Anatomy Lec 3
1/66
Earn XP
Description and Tags
USC DDS Tri 3 SUM-2025
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
Cranial neural Crest Cells:
What are they, origination, migrate where
group of cells that originate from ectoderm then migrate into mesenchyme
why are neural crest cells called ectomesenchyme cells?
bc they originate in ectorderm and then go and reside in the mesenchyme
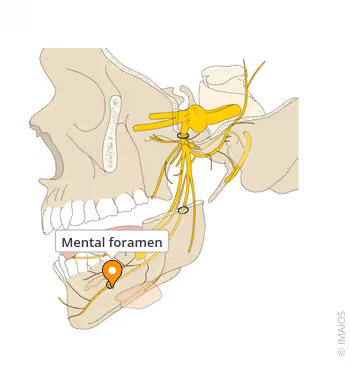
the mental foramen is always located below the ___ & _______ ________ this is important bc…
1st and second bicuspid, nerve and blood vessels exit the mental foramen
What nerve innervates the 1st pharyngeal arch?
CN V
What structures is the 1st pharyngeal arch make?
max + mand
muscles of mastication
mylohyoid
anterior belly of digastric
tensors
what does CN V innervate?
max + mand
muscles of mastication
mylohyoid
anterior belly of digastric
tensors
What nerve innervates the second pharyngeal arch
CN VII
what structures are included in the second pharyngeal arch
muscles of facial expression
