ACID BASE EQUILIBRIA
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
Convert Ka to pKa and vice versa.
pKa = -log Ka
Ka = 10^-pKa
Convert [H+] to pH and vice versa. Convert [OH-] to pOH and vice versa.
pH = -log[H+]
[H+] = 10^-pH
pOH = -log[OH-]
[OH-] = 10^-pOH
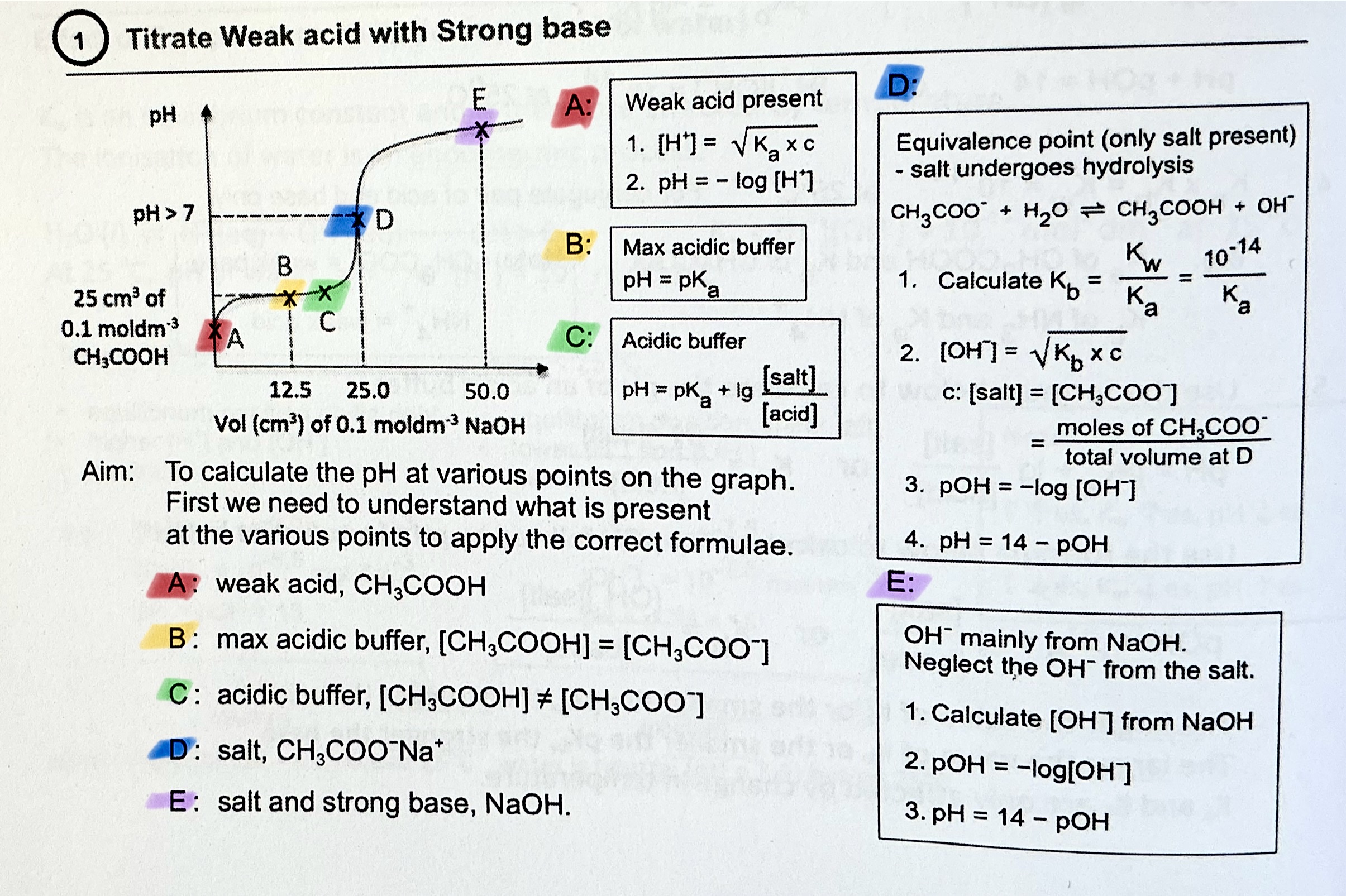
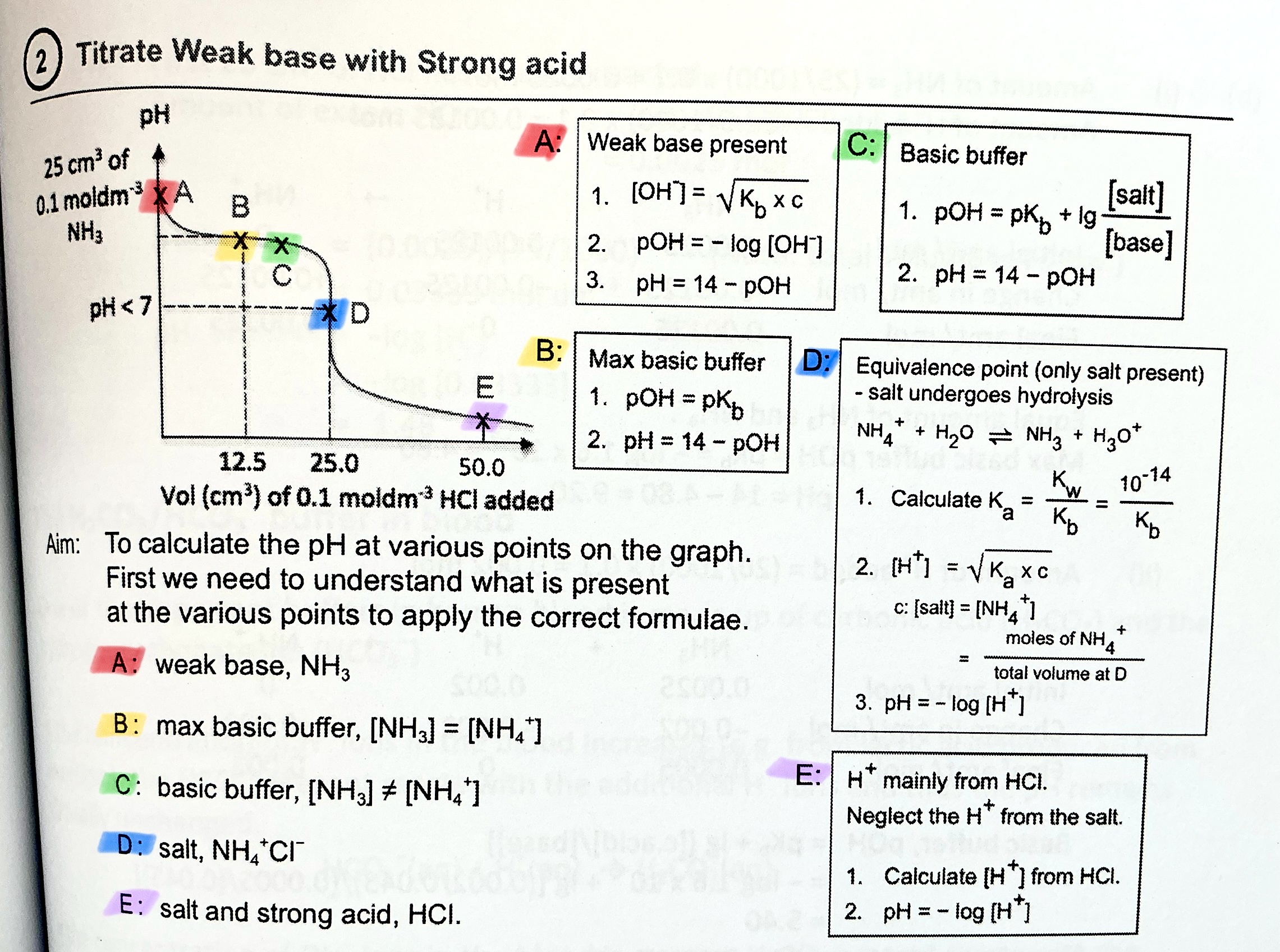
What happens at maximum buffer capacity?
pH = pKa, [acid] = [conj base]
What is the buffer equation for acidic and alkaline buffer?
acidic — pH = pKa + lg [conj base]/[acid]
alkaline — pOH = pKb + lg [conj acid]/[base]
Shortcut to calculate [H+] of weak acid. When can you use this short cut and when can you not?
[H+] =\sqrt{Ka\cdot c} , where c is the initial concentration of the weak acid.
pH = -log[H+]
→ You can use this to find initial pH of weak acid, if they ask for pH
→ if they ask for Ka, you should use the longer method of ICE table
Define Arrhenius acid and base.
→ acid releases H+ when dissolved in water
→ base releases OH- when dissolved in water
Define Brønsted-Lowry acid and base.
→ acid is a proton donor
→ base is a proton acceptor
Define Lewis acid and base.
→ acid is a (lone) electron pair acceptor
→ base is a (lone) electron pair donor