Atomic structure and the periodic table: full topic flashcards
1/95
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
96 Terms
What did scientists believe atoms were in the 1800’s?
Solid spheres that made up the different elements
Who created the plum pudding model?
JJ Thompson
Why did JJ Thompson disagree with the original definition of an atom in the 1800’s?
His measurements of charge and mass showed that an atom must contain even smaller, negatively charged particles-electrons
What is the plum pudding theory?
Shows the atom as a ball of positive charge with electrons spread throughout the inside
Who were the scientists on the alpha particle scattering experiment?
Rutherford and his student
Explain how they conducted the alpha particle scattering experiment.
They fired positively charged alpha particles at an extremely thin sheet of gold
What did Rutherford expect from the alpha particle experiment vs what actually happened?
He was expecting the particles to pass straight through the sheet or to be slightly deflected
Whilst most particles did go through the gold sheet some were deflected more than expected and smaller numbers were deflected backwards
This proved the plum pudding model couldn’t be right
What was Rutherfords nuclear model?
Tiny positively charged nucleus where the mass is concentrated
A cloud of electrons surrounds the nucleus
Most of the atoms are empty space
Explain what happened during the alpha particle scattering experiment with Rutherfords nuclear model.
When alpha particles came near the concentrated, positive charge of the nucleus, they were deflected
If they were fired directly at the nucleus, they were deflected backwards
Otherwise they passed through empty space
Why did scientists believe Rutherfords nuclear model was wrong?
Scientists realised that electrons in a cloud around the nucleus of the atom, would attract to the nucleus causing it to collapse.
What was Bohr’s nuclear model?
Suggested electrons were contained in shells
Electrons orbit the nucleus in fixed shells
Each shell is a fixed distance away fro the nucleus
This was supported by many experiments and helped explain lots of other scientists experiments at the time
How was the proton discovered?
Rutherford and other scientists showed the nucleus can be divided into smaller particles which have the same charge as the hydrogen nucleus
Who discovered neutrons?
James Chadwick carried out an experiment that provided evidence for neutral particles in the nucleus, now called neutrons
The discovery of which particle made a model of the atom that is most similar to the modern day accepted version?
The discovery of neutrons made it the most similar to the modern nuclear model.
What were the 2 obvious ways to categorise elements in the early 1800’s?
Their physical and chemical properties
Their atomic weight
Why were elements organised by their atomic weight in the early 1800’s?
Scientists had not discovered protons or the atomic numbers
They could only measure atomic weight
When this was done the periodic pattern was noticed between the properties of the elements ( where the name ‘periodic table’ came from )
The table was incomplete and some elements were placed incorrectly because it didn’t take into account their physical or chemical properties
How did Dimitri Mendeleev overcome the problems of old periodic table?
rearranged 50 elements
Mainly in order of atomic weight
Switched the order if their properties meant it should be switched
Why were their gaps in Mendeleev’s periodic table and what did they lead to?
Gaps were left to ensure the elements with similar properties stayed int he same groups
Some of these properties indicated undiscovered elements
This allowed Dimitri to predict what their properties might be
What later discovery confirmed Dimitri was right to not place elements in a strict order?
The discovery of isotopes-ensured different masses of the same elements were not placed in the wrong order because of their weight when their properties didn’t change
How are all the elements in the periodic table laid out?
In order of increasing atomic numbers
What does elements being in order of their atomic numbers cause in the modern periodic table?
Repeating patterns in their properties
What does the group number of an element tell you?
How many electrons it has in its outer shell
What trend is there for elements in the same group?
They are likely to react similarly
Give 2 examples of properties you can predict from elements being in the same group.
how or what with they might react
if their reactivity increases or decreases as you go down the group
What elements are in group 1?
Lithium, sodium, potassium, rubidium, caesium and francium
How many electrons are in there outer shells and how does it effect their reactivity for group 1 elements?
They have 1 electron in their outer shell
Makes them very reactive
Lose electrons easily to form ions and react with other elements
What are the 3 main properties of all group 1 metals?
soft metals
low density
very reactive
What are the trends as you go down group 1 metals?
Increasing reactivity
Lower melting and boiling points
Higher relative atomic masses
Why does the reactivity increase as you go down group 1?
The outer electron is more easily lost as the attraction between the nucleus and the electron decrease because the electron is further away from the nucleus the further down the group you go
What bond do group 1 metals form with what elements?
Ionic compounds with non-metals
What are the properties of group 1 compounds?
white solids that dissolve in water to form colourless solutions
How do group 1 elements react with water?
React vigorously to produce hydrogen gas and metal hydroxides
These compounds dissolve in water to produce alkaline solutions
The more reactive the metal, the more violent the reaction
The amount of energy given out the the reaction increases down the group
2 Na ( s ) + 2 H 2 O ( l ) → 2 NaOH ( aq ) + H 2 ( g )
How do group 1 elements react with chlorine?
React vigorously when heated in chlorine gas
Forms white metal chloride salts
Reactivity increases as you go down the group, so the reaction with chlorine gets more vigorous
2 Na ( s ) Sodium + Cl 2 ( g ) Chlorine → 2 NaCl ( s ) Sodium Chloride
How do group 1 elements react with oxygen?
