Osmosis Anatomy of Cerebral Cortex
1/112
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Osmosis
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
113 Terms
Parts of the brain
Cerebrum
Diencephalon
Cerebellum
Brainstem
Parts of cerebrum
2 cerebral hemispheres
Basal ganglia (nuclei)
Each cerebral hemisphere is divided in ___ main lobes and the _____ cortex
4
frontal
parietal
temporal
occipital
insular lobe (cortex)
The cerebral cortex is composed of ___ matter
gray containing billions of nuclei (neuronal cell bodies)
Allows for information processing and communication
Neuron
Subcortical cerebrum is _____ matter
white
Gray matter is composed of ____
nuclei neuronal cell bodies
White matter is composed of
myelinated axons
The largest white matter tract is the _______ ______
Corpus callosum
Sends signals between two cerebral hemispheres
corpus callosum
Within white matter there are collection of gray matter masses called _______ ______
basal ganglia/nuclei
Caudate
Putamen
External globus pallidus
Internal globus pallidus
Subthalamic nucleus
Substantia nigra
Basal ganglia
Striatum is the _____ and _____
caudate and putamen
Lentiform nuclei is the _____ and _______
putamen and globus pallidus
Corpus striatum is the _____, _____, and _____ _______
caudate, putamen, and globus pallidus
Collection of densely packed white matter which divides the corpus striatum
Is a highway for information between the cerebral cortex and brainstem and spinal cord
Internal capsule
Generally, the right cerebral hemisphere sends and receives signals from the ____ side of the body
Left
Generally, the left cerebral hemisphere sends and receives signals from the ____ side of the body
right
Folds of the external surface
Gyri
Grooves of the external surface
Sulci
Cleft of the external surface (deeper grooves)
Fissures
One function of these gyri and sulci is to allow the nearly ___ square feet of the cerebral cortex to fold in on itself, allowing it to fit within the small space of the neurocranium
2.5
Cortical folding effectively increases the _____ _____, allowing more nuclei to be packed into the cortex.
Surface area
The deep fissures also help to separate the brain into ____
lobes
gyri, sulci, and fissures actually create a relatively ______ pattern from person to person.
constant
This means that the neurons within a particular ________ area are all arranged in the same manner and partake in a similar function
Brodmann’s
Approximately ___ Brodmann’s areas have been identified in the human brain
180
The cerebrum has a deep midline sagittal fissure called the ________ fissure, which divides the brain into left and right cerebral hemispheres.
longitudinal
Around the middle of the longitudinal fissure and moving laterally, is the coronal _____ sulcus, also known as the fissure of _____ , which separates the frontal lobe rostrally, or anteriorly, from the parietal lobe caudally, or posteriorly.
central
Rolando
The coronal central sulcus aka fissure of Rolando separates the _____ lobe rostrally from the _____ lobe caudally
frontal
parietal
The rostral most point of the frontal lobe is called the frontal ____ .
Pole
From this lateral view, beneath the frontal and parietal lobes is the _____ fissure, also known as the lateral sulcus or Sylvian fissure.
Lateral
The lateral fissure aka lateral sulcus aka sylvian fissure separates the ____ and ____ lobes from the _____ lobe
frontal and parietal
temporal
The lateral fissure extends in three directions, rostrally as the ____ ramus, superiorly as the ______ ramus, and caudally as the ______ ramus.
anterior
ascending
posterior
The most rostral point of the temporal lobe is called the temporal _____
pole
The ______ lies at the bottom of the lateral fissure, hidden from the external surface of the brain
Insula/ insular cortex
The insula has the _____ sulcus of the insula running through it, forming both ____ gyri rostral to the sulcus, and ____ gyri caudal to the sulcus.
central
short
long
Looking at the brain from a posterior view, around the posterior middle portion of the cerebral hemisphere, there is a fissure called the ________ fissure, which travels inferiorly and anteriorly.
