topic 3 - chemical changes
1/69
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
state what acids are sources of
hydrogen ions
state what alkalis are sources of
hydroxide ions
state the pH of a neutral solution
7
state the general pH of acidic solutions
lower than 7
state the general pH of alkaline solutions
higher than 7
state the effect of acids on litmus indicator
red
state the effect of acids on methyl orange indicator
red
state the effect of acids on phenolphthalein indicator
colourless
state the effect of alkalis on litmus indicator
blue
state the effect of alkalis on methyl orange indicator
yellow
state the effect of alkalis on phenolphthalein indicator
pink
state what effect the concentration of hydrogen ions has on pH
increasing concentration of hydrogen ions decreases pH
state what effect the concentration of hydroxide ions has on pH
increasing concentration of hydroxide ions increases pH
state what effect increasing the concentration of hydrogen ions by factors of 10 has on pH
pH will decrease by 1
explain the method of how to investigate the change in pH of adding calcium hydroxide to hydrochloric acid
use a volumetric pipette to measure a fixed volume of dilute hydrochloric acid into a conical flask
add 1 spatula of calcium hydroxide into the flask and swirl
when the base has reacted, record the pH of the solution using a pH meter
repeat for different spatula amounts of calcium hydroxide but the same volume of hydrochloric acid
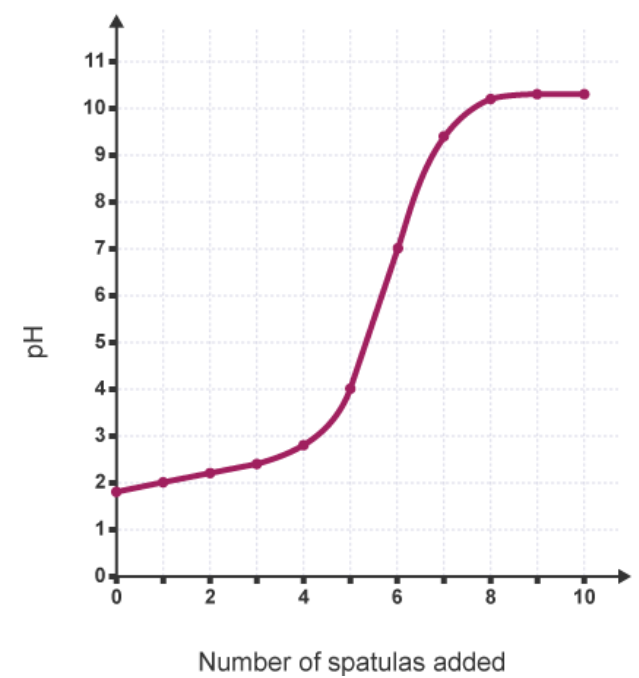
analyse the expected results from the experiment investigating the change in pH of adding calcium hydroxide to hydrochloric acid
the graph indicates a sudden change in pH which corresponds to the vertical section of the graph
this indicates that as the amount of solid base increases
the higher the pH is
therefore the base is neutralising the acid
explain what the term dilute means
dilute solutions contain a small amount of solute
in a large volume of solution
explain what the term concentrated means
concentrated solutions contain a large amount of solute
in a small volume of solution
explain what the term strong acid means
strong acids dissociate completely in water
to produce the maximum number of hydrogen ions
explain what the term weak acid means
weak acids don't fully dissociate in water
to only produce some hydrogen ions
state what a base is
a substance that only reacts with an acid
to form a salt and water only
state what alkalis are
soluble bases
state the general reaction of metals and acids
metal + acid → metal salt + hydrogen
state the general reaction of metal oxides and acids
metal oxide + acid → metal salt + water
state the general reaction of metal hydroxides and acids
metal hydroxide + acid → metal salt + water
state the general reaction of metal carbonates and acids
metal carbonate + acid → metal salt + water + carbon dioxide
describe the chemical test for hydrogen
place a lighted splint into a test tube containing the gas
if the gas is hydrogen, a squeaky pop will be produced
describe the chemical test for carbon dioxide
bubble the unknown gas through limewater
if a white precipitate is produced, the gas is carbon dioxide
state what a neutralisation reaction is
a reaction between
an acid and a base
state what an acid-alkali neutralisation is
a reaction in which hydrogen ions from the acid
react with hydroxide ions from the alkali
to form water
explain why, if soluble salts are prepared from an acid and an insoluble reactant, excess reactant is added
to ensure all of the acid has reacted
with the insoluble reactant
explain why, if soluble salts are prepared from an acid and an insoluble reactant, the excess reactant is removed
to yield a solution of only salt and water
explain why, if soluble salts are prepared from an acid and an insoluble reactant, the solution remaining is only salt and water
as all the acid has reacted
and the excess insoluble reactant has been removed
leaving only salt and water
due to a neutralisation reaction occurring
explain why, if soluble salts are prepared from an acid and a soluble reactant, a titration must be used
both the acid and reactant are soluble
so if one is in excess
it cannot easily be removed
meaning you need exact volumes of reactants
which can be done using titration
explain why, if soluble salts are prepared from an acid and a soluble reactant, the acid and soluble reactant are then mixed in correct proportions
so that the solution remaining is only salt and water
explain why, if soluble salts are prepared from an acid and a soluble reactant, the solution remaining is only salt and water
as a neutralisation reaction has occurred
leaving only salt and water
state the method of how to investigate the preparation of copper sulfate crystals from copper oxide
heat 50cm³ of dilute sulfuric acid in a beaker and warm gently with a bunsen burner
add the copper oxide slowly to the dilute acid until the copper oxide is in excess
filter the mixture into an evaporating basin to remove the excess base
gently heat the solution in a water bath to evaporate the water and saturate the solution
check the solution is saturated by dipping a cold glass rod into the solution and see if crystals form on the end
