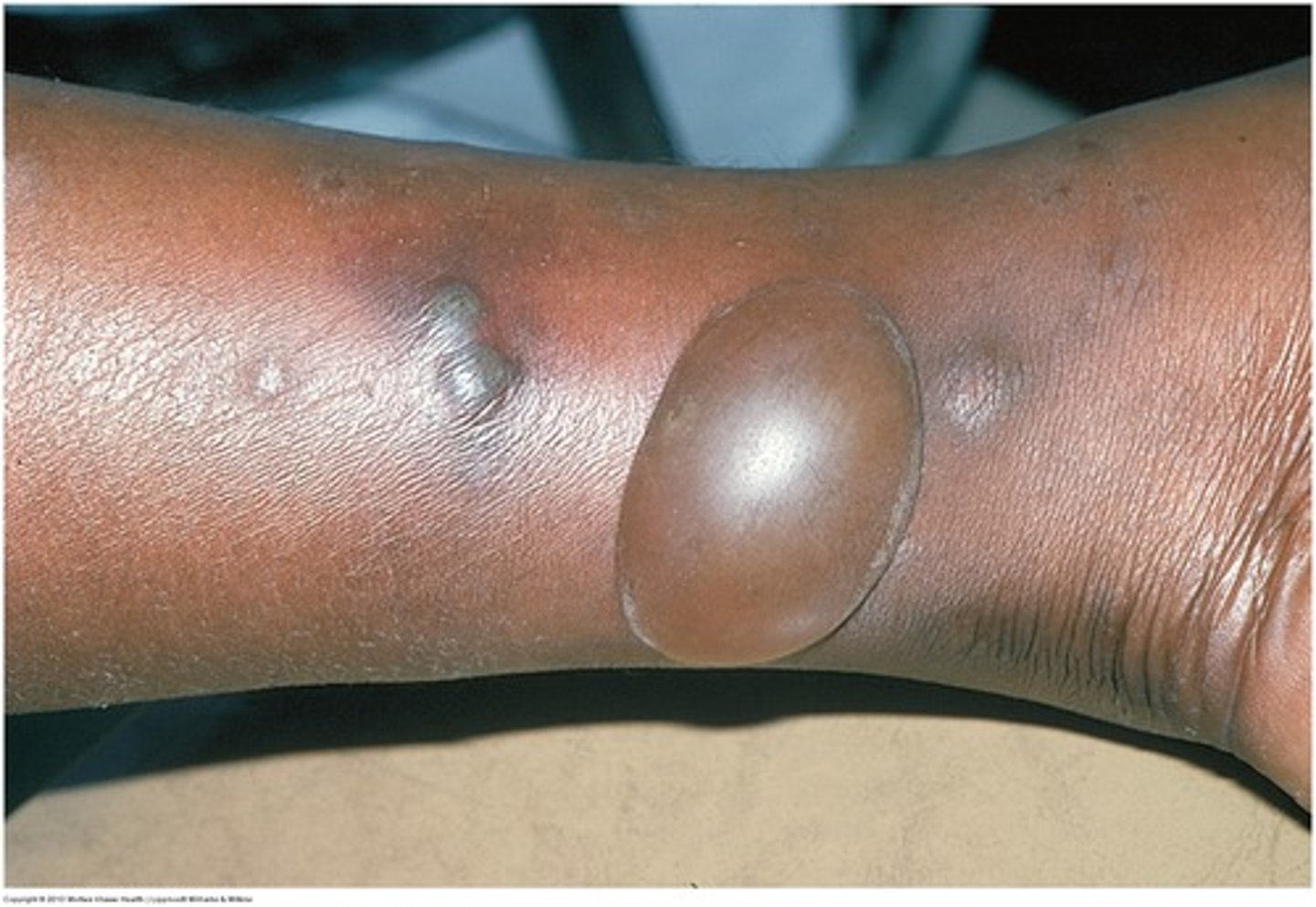
blister
inclusive synonym for bulla or vesicle (be specific)
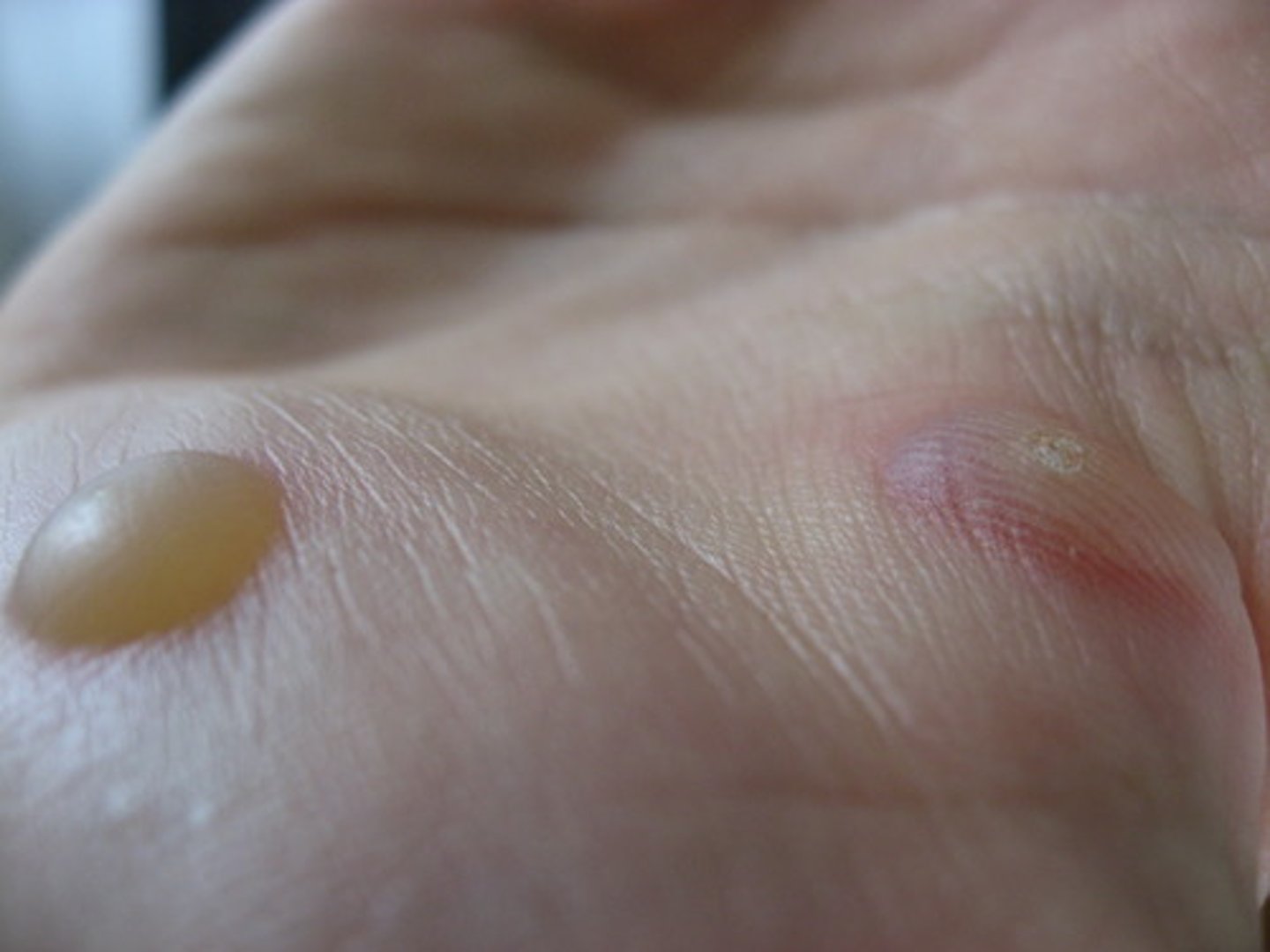
pustule
vesicle filled with pus (ie acne vulgaris)
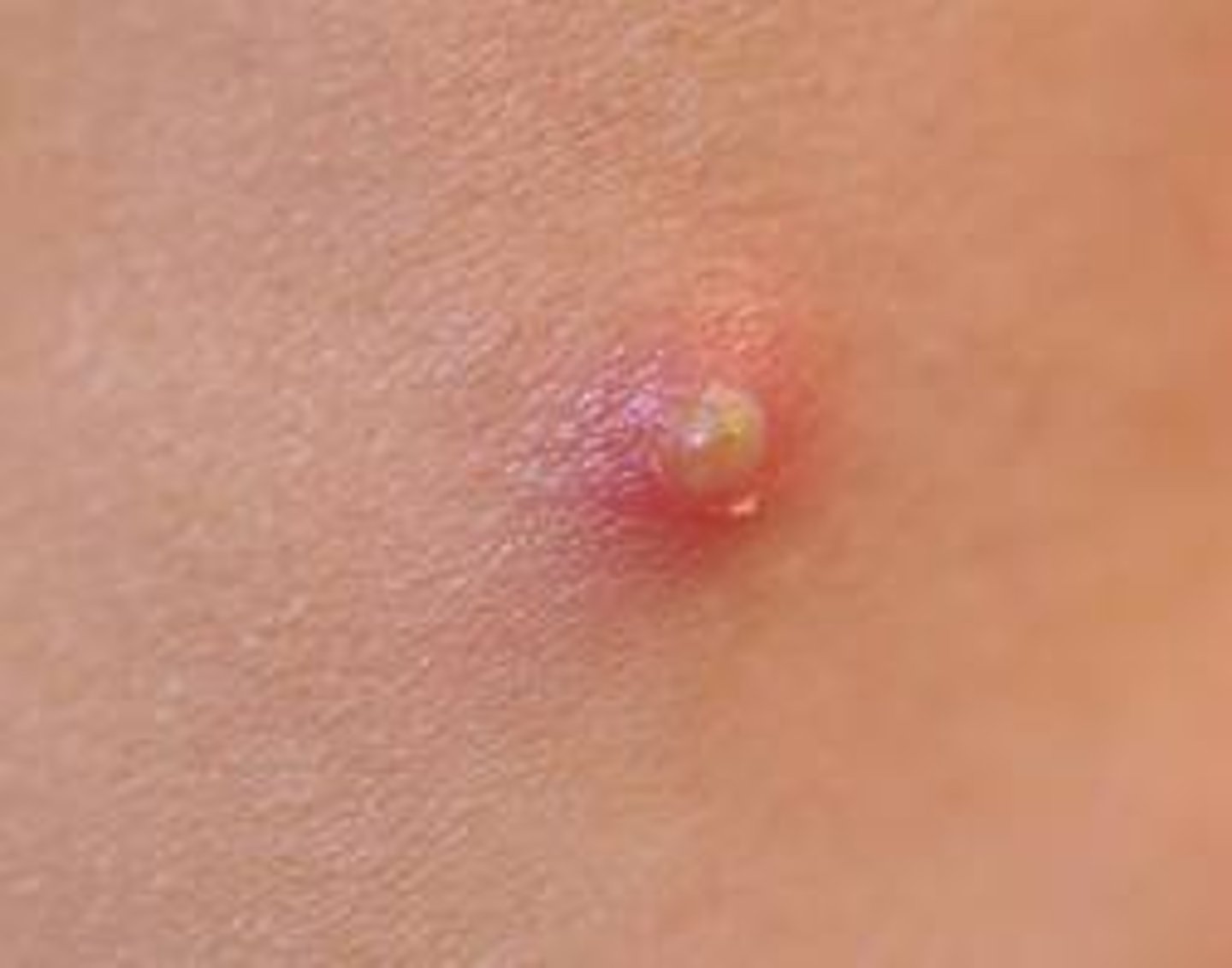
furuncle
larger pus filled lesion (ie. abscess)
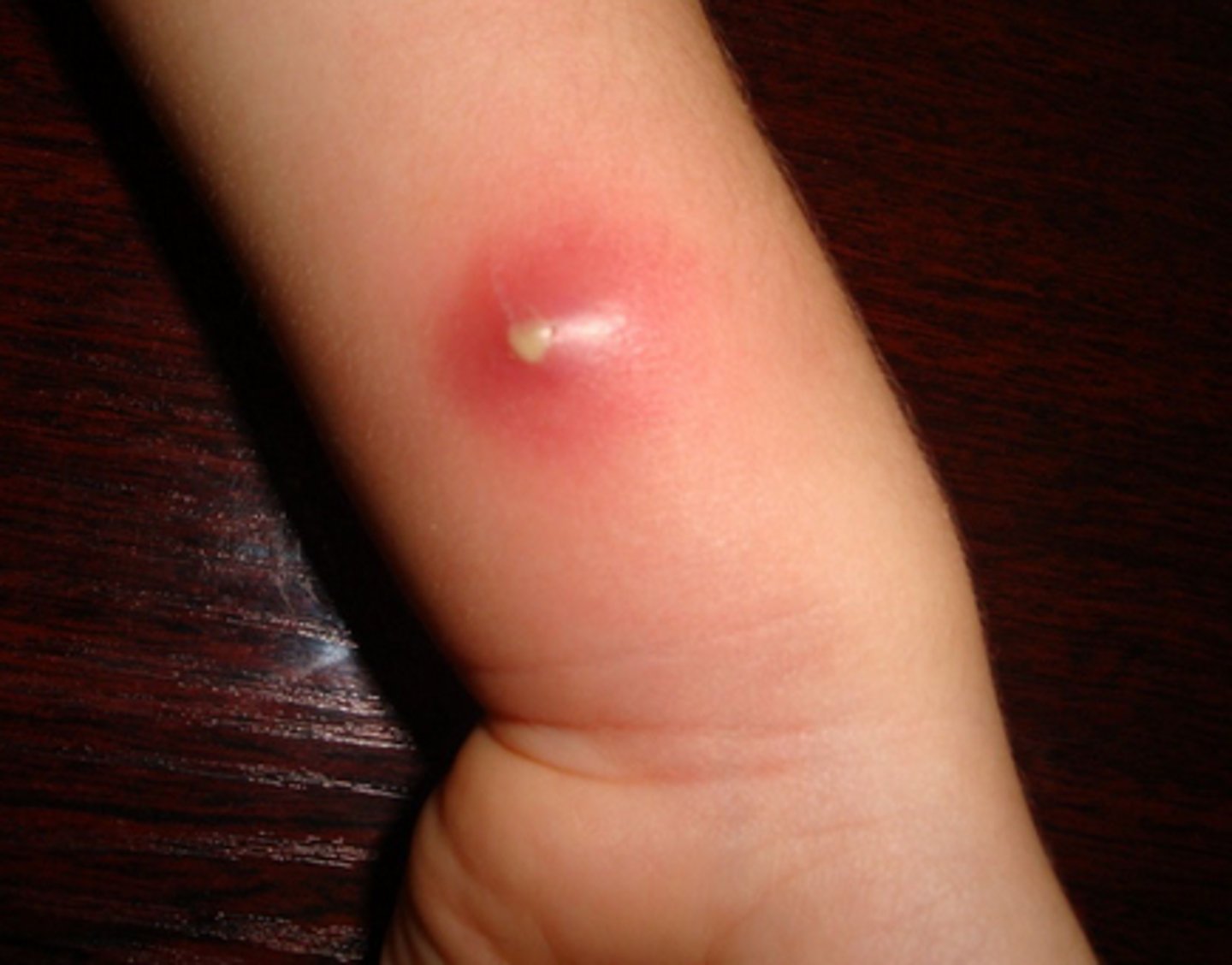
carbuncle
larger area with multiple draining points
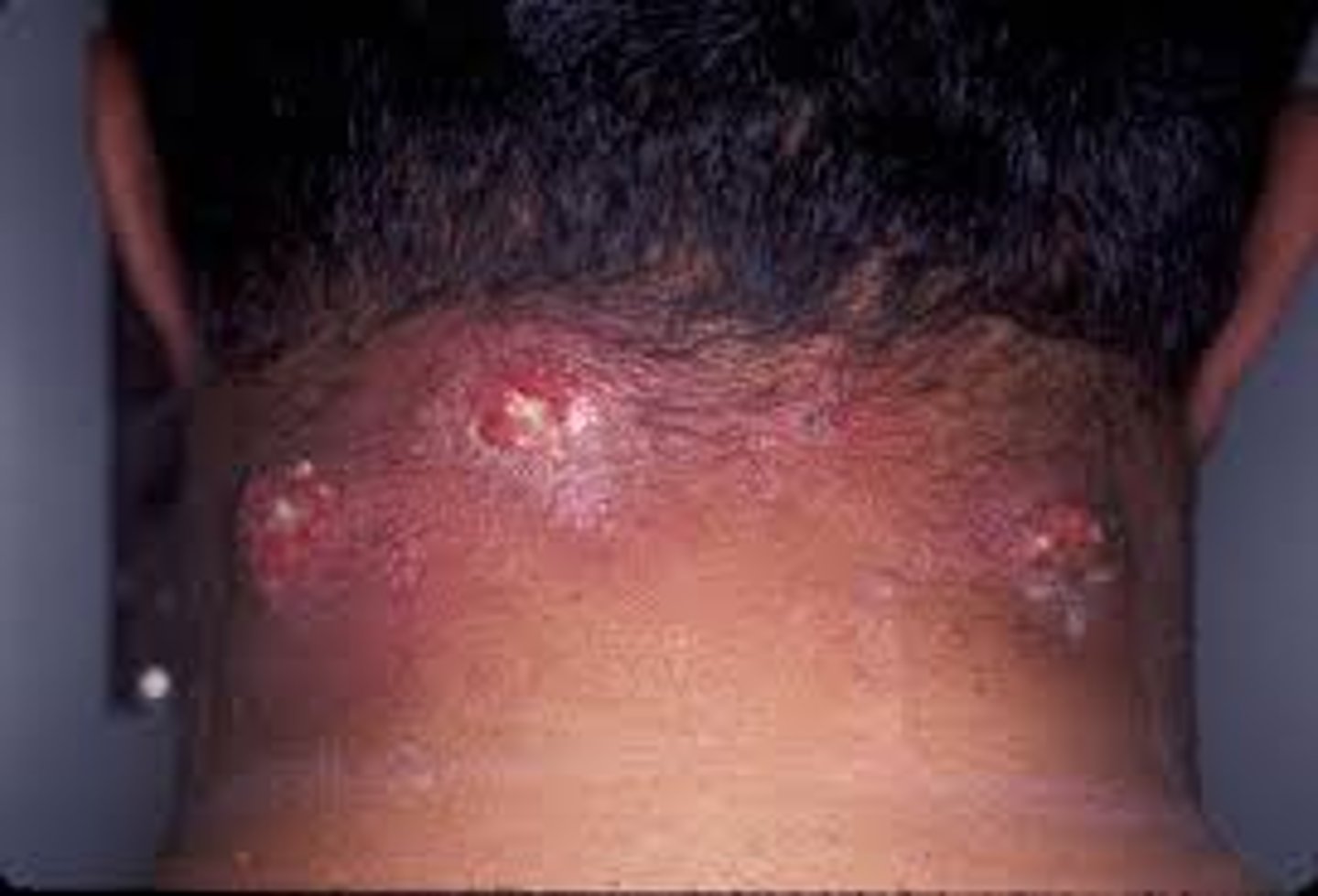
abscess
