electrophilic aromatic substitution
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
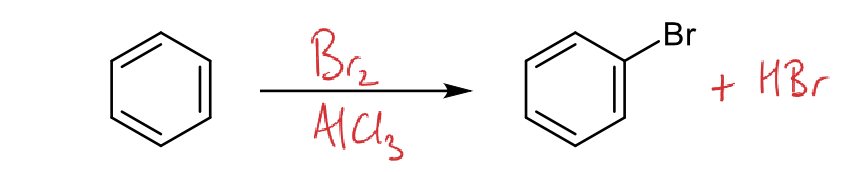
why is a lewis acid catalyst used for electrophilic substitution?
bromine must be activated by lewis acid (electron acceptor)
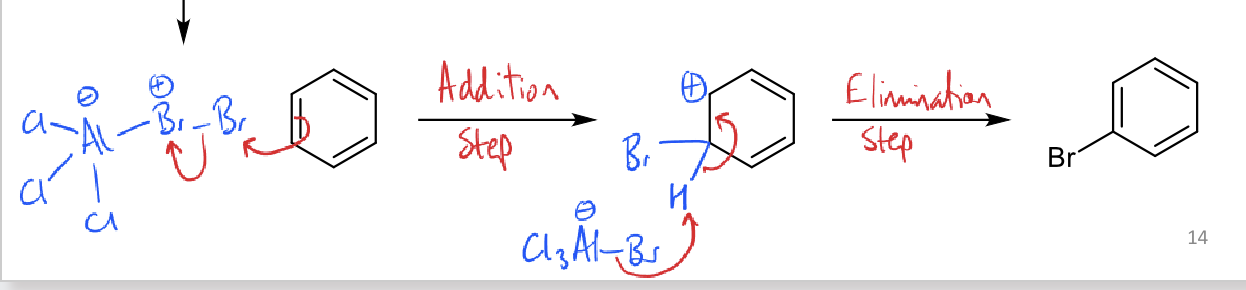
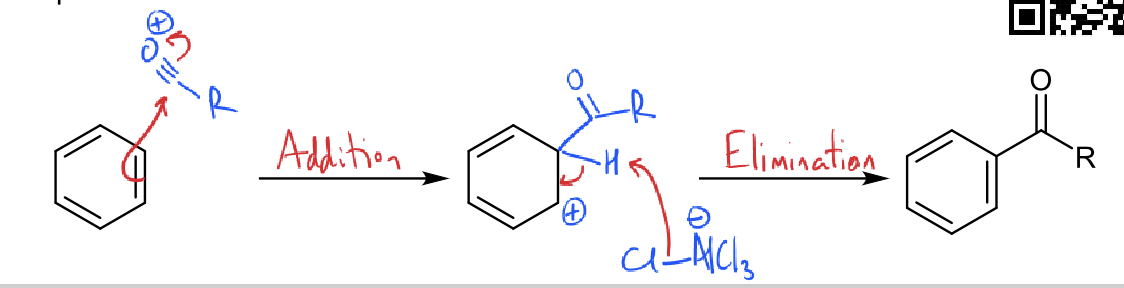
why is addition slow and elimination fast?
slow because breaking aromaticity
fast because restoring aromaticity
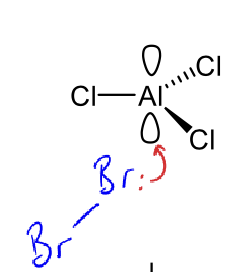
how does the lewis acid get involved in electrophilic substitution reaction (e.g. AlCl3)
what are electrophilic substitution steps for Br2 reacting with benzene?
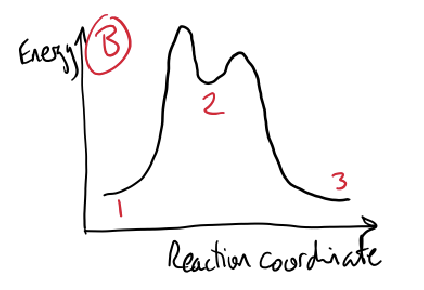
what is the energy profile diagram of electrophilic substitution?
higher activation energy for first step as breaking aromaticity
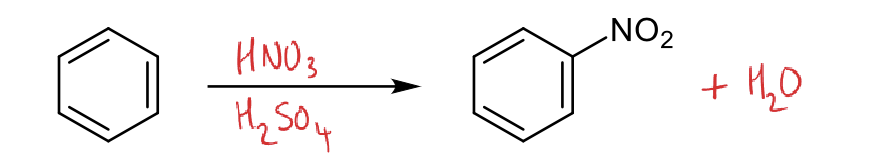
what is the reaction for nitration?
