Year 12 Chemistry Organic Compounds
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Cyclic molecules
Ring shaped molecules
Homologous Series
Organic Compounds with the same functional groups in which each member of the group differs from the previous member by a CH2
Alkanes
Hydrocarbons with only single covalent bonds between carbon atoms, which have the general formula CnH2n+2
Hydrocarbon
A compound that contains carbon and hydrogen only. Examples include alkanes and alkenes
molecular formula
A formula that gives the actual number and type of atoms present in a molecule
Alkenes
Hydrocarbons with one or more carbon to carbon double bonds. They have the general formula of CnH2n.
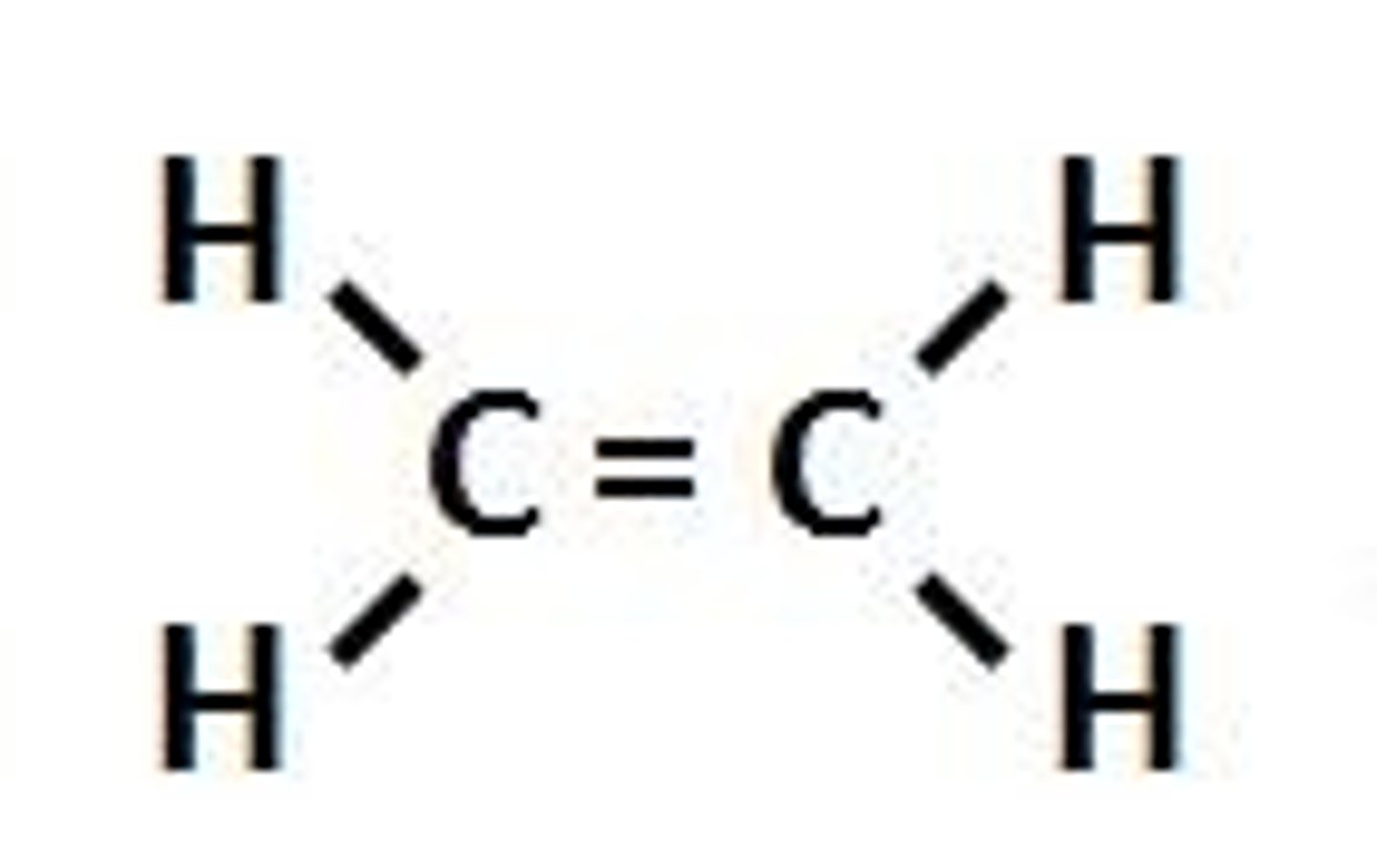
Systematic Name
The name of a molecule as determined by a set of rules involving the number of carbon atoms and the location and and type of functional groups present.
