Geology Final !
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
Streams
Flow along the path of least resistance from head to mouth.
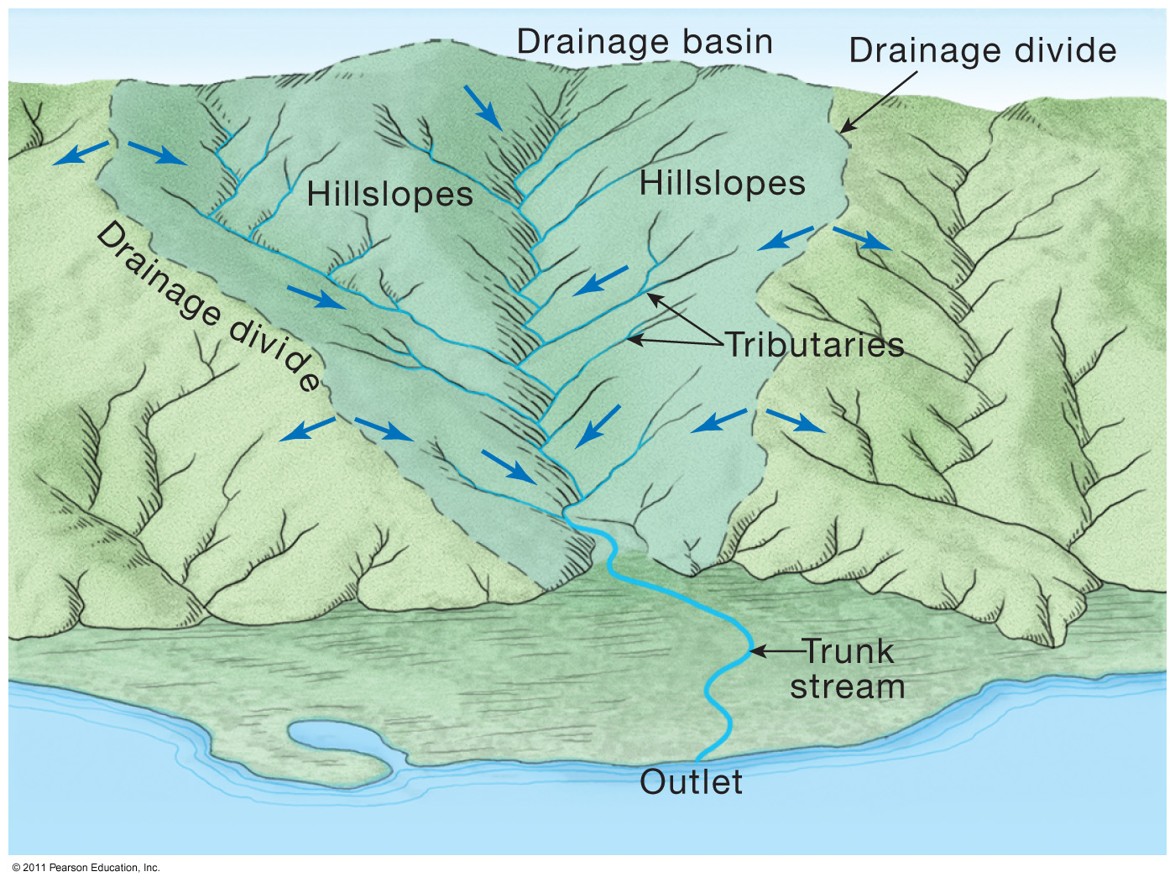
Drainage Basin/Watershed
The land area that collects water to a stream.
Drainage Divide
Imaginary line separating one basin from another, flowing from ridge.
