APC Nephrology and Urology
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
flank, vomiting
Nephrology: Chief Complaints
-_____ pain
-Fever (pyelonephritis)
-Fatigue/weakness (CKD)
-Pruritus (severe CKD)
-Seizures (severe CKD)
-_________ (severe CKD, pyelonephritis)
-HTN
UTIs, diabetes, CKD, labs
Questions to Ask
-Duration of symptoms?
-History of ____ or kidney stones?
-History of ________ or hypertension?
-Family history of UTIs, kidney stones, ___, hypertension, diabetes?
-When was the last time you had ____ done to check kidney function?
kidney, ureteral
Pain in #1 could be indicative of a ________ issue, while pain in #2 could be indicative of _________ pain
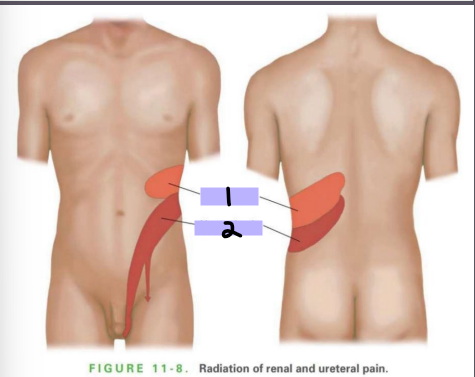
two, deeper, no, normal, palpable, thin, RUQ
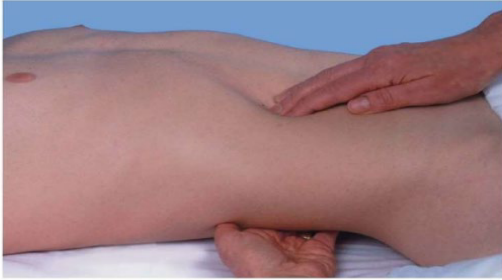
Kidney Exam: Palpation
-Search for the kidney by placing your hands together in a “duck-bill” at the person’s right flank. Press your ___ hands together firmly (you need ________ palpation than that used with the liver or the spleen) and ask the person to take a deep breath.
-In most people you will feel __ changes. Occasionally you may feel the lower pole of the right kidney as a round, smooth mass that slides between your fingers. Either condition is _______.
-A normal right kidney may be _________, especially when the patient is ____ and the abdominal muscles are relaxed. To capture the right kidney, return to the patient’s right side. Use your left hand to lift up from the back, and your right hand to feel deep in the ___. Proceed as before.
left, higher, palpable, left, abdomen, inhalation
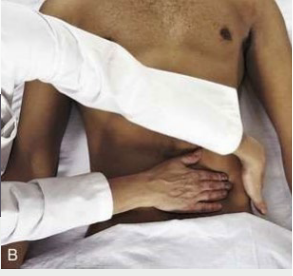
The Kidneys
-The _____ kidney sits 1 cm _______ than the right kidney, due to the liver, and is normally not _________.
-Search for it by reaching your _____ hand across the ________ and behind the left flank for support.
-Push your right hand deep into the _________ and ask the person to breathe deeply. You should feel no change with ____________.
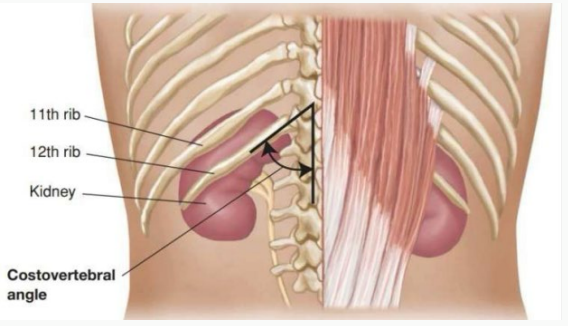
CVA, 12th, lumbar, tenderness
___ Tenderness
-CVA is formed by the lower border of the ____ rib and transverse processes of the upper _______ vertebrae
-Percussing the CVA is a way to exam kidney _____________
-Do this if the kidneys were tender to palpation
hematuria, stream, incontinence, pain, orgasm
Possible Chief Complaints: Urology
-Dysuria, _________, frequent urination
-Difficulty maintaining urine _____ / dribbling
-Difficulty urinating
-Scrotal / testicular ____
-Urethral discharge, urinary ____________
-Fever/chills (prostatitis)
-Suprapubic pain
-Dark/cloudy/malodorous urine
-Difficulty achieving erection or __________
-Premature orgasm
childbirth, symptoms, prostate, sexual
Questions to Ask: Urology
-__________ history?
