Athletic Injuries
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Williams & Andersen, 1998 Injury Model
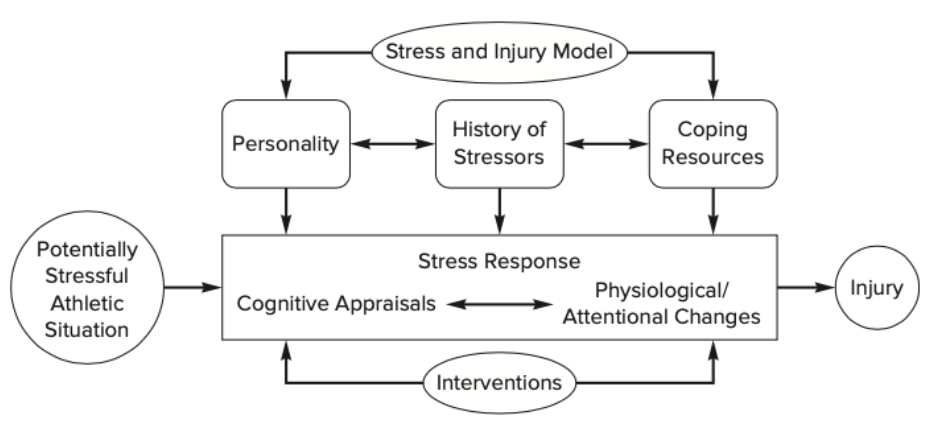
[Williams & Andersen 1998] certain ___ factors predispose individuals to injury, whereas others protect from injury
psychosocial
[Williams & Andersen 1998] central hypothesis of model: athletes with a history of (3 things) are more likely to appraise competition situations as stressful
history of many stressors
personality characteristics that intensify stress response
few coping resources
[Williams & Andersen 1998] stress response is a bidirectional relationship between …
cognitive appraisals and physiological/attentional responses to demanding athletic situations
[Williams & Andersen 1998] when an athlete views a competitive situation as challenging/exciting ...
good stress → increase focus → lower risk of injury
[Williams & Andersen 1998] when athletes appraise competition as threatening …
anxiety → perceive inadequate resources to meet demands of situation → higher risk of injury
[Williams & Andersen 1998] What do cognitive appraisals and physiological/attentional responses do to each other?
constantly modify each other (e.g. relaxing the body relaxes the mind)
[Williams & Andersen 1998] 3 culprits in stress-injury relationship
muscle tension
narrow visual field
increased distractibility
[Williams & Andersen 1998] important moments in history of stressors
major life changes
daily hassles
previous injury
[Williams & Andersen 1998] Which moment in history of stressors has most support from research?
major life events
especially those experienced in the year prior to the competitive season
risk of injury is directly correlated to level of life stress
personality and coping resources
desirable personality attributes and coping resources may help athletes perceive fewer situations as stressful
competitive state anxiety →
more injuries
optimistic and hardy →
fewer injury problems
high hardiness →
problem and emotion-focused coping
low hardiness →
avoidance coping
low sensation seeking
avoid unfamiliarity, lower tolerance for arousal, stay away from risky activities
risk taking predicts …
time loss and severity of overuse injuries
positive state of mind →
fewer injuries
negative state of mind →
higher rate of injury and/or severity
significant increases in mood disturbance immediately prior (3 hours to 3 days) to injury →
risk of serious injuries
