Bio (copy)
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
What is the enzyme responsible for catalyzing the capture of CO2 and produces 3-phosphoglycerate?
Rubisco
Each of the following is part of the energy transduction from solar energy to chemical energy EXCEPT:
All of the following are involved (Electron flow through an electron transport system, Light absorption by chlorophyll, Unidirectional proton pumping across a membrane, An electrochemical proton gradient)
What happens to water (H2O) as it goes through photosynthesis?
It gets oxidized
What are the major processes associated with photosynthesis? (select all that apply)
Energy transduction, Carbon fixation
Where in a chloroplast does the Calvin Cycle occur?
Stroma
What happens to CO2 as it goes through photosynthesis?
It gets reduced
What are the stages of the Calvin Cycle? (select all that apply)
Regeneration,Reduction,Carbon fixation
Where in a chloroplast do the light reactions occur?
Thylakoid
Which of the following initially traps solar energy in the process of photosynthesis?
Chlorophyll
Your house plant is growing slowly and lacks its normal bright green color, so you call a botanist for advice. She suggests that the plant may be deficient in magnesium (Mg2+). Why are these symptoms associated with Mg2+ deficiency?
Mg2+ is an important component in chlorophyll.
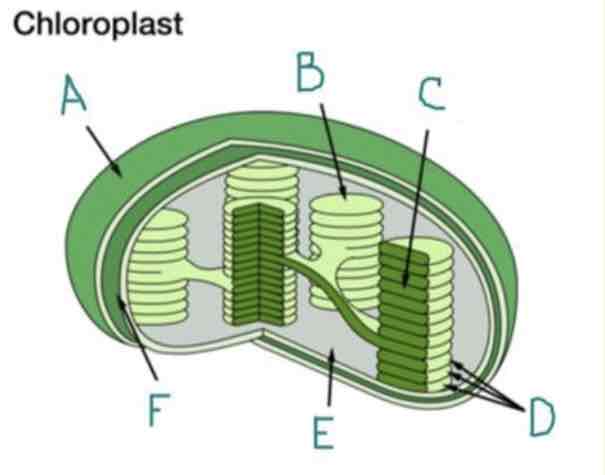
What is A?
Outer Membrane
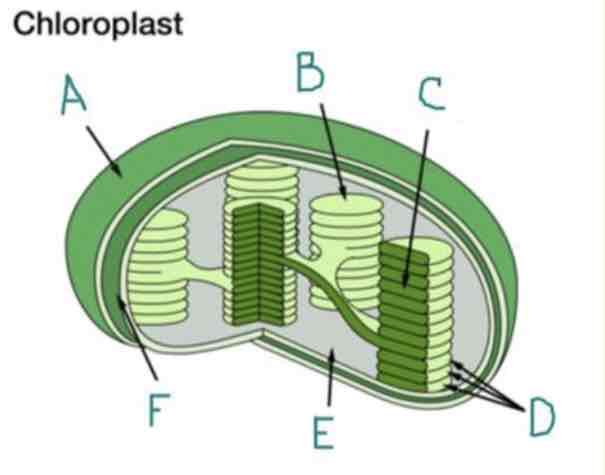
What is B?
Thylakoid
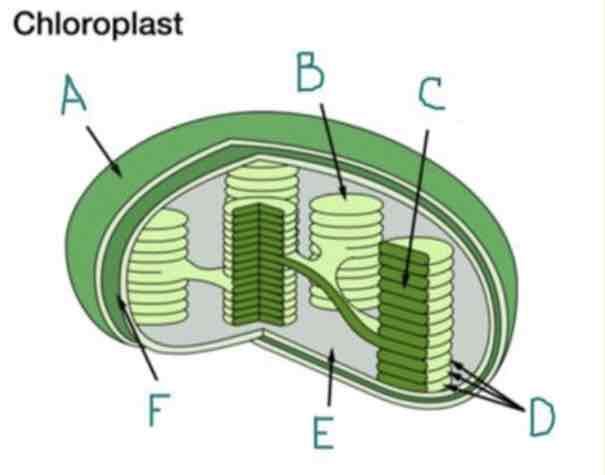
What is C?
