ATD EXAM
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
102 Terms
Weather
Daily condition of the atmosphere; Within the day in local areas
Season
Annual condition of the atmosphere; Within the year
Tropical Seasons
Dry (El Nino) and Wet (La Nina)
Temperate Seasons
Summer, Winter, Spring, and Autumn
El Nino
Warm phase of Tropical regions
La Nina
Cold phase of Tropical regions
Climate
Condition of the atmosphere for centuries; Within decades/centuries in large continental regions
Hot-Humid, Hot-Arid, Cold, and Temperate
Enumerate the 4 different climates around the world
Hot-Humid Climate
Regions near near or around the equator (Tropical Regions)
High Water Vapors
Hot-Humid Climate
Openings are limited for more air and less sun
Sloped roof for rain
Hot-Arid Climate
No Water Content
Too hot, and dry
Buildings are well-preserved
Hot-Arid Climate
Windows are small and limited to block sun (faces north)
Thick walls and Flat roofs
Cold Climate
Little to no sun
North and South Pole regions
Cold Climate
No windows for insulation to prevent cool temperature from coming in
Temperate Climate
Moderate Openings for adaptive use for the 4 seasons (Winter, Spring, Autumn, and Summer)
Tropical Design
Minimizes Sun + Maximizes Wind (Improves thermal Comfort of a building/Indoor Quality while conserving energy)
Design Solutions for Tropical Climate (adapts to Hot and Humid Air, and Rain)
Sun, Wind, and Rain
3 Climatic Factors of Tropical Design
Hip Roof
Best roof type for tropical design because all sides has eaves with equal overhangs.
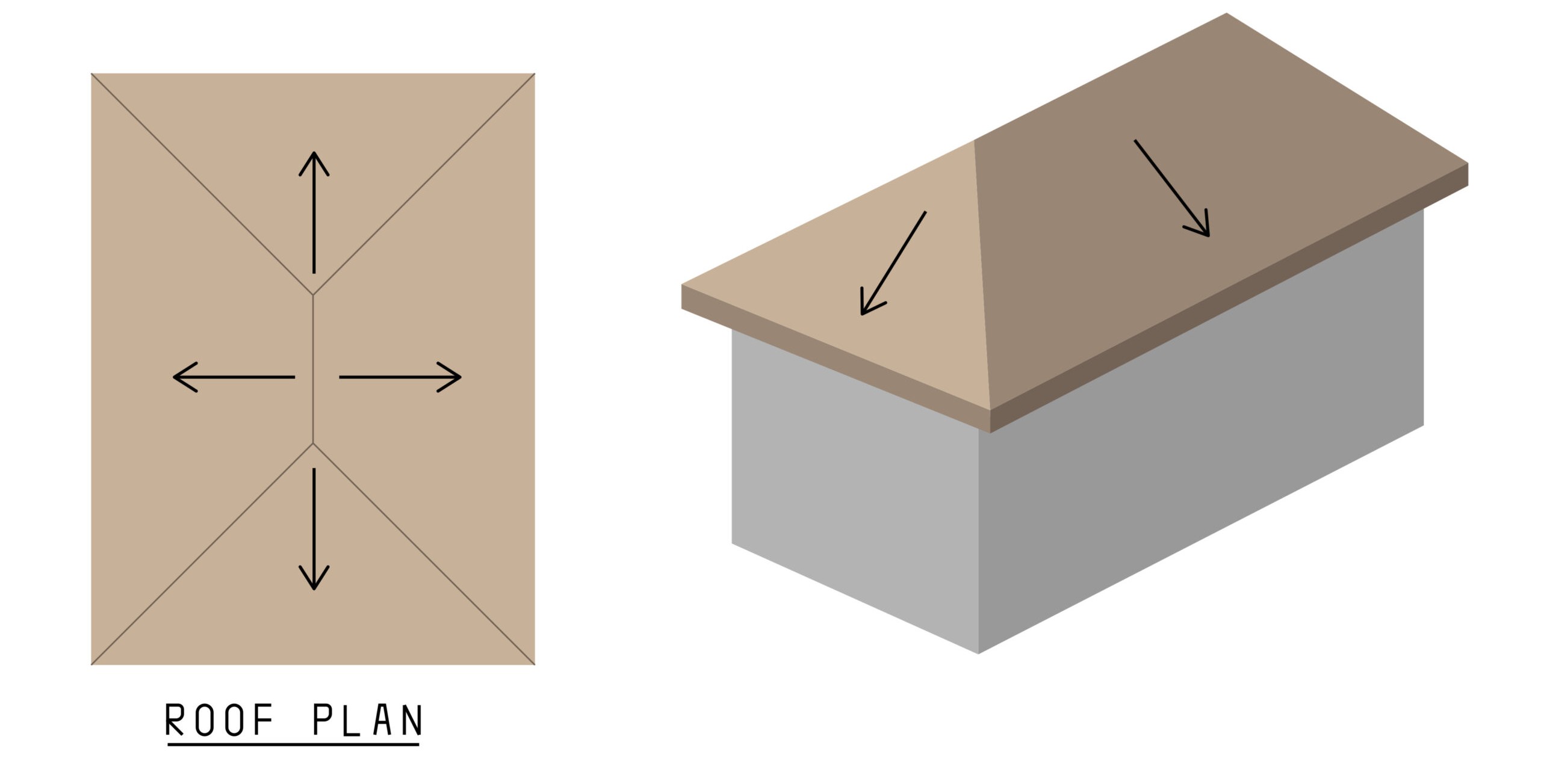
Gable Roof
Sides are protected but not front and back which is not optimal for tropical conditions
Ridge
A
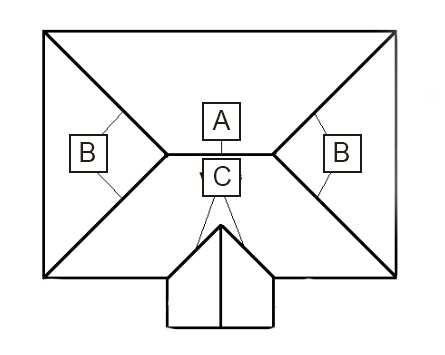
Hip
B
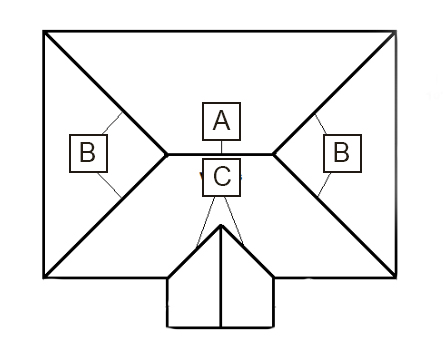
Valley
C
23 degrees 47 minutes