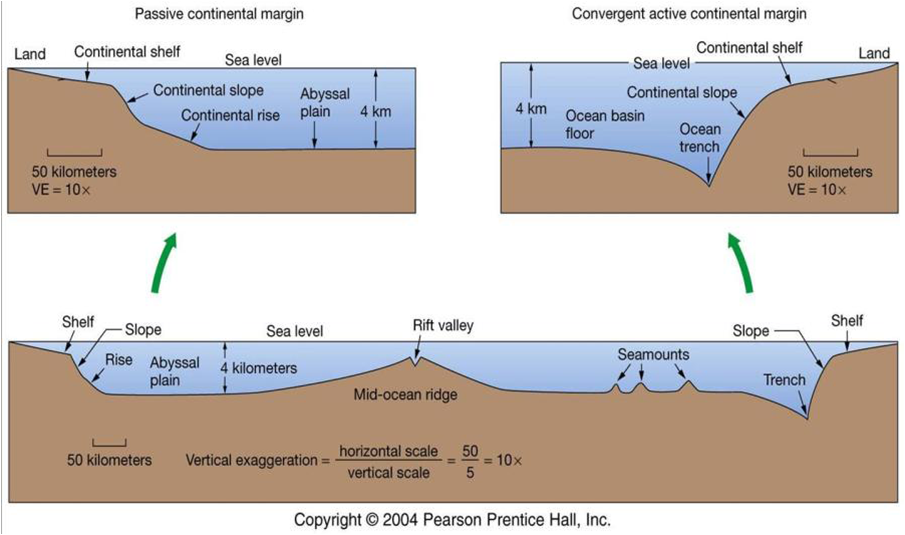
Continental Margin Labeling
Hydrologic Cycle
A summary of the circulation of Earth’s water supply
Watershed Label
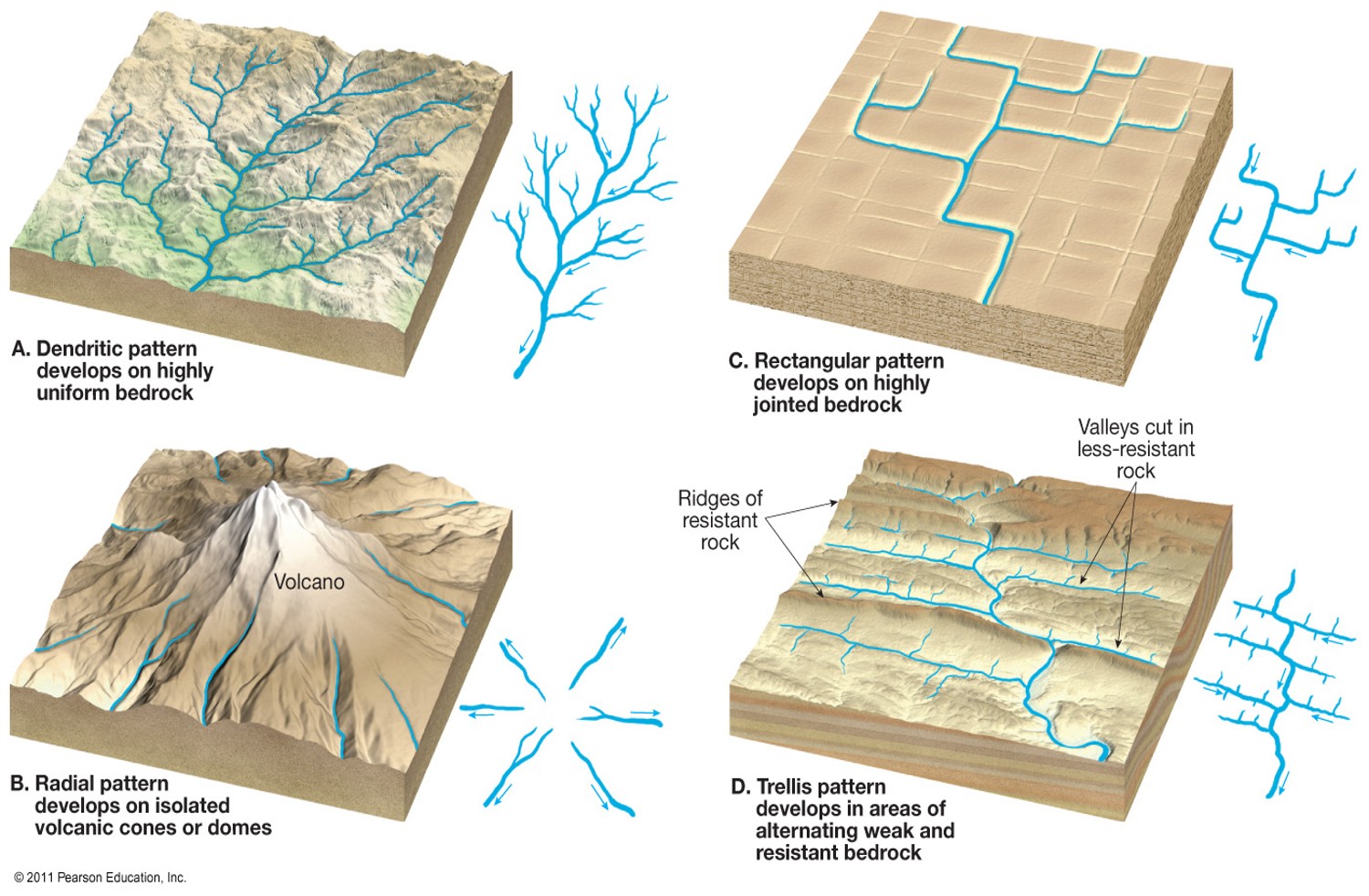
Stream Network Label
Dendritic, rectangular, radial, and trellis
Types of Streams
Perennial- Flows year round
Intermittent- Flows during part of the year
Ephemeral- Flows during a storm
Exotic- Flows in a dry region en route to the sea
Braided Stream
Networks of interweaving channels, low discharge, low sinuosity, and a lot of sediment.
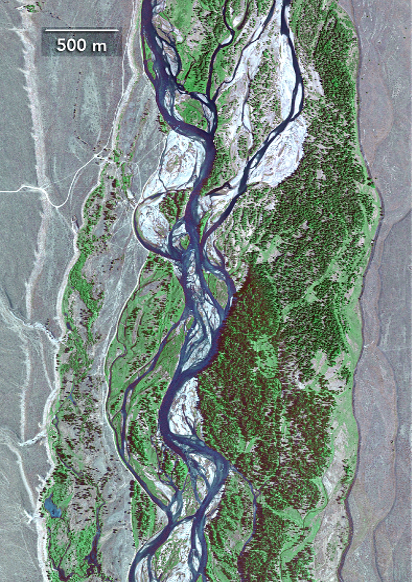

Meandering Stream
Formed when there is a low surface gradient and high sinuosity.

Stream Discharge
Volume of water passing a certain point per unit time.
Width*Height*3rd Dimension
Base Level
Lowest level to which a stream can erode its channel, the elevation at a streams mouth.
Stream Gradient
The slope aka vertical elevation drops over a horizontal distance.
Stream Hydrograph
Plot of discharge versus time.
Discharge increases during a flood.
Runoff from steep drainage is fast.
Runoff from a basin is spread over time.
Stream Discharge
Long term trends and sediment load vary throughout the year.
Downcutting
Forms new lower floodplain, leaving series of terraces.
Headword Erosion
One stream erodes upslope fast and intersects another stream, capturing or diverting the flow.
Dissolved Stream
Chemical matter dissolved in the water.
Suspended Load Stream
Largest amount of material transported by a stream.
Bed Load Stream
Particles moving along the stream bottom by saltation and traction.
Stream Capacity
Maximum load a stream can transport (stream discharge).
Stream Competence
Maximum particle sizes a stream can transport (stream velocity).