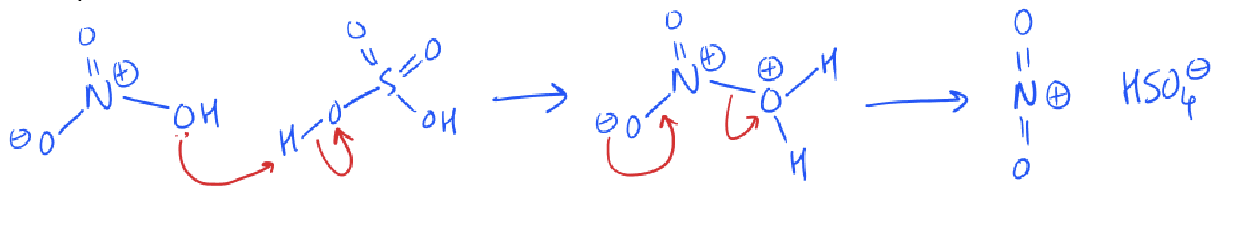
how is the nitronium ion formed? (from HNO3 and H2SO4)
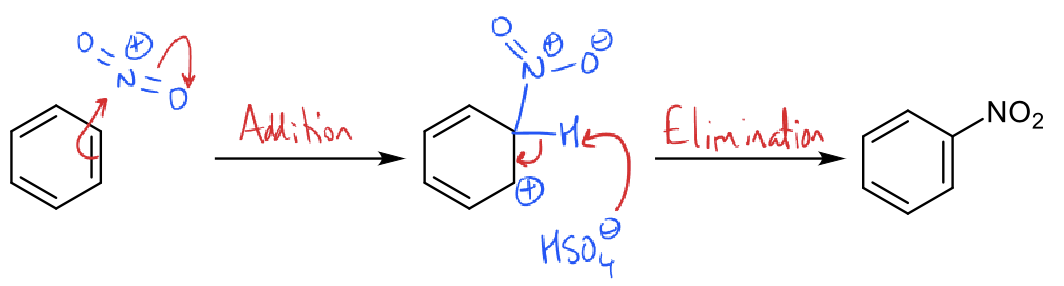
what is the mechanism for nitration?
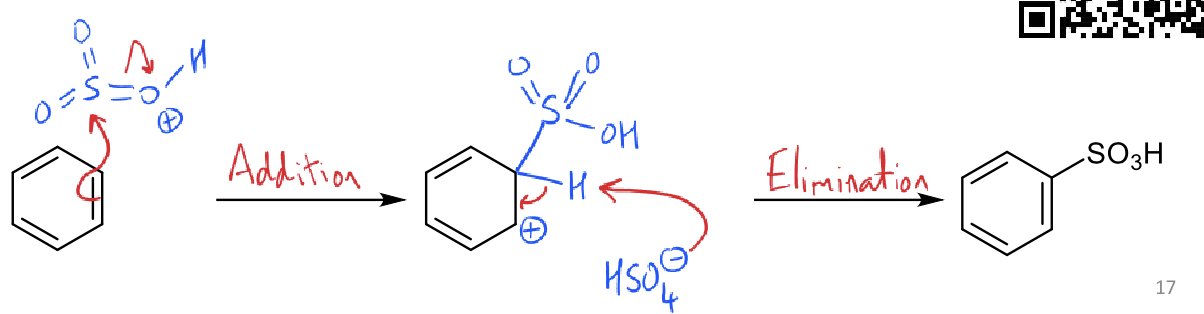
what is the sulfonation reaction?
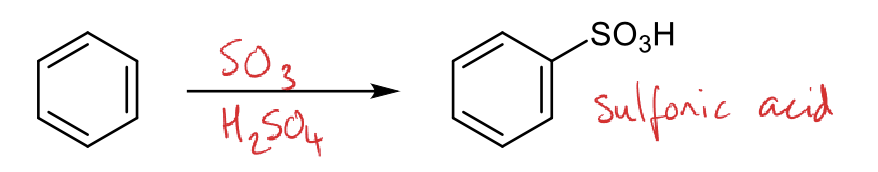
mechanism for protonation of sulfur trioxide (SO3 and H2SO4)

what is the mechanism for sulfonation?
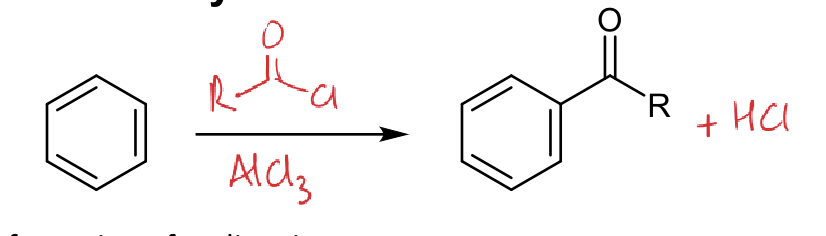
what is the friedel crafts acylation reaction?
mechanism for formation of acylium ion (acyl chloride and AlCl3)
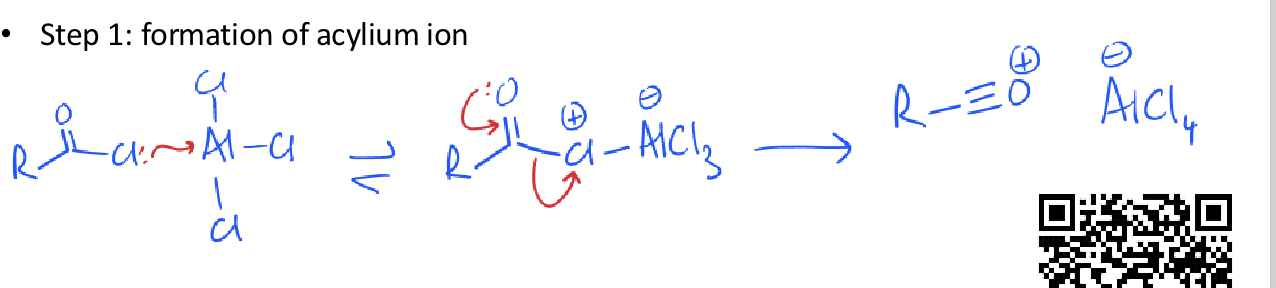
friedel crafts acylation mechanism
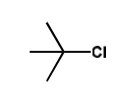
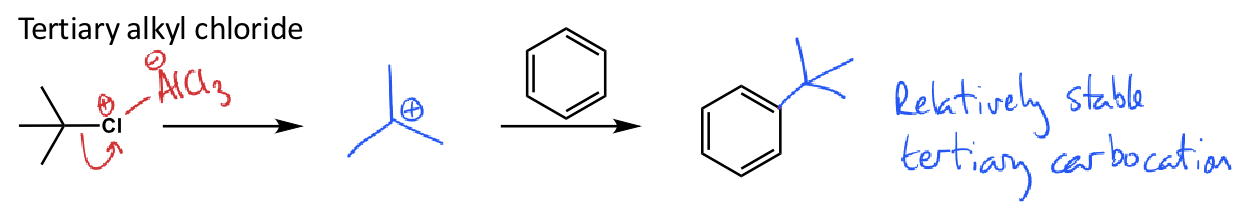
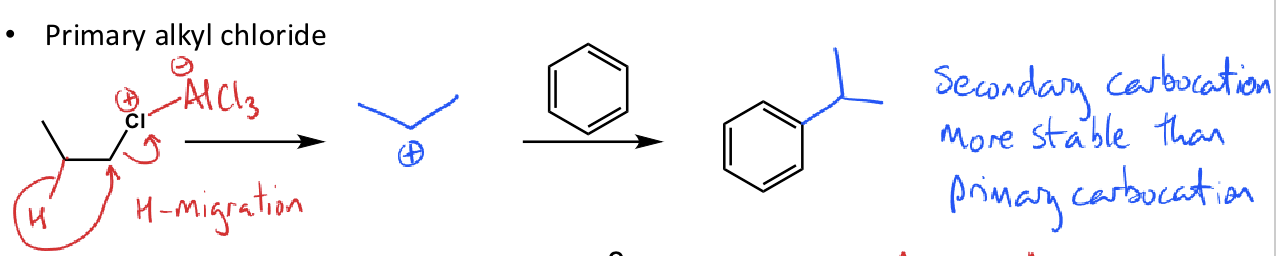
what is the friedel crafts alkylation for tertiary alkyl chloride?
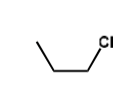
primary alkyl chloride friedel crafts alkylation
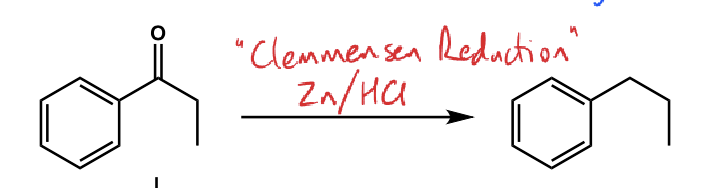
what is Clemmensen Reduction?
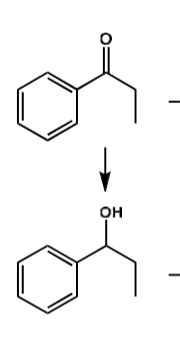
what is the conditions?
NaBH4
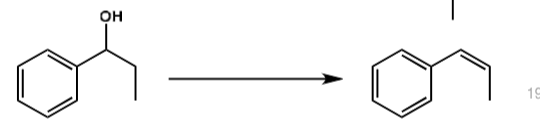
