Enzymes and Macromolecules: Organic Chemistry in Biology
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
88 Terms
Metabolism
All of the chemical reactions within each cell of an organism.
Chemical reactions
The breaking and forming of bonds.
Endothermic
Net absorption of energy (in the form of heat or light).
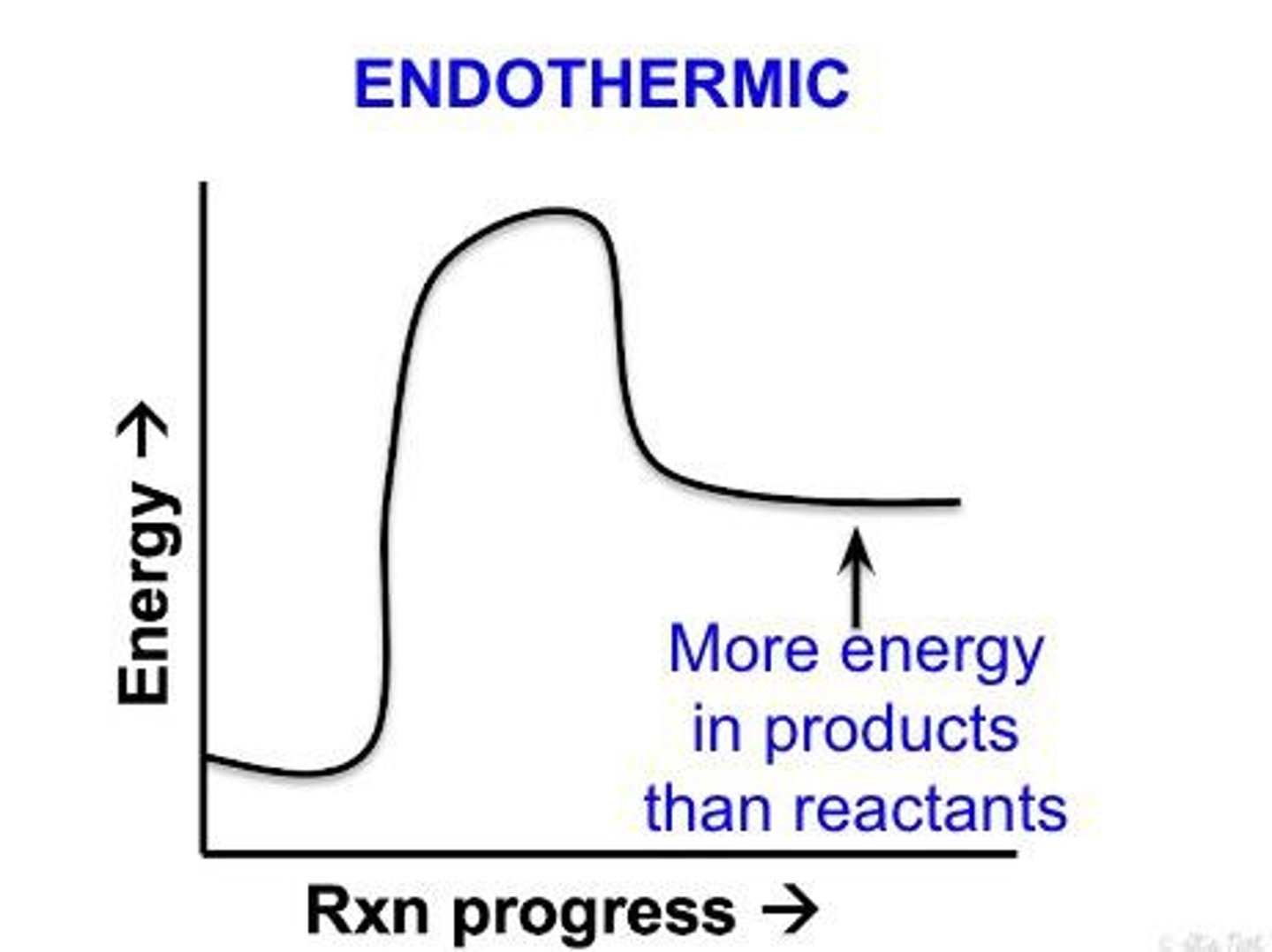
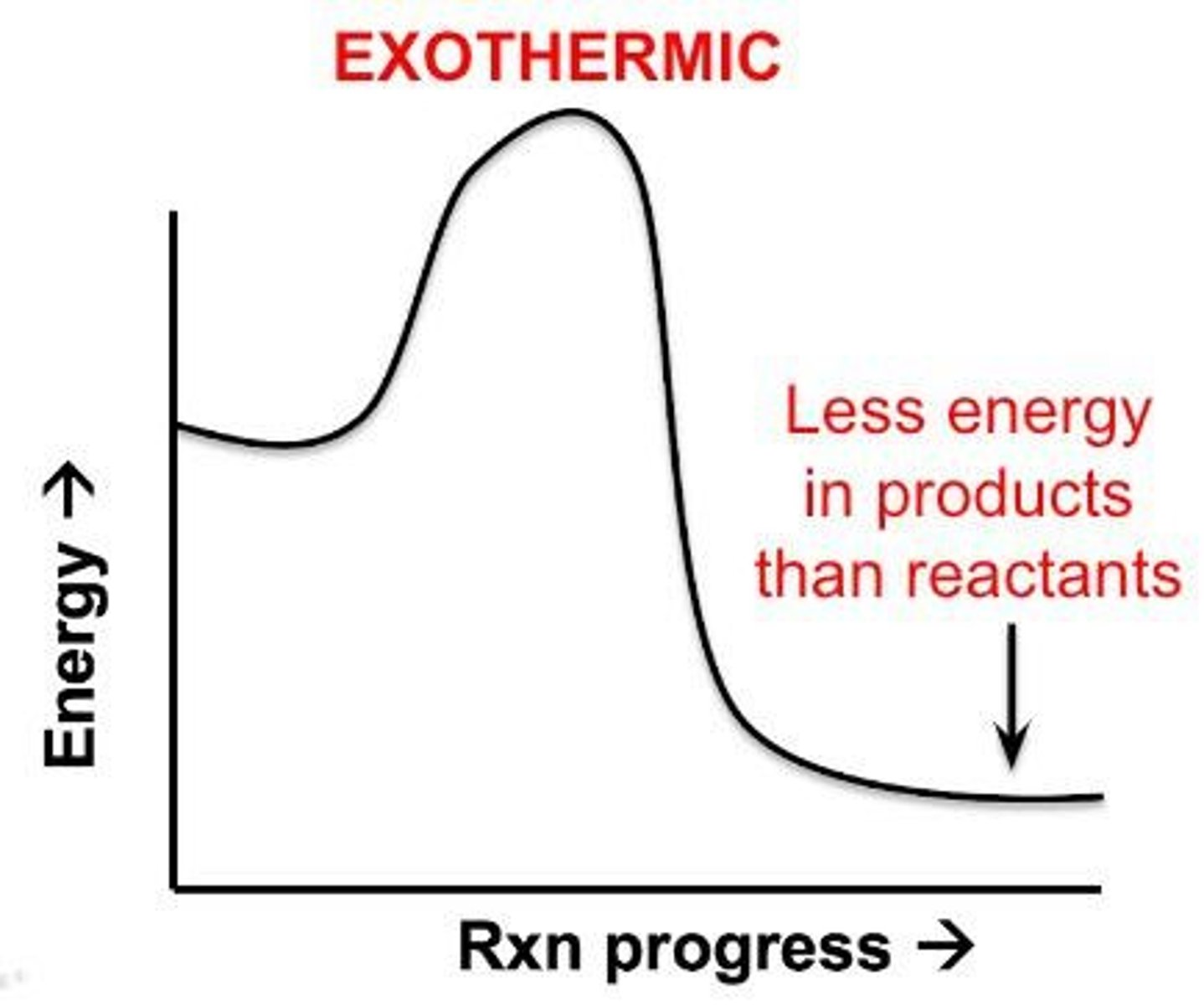
Exothermic
Net release of energy (in the form of heat or light).
