lec 1 (mcbride) - vitamins and coenzymes
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
water soluble vs fat soluble vitamins
water soluble
vitamin C
B vitamins
thiamin (B1)
riboflavin (B2)
niacin (B3)
biotin
pantothenic acid
vitamin B6
folate
vitamin B12
fat soluble (ADEK)
vitamin A
vitamin D
vitamin E
vitamin K
water soluble vitamins
hydrophilic molecules
limited tissue storage
rapidly cleared in urine
fat soluble vitamins
hydrophobic molecules
stored in fatty tissue and liver
slow clearance
enzymes function
accelerate the rate of rxns
enzymes require…
require cofactors for their catalytic activity
enzymes function = limited by the chemical properties of the encoded amino acids (enzymes = proteins)
enzymes often use nonprotein molecules to perform rxns impossible to do with AA sidechains alone
nonprotein molecules = cofactors
what makes up a holoenzyme
holoenzyme = complete, active form of enzyme
apoenzyme (protein portion of enzyme, inactive on its own) + cofactor (non protein factor required for enzymatic activity)
cofactors are divided into 2 groups…
metal ions (Mg2+, Fe2+, Zn2+)
bound to the active site of enzymes to facilitate formation of the transition state by tuning the positioning of the rxn substrates, typically with their pos. charge
coenzymes
small organic molecules which can be:
tightly bound and chemically unchanged by the catalyzed reaction (prosthetic groups)
loosely associated and behave as second substrate so must be present in stoichiometric ratios with other substrates
B vitamins produce…
many coenzymes critical for cellular metabolism
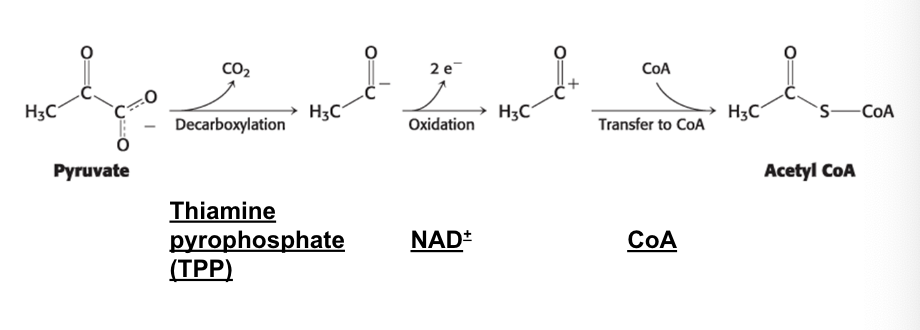
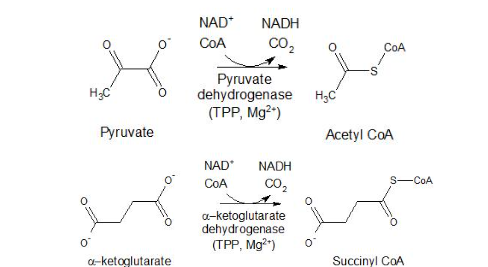
pyruvate and TCA cycle
pyruvate dehydrogenase complex links glycolysis to TCA cycle