Lumen
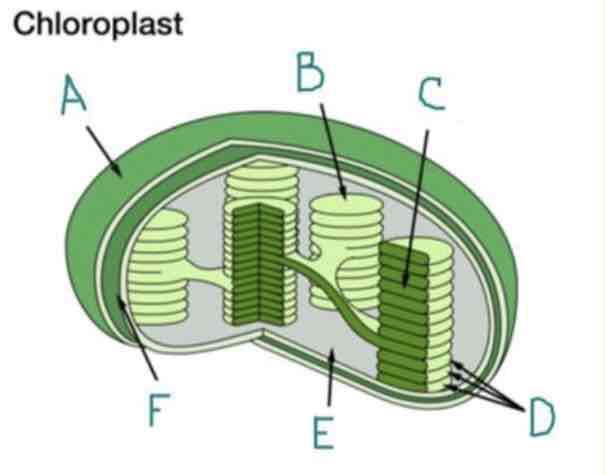
What is D?
Granum
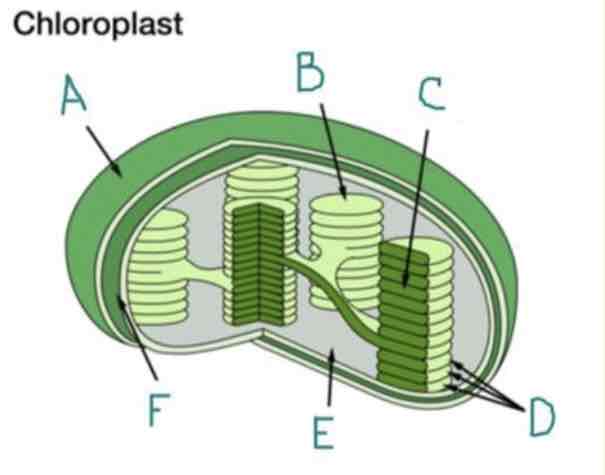
What is E?
Stroma
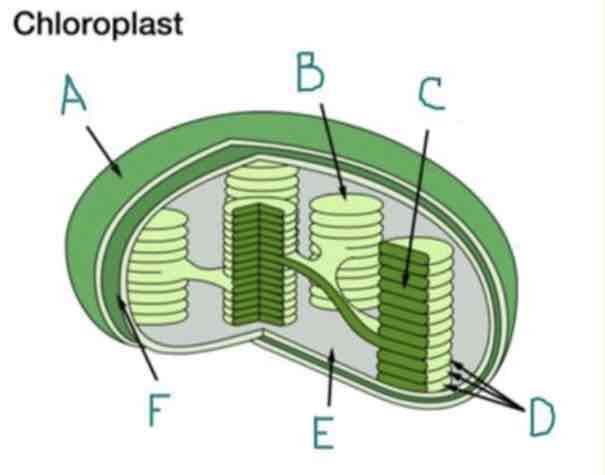
What is F?
Inner Membrane
What is the protein responsible for binding and transporting proteins across the nuclear membrane?
Importin
Which is organelle plays a major role in glycosylation of proteins?
Golgi apparatus
Which are components of the endomembrane system of an eukaryotic cell? (select all that apply)
Golgi apparatus, Lysosome, Endosome, Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Phagocytosis:
ingestion of large solid particles
Pinocytosis:
ingestion of liquid containing soluble particles
Which is organelle plays a major role in protein synthesis?
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Which is organelle plays a major role in processing and storing of nonprotein molecules?
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
What organelle contains digestive enzymes capable of degrading all biological macromolecules and extracellular material?
Lysosome
What is the enzyme that plays an important role in xenobiotic detoxification?
Cytochrome P-450
COPI:
transport materials within the Golgi
COPII:
transports material from ER to Golgi
Clatherin:
transports materials into the cell after the receptor has been activated
Statins are drugs that are administered to inhibit the biosynthesis of cholesterol in the liver, and thus are used to lower blood plasma cholesterol levels in order to decrease patient risk of atherosclerosis and associated diseases such as myocardial infarction (heart attack).Which of the following components of the endomembrane system is the site of action of statin drugs?