occlusion of drainage results in pus filed cavity within dermis and/or subcutaneous fat (fluctuant mass) treatment is incision and drainage
how to document size
at least 2 dimensions unless it is round or linear (laceration)
border
demarcation, regular circular, irregular borders =abnormal
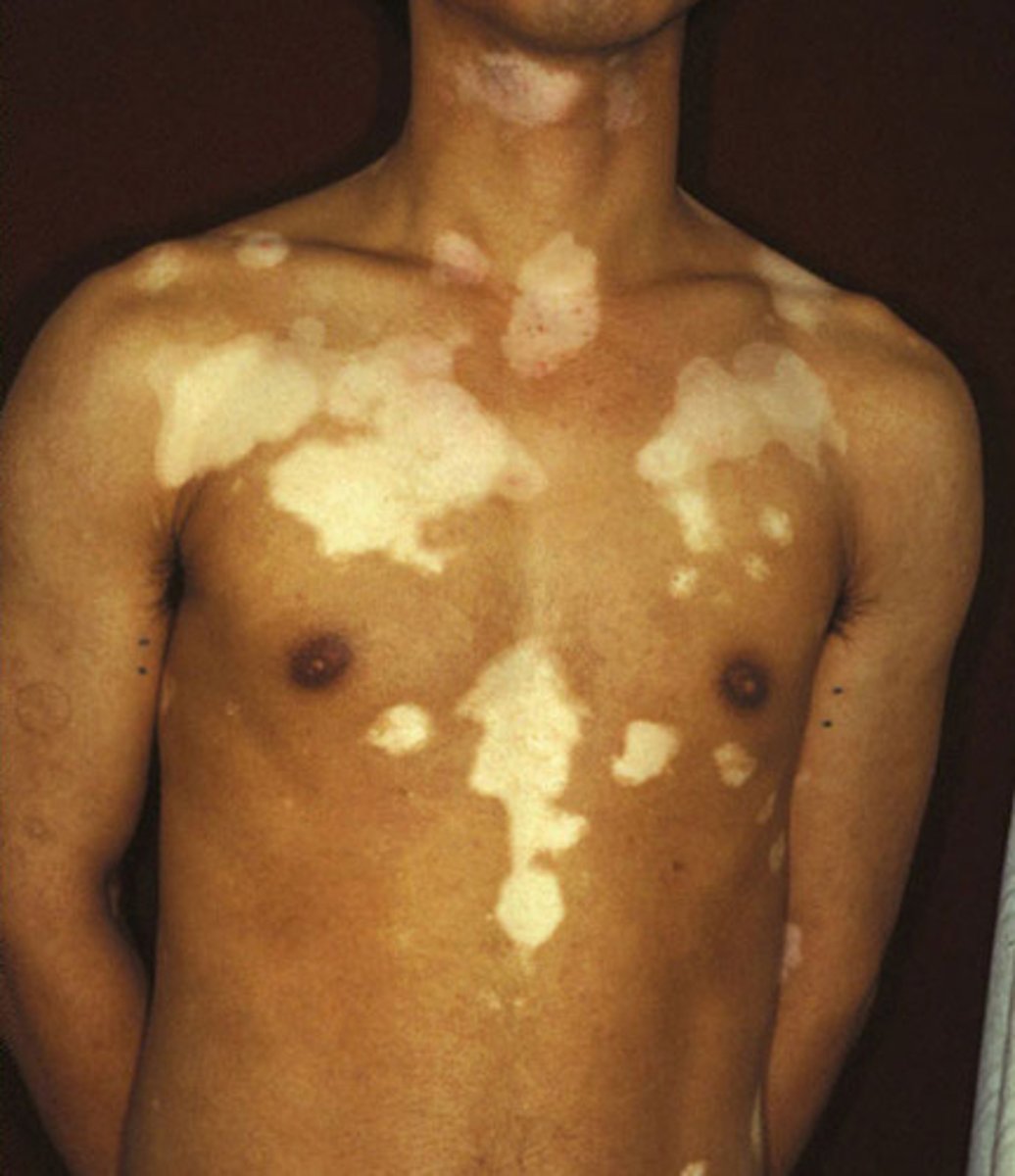
vitiligo
white
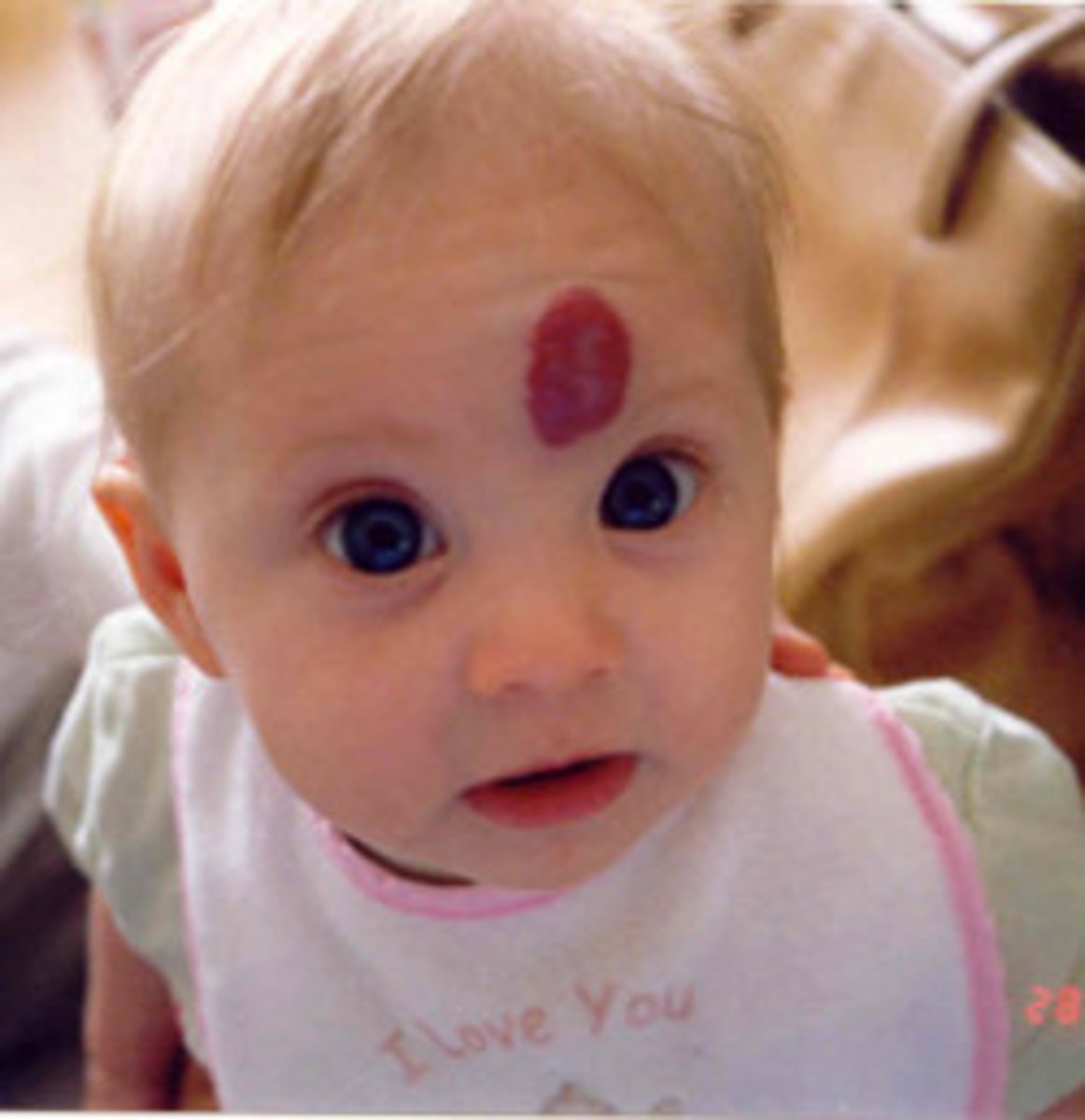
hemangioma
red
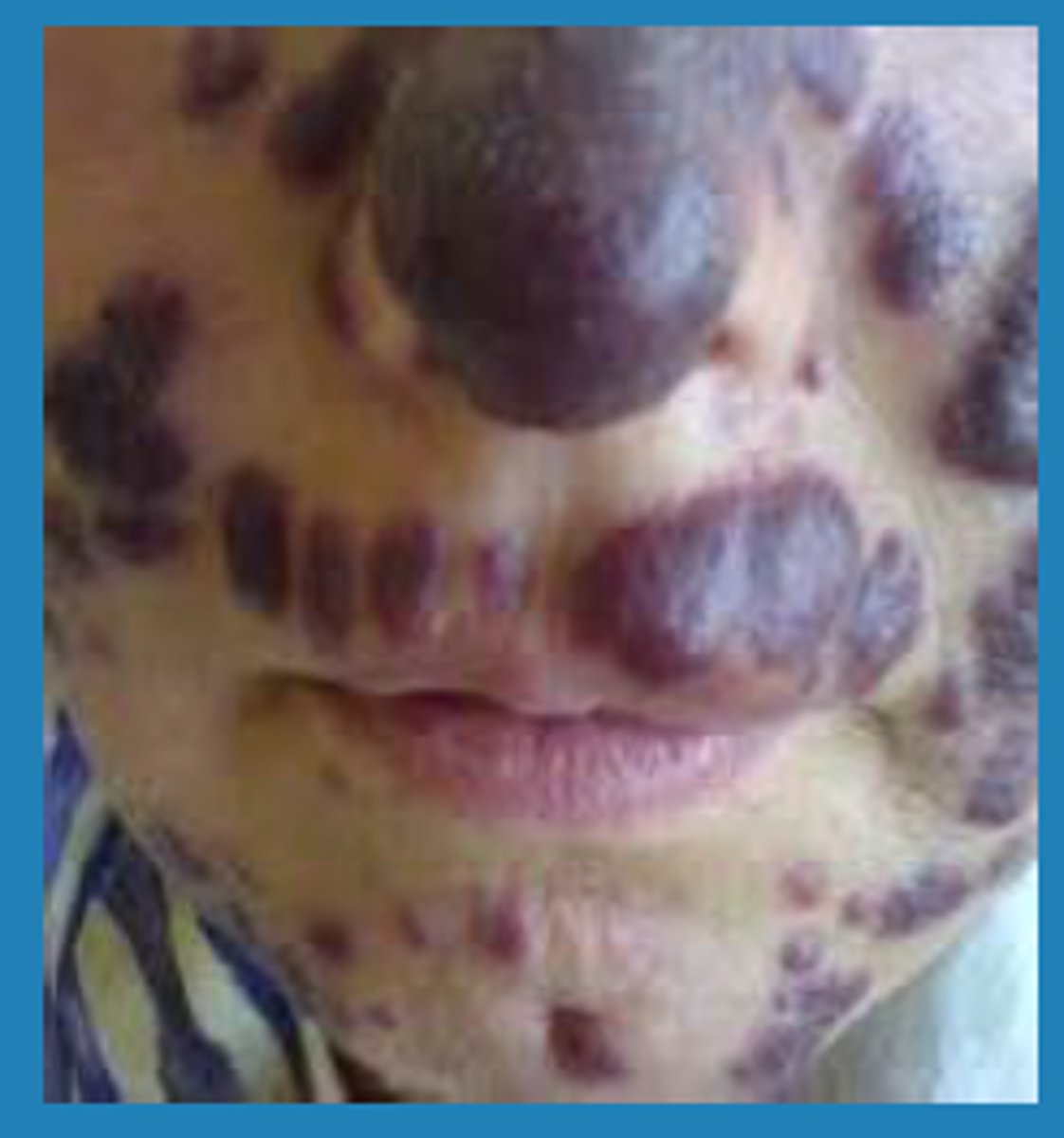
karposi sarcoma
purple
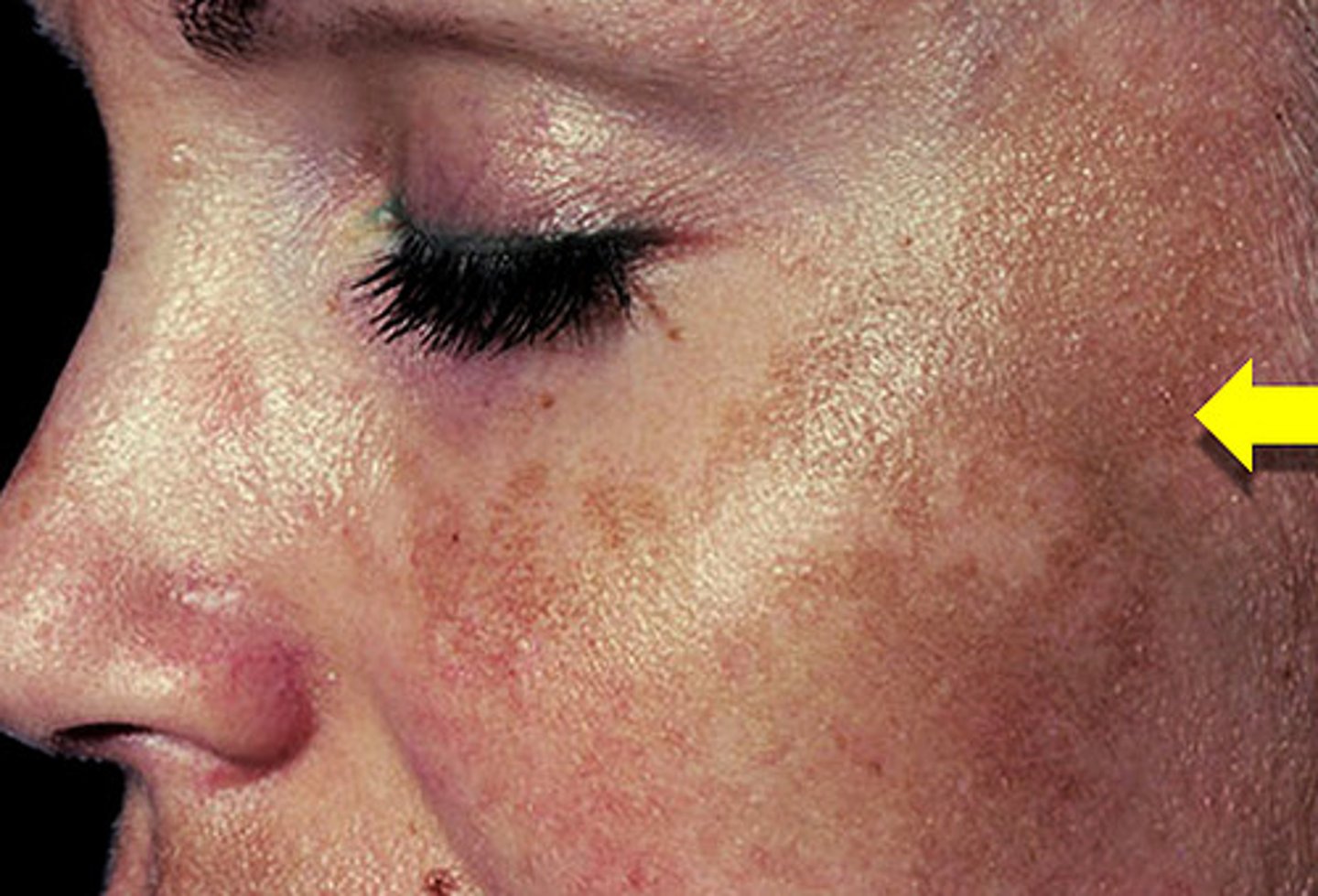
melasma
brown
