RP 4: Simple test-tube reactions to identify cations and anions
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms

Do group 2 elements for anions or cations?
Cations
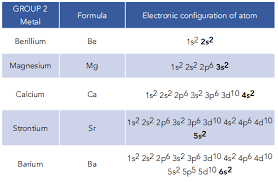
Group 2 elements:
Beryllium, magnesium, calcium, strontium, barium
What two reagents are used to conduct two different tests for group 2 ions?
Sodium hydroxide and sulfuric acid
What four group two compounds are tested?
Barium chloride, calcium bromide, magnesium chloride and strontium chloride
Why must the test tube used be clean?
To ensure a clear test result
When finished, how should the contents be disposed of?
By placing them in a bowl of water
What is the method for testing for group 2 ions using barium chloride, calcium bromide, magnesium chloride and strontium chloride with sodium hydroxide?
Place 10 drops of barium chloride in a clean test tube.
Add 10 drops of sodium hydroxide solution, mixing well and recording any observations.
Continue adding sodium hydroxide, dropwise with gentle shaking until it is in excess. Record any observations.
Once completed, dispose of the contents then repeat the test with calcium bromide, magnesium chloride and strontium chloride.
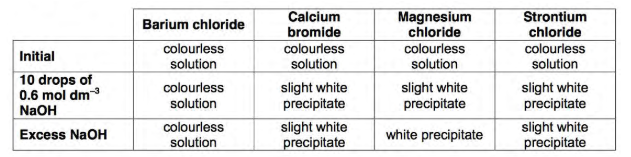
How colour does barium chloride, calcium bromide, magnesium chloride and strontium chloride all start off as?
Colourless
Which group two ion remains colourless after having 10 drops of NaOH added and even after excess NaOH added?
Barium (chloride)
What observations are seen after 10 drops of NaOH are added to calcium bromide, then after excess NaOH is added? (same observation)
The solution forms a slightly white precipitate
What observations are seen after 10 drops of NaOH are added to magnesium chloride?
Solution forms a slightly white precipitate
What observations are seen after adding excess NaOH to magnesium chloride?
Solution then forms a white precipitate
What observations are seen after 10 drops of NaOH are added to strontium chloride, then after excess NaOH is added? (same observation)
The solution forms slightly white precipitate
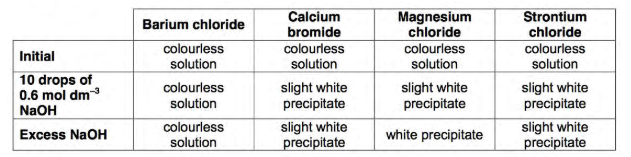
What are the expected results when testing for group 2 ions with sodium hydroxide?
Summary of results:
What method is used for testing for group 2 ions in barium chloride, calcium bromide, magnesium chloride and strontium chloride with sulfuric acid?
Same method as with sodium hydroxide:
Place 10 drops of of barium chloride in a clean test tube.
Add 10 drops of sulfuric acid, mixing well and recording any observations.
Continue adding sulfuric acid, dropwise with gentle shaking until it is in excess. Record any observations.
Once completed, dispose of the contents then repeat the test with calcium bromide, magnesium chloride and strontium chloride.
What observations are seen after 10 drops of sulfuric acid to barium chloride, then after excess sulfuric acid is added? (same observation)
The solution forms a white precipitate
What observations are seen after 10 drops of sulfuric acid to calcium bromide, then after excess sulfuric acid is added? (same observation)
The solution forms a slightly white precipitate
What observations are seen after 10 drops of sulfuric acid to magnesium chloride?
A slightly white precipitate is formed
What observations are seen after excess sulfuric acid is added to magnesium chloride?
The solution goes back to colourless
What observations are seen after 10 drops of sulfuric acid to strontium chloride, then after excess sulfuric acid is added? (same observation)
The solution forms a white precipitate
Anions: Which three halide ions are tested?
(Potassium) chloride, bromide and iodide
Which two reagents are added to potassium chloride, potassium bromide and potassium iodide to form precipitates?
Nitric acid and silver nitrate solution
Why is dilute ammonia solution then added to the test tubes?
To identify the halide ions clearly as it may be hard to distinguish between cream, white and yellow precipitates
Which halide turns colourless after dilute ammonia is added and which two has no change?
Potassium chloride turns colourless (precipitate dissolves) and there is no change in potassium bromide or iodide
How can bromide and iodide ions be identified after both solutions had no change after adding dilute ammonia?
By adding excess concentrated ammonia solution to the samples
What happens to the solutions containing bromide and iodide ions when excess concentrated ammonia is added?
