Small Animal Nursing I Lecture Exam 2 - Zoonotic Disease, Small Animal Diseases, Therapeutic Techniques, and Small Animal Medical History
1/397
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
398 Terms
By contact with an infected animal's saliva (bite, open wound, or contact with mucous membranes)
How is rabies most commonly transmitted?
• About 5,000 cases, with more than 90% of cases occurring in wildlife
• Only about 10% of cases in the US occur in domestic animals
How many rabies cases are reported in the US each year?
3-12 weeks
Incubation of rabies takes _____ weeks after exposure for symptoms to appear
• Flu like symptoms
• Weakness
• Fever
• Headache
• Discomfort
• Prickling or itching at the site of the bite
What are early clinical signs of rabies?
The condition is fatal
What is the prognosis of a rabies-infected animal once they start showing symptoms?
Human rabies immune globulin (HRIG) with rabies vaccine on the day of the exposure/bite, followed by a dose of the vaccine on days 3, 7, and 14
What does post-rabies exposure prophylaxis consist of?
• Salmonella spp
• Pasteurella spp
• Escherichia coli
• Pseudomonas spp
• Resistant staphylococcus spp
What are examples of zoonotic bacteria that veterinary professionals may be exposed to?
Methicillin-resistant S. pseudointermedius (MRSP)
The evolution of _____ bacteria is causing great concern among public health authorities and health care facilities
Exudate
Fluids that leak out of blood cells into nearby tissues
• Through direct contact with animals and their exudates
• Cuts or open sores
• Some bacteria may be aerosolized and inhaled or absorbed through mucous membranes
How is bacteria most likely to be transferred in a hospital setting?
Good personal hygiene
What is the best protection against exposure to bacteria?
Lyme disease and leptospirosis
What are common bacterial zoonotic diseases?
Spirochete bacteria
What type of bacteria is lyme disease?
• Deer tick (Ixodes spp.)
• Borrelia burgdorferi
What type of tick is responsible for spreading lyme disease, and what bacterium does it transfer to a host?
Aches in the joints, fever, and other flu-like symptoms
Lyme disease in humans is characterized by _____
• Direct contact of mucous membranes
• Abraded skin with infected urine
How is leptospirosis commonly transmitted?
Gram-negative spirochete bacteria
What type of bacteria is leptospirosis?
Causes kidney, liver, and respiratory disease
How does leptospirosis affect most mammals?
• Fever
• Rash
• Meningitis
• Hemorrhage
• Liver and kidney disease
How does leptospirosis affect infected humans?
Microsporum canis
Name the fungus that causes ringworm
Cats and horses
Which animals are particularly susceptible to ringworm infection?
Ringworm (a fungal infection)
An infection of the skin caused by Microsporum canis
Internal larvae migrates
A parasitic infection in which roundworm larvae migrate to other organs in the body and develop into a cyst-like growth
A parasitic infection in which roundworm larvae migrate to the eye potentially causing permanent damage to the retina and blindness
What is ocular larval migrans, and what damage can it cause to an infected patient?
The passage of worms from the female dog to the fetus occurs through the placenta and via lactation
Why do puppies always have some level of roundworm infestation?
A parasitic infection in which hookworm larvae migrate and cause pruritic tracks under the skin
What is cutaneous larval migrans?
An infestation by a protozoan known as toxoplasma gondii
What is toxoplasmosis?
• Non-sporulated Toxoplasma eggs are shed in the feces of infected cats
• These eggs sporulate (evolve from a non-infective into an infective form) 2- 4 days later
• 3-day-old sporulated oocysts pose a danger to a fetus if ingested by a pregnant person
How does toxoplasmosis spread/develop infection?
Giardia and coccidia
List two zoonotic protozoal agents that may cause diarrhea and gastrointestinal cramping in humans
• Through contact with infected animals (particularly puppies and kittens)
• By drinking contaminated water
How can giardia and coccidia spread to humans?
Harbors the adult parasite
What is the role of a definitive host?
Harbors the immature parasite
What is the role of an intermediate host?
Harbors a parasite but is not affected by the parasite
What is the role of a reservoir host?
Definitive host
An organism which supports the adult or sexually reproductive form of a parasite
Intermediate host
An organism that supports the immature or non-reproductive forms of a parasite
• Number of parasites
• Location in the host
• Production of toxin
• Interference with patient's biology
Parasites can cause significant damage to the host. What can the amount of damage be affected by?
Ectoparasites
Fleas, lice, ticks, mites, chiggers, biting flies, and myiasis-inducing flies are examples of
Endoparasites
Nematodes, cestodes, trematodes, and protozoa are examples of
• Parasitic life cycles
• Clues regarding risks
• Clues to prevention
• Clues to treatment interval protocols
What should you discuss with a client regarding parasites?
Parasites with jointed appendages or feet
What are arthropods?
Fleas, ticks, lice and mites (scabies mites, walking dandruff mites)
What is an example of an arthropod?
Ascarines
An arthropod that falls under the classifications of ticks or mites
Scabies mites
Sarcoptes scabiei are also known as
Sarcoptes scabiei
What is the scientific name for scabies mites?