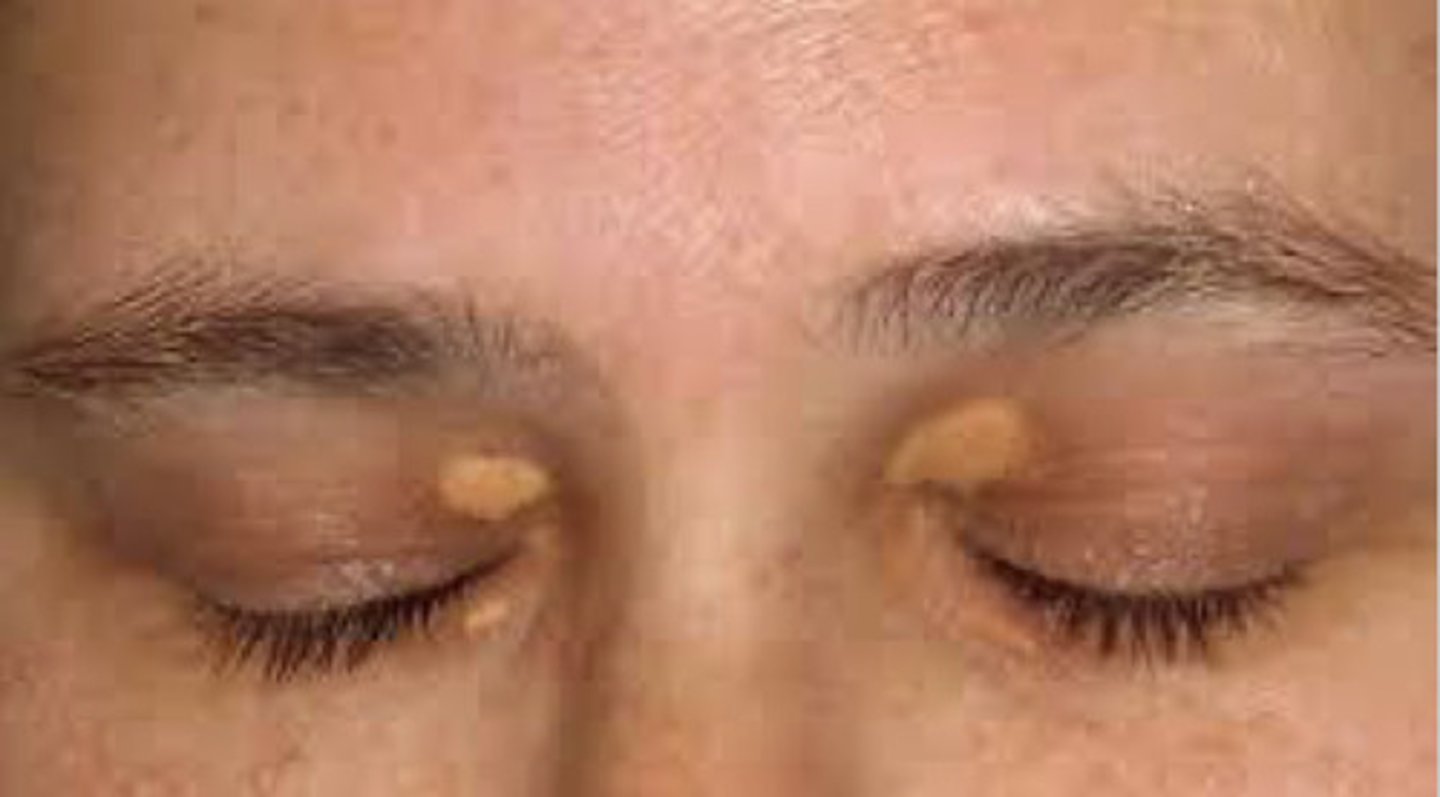
xanthelesma
yellow
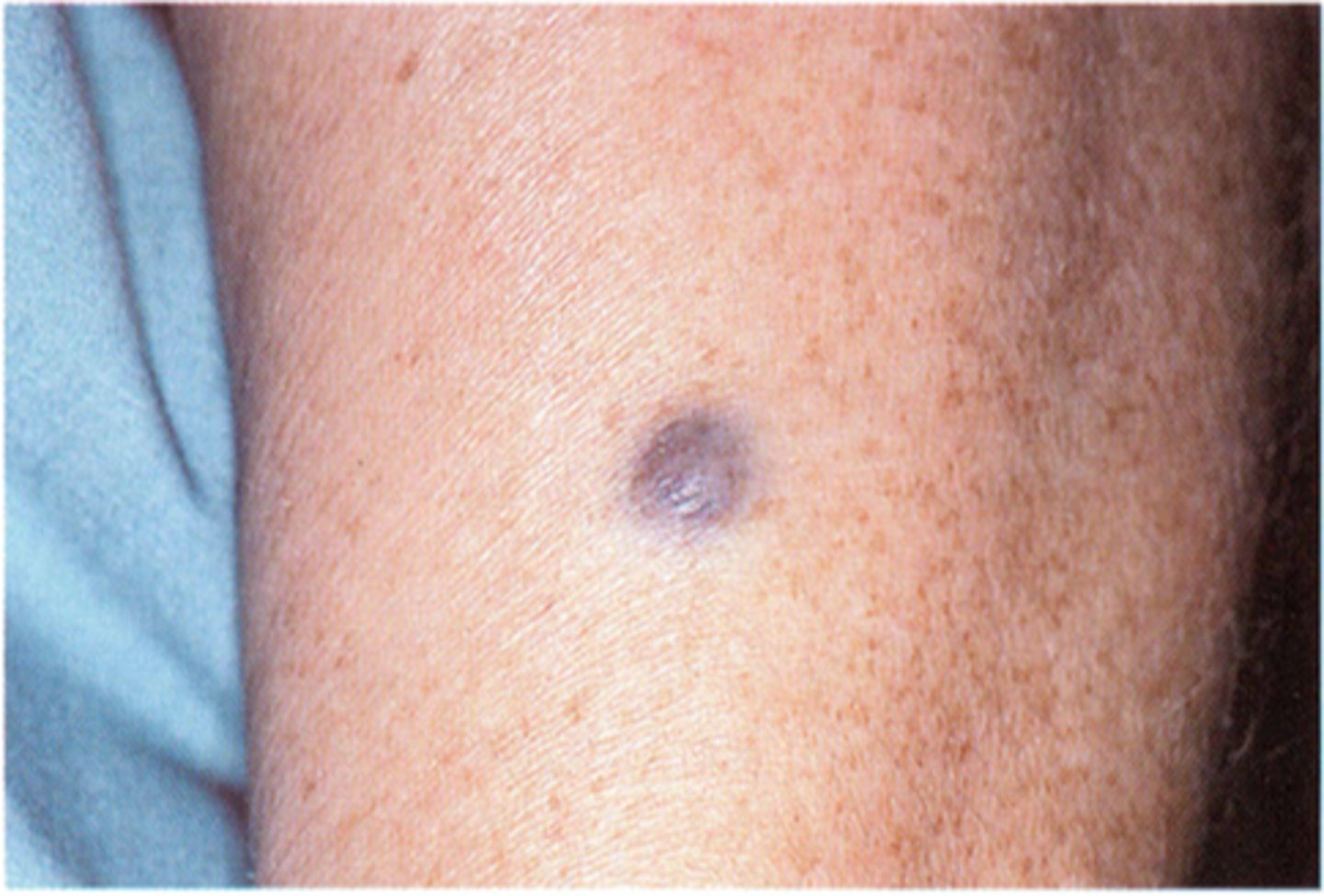
blue nevus
blue
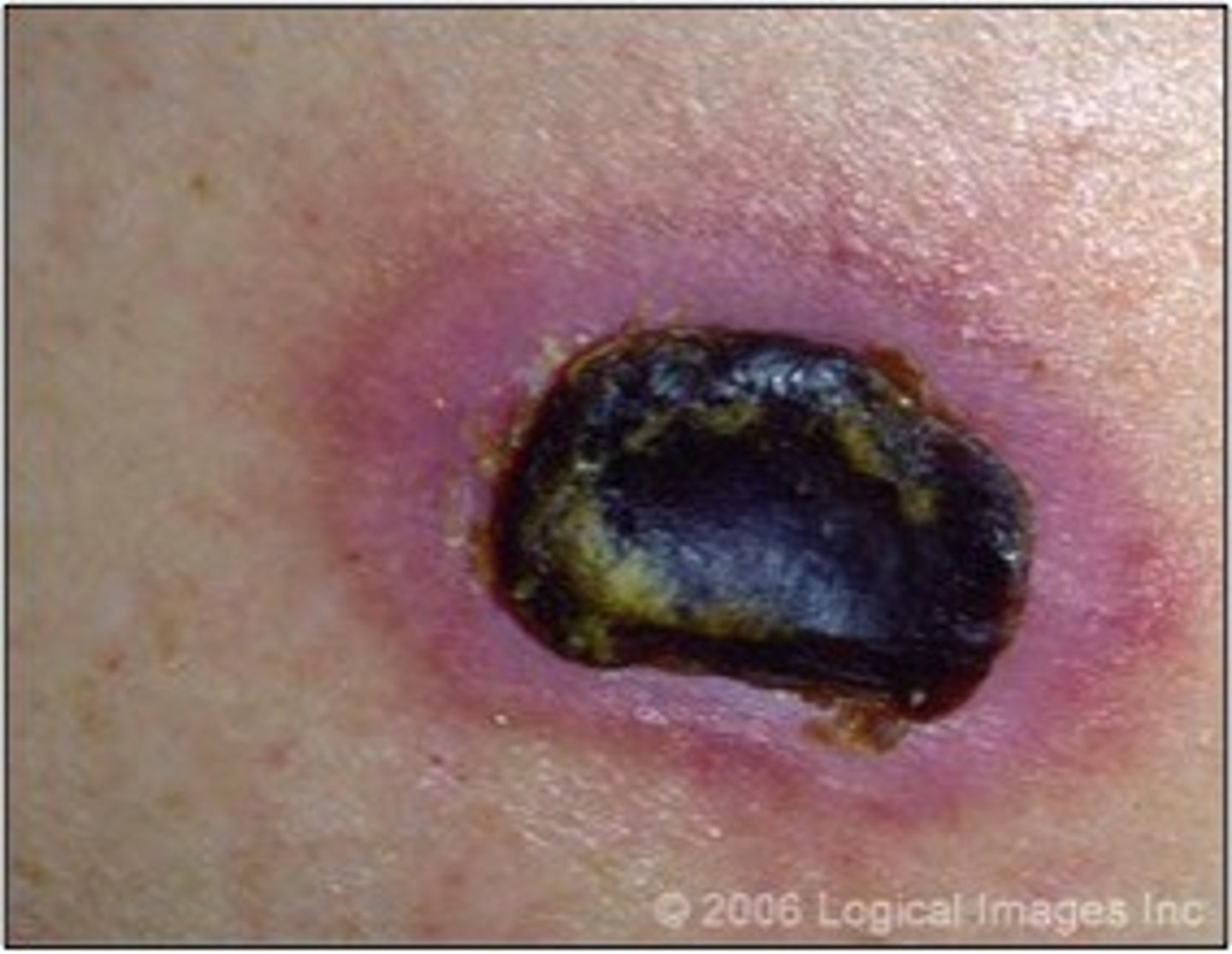
eschar
black
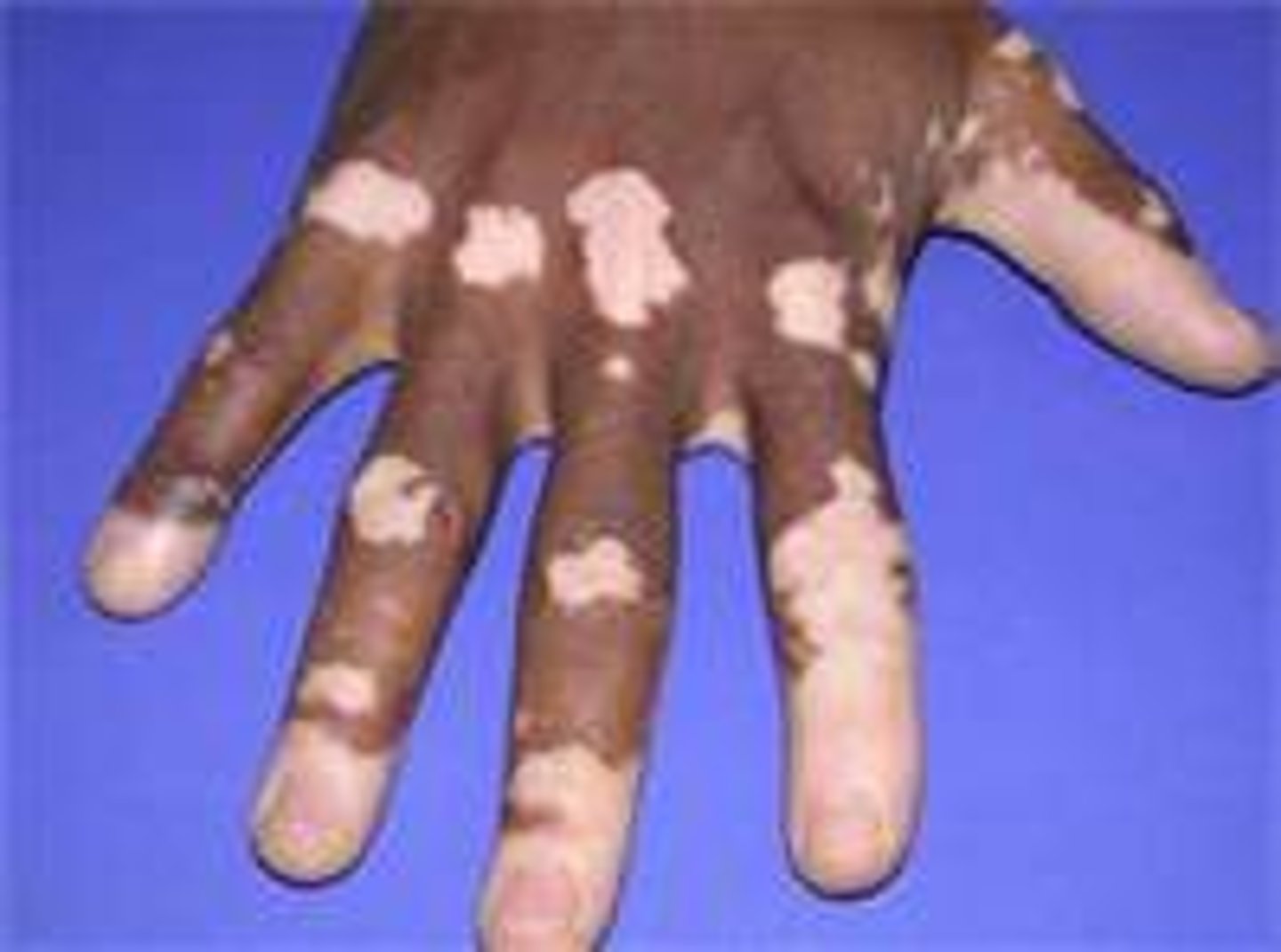
leukoderma
white/vitiligo
erythema
distinct area of redness
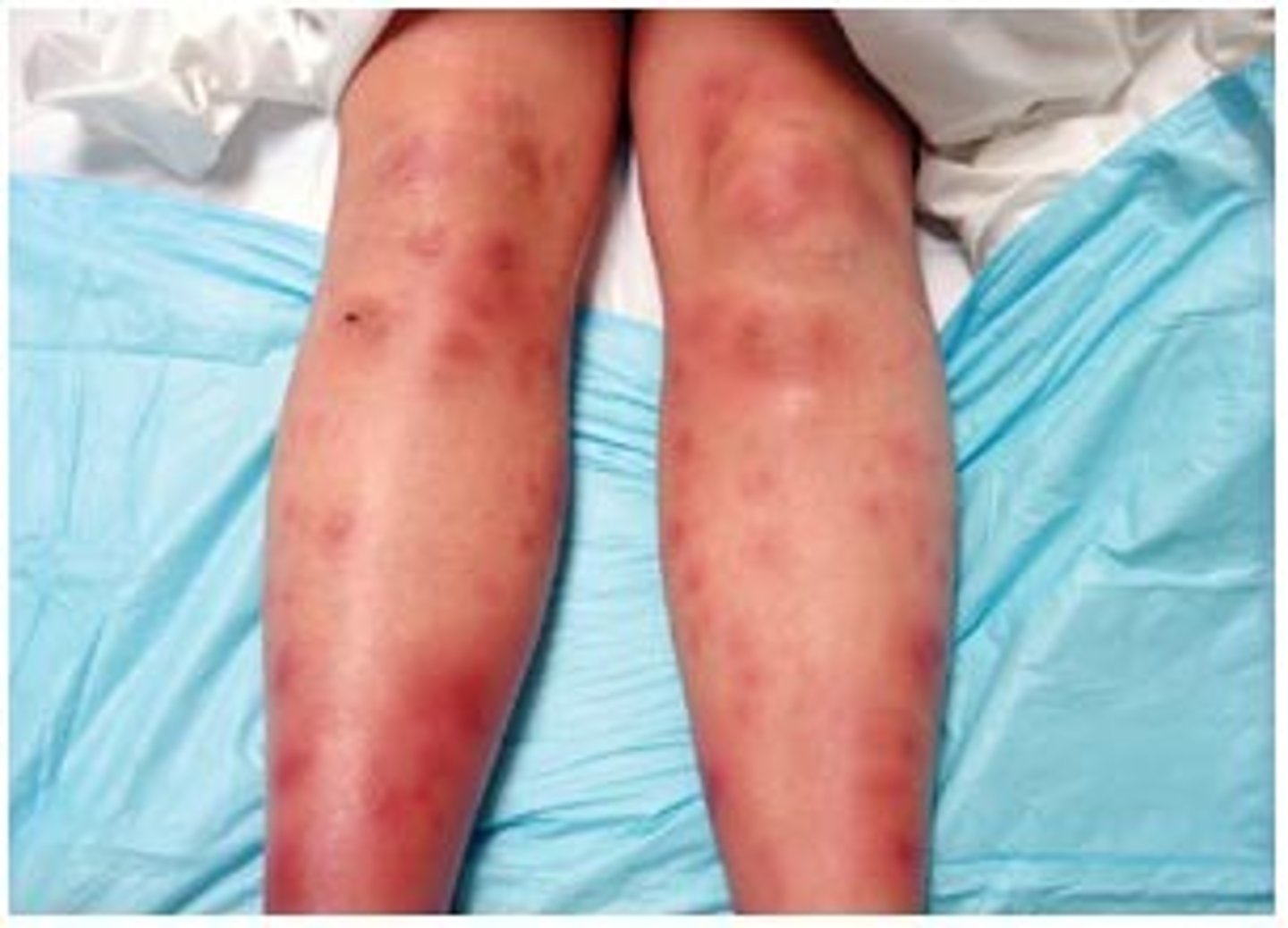
petichiae
blood in the skin, less than 4 mm
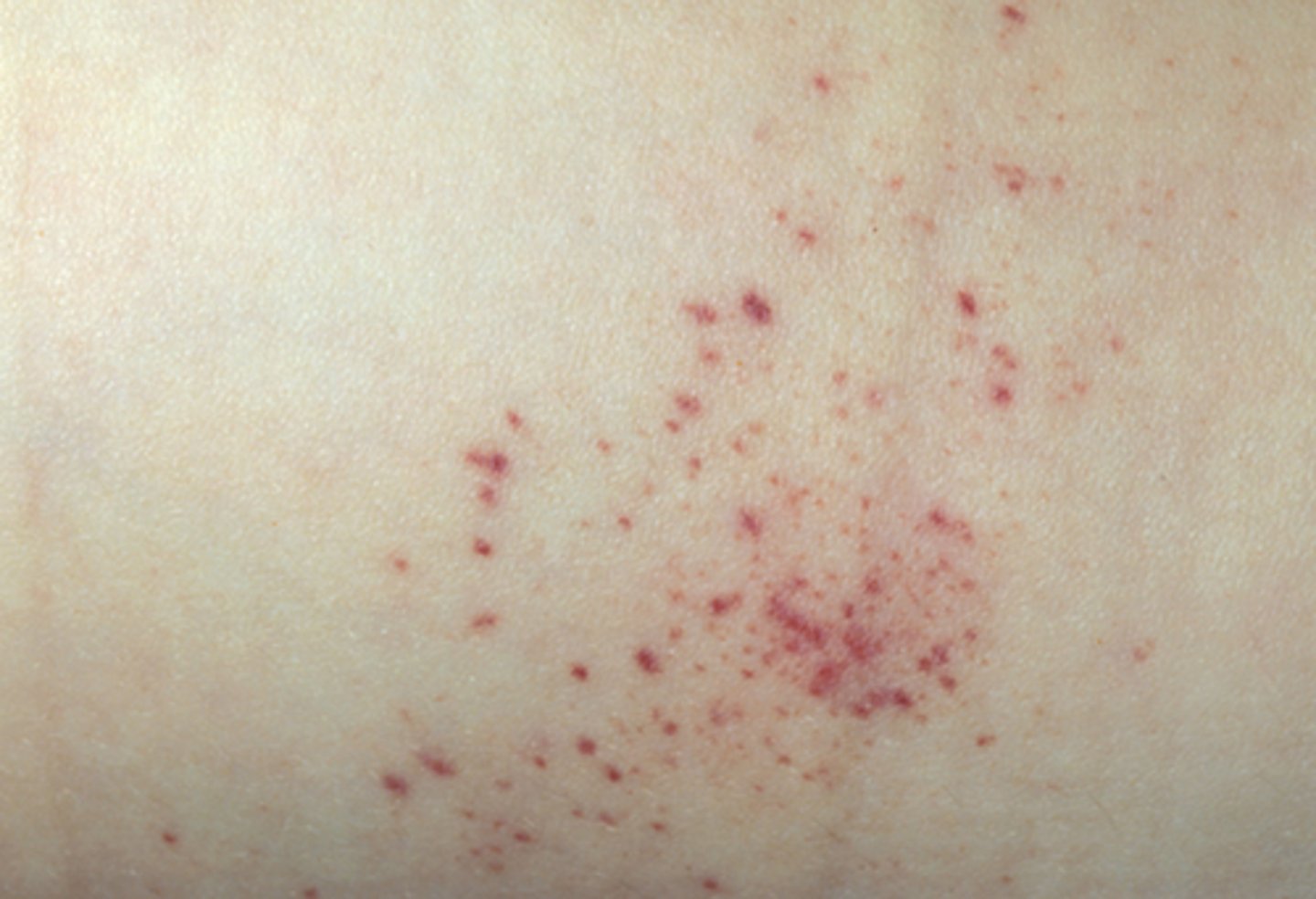
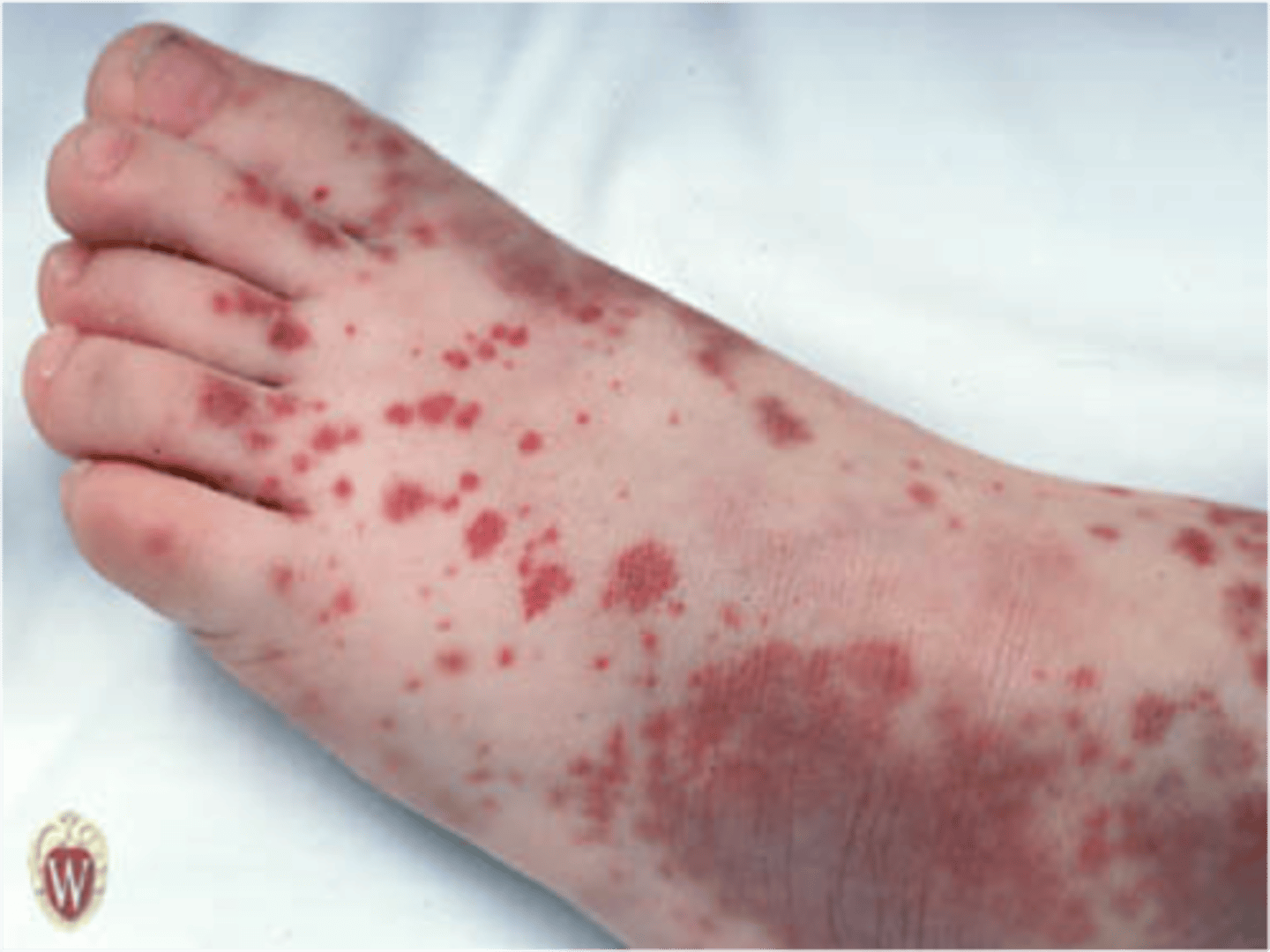
purpura
blood in skin 4 to 10 mm