SER
Proteins destined for secretion are a common type of cargo that transits through the Golgi apparatus. These proteins begin in the_________________________ and are next routed to the _______________________ . From there, they pass through the __________________________________, then the _____________________________, and eventually are secreted at the _________________________.
RER, Cis-golgi, medial cisternae, trans-golgi, plasma membrane
Each of the following is an endoplasmic reticulum function except
protein folding, addition of carbohydrate to proteins to make glycoproteins, the assembly of multimeric proteins., the export of protein that cannot be folded into the cytoplasm for destruction. (All are endoplasmic reticulum functions.)
A patient was diagnosed to possess a mutation in an ER-resident protein in which the ER- signal sequences of the protein were inappropriately deleted and instead replaced with a mannose-6-phosphate during protein synthesis and posttranslational modification. What is the likely fate of this mutant protein?
The protein would be targeted to the lysosomes.
Nuclear trafficking requires which of the following? Mark all that apply.
Importin, Ran-GTP
In receptor-mediated endocytosis, each of the following is a fate for the receptors and/or vesicle contents except
release from the vesicle into the nucleus.
Endocytosis moves materials _____ a cell via _____.
into ... membranous vesicles
Each of the following is true about botulinum toxin (Botox) except
Botox is a SNARE protein.
For each of the following statements, indicate for which coated vesicle the statement is true: clathrin, COPI or COPII-coated. Transport materials from ER to Golgi: , Transport materials into the cell after a receptor has been activated: , Transport materials within the Golgi:
COPII, Calthrin, COPI
The low pH of lysosomes is established by
ATP-dependent proton pumps.
In an animal peroxisome you would likely find a large amount of __________ protein and a crystallized core of this protein, _____________.
Catalase; urate oxidase
Each of the following is a lysosomal storage disease caused by a deficiency in lysosomal enzymes except
Familial hypercholesterolemia
Which part of the cytoskeletal system is composed of tetrameric protofilaments?
Intermediate filaments
Tubulin:
Microtubules
Actin:
Microfilaments
Which part of the cytoskeletal system is essential for muscle fibrils?
Microfilaments
What are important roles of the cytoskeleton? (select all that apply)
Movement of membrane-bound organelles through cytoplasm, Cell-cell adhesion, Cell division, Cell signaling, Cell motility
Which part of the cytoskeletal system is essential for movement?
Microtubules
A cell treated with vinblastine, which of the following would you expect to occur?
Microtubule protofilaments would not be able to assemble properly
Which part of the cytoskeletal system is essential for tension-bearing, structure, and scaffolding?
Intermediate filaments
What is the role of GTP in microtubule polymerization?
GTP stabilizes the (+) end of the microtubule, allowing more monomers to be added
What is the protein that creates a network of filaments beneath the plasma membrane of red blood cells to give them strength and flexibility?
Spectrin
The ________ is a complex network of interconnected filaments and tubules that extends throughout the cytosol from the nucleus to the inner surface of the plasma membrane.
Cytoskeleton
A cell treated with vinblastine, which of the following would you expect to occur?
Microtubule protofilaments would not be able to assemble properly
Which of the following is true regarding microfilament assembly?
ATP bound monomers assemble at the (+) end
The core of an intestinal microvillus is composed of a tight bundle of ________.
Actin filaments
Consider Listeriosis:
Pregnant women are at high risk, It is caused by a bacterial infection, The microbe recruits host G-actin to form a “flagellum”, The microbe uses great speed to leave one cell and enter the next (All of these are true regarding listeriosis)
A(n) ________ is composed of tetrameric protofilaments.
Intermediate filaments
You are using immunofluorescence to study the cytoskeleton of armadillo cells. You are using antibodies toward the cytoskeletal structures and they are fluorescently tagged to show: Red = microtubules, Blue = microfilaments, yellow = intermediate filaments. Your colleague asks you what color tubulin will be, you answer?
Red
Myosin heavy chain:
fines to Acton aunt is the ATPase
Myosin light chain:
binds to cargo and regulates the ATPase
What ions are essential to regulate muscle contraction?