what are the conditions?
H2SO4
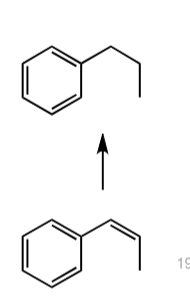
what are the conditions?
H2 / Pd
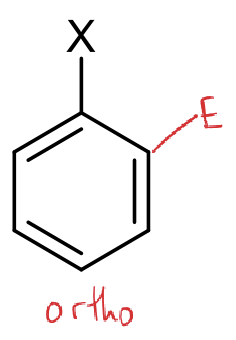
where is the ortho position?
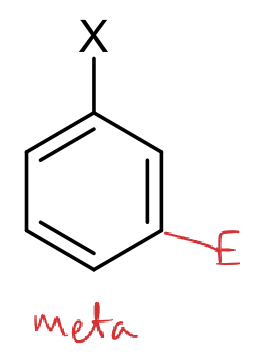
where is the meta position?
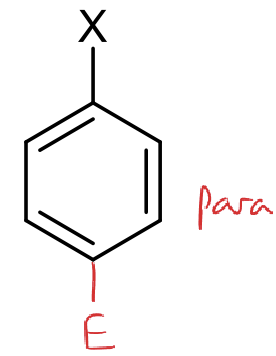
where is the para position?
if X is an electron donating group, how does this affect electrophilic substitution reactions?
rate? position?
rate increases
happens preferentially at ortho and para
if X is an electron withdrawing group, how does this affect electrophilic substitution reactions?
rate?
positons?
rate decreases
happens preferentially at meta
where does electrophilic attack occur?
at carbons with highest electron density
what does a lower chemical shift mean?
more shielding
more electron density
more nucleophilic
does electron rich or deficient aromatics react faster?
electron rich reacts faster
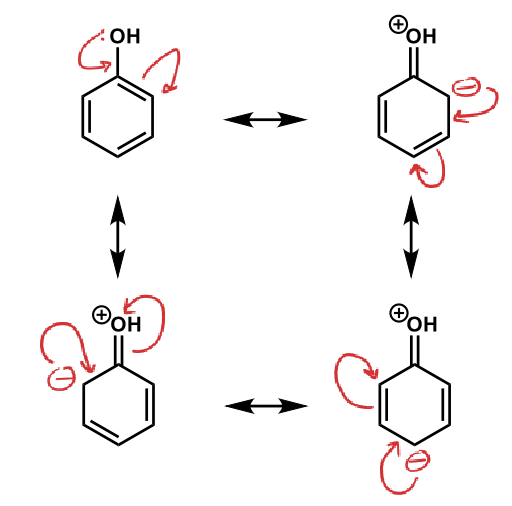
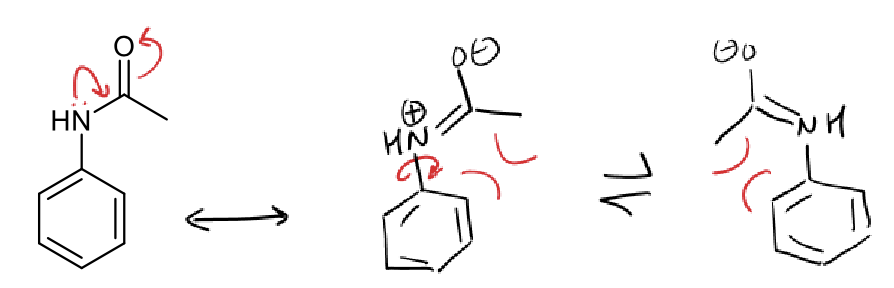
show resonance of phenol
what does a higher chemical shift mean?