Cutbank and Point Bar Label
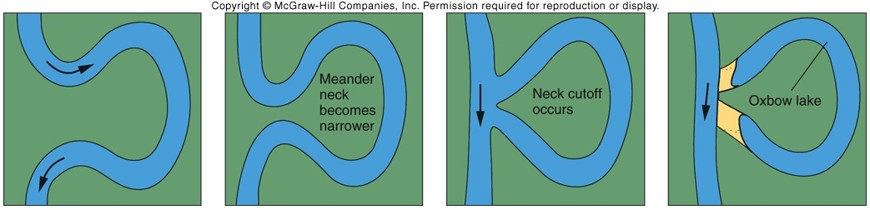
Oxbow Lake
Formed by meander cutoff.
Cutoffs
Formed when cut banks coverage and meander neck thins.
Levee
Raised embankment built up on either side of a river from flooding, keep flow in channel.
River Terraces
Formed by downcutting the lower floodplain.
Weathering
Physical breakdown and chemical decomposition of rock.
Erosion
Physical removal of material by water, wind, ice, or gravity.
Mass Wasting
Transfer of rock and soil downslope under the influence of gravity.
Type of rock, geologic structure, climate, chemicals in water, biotic activities, and time.
Exfoliation
Release of overburden from the overlying rocks, layers become detached.
Movement of Grains
Saltation- Swept up and suspended
Rolling- Roll along the surface
Suspension- Skip along the surface
Oxidation
Reactions with O2, iron bearing rocks, and wet climates.
Hydrolysis
Occurs when silicate materials are exposed to water and natural acids.
Dissolution
Minerals are dissolved away, releasing ions.
Types of Chemical Weathering
Oxidation, hydrolysis, and dissolution.
Differential Weathering
Exists as temperature changes, physical weathering in cold areas.
Climate
Weathering is more rapid in warm areas.
Geological Structures
Provide pathways for water to weather and erode rocks.
Soil Thickenss
As temp increases, weathering increases.
As precipitation increases, weathering increases.
Soil Horizons
O- Organic material
A- Organic material and mineral grains
E- Leached zone
B- Clay, iron oxides, and calcite
C- Weathered bedrock
Rock Falls
Loose rocks detach from steep slope.
Identification
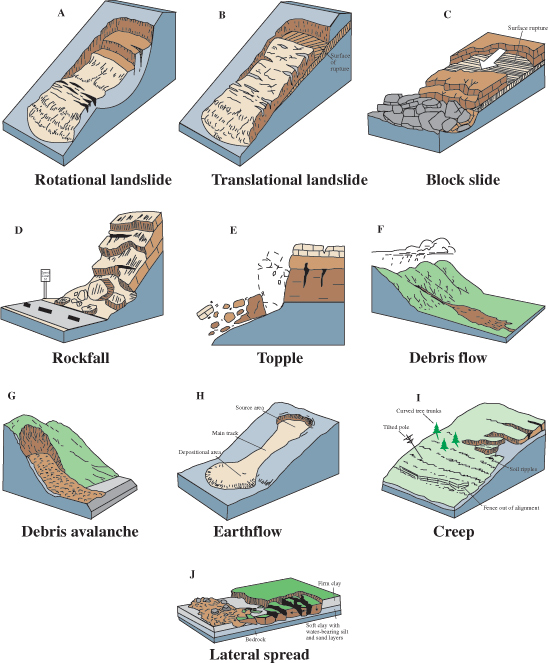
Landslide
Collapse of a slope along a planar rupture surface.
Slump
A slide in which a coherent body of rockslides downward along curved rupture surface.
Creep
Slowly moving forward, hardly perceptible.
Avalanche
Downslope slide of snow and rocks.
Lahar
Mudflow triggered by volcanic activities.
Glaciers
Snow is recrystallized under the weight of overlying snow, forming firn, exceeding 5 meters forms glacial ice.
Move the fastest from zone of accumulation to ablation.