Catabolic
Breaking down complex molecules into simpler ones.
Anabolic
Building simpler molecules into more complex ones.
Energy absorption
Breaking a bond requires energy to be absorbed.
Energy release
Forming a bond allows energy to be released.
Reactant (substrate)
Substance that is changed during a chemical reaction
Products
Substance that is made by a chemical reaction
Reactant energy
The amount of energy in the reactants
Product energy
The amount of energy in the products
Activation energy
The amount of energy required to be added to the system to lead to the reactants becoming the products
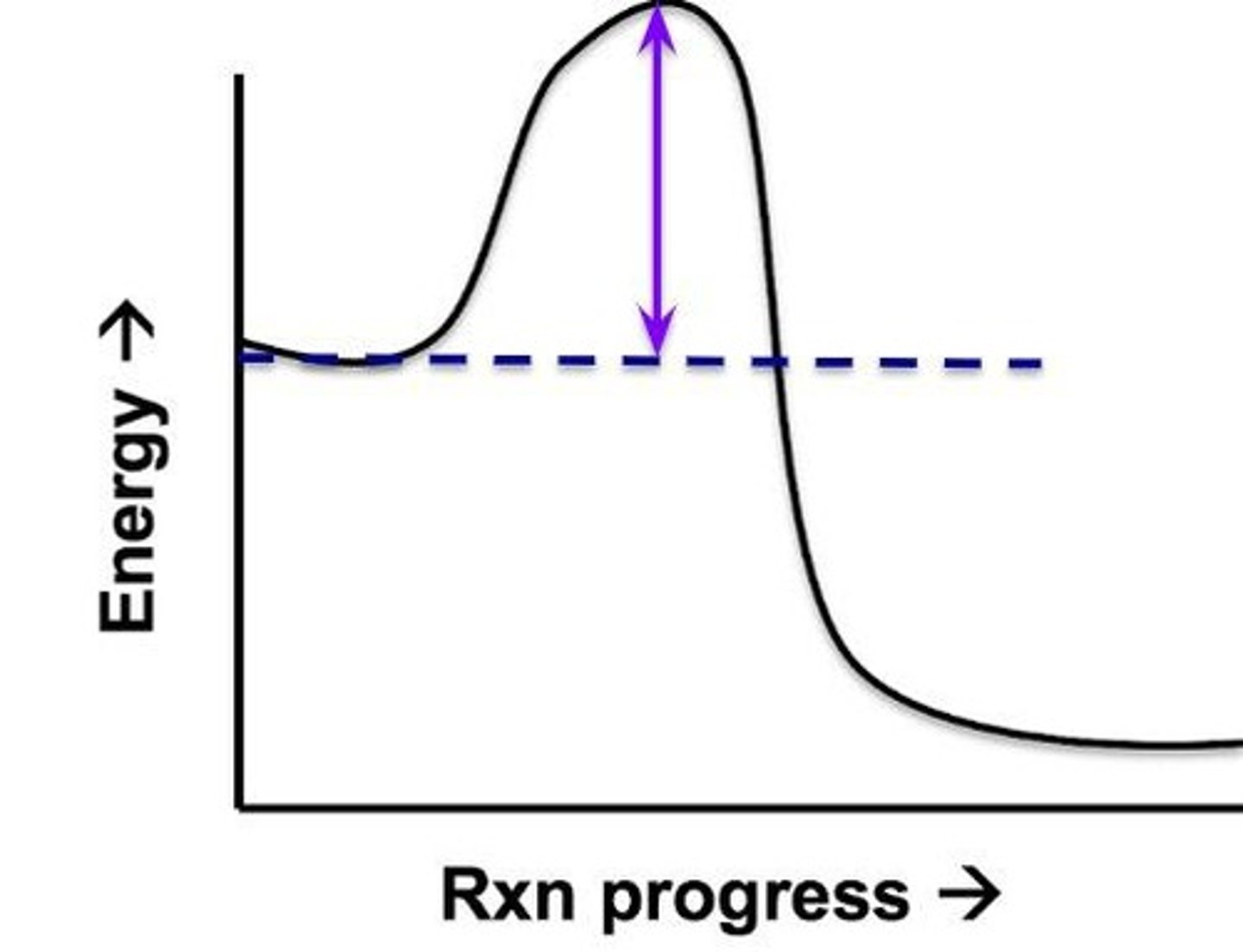
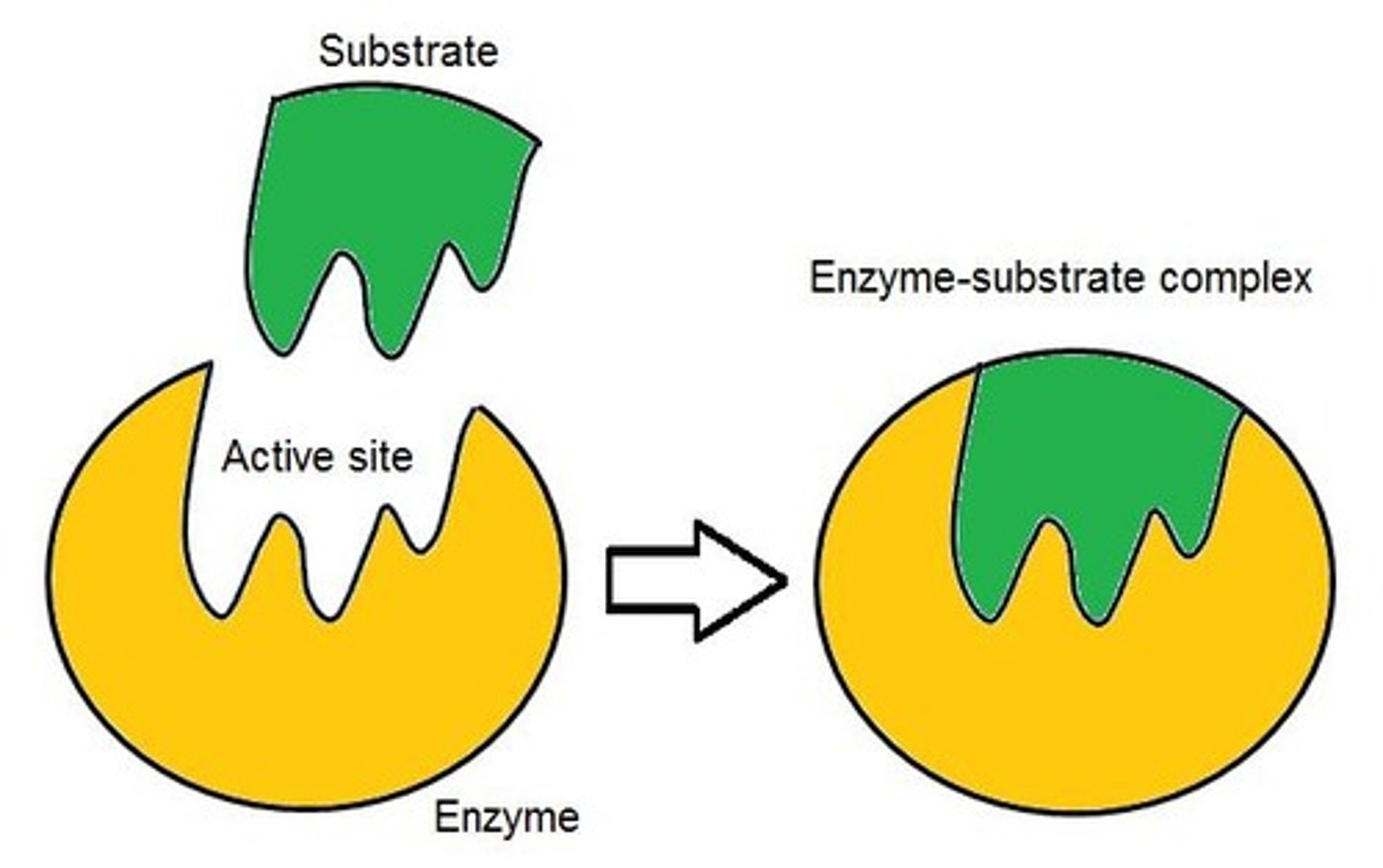
Enzymes
Proteins that speed up chemical reactions
Active site
The part of the enzyme that binds to the substrate
Lock-and-Key model
Enzymes are specific to certain substrates
Ball-and-Glove model
When the substrate binds to the active site, the enzyme-substrate complex changes shape (induced fit)
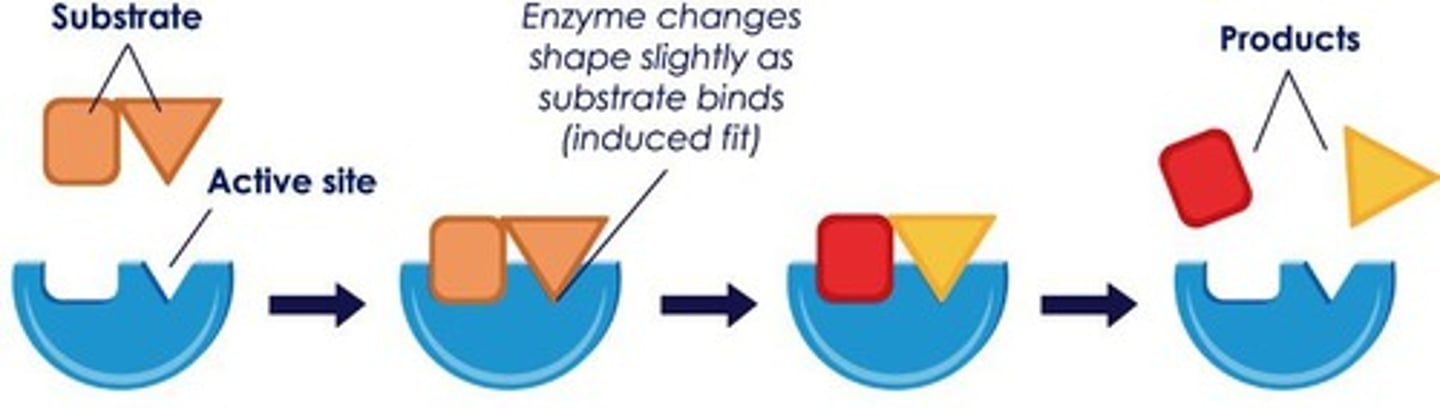
Enzymes: Action
Enzymes can break bonds to form two products or make bonds between substrates to form one product
Coenzyme
