Social Influence
1/119
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
120 Terms
Types of Conformity
Compliance, Internalisation, Identification
Who identified 3 types of conformity
Kelman in 1958
Define Compliance
Most superficial form of conformity
Only a public change
Define identification
Middle change of conformity
Public change in behaviour, person thinks there is something in a group that is valued
Define internalisation
Deepest level of conformity
Person genuinely accepts norms
Changes behaviour publicly and privately
What are the two explanations of conformity
NSI (Normative Social Influence)
ISI (Informational Social Influence)
Define NSI
When an individual conforms to avoid feelings of rejection or gain approval
EMOTIONAL CHANGE
Define ISI
When an individual conforms because they accept others information
COGNITIVE CHANGE
Often occurs in new situations
NSI Studies
Asch: Conformity decreased when PPTs were told to answer on paper instead of aloud
McGhee and Teevan : Students with a greater need to be affiliated to others (naffiliators) were more likely to conform
ISI Studies
Lucas et al. : Asked students maths questions ranging in difficulty, harder the questions = more likely to conform
Perrin and Spencer : STEM students are less likely to conform, more secure in knowledge
EVAL: ISI and NSI work together
Both processes work together, cannot always tell which one is the driving factor behind conformity
EVAL : Individual differences in ISI
Asch: students are less conformist (28%) than other participants (37%)
EVAL: Support for NSI
Asch: Repeated his study and had participants write answers down, conformity fell to 12.5%
When was Asch’s Study
1951
ASCH
Aims
Study the extent social pressure can change a person’s mind and lead them to conform
ASCH
Procedure
123 Male Undergraduate American Students
18 test, 12 of those are critical
ASCH
Findings
33% conformity on the 12 critical tests, 75% of participants conformed at least once
ASCH
3 variations
Group size
Unanimity
Difficulty
ASCH
Variations : Group size
Increase to 3 confederates = Conformity increases by 30%
Most conformity occurred at 7 confederates
ASCH
Variations: Unanimity
Add a non-conforming dissenter = decreased conformity by 25%
ASCH
Variations: Difficulty
Make difference between lines harder = Increase in conformity
EVAL: Asch ‘s study is product of it’s time
Perrin and Spencer reproduced study in 1980, found 1 student conformed
1950’s America VS. 1980’s UK could be a large differentiating factor between the results
EVAL: Demand characteristics in Asch
Task of identifying lines is trivial, less likely to be taken seriously
Group was not one that formed bonds of a regular group, less incentive to conform
Limits the generalisability of the study
EVAL: Limited application of Asch
Collectivist (china, India) vs. Individualistic (USA,uk) cultures
Bond and Smith: Collectivist cultures are more oriented to group needs, more likely to conform for own good
Neto: Women are more likely to conform than men, but only men were in the study
EVAL: Asch only applies to certain scenarios
Williams and Sogon: Conformity is higher when group is friend, not strangers
ZIMBARDO
When was the SPE
1971
ZIMBARDO
Aims
Examine whether people would conform to rules in a role
ZIMBARDO
Procedure
Newspaper ad = 24 male participants
Arrested, blindfolded and deloused during night
Randomly assigned roles, given uniforms and numbers
ZIMBARDO
Define deindividuation
Loss of social awareness through fact that they cannot be identified individually
ZIMBARDO
Findings
After 2 days = Prisoners rebelled, guards retaliated, punishments began for minor infractions
3 prisoners removed due to psychological damage
EVAL: Control of SPE
High levels of control over variables: random assignment of roles, made sure all volunteers are stable
High internal validity = more confidence in conclusions drawn
EVAL: Lack of realism in SPE
Banuazizi and Mohavedi: Ptp were play-acting, used stereotypes to guide their behaviours
BUT Zimbardo said 90% of prisoner conversations were about ‘prisoner life’
EVAL: Role of dispositional influences
Fromm: Accusses Zimbardo of over exaggerating how the situation influenced behaviour, and minimised personality factors. Claimed 1/3 behaved harshly, 1/3 stuck to the rules, 1/3 were sympathising with prisoners
EVAL: BBC prison study
Reicher and Haslam: Reproduced study, prisoners overtook the mock prison
Claim it was due to social identity theory, prisoners managed to form a cohesive, social identity which made them strong as a group
EVAL: Zimbardo’s ethics
Dual roles - Superintendent and lead researcher, when a prisoner would ask to leave he would act in a way as the superintendent not as a researcher allowing someone’s right to leave
EVAL: Real life application to Abu Ghraib
Could argue that social positions and the shared social identity between soldiers in Abu Ghraib could explain their behaviours
When was Milgram’s study
1963
MILGRAM
Aims
Wondered why so many Germans went along with Hitler’s plan
He wanted to know if Germans were inherently more obedient
MILGRAM
Procedure
40 male participants from flyers about memory test
Between 20 and 50
Offered $4.50
MILGRAM
Procedure of test
Experimenter and student were always confederate
Student strapped to electrodes, teacher required to give shock every time a wrong answer given
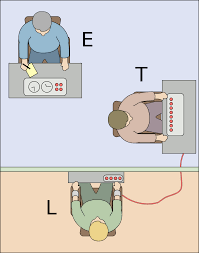