less shielding
less electron density
less nucleophilic
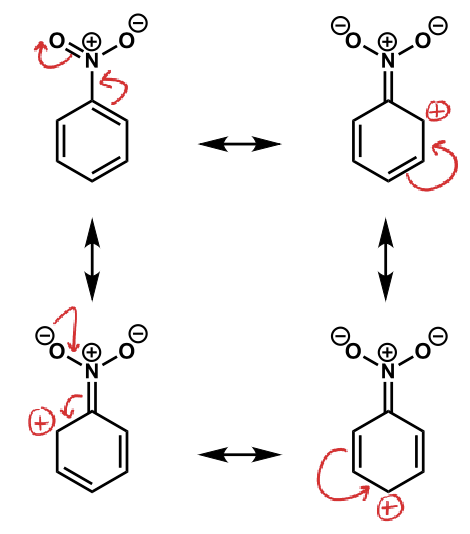
show resonance
how does positive charges (electron withdrawing) affect positions?
deactivates ortho/para
least deactivated is meta which is why reactions happen here
how do inductive electron withdrawing groups affect position?
activate/deactivate?
strongly deactivating and meta directing
meta most likely, then ortho
how do inductive electron donating groups affect position?
activating/deactivating?
weak activating and ortho/para directing
ortho most likely, then para
how do electron donating groups affect positive charge on ipso carbon?
what substitution position is favoured?
stabilises positive charge
ortho/para substitution favoured
how do electron withdrawing groups affect positive charge on ipso carbon?
what substitution position is favoured?
positive charge destabilised
meta substitution favoured
diagram of ortho substitution and resonance structures stabilising positive charge on ipso carbon
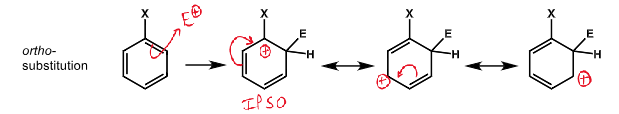
diagram of para substitution and resonance structures stabilising positive charge on ipso carbon
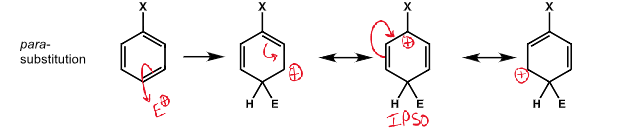
diagram of meta substitution and resonance structures destabilising positive charge on ipso carbon
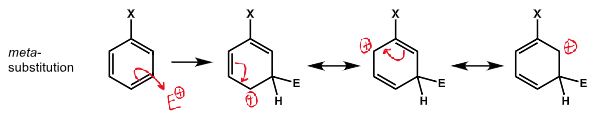
are halogens activating/deactivating?
what position do they direct?
deactivating
ortho/para directing
para more likely than ortho
why is N activating by resonance while Cl is not (when they are both deactivating by induction)?
N has better orbital overlap than Cl for lone pair donation
why is fluorobenzene more reactive than chlorobenzene?
fluorine lone pairs overlap better with benzene pi system than chlorine lone pairs
more efficient at electron donation by resonance
what is chemo selectivity?
which functional group in a molecule reacts
how is phenol an ambidentate nucleophile?
it can react at either carbon or oxygen depending on the electrophile
is phenol more or less reactive than benzene?
phenol is much more reactive
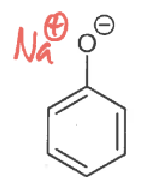
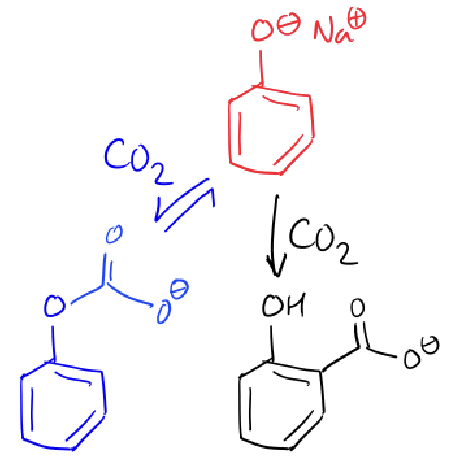
phenol + NaOH → ?
phenolate ion + CO2 → ?
draw resonance structures
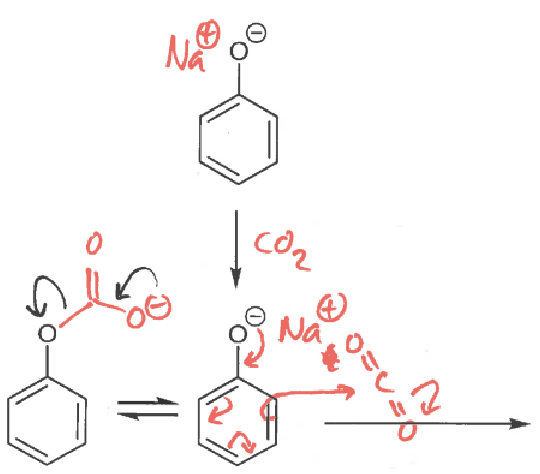
what are the two reaction pathways for CO2 and phenol?