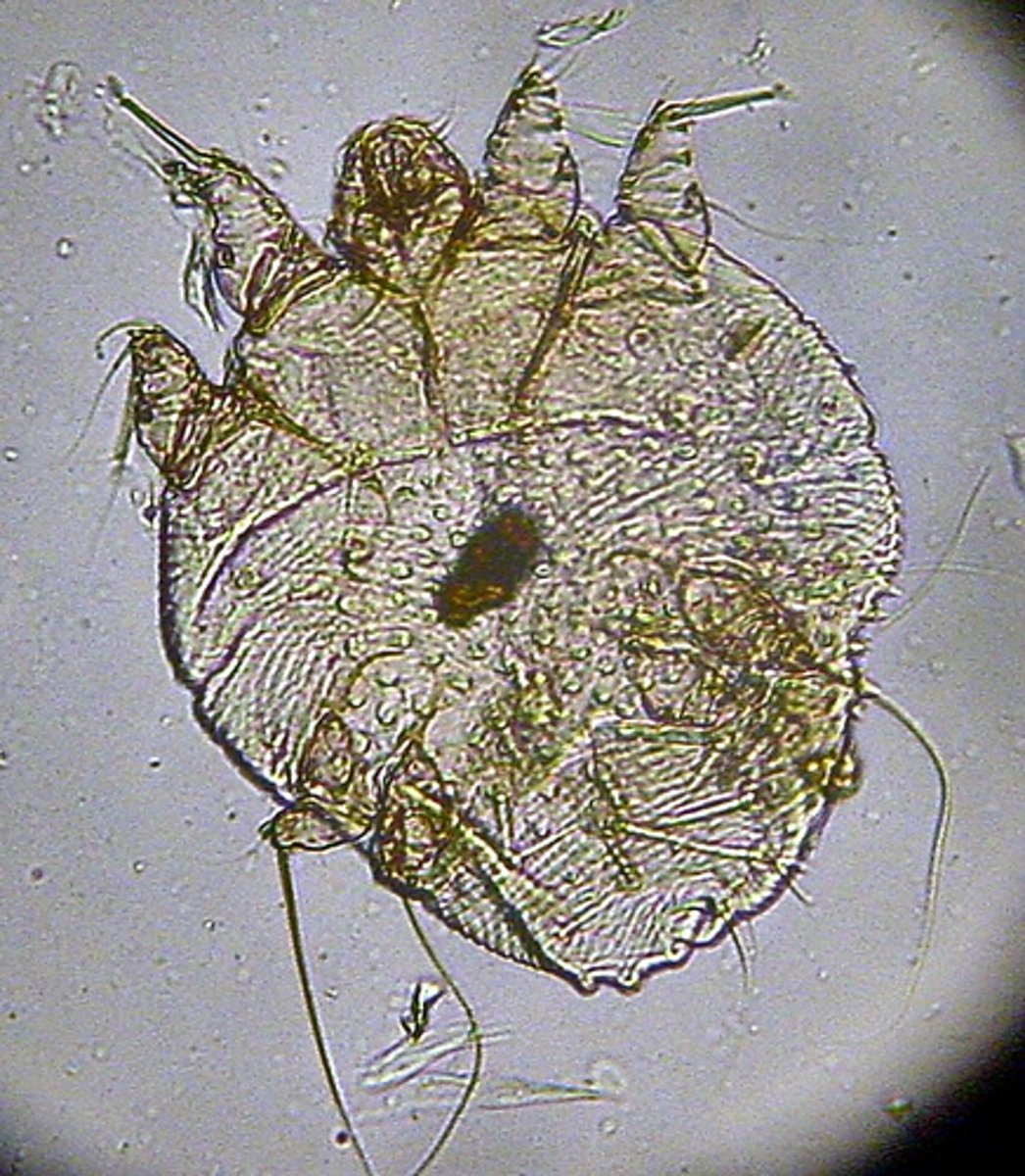
Otoacariasis
Ticks and mites of the ear canal
Selamectin (Frontline)
What is the treatment for a patient infected with arthropods?
Sarcoptes scabiei (scabies mites)
An arthropod that causes extreme pruritus, hyperemia and alopecia
By placing a superficial skin scraping on a glass slide with a drop of mineral oil
How is scabies diagnosed?
• Transmission to humans occurs from direct contact with an infected dog, contact with a contaminated environment, and fomites
• Hospital should be disinfected with pyrethrins (found naturally in chrysanthemum flowers)
What is the zoonotic risk of scabies?
Patients bathed to remove debris and crusting scabs. Treated with two topical treatments of Selamectin (Frontline) 30 days apart.
How do you treat a patient infected with scabies?
Walking dandruff mite
Cheyletiella parasitivorax is also known as
Cheyletiella parasitivorax
What is the scientific name for walking dandruff mite?