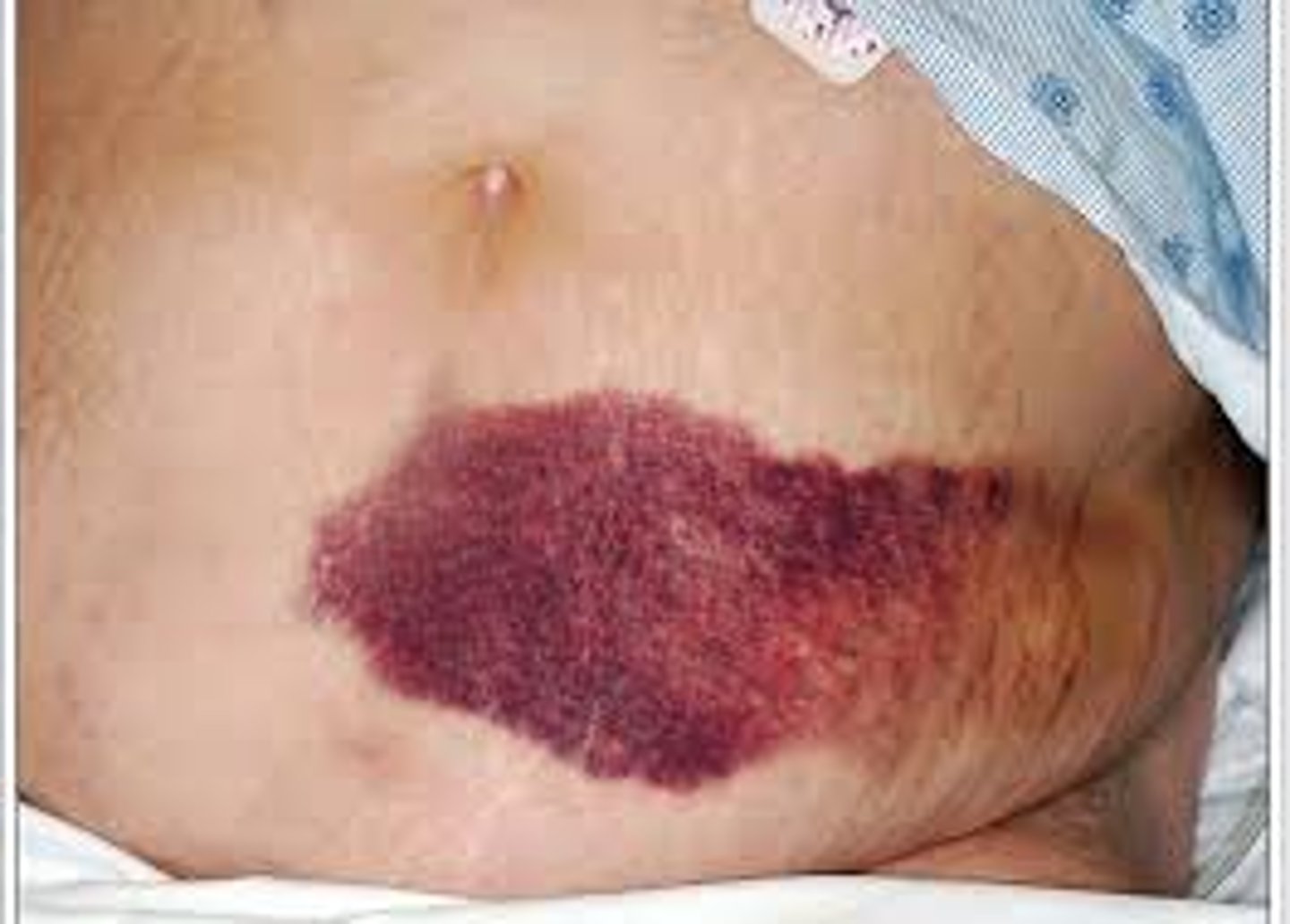
eccymoses
greater than 10 mm, bruise
annular
circle with central clearing
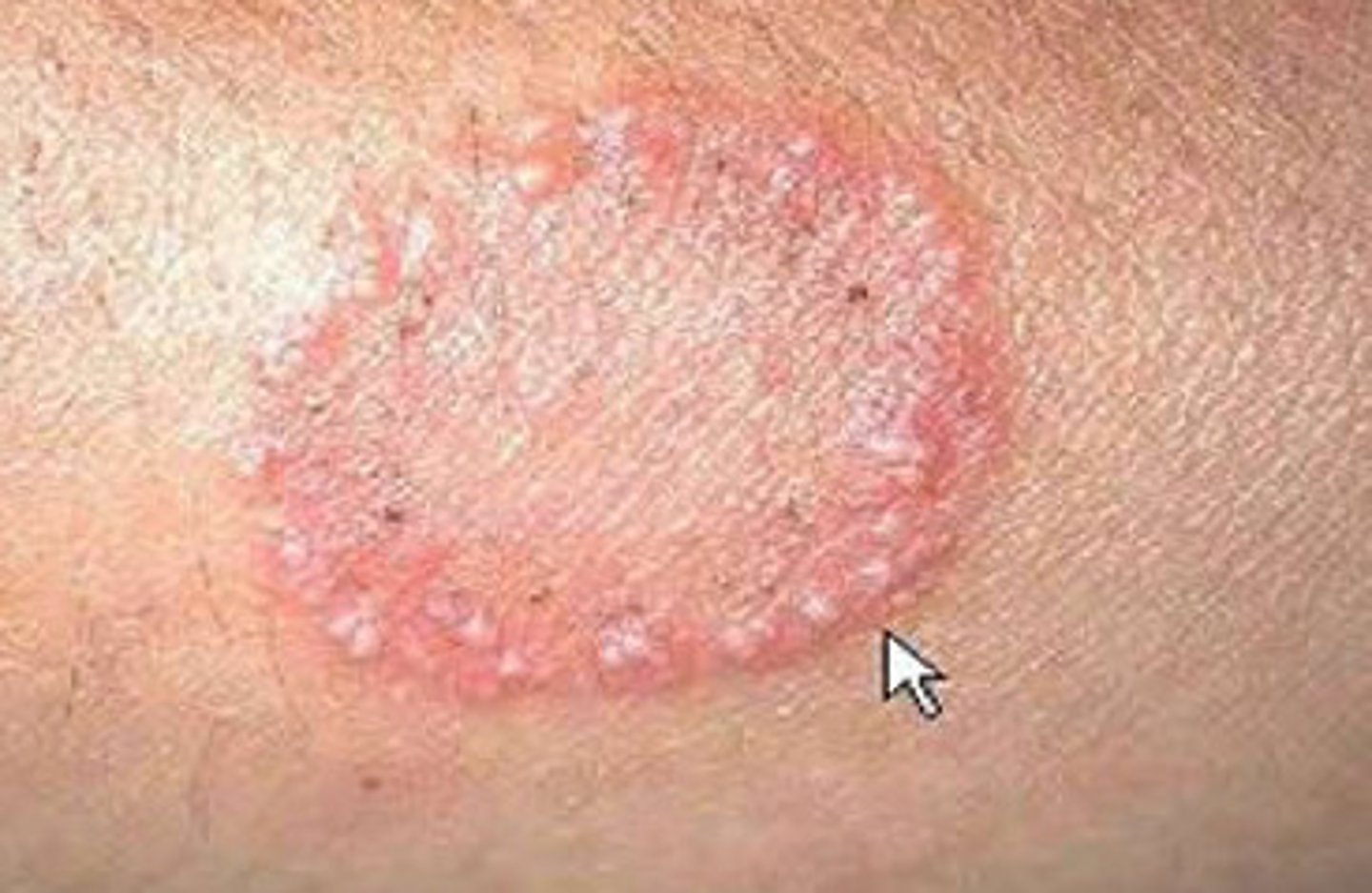
gyrate
whirling in a circle
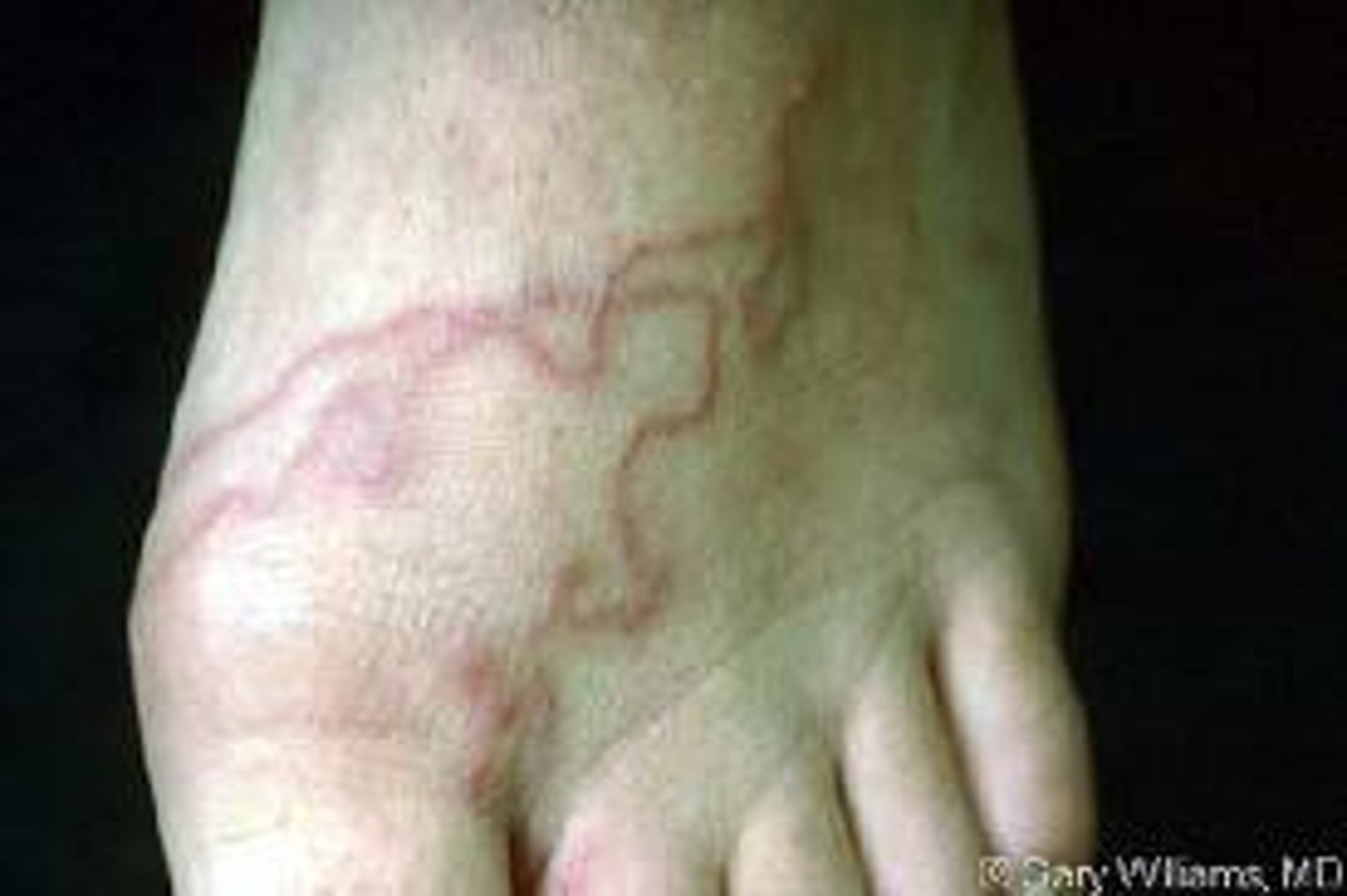
curvilinear lesion
half circle
discoid
round, nummular, coin shape
Lyme disease
bullseye, target
serpiginous
serpent
reticular rash
lace like
serum
dried crust, exude blood plasma
fissure
crack
excoriation
Skin sore or abrasion produced by scratching or scraping