for pyruvate to enter TCA it needs to be converted into acetyl coA
requires multiple coenzymes
thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP) (prosthetic)
NAD+ (stoichiometric)
CoA (stoichiometric)
what is collagen
most abundant protein in mammals
accounts for 25-30% of total protein mass
main fibrous component of skin, bone, tendon, cartilage and teeth
collagen is extremely rich in…
glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline
AA of part of collagen chain reveals that every third residue = glycine

collagen formation
3 helical polypeptide chain - each in an extended conformation
hydrogen bonds within strand of collagen helix are absent
helix is stabilized by steric repulsion of the pyrrolidine rings of the proline and hydroxyproline residues
forms a rope-like superhelix
consists of 3 intertwined helical polypeptide strands
stabilized by hydrogen bonds between strands
interior is crowded; only glycine can fit
what is required for collagen production
vitamin C
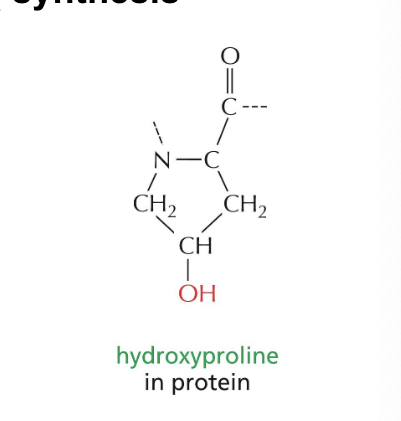
hydroxyproline
is a modified AA formed as part of collagen synthesis
procollagen molecules = synthesized containing unmodified proline residues
many proline residues of procollagen polypeptide → hydroxylated
hydroxyl group of hydroxyproline form interchain hydrogen bonds that help stabilize the triple-stranded helix
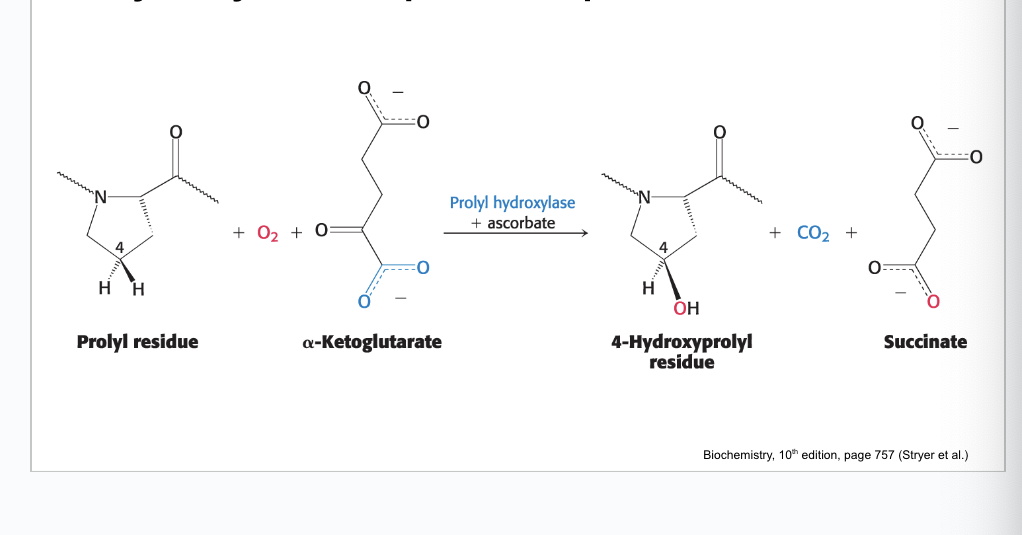
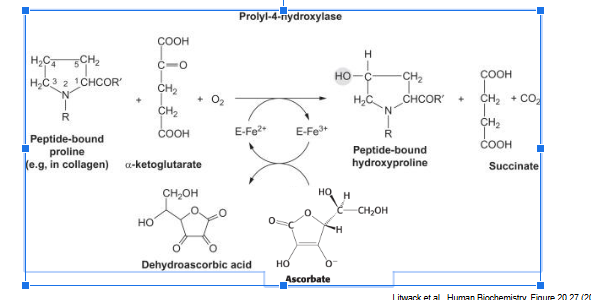
hydroxylation of proline requires…
ascorbate
ionized form of vitamin C → originally ascorbic acid and then one of the OH becomes O- (ionized) (ascorbate)
ascorbate salt
“improved” vitamin C supplements = often an ascorbate salt
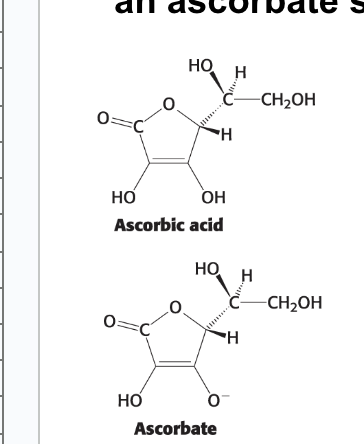
what does each hydroxylation of proline do?