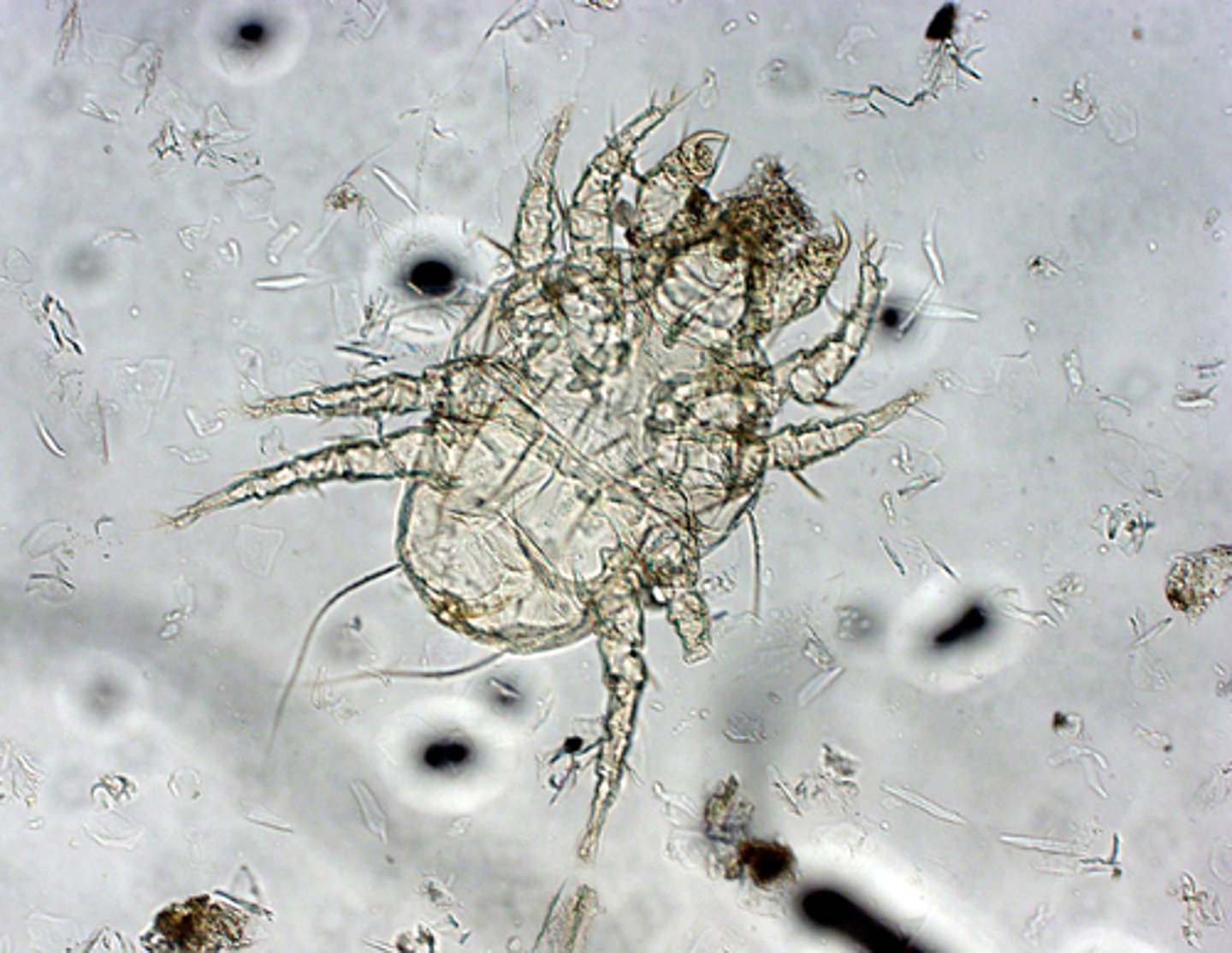
Cheyletiella parasitivorax (Walking dandruff mite)
Arthropod that affects dogs, cats, and rabbits with intense pruritus from excess keratin
Breeding female dogs and cats (yagura is the dog mite and C. blakei is the cat mite)
Asymptomatic carriers of walking dandruff mites
By parting the hair to observe mites walk along the skin or using a flea comb.
They have accessory "hooks" on the head and a "comb-like" structure at the feet.
How do you diagnose walking dandruff mites?
• Spreads to humans through direct contact with infected patient or via fomites (can live up to 10 days off the host within the environment)
• Causes severe pruritus in humans
What is the zoonotic risk of walking dandruff mites?
Patients bathed to remove debris and crusting scabs.
Systemic treatment with Ivermectin, Selamectin, or Moxidectin for 6 weeks
What is the treatment for a patient with walking dandruff mites?