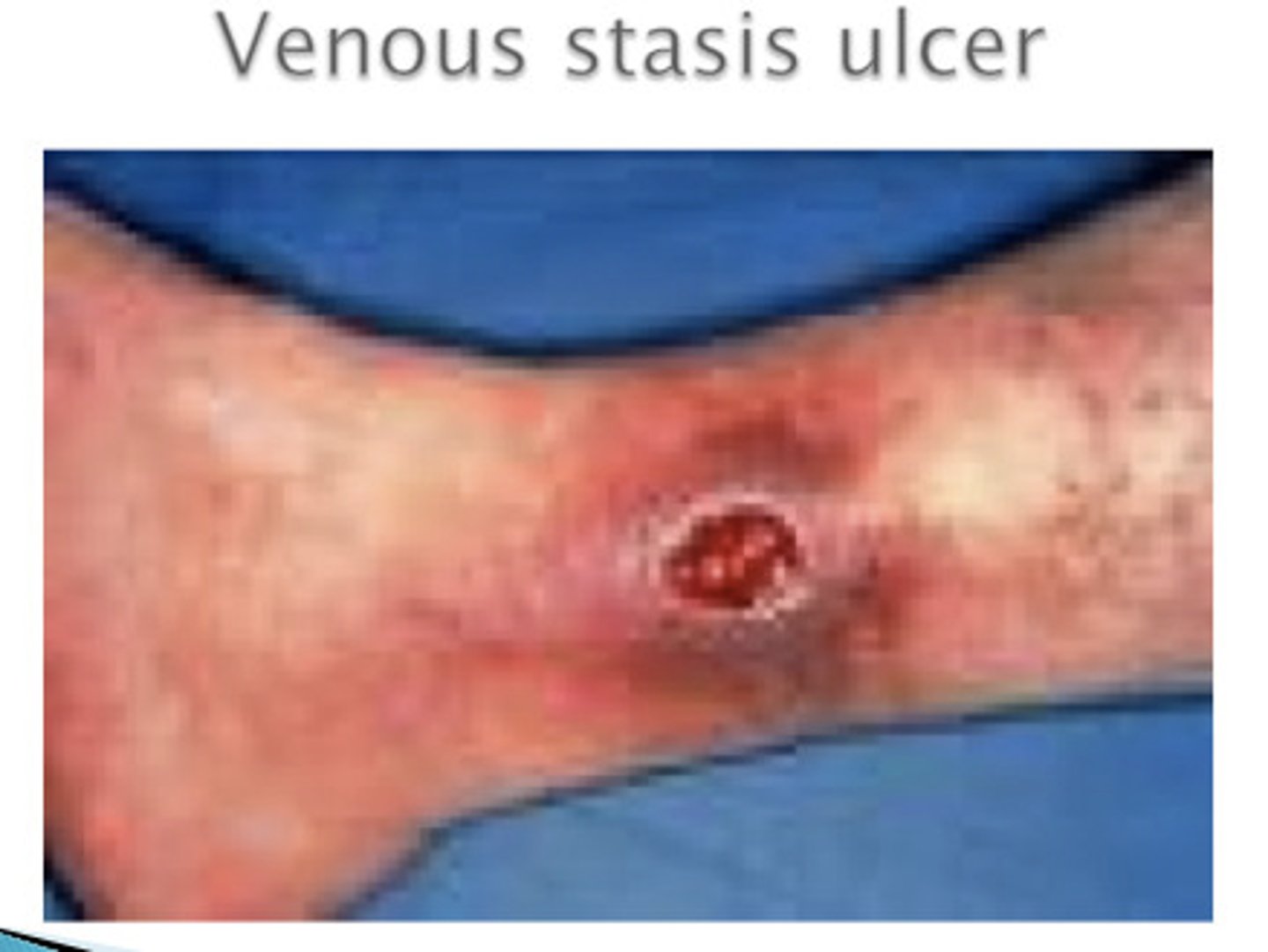
ulcer
open sore or lesion in the skin or mucous membrane- usually from lack of blood flow, hole from tissue decay
scaling
dry skin
Pedunculated
small neck and bigger in middle, like a skin tag
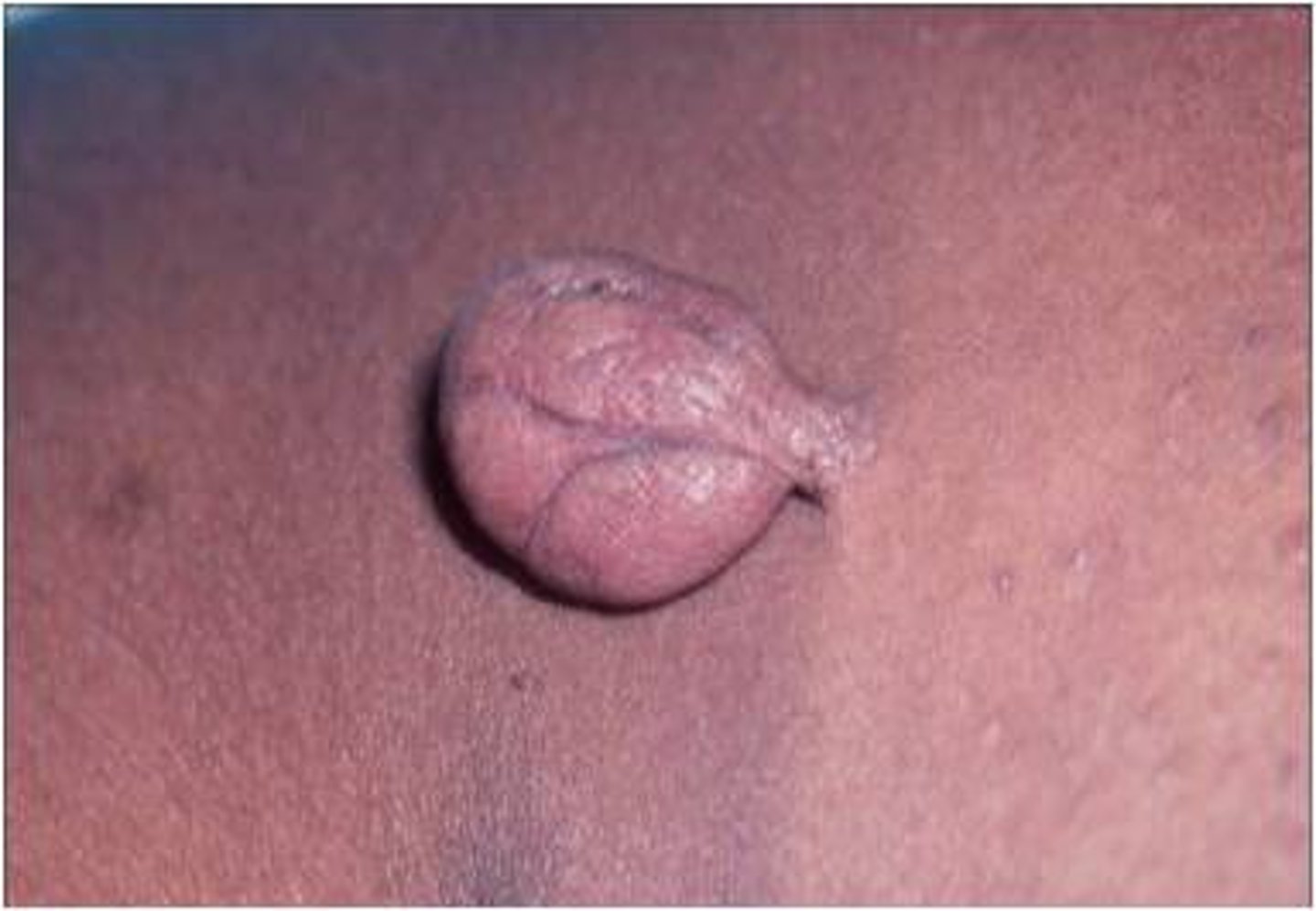
umbilicated
central depression (belly button)
extensor surfaces
Skin of the elbows, knees hands and feet that is on the outside of the joint, ie that is stretched when the joint is flexed.