Parieto-occipital
The parieto-occipital fissure separates the _____ lobe rostrally, from the ______ lobe caudally, and from a medial view of the hemisphere the parieto-occipital sulcus is joined halfway by the _____ sulcus.
parietal
occipital
calcarine
The most caudal point of the occipital lobe is called the occipital _____
Pole
Histologically similar areas
Brodmann areas
In the frontal lobe, the _____ sulcus is rostral and parallel to central sulcus
precentral sulcus
Central sulcus and precentral sulcus of frontal lobe borders the precentral _____
gyrus
Superior and inferior frontal sulcus divided the rest of the frontal lobe into 3 gyri ____, ______, _____
Superior
Middle
Inferior
The inferior frontal gyrus is divided into 3 parts by the branching rami of the lateral fissure
inferior to anterior ramus:
between anterior and ascending ramus:
Posteriorly between ascending and precentral sulcus:
Pars orbitalis
Pars triangularis
Pars opercularis
Looking at the frontal lobe from a medial view there is another sulcus the _____ sulcus and an anterior _______ lobule, which forms the medial aspect of the ___central gyrus, and the posterior ______ lobule, which forms the medial aspect of the ____central gyrus
cingulate
paracentral; pre
paracentral; post
The _____ lobe contains the primary motor cortex, Brodmann’s area 4
frontal
occupies the area of the precentral gyrus and extends over to the medial aspect of the hemisphere as the anterior paracentral lobule.
The primary ______ cortex houses neurons responsible for carrying out voluntary movements of different parts of our body, mainly to the contralateral, or opposite, side
motor
frontal lobe
Extending anteriorly from the primary motor cortex, and over the posterior parts of the superior, medial and inferior frontal gyri is the _______ cortex, or Brodmann’s area 6.
promotor
This ______ cortex receives input from other parts of the cerebral cortex, the thalamus, the basal ganglia, and directly communicates with the primary motor cortex.
premotor
frontal lobe
Assist the primary motor cortex plan and carry out voluntary movements and therefore it is called an association cortex
premotor cortex
frontal lobe
Stores and processes information about past activity, and helps to integrate sensory and motor information for planning of future voluntary movements.
premotor cortex
frontal lobe
Rostral to the premotor cortex and extending into the middle frontal gyrus is the frontal ____ field, Brodmann’s area 8, which controls voluntary eye movement, and allows us to move our eyes together in the same direction at the same time, known as conjugate gaze.
eye
frontal lobe
Controls voluntary eye movement, and allows us to move our eyes together in the same direction at the same time, known as conjugate gaze.
frontal eye field, Brodmann’s area 8
Frontal lobe
______ area and Brodmann’s area 44/45, which is formed by two regions of the inferior frontal gyrus, namely the pars opercularis and the pars triangularis.
Broca’s
frontal lobe
Usually located in the dominant hemisphere, which in most individuals is the left hemisphere. This area has connections to the nearby motor cortex, specifically to the areas that control the muscles of the larynx, mouth, soft palate, and the tongue, as well as respiratory muscles, to assist in the formation, or production, of words and speech.
Broca’s area
frontal lobe
Located anterior to the premotor cortex and overlies the anterior portions of the superior, middle, and inferior frontal gyri.
prefrontal cortex
Responsible for mainly what has been coined as executive functions, which include reasoning, planning, social behavior, judgement, and much more.
