NASAL BONES - ZYGOMA
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
nasal bones
are two small, thin bones which form the superior bony wall (called the bridge of the nose) of the nasal cavity.
bridge of the nose
nasal bones are two small, thin bones which form the superior bony wall (called the _______) of the nasal cavity
MSP // with the tabletop
IPL ⊥ to the tabletop
IOML // to the transverse axis of the IR
NASAL BONES(R or L Position) LATERAL PROJECTION
IR: 8x10” CW (for two exposures on one IR) or 2 ½ x 3” occlusal film for each
LP?
Perpendicular
to the bridge of the nose at a point ½” (1.3 cm) distal to the nasion.
NASAL BONES(R or L Position) LATERAL PROJECTION
IR: 8x10” CW (for two exposures on one IR) or 2 ½ x 3” occlusal film for each
CP:
RP:
frontonasal region
nasion
NASAL BONES(R or L Position) LATERAL PROJECTION
IR PLACEMENT: When using an 8x10” IR, slide the unmasked half of the lR under the _____ and center it to the ____. This centering allows space for the identification marker to be projected across the upper part of the IR.
¾” above the supraorbital ridge
NASAL BONES(R or L Position) LATERAL PROJECTION
FILM PLACEMENT:
Adjust the film packet so that the pebbled surface faces and is parallel with the MSP and so that its upper border projects
glabelloalveolar line
NASAL BONES TANGENTIAL PROJECTION
The success of this projection depend on the following
directing the central ray along the _____ perpendicular to the plane of the IR.
MSP ⊥to the plane of the IR.
Adjust the inclination of the IR so that its plane is ⊥to the glabelloalveolar line (GAL)
NASAL BONES TANGENTIAL PROJECTION Extraoral IR
IR: 8x10” IR placed CW under the chin
LP:?
Parallel
to glabelloalveolar line and perpendicular to the plane of the IR
NASAL BONES TANGENTIAL PROJECTION Extraoral IR
IR: 8x10” IR placed CW under the chin
PP: Elevate the side of the IR adjacent to the patient on a small sandbag or a folded towel. Rest the patient's head on the fully extended chin, and center the IR to the MSP just anterior to the chin.
LP: MSP ⊥to the plane of the IR. Adjust the inclination of the IR so that its plane is ⊥to the glabelloalveolar line (GAL)
CR/RP:?
occlusal film
The use of ____ is recommended because of the reduced object-to-image receptor distance (OID).
Parallel
to GAL and perpendicular to the plane of the IR.
NASAL BONES TANGENTIAL PROJECTION Intraoral IR
IR: 2 ¼ x 3” occlusal filmheld between the anterior teeth
CR/RP: ?
tangential projection
Because the nasal bones do not have sufficient body to cast a shadow through the dense superjacent and subjacent structures, the ____ cannot be used successfully in children or in adults who have very short nasal bones, a concave face, or protruding upper teeth.
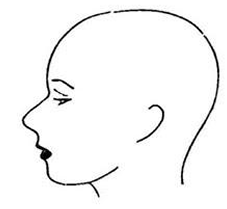
Convex
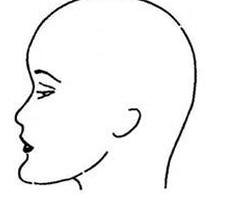
Concave
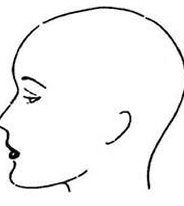
Straight
zygomatic bones
form the prominence of the cheeks and a part of the side wall and floor of the orbital cavities
zygomatic arch
A posteriorly extending temporal process unites with the zygomatic process of the temporal bone to form the
MSP ⊥ to the plane of the IR.
IOML is as nearly // with the plane of the IR as possible
ZYGOMATIC ARCHES SUBMENTOVERTICAL PROJECTION
IR: 8x10” CW
LP:?
Perpendicular
to the IOML and entering the MSP of the throat at a level approximately 1 inch (2.5 cm) posterior to the outer canthi.
ZYGOMATIC ARCHES SUBMENTOVERTICAL PROJECTION
IR: 8x10” CW
LP: MSP ⊥ to the plane of the IR.
IOML is as nearly // with the plane of the IR as possible
CR/RP:?
MSP ⊥ to the plane of the IR.
ZYGOMATIC ARCHES PA AXIAL PROJECTION MODIFIED TITTERINGTON METHOD
IR: 8x10” CW
LP:?
23 to 38 degrees caudad
Enters the vertex midway between the zygomatic arches.
ZYGOMATIC ARCHES PA AXIAL PROJECTION MODIFIED TITTERINGTON METHOD
IR: 8x10” CW
LP: MSP ⊥ to the plane of the IR.