Bromide - precipitate dissolves and the solution turns colourless
Iodide - no change
What method is used for testing for halide ions using potassium chloride, potassium bromide and potassium iodide?
Place about 10 drops of potassium chloride, potassium bromide and potassium iodide in three separate test tubes.
Add 5 drops of dilute nitric acid to each text tube and mix well.
Add 10 drops of silver nitrate solution to each test tube and record the observations of the precipitates formed.
Then add 2 mol dm-3 of ammonia solution (dilute) in excess and shake to mix. Record observations.
In a fume cupboard, add excess concentrated ammonia solution to the test tubes containing potassium bromide and potassium iodide and record the observations.
Discard contents of the test tubes.
In what state can halide ions can be identified using concentrated sulfuric acid?
Solid - halide ions present in solid salts
What method is used for testing for halide ions in solid salts using sulfuric acid?
Put half a spatula of solid potassium chloride in a test tube
Working in a fume cupboard, add a few drops of concentrated sulfuric acid. Record any observationns.
Repeat the experiment with solid potassium bromide and solid potassium iodide, recording any observations.
Test any gas evolved with moist blue litmus paper.
What observations do you see when adding drops of concentrated sulfuric acid to halide ions in solid salts?
Different coloured fumes:
Chloride ions = white fumes
Bromide ions = orange fumes
Iodide ions = purple fumes
What colour does the damp blue litmus paper change when the fumes from the halide ions of the solid salts come in contact with it? (Same colour)
Litmus paper turns red
Cations: What reagent is used for testing for ammonium ions, NH4+?
Ammonium chloride
What reagent is added to ammonium chloride?
Sodium hydroxide
Why is the mixture of ammonium chloride and sodium hydroxide heated gently?
Because ammonia gas is very soluble
What colour should the damp red litmus paper turn as it comes into contact with the ammonium ions and why?
Should turn blue as ammonium ions are basic
What method is used for testing for ammonium ions in ammonium chloride?
Place 10 drops of ammonium chloride in a clean test tube. Add about 10 drops of sodium hydroxide solution and shake the mixture.
Warm the mixture gently using a water bath
Test the fumes released by the mixture using damp litmus paper held by forceps to the mouth of the test tube.
Dispose of the contents by placing in a test tube full of boiling water.
Record the observations of the litmus paper.
What four ions are you testing for when testing for anions?
Halide ions, hydroxide ions, carbonate ions and sulfate ions
Anions: What colour will hydroxide ions in sodium hydroxide turn the red litmus paper?
Blue
What method is used to test for hydroxide ions using an aqueous solution containing hydroxide ions?
Test a 1 cm depth of solution on a test tube using red litmus paper or universal indicator solution
Record your observations then dispose of the litmus paper
Litmus paper will turn blue in the presence of hydroxide ions
Why can you test for hydroxide ions with ammonia?
When ammonia comes into contact with water, hydroxide ions form:
NH3 + H2O → NH4+ + OH- + H+
What method is used to test for hydroxide ions using ammonia?
Take 5 drops of 1.0 mol dm-3 ammonia solution and place on a filter paper and place inside a petri dish with lid.
Dampen a piece of red litmus paper with distilled water and place on the other side of the petri dish.
Replace the lid and observe over a few minutes.
Ammonia solution vapours will turn damp red litmus paper blue.
Anions: What reagent do you use to test for carbonate ions?
Sodium carbonate solution
What method is used to test for carbonate ions?
Add an equal, small volume of dilute hydrochloric acid to sodium carbonate solution in a test tube.
Use a delivery tube to transfer the gas produced into another test tube containing a small volume of limewater (calcium hydroxide solution).
Put a stopper into the test tube containing the calcium hydroxide solution (limewater).
Limewater goes cloudy is carbonate ions are present
Write the equation for when dilute hydrochloric acid is added to sodium carbonate solution
Na2CO3 + 2HCl → 2NaCl + H2O + CO2
Write the equation for when the carbon dioxide gas produced in the first stage is bubbled with the calcium hydroxide solution (limewater)?
CO2 + Ca(OH)2 → CaCO3 + H2O
What reagent is used to test for sulfate ions?
Magnesium sulfate
What reagents are used to test for SO4²-
Dilute HCl and BaCl2
What method is used to test for sulfate ions?
Add a recorded volume of the magnesium sulfate solution in a test tube and add an equal volume of dilute hydrochloric acid using a pipette. Tap gently to mix.
Add an equal volume of barium chloride to the solution using a clean pipette.
A white precipitate will form.