Tilt of the Earth’s Axis which causes Solstices and Equinoxes
Sun
In the word “Solstices”, Sol means ________
Summer Solstice
March 21st to June 21st
Sun moves from North east to North west (longest duration of sun path which makes the nights shorter and season hotter)
Winter Solstice
September 21st to December 21st
Sun moves from South east to South west (shortest duration of sun path which makes the nights longer and season colder)
Equinox
June 21st to September 21st; December 21st to March 21st
Sun moves from East to West (Average sun path duration)
Equal
In the word “Equinox”, Equi means _______
Azimuth
Angular distance WITHIN the horizon
measurement always starts from the north, clockwise
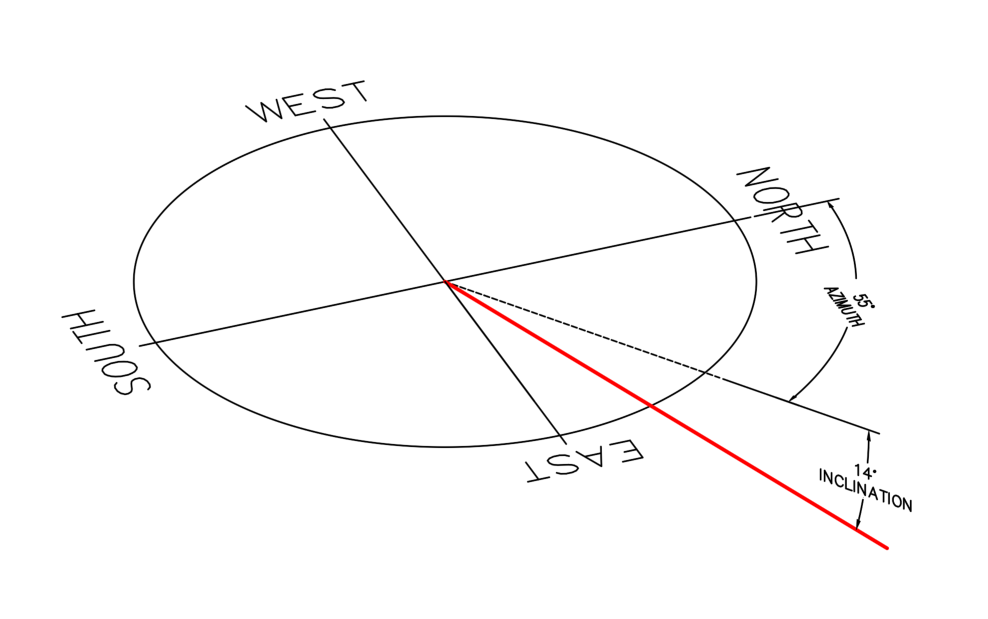
Altitude
Angular distance FROM the horizon
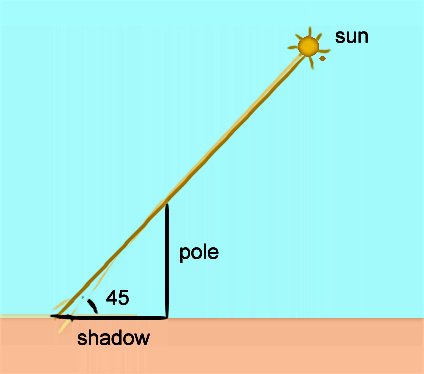
Kung gano katarik ang sun
Heat Transfer
When high temperatures pass on objects with lower temperatures
Conduction
Heat transfer through solid materials
Convection
Heat transfer through liquid or gaseous materials
Radiation
Heat transfer through electromagnetic waves
Fenestration
Openings like doors and windows which are important in shading
Building Envelope
Outermost covering of the building (Walls and roof)
Darker Colors
colors that absorb heat
Light and cool colors
Colors that reflet heat
Conduction
What type of heat transfer occurs in a building envelope?
Convection
What type of heat transfer occurs in ventilation systems?
Radiation
What type of heat transfer occurs in sunlight?
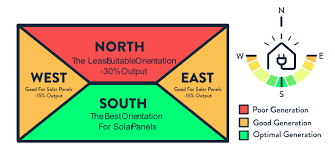
South
The direction closer to the sun and is most likely hotter which makes it the best direction to orient solar panels as well.
South
Best Dining area location according to sir Sotto
South-west
Best Kitchen location according to sir Sotto
North/North east
