24 Trypanosomiasis, West Nile Virus, Schistosomiasis
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Sleeping Sickness or Chagas Disease
What are the common names for Trypanosomiasis?
African: Trypanosoma brucei gambiense and brucei rhodesience
American: Trypanosoma cruzi
What are the causative agents of Trypanosomiasis?
Yes
Is Trypanosomiasis zoonotic?
Trypanosoma brucei gambiense
Humans are the primary reservoir, with ungulates and primates also able to host in what species of Trypanosoma?
Cattle
Which animal is the primary reservoir for Trypanosoma brucei rhodesience?
All mammals
What animals are susceptible to Trypanosoma cruzi?
T. cruzi
Which Trypanosoma species is found in the Americas?
Trypanosomiasis
Signs for this infection include intermittent fever, anemia, weight loss, lethargy, vomiting, diarrhea, swollen lymph nodes, serous atrophy of fat, with extensive petechiation of serosal membranes in fatal cases
1-4 weeks
What is the incubation period for Trypanosomiasis?
Can have rapid death or death with chronic, untreated cases
What is mortality like for Trypanosomiasis?
Trypanosomiasis
What infection can you diagnose with observation of stained blood smears and wet mounts to look for motile parasites?
Bites from Tsetse fly
What is the vector for the AFRICAN variant of Trypanosomiasis?
Ingestion of or Bites from Kissing (redvuiid) bug
What is the vector for the AMERICAN variant of Trypanosomiasis?
Fly control (spray, dipping). Pesticides
How can you control Trypanosomiasis?
YES
Is Trypanosomiasis reportable?
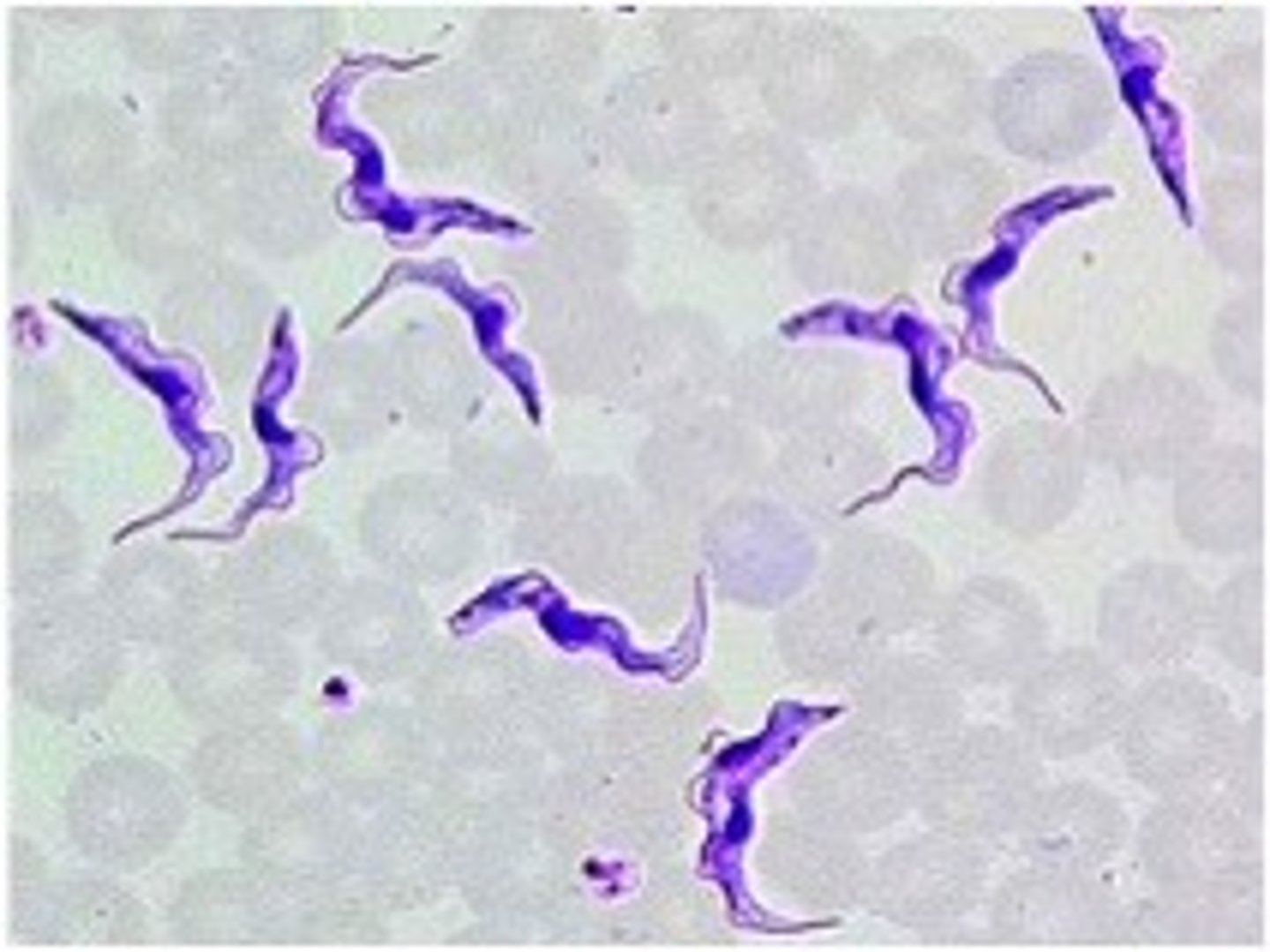
Trypanosomiasis
What is this?
West Nile Encephalitis or West Nile Virus
What does WNE/WNV stand for?
West Nile Virus
What is the leading cause of mosquito borne disease in the continental U.S.?
Flavivirus: Orthoflavivirus nilense
What is the causative agent of West Nile Virus?
Birds and alligators
What animals are the definitive host for West Nile Virus?
Horses and Humans mainly (though many other mammals are obviously included)
Though birds and alligators are the definitive West Nile Virus hosts, what other species can be infected?
Yes
Is West Nile Virus zoonotic?
West Nile Virus