-Duration of __________?
-Family history of _______ issues or cancer?
-Recent trauma?
-_________ history?
prepuce, glans, slit
Penile Anatomy: Important for Exam
-Penis is covered by _______
-Distal end of the penis is called the _____, and the base of the glans penis is called the corona of glans penis
-Penile urethra ends normally slightly posterior in flaccid penis with the vertical ____
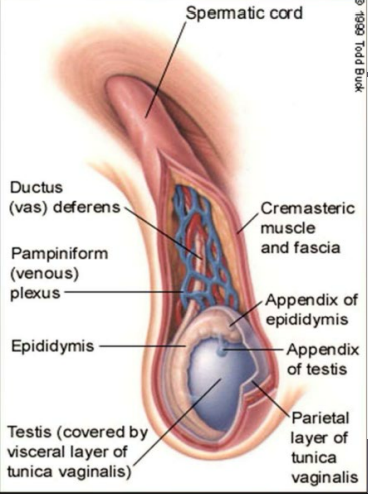
left, lower, epididymis
Testicular Anatomy
-____ testis is often ________ in the scrotum than the right testis, due largely to the length of the spermatic cord
-Posterior to testes is the _________ (comma shaped), assists in sperm maturation
suprapubic, tenderness, dull, tympanic
Bladder Exam
-Palpate for __________ mass, distention, or ____________
-Percuss the bladder
Distended bladder (full of urine) → ____ sound
Distended loops of bowel (extra gas) → __________
inguinal, femoral
Lymph Node Exam
-Check the ________ and ________ lymph nodes
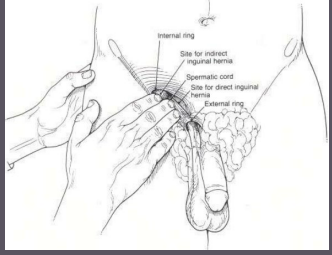
L1, L2, downward, contraction, side, absence, torsion
Cremaster Reflux
-Reflex dependent on __ and __ nerve roots
-Reflex is elicited by lightly stroking the superior and medial part of the thigh in a _________ direction
-Normal response is ___________ of the cremaster muscle that pulls up the scrotum on the ____ stroked
-Upper and lower motor neuron disorders can cause an _________ of reflex or acute testicular _______
Epididymitis
Prehn’s Test
-Scrotal elevation induces decrease of pain
-A positive result is indicative of _____________
Testicular torsion
Blue Dot Sign
-Discoloration of the scrotum that could represent ___________ _______
firm, hard, symmetric, without, tubular
Palpation of the Testis, Epididymis, and Spermatic Cord
-If using a one-handed technique, palpate each testis and epididymis between your thumb and first two fingers. If using two hands, cradle the testis at both poles in the thumb and fingertips of both hands. Palpate the scrotal contents as you gently slide them back and forth from your fingertips of one hand to the other, without changing the position of your hands as they cup the scrotum.