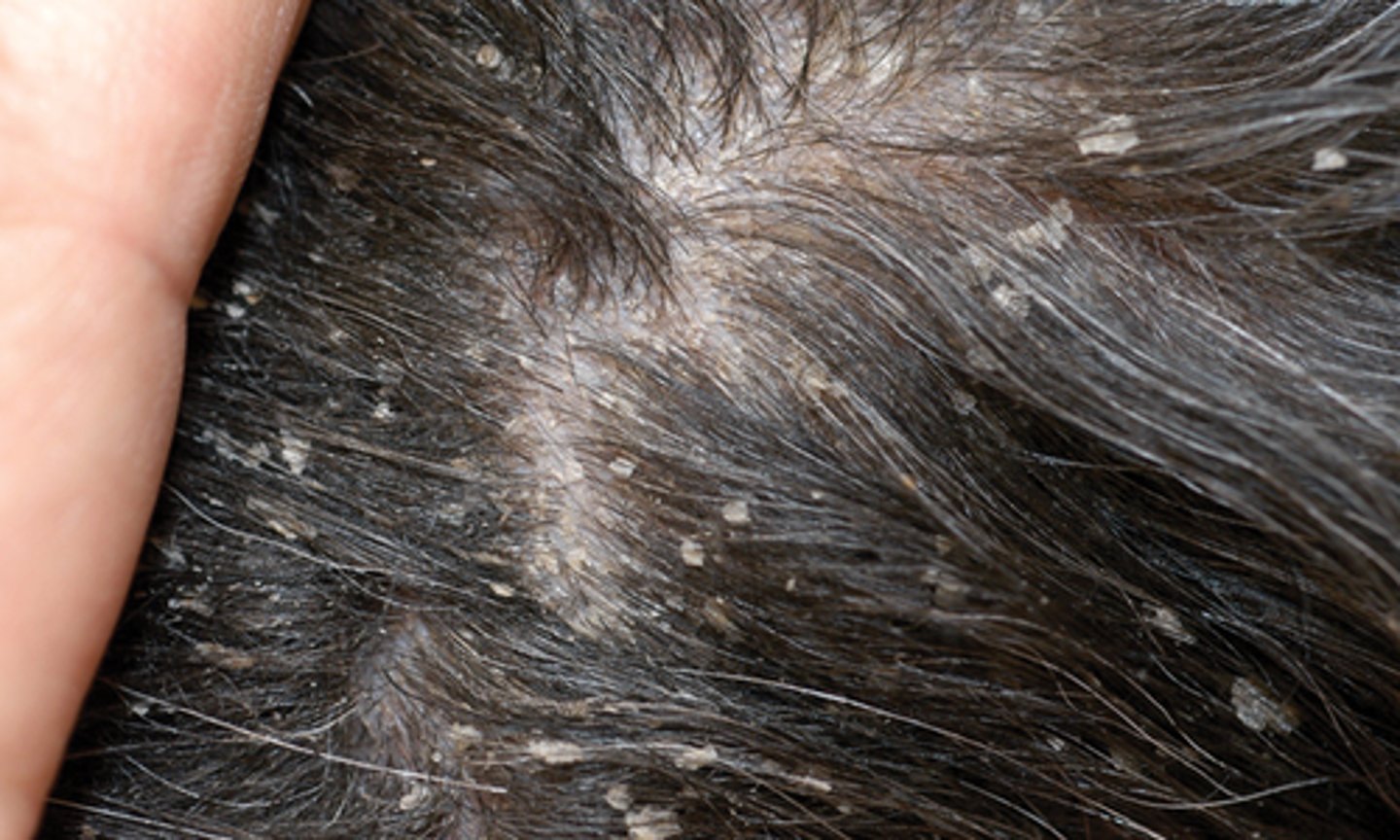
Demodex sp
Common names for this parasite include "skin mite" or "mange mite"
• Transmission of tick-borne diseases such as Rocky Mountain Spotted fever, Q fever, Tularemia, Tick paralysis, and Cytauxzoonosis
• Protozoan parasites
• Serve as a vector for bacteria, viruses, chlamydia, and spirochetes
What is the zoonotic risk of ticks?
• Fipronil, and Amitraz for dogs
• Fipronil and Selamectin for cats
• Always notify owners that tick products are species specific and should not be used interchangeably
What is treatment for a patient with a tick infestation?
The fleas of the dog and cat, respectively
Ctenocephalides canis and ctenocephalides felis are known as
Ctenocephalides canis and ctenocephalides felis
What are the scientific names for the dog flea and the cat flea?
• The cat flea has the potential to spread Bartonella henselae (cat scratch fever) via fecal matter
• Yersinia pestis also known as "the plague"