MILGRAM
Volt scale
15 to 450 volts
At 300 = student pounds on wall and gives no response
MILGRAM
encouragement
If PPT was unsure they were told 1 of 4 things
Please continue, please go on, the experiment requires you continues, you have no choice you must go on
MILGRAM
Findings
QUANTITATIVE
12.5% (5/40) stopped at 300 volts
65% (26/40) went all the way to 450 volts
QUALITATIVE
Signs of extreme tension e.g. sweating, trembling, biting lips, 3 had seizures
MILGRAM
prior assumptions
M asked 14 students to predict behaviour
Estimated 3% would go to full 450 volts
MILGRAM
Post information
All PPTS debriefed
84% said they were glad they participated
EVAL: Low internal validity for Milgram
Orne and Holland: Participants didnt think shocks were real, low internal validity
Perry: Listened to tapes of the participants, found many expressed doubt about shocks
BUT Sheridan and King: 54% of men and 100% of women gave apparently fatal shocks to a puppy
EVAL: High external validity for Milgram
Central feature of experiment is the relationship between participant and ‘experimenter’
Hofling et al: 21/22 nurses obeyed a doctor asking them to give a fatal dosage to patients (mirrors the dynamic that milgram’s study was aimed at)
EVAL: Supporting replication
Le Jeu de la Mort: Replicated Milgram on a fake pilot for a show, 80% participants delivered full 460 volts to an ‘unconscious’ man
Showed similar behaviour to Milgram’s study, nail-biting, nervous laughter
EVAL: Alternative explanation to obedience, social identity theory
Suggested reason for obedience: Participant identified with experimenter and the science of the study
Haslam and Reicher: Analysed behaviour from participants at the prompts from the experimenter, every time the fourth prompt was used (you have no choice, you must go on), the participant quit
MILGRAM
3 situational variables
Proximity
Location
Uniform
MILGRAM
Situ Vari : Proximity
1 ‘Student’ and PPT placed in same room
65% full obedience → 40% full obedience
2 PPT has to force ‘student’s hand onto electroshock plates
65% FO → 30% FO
3 ‘Experimenter’ gave PPT instructions over the phone
65% FO → 20.5% FO
PPTs also gave lower shocks that supposed to
MILGRAM
Situ Vari : Location
Yale University basement → run down building
Experimenter has seemingly less authority
65% FO → 47.5% FO
MILGRAM
Situ Vari : Uniform
Experimenter taken away by a phone call, role taken over by ‘member of public’
65% FO → 20% FO
LOWEST OF ALL
EVAL: Research support for variation
Bickman: 3 confederates in 3 outfits: jacket and tie, milkman’s outfit, security guard uniform
Asked passers-by to perform basic tasks e.g. pick up litter, ask for change
People twice as likely to obey security guard than man in jacket and tie
EVAL: Lack of internal validity variations study
More likely for participants to guess procedure was fake e.g. member of public giving orders
Unclear whether results are from obedience or because they guessed it was faked
EVAL: Cross-cultural replications
Miranda et al: 90% obedience from Spanish students, not all male and in a different culture
BUT Smith and Bond: Most replications are in Western, developed countries, which are culturally not to different
EVAL: High control of variations study
Milgram systematically altered the variables for each situation, meaning the conclusions drawn are more internally valid
EVAL: Provides obedience alibi
Provides situational explanation for obedience
Mandel: Criticises obedience alibi provides an out for people who commit acts under the excuse of obedience e.g. the Holocaust
2 socio-psychological factors
Agentic state
Legitimacy of authority
Define agentic state
When a person doesn’t take responsibility as they are acting for someone else
They experience high amounts of anxiety but feel powerless to disobey
Define autonomous state
Person is free to act in accordance to their own principles
Can sense the responsibility of their actions
Define agentic shift
Shift from autonomy to agency
Why does agentic shift occur
Milgram suggested this occurs when someone perceives someone as an authority figure
They have more power due to the social hierarchy
When someone is in charge, others defer to the person and shift
Define binding factors
Aspects of a situation that allow a person to minimise the damaging effect of their behaviour and reduce their moral strain
Example of binding factors
Shifting responsibility
Denying damage
Legitimacy of Authority
Hierarchy of power, that we as a society have agreed they deserve to hold e.g. police officers, teachers
Most accept that they deserve to exercise social power over others, we are willing to give independence and control of power over to people as we trust they will wield it properly
Destructive authority from Legitimacy of authority
Problems arise when legitimate authority is used destructively e.g. Hitler, Stalin, Pol Pot
EVAL: Cultural difference in legitimacy of authority
Kilham and Mann: Replicated Milgram in Australia, only 16% went to the full voltage
Mantel: Replicated in Germany, found 85% went to the full voltage
Shows that some cultures are view authority in varying ways especially in terms of legitimacy
EVAL: Research support for legitimacy of authority
Blass and Schmitt: Showed film of Milgram’s study to students, asked them who they thought was responsible
Students blamed the experimenter not the student, as they were in the position of authority