Unsaturated hydrocarbon
Hydrocarbons composed of molecules with at least one carbon to carbon double or triple bond
Esters
The name of a homologous series of molecules that contain the ester (-COO-) functional group
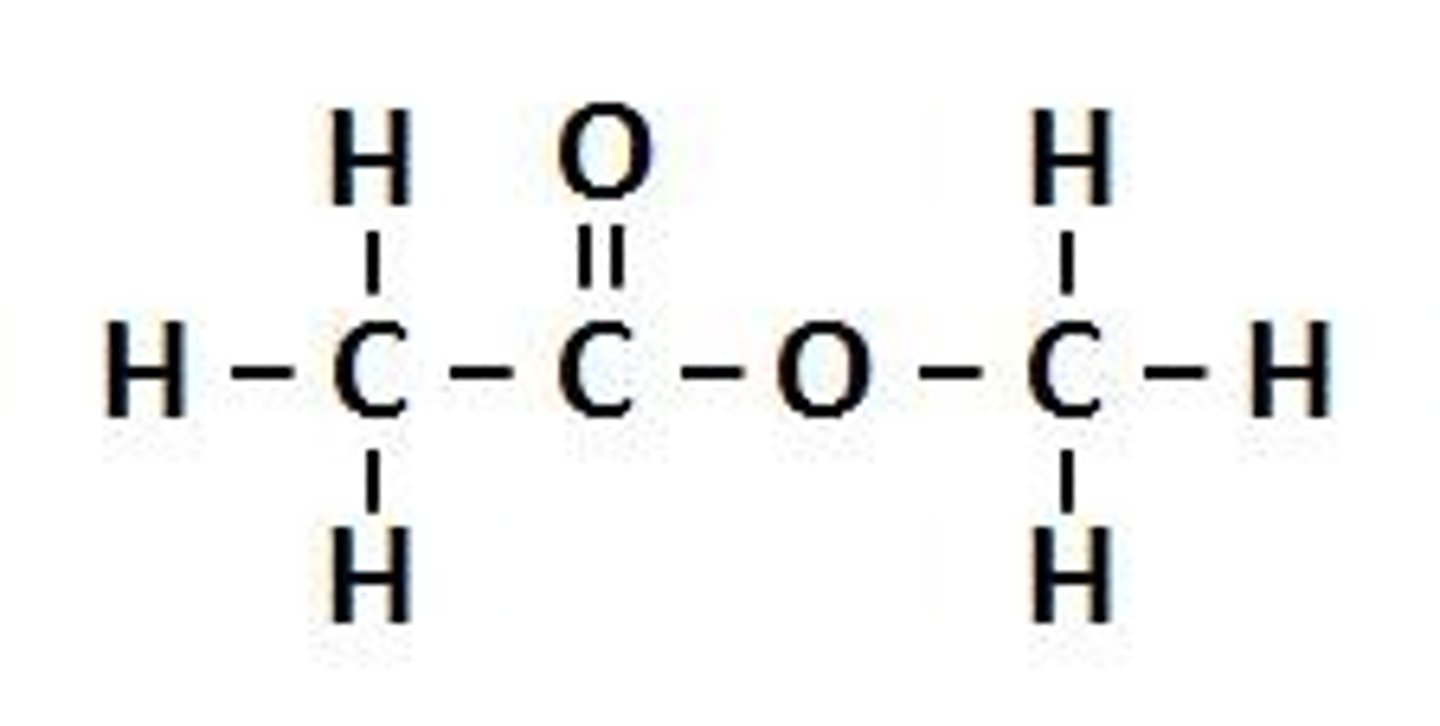
Structural formula