What is the zoonotic risk of fleas?
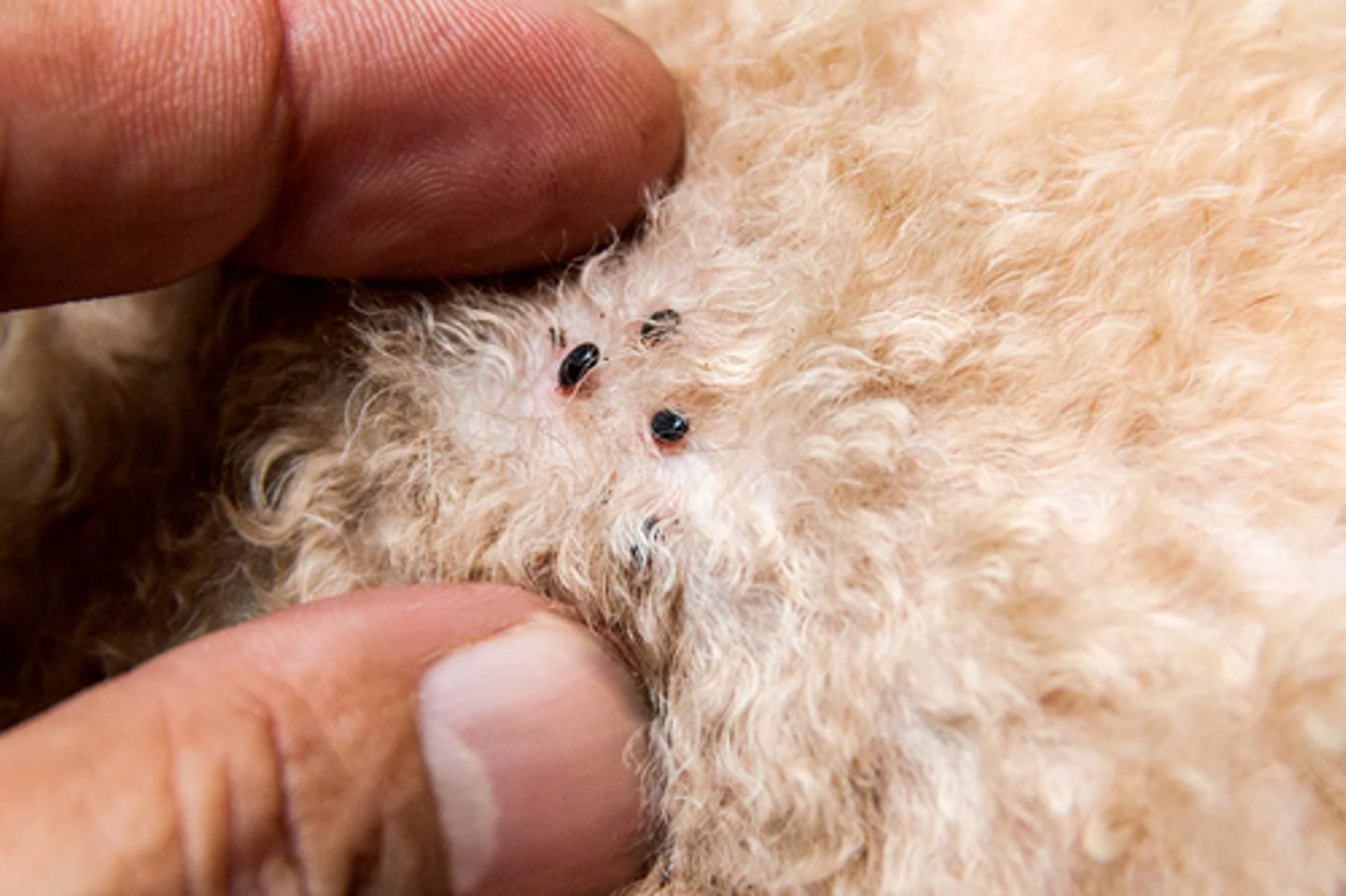

A flea-borne disease that can spread to humans by the fecal matter of a cat and cause the immunocompromised to develop tumors
What is cat scratch fever?
Bubonic, septicemic, and pneumonic
Pneumonic is the only form that can spread from person to person
What are the three forms of yersinia pestis ("the plague") and which form can spread from person to person?
Cestodes
Adult tapeworms of dogs and cats
Metacestodes
Tapeworm larvae are known as
The intestinal tract of dogs, cats, ferrets, and humans
Where can cestodes be found?
Scolex (head), the neck, and the strobila (body)
What are the three basic parts of a cestode?
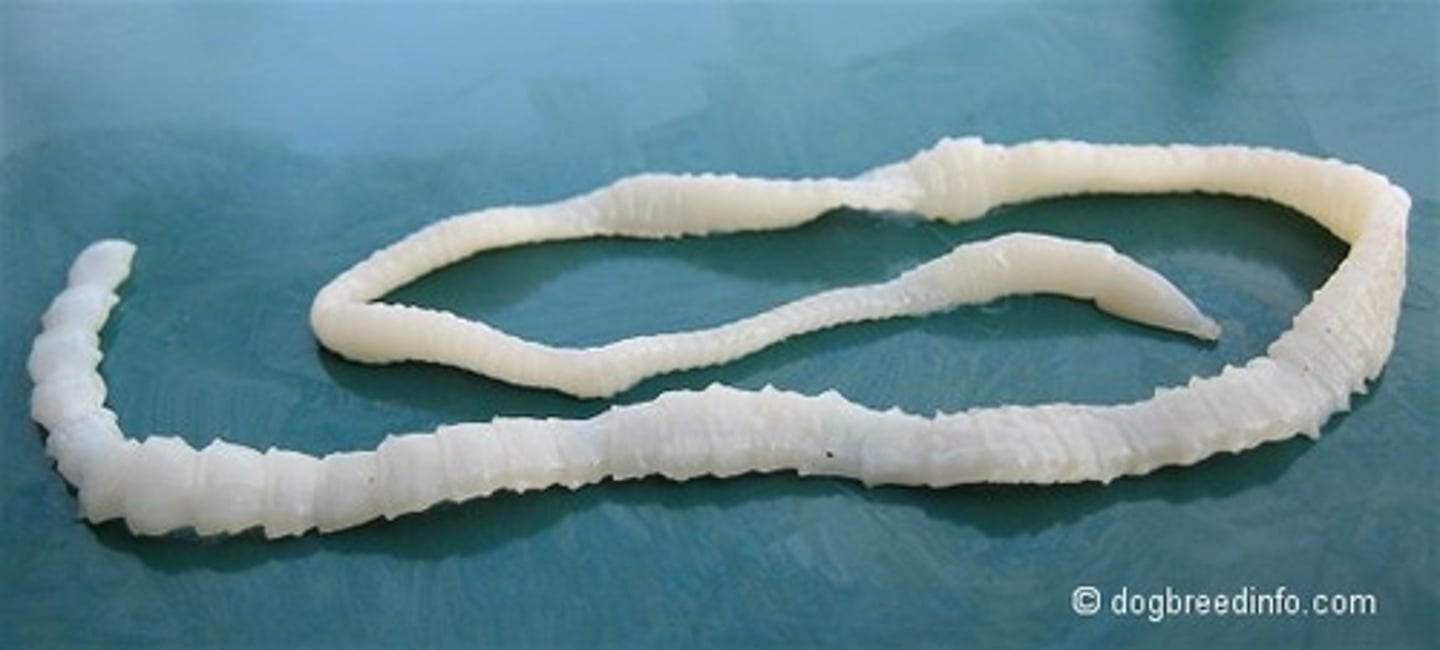
• A type of cestode with cucumber seed-like proglottids (chain of segments)
• Double pore possesses two sets of male and female reproductive organs
• Egg packets contain 20- 30 embryos; thousands per segment
What is dipylidium caninum?