which is faster?
the reaction with the phenolate oxygen is faster
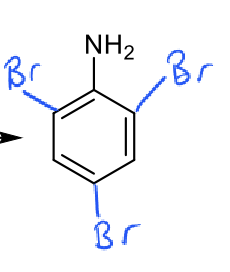
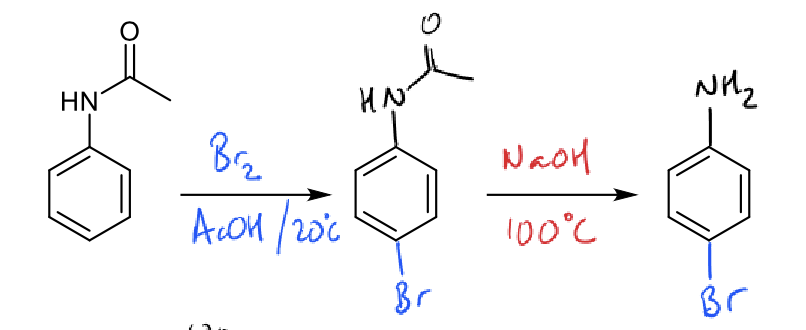
conditions and product of aniline reacting with bromine
0ºC
aniline and acetic anhydride product
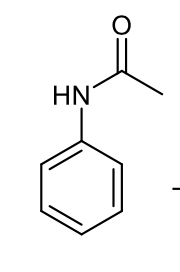
how does the acetylation of amine group on aniline affect electron donation?
reduces electron donation into aromatic ring
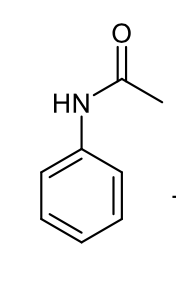
how does acetylation of amine group on aniline affect steric hindrance?
creates steric hindrance around ortho position
double bond is in the same place
how to make monobromine aniline? (hint: with acetylation)
hydrolysis with NaOH
how do deactivating groups affect substitution?
more deactivating groups allows clean mono-substitution
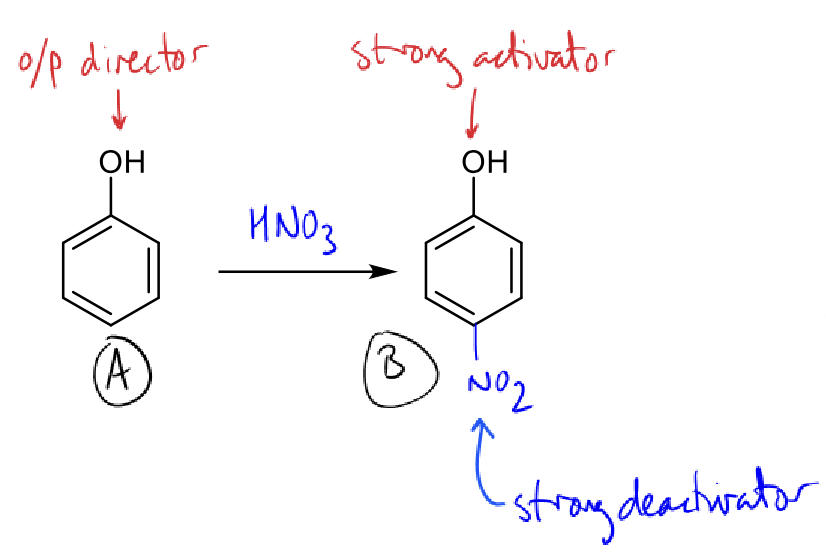
why does the nitration reaction stop at mono-substitution?
B is less reactive than A due to deactivating group
how do activating groups affect substitution?
more activating groups encourage multiple substitutions
how do multiple activating groups affect position?
the strongest activator will determine which position reacts next
alkylation reactions
what type of groups do they introduce (activating/deactivating)?
when do they stop?
introduce additional activating groups
alkylations occur until steric factors prevent additional reaction
do acylation reactions favour mono substitution or multiple substitutions?
acyl group deactivates the ring so product is less reactive than reactant
stops at mono substitution
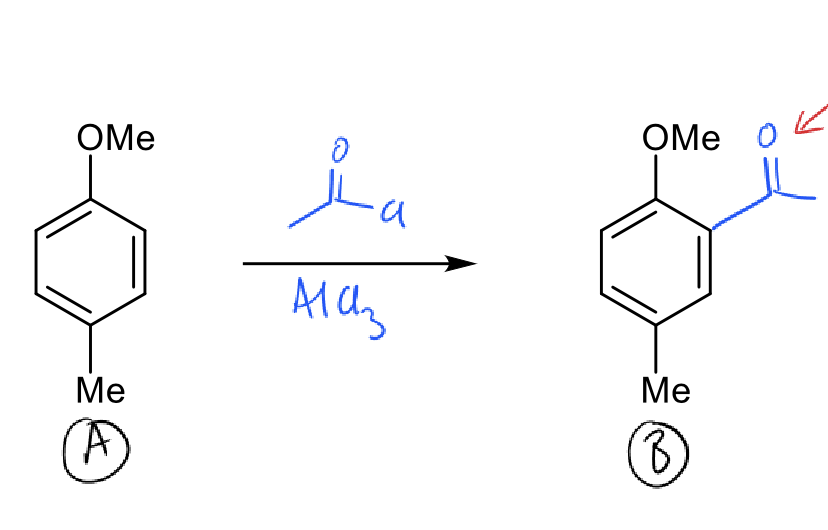
how to do monoalkylation (hint: acylation)?