social support →
influences injury outcome directly and lessens negative effects of high life-event stress
most injuries occur in athletes who … (2)
experience high stress negative life events
lack social support and psychological coping skills
integrated sport injury model
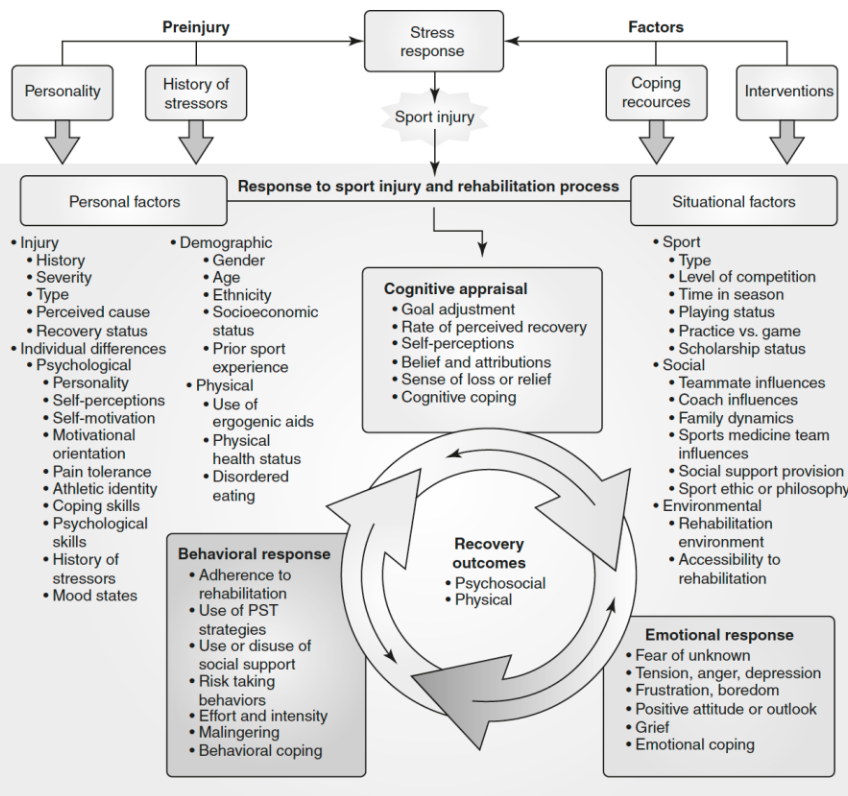
emotional responses to injury
disastrous
opportunity to show courage
relief from long season of poor performance
worry about recovery and return to previous physical state
underestimate severity of injury
depression, confusion, mood disturbance
cognitive appraisal chart
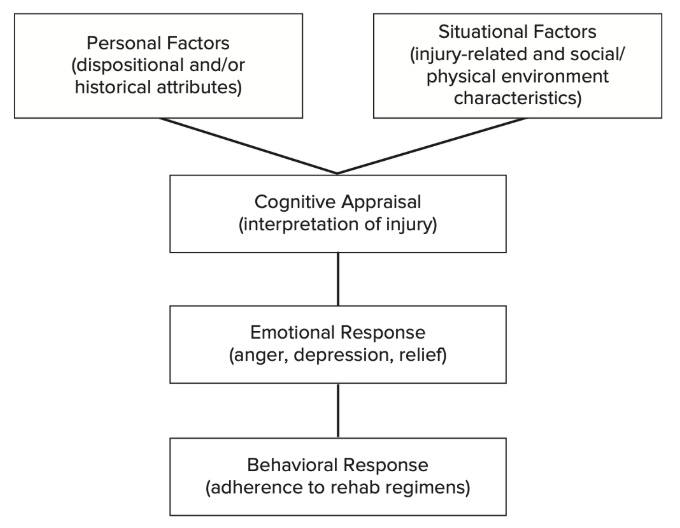
[cognitive appraisals] athletic injury is conceptualized as a stressor to the athlete, who then appraises the stressor in accordance with ___ and ___ factors
personal, situational
[cognitive appraisals] injury response comes from how the athlete …
perceives the injury
[cognitive appraisals] What do cognitive appraisals lead to?
cognitive appraisal → emotional response → behavioral response
[cognitive appraisals] What do behavioral responses typically entail?
responses to injury rehab
[models to explain reaction to injury] grief models
injured athletes proceed thru a series of stages on the way to recovery
[injury reaction models] cognitive appraisal model
response to injury comes from how the athlete perceives the injury
[injury reaction models] integrated model of response to sport injury
injury reaction is determined by personality, social, and emotional factors
[injury reaction models] biopsychosocial model
reciprocal interaction of psychological factors with biological and social/contextual factors in the rehab process
What is often the main identity focus for atheltes?
athletic identity
the more narrowly focused an injured athlete’s sense of self is, the more ___ the athlete will be
threatened
athletes more involved in sport before injury may perceive … at end of rehab
lesser degree of recovery
strong athletic identity may also correspond with greater ___ during rehab
motivation
How can coaches and trainers help an athlete during injury?
they can push athletes to focus on other hobbies in life
What are some benefits following injury?
personal growth
psychologically based performance
physical/technical development
improved social networks
increased knowledge of anatomy
increased resilience
growth
Who else might be a good fit to provide sport psych services?
athletic trainers