Best Bedroom location according to sir Sotto
West
Best T&B location according to sir Sotto
West
Best carport location according to sir Sotto
Carport
A space that helps block sun
North east/East
Best Living area location according to sir Sotto
Vertical Sun Shade
Sun shade type used for Low Altitude directions (East and West)
Horizontal Sun Shade
Sun shade type used for High Altitude directions (South)
Eggcrate Sun Shade
Combination of Vertical and Horizontal Sun Shade used for intermediate directions (NE, NW, SE, SW)
Prevailing Winds
Amihan (Northeast Monsoon) and Habagat (Southwest Monsoon)
Amihan
Cold and Low Velocity Wind (Winter Monsoon)
October to April
Month range of Amihan
Northeast
Direction of Winter Monsoon (Amihan)
The positive (+) zone
Trade Winds
Constant winds (present throughout the year)
They are Easterly winds (winds coming from the east)
Habagat
Hot and Humid, and High Velocity Wind (Summer Monsoon)
It comes along with rain (Tagulan and Typhoons)
May to September
Month range of Habagat
Southwest
Direction of summer monsoon (Habagat)
The negative (-) zone
Trees
Wind breakers, a solution to break wind from typhoons caused by Habagat
Amihan
desirable wind for buildings
Habagat
undesirable wind and should be avoided in buildings
6:1
Ratio of roofing
West-East
Best orientation of roofing
Windward
Positive Zone (+) (Northeast), where the wind enters or originates
Leeward
Negative Zone (-) (Southwest), where the wind exits
High Pressure to Low Pressure
What happens to wind pressure if wind enters (Windward) a building (Leeward)
Windward to Leeward
Flow of Wind: From positive zone to negative zone
Awning Windows
Best window considering Tropical Design
Casement Windows
If wind is sideways, wind cannot enter this type of window because it is only open upfront
Least resistance
Wind flows through areas with what?
