Structure of transport tissues
1/22
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Why do plants need transport systems
to move sucrose and oxygen to roots and shoots for respiration
To move ions from roots to leaves
Plants can be very large, multicellular
Stems, trunks and roots have a small surface area to volume ratio so diffusion is too slow
Define dicotyledonous plant
A plant whose seeds contain two cotyledons, organs that store food for developing plants (have two shoots when growing)
Define vascular system
Transport vessels that run through roots, stems and leaves (eg xylem and phloem)
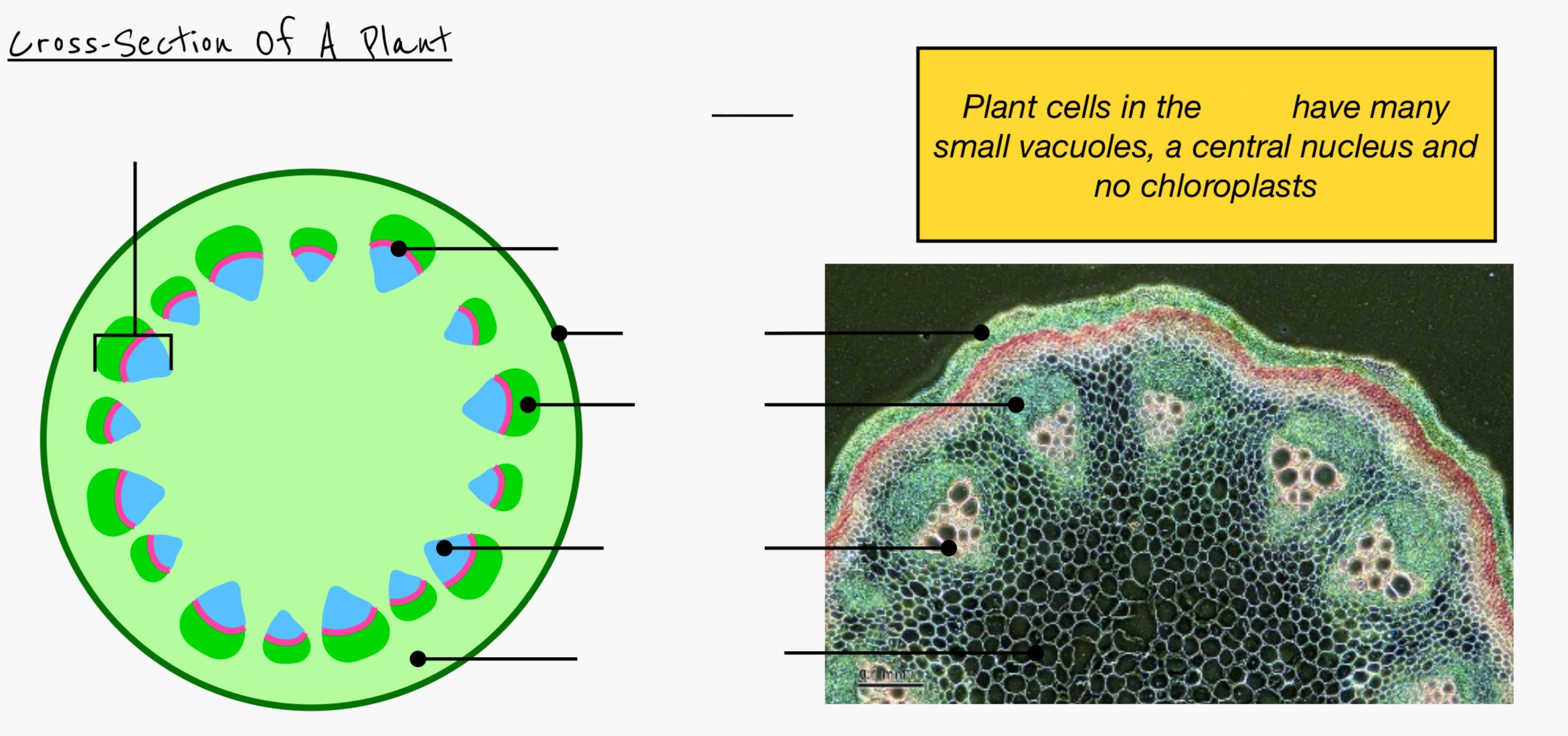
Identify and label the tissues in this organ
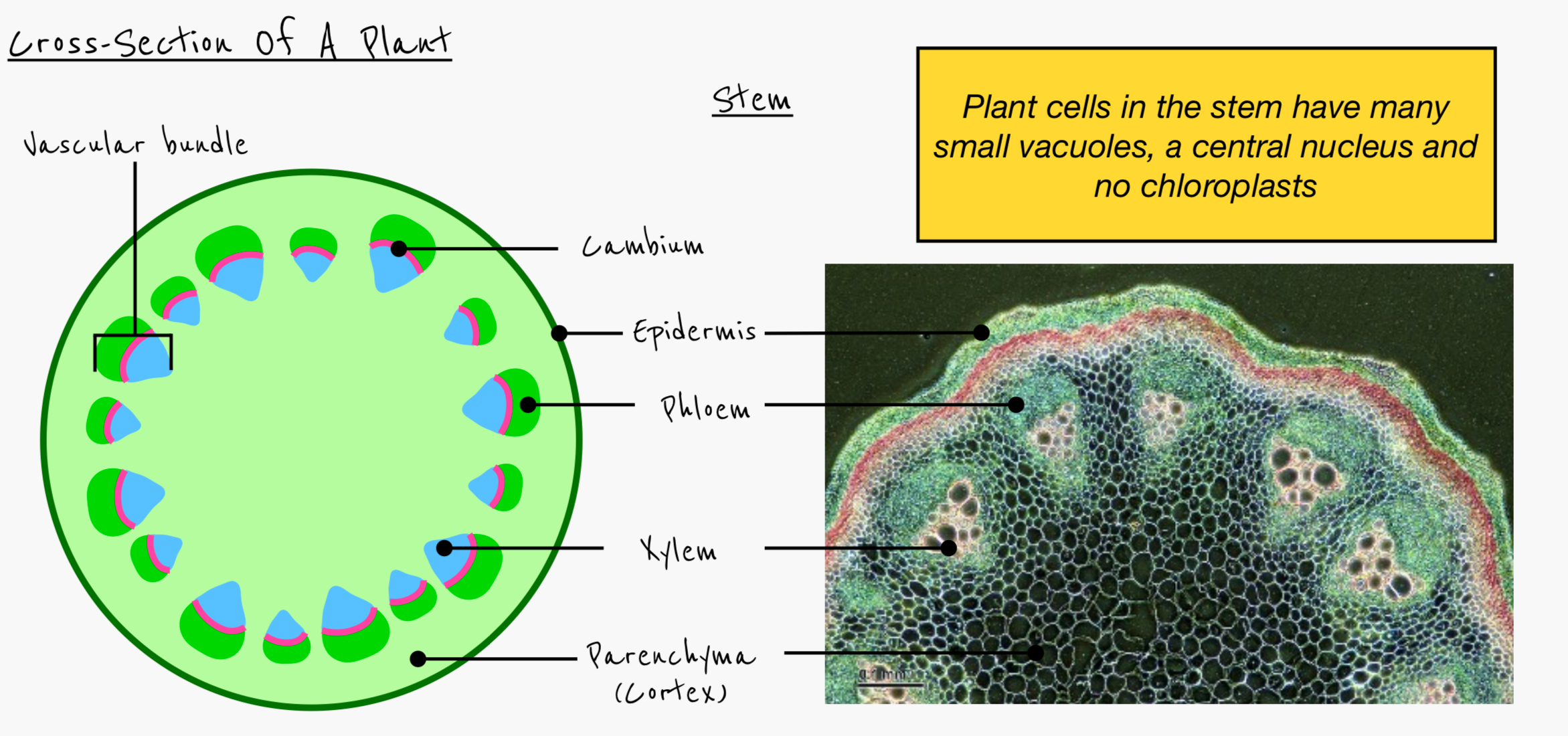
Identify and label the tissues in this organ
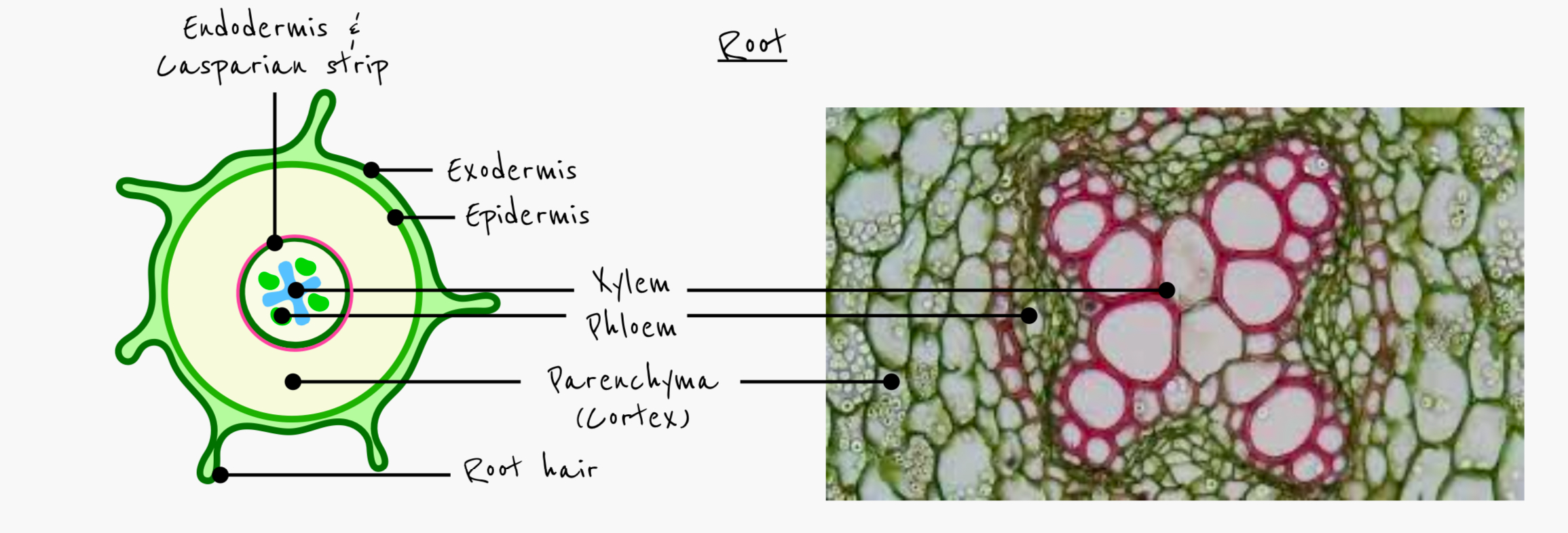

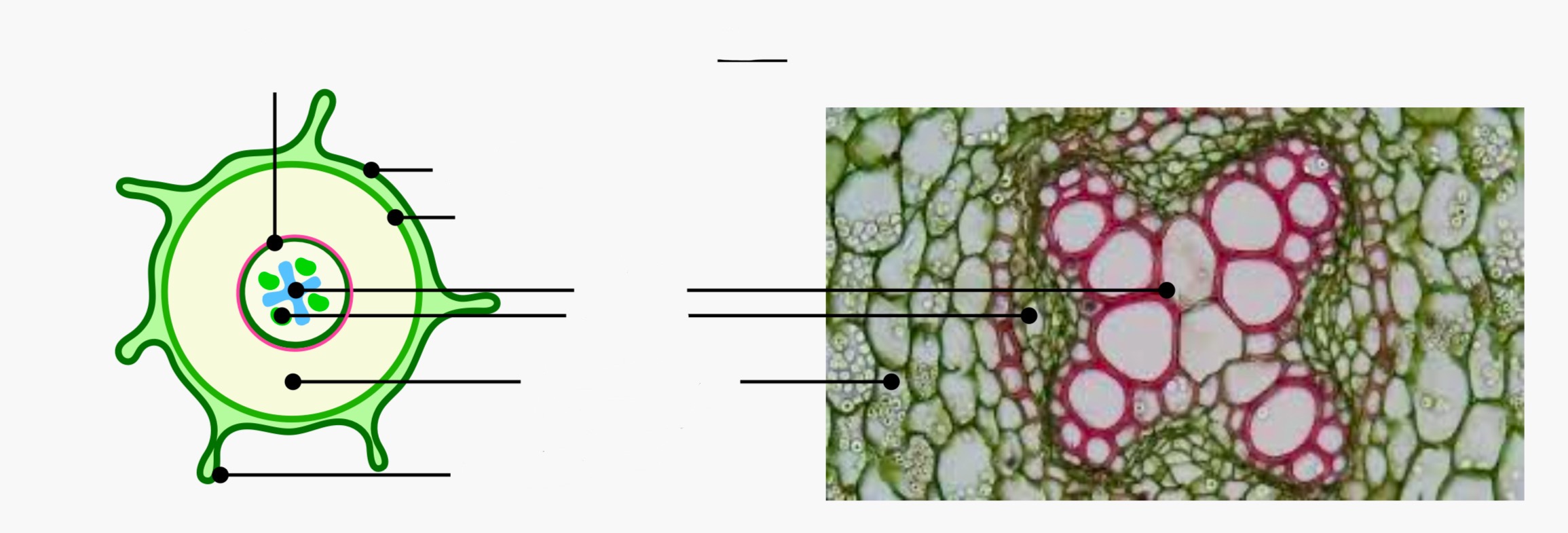
Identify and label the tissues in this organ
Describe the role of the parenchyma
Packing material in the root and stem
Describe the role of the epidermis
Prevents water loss
Define vascular bundle
Arrangement of xylem and phloem tissue