each hydroxylation of proline residue converts ascorbate → dehydroascorbic acid
ascorbic acid deficiency
deficiency of ascorbic acid aka vita C causes scurvy
common in sailors until 19th century
prevents hydroxylation of proline residues of collagen
ascorbate regenerates active prolyl-hydroxylase enzyme
NO ascorbate → build up of inactive enzyme
lack of active enzyme decreases hydroxylation of collagen proline residues
loss of proline hydroxylation …
decreases stability of newly synthesized collagen
the loss of OH groups → fewer interchain hydrogen bonds → collagen triple-stranded helix is less stable and weaker
deficiency of vit c & collagen results
as collagen is replaced, tissue loses structure and rigidity → scurvy
in healthy tissues, collagen is continually degraded and replaced
complete collagen turnover time can be months or years → depends on tissue
as more defective collagen (lacking hydroxyproline) accumulates in tissues → scurvy symptoms develop and worsen
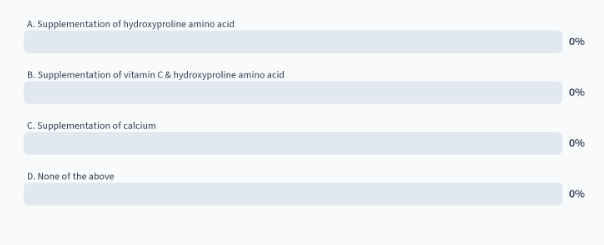
in a pt with scurvy, which of the following treatments is more effective than supplementation of vitamin C alone?
D. none of the above
explanation: the key part of the sentence is more effective than supplementation of vitamin C alone
supplementing with hydroxyproline AA CANNOT be incorporated into the synthesis of the polypeptide collagen, you have to incorporate the unmodified proline into polypeptide of collagen and then proline hydroxylase will hydroxylase it once its part of the polypeptide
thiamine (vit B1) deficiency
causes beriberi
neurologic and CV disorder
symptoms of beriberi
swelling in abdomen and legs
pain in limbs
muscle weakness
mental confusion
heart enlargement & other cardiac issues
thiamine is the precursor…
for synthesis of the coenzyme thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP)
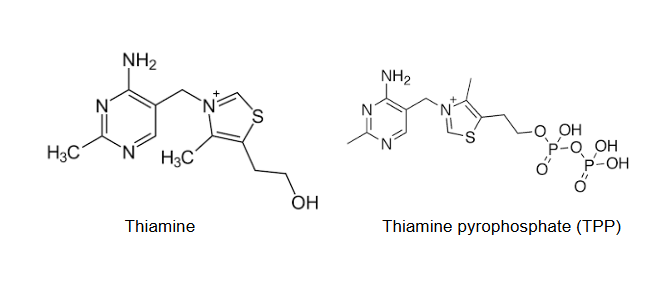
TPP is critical for…
central carbon metabolism
glycolysis
TCA cycle
AA catabolism
TPP is the coenzyme for…
pyruvate dehydrogenase and α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
TPP = coenzyme for enzyme pyruvate dehydrogenase
pyruvate → acetyl CoA
TPP = coenzyme for enzyme α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
α-ketoglutarate → succinyl CoA
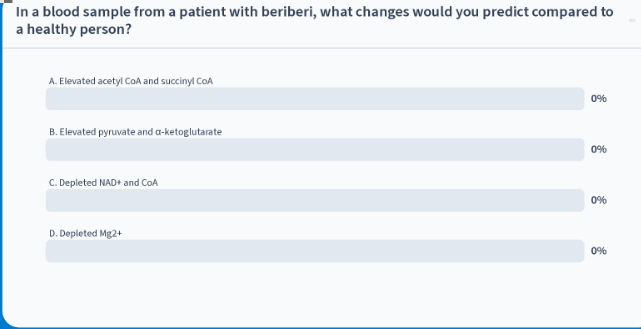
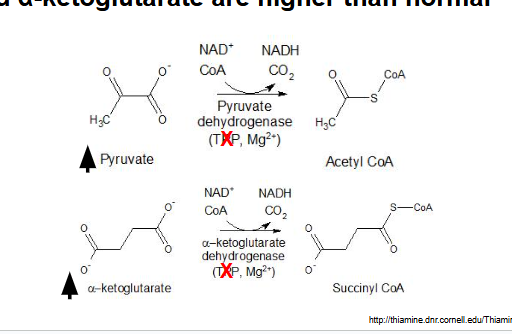
in a blood sample from a pt with beriberi, what changes would you predict compared to a healthy person?