CR:?
RP:?
ZYGOMATIC ARCHES PA AXIAL PROJECTION MODIFIED TITTERINGTON METHOD
Zygomatic arches are well shown in this projection. The image presented is similar in appearance to the parietoacanthial projection (Waters Method)
IOML is as // with the plane of the IR as possible.
Rotate the MSP of the head ~15 degrees toward the side being examined and
tilt the top of the head ~15 degrees away from the side being examined
ZYGOMATIC ARCH TANGENTIAL PROJECTION
IR: 8x10” LW
LP:?
Perpendicular
to the IOML and entering the MSP of the throat at a level approximately 1 inch (2.5 cm) posterior to the outer canthi
ZYGOMATIC ARCH TANGENTIAL PROJECTION
IR: 8x10” LW
LP: IOML is as // with the plane of the IR as possible.
Rotate the MSP of the head ~15 degrees toward the side being examined and
tilt the top of the head ~15 degrees away from the side being examined
CR/RP:
mandibular angles
ZYGOMATIC ARCHES AP AXIAL PROJECTION
IR: 8x10” CW
Center the cassette at the level of ___
MSP is perpendicular to the IR
OML is perpendicular to the IR
ZYGOMATIC ARCHES AP AXIAL PROJECTION
IR: 8x10” CW
LP:?
30 degrees caudad
Enters glabella, approximately 1 inch above the nasion
ZYGOMATIC ARCHES AP AXIAL PROJECTION
IR: 8x10” CW
LP: MSP is perpendicular to the IR
OML is perpendicular to the IR
CR/RP:
37 degrees caudad
or the patient unable to sufficiently flex the neck, adjust the IOML perpendicular with the film and direct the central ray
perpendicular
45 degrees
away
15 degrees
ZYGOMATIC ARCHES PA AXIAL OBLIQUE PROJECTION MODIFIED FUCHS METHOD
IR: 8x10” LW
Adjust the flexion of the neck so that the AML is ___ to the film. Rotate the MSP approximately ___, then tilt the top of the head ___ from the side being examined approximately ____.
MSP forms 45 degree to the IR.
AML is perpendicular to the IR.
ZYGOMATIC ARCHES PA AXIAL OBLIQUE PROJECTION MODIFIED FUCHS METHOD
IR: 8x10” LW
LP:?
35 degrees caudad
Enters most prominent point of the zygoma farthest from the IR
ZYGOMATIC ARCHES PA AXIAL OBLIQUE PROJECTION MODIFIED FUCHS METHOD
IR: 8x10” LW
LP: MSP forms 45 degree to the IR.
AML is perpendicular to the IR.
CR/RP:?
ZYGOMATIC ARCHES PA AXIAL OBLIQUE PROJECTION MODIFIED FUCHS METHOD
An oblique image of the uppermost zygomatic arch is shown, projected free of superimposition shadows. The lateral portion of the maxillary sinus is also well demonstrated.
IOML is as // with the plane of the IR as possible.
Rotate the MSP of the head ~15 degrees away from the side being examined
tilt the top of the head ~15 degrees away from the side being examined
ZYGOMATIC ARCH TANGENTIAL PROJECTION MAY METHOD
IR: MAY METHOD 8x10” CW for two exposures
LP:?
Perpendicular
to the IOML and through the zygomatic arch at a point approximately 1 ½ inches (3.8 cm) posterior to the outer canthus
ZYGOMATIC ARCH TANGENTIAL PROJECTION MAY METHOD
IR: MAY METHOD 8x10” CW for two exposures
LP: IOML is as // with the plane of the IR as possible.
Rotate the MSP of the head ~15 degrees away from the side being examined
tilt the top of the head ~15 degrees away from the side being examined
CR/RP:?
May Method
demonstrates the zygomatic arch free of superimposition. This projection is particularly useful with patients who have depressed fractures or flat cheekbones.
MSP ⊥to the plane of the IR.
OML ⊥to the plane of the IR.
ZYGOMATIC ARCHES AP AXIAL PROJECTION MODIFIED TOWNE METHOD
IR: 8x10” CW
LP:?
30 degrees caudad
Directed to enter the glabella approximately 1 inch (2.5 cm) above the nasion If the patient is unable to sufficiently flex the neck, adjust the IOML ⊥ with the IR and direct the central ray 37 degrees caudad.
ZYGOMATIC ARCHES AP AXIAL PROJECTION MODIFIED TOWNE METHOD
IR: 8x10” CW
LP: MSP ⊥to the plane of the IR.
OML ⊥to the plane of the IR.
CR/RP:?