Form metal oxides
Different types of oxides form depending on the metal:
Lithium-lithium oxide (Li2O)
Sodium- sodium oxide (Na2O), sodium peroxide (Na2O2)
Potassium - potassium peroxide(K2O2), Potassium superoxide (KO2)
4 N a + O 2 → 2 N a 2 O
How do alkali metals compare to transition metals?
Group 1 metals are much more reactive
React more vigorously with oxygen water and the group 7 elements
Less dense, strong and hard
Group 1 metals have much lower opt and bpt
What are the subatomic particles in an atom?
Neutrons protons and electrons
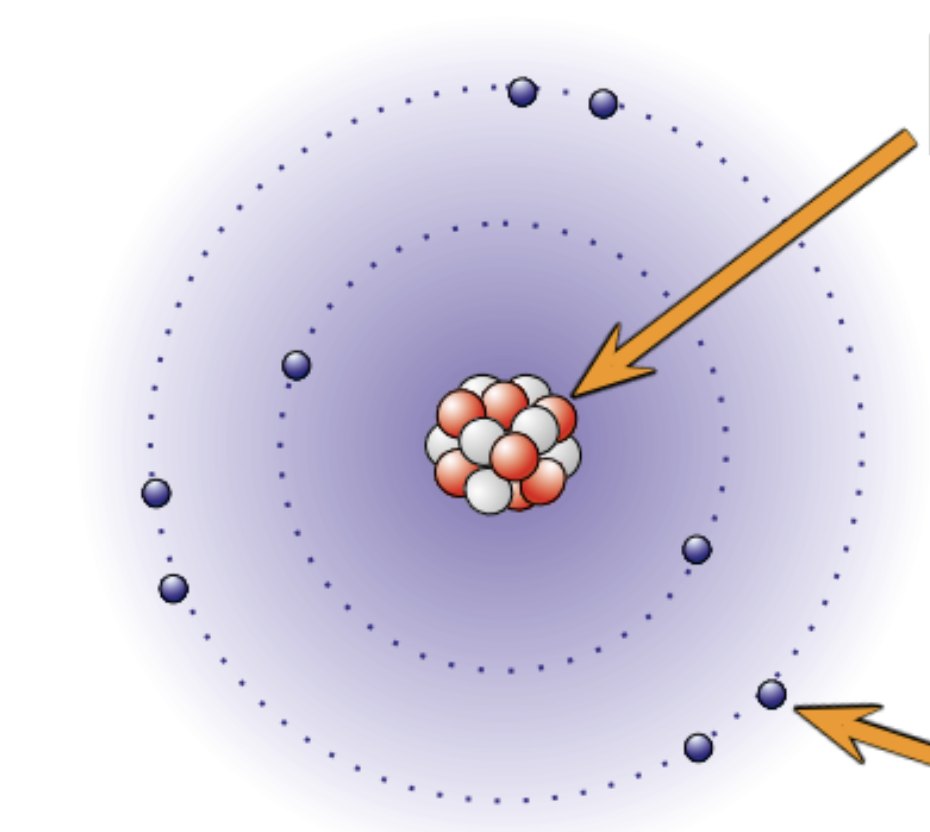
Explain where and what the nucleus is.
In the middle of the atom
Contains neutrons and protons
the radius is about 1 ×10-14
It has a positive charge because of the protons
Almost the whole mass of the atom is concentrated at the nucleus
Explain where and what electrons are in an atom?