Screens
They offer wind resistance. Remove for Stronger wind current
Lower and Higher
Ideally, Windows in windward should be _____ and ______ on Leeward. (Hot air rises)
above and below
Hot air is always _____ and cold air stays ______
Materials Recovery Facility
MRF
Habagat (Southwest Monsoon)
MRF is an exception, it needs this type of wind
Ground Level windows
This window level works best with Tropical design. However, it is not recommended considering electrical, privacy, and child safety
Artificial Ventilation
Ventilation that requires energy
Active Ventilation
another term for artificial ventilation
2.4 meters
minimum ceiling height for atificially ventilated spaces
For faster process of cooling a space. (Lesser volume, faster cooling)
Why are standard ceiling heights lower in artificially ventilated spaces?
Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning
HVAC
Window-type aircon

Cabinet-type aircon

Split-type aircon

Cassette-type aircon
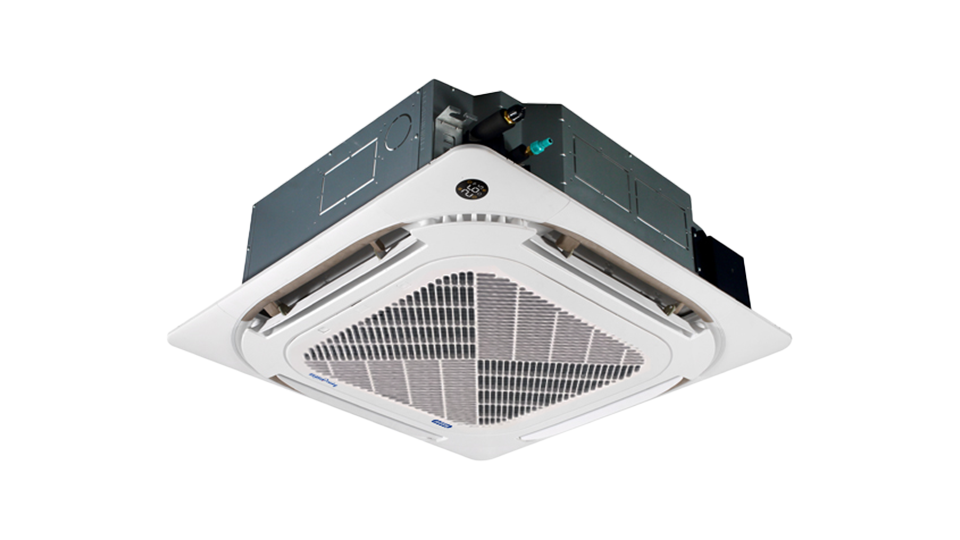

Energy Efficiency Ratio (ERR)
Identifies an aircon’s rating of energy consumption (Higher rating = Lesser energy consumption)
Natural Ventilation
Ventilation that does not require energy to work
Passive Ventilation
Another term for natural ventilation
2.7 meters
minimum ceiling height for naturally ventilated spaces
Primarily to separate hot air from spaces that are accessible to users (hot air circulates upwards). Also, for better air circulation.
Why are standard ceiling heights higher in naturally ventilated spaces?