Cysticercoid
The infective stage of dipylidium caninum carried in the larval stage of the flea
• The small tapeworm of the dog
• Intermediate hosts are sheep and cattle within the visceral organs
What is echinococcus granulosus?
• The small tapeworm of cats and foxes
• Rodents as intermediate hosts within the liver and lungs
What is echinococcus multilocularis?
Echinococcus granulosus
Give the scientific name for the small tapeworm of the dog
Echinococcus multilocularis
Give the scientific name for the small tapeworm of the cat
• "Zipper tapeworm" of dogs and cats
• Crustaceans are intermediate hosts as they harbor the first larval stage
What is spirometra mansonoides?
Spirometra mansonoides
What is the scientific name for the zipper tapeworm of cats and dogs?
Dogs and cats are usually asymptomatic but tapeworm segments may be found in the feces or around the anus
What are symptoms of cestodes in dogs and cats?
Praziquantel, epsiprantel, or fenbendazole
What is the treatment for cestodes?
A child can develop an adult tapeworm if they ingest a cysticercoid
What is the zoonotic potential of cestodes?
Nematodes
Roundworms are also known as
Nematodes (roundworms)
Parasitize the widest assortment of wild and domestic animals
In the small intestine of dog and cat hosts
Where can roundworms be found?
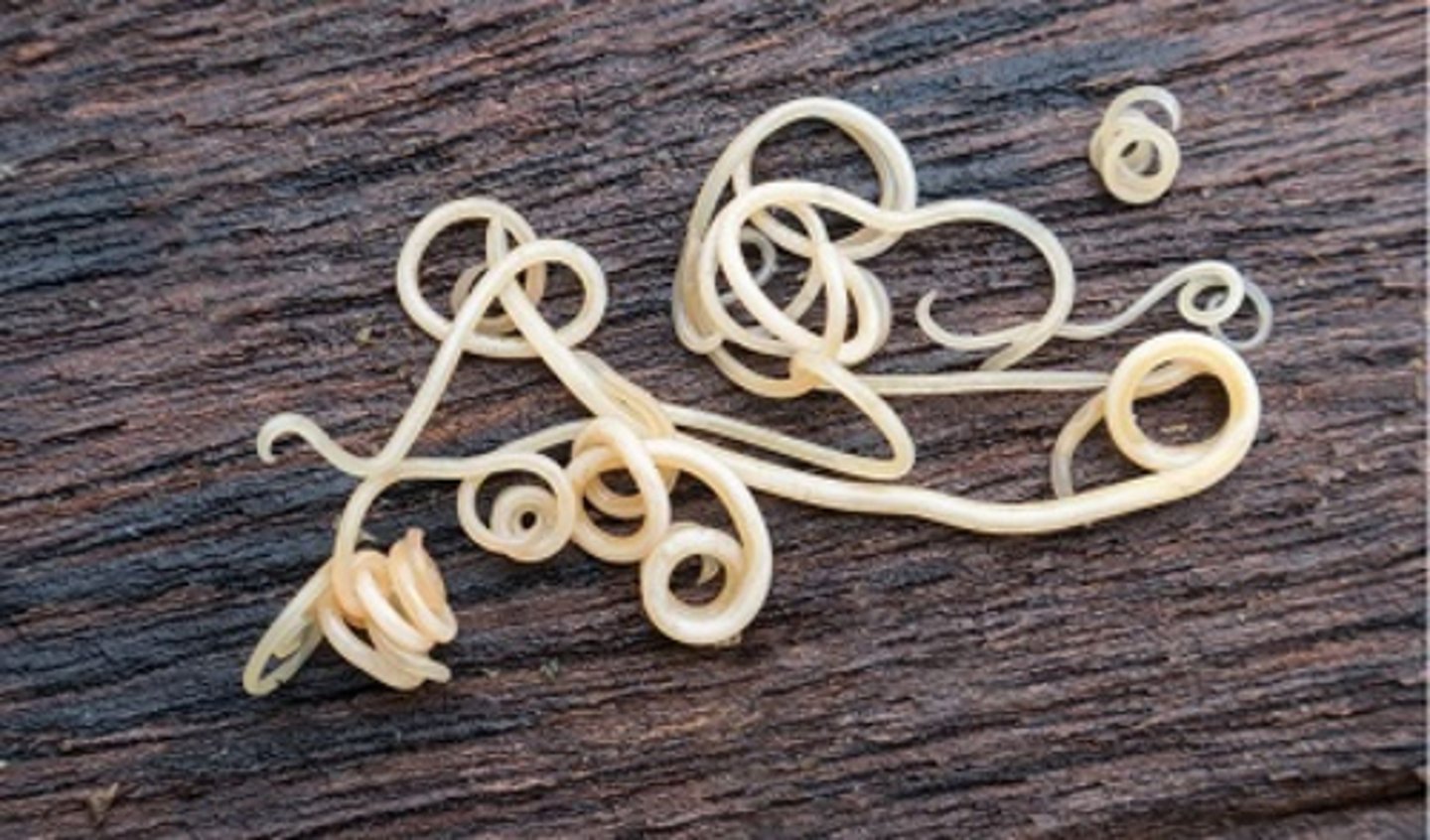

Roundworms that affect the small intestine of the dog, cat, and dog and cat, respectively
Toxocara canis, cati, and leonine are known as
Toxocara canis
What is the scientific name for the roundworm that affects the dog?