Move around the nucleus in shells
Negatively charged
The volume of their orbits determine the size of the atom
Electrons has virtually no mass
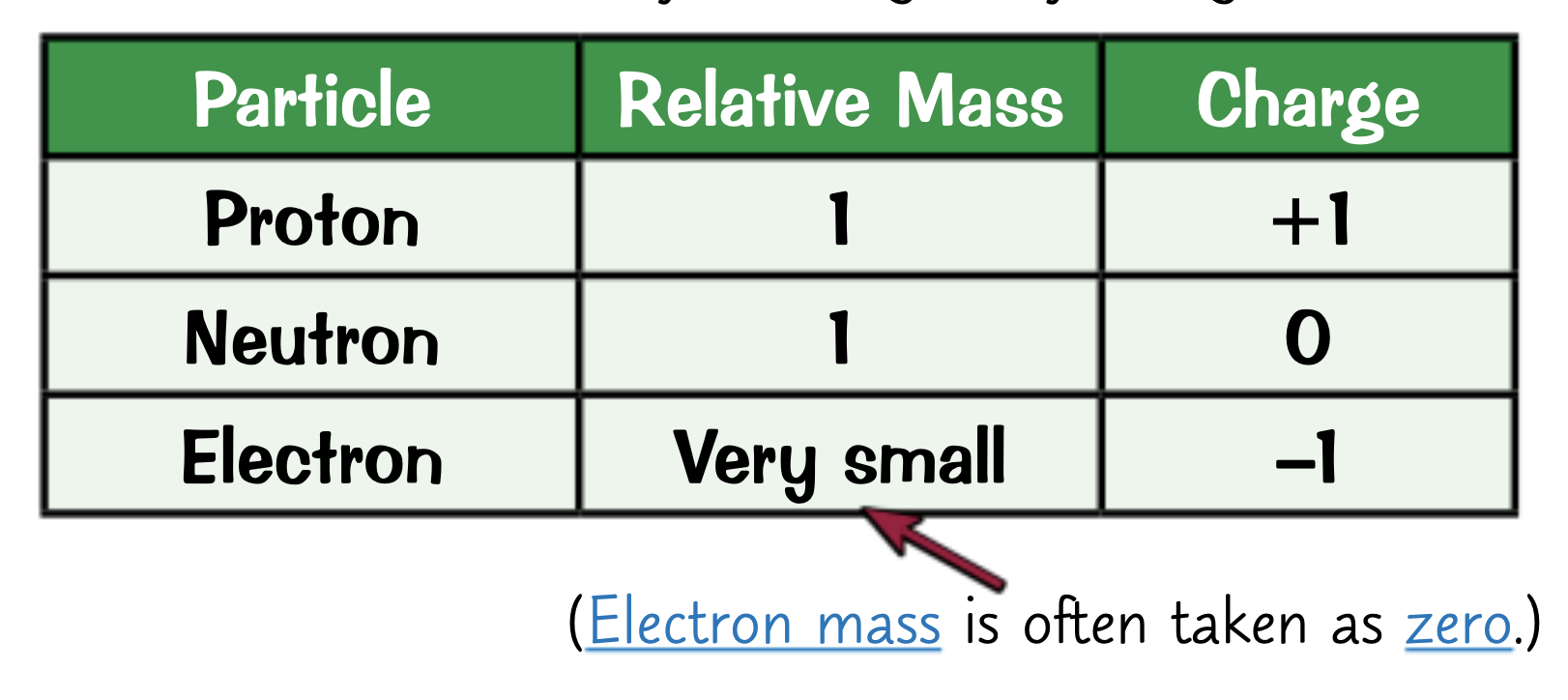
What are the masses and charges of subatomic particles?
Do atoms have a charge?
No they are neutral because they have the same number of protons and electrons
Why do ions have charges?
The proton and electron numbers aren’t equal so the charges do not cancel out
What does the atomic number tell you?
How many protons there are
What does the mass number tell you?
the total number of protons and neutrons in an atom
Where are the atomic number and atomic mass on a nuclear symbol?
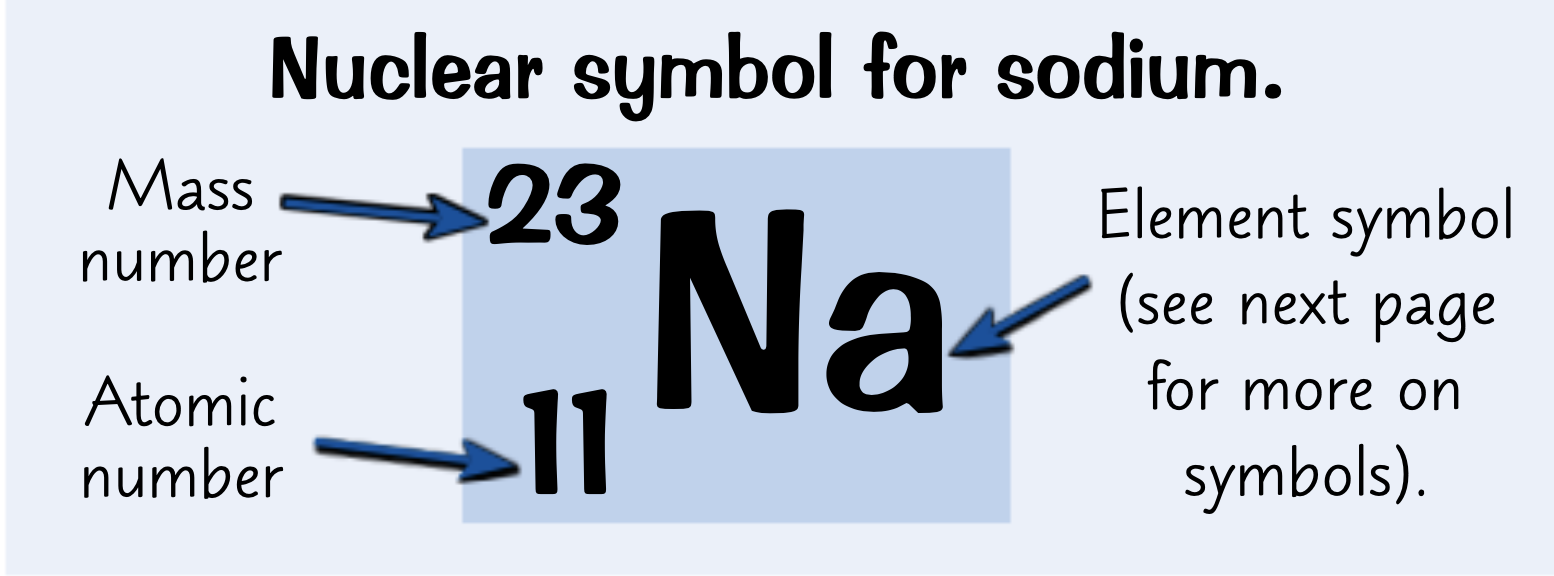
What is the definition of an element?
a substance made up of atoms that all have the same number of protons
What is the role of protons in an element?
