VTNE Review: Dentistry
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
apical
direction toward the root
attrition
wearing of the teeth from mastication or teeth rubbing together
buccal
direction toward the cheek
calculus
calcified plaque which hardens on the tooth and sometimes the crown
cementum
hard connective tissue covering the tooth root and sometimes the crown
crown
portion of the root that sits above the gum line and is covered in enamel
dentin
the bulk of the tooth; hard connective tissue made mostly of calcium and collagen
enamel
the white hard outer layer of the crown (made mostly of calcium)
endodontics
treatment involving the pulp cavity
floating
smoothing a horses teeth with a file to rid of sharp edges
gingiva
mucosa/gums surrounding the teeth
halitosis
bad breath
lingual
direction toward the tongue
malocclusion
abnormal position of the teeth
occlusal
the chewing surface of the tooth, which meets the tooth surface on the opposite jaw
periodontal ligament
collagen fiber that attaches tooth to the bone and holds the tooth in place
periodontium
supportive tissues around the tooth, including bone of alveolus, periodontal ligament, cementum, and gingiva
plaque
a film which accumulates on the tooth made of food, bacteria, cells, and mucin
pulp
the soft part inside the tooth made of nerves, vessels, odontoblasts, connective tissues, and lymphatics
ranula
a salivary cyst under the tongue
recession
apical gingival movement away from the tooth crown
root
lower part of the tooth that is in the alveolus
stomatitis
inflammation of the soft tissues in the mouth
sulcus
pocket under the gingiva; normal is 0-3 mm, greater than this suggests periodontal disease