B: elevated pyruvate and α-ketoglutarate
explanation: pts with beriberi have a thiamine deficiency which is the precursor for TPP so lack of TPP means that pyruvate and α-ketoglutarate would NOT be able to proceed forward with their rxn into becoming CoA
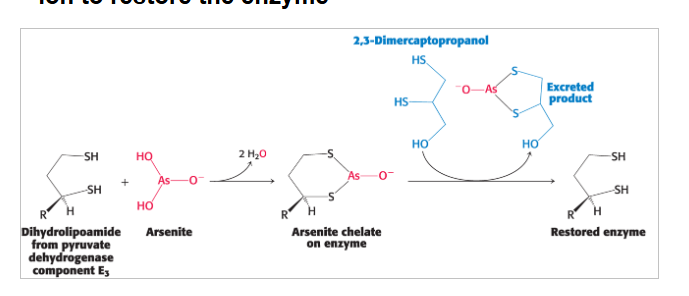
symptoms of mercury and arsenic poisoning are similar to beriberi due to…
inhibition of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
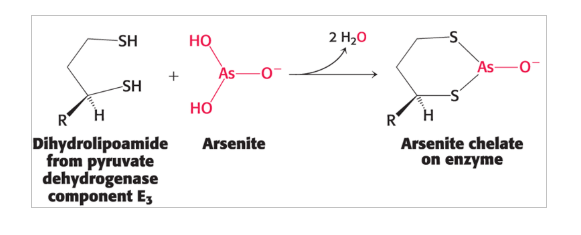
treatments for mercury and arsenic poisoning
sulfhydryl compounds that outcompete binding for the metal ion to restore the enzyme
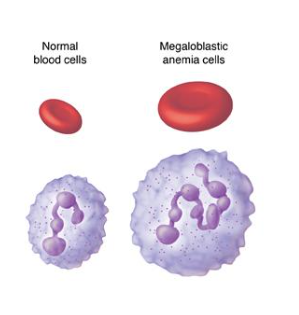
cobalamin (vit b12) deficiency
causes anemia
blood cells require cobalamin for proliferation
low cobalamin levels cause:
enlarged RBCs
nuclear hypersegmentation of DNA in neutrophils
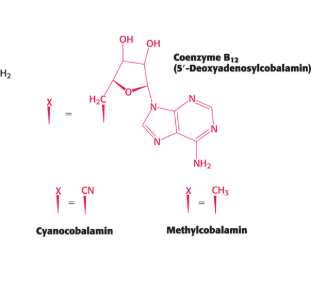
cobalamin structure
has a complex structure and forms a few similar coenzymes
coenzyme B12
cyanocobalamin
methylcobalamin
cobalamin catalyzes…
a rearrangement reaction
group on one carbon is exchanged with a proton on an adjacent carbon
R group can be amino group, OH group or substituted carbon

cobalamin is coenzyme for 2 rxns in mammals
methylmalonyl-CoA mutase as part of fatty acid degradation
methionine synthase for remethylation of homocysteine
cobalamin deficiency disrupts folate cycle → important for nucleotide synthesis and cell proliferation
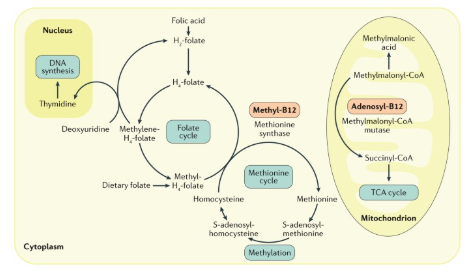
methylation of homocysteine by methionine synthase
homocysteine → methionine (methylated version)
methyl-B12 → B12
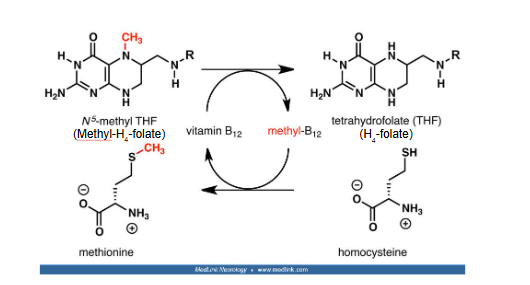
in a blood sample from a pt with a cobalamin deficiency, what changes would you predict compared to a healthy person?