staepidus + Stylohyoid
Posterior belly of digastric
what nerve innervates the third pharyngeal arch?
CN IX
What strucures are included in arch of CN IX
stylopharyngeus
4th/6th pharyngeal arch structures included
cricothyroid
levator
constrictor of pharynx
larynx muxcles
esophagus muscles
what nerves innervate 4/6 pharyngeal arch
superior laryngeal branch of Vagus nerve (X)
Recurrent Laryngeal branch of vagus nerve X
anterior 2/3 of tongue is derived from what arch
1st pharyngeal
Infraorbital Foramen
Canine Eminence
What is the fancy name for ur chin?
mental protuberance
on the mylohyoid line we will find attachment of
mylohyoid muscle
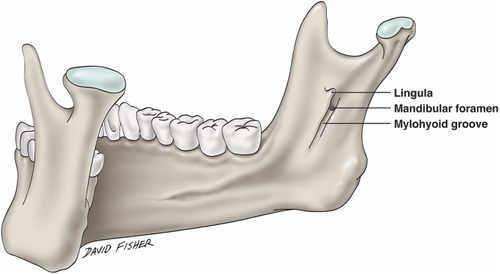
What nerve exits/enters mandibular foramen
Lingual nerve
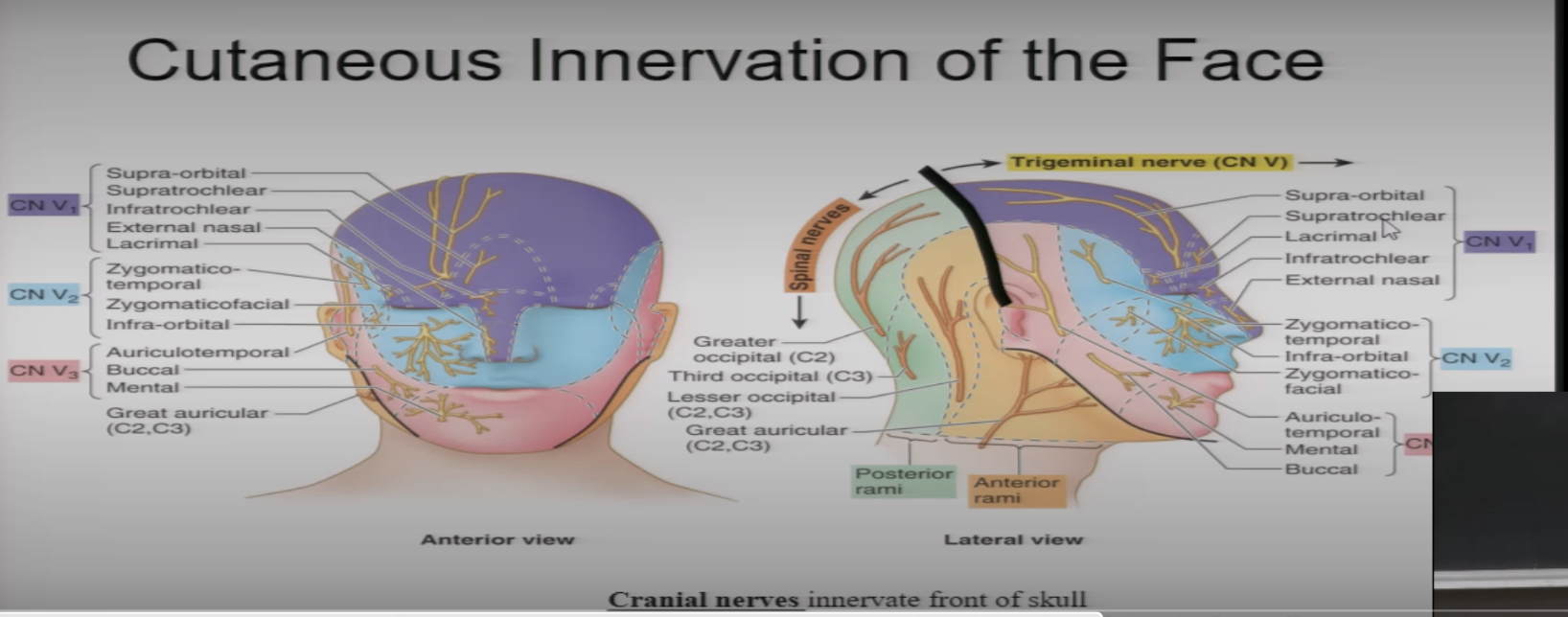
Sensory innervation of the face is by
CN V Trigem nerve
By sensory info we mean
ppicks up general info such as touch, pain, temp, and takes it to brain
V1 includes
Bridge of nose, Eyes, and up
What is another name for V1
opthalmic
V2 includes