hypsodont teeth
high crowned teeth
seen in horses, cattle, deer (radicular continuously erupting but not growing)
in rodents, lagomorphs, chinchillas (aradicular: continuously growing)
brachydont teeth
low crowned teeth
seen in dogs, cats, and humans
dog dental formula
2 (I 3/3 C 1/1 P 4/4 M 2/3) = 42
cat dental formula
2 (I 3/3 C 1/1 P 3/2 M 1/1) = 30
cow/sheep/goat dental formula
2 (I 0/3 C 0/1 P 3/3 M 3/3) = 32
horse dental formula
1 (I 3/3 C 0-1/0-1 P 3-4/4 M 3/3) = 36-42
pig dental formula
2 (I 3/3 C 1/1 P 4/4 M 3/3) = 44
lagomorph dental formula
2 (I 2/1 C 0/0 P 3/2 M 3/3) = 28
rat/mouse dental formula
2 (I 1/1 C 0/0 P 0/0 M 3/3) = 16
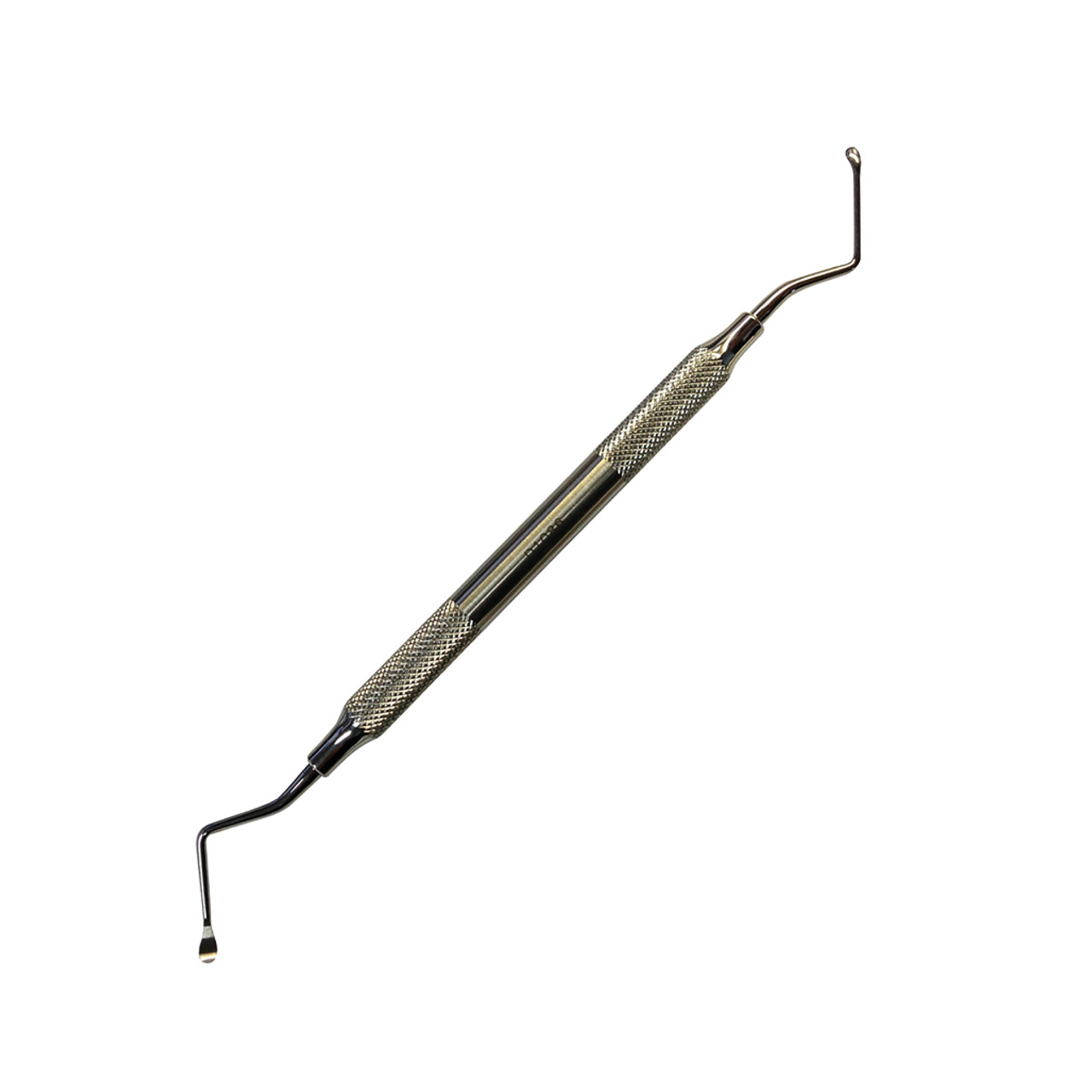

curette
used for subgingival removal of calculus and root planing; can also be used supragingivally; has a rounded back and tip
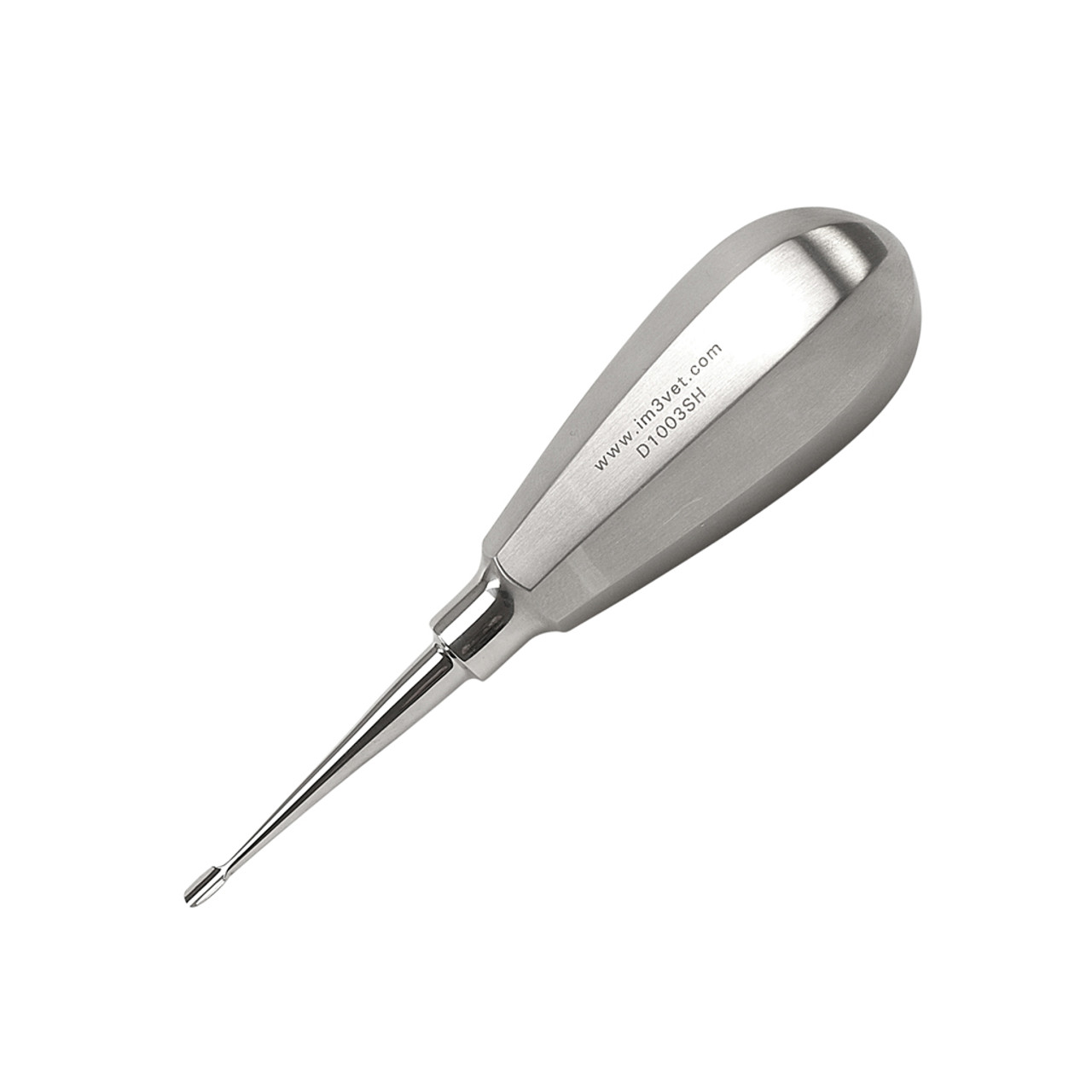

dental elevator
used for breaking down the periodontal ligament with pressure and leverage
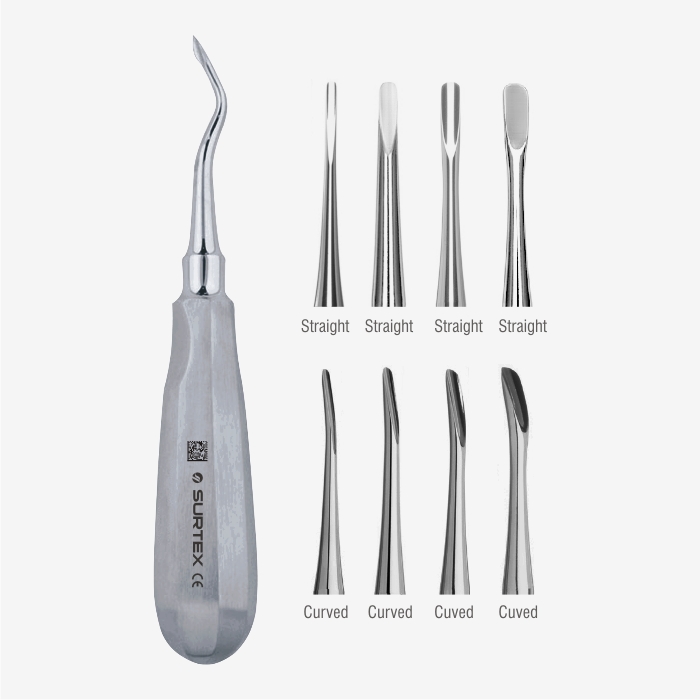
luxator
used for breaking down/cutting the periodontal ligament; not used for leverage
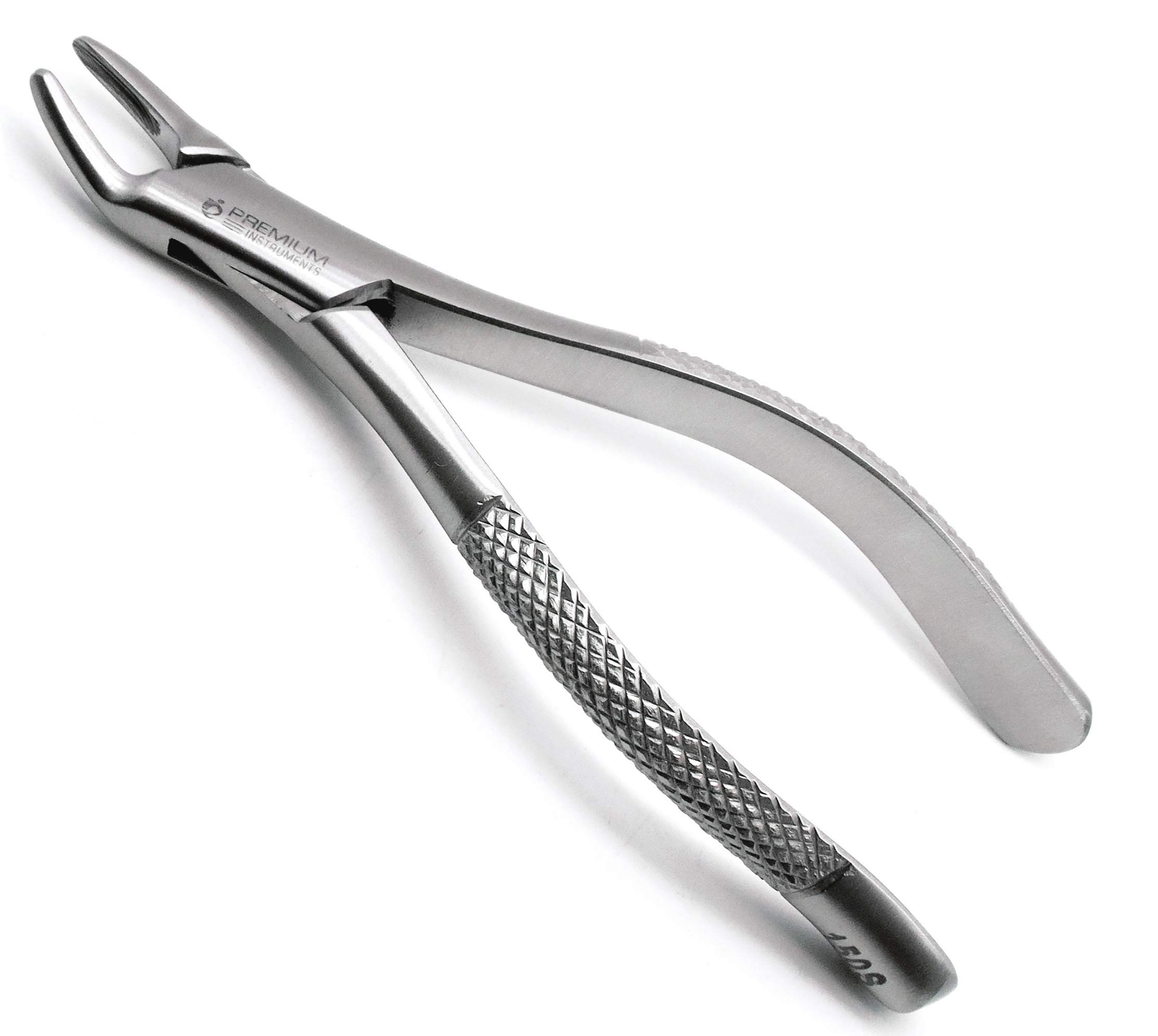