-This technique is comfortable for the patient and allows a subtle controlled and accurate examination. The testes should be ____ but not _____, descended, _________, nontender, and _______ masses
-Palpate each spermatic cord, including the vas deferens, between your thumbs and fingers, from the epididymis to the external inguinal ring. The vas feels slightly stiff and ______ and is distinct from the accompanying vessels of the spermatic cord
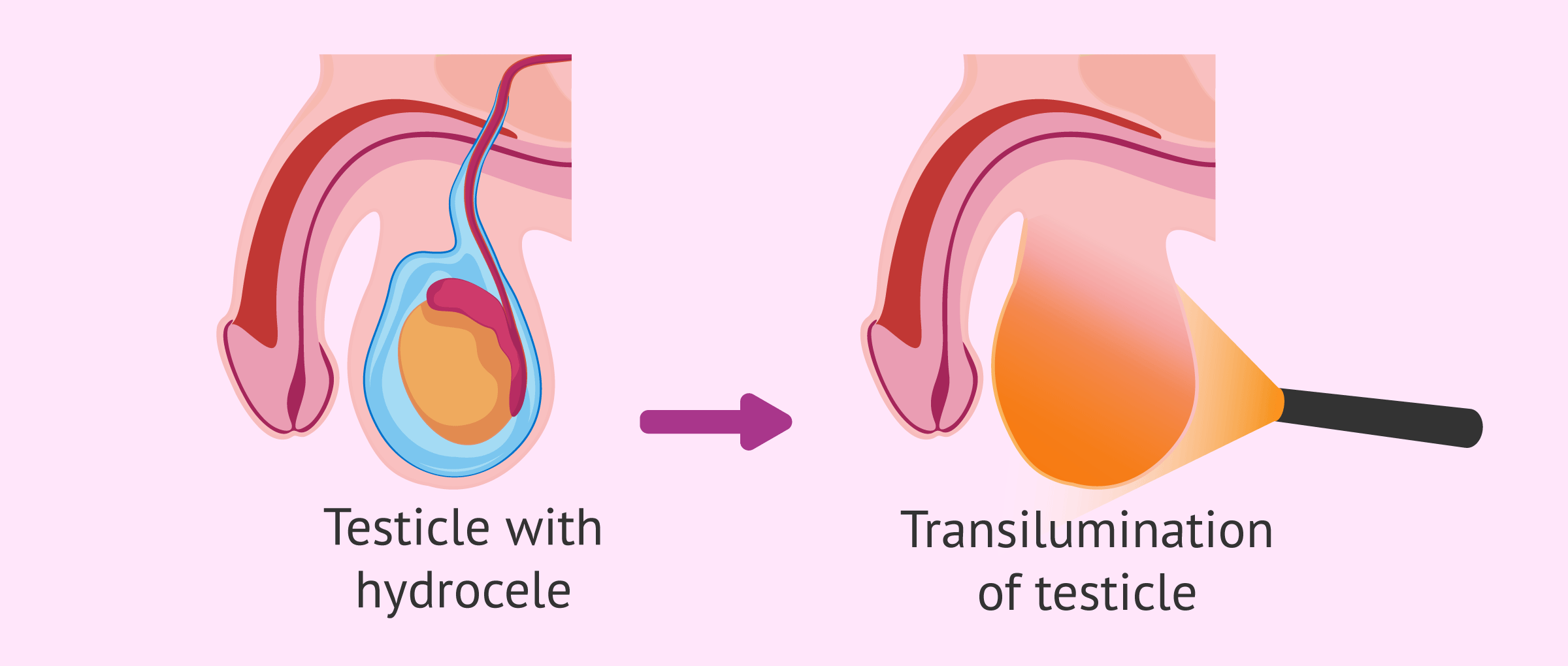
light, lump, illuminates, hydroceles, cysts, solid
Scrotal Transillumination
-Using a pen light, shine ______ from behind a scrotal ______ to observe whether the light travels through and ___________ the lesion
Cystic (light shines through) → ____________ and large epididymal _____
_____ (light blocked by the mass) → mass readily transmits light
inspect, retract, lesions, discharge, urethra, shaft, young, foreskin, paraphimosis
Penile Exam
-_______ the penis → skin and prepuce, glans (having the pt ______ the foreskin), base, shaft, pubic hair, and urethral meatus
Note any _______, nits indicating pubic lice, etc.
Note location of urethral meatus and any _________
-Palpation
Compress the glans penis gently to open the penile ________, inspect for discharge
Palpate the _____ of the penis between thumb and forefinger, checking for masses and tenderness. May omit in _____ and healthy patients.