nostrils + upper lip, + middle region of face
v2 is also called
maxillary nerve
V3 referred to as
mandibular
V3 includes
lower lip + Mandibular region
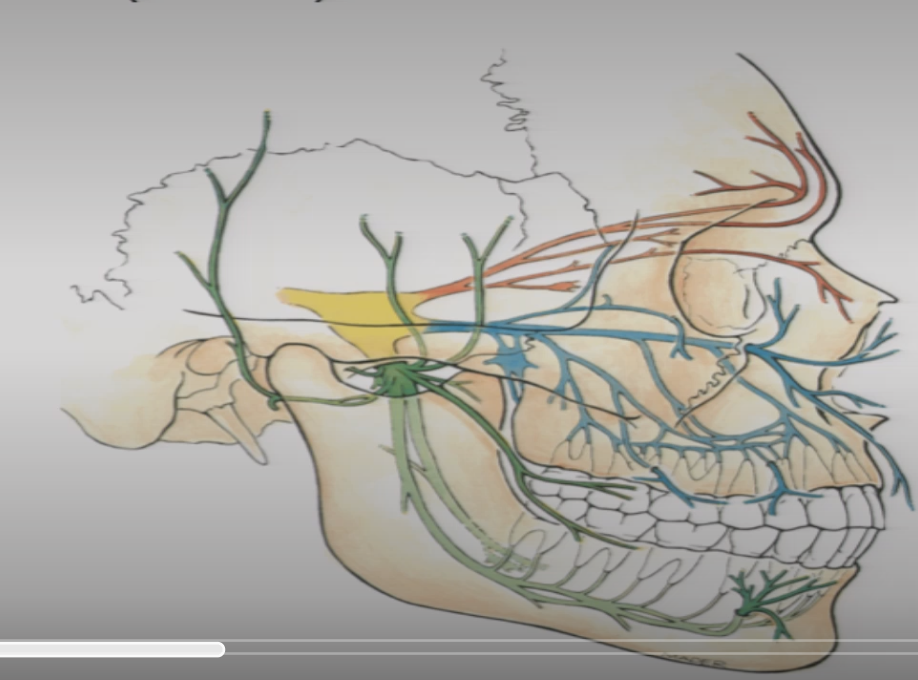
Yellow=CN V ganglia
Red=V1 opthalmic
BLue=V2 maxillary
Green=V3 mandibular
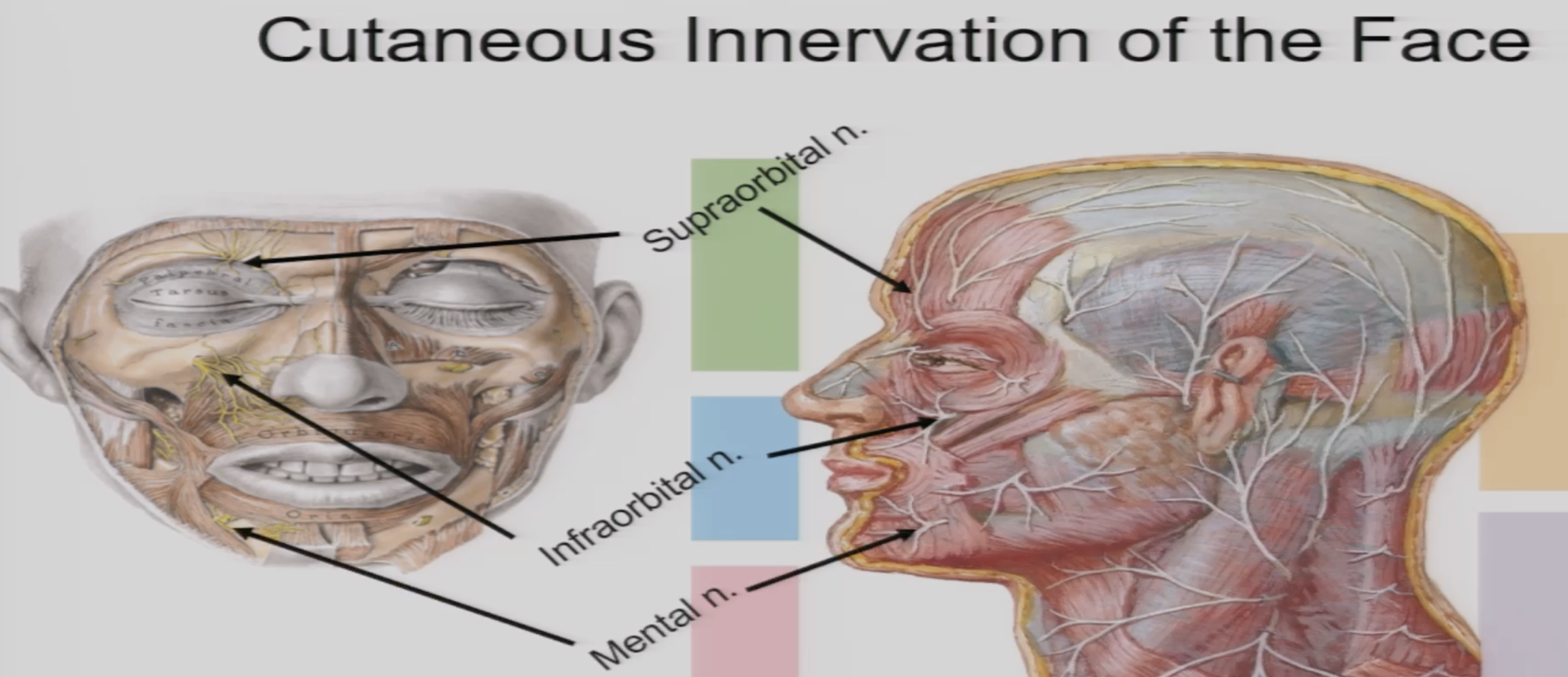
V1 exits the skull at what opening
Supraorbital Foramen/Notch
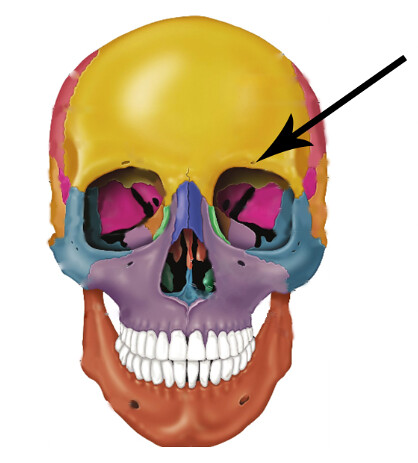
In the supraorbital Foramen what else can we find,
derived from…
Supraorbital nerve, artety, and vein
derived from frontal nerve + superior opthalmic artery & Vein
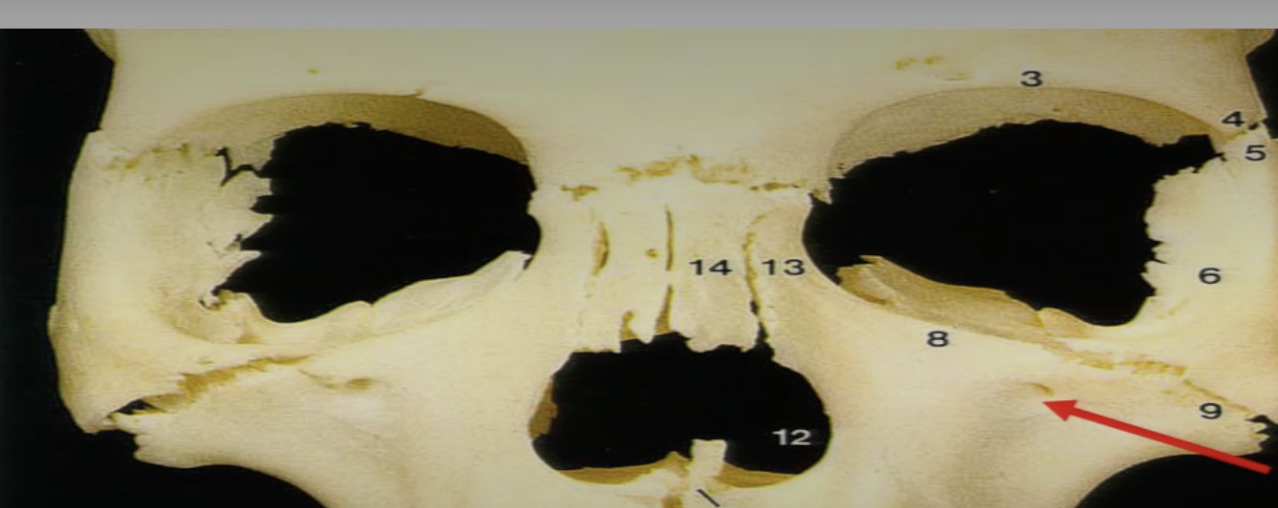
V2 exits skull from
and includes what
infraorbital foramen
infraorbital nerve, artery and vein
V3 exits skull from
and includes
derived from…
Mental Foramen
mental nerve, artery and vein (from inferior alveolar nerve)
What are the muscles of mastication, what are the associated muscles around the mouth,
and what nerve innervates all of these
Muscles of mastication:
temporalis
masseter
medial pterygoid
lateral pterygoid