Firn
When show forms dense mass of grains.
Valley Glacier
Mountain areas, flow down a valley from accumulation center.
Continental Glacier
Exist on a larger scale than valley glaciers.
Zone of accumulation
Net gain of ice.
Zone of ablation
Ice loss by melting, evaporating, and calving along its edge.
Snowline
Lowest topographic limits to sustain a year-round snow cover, boundary between accumulation and ablation.
Milankovitch Hypothesis
Earth’s movement around the sun causes natural fluctuations in the climate.
Shape of Earth’s orbit, angle of Earth’s axis, and Earth’s axis wobbles.
Glacial Plucking
Loosened bedrock freezes to the bottom of a moving glacier.
Glacial Striations
Forms grooves in the bedrock by abrasion, moving ice and debris against bedrock.
Cirques
Spoon-shaped circular depression scoured by glacier.

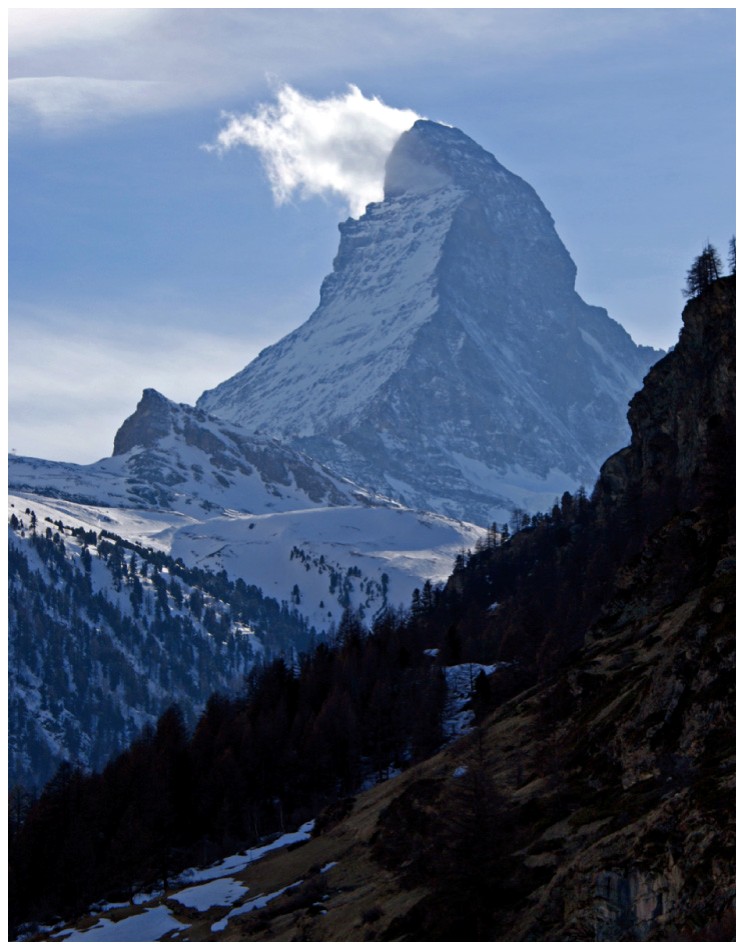
Horns
Sharp pointy peak sculpted by several cirques.

Aretes
Sharp ridge formed due to erosion of two adjacent valley glaciers.

Trough
U-shaped by a cross section.