leave the filtrate in a warm place to dry and crystallise
decant the excess solution and dry the crystals
state the results of the investigation of the preparation of copper sulfate crystals from copper oxide
bright blue
regularly shaped
hydrated copper sulfate crystals
state the method of an acid-alkali titration to create a pure, dry salt
add 25cm³ of base to a conical flask using a pipette and a pipette filler
add a few drops of phenolphthalein indicator into the conical flask
place the conical flask on a white tile
setup the burette in the clamp and stand
close the tap and use the funnel to pour approximately 10cm³ of acid into the burette
place a beaker under the burette and open the tap, allowing the tip of the burette to fill with acid and displace any air bubbles
close the tap before the burette empties
use a funnel to fill the burette with acid
record the initial volume of acid to the nearest 0.05cm³
place the burette above the conical flask and carry out a rough titration, swirling the flask constantly
close the burette tap as soon as the solution decolourises
record the final volume of the acid
use the rough titre as a guide and repeat the titration until two concordant titres are obtained
use the concordant results to calculate a mean titre
pour the solution in the conical flask into an evaporating basin and heat over a bunsen burner
heat the solution until the water evaporates
leave the crystals in the basin to dry at room temperature
state which sodium salts are soluble
all
state which potassium salts are soluble
all
state which ammonium salts are soluble
all
state which nitrates are soluble
all
state which chlorides are insoluble
silver
lead
state which sulfates are insoluble
lead
barium
calcium
state which carbonates are soluble
sodium
potassium
ammonium
state the method to prepare a pure, dry insoluble salt
measure out 25cm³ of one soluble salt into a beaker
measure out 25cm³ of another soluble salt into the beaker
add water to the beaker and stir with a glass rod
filter to remove the precipitate from the mixture
wash the filtrate with distilled water
leave in an oven to dry
state what electrolytes are in molten state
ionic compounds
state what electrolytes are when dissolved in water
ionic compounds
state what electrolysis is
a process in which
electrical energy from a direct current supply
decomposes electrolytes
explain the movement of cations during electrolysis
positively charged cations migrate
to the negatively charged cathode
explain the movement of anions during electrolysis
negatively charged anions migrate
to the positively charged anode
explain the formation of copper chloride solution using electrolysis
copper is below hydrogen in the reactivity series
so copper cations are preferentially discharged at the cathode
chlorine is a halogen, so preferentially discharged at the anode
state what product is formed on the cathode when copper chloride is formed by electrolysis
copper metal is discharged
state what product is formed on the anode when copper chloride is formed by electrolysis
chlorine gas is released
explain the formation of sodium chloride solution using electrolysis
sodium is above hydrogen in the reactivity series
so hydrogen cations are preferentially discharged at the cathode
chlorine is a halogen, so chlorine anions are preferentially discharged at the anode
state what product is formed on the cathode when sodium chloride is formed by electrolysis
hydrogen gas is released
state what product is formed on the anode when copper chloride is formed by electrolysis
chlorine gas is released
explain the formation of sodium sulfate solution using electrolysis
sodium is above hydrogen in the reactivity series
so hydrogen cations are preferentially discharged at the cathode
hydroxide anions are preferentially discharged over sulfate anions
so oxygen is produced at the anode
state what product is formed on the cathode when sodium chloride is formed by electrolysis
hydrogen gas is released
state what product is formed on the anode when sodium chloride is formed by electrolysis
chlorine gas is released
explain the formation of acidified water solution using electrolysis
hydrogen cations are discharged at the cathode
oxygen from water molecules is preferentially discharged at the anode
explain the formation of a molten lead bromide solution using electrolysis
lead cations gain 1 electron at the cathode
to become lead atoms
bromide anions lose 1 electron at the anode
to become bromine atoms
which covalently bond
to become bromide molecules
state what oxidation is in relation to electrons
the loss of electrons
state what reduction is in relation to electrons
the gain of electrons
state the half equation occurring at the anode during electrolysis
oxidation
4OH-(aq) → O2 (g) + 4e- + 2H2O (l)
state the half equation occurring at the cathode during electrolysis
reduction
H2O → H+ + OH-
state which electrode oxidation occurs at
anode
state which electrode reduction occurs at
cathode
explain what product is formed at the anode during the electrolysis of copper sulfate solution
oxygen gas (O2)
as sulfate is being oxidised
causing it to lose electrons
and form oxygen gas