Associated:
anterior belly of digastric
mylohyoid
tensor veil
tensortympani
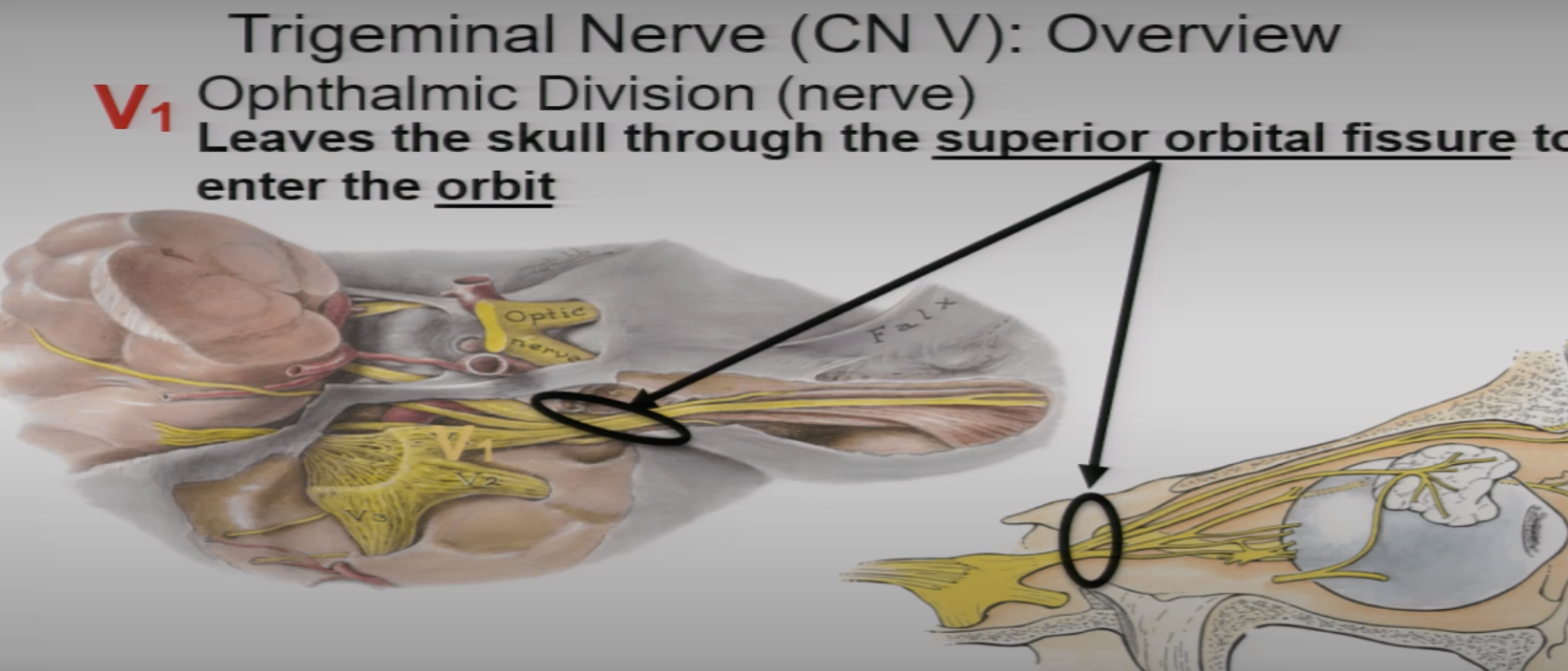
V1 leaves inner part of skull and enters the orbit from
superior orbital fissure
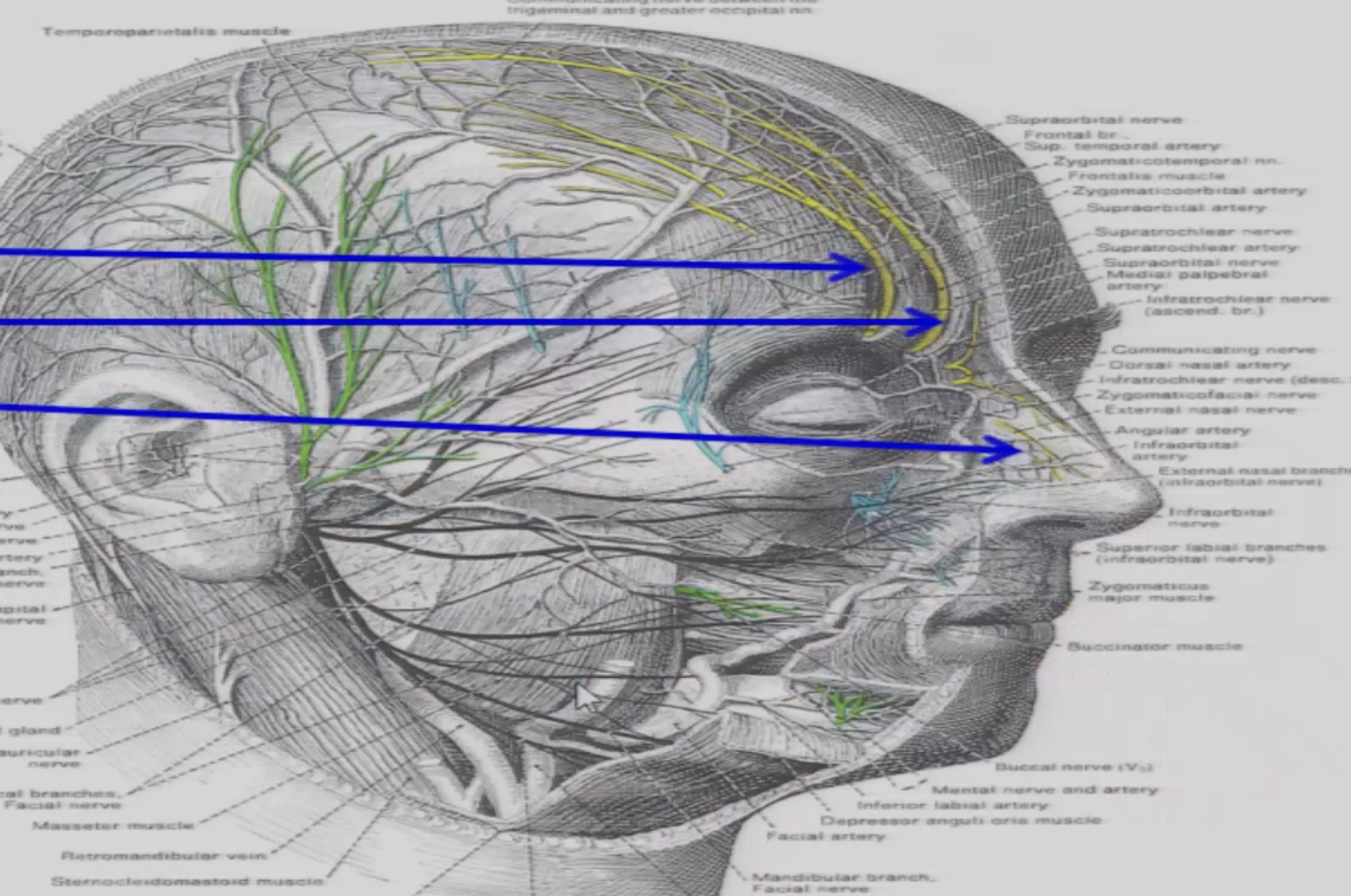
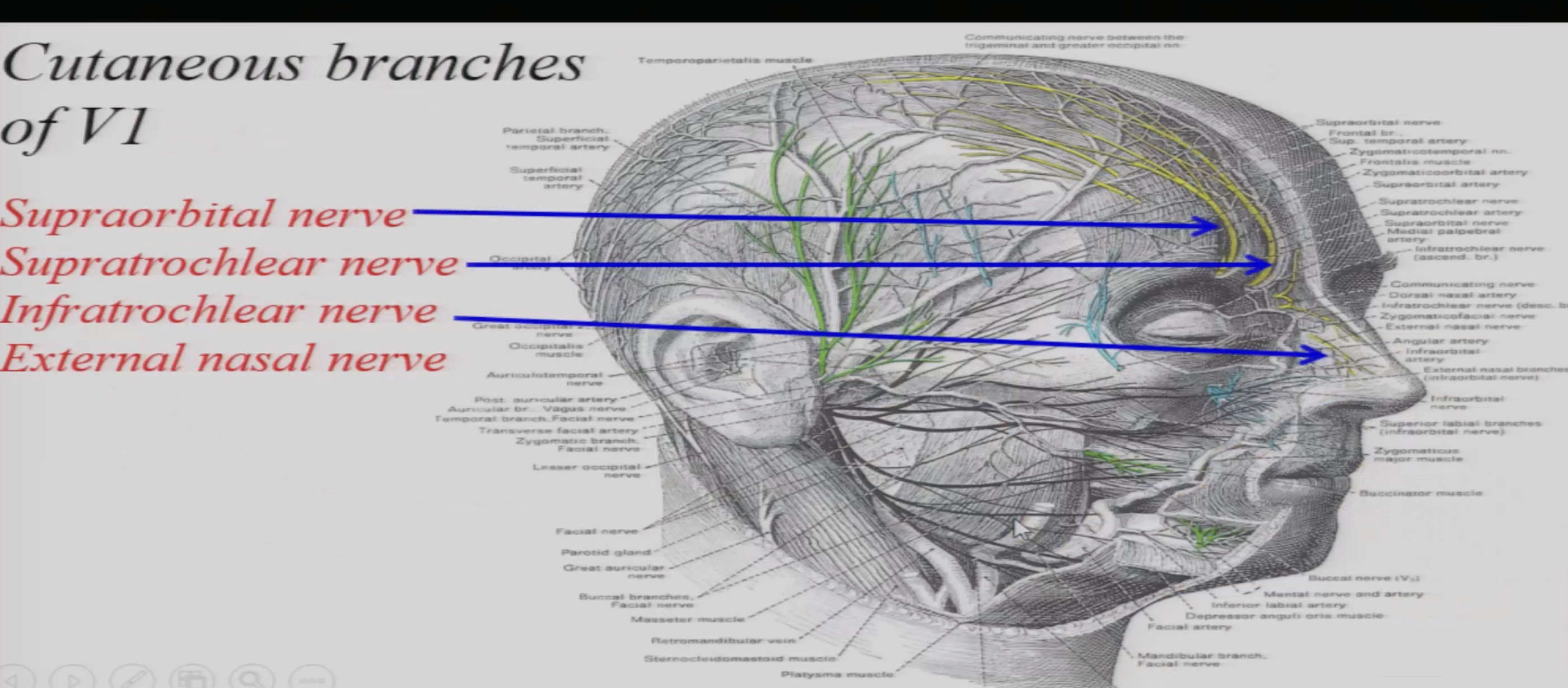
What are the cutaneous branches of V1
supraorbital n
supratrochlear n
infratrochlear n
external nasal n
V2 internally goes through the ____ ____ to enter the _________ fossa
foramen rotindum
pterygopalatine fossa
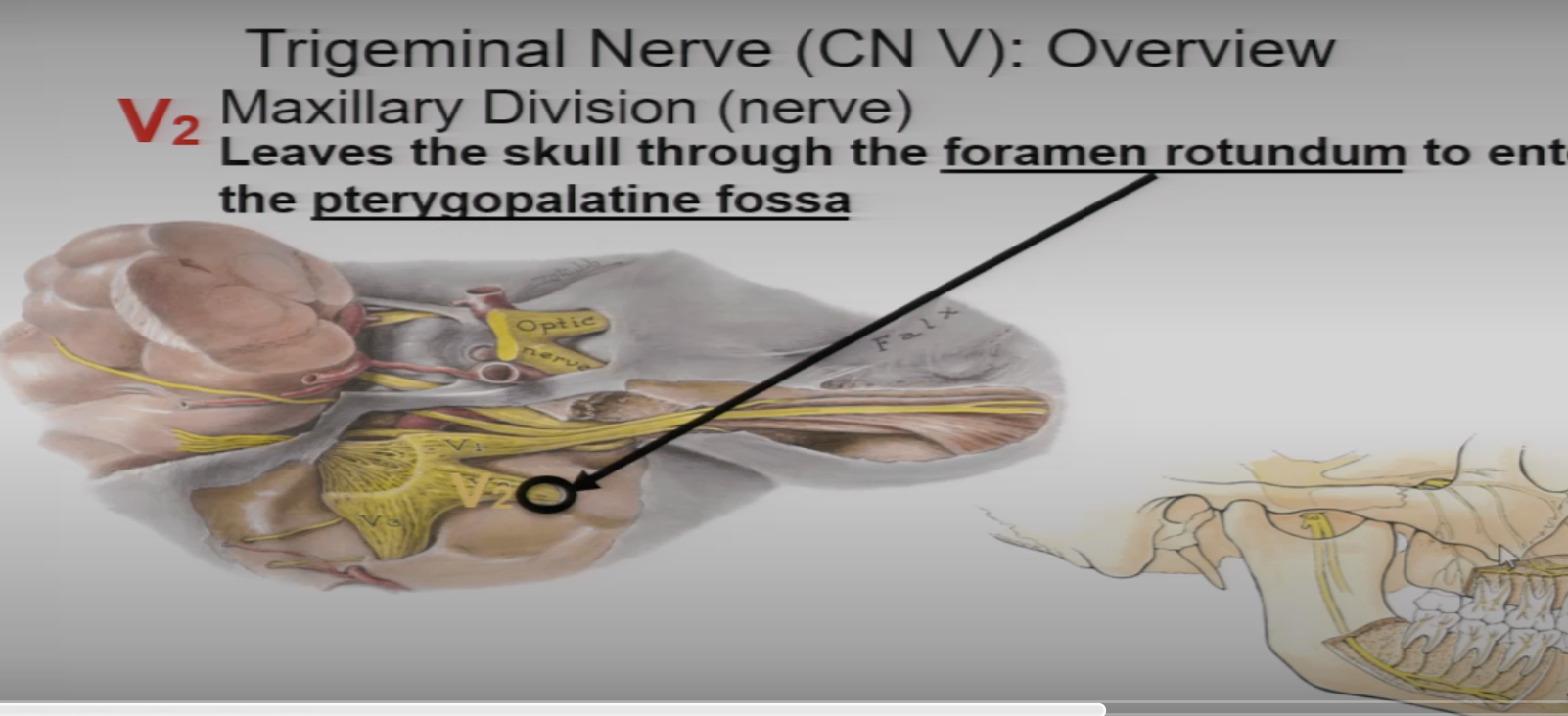
what is foramen rotundum
opening within the sphenoid bone
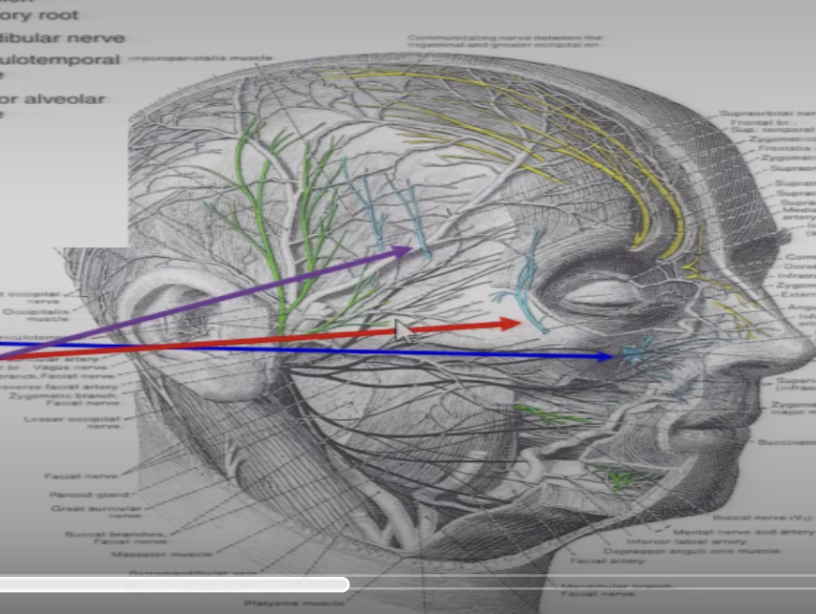
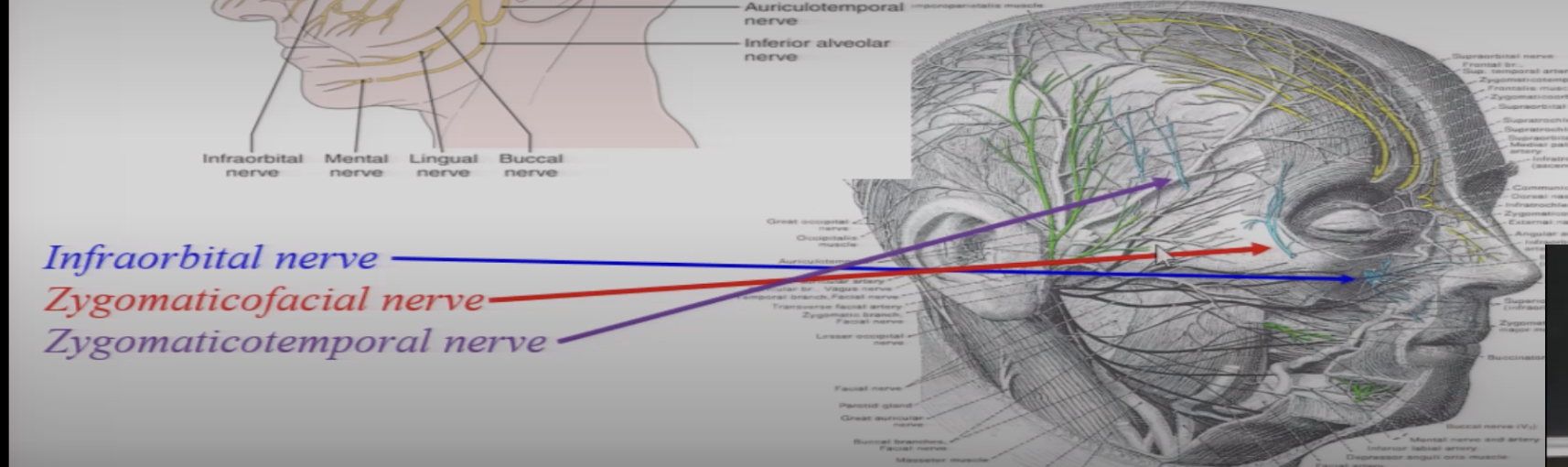
what are the terminal branches of V2
Infraoribital nerve
zygomaticofacial
zygomaticotemporal
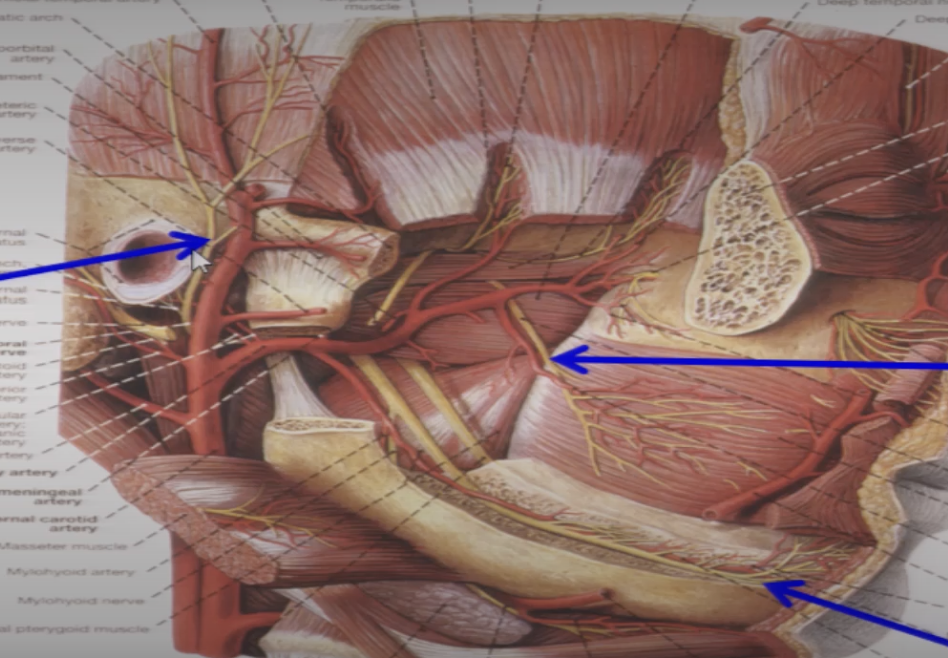
V3 exits the internal skull through the ____ ____ to enter the ____ ____
foramen ovale
infratemporal fossa
what is the foramen ovale
an opening behind the foramen rotundum
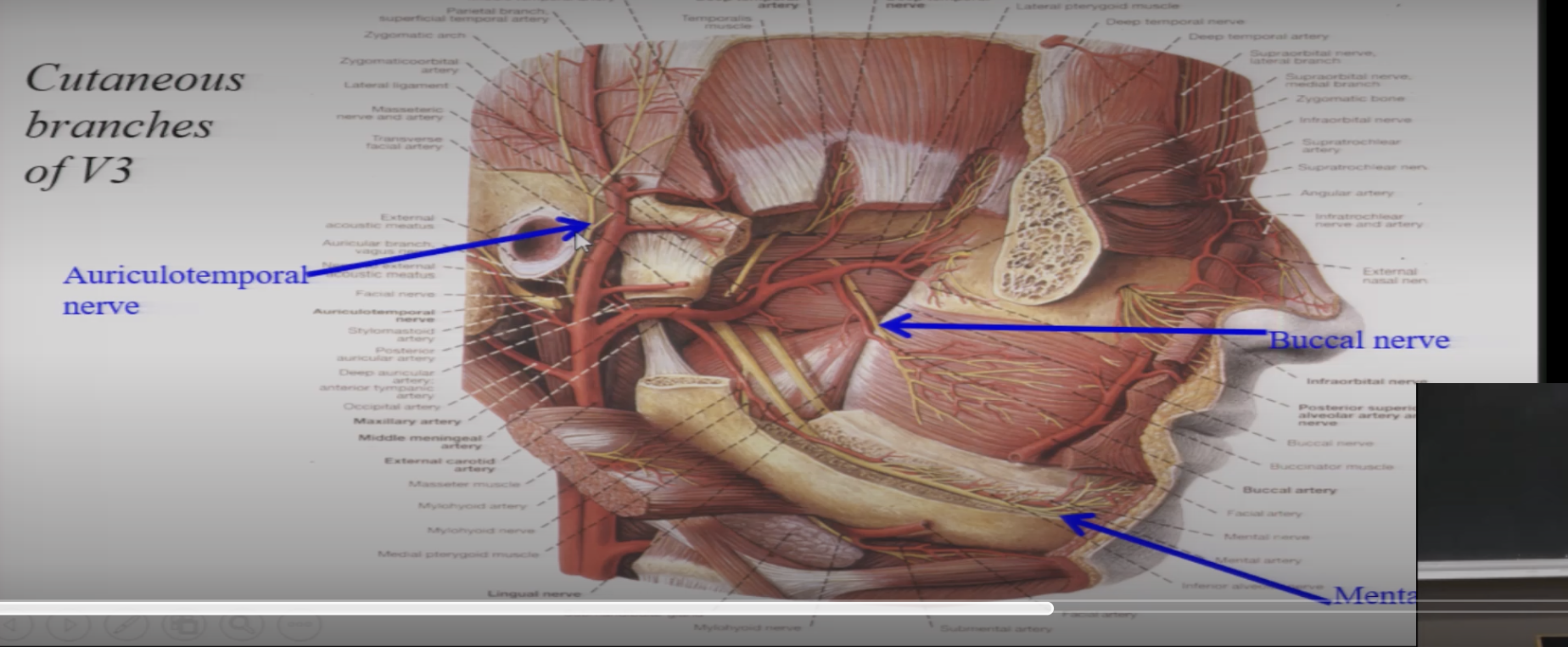
branches of V3?