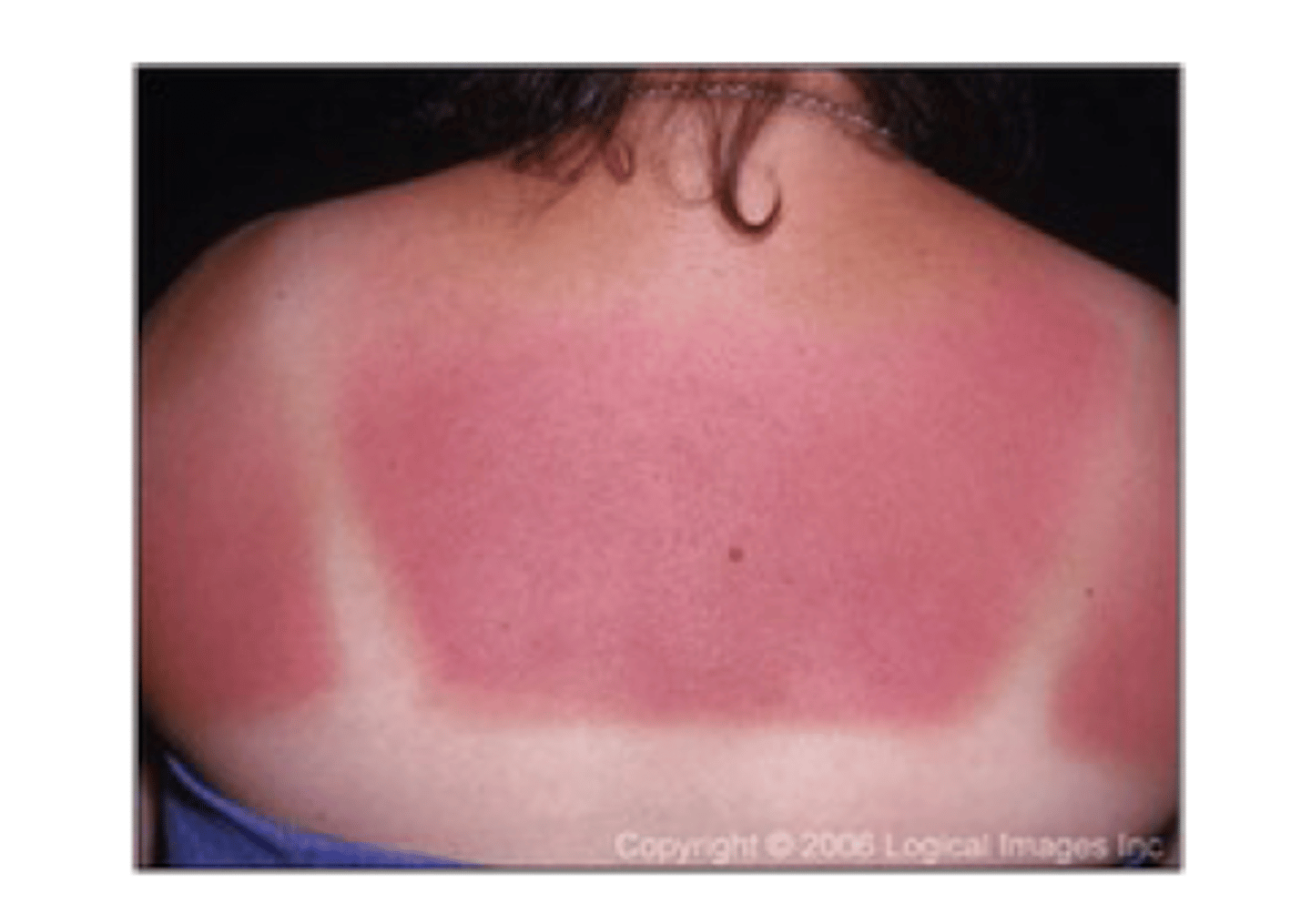
Photodistrubuted
sunburn
Dermatomal
referring to a lesion that follows a nerve or segment of the body. shingles
Acral
pertaining to the extremities
truncal
occurring on the trunk or central body
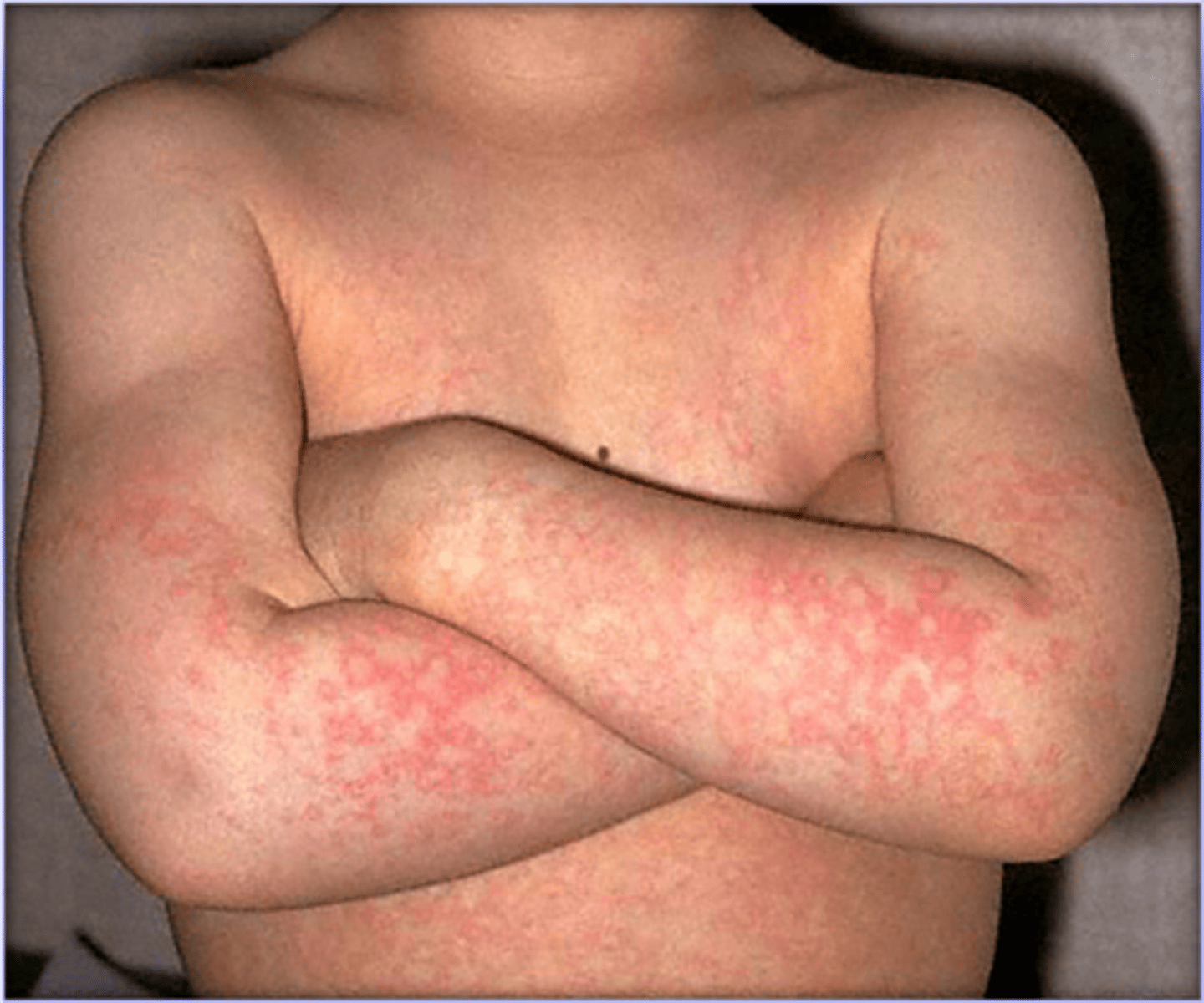
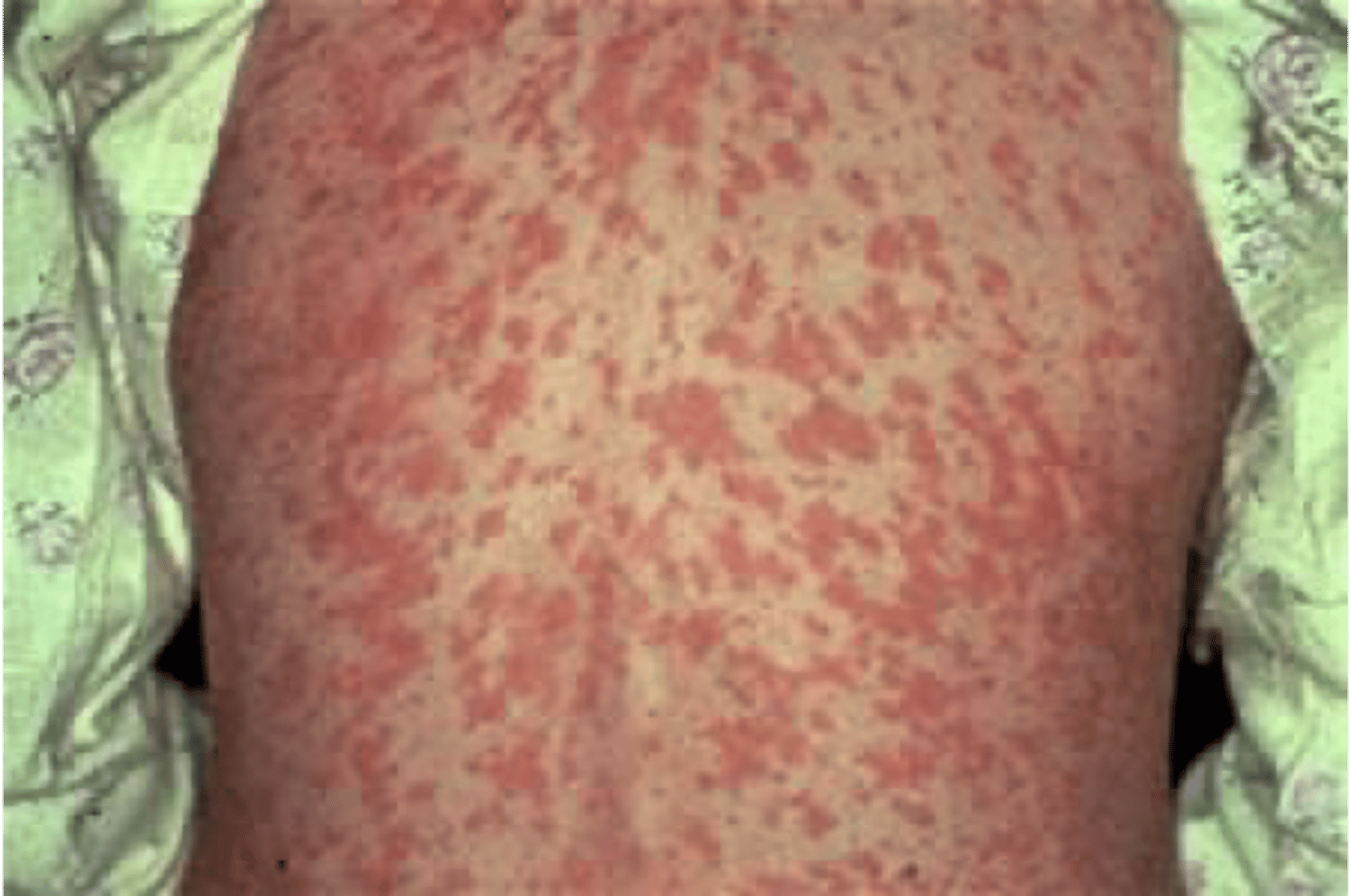
morbiliform rash
a rash that looks like measles
the rash consists of macular lesions that are red and usually 2-10 mm in diameter but may be confluent in places
cyanosis
Blue skin color - low oxygenation of hemoglobin
Pallor (blanching)
pale
icteris
jaundice (yellowing)
Diaphoretic
Characterized by light or profuse sweating. cold, clammy, appearing unwell
onchodystrophy
Pour nourishment and development of the nail
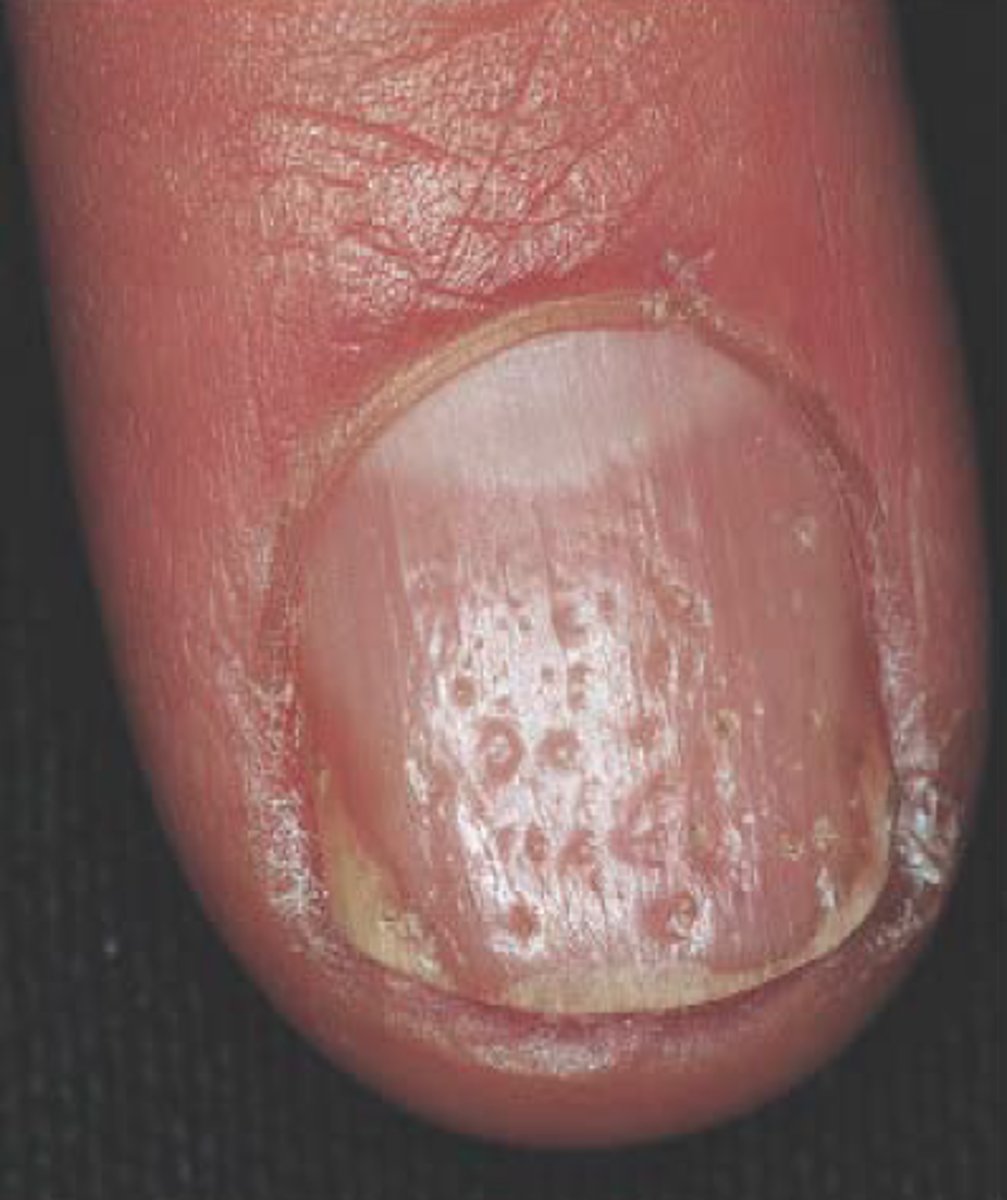
Pitting nails
punctate depressions of the nail plate caused by defective layering of the superficial nail plate by the proximal nail matrix; may be seen with psoriasis, Reiter's syndrome, sarcoidosis, alopecia areata, and localized atopic or chemical dermatitis.