Prefrontal cortex
frontal lobe
Responsible for controlling voluntary movements of our body
Primary motor cortex
Frontal lobe
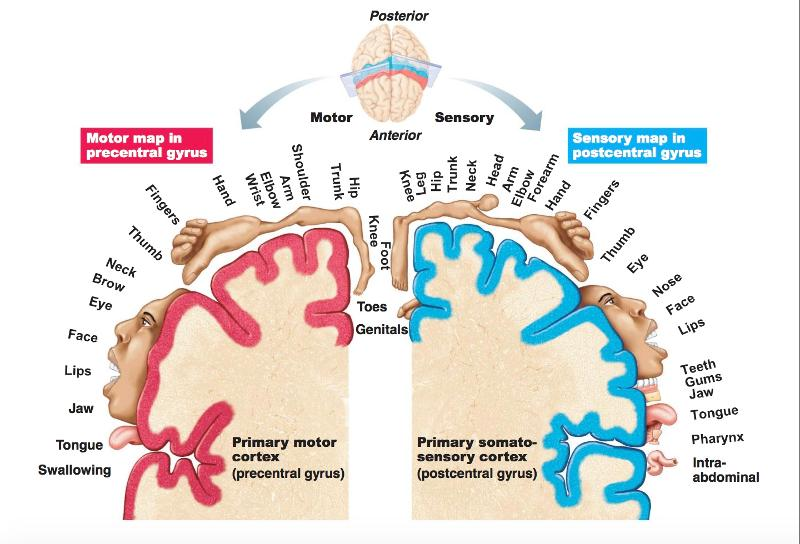
This unique and elegant arrangement of body parts in the cortex is called _____ .
Somatotopy
Now, the proportion of the primary motor cortex, or the _____ of neurons dedicated to a particular movement depends upon how much that muscle, or group of muscles, is actually used
number
The more a muscle is used, the more nuclei will be dedicated to it within the _____ _____ cortex.
primary motor
frontal lobe
The number of nuclei is ________ upon the size or mass of the muscle performing that movement.
independent
Primary motor cortex map creates an awkwardly large representation of the hands, fingers and face. This means that _____ cortex, and hence ____ neurons, are dedicated to those regions, since we use them more often in our daily lives to explore our world.
more
frontal lobe
In the primary cortex map the location of body parts is essentially ______
inverted
Formation of words and speech
Broca’s area
Frontal lobe
In the parietal lobe just caudal to the central sulcus running parallel to it is the ______ sulcus.
postcentral
the central sulcus and the postcentral sulcus form the borders of the postcentral _____
gyrus
(parietal lobe)
Running caudally from the middle of the postcentral sulcus, or near it, is the _____ sulcus, which divides the rest of the parietal lobe into the ____ parietal lobule above it, and the ______parietal lobule below it.
intraparietal
superior and inferior
part of the inferior parietal lobule that folds over the end of the posterior ramus and is called the _________ gyrus, and behind it is the _____ gyrus that folds over the end of the superior temporal sulcus found in the temporal lobe.
supramarginal
angular
Primary somatosensory cortex, Brodmann’s area 3,1,2, which is located in the postcentral gyrus and extends medially to the posterior paracentral lobule.
Parietal lobe
Receives sensory input from the opposite side of the body through the ventral posteromedial, or VPM, and ventral posterolateral, or VPL, nuclei of the thalamus, enabling us to process and interpret sensory information from our body like touch or pain.
Primary somatosensory cortex
parietal lobe
The primary somatosensory cortex receives sensory input from the opposite side of the body through the ventral posteromedial, or VPM, and ventral posterolateral, or VPL, nuclei of the _____ , enabling us to process and interpret sensory information from our body like touch or pain
thalamus
Similar to the motor homunculus, we have a ______ homunculus to visually represent the proportion of sensory fibers that the primary somatosensory cortex receives from a particular part of the body.
sensory
(parietal lobe)
Motor homunculus ______ lobe
Sensory homunculus ______ lobe
frontal
parietal
The more ______ a body part is, the more neurons it requires for processing sensory stimuli, and therefore it occupies a larger area of the somatosensory cortex.
sensitive
parietal lobe
First body part represented in primary motor cortex are the ____
First body part represented in the primary somatosensory cortex is the _____
toes
anogenital area (followed by foot, leg, thigh)
Located over the superior parietal lobule is the somatosensory _______ cortex, which has many connections with other sensory regions of the cerebral cortex.