Decides what type of atom it is
What is the definition of an isotope?
different forms of the same element, which have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons
What is relative atomic mass?
average mass taking into account the different masses and abundances of all the isotopes that make up that element.
What is the formula for relative atomic mass?
Ar = sum of (isotope abundance x isotope mass number) / sum of abundances of all the isotopes

How is a compound formed?
atoms react to form compounds
What is the definition for a compound?
substances formed from 2 or more elements, that are chemically bonded in fixed proportions
How are chemical bonds made in compounds ?
taking in, removing or sharing electrons
Why are compounds difficult to separate?
A lot of energy is needed to separate the chemical bonds
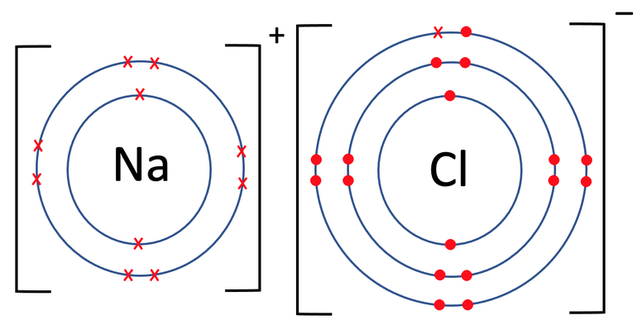
What is ionic bonding?
compound formed from a metal and non-metal
Metal loses electrons to form positive ions
non-metal gains electrons to form negative ions
The opposite charges mean they are strongly attracted to each other
What is covalent bonding?
A compound formed from non-metals
Each atom shares an electron with another atom
What are the chemical formulas for:
carbon dioxide
ammonia
water
sodium chloride
carbon monoxide
hydrochloric acid
calcium chloride
sodium carbonate
sulfuric acid

What is the definition of a mixture?
a substance made of 2 more more elements or compounds that are not chemically bonded
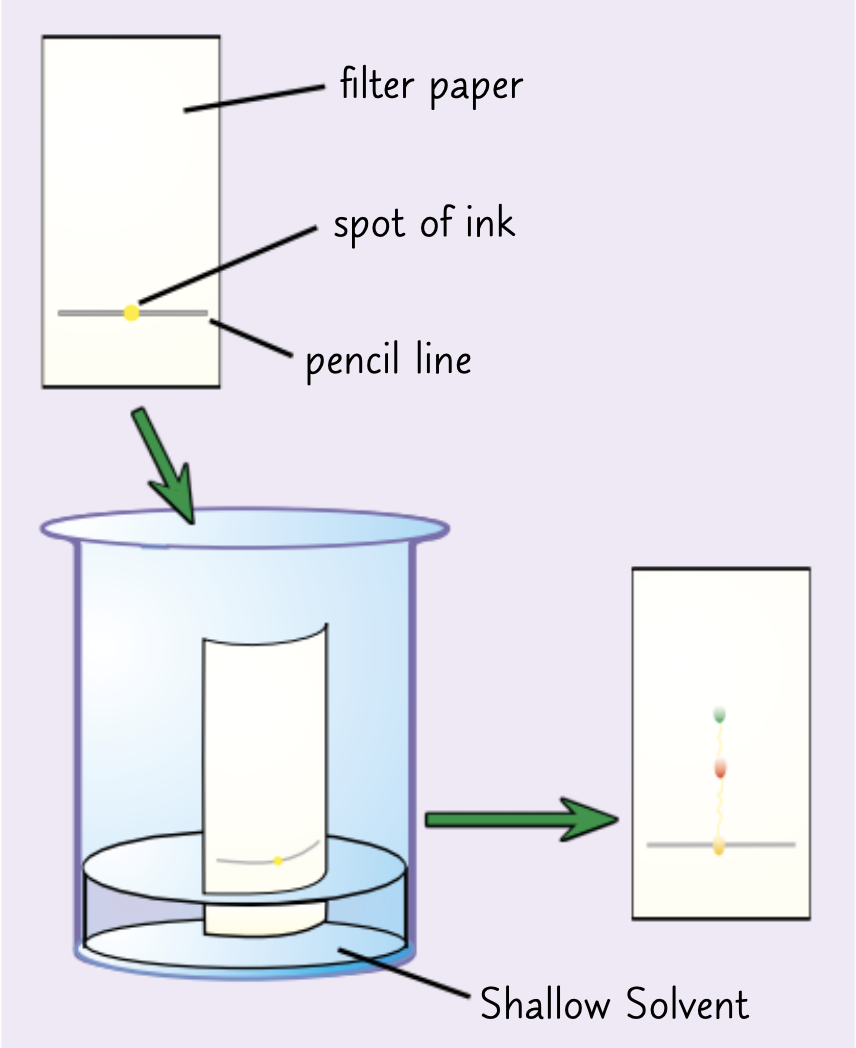
Explain the method of the chromatography practical.
