CENG112 - Lec1 & Lec2
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
Solid Waste
discharged by water closet
Liquid Waste
coming from various fixtures other than the water closet
Soil Pipe
pipes that convey solid waste
Waste Pipe
pipes that convey liquid waste
D
(DWV System) drainage of solid waste
W
(DWV System) waste coming from various fixtures other than the water closet
V
(DWV System) ventilation of the piping system
PLUMBING
is the ART and SCIENCE of installing pipes, fixtures, and other apparatus to convey and supply water in buildings and to dispose and discharge waste water and other liquids, gases, and other substances out of the buildings in a safe, orderly, healthy, and sanitary way to ensure health and sanitation of life and property
MASTER PLUMBER
a person technically and legally qualified and licensed to practice the profession of Master Plumbing without limitations in accordance with Republic Act 1378, having passed the examinations conducted by the Professional Regulation Commission, has received a Certificate of Registration from the Board of Master Plumbing, and possesses the current license to practice.
PIPE
a cylindrical conduit or conductor conforming to the particular dimensions commonly known as "pipe size" and is denoted by its interior diameter or ID.
MAIN
any system of continuous piping, which is the principal artery of the system where branches are connected.
RISER
a water supply pipe, which extends vertically to one full story or more to convey water into pipe branches or plumbing fixtures.
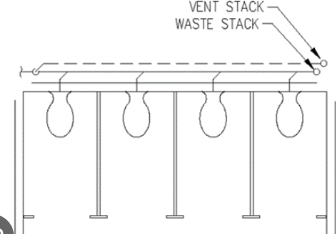
STACK
the vertical main of a system of soil, waste, or vent pipings extending through one or more stories and extended thru the roof.
BRANCH
any part of the piping system other than a main, riser or stack; a pipe that branches off from a main that serves only one terminal water fitting.
BUILDING SUPPLY
the pipe carrying potable water from the water meter or other source of water supply to a building or other point of use or distribution on the lot. Building supply shall also mean water service connection.
WATER - DISTRIBUTING PIPE
a pipe which conveys potable water from the building supply pipe to the plumbing fixtures and other water outlets.
SOIL PIPE
any pipe, which conveys the discharge of water closet, urinal or fixtures having similar functions, with or without the discharges from other fixtures to the building drain or building sewer.
WASTE PIPE
a pipe, which conveys only wastewater or liquid waste, free of fecal matter.

VENT PIPE
a pipe or opening used for ensuring the circulation of air in a plumbing system and for relieving the negative pressure exerted on trap seals.

PIPE FITTINGS
are used in pipe systems to connect straight sections of pipe, adapt to different sizes or shapes, allow rigid straight pipes to change direction, and for other purposes such as regulating (or measuring) fluid flow.
FIXTURE
a receptacle other than a trap attached to a plumbing system in which water or wastes may be collected or retained for ultimate discharge into the plumbing system.
BATTERY OF FIXTURES
any of two or more similar adjacent fixtures which discharge into a common horizontal soil or waste branch.
PLUMBING APPLIANCE
any one of a special class of device or equipment intended to perform a special plumbing function. Its operation and/or control may be dependent upon one or more energized components, such as motors, controls, heating elements and pressure-temperature-sensing elements. Such device or equipment may operate automatically through one or more of the following actions: a time cycle, a temperature range, a pressure range, a measured volume, or weight; or the device or equipment may be manually adjusted or controlled by the user or operator
PLUMBING APPURTENANCE
a manufactured device or a prefabricated assembly or an on-the-job assembly of component parts, and serves as adjunct to the basic piping system and plumbing fixtures. An appurtenance demands no additional water supply nor does it add any discharge load to a fixture or the drainage system. It performs some useful functions in the operation, maintenance, servicing, economy, or safety of the plumbing system.
DRAINAGE SYSTEM
includes all the pipings within public or private premises which convey sewage or other liquid wastes to a legal point of disposal but does not include the mains of a public sewer system or a public sewage treatment or disposal plant.
DOMESTIC SEWAGE
the liquid and water-borne wastes derived from the ordinary living processes, free from industrial wastes and of such character that permit satisfactory disposal without special treatment. It is discharged into the public sewer or into a private sewage disposal system.
LIQUID WASTE/GREYWATER –
is the discharge from any fixture, appliance, or appurtenance in connection with a plumbing system which does not receive fecal matter.
SOIL WASTE/BLACKWATER
a wastewater containing feces, urine, and flush water from toilets, often needing more intensive treatment due to the presence of pathogens.
STORM WATER
water from rainfall or snowmelt that runs off surfaces such as roads, rooftops, and other impermeable areas, often carrying pollutants with it.