A middle-man that binds to the enzyme's active site, allowing substrates to bind
Inhibition
A way to slow down enzyme activity
Competitive inhibitor
Has a shape similar to the substrate, binds to the enzyme's active site without producing the product, preventing the reaction from taking place
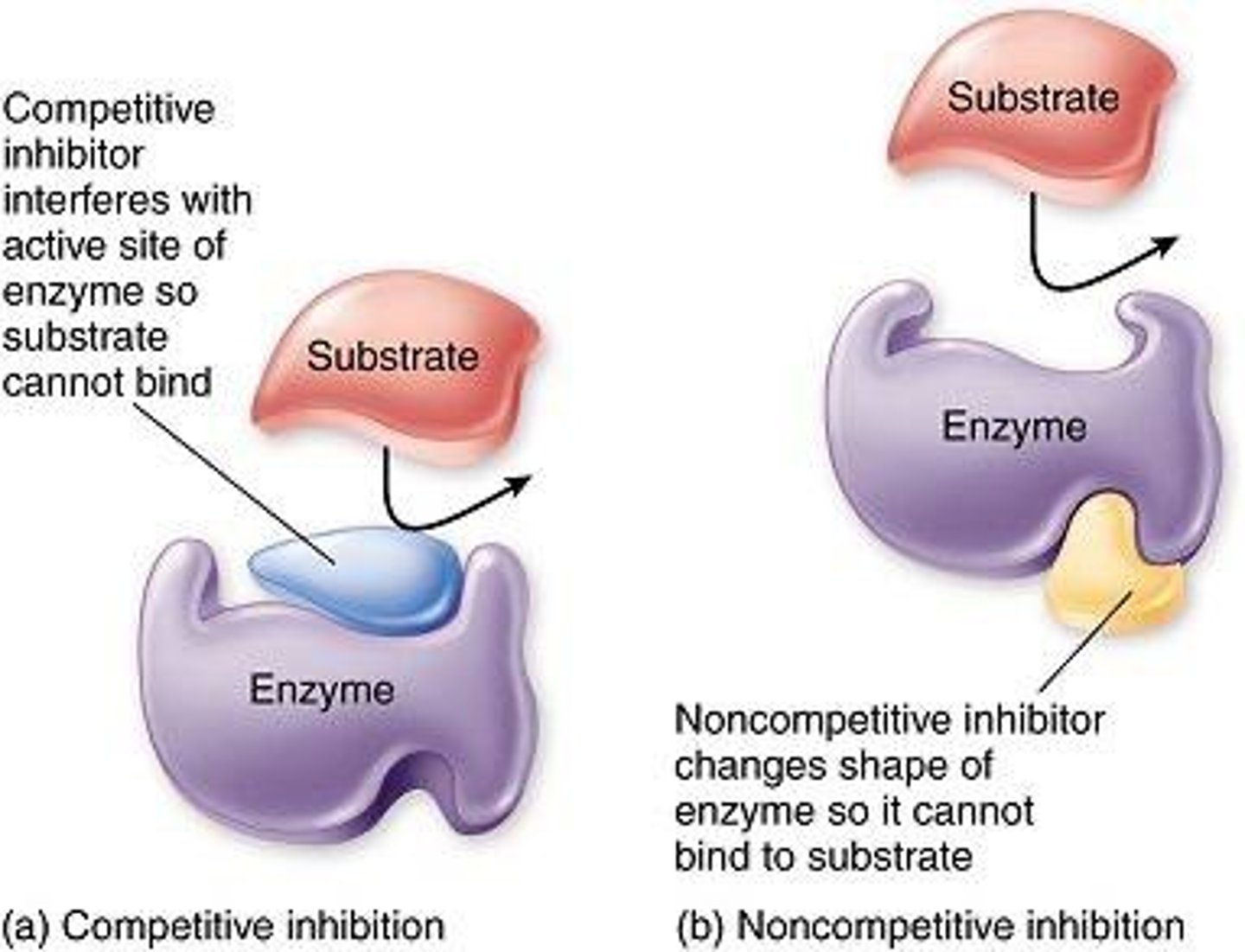
Noncompetitive inhibitor
Does not bind to the active site of the enzyme, but binds to another part of the enzyme known as the allosteric site, changing the shape of the enzyme
Denature
Modifying the structure of a protein, generally making it nonfunctioning
Effects of denaturation
If the enzyme is denatured, the active site will be deformed and not be able to bind to the substrate
Environmental changes affecting enzymes
Can be caused by extreme changes in pH, temperature, ion strength, and solubility
Allosteric site
The alternative site on the enzyme where a noncompetitive inhibitor binds.
Rate of Chemical Reaction
Affected by environmental factors such as temperature and pH.
Temperature effect on reaction rate
Generally accepted that increasing temperature increases the rate of reaction due to faster molecular movement.