extraction forceps
used to extract the tooth after the periodontal ligament has been broke down
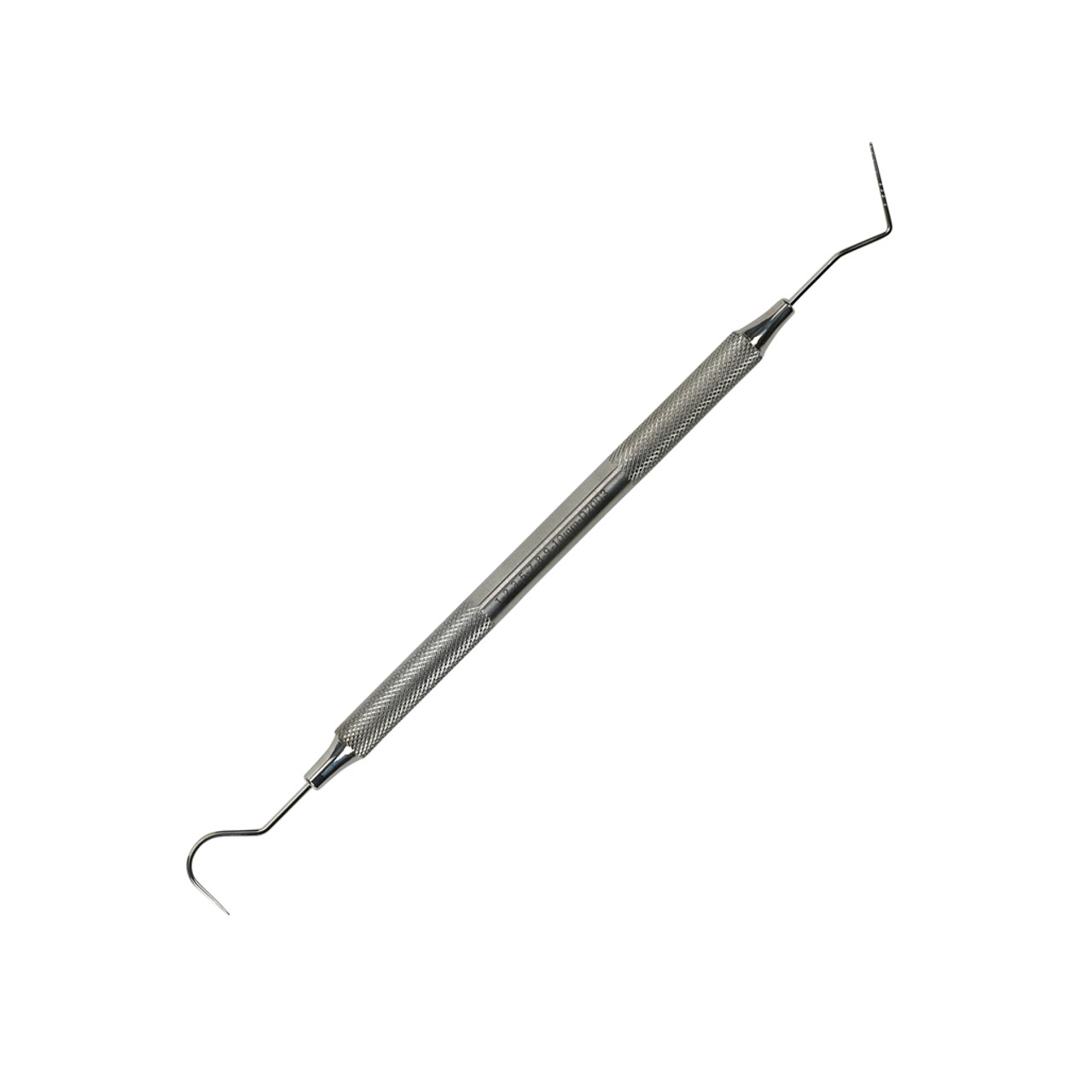

probe
has a blunted tip; inserted into gingival sulcus to measure pocket depth and evaluate mobility
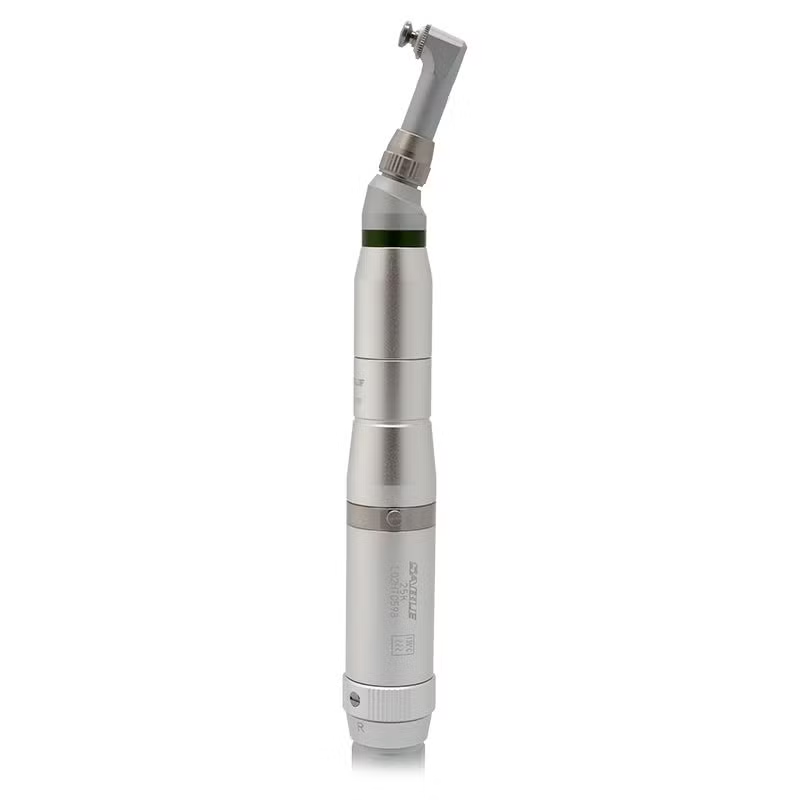
polisher
removes plaque and smoothes the scaled tooth surface
used with prophy paste and done on slow speed (not faster than 1000 rpm or may cause thermal damage)
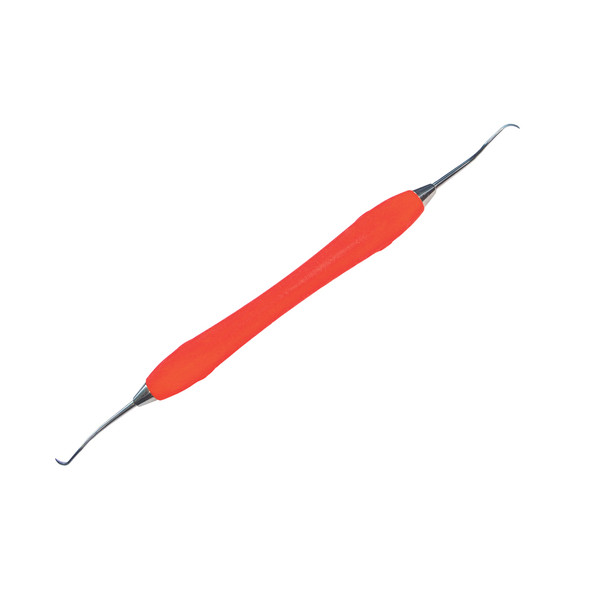

scaler
used for supra-gingival removal of calculus (not sub-gingival due to sharp tip)