Auriculotemporal nerve
Buccal n
Mental n ( branch from inf. alveolar n)
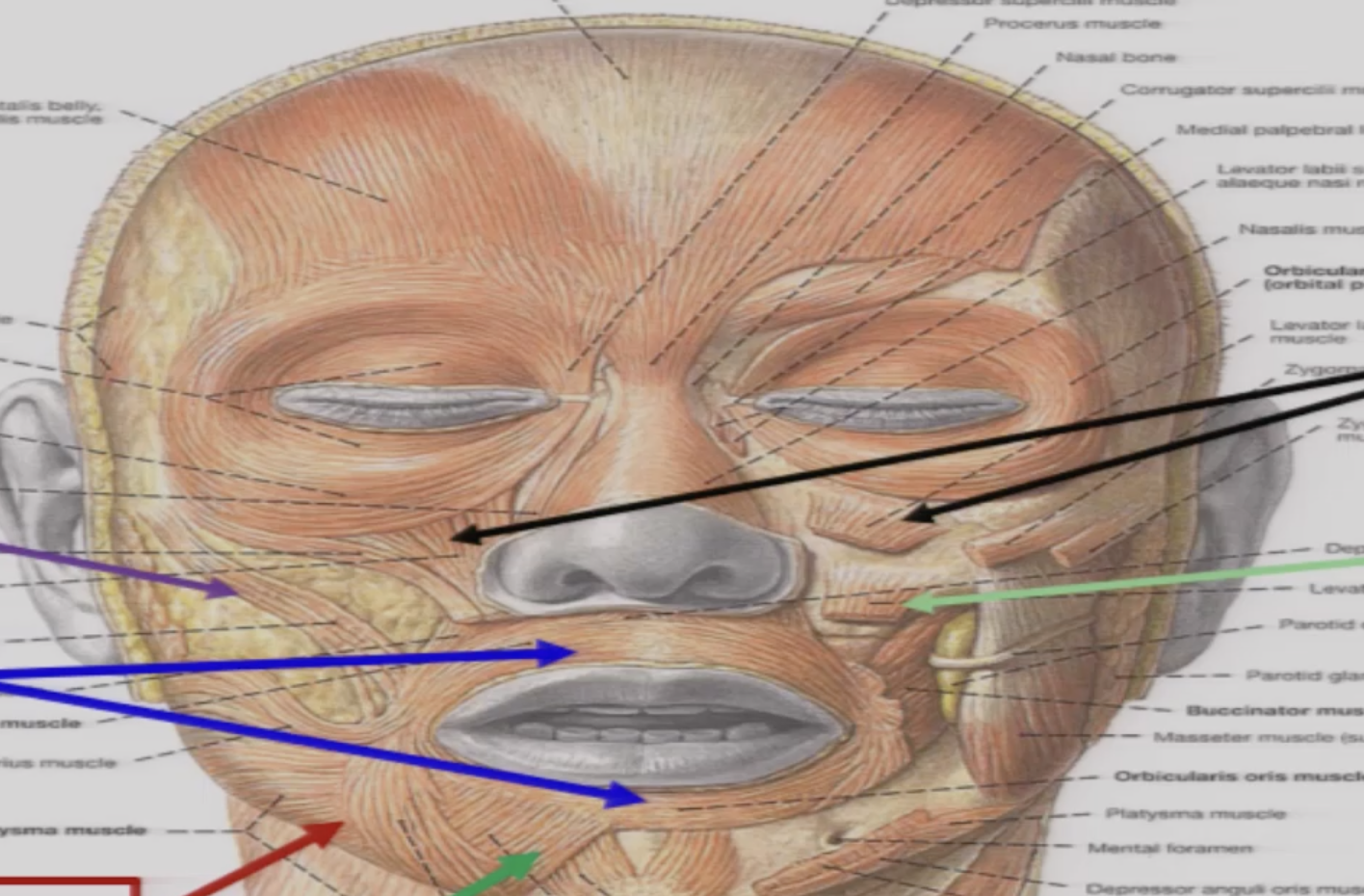
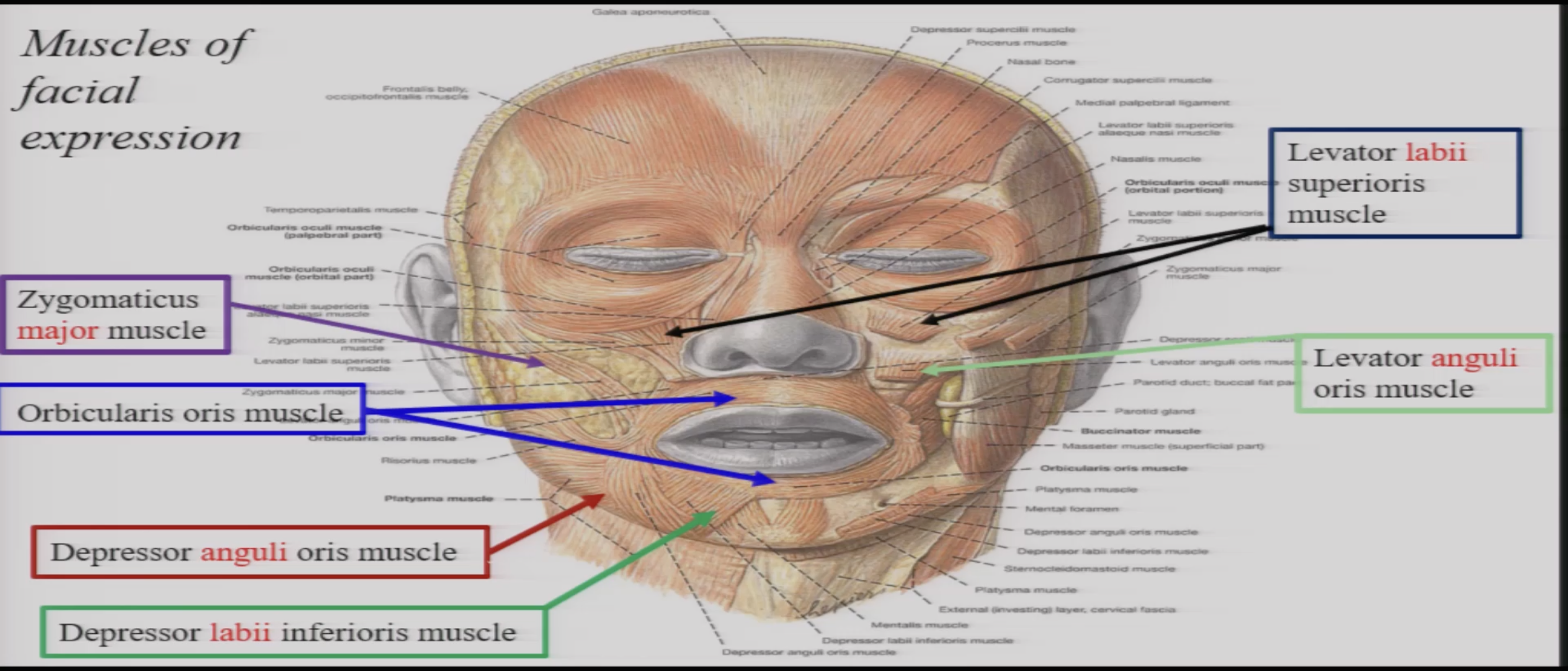
which facial muscles are responsible for elevating the lips
lavator anguli oris
zygomaticus major
levator labii superioris
what about to depress the lip
depressor anguli oris
depressor labii inferioris
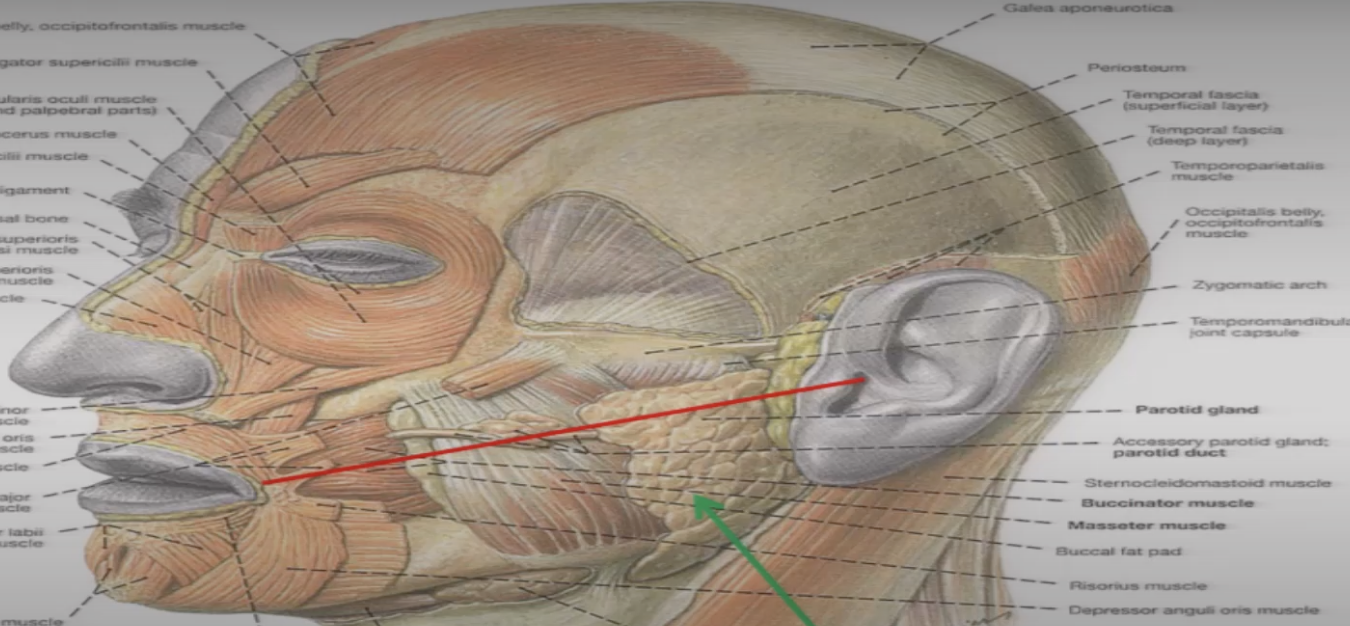
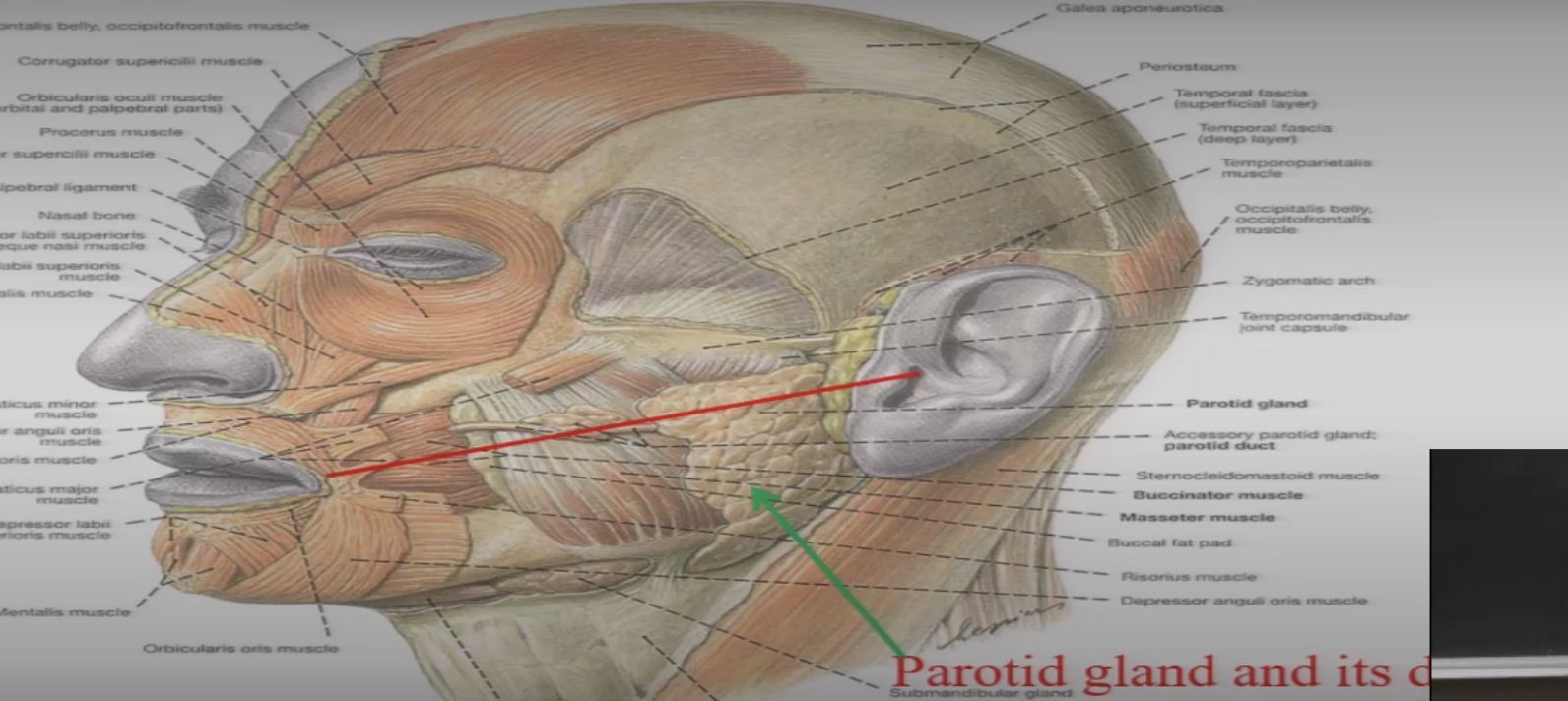
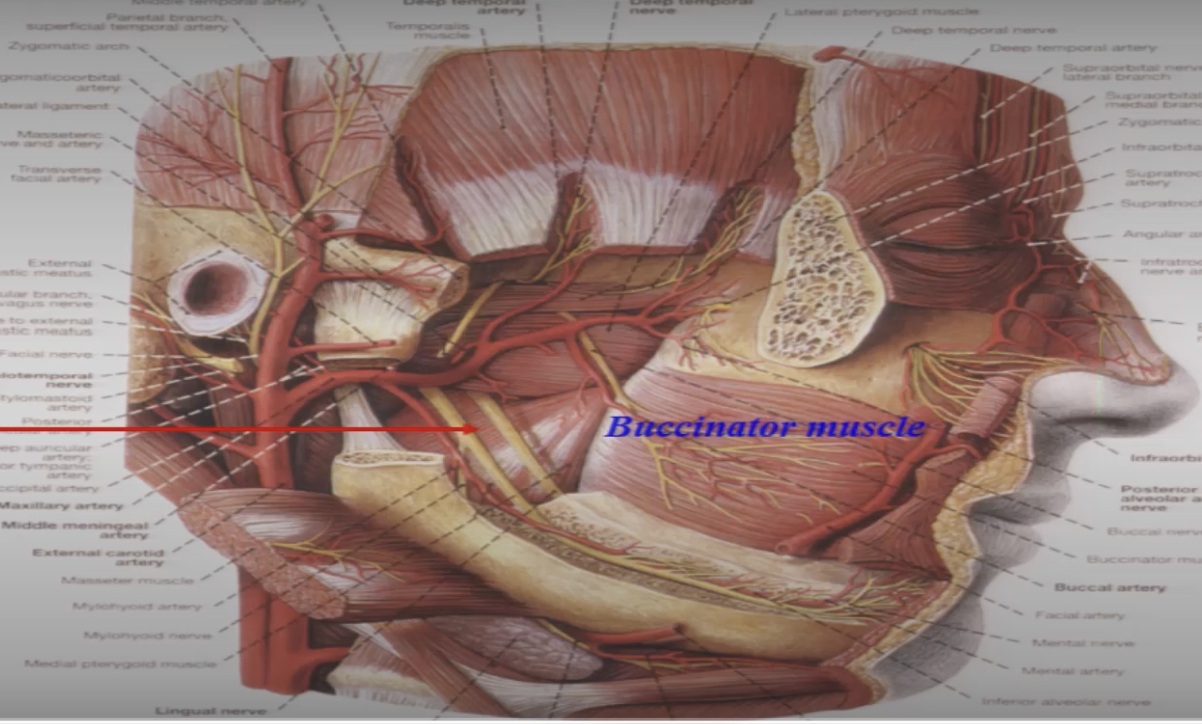
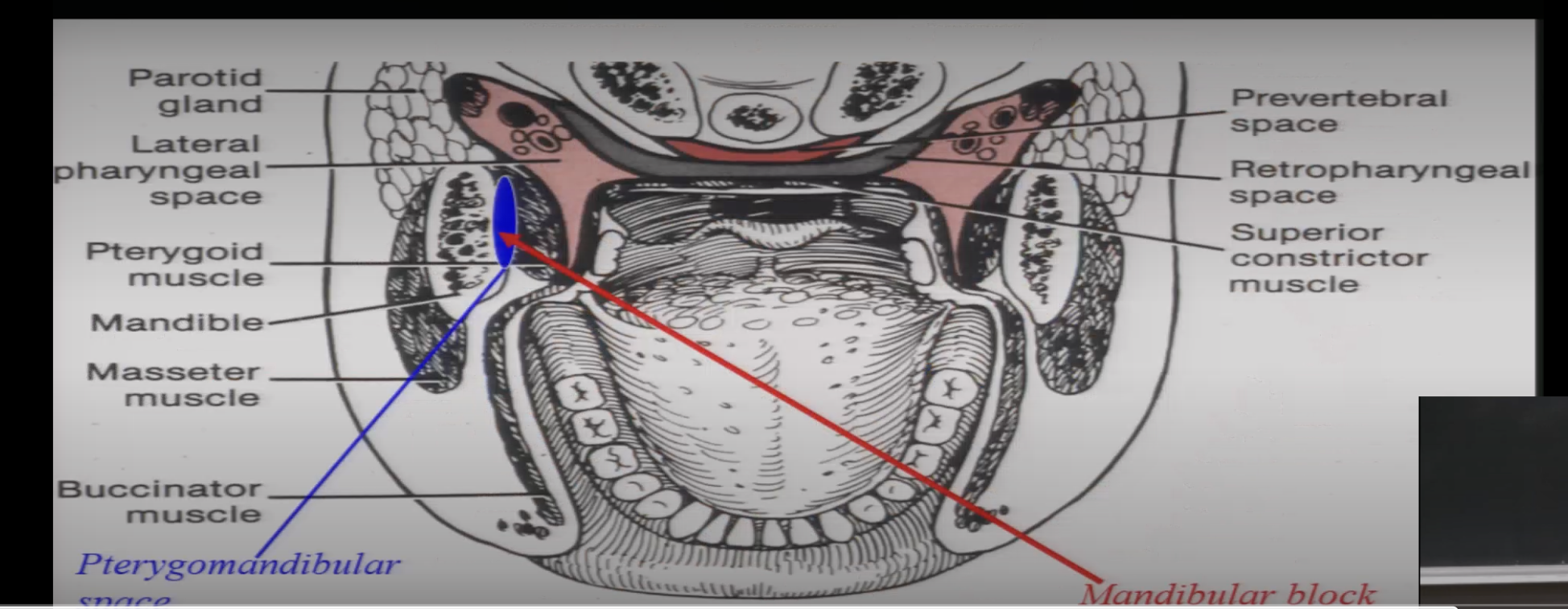
what is parotid duct and what is its path of travel from paritd gland to mouth