Optimal pH
Most enzymes have an optimal pH, and modifying it will impact the rate of reaction.
Denaturation temperature range
Enzymes can denature around 40-45°C.
Macromolecule
Large organic molecules (contain carbon) that make up all living things.
Organic molecule
Contains carbon.
Carbohydrates
One of the four main classes of macromolecules.
Lipids
One of the four main classes of macromolecules.
Proteins
One of the four main classes of macromolecules.
Nucleic acids
One of the four main classes of macromolecules.
Polymer
Larger, complex structure made of monomers.
Monomer
Small, basic sub-unit.
Dehydration synthesis
Process by which monomers undergo to form polymers.
Condensation
Another term for dehydration synthesis.
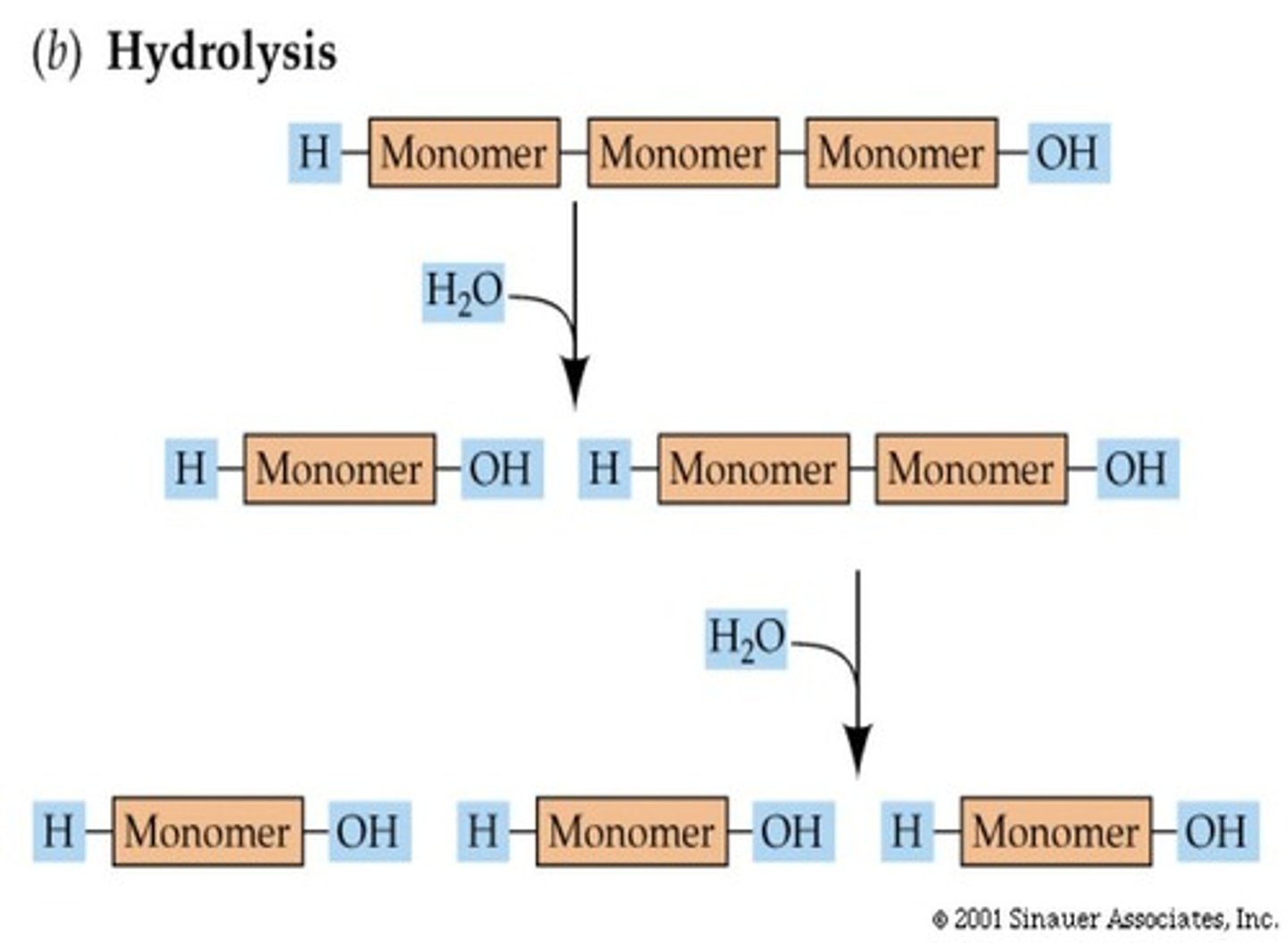
Polymer Decomposition
To break a polymer down into monomers, the opposite reaction is performed.