Ca2
If disruption of the function of the dynactin complex results in disruption of transport from the ER to the Golgi and collapse of the Golgi apparatus which of the following could you conclude?
Dynein is involved in transportation of items from the ER to the Golgi
Motor proteins convert _________.
chemical energy to mechanical energy
Cell motility may involve the following EXCEPT?
The movement of components within a cell,The shortening of a cell itself, The movement of the environment past or through a cell, The movement of a cell through its environment (ALL CORRECT)
What proteins are involved with muscle contractions? Select all that apply.
Acton, tropomyosin, myosin, troponin
What are the main proteins involved in microtubules cellular movement select all that apply
Dyneins, kinesins
Rigor results from a failure to break the cross-bridges that link thick filaments to actin in the contraction cycle. In a living cell, detachment occurs upon binding the next molecule of ATP. After death, however, the supply of cellular ATP is quickly depleted.
What effect do you think the addition of ATP might have on muscles in rigor?
Addition of ATP will have a relaxing effect because it will induce detachment of the cross-bridges between filaments
Which step initiates the power stroke of muscle contraction?
The phosphate ion is released
What protein interacts with a cargo vesicle and a microtubule?
Dynactin
The ________ protein complex facilitates the interaction between cytoplasmic dynein, a
cargo vesicle, and a microtubule.
Dynactin
If disruption of the function of the dynactin complex results in disruption of transport from
the ER to the Golgi and collapse of the Golgi apparatus which of the following could you
conclude?
Dynein is involved in transportation of items from the ER to the Golgi
Which component of the actin / tropomyosin / troponin complex in the sarcomere is able to
bind to four calcium ions?
Tripoan
Rigor results from a failure to break the cross-bridges that link thick filaments to actin in
the contraction cycle. In a living cell, detachment occurs upon binding the next molecule
of ATP. After death, however, the supply of cellular ATP is quickly depleted.
What effect do you think the addition of ATP might have on muscles in rigor?
Addition of ATP will have a relaxing effect because it will induce detachment
of the cross-bridges between filaments
What is the major protein involved in tight junctions?
Claudin
Adherens junctions:
cell-cell adhesions
Tight junctions:
sealing spaces between cells
Hemidesmosomes:
cell-basal lamia adhesion
What ions are essential for adherens junction stability?
Ca2
What protein is involved in transient cell-cell adhesion?
Selectin
What is the protein involved in cell-cell adhesion inside the cell in adherens junctions?
Catenin
What is the protein involved in cell-cell adhesion outside the cell in adherens junctions?
Cadherin
What are the major types of cell attachments? (select all that apply)
Tight junctions, gap junctions, desmosomes
What is the major protein involved in gap junctions?
Connexin
Epithelial cells that line the surface of the intestine are critical in maintaining a healthy intestinal barrier. Disruptions of this monolayer can have profound effects on human health. For example, "leaky gut" occurs when certain microbes and toxins disrupt cell-cell attachments within the intestinal epithelium. This results in water passing into the gut lumen and subsequent diarrhea. Which of the major cell-cell attachments is most likely affected when "leaky gut" occurs?
Tight junctions
Animal extracellular matrices contain each of the following EXCEPT:
Actins
Which of these cell junctions form a barrier to the passage of materials?
Tight Junctions
The primary role of _____ is to bind animal cells together.
Desmosomes
_____ aid in the coordination of the activities of adjacent animal cells.
Gap Junctions
________ are Ca2+-dependent adhesive glycoproteins that function in animal cell - cell recognition and adhesion.
Cadherins
Which of the following is the most accurate summary concerning the common adhesive glycoproteins of the ECM, fibronectins, and laminins?
Both of these proteins are extremely large adaptor proteins, containing multiple domains that serve as attachment sites for collagen, heparin, heparin sulfate, and cell-surface receptors.
Animal extracellular matrices contain each of the following except
Elastins, Proteoglycans, Collagens, Fibronectins (All of these are found in the ECM)
In cartilage, proteoglycans form large complexes by attaching to
Hyaluronate(sugars)