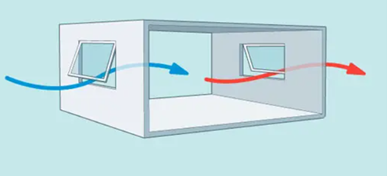
Cross-ventilation
2-opposite windows in a single space
Single-sided ventilation
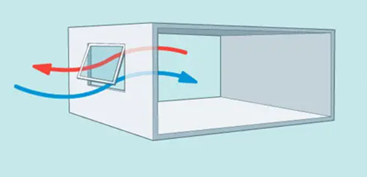
smaller, larger
2 separate _______ windows (for entry and exit) are more preferrable than 1 _______ window in a single-sided ventilation
Wind Catcher (Concrete Ledge)
an exterior element that helps redirect wind into the windows.

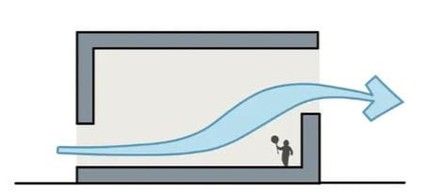
Stack effect Ventilation
Use of hot air pressure to suction heat from the building outside through a space in the middle called the atrium.
Mostly used in high-rise buildings
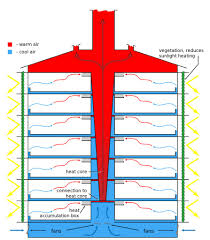
Chimney Effect ventilation
Another term for Stack effect Ventilation
Courtyard Ventilation
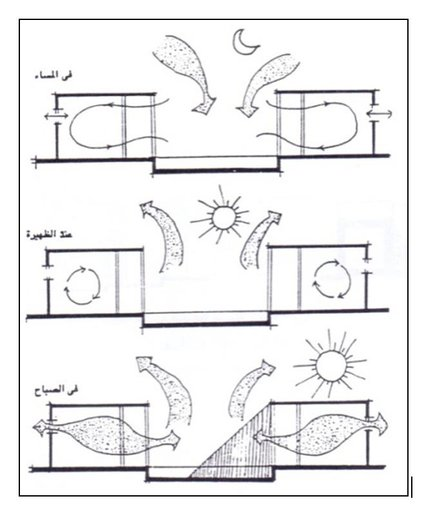
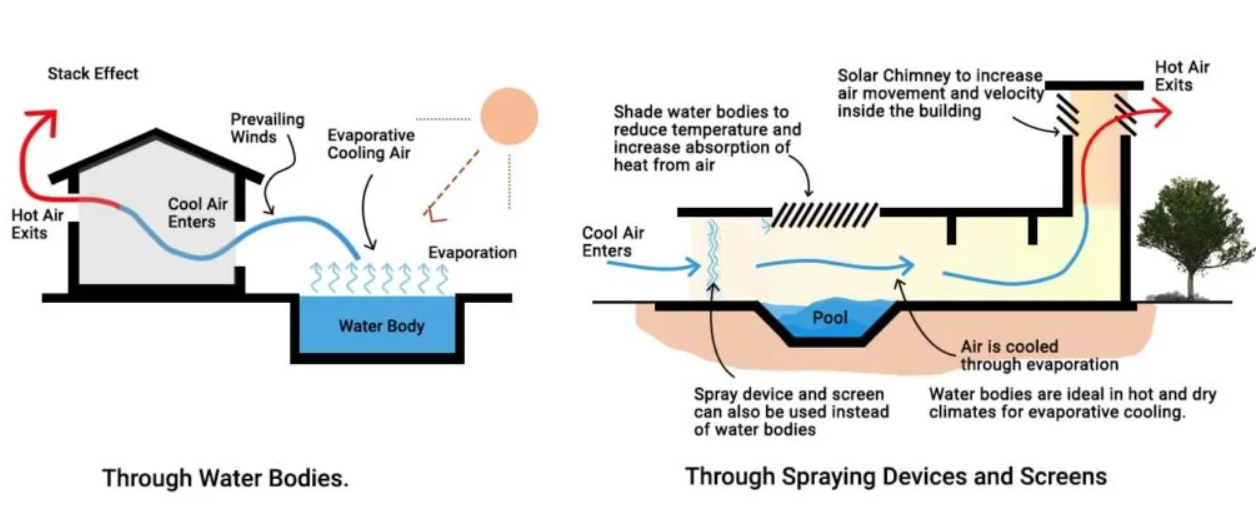
Evaporative Cooling
Use of any forms of water through evaporation to cool the building