acylation reaction which stops at monosubstitution
reduce by Clemmensen reduction (Zn/HCl)
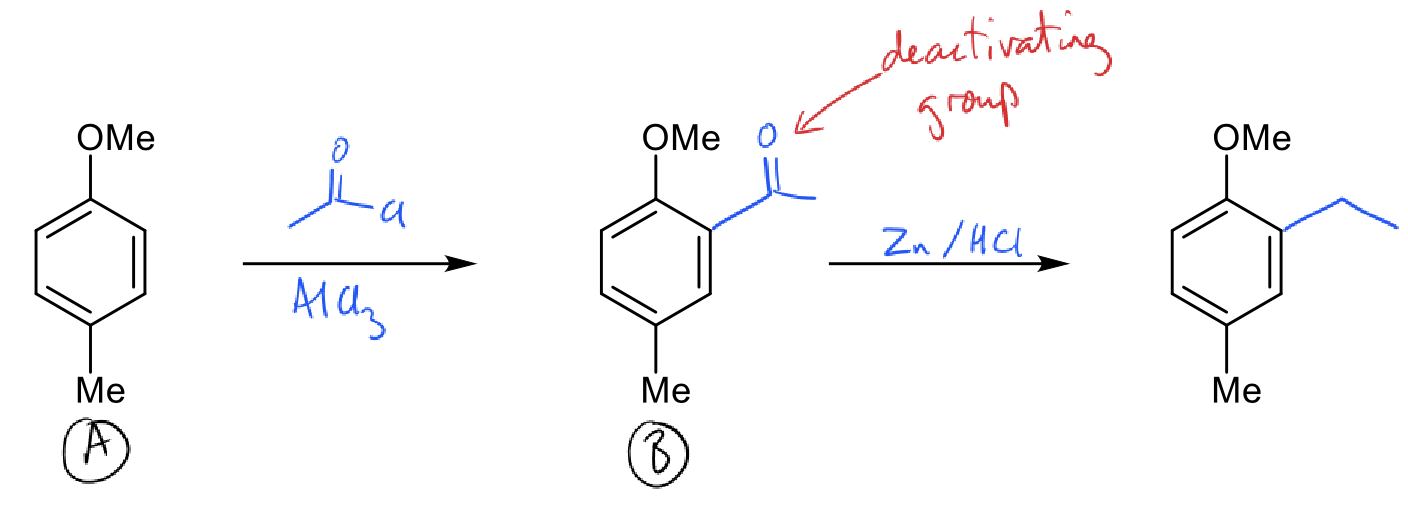
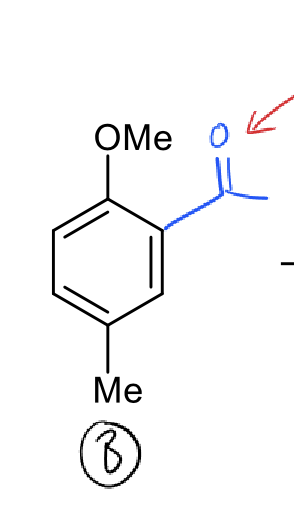
why is the carbonyl group deactivating?
conjugation, so pulls electron density out of the ring
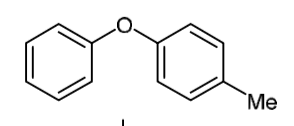
which of these rings is more reactive?
which positions are most reactive?
the ring on the right is more reactive
extra EDG, Me is weakly activating
the most reactive positions are the ortho positions on the right
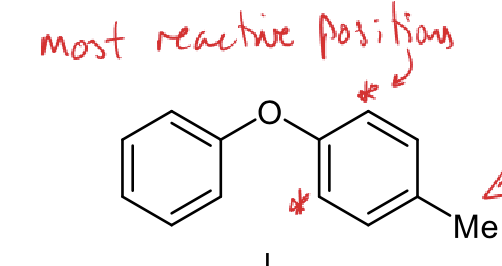
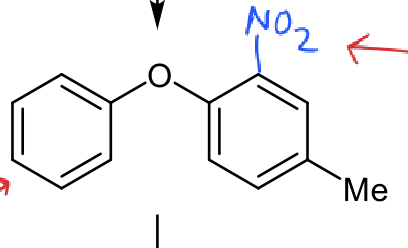
which ring is most reactive?
although Me is weakly activating, NO2 is strongly deactivating so the ring on the left is most reactive
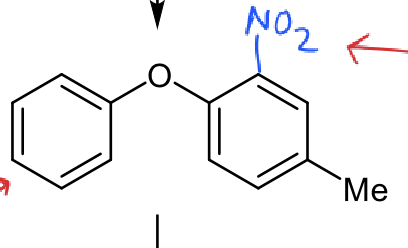
where will further nitration take place on this molecule?
on left ring
para position
least sterically hindered
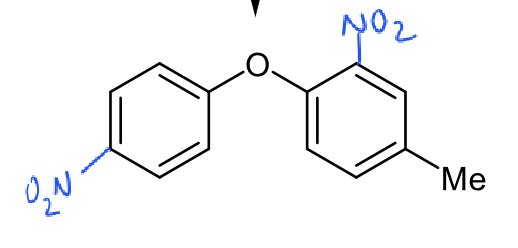
how to brominate phenol at the meta position?
why is this not usually possible?
hydroxy group is o/p directing so Br won’t go to meta position
use a nitro group as a meta directing deactivator
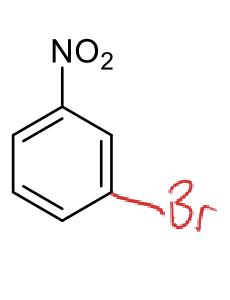
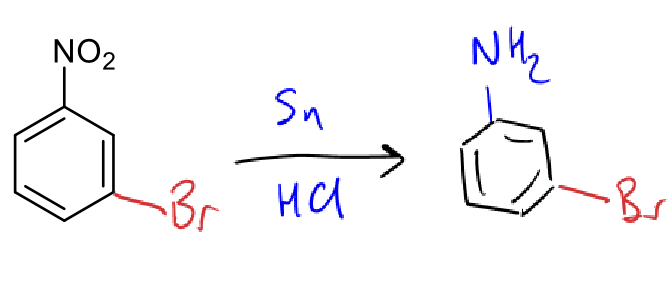
how to reduce?
diazotisation reactants?