Describe the arrangement of the vascular bundle in the stem
Around the edge of plant to give strength and support
Phloem closest to the outside edge
Describe the arrangement of the vascular bundle in the root
in the middle of the root
Protects bundle from tugging strains in the wind
Xylem forms an X shape
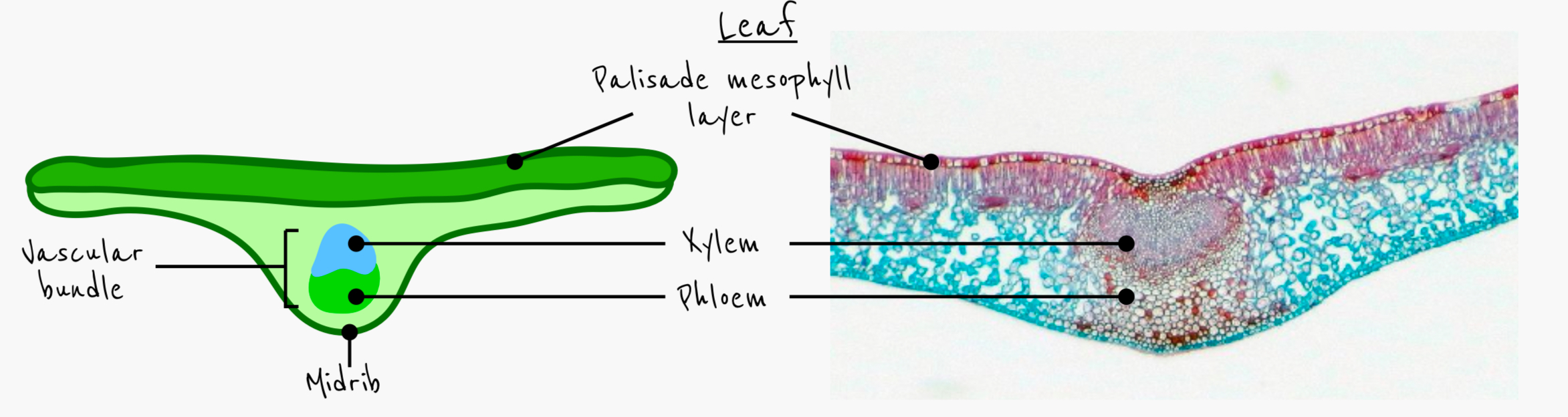
Describe the arrangement of the vascular bundle in the leaf
midrib is main vein carrying vascular tissue
Give support to structure of leaf
Xylem closest to upper side of the leaf
Smaller branching veins also carrying vascular bundles