Toxocara cati
What is the scientific name for the roundworm that affects the cat?
Toxocara leonine
What is the scientific name for the roundworm that affects both the dog and cat?
A type of roundworm that affects raccoons
What is baylisascaris procyonis?
Toxocara canis (canine roundworm)
Form in the dog, are shed into the environment where they develop and then are re-ingested by the dog and become encysted
• Vomiting, diarrhea, and enlarged abdomen in puppies
• Flatulence
• Poor growth
What are symptoms of toxocara canis?
Young kittens are often asymptomatic, but heavy infection can cause diarrhea, abdominal distention, rough hair coat, and dehydration
What are the symptoms of toxocara cati?
Paratenic host
Harbors the immature parasite but is not necessary in its development. It stays in suspended animation until eaten by a new host.
Fecal flotation or centrifugation with ID of eggs (fresh fecal sample is best for diagnosis)
How do you diagnose hookworms, roundworms, and whip worms?
• Pyrantel pamoate
• Fenbendazole (Panacur)
• Moxydexin (NexGard/ Trifexis)
• Milbemycin oxime (Interceptor)
• Selamectin (Selarid)
How do you treat a patient with roundworms?
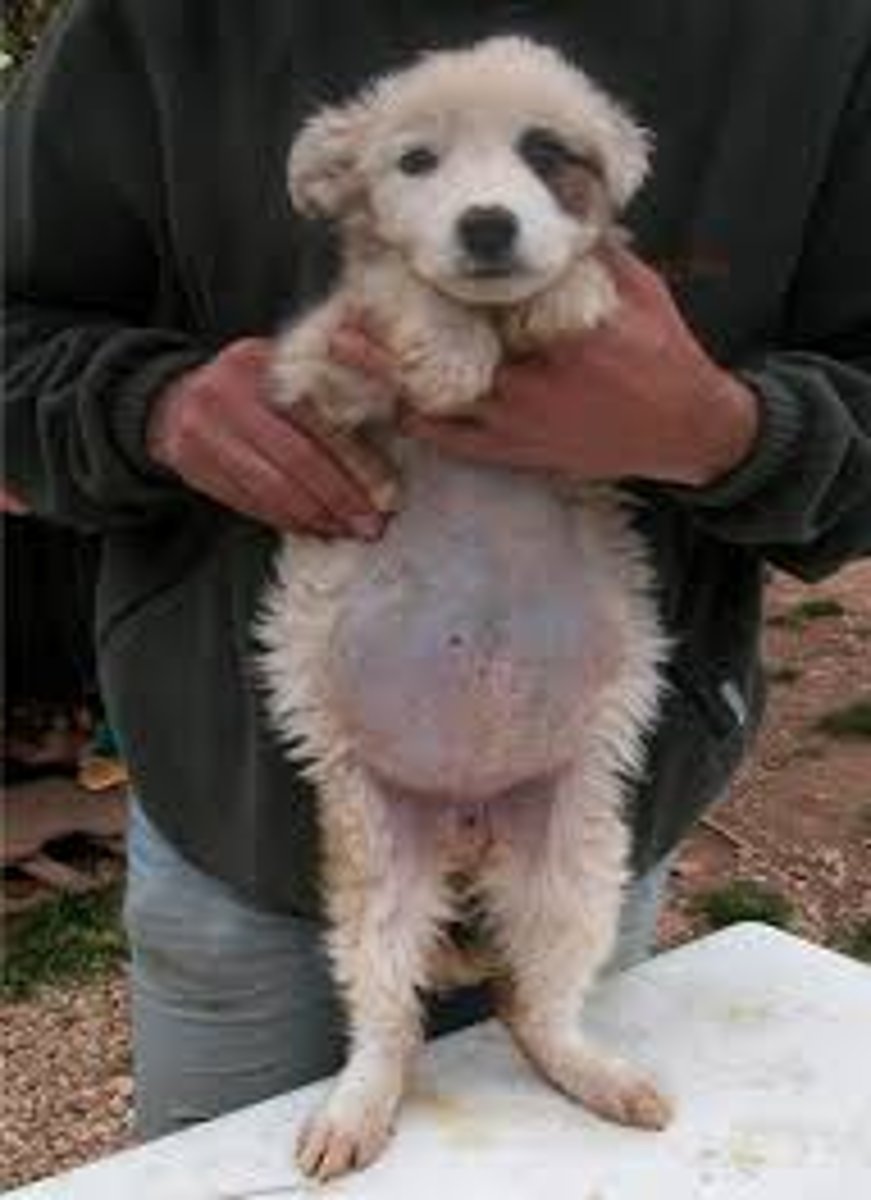

Abiding by leash laws, picking up feces, discouraging pica and geophagia in children, and enforcing hand washing
How can humans aid in the prevention of roundworm infestations?