Onychoschizia
splitting or lamination of the nail plate into layers that flake off
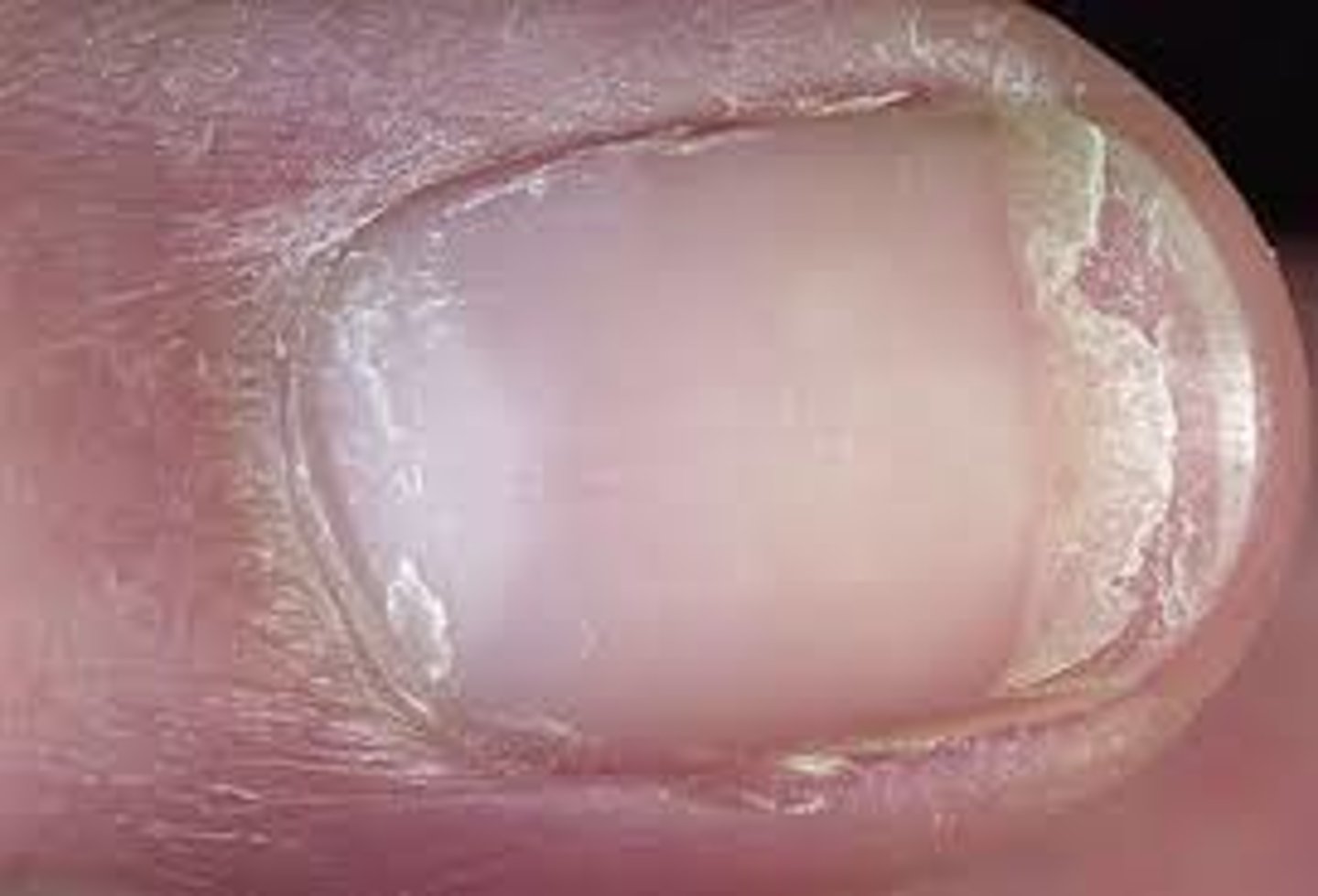
Koilonychia
Spoon nails
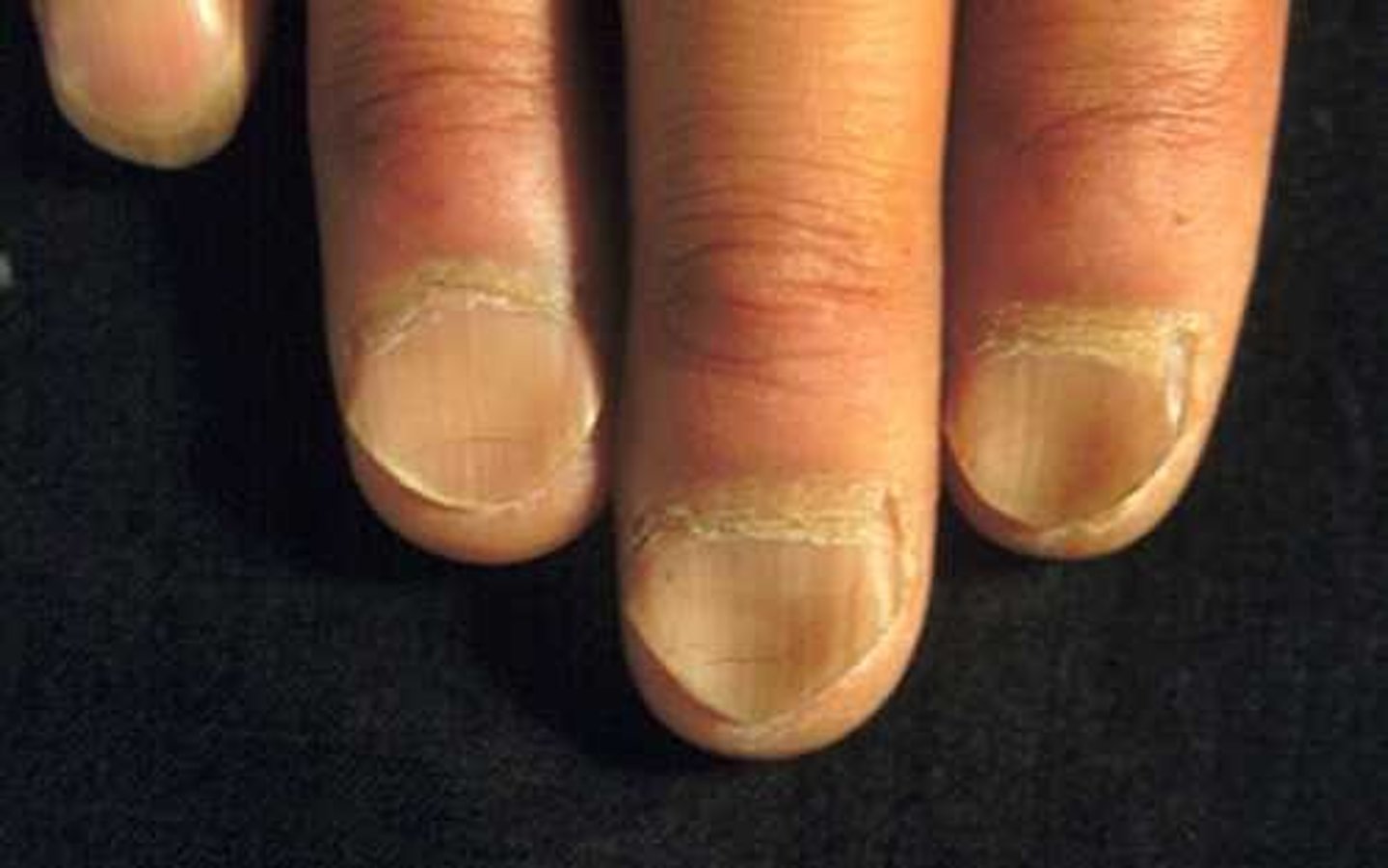
clubbing
bulbous enlargement of distal phalanges of fingers and toes that occurs with chronic cyanotic heart and lung conditions
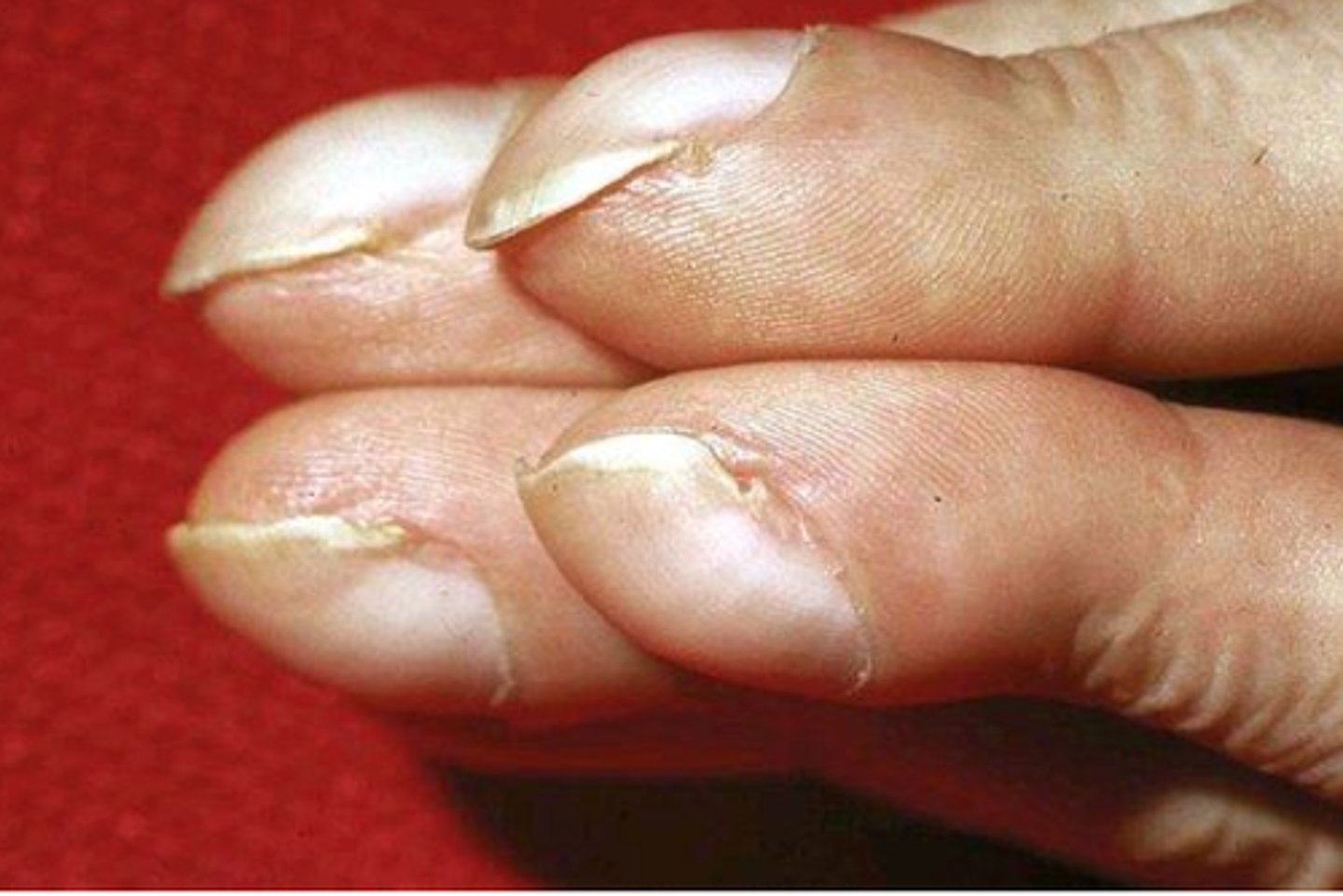
subungual
pertaining to under the nail
alopecia
hair loss
hirsutism
excessive hair growth over the body, male pattern
palpate
to examine by touch
percussion
tapping on a surface to determine the difference in the density of the underlying structure

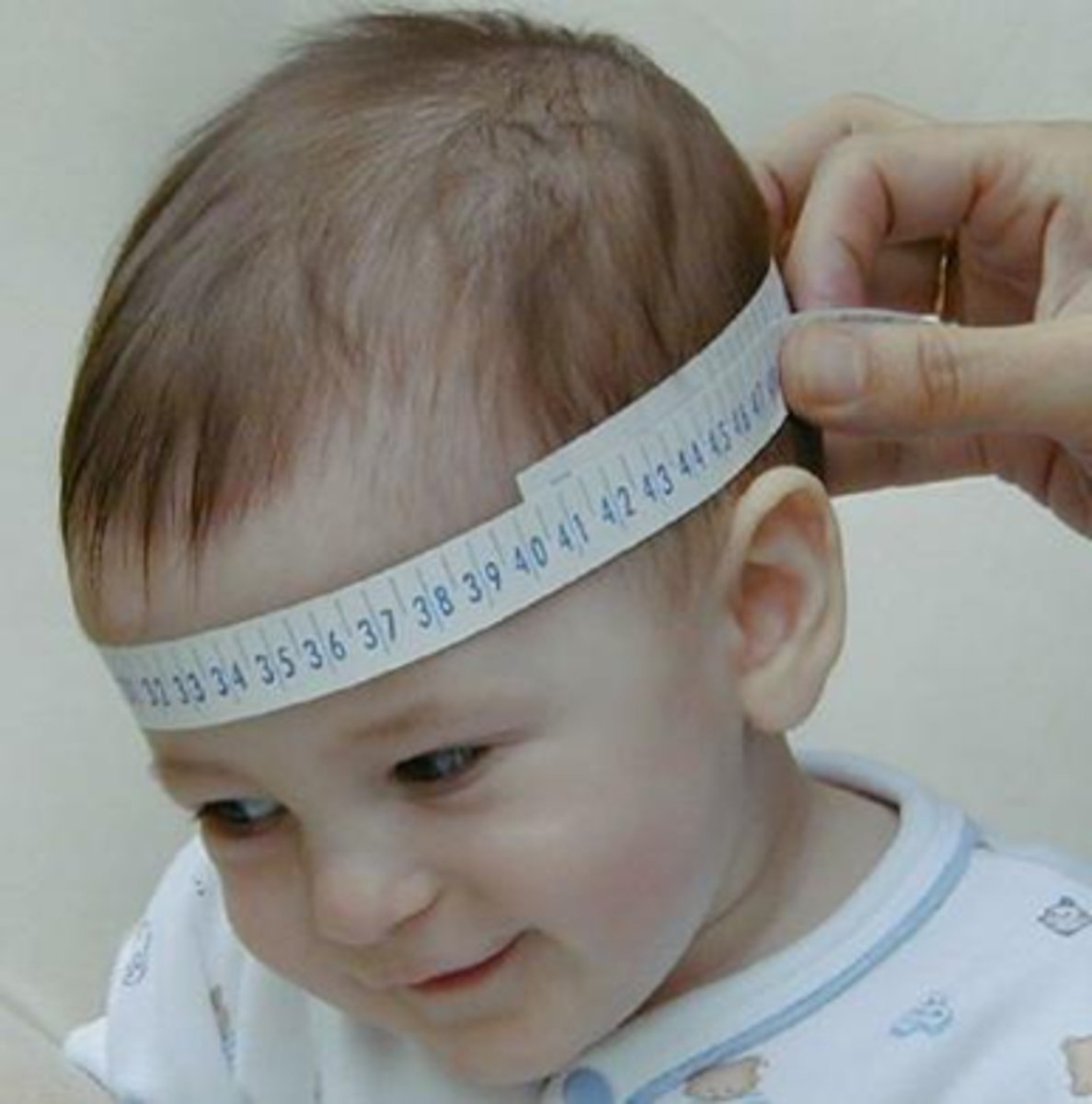
head circumference
a measurement that should be obtained on each visit until a child reaches 2 years of age.