Retract the _________ if not circumcised
Reduce the foreskin upon completion of exam, preventing ____________, which is strangulation due to tight foreskin
tight, unable, infants, scarring
Phimosis
-_____ prepuce over the glans penis that is ________ to be retracted
-Normal in ______ and toddlers
-In older children and adults, can be caused by _________, infection, or inflammation. Difficult to keep clean
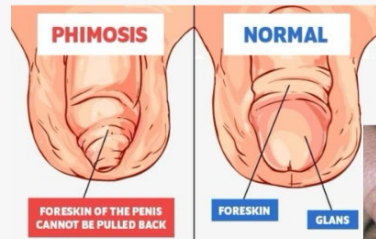
trapped, band, back, emergency
Paraphimosis
-Prepuce (foreskin) becomes _________ behind the corona and forms a tight ____ that cannot be pulled _____ over the glans
-Urologic __________
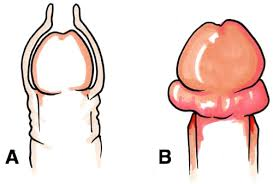
opening, urethra, tip, underside
Hypospadias
-Birth defect in which the ___________ of the ________ is not located at the ___ of the penis
-Typically on the ________ of the penis instead
urethra, develop, opening, top, tube
Epispadias
-Rare birth defect in which the _________ does not fully _________ and the urethral _________ is on the ___ of the penis
-Urethra may not develop into a full ____
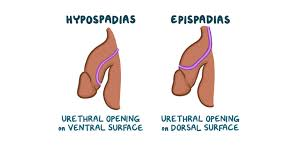
plaques, scar, painful, erection
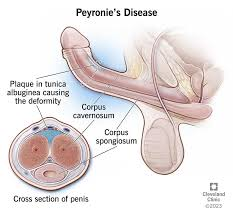
Peyronie’s Disease
-Hard, nontender, subcutaneous _________ palpated on dorsal or lateral surface of penis. Plaques are made up of fibrous ____ tissue
-Causes ________ bending of the penis during _________
undescended, scrotum, no
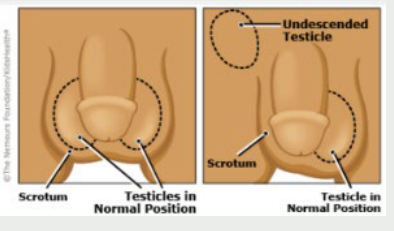
Cryptorchidism
-Absent testis or ____________ testis
-Physical exam → atrophic ________ on affected side, __ palpable testis
papule, ulcer, discharge
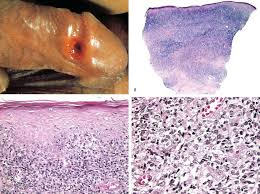
Syphilitic Chancre
-Silvery ______ that erodes to a red, oval _____ with serous ________
-Painless
swelling, glans, candida
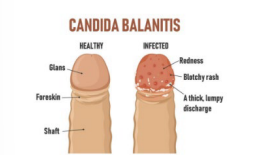
Balanitis
-Pain, _________, and inflammation of the _____ penis
-Can be caused by _______ (MC), bacteria, or dermatologic condition
pain, elevation, enlarged, tender
Epididymitis
-Severe ______ of sudden onset in scrotum, relieved by ________ (+ Prehn sign), also rapid swelling and fever
-Inspection → __________ and erythematous scrotum
-Palpation → exquisitely _____, enlarged epididymis
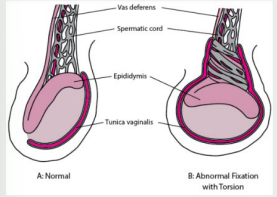
unilateral, sudden, nausea, scrotum, higher, Bell-clapper, thick, absent
Testicular Torsion
-Excruciating ________ pain in testicle of _______ onset, often during sleep or following trauma; may also have lower abdominal pain, _______, and vomiting
-Inspection → red, swollen __________, one testis (usually left) is ________ due to rotation and shortening (known as the ____-______ deformity)
-Palpation → spermatic cord feels _____, swollen, and tender. Epididymis may be anterior
-Cremasteric reflex ________ on side of torsion
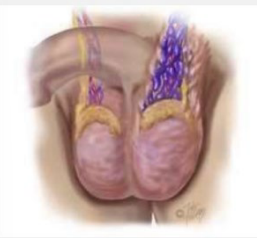
veins, asymptomatic, bluish, standing, palpable, smaller
Varicocele
-Enlarged _____ within the scrotum. May be ____________ or may cause dull pain or a constant pulling/dragging feeling
-Inspection → usually no sign, ______ color may be seen through light scrotal skin
-Palpation → when _________, soft, irregular mass posterior and superior testis is ________. Mass collapses when supine and refills when upright
-Feels distinctive, like a “bag of worms”
-Testis on the side of varicocele may be _________ due to impaired circulation
cyst, higher, movable, testicle
Spermatocele
-Also called an epididymal ____, usually painless
-Transilluminates ______ in the scrotum than a hydrocele
-Palpation → round, freely _________ mass lying above and behind the testis
If large enough, can sometimes feel like a third _________
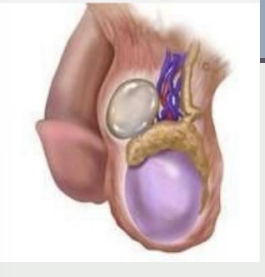
painless, fluid, inflammation, pink, nontender
Hydrocele
-___________ scrotal swelling due to _____ collecting in the sheath surrounding the testicle
-Common in newborns, usually resolving by age 1. In older children and adults, may develop due to ____________ or scrotal injury
-Inspection → mass does transilluminate with ____ or red glow
-Palpation → _________ mass
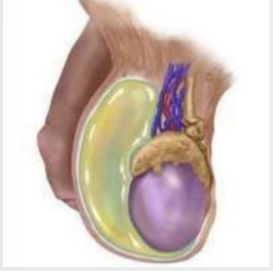
hernia, swelling, supine, not, mass
Scrotal Hernia
-Inguinal ______
-Inspection → scrotal __________. Swelling may worsen or may have pain with straining, may reduce when ______, and does ___ transilluminate
-Palpation → soft, fluctuant mass. Palpating fingers cannot get above mass, meaning ____ is distinct from testicle that is normal.