D: elevated homocysteine (and methylmalonic acid)
explanation:
cobalamin is a coenzyme for methionine and methylmalonyl-CoA mutase which convert homocysteine and methylmalonic acid → their products
w/out cobalamin, this wouldn’t occur so high levels of the precursors
vitamins must be obtained from __ in humans
diet
both E. coli and humans use vitamins to produce coenzymes for metabolic rxns yet e. coli can thrive on glucose and organic salts alone while humans need at least 13 vitamins in their diet why?
e. coli have biosynthetic pathways to synthesize their vitamins while humans (and mammals) do NOT
biosynthetic pathways for vitamins are complex and it is more efficient to ingest vitamins than to synthesize the enzymes required to make vitamins from simple molecules
efficiency comes at cost: dependence on other organisms for chemicals essential for life
are there 12 or 13 vitamins required for humans?
13 vitamins listed on slide
nuance due to vitamin D b/c we can synthesize it so its not considered a vitamin sometimes
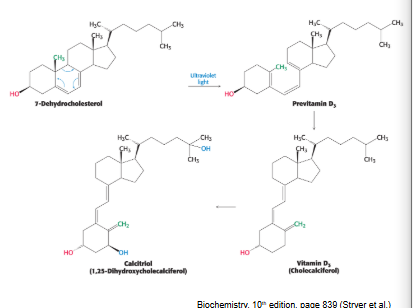
vitamin D can be synthesized from…
cholesterol by UV light from sunlight exposure
Vitamin D3 is formed from cholesterol in a series of steps, one of which requires ring-splitting by UV light
vitamin D3 is converted to the hormone calcitrol, active form of vitamin D, by hydroxylation rxns in liver and kidneys
vitamin D3 = critical for absorbance of calcium and phosphorus → required for bone health
synthesis of vit D is NOT sufficient for demand so dietary vit D is essential
subset of amino acids
similar to vitamins, a subset of AA must also be obtained from diet
essential AA must be supplied in the diet
histidine
isoleucine
leucine
lysine
methionine
phenylalanine
threonine
tryptophan
valine
nonessential AA can be synthesized from other nutrients
carbon skeletons of each AA come from intermediates of glycolysis, pentose phosphate pathway, or TCA cycle
alanine
arginine
asparagine
aspartate
cysteine
glutamate
glutamine
glycine
proline
serine
tyrosine
microorganisms can synthesize…
the entire set of 20 AA yet humans have lost some of these biosynthetic routes
AA can be sorted into biosynthetic families
major metabolic precursors = blue
AA that give rise to other AA are in yellow
essential AA are in bold
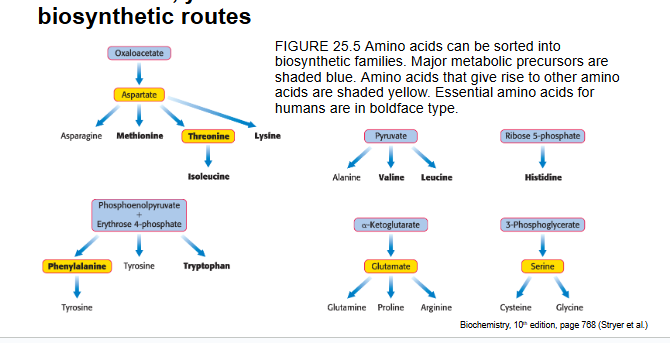
essential AA require...
a greater number of biosynthetic steps that have been lost in humans
essential and nonessential AA can be distinguished by required # of biosynthetic steps
some AA are nonessential b/c they can be biosynthesized in small # of steps
AA requiring a large # of steps for their synthesis are essential in the diet b/c some of the enzymes for these steps have been lost in the course of evolution