Draw a line near the bottom of the filter paper sheet ( with pencil because its insoluble)
Add a drop of ink onto the line and place it into a beaker of solvent
The solvent depends on what is being tested-some compounds dissolve well in water however others may require stronger solvents such as ethanol
Make sure the ink isn’t touching the solvent
Place a lid on top of the container to prevent the solvent evaporating
The solvent seeps up the paper carrying the ink with it
Each dye in the ink will move up the paper at different rates so the dyes will separate
Any insoluble dyes will stay on the baseline
When the solvent has nearly reached the top of the paper take it out and let it dry.
This will result in the creation of a chromatogram
What is chromatography used for?
Separating substances in a mixture based on their solubility
Explain why you use pencil to draw the baseline in chromatography.
Pencil is insoluble and therefore will not dissolve and seperate with the solvent
Explain why the dyes seperate with the solvent in chromatography .
Each dye will move up the paper with the solvent at different rates causing them to separate
What will happen to dyes that are insoluble in chromatography?
They will stay on the baseline
What is the pattern called that forms at the end of a chromatography test?
chromatogram
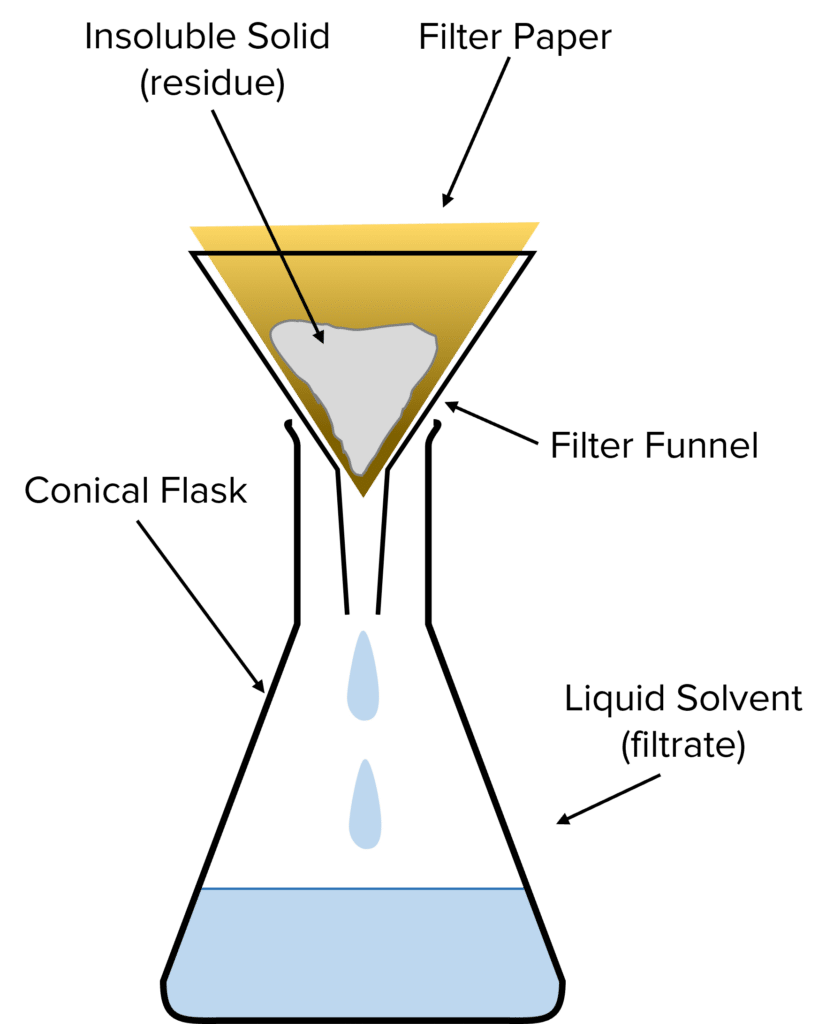
When can filtration be used s a separation method?
When your product is an insoluble solid that needs to be separated from a liquid reaction mixture
Can be used to filter solid impurities in a reaction mixture
When can you use evaporation as a separation technique?
to separate a soluble solid from a solution, if the salt won’t decompose when heated
Explain the process of evaporation as a separation technique
Pour solution into an evaporating dish
Slowly heat the solution. The solvent will evaporate and the solution will get more concentrated. eventually crystals will start to form
Keep heating the evaporating dish until you are left with dry crystals
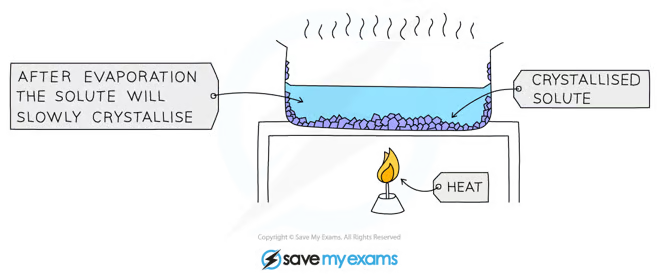
When should you use crystallisation as a separation technique?