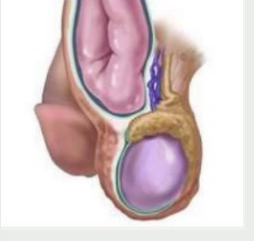
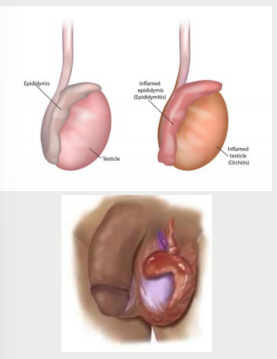
inflammation, STI, mumps, sudden, scrotum, not, tender, testis
Orchitis
-____________ of one or both testicles, usually caused by bacterial infection (___) or viral infection (_____)
-Moderate pain of ______ onset, swollen testes, fever
-Inspection → enlarged, erythematous ________. Does ___ transilluminate
-Palpation → swollen, congested, tense, and _____. Difficulty distinguishing ______ from epididymis
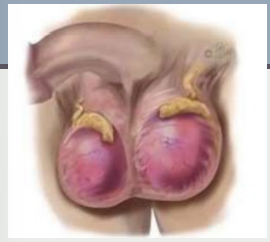
undescended, firm, testicle, heavier, not
Testicular Tumors
-Early → painless, may have history of ____________ testicle or familial testicular cancer
Palpation → ____ nodule or harder than normal section of _______, testicular swelling occurs in most
-Large → enlarging testis that feels “_______”
Mass does ___ transilluminate
Palpation → enlarged, smooth, ovoid, firm
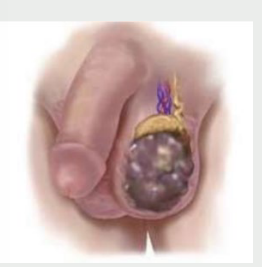
benign, scrotum, taut, scrotal
Scrotal Edema
-Usually ______ and self-limiting, tenderness
-Inspection → enlarged _______ that may be erythematous
-Palpation → ____ with pitting, difficulty palpating ______ content
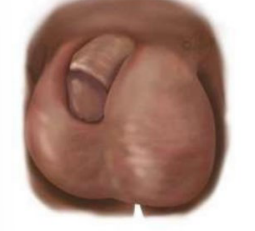
lubricated, canal, prostate, urinate, rubbery, seminal
Prostate Exam
-Have patient bend over the table or lay in the left lateral decubitus position
-With a __________ finger, gently insert into the anal _____. Flex finger anteriorly to palpate the _______ gland. Inform the patient that examining their prostate gland may prompt an urge to ________.
-Sweep your finger carefully over the prostate, identifying its lateral lobes and the groove of the median sulcus between them. Note the size, shape, mobility, and consistency of the prostate, and identify any masses/tenderness/enlargement.
