Bio Unit 2: Macromolecules and Cell Biology
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
Organic Compounds
formed because of Carbons ability to make FOUR bonds
Isomers
have the same molecular formula but different structures
Hydrocarbons
composed of only one carbon and hydrogen
Organic Compound’s Properties
depends on the SIZE AND SHAPE of its carbon backbone and the ELEMENTS ATTACHED TO its skeleton
Functional Groups
give organic molecules specific chemical properties
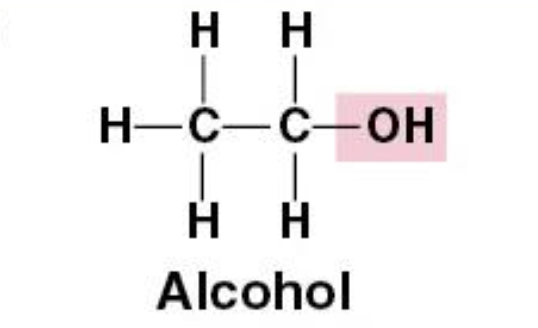
Hydroxyl Group
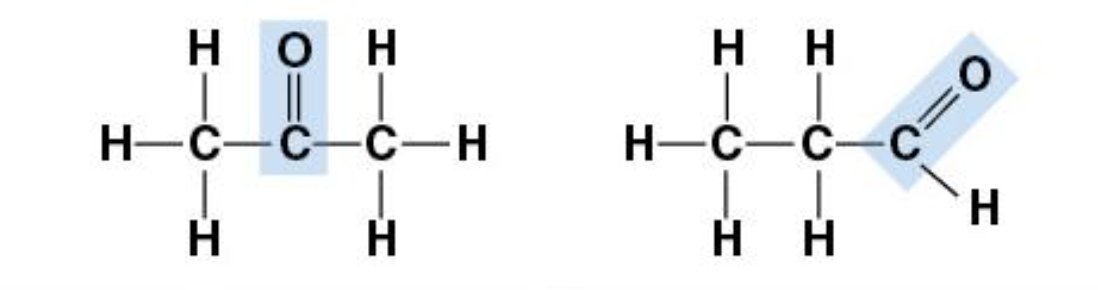
Carbonyl Group
Amino Group
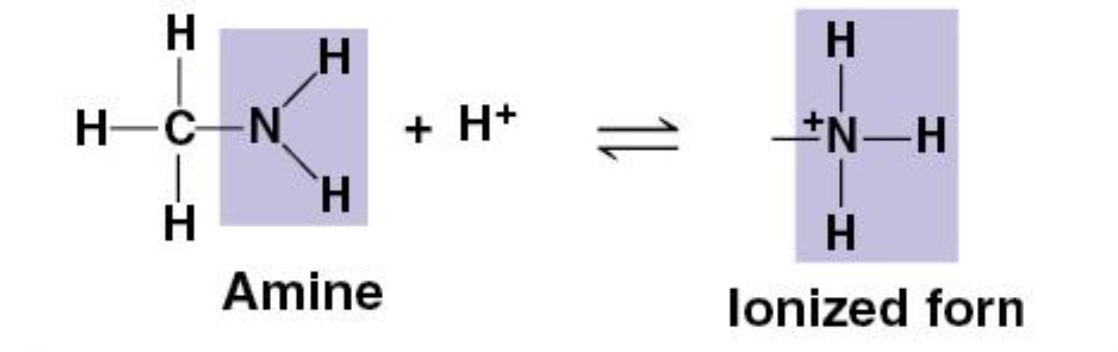
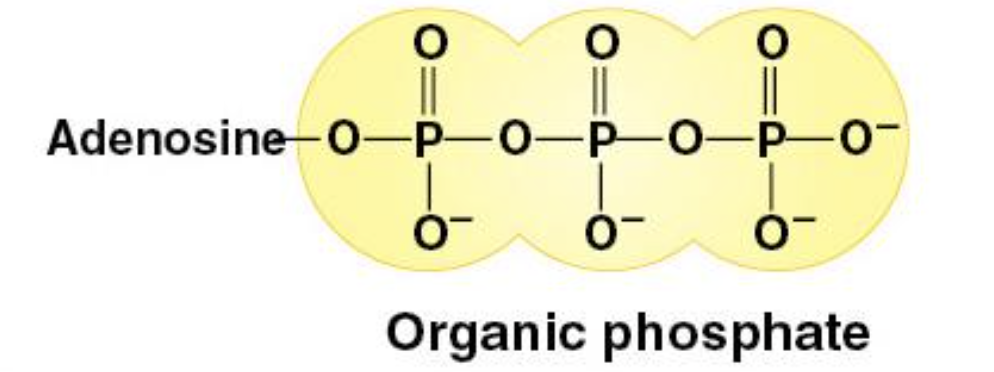
Phosphate Group
Methyl Group
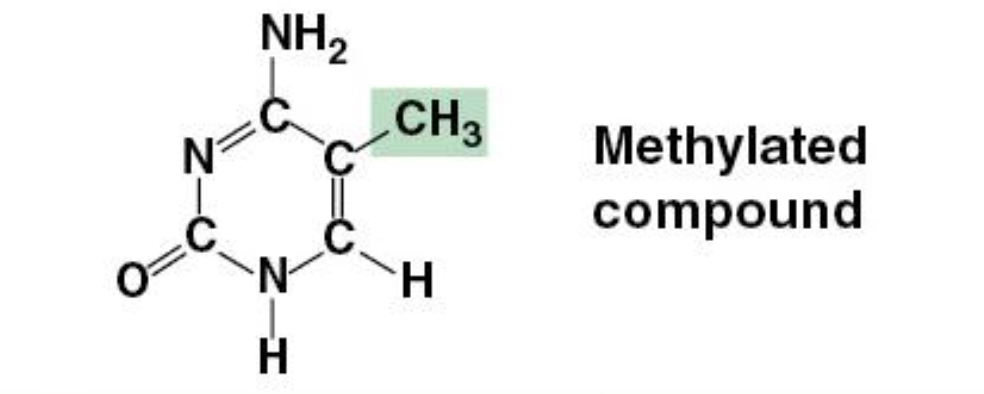
Macromolecules
large molecules also called polymers
Polymer
made of the same or similar building blocks strung together
Monomers
The building blocks of polymers
Dehydration Reaction
links monomers together to form polymers
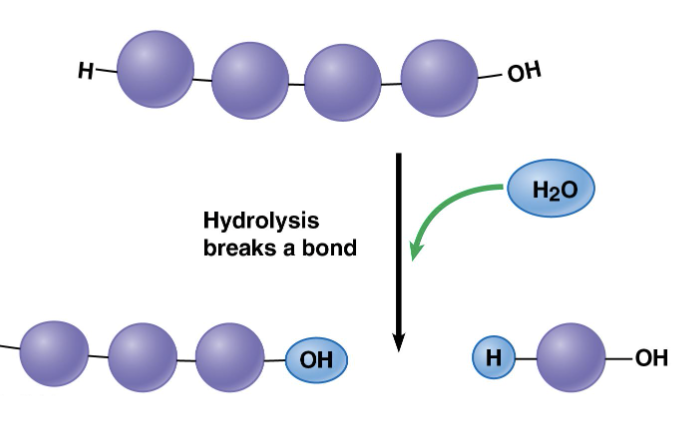
Hydrolysis
opposite of dehydration reaction and breaks polymers apart
Enzymes
mediate dehydration reaction and hydrolysis
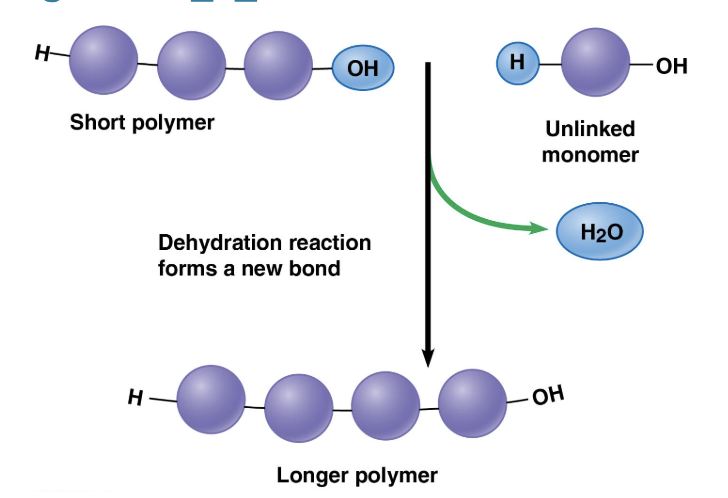
Dehydration Reaction

Hydrolysis
Carbohydrates
range from small sugar molecules (monomers) to large polysaccharides
Monosaccharides
sugar monomers
Glucose
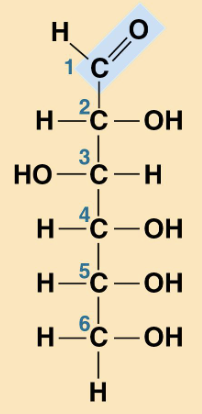
Simple Structure of Glucose

Disaccharide
two monosaccharides (monomers) bond in dehydration reaction
Glycosidic linkage
the bond between monosaccharides
Cellulose
the structure found in plant cells
Chitin
structure of insect and crustacean and fungal cell walls
Starch and Glycogen
energy storage polysaccharides
Lipids