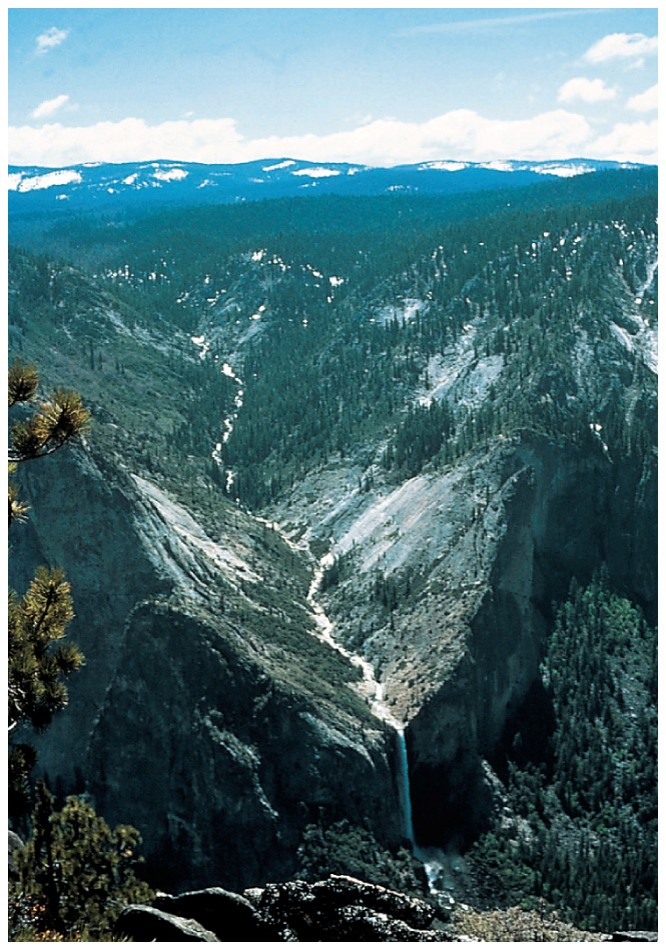
Hanging Valley
Tributary glaciated valley hanging above main glacial valley.

Till
Unstratified sediment dropped by glacial ice mode of grain sizes, deposited directly by the ice.

Moraines
Form along the side of a valley glacier, layers of till left by retreating glacier.

Erratic
Large boulder transported by glacier from very far away.
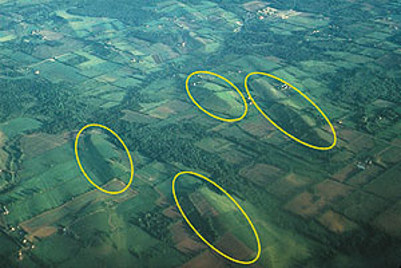
Drumlins
Reshaped ground moraine into streamlined elongated hills.
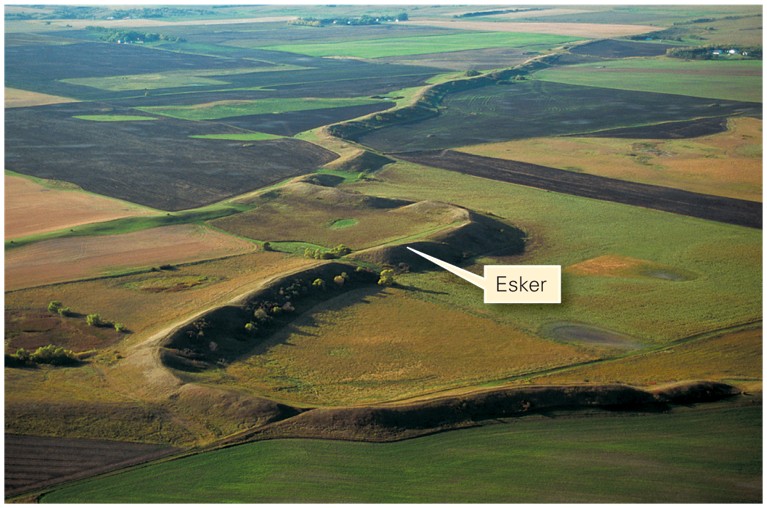
Eskers
Small sinuous ridges deposited by the melt water of the under-glacier tunnels.
Kettle Lakes
Scattered around the zone of ablation and glacier margins due to melting of remnant blocks of ice as glacier retreats.