EVAL: Agentic state is limited explanation
Doesn’t explain why some people don’t obey (humans naturally obey their social hierarchies)
Doesn’t explain Hofling et al, as it predicts that the nurses would display signs of anxiety
EVAL: Obedience alibi can fail in circumstances
German Reserve Police Battalion 101: Refused to shoot civilians in Poland
Does not fall into the assumptions of agentic shift
EVAL: My Lai massacre and legitimacy of authority
Can explain how real life war crimes can occur, My Lai Massacre and Abu Ghraib
Who did and when was the F-Scale test
Adorno, 1950
ADORNO
Procedure
2000 middle-class white Americans
Had to answer 30 questions on a 6 point scale
ADORNO
Aim
Investigate cause of obedient personality types
Investigate relationship between unconscious prejudice and authoritarianism
ADORNO
Findings
High F-Scale = Authoritarian leanings
Authoritarian leanings = Identify with ‘strong’ people, contemptuous of weak, aware of social status
ADORNO
Findings : Correlation
Positive correlation between authoritarianism and prejudice
Distinct cognitive style
EVAL: Correlation
Only correlational link can be established between obedience and an authoritarian personality type
May be a third factor
EVAL: Limited explanation, especially in regards to Holocaust
Any explanation of obedience is hard to generalise to an entire country, nearly all Germans showed racist, anti-Semitic attitudes pre and during WW2, despite personality differences
Social identity theory is much more likely in this case
EVAL: Political bias in F-Scale
Christie and Jahoda: Politically biased interpretation of authoritarian personality, focuses on right wing. Ignores left-wing authoritarianism e.g. Russian Bolshevism
Extremes on both sides have shared factors, only focuses on right wing authoritarianism
EVAL: Methodological problems
Each item is worded in the same direction, possible to get high score by ticking same box for every question
Characteristics of authoritarian person
Inflexible thinking, no grey areas
Need a strong leader to enforce traditional values → country, religion and family
Contempt to those they view as lesser → conventional attitudes to sex, gender and race
Especially obedient to authority → extreme respect to authority
Origins of authoritarian personality
Harsh parenting in childhood
Shown conditional love
What characteristics did Adorno identify in parenting that builds authoritarian personality
Severe discipline
Expectations of extreme loyalty
Impossible standards
Severely criticised for not meeting expectations
How does parenting build authoritarian personality type
Creates inexpressible hostility and resentment towards parents
Emotions are displaced onto other people as scapegoats
Creates a central tendency of obedient personality types = Dislike of people they view to be socially inferior
Why would social support help someone not conform
Pressure is lower when there are other people
EVAL: Research support for resistance to conformity
Allen and Levine: Conformity decreases in Asch like studies when there is one dissenter
Supports view that resistance is motivated by feeling free of pressure from a social group
Why would social support help someone not obey
Less pressure to obey when there is another going against
EVAL: Research support for resistance to obedience
Gamson et al: Higher levels of resistance when working in groups, ptp had to produce evidence for an oil company to use in a smear campaign, 29/33 participants rebelled against an unjust authority
Define Locus of Control
How much control a person believes they have over what they do and what happens to them
Internal Locus of Control
Believe that things that happen are done by themselves
e.g. doing well on a test was because they revised properly
External Locus of Control
Believe that things that happen occur without their control
e.g. doing poorly on a test was because they had bad luck and the questions were bad
How do locus of control and resistance to social influence link
Having an internal LOC means more likely to resist pressure to obey or conform
Why does having an ILOC mean less likely to conform / obey
Take responsibility for own actions
ILOC means more likely to have more self-confidence, be more intelligent and goal oriented
EVAL: Research support for LOC and resistance
Holland: Reproduced Milgram, and measured whether participant was internal or external
37% of internals did not go to highest level, 23% of externals did not go to highest level
Increase of validity as locus of control as an explanation
EVAL: Contradictory research for LOC and resistance
Twenge et al: Analysed data from LOC studies, found people have become more resistant to obedience but LOC have become more external
If the two were linked then the relationship should be the inverse
EVAL: Limited role of the LOC
Role of LOC in resisting social influence is exaggerated
Rotter: LOC many comes into play with novel situations, has little influence in familiar situations
3 main features for minority influence
Consistency
Commitment
Flexibility
2 types of consistency (minority influence)
Diachronic = Everyone has been saying same thing for a period of time
Synchronic = Everyone saying same thing presently
Why is consistency key to minority influence
Consistency leads people to believe their message must have validity
Depth of thought for majority