To separate a soluble solid from a solution when the desired salt will decompose when heated or when you want big crystals of a salt
Explain the process of crystallisation as a separation technique
Pour solution into an evaporating dish and gently heat the solution. Some of the solution will evaporate and the solution will get more concentrated.
Once some of the solvent has evaporated or you see crystals starting to form, remove the dish from the heat and leave solution to cool
The salt should start to form crystals as it becomes insoluble in the cold, highly concentrated solution
Filter the crystals out of the solution and leave them in a warm place to dry. You could use an oven or desiccator
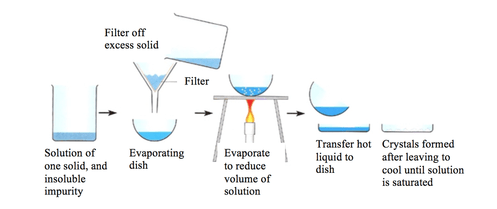
What is rock salt?
a mixture of salt and sand
How and why can you separate rock salt to only get the salt?
Salt is soluble will sand is in soluble
Grind the mixture to make sure the salt crystals are small so they will dissolve easily
Put the mixture in water and stir so the salt dissolves and the sand doesnt
Filter the mixture. The sand will be your residue and the solvent will be your salt solution
Evaporate the water from the solution so the salt forms dry crystals
What is distillation used for?
Separate a mixture of liquids according to their boiling points
What is simple distillation?
Used to separate a liquid from a solution
Explain the process of simple distillation.
The solution is heated. The part of the solution with the lowest boiling point evaporates first
The vapour is then cooled, condenses and is collected
The rest of the solution is left in the flask
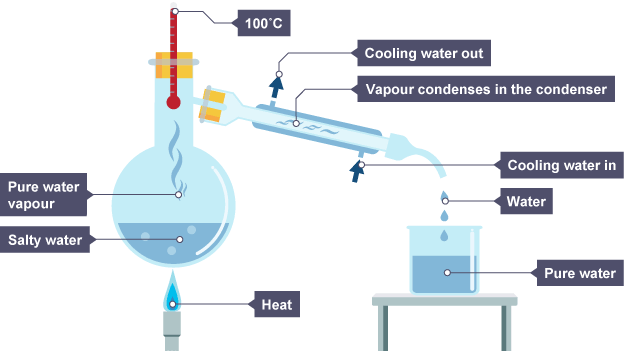
How can you use simple distillation to get pure water from seawater?
The water evaporates and is condensed and collected. eventually you will end up with just salt in the flask
What is a problem with simple distillation?
You can only separate liquids with a significant difference in boiling points otherwise the temperature will increase so both liquids evaporate and become a mixture again when collected
What is fractional distillation used for?
To separate a mixture of liquids with similar boiling points
Where is fractional distillation used on a much larger scale?
Used for the separation of crude oil
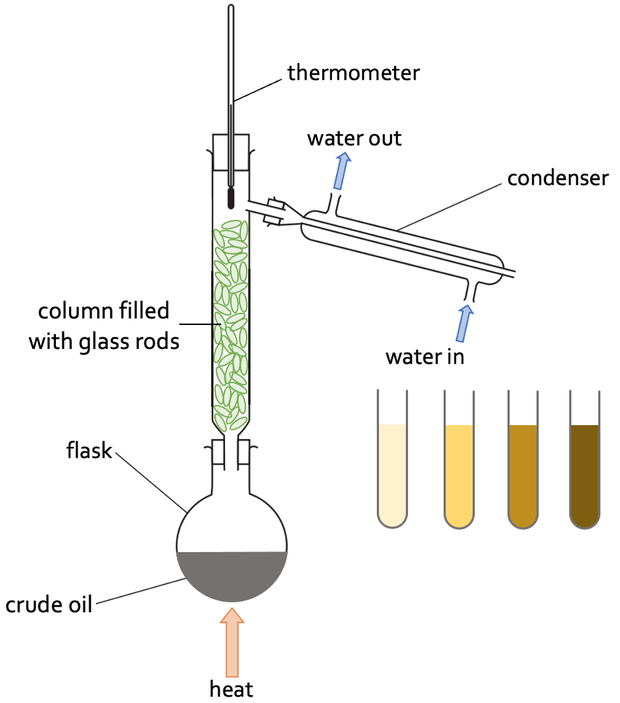
Explain the process of a lab fractional distillation
Put your mixture in a flask and stick a fractioning column on top and then heat it.
The different liquids have different boiling points so will evaporate at different temperatures
The liquid with the lowest boiling point evaporates first. Then the thermometer matches the boiling point of the liquid it will reach the top of the column
Liquids with higher boiling points may start to evaporate, but the column is cooler towards the top so they will only reach part way up before condensing and running down towards the flask
When the first liquid has been collected you raise the temperature until the next liquid reaches the top.