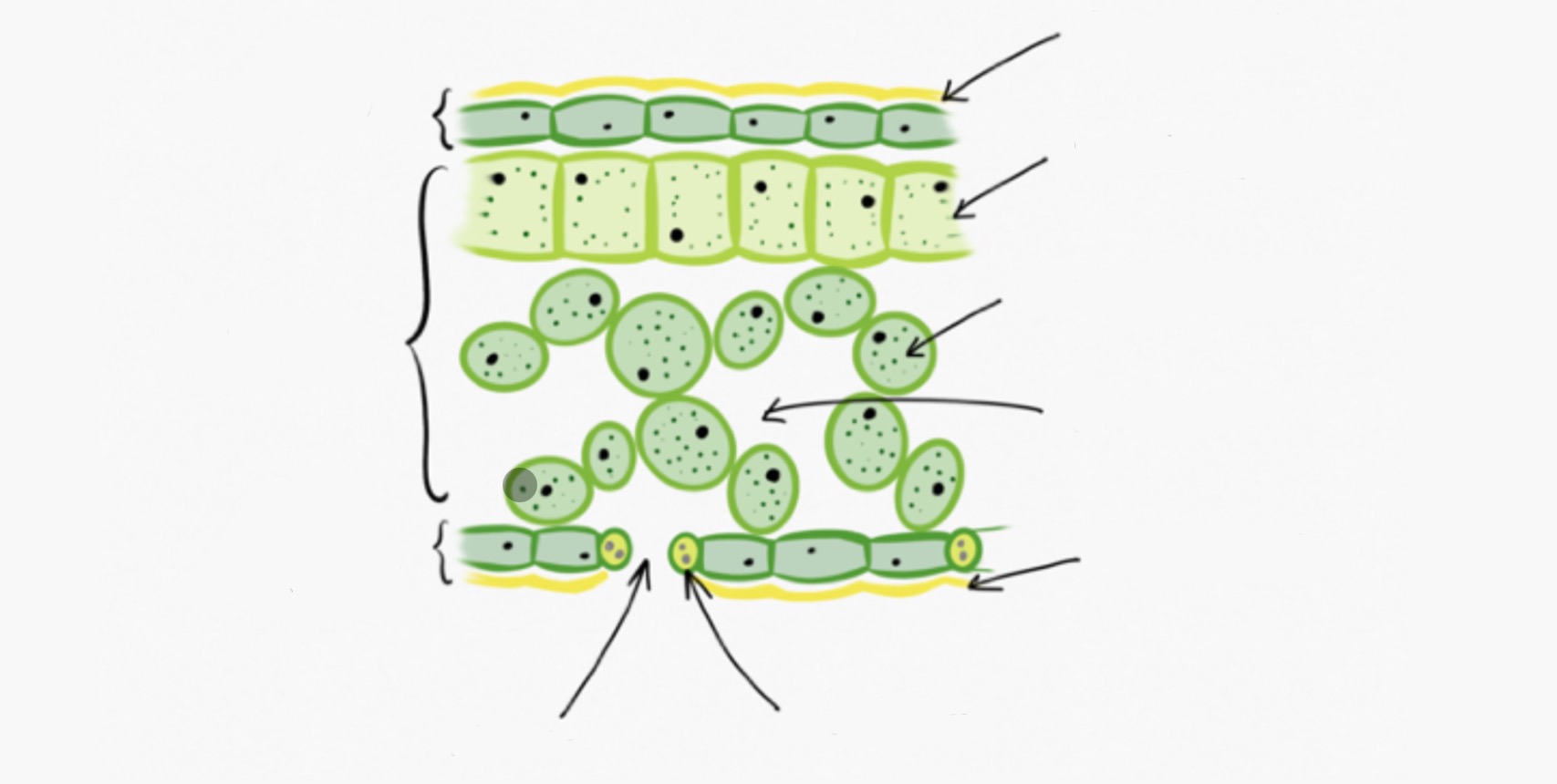
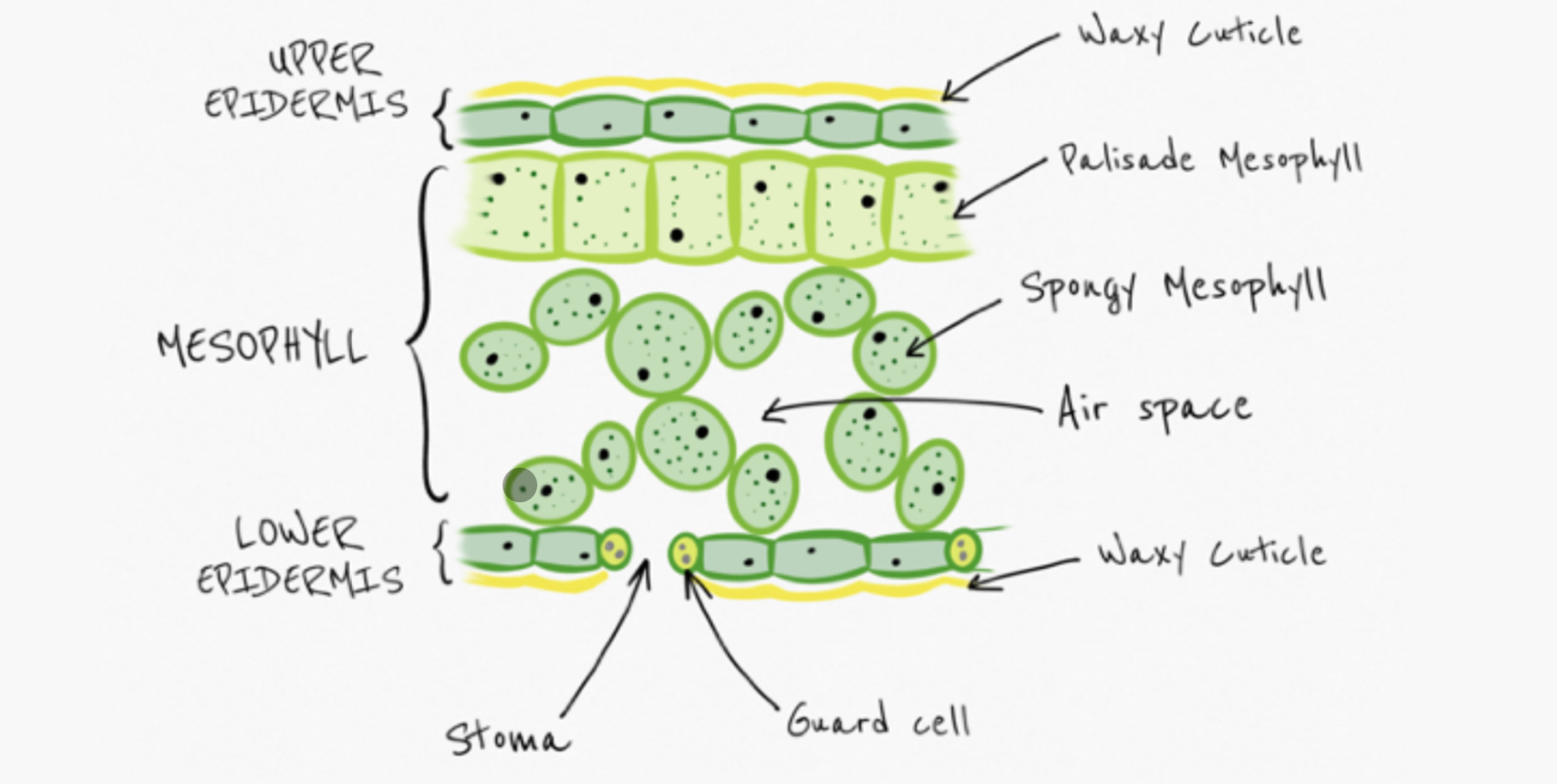
Describe and explain the structure of leaves
Waxy cuticle - prevents transpiration
Upper epidermis - transparent to allow light to enter leaf
Palisade mesophyll - contains lots of chloroplasts to absorb light
Spongy mesophyll - air spaces allow gases to diffuse
Guard cells - control opening and closing of stomata
Stomata - allow gases exchange - carbon dioxide enters, oxygen (and water) leaves
Label the different tissues
Describe how plants carry out gas exchange in the leaves