A formula that represents the three dimensional arrangement of atoms in a molecule
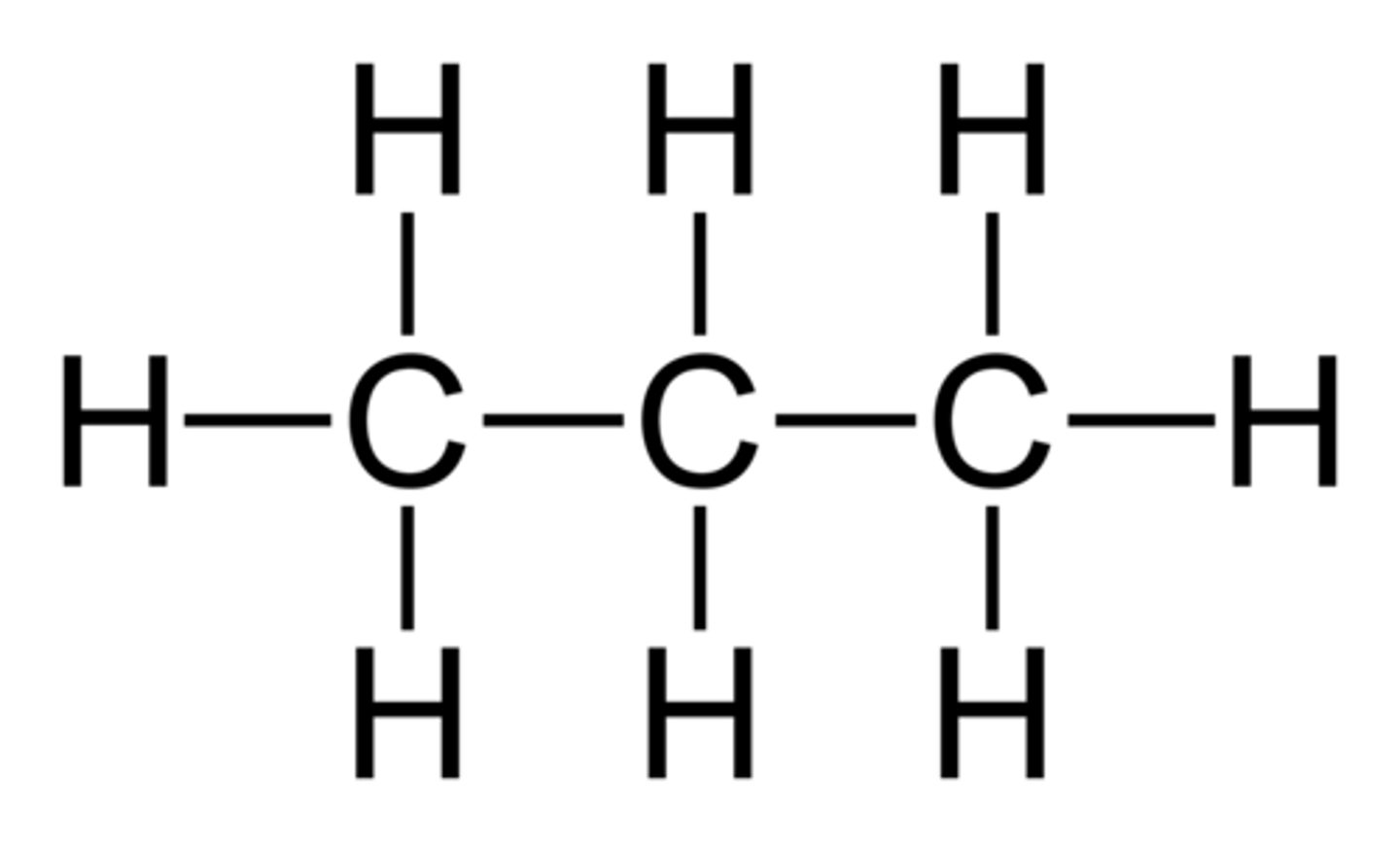
Alkyne
Hydrocarbons with one carbon to carbon triple bond, which have the general formula of CnH2-2
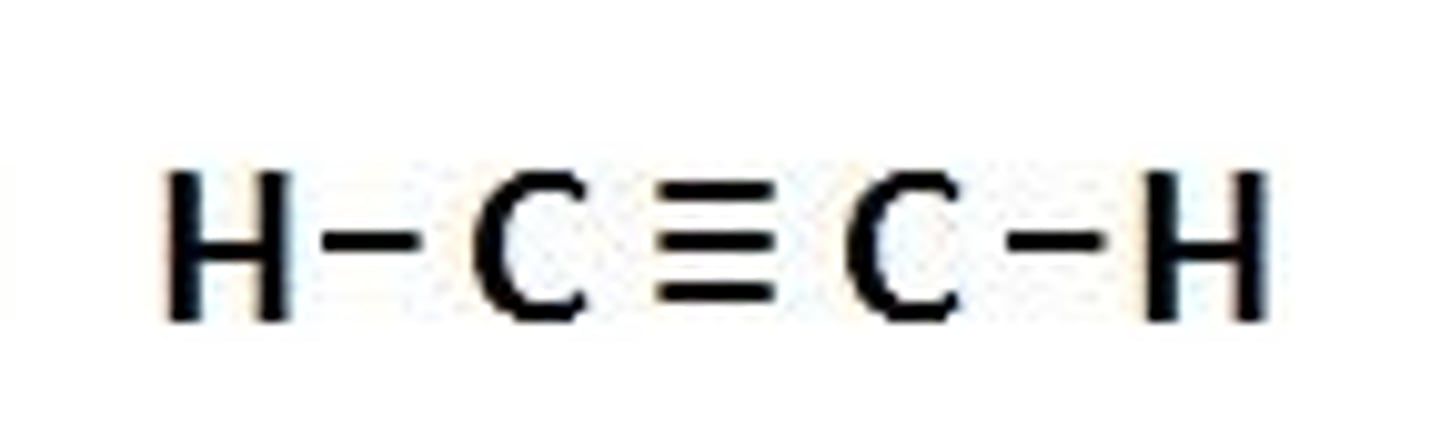
Functional group
Atoms or groups of atoms in an organic molecule that largely