Repeat this until you have collected all the liquids separately
How do atoms generally gain a full outer shell?
By losing or gaining electrons
Why do metals form positive ions easily?
Don’t have many electrons to lose
Electrons towards the bottom’s electrons are far away from nucleus so have weaker intermolecular forces
Why do non-metals form positive ions, and how do they gain a full outer shell?
They are often only missing a small number of electrons
Easier to share or gain electrons
What causes metals to have similar properties?
metallic bonding
What are the properties of metals?
Strong and malleable
Conduct heat and electricity
High melting and boiling points
Shiny
Have high densities
What are the properties of non-metals?
Dull
Brittle
Aren’t always solids
Insulators
have a lower density
What are the properties of transition metals?
Conduct heat and electricity
dense
strong
shiny
Can form more than one type of ion
Ions are often coloured so form colourful compounds
Make good catalysts
What are the group 7 elements called?
Halogens
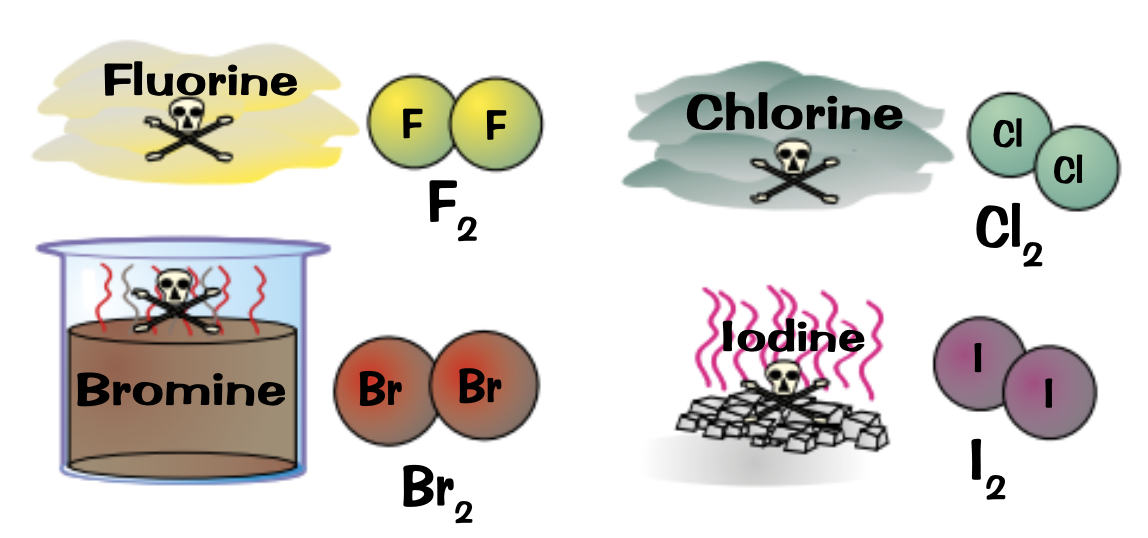
Explain what the following elements are in terms of colours and properties:
Flourine
Chlorine
Bromine
Iodine
Fluorine: very reactive, poisonous, yellow gas
Chlorine: fairly reactive, poisonous, dense green gas
