Animal Behavior Exam 1
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
Tinbergen’s 4 Questions
Function
Phylogeny
Ontogeny
Mechanism
Instinct
innate fixed pattern of behavior
Instraspecific variation
variation among individuals of the same species
Reaction Norms
Polygenic
Several genes, one effect
Pleiotropic
one gene, several effects.
Broad sense heritability H2
Measure of degree of heritable genetic variance in a population.
Broad sense heritability equation
H2 = Vg (genotypic variance)/VT (total phenotypic variance) where VT = VG + VE (variance due to environment)
Narrow sense heritability
Measure of the response of a particular trait to selection.
Narrow sense heritability equation
R/S, R = difference between mean of offspring of selected parents and mean of overall population, S = difference between mean of selected parents and mean of population
Common Garden Experiment
Put different phenotypes into the same environment and see if differences disappear.
Knockout Gene type Studies
Produce mutants that are homozygous for hidden gene
Gene transfer
Use molecular techniques to insert gene into DNA of another species.
Genome-wide association studies
correlational study using whole genome databases
Epigenetics
experience and the environment can alter gene expression w/out altering DNA code.
Proximate gene expression control
proteins bind to promotor regions, encourage or discourge RNA polymerase binding
Epigenetics — DNA Methylation via DNMTs, downplays transcription genes
Hormone
signaling molecule secreted in one part of body that causes change in other part of body
Endocrine gland
ductless gland that secretes molecules into space between molecules, then bloodstream
Peptide hormones
amino acid chains that bind to receptors on cell surfaces because they are water soluble and can’t cross the cell membrane
Steroid hormones
secreted mainly by gonads and adrenal glands, fat soluble so they can cross cell membrane.
Axis of Hormonal Control
Hypothalamus → hypophysis (pituitary gland) → targets in body
Stress pathway
stressor triggers brain to release corticotrophin-releasing hormone and arginine vasopressin → bloodstream → pituitary gland produces adrenocorticotrophin hormone → adrenal gland produces cortisol.
LH and FSH
reproduction, secondary sex characteristics
adrenocorticotrophin hormone
stress, digestion, circadian rhythm.
Prolactin
brooding behavior, milk production, amphibian metamorphosis, fish migration
Melatonin
pigmentation, biological rhythmicity
Hamilton-Zuc hypothesis
females prefer brightly colored males because they have fewer parasites
Immunocompetence Handicap Hypothesis
Even though secondary sex characteristics may be linked with weaker immune systems, males with fewer deleterious alleles can handle this tradeoff and develop stronger secondary sex characteristics
Factors that influence Behavioral Development
nervous system, hormonal development, changes in non-neural morphology, changes in environment
Learning
relatively permanent change in behavior as result of experience
Habituation vs Sensitization
animal becomes less sensitive to stimulus over time, animal becomes more sensitive to stimulus over time.
Associative Learning (Pavlovian)
conditioned stimulus at first don’t cause specific response, but then does, unconditioned stimulus cause response even without training
Associative Learning — Instrumental (operat)
learning that occurs when response made by animal is reinforced, animal must take action
Local enhancement, Social facilitation, Copying, Imitation
animal is drawn to where others are, pressure of other animals increases behavior, animal repeats what others do (does not need to be novel), animal acquires novel response by observing new behavior.
How to develop optimality model
identify problem to be solved
choose “currency” (fitness or fitness correlate)
identify alternatives and constraints
Quantify costs and benefits of available alternatives in relevant currency
Charnov’s Optimal diet model (big prey = 1, small prey = 2)
E2/h2 > E1/(S1 + h1)
Marginal Value Theorem
Game theory
Type of Optimality theory where optimal strategy depends on behavior of others
Evolutionary Stable Strategy
When average payoff for Hawks is equal to the average payoff to doves
Competition, Mutualism, Antagonistic (predatory parasistims, herbivory)
(-,-); (+,+); (-,+);
Amensalism, Commensalism, Neutralism
(-, 0); (+,0); (0,0)
Pursuit Predation
chasing and capturing prey, relies on speed, endurance, often group coordination
Ambush Predation
sit and wait, luring, or stalking strategies that rely on camouflage and stealth.
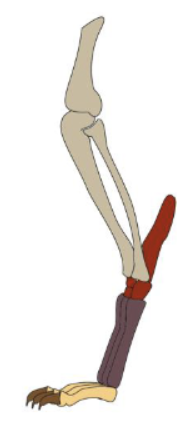
Digitigrade
walking on phalanges
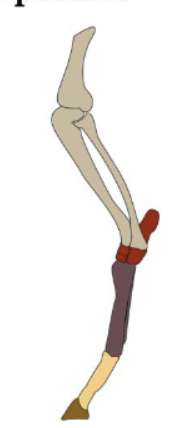
Unguiligrade
walking on tips of digits
pursuit deterrence
prey signals to predator they have been detected