INDUSTRIAL WASTE
any, and all liquid or water-borne waste from industrial or commercial processes, except domestic sewage.
BACKFLOW
the flow of water or other liquids, mixtures, or substances into the distributing pipes of a potable supply of water from any source other than from its intended source.
BACK-SIPHONAGE
the flowing back of used, contaminated, or polluted water from a plumbing fixture or vessel into a water supply pipe due to a negative pressure in such pipe.
1999 National Plumbing Code of the Philippines (R.A. 1378)
The basic principles of the ______________________ is an update of the tenets established in the “Plumbing Law of the Philippines” approved on 18 June 1955 as amended on 28 November 1959.
PRINCIPLE NO. 1
All premises intended for human habitation, occupancy or use shall be provided with a supply of pure and wholesome water supplies nor subject to hazards of backflow or back-siphonage.
PRINCIPLE NO. 2
Plumbing fixtures, devices and appurtenances shall be supplied with water in sufficient volume and at pressure adequate to enable them to function satisfactorily and without undue noise under all normal conditions.
PRINCIPLE NO. 3
Plumbing shall be designed and adjusted to use the minimum quantity of water consistent with proper performance and cleaning.
PRINCIPLE NO. 4
Devices for heating and storing water shall be so designed and installed as to prevent dangers from explosion through overheating.
PRINCIPLE NO. 5
Every building having plumbing fixtures installed and intended for human habitation, occupancy or use on premises abutting on a street, alley, or easement where there is a public sewer, shall be connected to the sewer system.
PRINCIPLE NO. 6
Each family dwelling unit on premises abutting on a sewer or with a private sewage-disposal system shall have at least one water closet and one kitchen type sink. Further, a lavatory and bathtub or shower shall be installed to meet the basic requirements of sanitation and personal hygiene.
PRINCIPLE NO. 7
Plumbing fixtures shall be made of smooth non-absorbent material, free from concealed fouling surfaces and shall be located in ventilated enclosures.
PRINCIPLE NO. 8
The drainage system shall be designed, constructed, and maintained to safeguard against fouling, deposit of solids, clogging and with adequate clean outs so arranged that the pipes may be readily cleaned.
PRINCIPLE NO. 9
All pipings of plumbing systems shall be of durable NAMPAP (National Master Plumbers Association of the Philippines) APPROVED materials, free form defective workmanship, designed and constructed by Registered Master Plumbers to ensure satisfactory service.
PRINCIPLE NO. 10
Each fixture directly connected to the drainage system shall be equipped with a water-sealed trap.
PRINCIPLE NO. 11
The drainage piping system shall be designed to provide adequate circulation of air free from siphonage, aspiration or forcing of trap seals under ordinary use.
PRINCIPLE NO. 12
Vent terminals shall extend to the outer air and installed to preempt clogging and the return of foul air to the building.
PRINCIPLE NO. 13
Plumbing systems shall be subjected to such tests to effectively disclose all leaks and defects in the workmanship.
PRINCIPLE NO. 14
No substance which will clog the pipes, produce explosive mixture, destroy the pipes or their joints or interfere unduly with the sewagedisposal process shall be allowed to enter the building drainage system.
PRINCIPLE NO. 15
Proper protection shall be provided to prevent contamination of food, water, sterile goods, and similar materials by backflow of sewage. When necessary, the fixture, device or appliance shall be connected indirectly with the building drainage system.
PRINCIPLE NO. 16
No water closet shall be located in a room or compartment which is not properly lighted and ventilated.
PRINCIPLE NO. 17
If water closets or other plumbing fixtures are installed in buildings where there is no sewer within a reasonable distance, suitable provision shall be made for disposing of the building sewage by some accepted method of sewage treatment and disposal, such as a septic tank
PRINCIPLE NO. 18
Where a plumbing drainage system may be subject to backflow of sewage, suitable provision shall be made to prevent its overflow in the building.
PRINCIPLE NO. 19
Plumbing systems shall be maintained in serviceable condition by Registered Master Plumbers.
PRINCIPLE NO. 20
All plumbing fixtures shall be installed properly spaced, to be accessible for their intended use.
PRINCIPLE NO. 21
Plumbing shall be installed by Registered Master Plumbers with due regard to the preservation of the strength of structural members and the prevention of damage to walls and other surfaces through fixture usage.
PRINCIPLE NO. 22
Sewage or other waste from a plumbing system which may be deleterious to surface or sub-surface waters shall not be discharged into the ground or into any waterway, unless first rendered innocuous through subjection to some acceptable form of treatment.