association
Believed to allow the ability to integrate different sensory modalities, such as being able to recognize objects through touch without visual input, like reading braille, by comparing and associating the sensations to past sensory experiences.
somatosensory association cortex
parietal lobe
The lateral surface of the temporal lobe includes the superior temporal sulcus and the middle temporal sulcus, which divide the temporal lobe into the _____ , _____, and ______ temporal gyri
superior, middle, inferior
______ temporal gyri of _____, which is found on the deep upper surface of the superior temporal gyrus
Transverse temporal gyri of heschl
Located in the transverse temporal gyri of Heschl is the primary ______ cortex, Brodmann’s area 41/42, which receives auditory input from the medial geniculate body of the thalamus and interprets auditory information, or sound, such as when the next door neighbours are being way too loud.
auditory
Receives auditory input from the medial geniculate body of the thalamus and interprets auditory information, or sound, such as when the next door neighbours are being way too loud.
Primary auditory cortex
temporal lobe
Brodmann’s area 22/39/40, which encompasses a part of the superior temporal gyrus along with the supramarginal and angular gyri of the parietal lobe.
Wernicke’s area (dominant hemisphere)
temporal lobe
Responsible for the processing and understanding of both written and spoken language, allowing us to read a sentence, understand it, and say it out loud comprehensively.
Wernicke’s area
temporal lobe
Wernicke’s area is connected to Broca’s area by a bundle of axons called the _____ _____ , which allows us to tie together speech comprehension from Wernicke’s area, and speech production from Broca’s area.
Arcuate fasciculus
The limbic system with structures related to learning, memory and emotion is located in the _____ aspect of the _____ lobe
Medial
temporal
The insula is usually divided into _____ and ______ aspects.
anterior and posterior
Functions are diverse and complex with convergence of inputs from temporal, parietal, and frontal lobes
Insula
Has been associated with processing viscero-autonomic sensations, limbic and emotional elements, somatosensation, and possibly motor elements too.
The insula
The _____ lobe contains the cuneus, a wedge-shaped area bounded by the parieto-occipital fissure rostrally, and by the calcarine sulcus inferiorly
occipital
A wedge-shaped area bounded by the parieto-occipital fissure rostrally, and by the calcarine sulcus inferiorly
cuneus of occipital lobe
Inferior to the cuneus and the calcarine sulcus is the ______ gyrus.
lingual
occipital lobe
Dedicated to vision and hence a substantial part is occupied by the primary visual cortex, Brodmann’s area 17.
Occipital lobe
Located on the medial aspect of the hemispheres, and lines both the superior and inferior banks of the calcarine sulcus. It also extends around the occipital pole onto the lateral surface of each hemisphere.
Primary visual cortex
occipital lobe
This area receives, processes, and interprets visual input from the lateral geniculate body of the thalamus.
Primary visual cortex
occipital lobe
Medial side of each hemisphere: There is a region of cortex surrounding the corpus callosum that is a part of the limbic system. This region contains the _____ gyrus, located below the rostral part of the corpus callosum; as well as the _____gyrus, which begins beneath the rostral end of the corpus callosum and continues superiorly and caudally until it reaches the posterior end of the corpus callosum.
subcallosal
cingulate
The _______ gyrus, which is part of the medial temporal lobe, lies rostral to the lingual gyrus of the occipital lobe and ends rostrally as the uncus, also a component of the limbic system.
parahipocampal
Subcallosal gyrus, cingulate gyrus, parahippocampal gyrus, and uncus, along with the olfactory cortex, the amygdala, the hypothalamus, and the hippocampus, constitute the major structures of the _____ system. They are responsible for functions related to the “preservation of the species”, such as fight or flight responses, emotion, memory, and reproductive, endocrine, and other behavioral responses.
limbic
They are responsible for functions related to the “preservation of the species”, such as fight or flight responses, emotion, memory, and reproductive, endocrine, and other behavioral responses.
Limbic system