structure that carries saliva from parotid duct, travels sitting on top of masseter, then goes INTO buccinator to then opening into mouth opposite to upper second molar
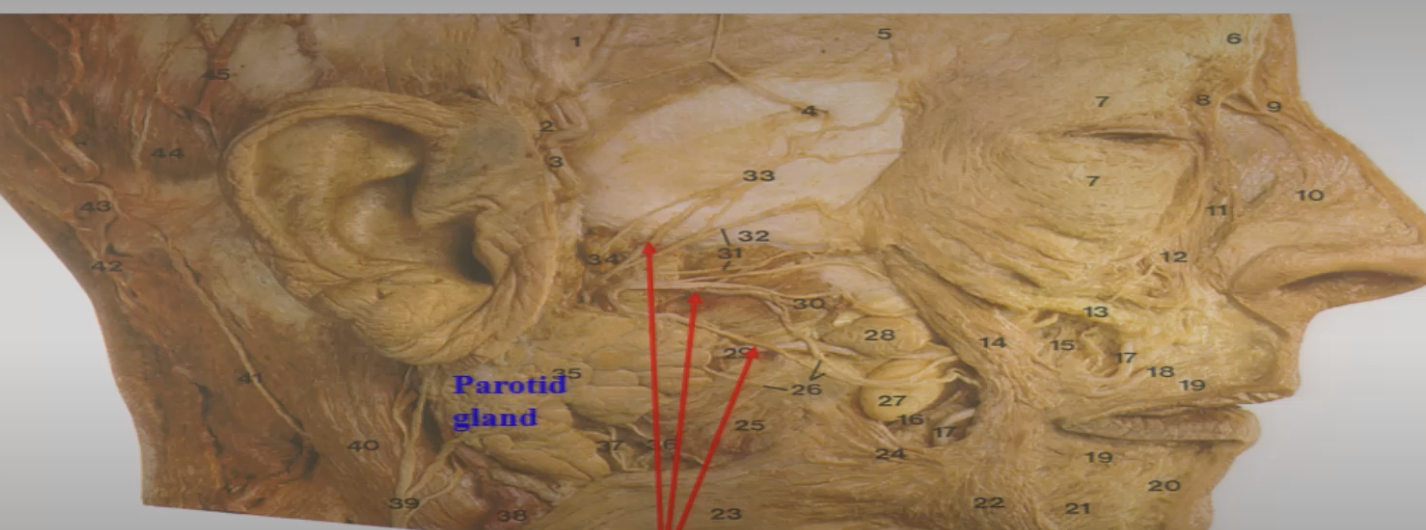
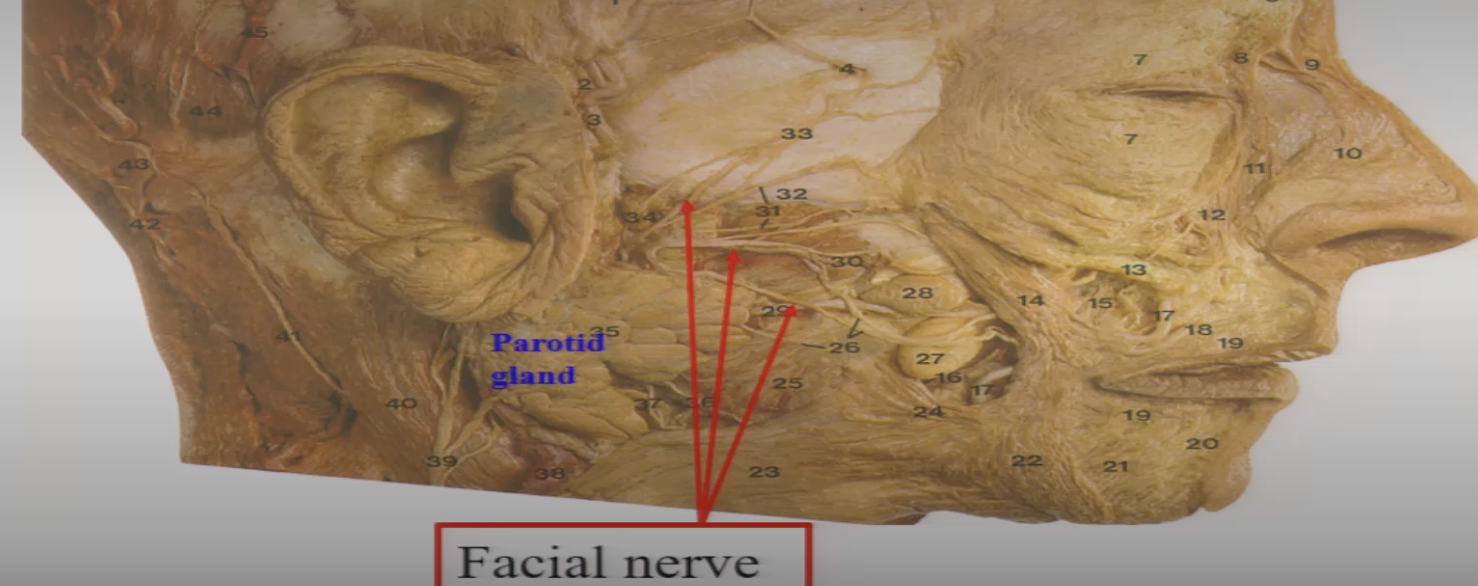
CN VII
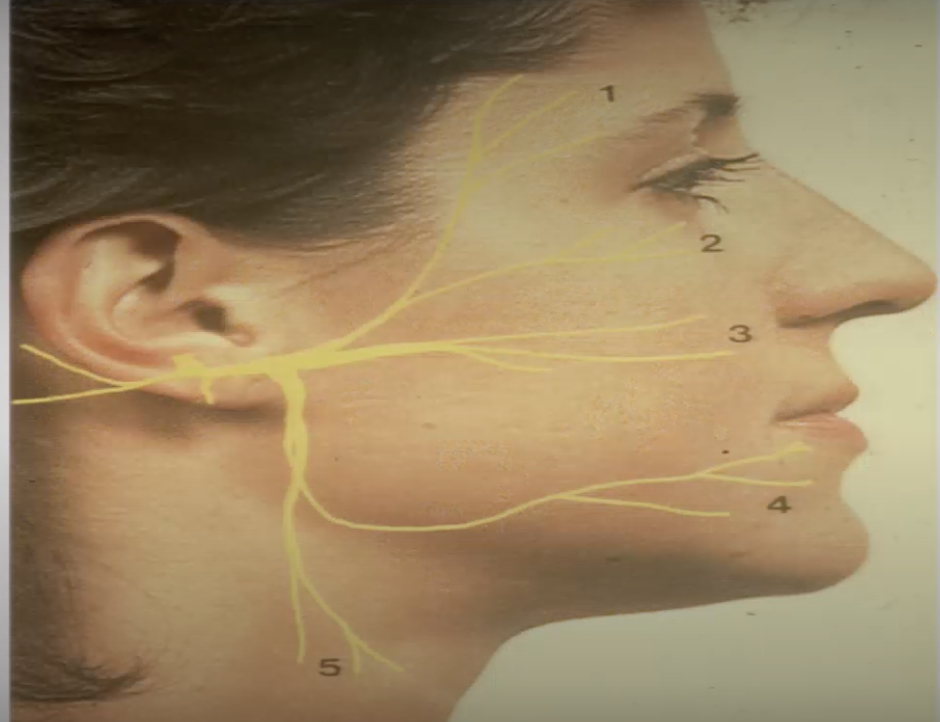
1=Temporal
2=zygomatic
3=buccal
4=marginal mand
5=cervical
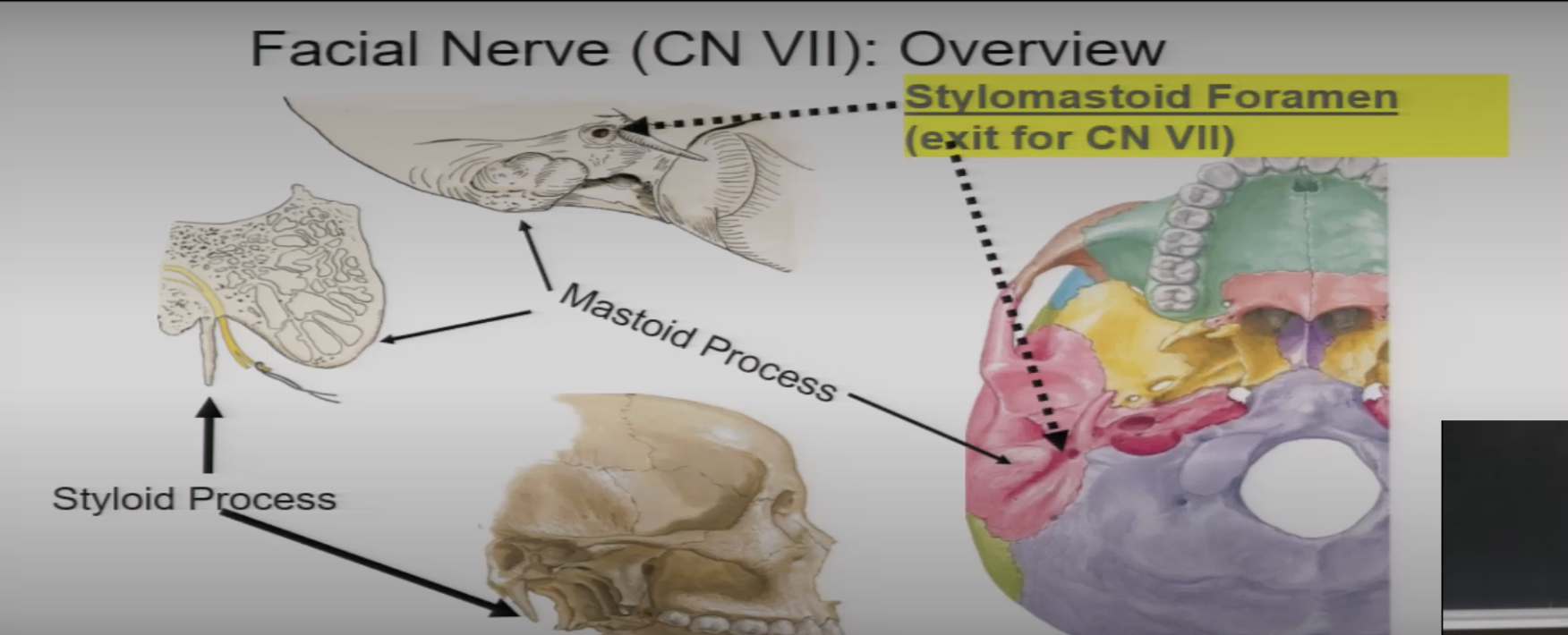
facial nerve exits from the brain and enters the ___ ___ ___ of the petrtous bone and exit through the __ ___ ___ and _____ ___
internal acoustic meatus
external acoustic meatus