-The normal prostate will be ________ and nontender
-If possible, extend your finger above the prostate to the region of the _______ vesicles and the peritoneal cavity and sweep the anterior wall. Note any nodules or tenderness
-Gently withdraw your finger, and wipe the anus or give the patient tissues
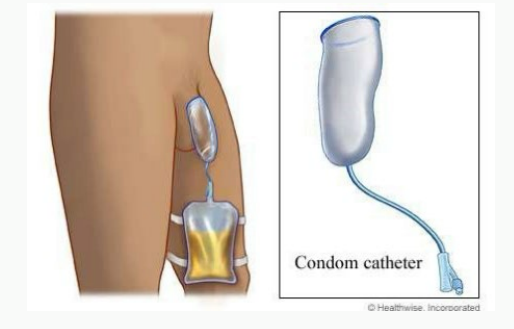
sheath, slip, decompress, AUR
Condom Catheter
-A ______ similar to a condom fits around the penis, and a tube takes the urine into a bag
-It can ____ or leak
-Doesn’t ___________ the bladder, not an option if patient is in ___
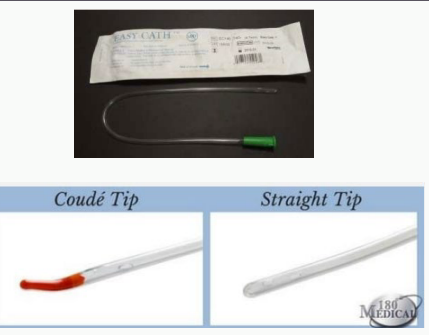
urethra, drains, several, full, straight
Intermittent Catheter
-Goes in through the _______ and ______ the bladder. Requires patient education, how toput it in and take it out
-Insert _______ times a day, either at scheduled times or whenever the bladder feels ____. The tip is either ________ or coude
suprapubic, comfortable, infection, erosion, foley
_________ Catheter
-Inserted into the bladder from the outside
-Typically more _____________ than an indwelling catheter and is less likely to cause an ___________
-Good option for patients who develop urethral ________ from urethral _____
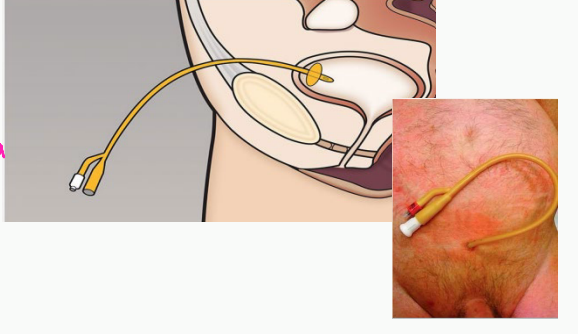
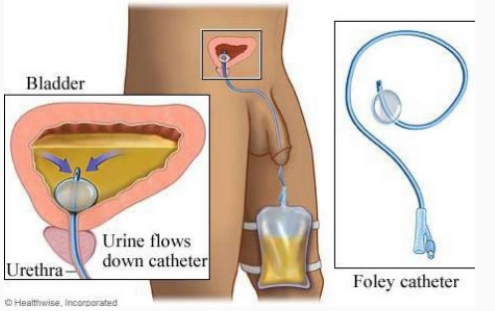
Foley, urethra, balloon, drains, 1
Indwelling Catheter
-Also called a _____ catheter
-Goes in through the _______. A tiny ________ filled with water keeps one end inside the bladder. The other end ______ out into a bag that is either strapped to the leg or hanging from the side of a bed or a stand.
-An indwelling catheter needs to be replaced at least every _ month
indwelling, surgery, trauma, prostate, meatus
Contraindications to Catheterization
-The following are only relative contraindications to insertion of an __________ urinary catheter:
Previous urethral ________
Suspected or known urethra ______ (free-floating _______, blood draining from urethral ______)
In that case, perform a urethrogram before urethral catheterization is attempted
UTI, obstruction, stones, erosion
Risks
-Catheter-associated ___
In men, epididymitis and orchitis can develop
-Urinary tract ____________ from retained balloon fragments
-Bladder fistula or perforation
-Bladder ______
-Urethral stricture, incontinence, or urethral ________ (long-term)
drainage, balloon, larger, diameter, 5, 30, rubber, 14, 18, 5, BPH, larger
Selecting a Catheter
-Foley consists of a double-lumen rubber tube with a terminal retaining balloon. The larger channel is for ________ of urine and the smaller is for inflation of the _________.
-Foley catheters are of standard length. The ______ the number, the larger the ________.
-Two sizes of balloons are commonly available → _mL balloons for routine catheterizations and __-mL balloons
-Most are made of rubber
-For routine catheterization, __F or __F rubber catheter with a _-mL balloon is satisfactory.
-Men with ___ may require larger catheters
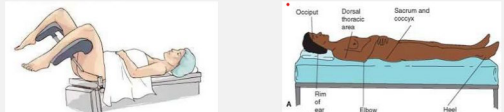
lithotomy, supine
Positioning the Patient
-Females should be in the ________ position to get a catheter, while males should be in the _____ position.