This infection often presents mildly in horses, but can cause neurologic disease, lethargy, inappetence, ataxia, weakness, head/neck tremors, muscle fasciculations, opisthodomos, and convulsions/paddling
West Nile Virus
In humans, this infection presents with fever, headache, body ache, vomiting, neuroinvasive disease, encephalitis, and meningitis
Human: Morbidity: 20%, mortality 5%
Birds: normally nonpathogenic but higher mortality in American birds
Horses: Morbidity: 20%, mortality 30%
What is morbidity and mortality of West Nile Virus like in humans? What about birds and horses?
Low viral load
Why is virus detection of West Nile Virus unreliable in horses?
Bite of infected mosquito (Culex), vertical transmission (pregnancy, delivery, breast feeding)
How is West Nile Virus transmitted?
Dead End host
What types of hosts are horses and humans for West Nile Virus?
Supportive care or euthanization (horses)
How can you treat West Nile Virus?
YES
Is West Nile Virus reportable?
None for humans, vaccines for horses available
What type of vaccine is available for West Nile Virus?
Snail Fever
What is the common name for Schistosomiasis/Billharzia?
Schistosoma haematobium or japonicum or mansoni
What is the scientific name for Schistosomiasis?
Intestinal, urogenital, systemic, CNS
What different tracts can Schistosomiasis affect?
Schistosomiasis
This infection can present with a range of symptoms: abdominal pain and blood in stool, hematuria, fibrosis of bladder/ureter, infertility, eosinophilia, CNS lesions, scarring, calcification, and embolic egg granulomas
Morbidity: 75 million globally
Mortality: 12,000 deaths
How many people are affected with Schistosomiasis every year? How many die worldwide?
Fecal/urine examination for ova, serologic testing for antischistosomal antibodies
How can you diagnose Schistosomiasis?
Eggs excreted through urine, eggs hatch in freshwater and penetrate IH snail. Parasites reshed into water and penetrate DH mammal via skin contact
How is Schistosomiasis transmitted?
Praziquantel
What is the recommended treatment of choice for Schistosomiasis?
Avoid urine contact with freshwater sources
How can you avoid Schistosomiasis?
Schistosoma
This parasite lives primarily in urogenital venules and feed off RBCs, but can live in other mesenteric venules and release eggs into host intestines.