Hydrolysis
Water is added to break down the polymer.
Carbohydrate
Main function: short-term energy storage; Found in: sugars and starches; Elements: C, H, O; Properties: polar and hydrophilic.
Carbohydrate Structure
Monomer: monosaccharides; Polymer: polysaccharides.
Glucose
Main fuel for animal cells.
Galactose
Sugar in milk.
Fructose
Sugar in fruit.
Glycogen
Composed of glucose, how animals store energy.
Cellulose
Structural support in plant cell walls.
Starch
How plants store sugar.
Energy storage in carbohydrates
4 calories/gram.
Lipids Structure
Monomer: fatty acids; Polymer: triglycerides.
Energy storage in lipids
9 calories/gram.
Compact structure of lipids
Better than carbs for storage because they hold more energy.
Body's energy source order
The body can break carbohydrates down easily—typically the first thing the body will break down when it needs energy.
Lipids as energy source
When the body needs energy and runs out of easy-to-access carbs, it will break down lipids next.
Saturated fatty acid
All single bonds in the chain allows it to compact—tend to be solid at room temperature.
Unsaturated fatty acid
Double or triple bonds in the chain prevents it from compacting—tend to be liquid at room temperature.
Saturated Fats
Unhealthy because they easily solidify and clog body's pathways.
Phospholipid
Type of lipid used in cell membranes.
Phospholipid Structure
2 fatty acids (2 lipid monomers) and 1 phosphate.
Hydrophilic head
Phosphate group.
Hydrophobic tail
Fatty acids.
Phospholipid bilayer
2 layers make up the plasma membrane of our cells.
Energy storage in Proteins
4 calories/gram.
Proteins as energy source
Used by the body for energy as a last resort when it enters starvation.
Elements in Proteins
C, H, O, N.
Monomer of Proteins
Amino acids.
Polymer of Proteins
Polypeptide.
Peptide bond
Amino acids are linked together by a peptide bond.
Protein Properties
Some are polar, some are nonpolar (some are hydrophilic, some are hydrophobic).
Functions of Proteins
Many important functions including enzymes, hormones, antibodies, receptors, and energy source.
Hormones
Regulate cell processes.
Antibodies
Help immune system fight diseases.
Receptors
Aid in cell signaling.
Beta-pleated sheet
A type of secondary structure in proteins.
Alpha-helix
A type of secondary structure in proteins.
Protein Folding Levels
4 levels: Primary, Secondary, Tertiary, Quaternary.
Primary structure
Straight chain of amino acids.
Secondary structure
First-level of folding, either into alpha-helices or beta-pleated sheets; hydrogen bonding exists between different segments.
Tertiary structure
Final shape, further folding from 2O structure.
Quaternary structure
Only some proteins form this stage; multiple proteins are held together by H bonding.
Nucleic Acids Found in
DNA and RNA.
Energy storage in Nucleic Acids
Not used for energy.
Elements in Nucleic Acids
C, H, O, N, P.
Monomer of Nucleic Acids
Nucleotides.
Polymer of Nucleic Acids
Nucleic acid.
Properties of Nucleic Acids
Polar and hydrophilic.