Bromine: Dense, poisonous, red-brown volatile liquid
Iodine: Dark grey crystalline solid or purple vapour
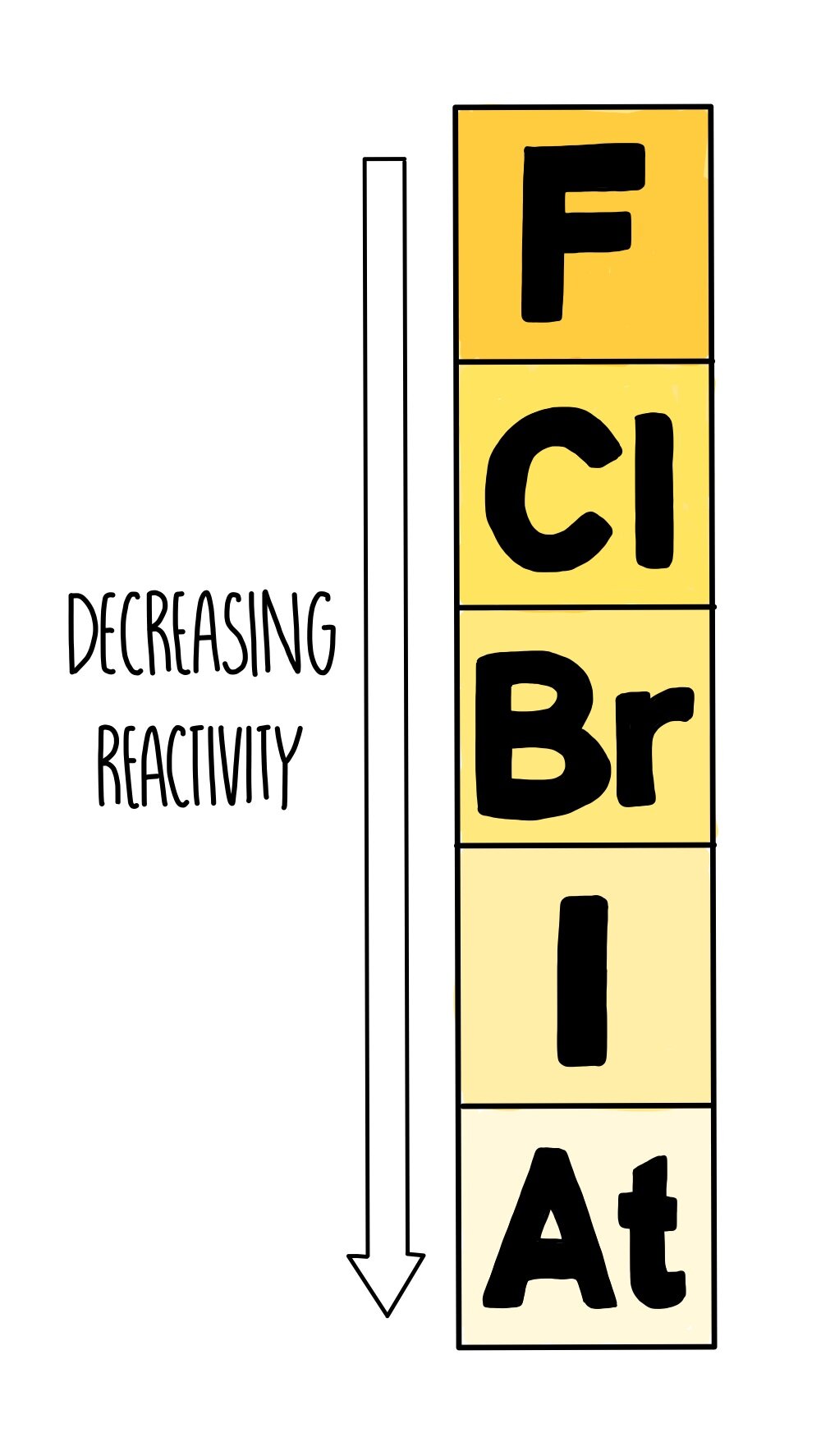
What are the trends as you go down group 7?
less reactive: harder to gain an extra electron because the outer shell is further from nucleus
High mot and bpt
higher relative atomic masses
What compounds and with what bonds do halogens form when they react with non-metals?
molecular compounds via covalent bonding
What bonds do halogens form with metals?
Ionic bonds
What ions do halogens form when bonded with metals?
1- ions called halides when bonded with metals
How do displacement reactions between halogens work?
occurs between a more reactive halogen and the salt of a less reactive one
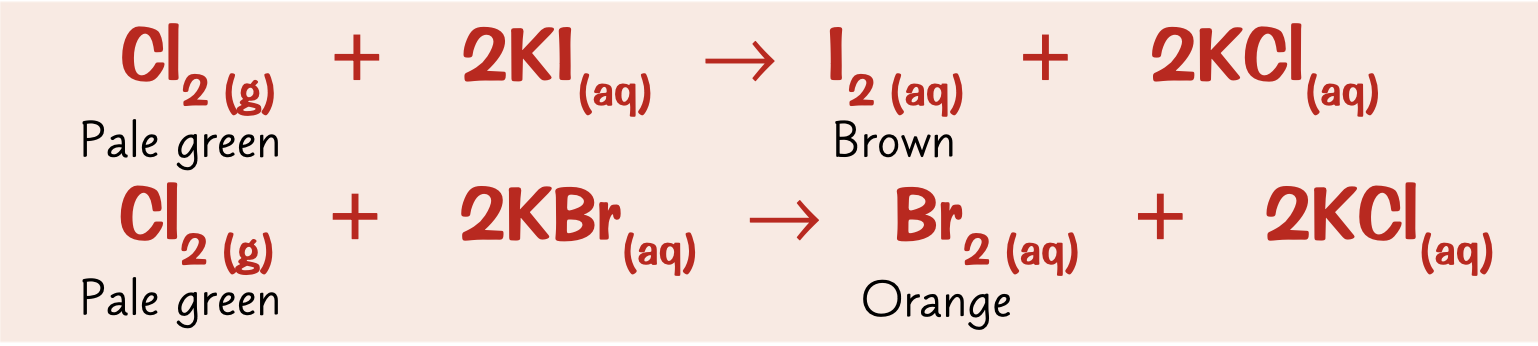
What are the group 0 elements called?
Noble gases
What are the properties of noble gases?
full outer shells
Inert (don’t react much or at all)
monatomic gases (don’t react with each other)
Colourless at room temperature
Non-flammable
What are the properties of noble gases as you go down the group?
Bpt increases
mass increases

Why does the boiling point of noble gases increase as you move down the group?
Increase in the number of of electrons in each atom leading to greater intermolecular forces between them which we need t overcome.