Ingestion of b. procyonis eggs can lead to neurologic larva migrans (NLM), the migration of larvae to the brain and spinal cord
What is the zoonotic potential of baylisascaris procyonis?
Baylisascaris procyonis (raccoon roundworms)
Mainly found in the small intestine of the raccoon
Ancylostoma
"Hookworm" found in the intestines of dogs and cats
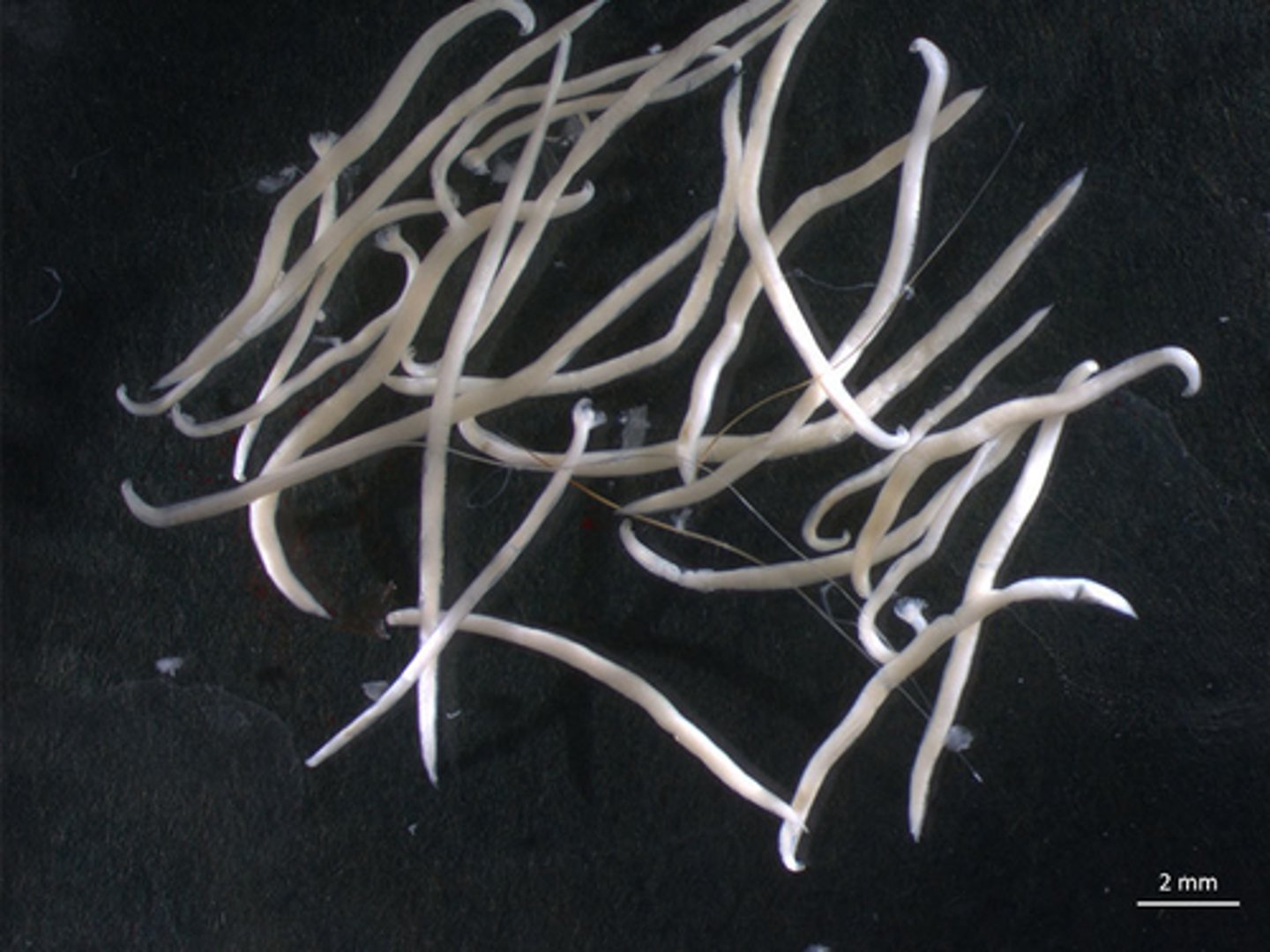

Ancylostoma (hookworms)
Parasites that have unique teeth and large buccal cavities
Pale mucous membranes/anemia, blood-tinged/tarry stools, or weight loss in cats
What are the clinical signs of hookworms?