diverse hydrophobic (water fearing) compounds composed largely of carbon and hydrogen
Fats
consist of glycerol linked to fatty acids
Unsaturated Fats (plant oils)
fatty acids with one or more double bonds
Saturated Fats (animal fats)
fats with the max number of hydrogens
Hydrogenation
unsaturated fatty acids become saturated when hydrogen is added
Trans Fats
created when hydrogenation takes place and is linked to health risks
Ester linkage
the bond between a glycerol and a fatty acid
Phospholipids
componets of cell membranes
Steroids
cholesterol and some hormones
Cholesterol
common component in animal cell membrane. Also the precursor for making other steroids and sex hormones
Anabolic Steroids
synthetic variants of testosterone that are abused by some athletes with serious consequences
Proteins
Involved in many dynamic functions in your body. composed of different arrangements of a common set of 20 amino acids
Protein Functions
depends on there shape
Denaturation
a protein unravels, loses its shape, and therefore its function. Changes by environment
Amino Acids
Protein monomer. contain an amino group, carboxyl group, H atom and R group
R Group
Distinguish the 20 amino acids. Each have specific properties
Peptide Bonds
amino acids come together in a dehydration reaction
Polypeptide
A chain of amino acids
Primary Structure
protein in the order of amino acids
Secondary Structure
the coiling and folding of the protein
Tertiary Structure
the 3D globular shape making a functional protein
Quaternary Structure
many tertiary proteins together
Nucleotides
The monomer of a nucleic acid
Nucleic Acids
composed of sugar, phosphate group, and nitrogenous base
DeoxyriboNucleic Acid
DNA
DNA
double helix
RiboNucleic Acid
RNA
RNA
single chain