NaNO2 and HCl
aniline
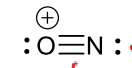
how is diazotisation reactant formed?
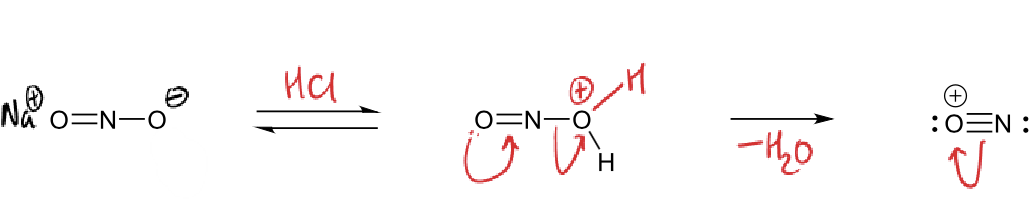
diazotisation mechanism
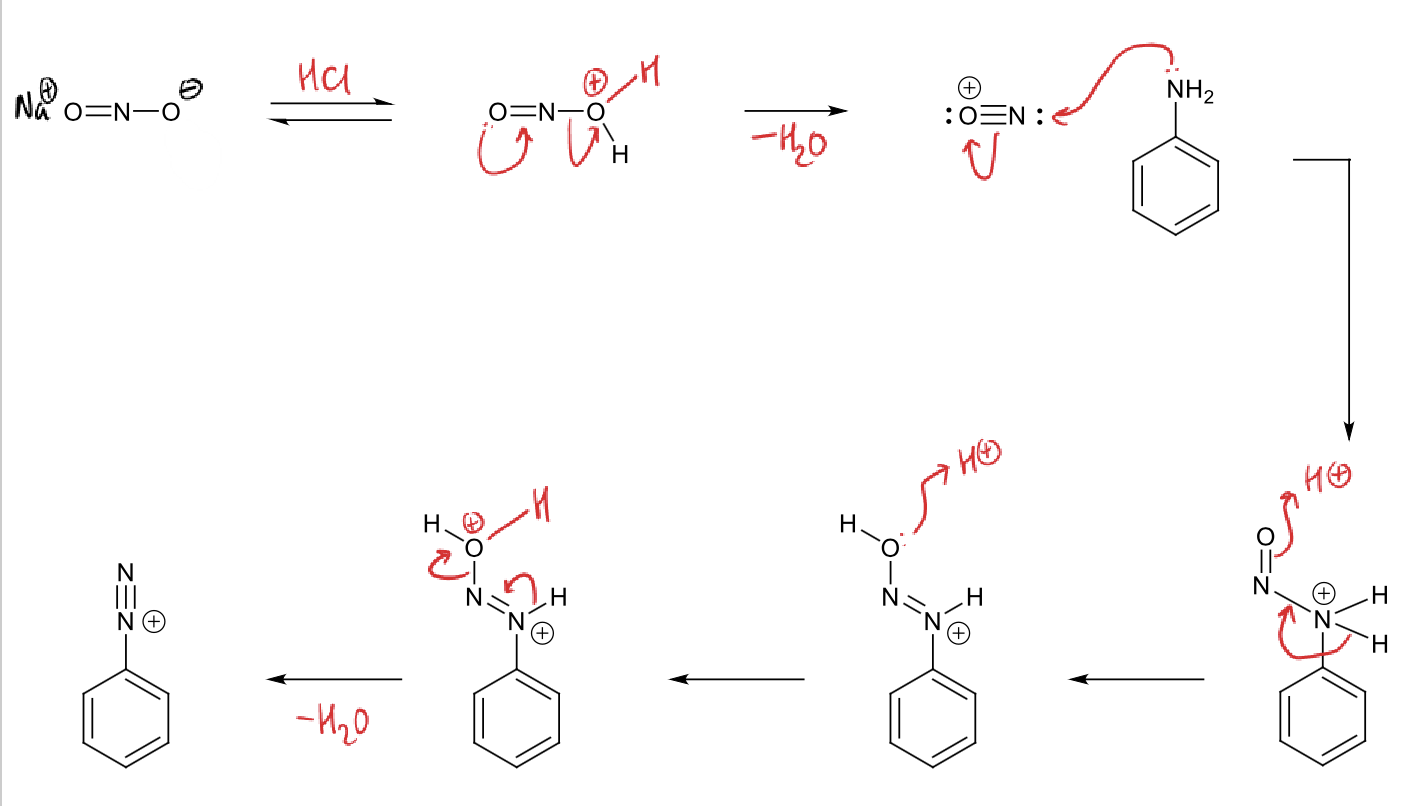
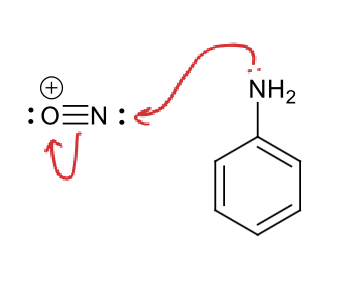
why does this step happen?
from most electron rich to most electron deficient
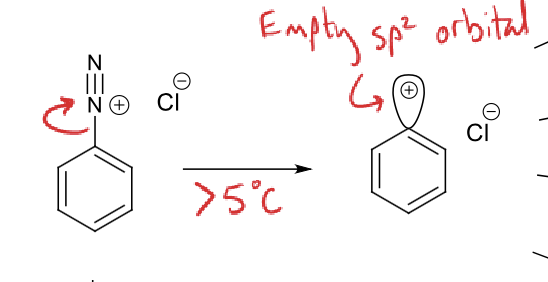
what happens when diazonium ion is in conditions above 5ºC?
how does this help Sn1 reactions?