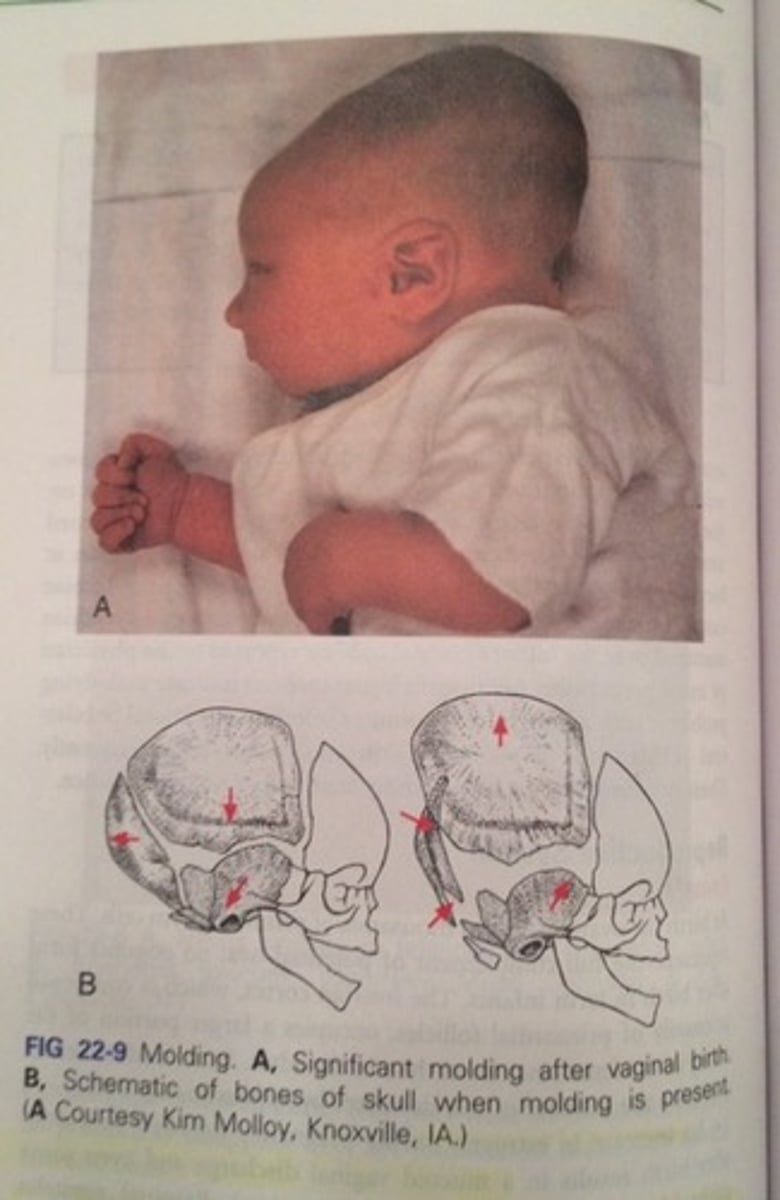
Molding
Shaping of the fetal head during movement through the birth canal.
subdural hematoma
collection of blood under the dura mater
Subgaleal hemorrhage
bleeding into the subgaleal compartment, forceps during birth
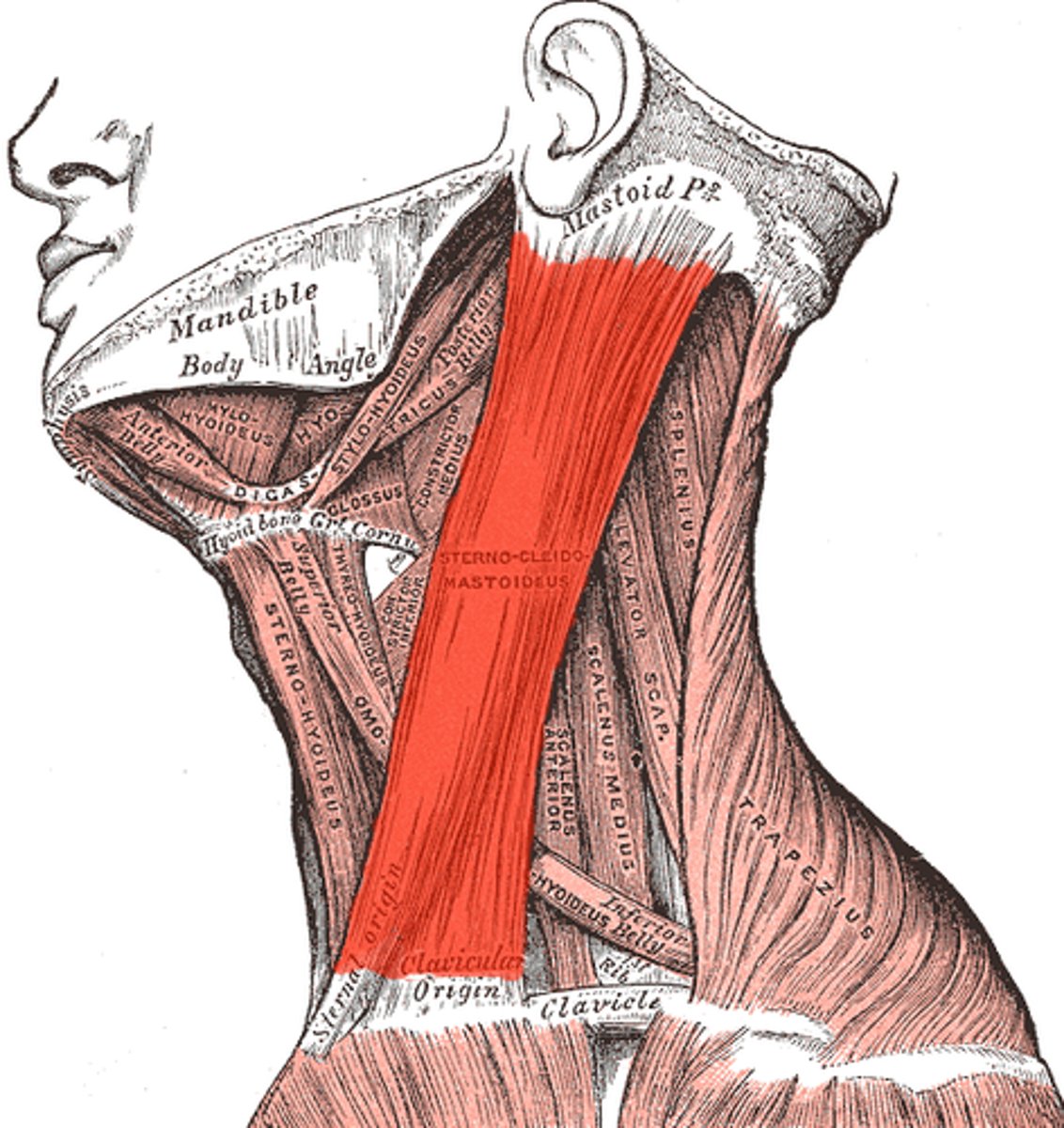
Sternocleidomastoid
flexes neck; rotates head
Trachea
windpipe, midline
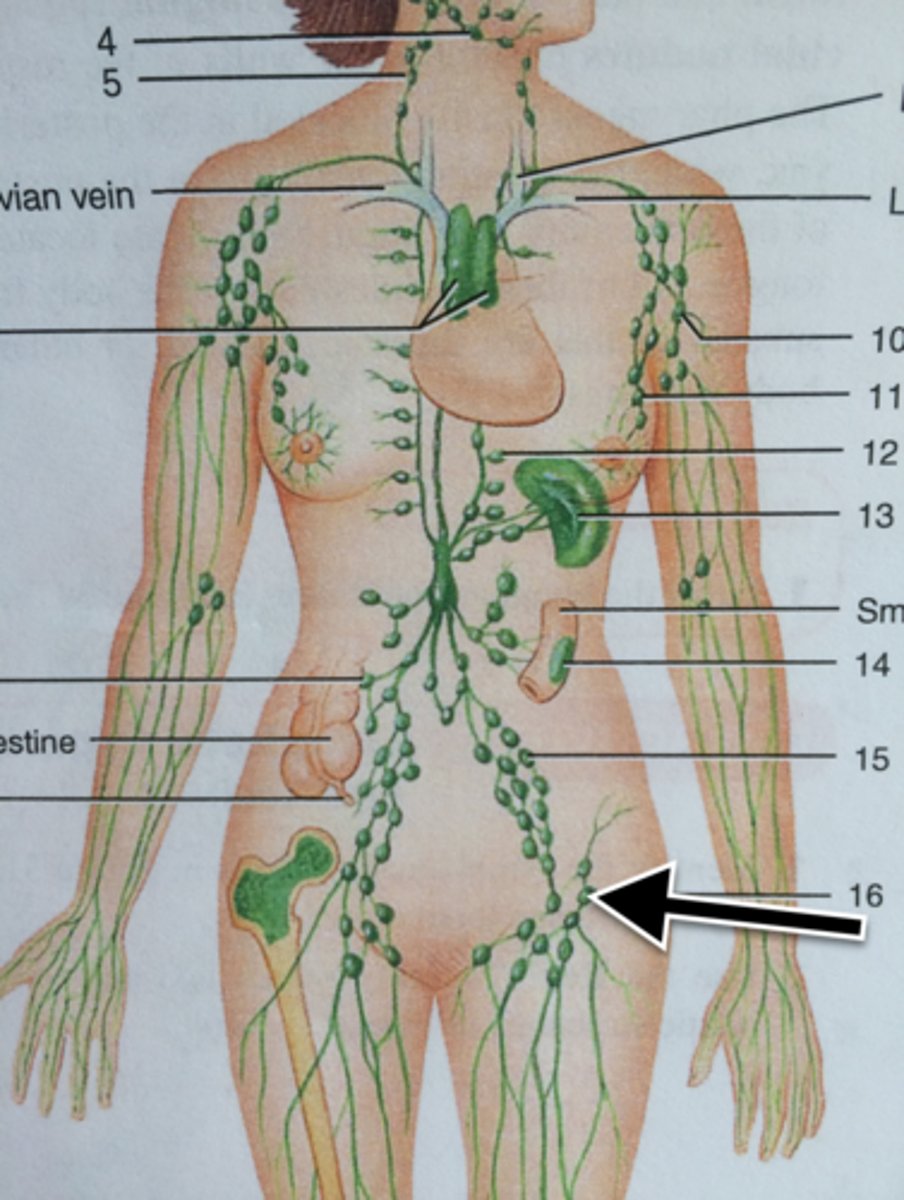
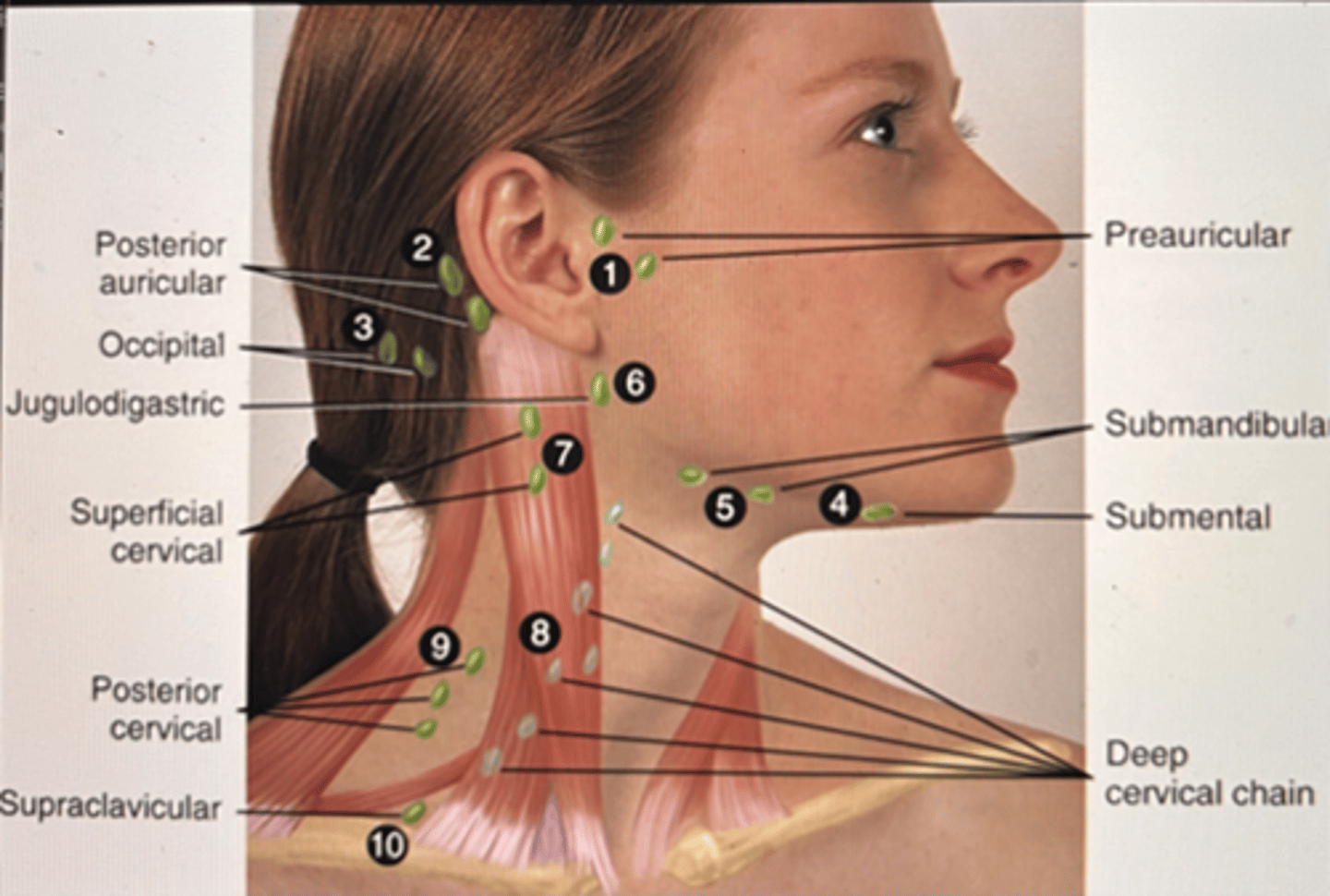
neck lymphatics
lumps, "swollen glands" (lymphadenopathy), goiter, neck pain or stiffness
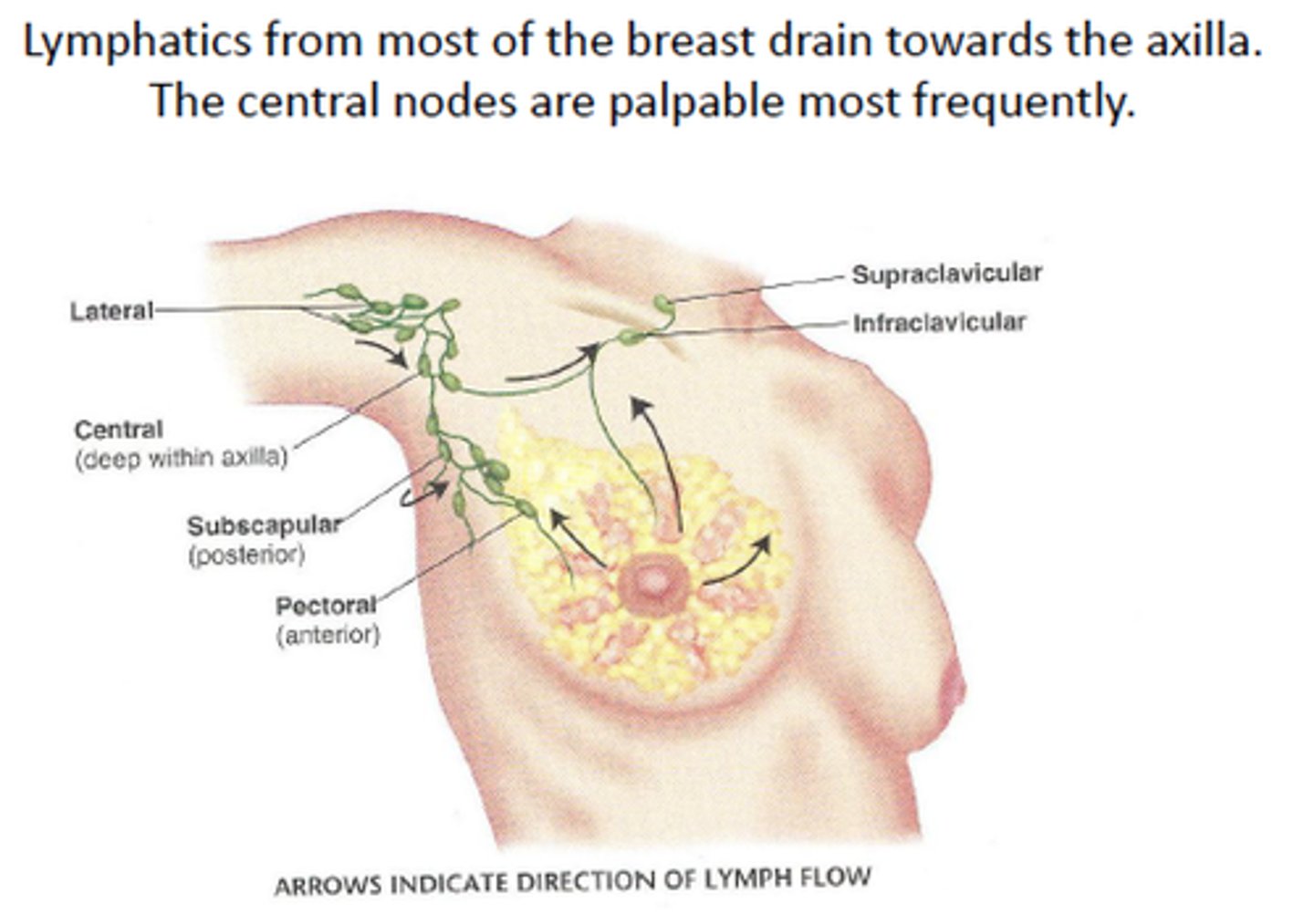
axillary lymph nodes
concentrated in armpit, receive lymph from upper limb and female breast
inguinal lymph nodes
located in the inguinal (groin) area of the lower abdomen