determine a molecule's properties and functions
Amine
An organic molecule containing the NH2 (amino) functional group
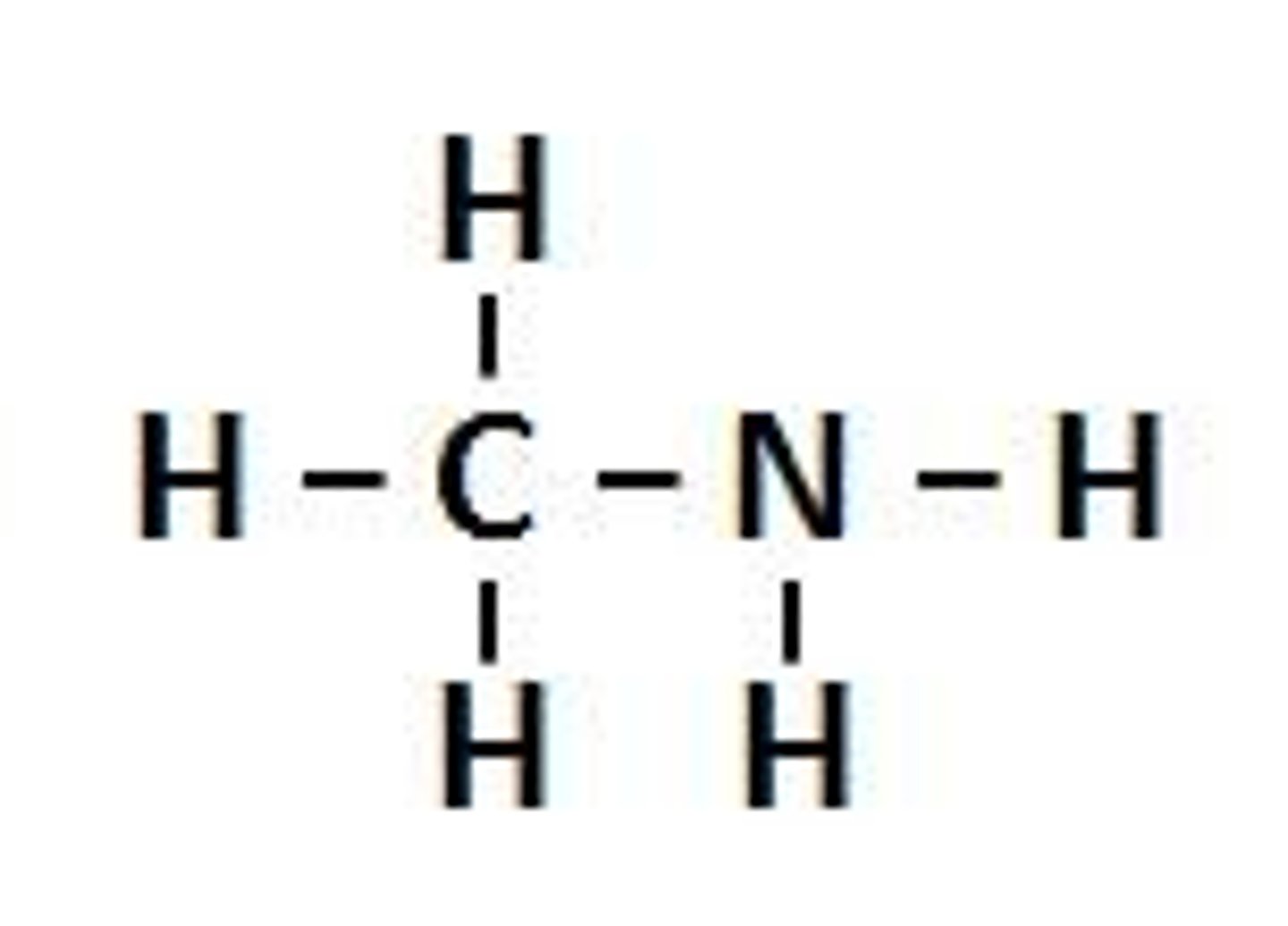
Alkyl group
A group obtained by removing a hydrogen atom from an alkane, with the general formula of CnH2n+1
Alcohol