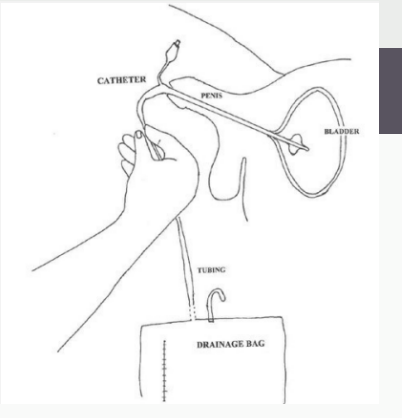
shaft, palm, right, antiseptic, tip, lubricating, urethra, base, membranous, hilt, sterile, withdraw, trigone, retract
Male Catheter Procedure
-After opening the tray and preparing the lubricant, antiseptic, and syringe, use your left hand and grasp the penis so that the _____ is in the ____ and the glans of the penis is free but secure. Should be held at a _____ angle to the abdomen. The left hand should remain in this position for the remainder of the procedure, as it is no longer sterile.
-Sterilize the ____ and urethral meatus with 3-4 swabs dipped in ________.
-Put a single loop in the Foley for easier handling, grasp the catheter in the right hand, and coat the ___ of the catheter with _________ jelly. Often helpful to place some on the meatus as well
-Insert the catheter into the urethral meatus and advance it down the penile ______ to the ____ of the penis with successive, steady movements. Advance the catheter through the _________ and prostatic urethra into the bladder.
-Advance the catheter to the ____ to ensure that the balloon is not inflated into the urethra. Release the penis
-Inflate the balloon with the proper amount of ______ water for its size and ________ the catheter until the balloon is pulled snugly against the ______
-Connect the urinary drainage system bag and tape the catheter to the upper thigh.
-If the patient is uncircumcised, remember to ______ the foreskin back.
labia, clitoris, antiseptic, two, labia, proximal, clitoris, urine, trigone, vagina
Female Catheter Procedure
-Same preparation steps as the male procedure
-Using the left hand, spread the ____ and identify the superior fornix with the ________ at the apex. Thoroughly cleanse the entire area with 4-5 swabs soaked in _________. Clean the labia with front to back strokes with ___ successive swabs; then cleanse the urethral meatus with another two successive swabs.
-Make a loop in the Foley for easier handling. Grasp catheter with right hand, coat the ___ and _________ portion with lube, and insert the catheter into the urethral meatus, which lies just below the _________.
-Advance the catheter until _____ returns. Then advance it 4-5 cm farther to make sure that the balloon is well within the bladder. Inflate the balloon with the appropriate amount of water and withdraw the catheter gently until the balloon is pulled snugly against the ______.
-Connect the catheter to the urinary drainage bag and tape it down. The most common mistake is to miss the urethral meatus and inadvertently slip the catheter into the ______. No urine will return. Try again.
upwardly, narrowed, standard, anteriorly, prostatic
Coude Catheter
-Has an ________ deflected tip, which may navigate through a __________ prostatic urethra more successfully than a _________ Foley catheter.
-The tip of the catheter should be directed ___________ to facilitate passage through the ________ urethra.
-Typically used more with males.
Foley, resuscitation, rectal, major, prostate, rupture, RUG
Trauma Patients
-Most patients with major trauma have a _____ catheter inserted during ____________. A _____ examination MUST be performed before a catheter is inserted in a male patient with _____ blunt trauma.
Feel for the ________ and make sure that it is firmly attached to the surrounding tissues.
A free-floating prostate or gross blood escaping from the urethra signifies urethral _________ until proven otherwise
A ___ may help to determine urethral integrity
urethra, stricture
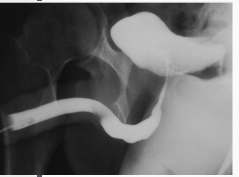
Retrograde Urethrogram (RUG)
-Shows the integrity of the ________. Retrograde injection of radiopaque contrast into the urethra, shows _________ and injury
deflated, syringe, water, empty, 24
Removing a Foley
-The catheter balloon is __________ by inserting a ________ into the catheter valve and pulling back on the syringe.
The pressure in the balloon will cause the _____ to flow into the syringe.
-Once the balloon is ______, the foley catheter can be pulled out
-Monitor urinary output for __ hours or more