oxygen and carbon dioxide exit the leaf through the stomata by diffusion
Photosynthesis maintains gas concentration gradients in the leaf
Guard cells open the stomata during the day and close the stomata at night
Oxygen and carbon dioxide move through air spaces in spongy mesophyll
Carbon dioxide dissolves in moisture in mesophyll cell walls
Explain how water is absorbed by the roots
By root hair cells via osmosis
What is the role of the xylem
transport of water and mineral ions
From roots upwards
Provides mechanical support
Describe the structure of the xylem
continuous column
Made from dead cells
Lignin to strengthen - either spiral or annular (rings)
Pores/pits in outer cellulose wall allows water to leave xylem into adjacent leaf cells or xylem vessels
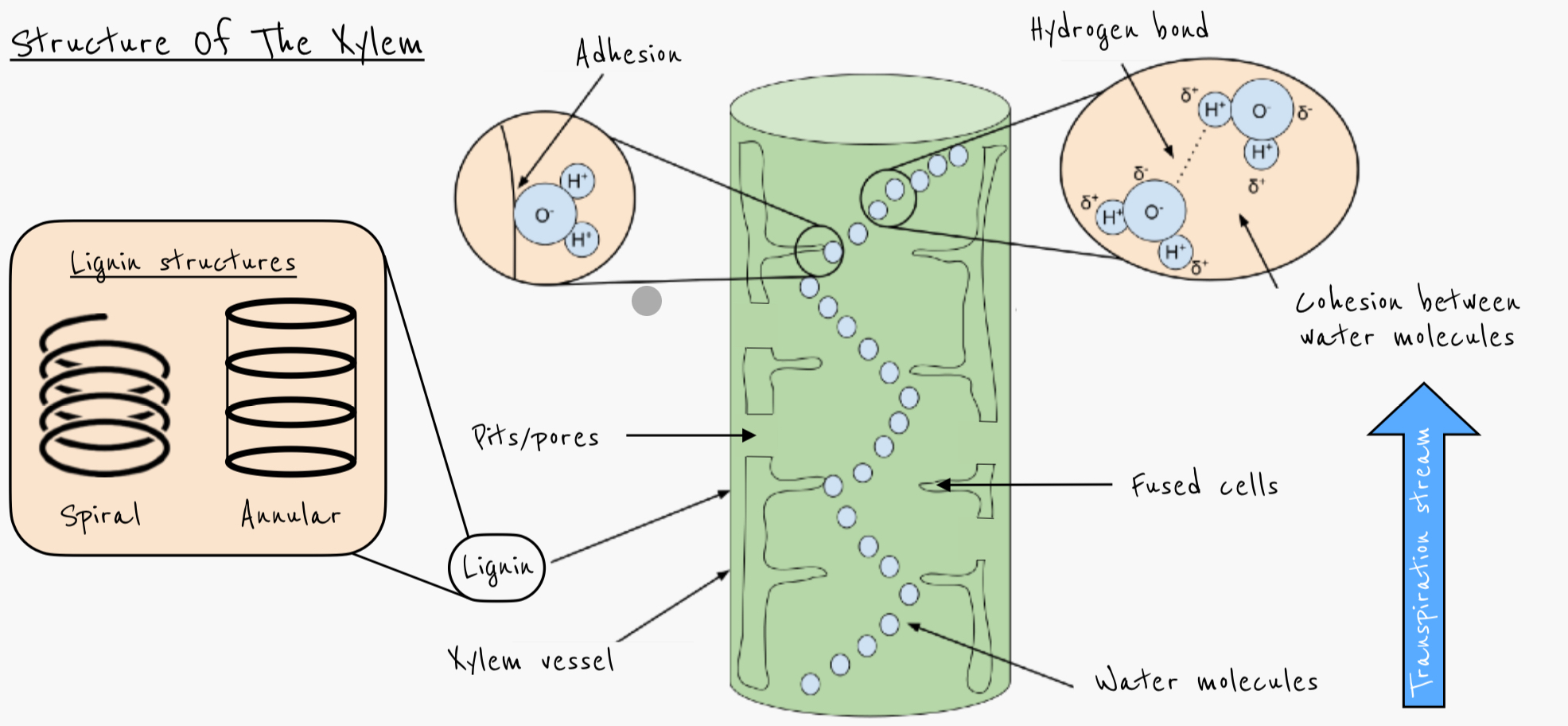
Explain why lignin is essential in the wall of a xylem vessel
Provides support to prevent collapse of the xylem
Necessary because transpiration produces tension
Waterproofs cell
Cell dies and creates continuous hollow tube
Narrow tube enables adhesion between water molecules and wall