N2 leaves
leaving empty sp2 orbital for nucleophile to attack
diazonium ion + HBF4 (heat)?
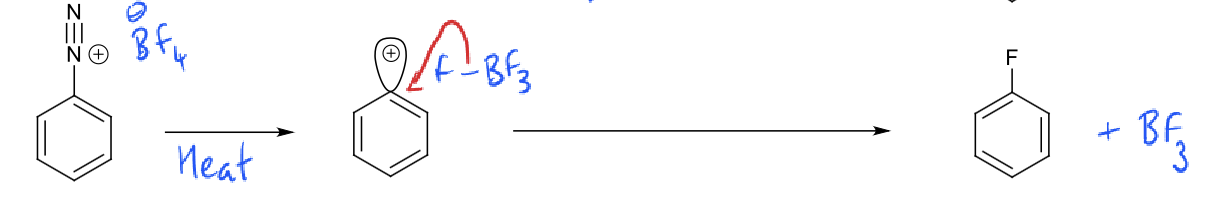
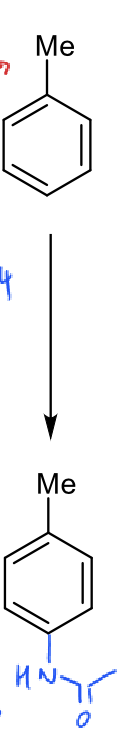
three steps to add amide group?
why would you add an amide group?
HNO3 and H2SO4 (nitration)
Pd / H2 (amine)
Ac2O (amide)
stronger ortho/para director so can add another atom at meta to Me position
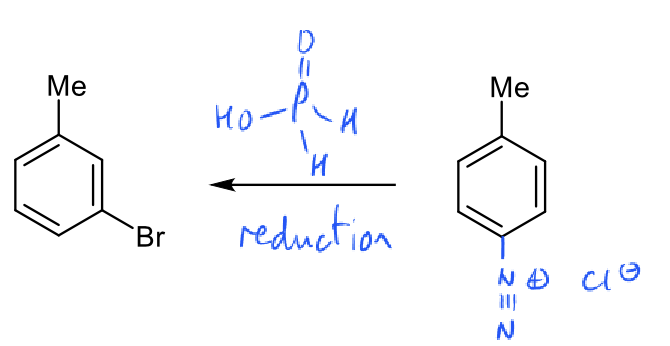
how to reduce diazonium ion to H atom?
heat above 5 degrees
hypophosphorous acid
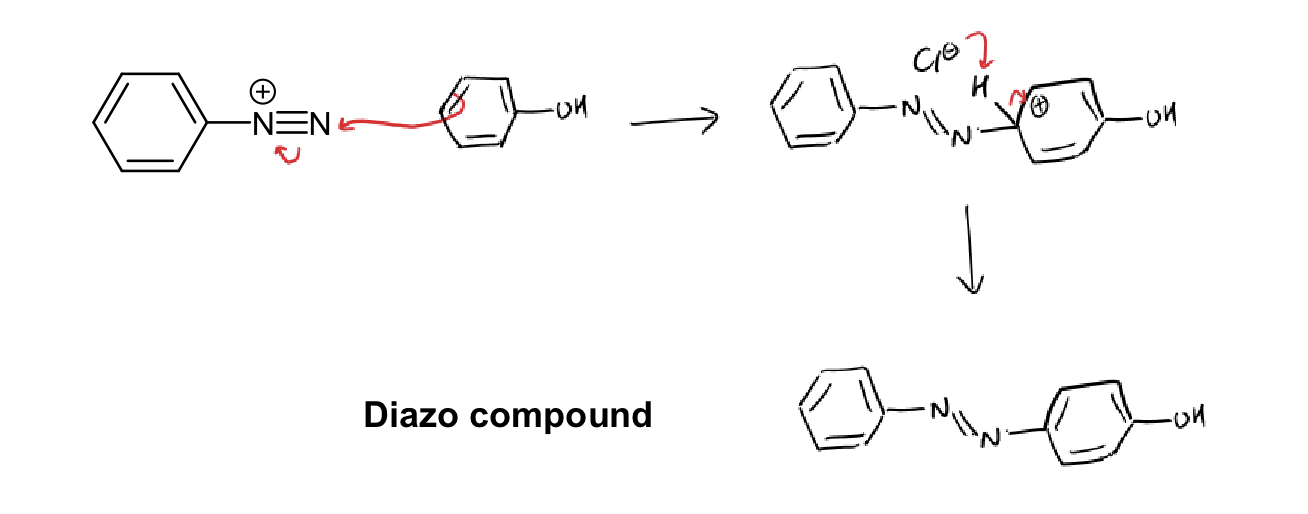
reaction for diazonium ion to phenol
heat above 5 degrees
H2O
diazonium ion reaction with electron rich aromatic mechanism (electrophilic substitution) - using phenol