stylomastoid foramen
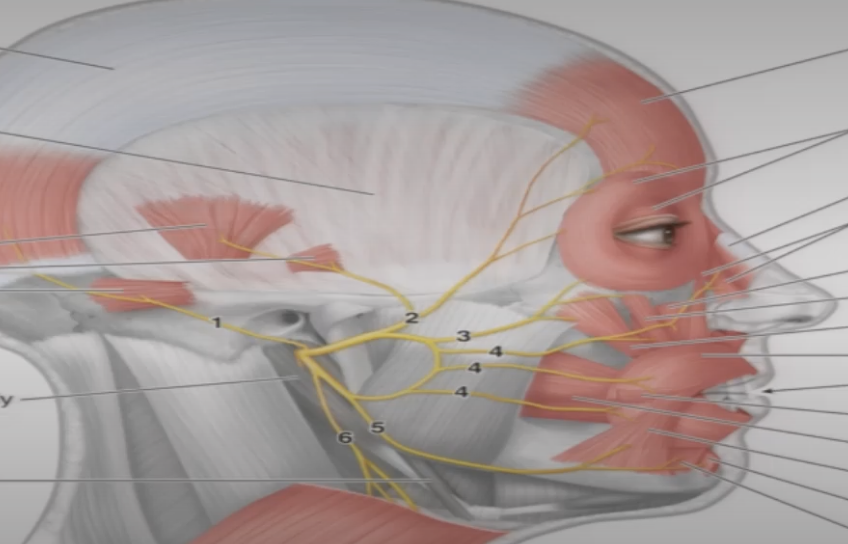
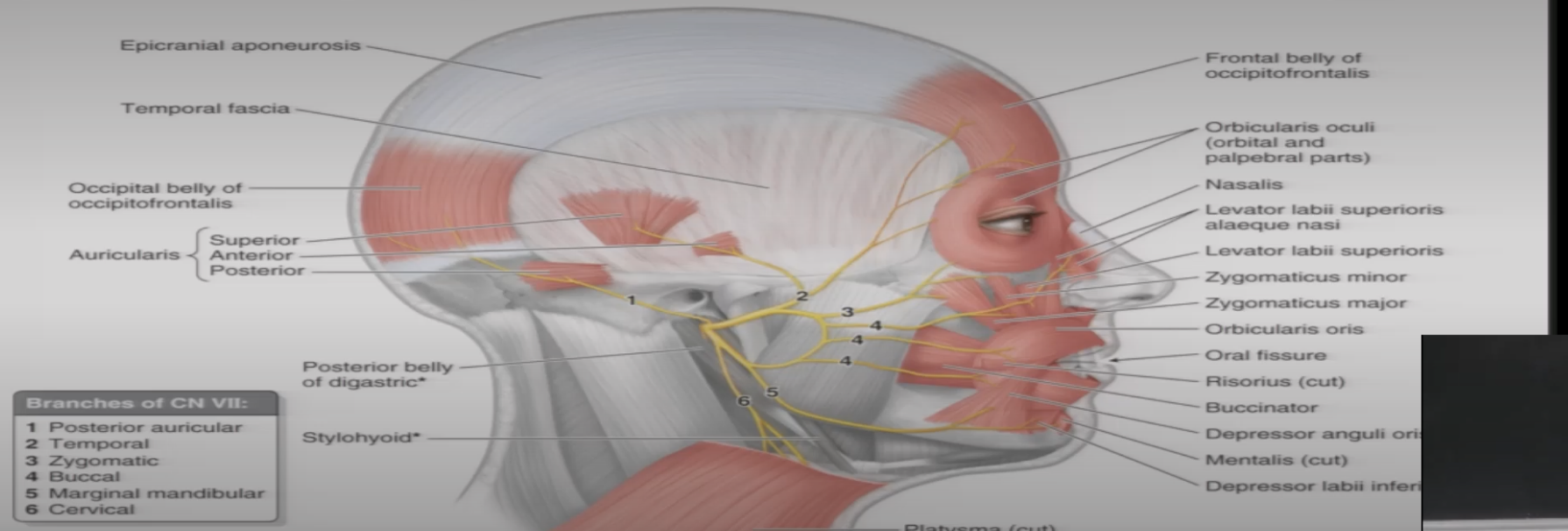
what does temporal nerve branch of CN VII innervate
Frontalis muscle
what does zygomatic nerve branch of CN VII innervate
orbicularis oculi
what does buccal nerve branch of CN VII innervate
Buccinator, orbicularis oris
what does Marginal Mand nerve branch of CN VII innervate
depressor anguli oris, depressor labii inferioris, and mentalis muscles.
what does cervical nerve branch of CN VII innervate
Platysma
Taste sensation travels along that path with an ultimate destination of
geniculate ganglion
what is that path for taste again?
anterior 2/3 of tongue→ lingual nerve→chorda tympani→facial nerve and geniculate ganglion
afferent
what about pain (SS) path
needle through ante 2/3 of tongue→goes through lingual nerve→semilunar ganglion (ganglion of trigeminal nerve) responsible for somatosensory
afferent
parasympathetic nerve fibers path
first part of cell body comes from pons (from CNS) (para pre)→travel w/ facial nerve→chorda tympani→ lingual nerve→submandibular ganglion→ para post begins providing innervation to submand and sublingual glands
efferent