What is the role of the phloem
transport of sugars (eg sucrose)
From source (eg leaves) to sink (storage tubers, growing shoots)
Describe the structure of the phloem
Sieve tube elements
Companion cells
Plasmodesmata between sieve tube elements and companion cells
Connects cytoplasm of the cells
Allows diffusion of sucrose from one cell to an adjacent cell
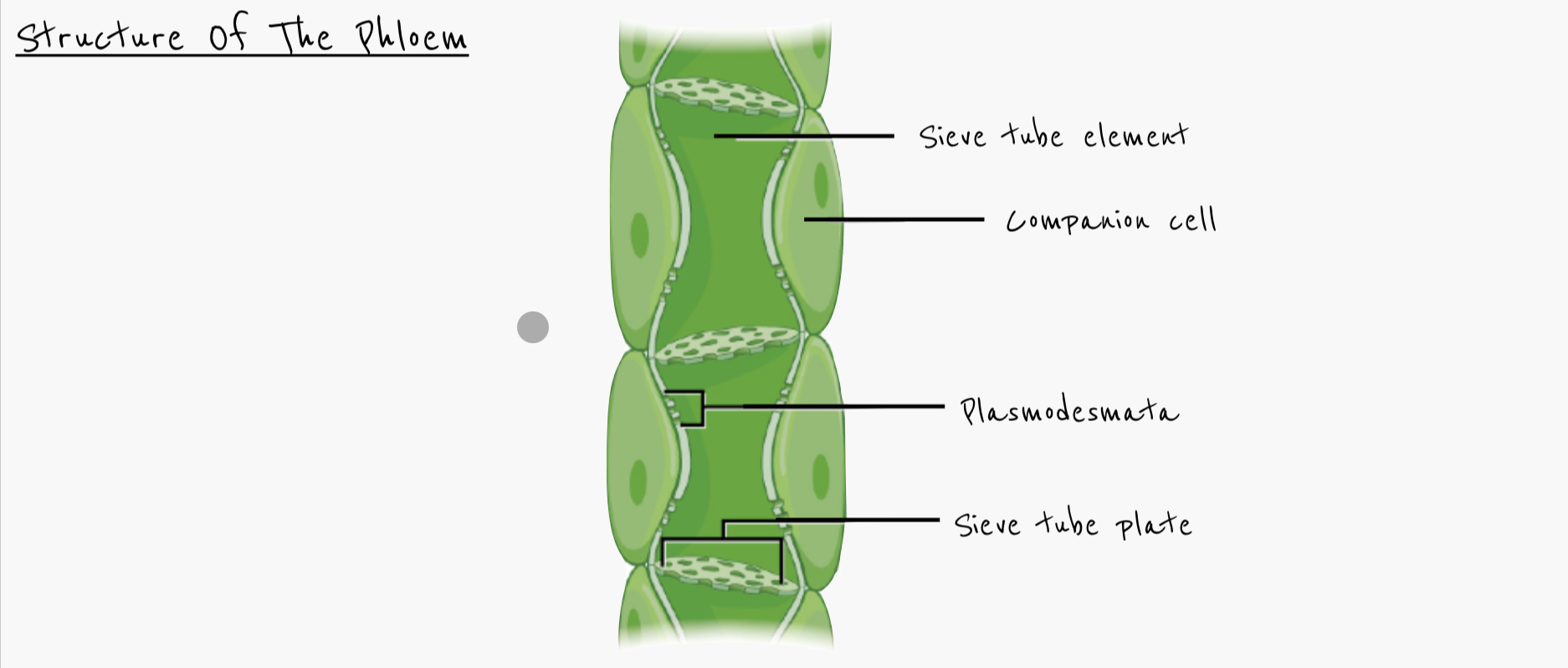
Describe the structure of sieve tube elements
long and narrow cells connected together to form the sieve tube
Connected by porous sieve plates at end of sieve elements
No nuclei or vacuole, reduced numbers of organneles
Allows maximum space for the translocation of materials
Little cytoplasm
Thick and rigid cell walls
Describe the structure of companion cells
infolding plasma membrane - increases surface area to volume ration
Allows for more material exchange
Many mitochondria - provides ATP for active transport of materials between phloem and source/sink
Transport proteins within plasma membrane move materials into or out of the phloem
Plasmodesmata between companion cells and sieve tube elements