An organic compound that has the hydroxyl (-OH) functional group attached to an alkane chain E.g. CH3CH2OH
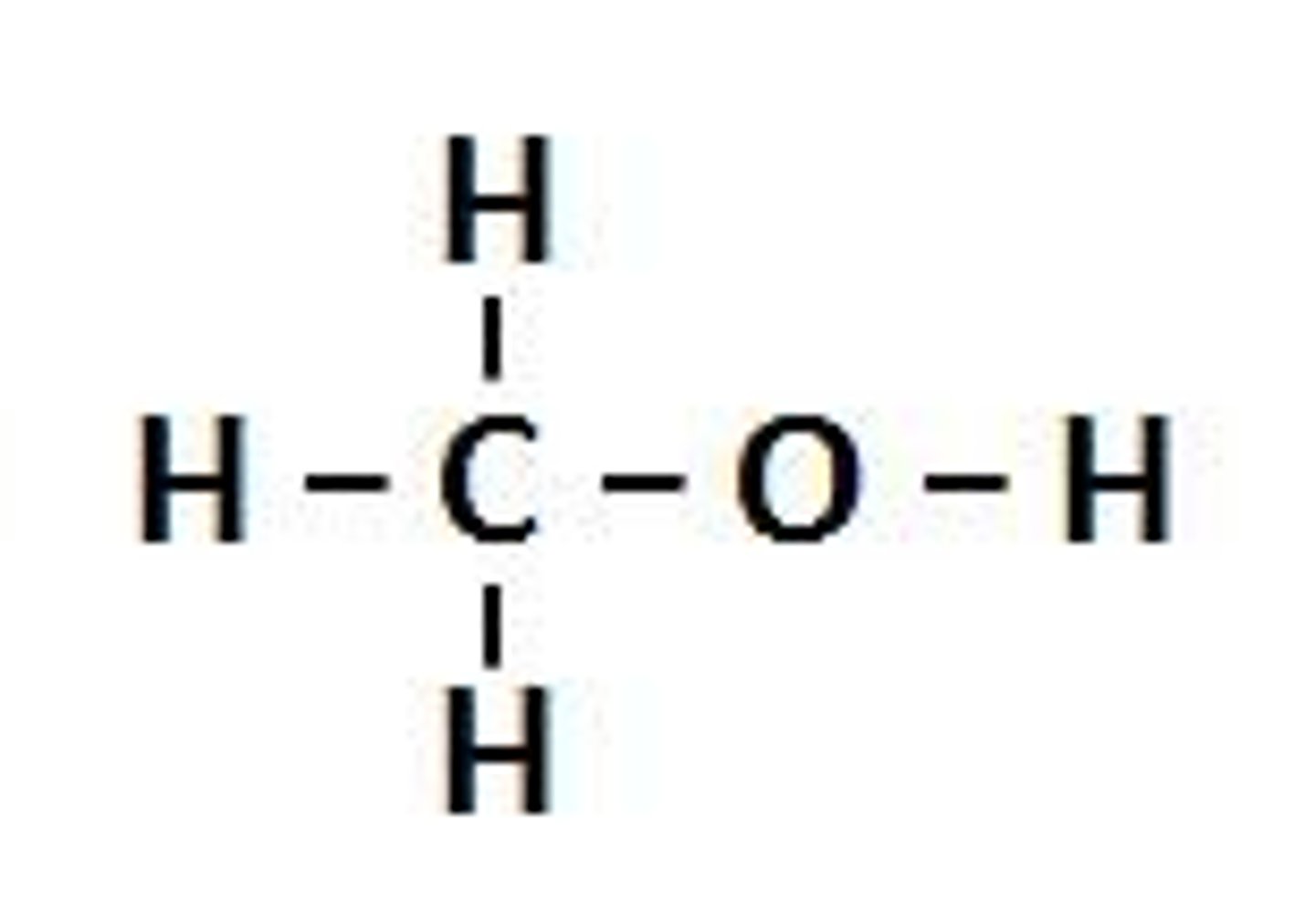
Skeletal structure
A 'chain link' of two carbon atoms linked by a single covalent bond (together with the hydrogen atoms attached to them) that is represented by a single line when drawn.
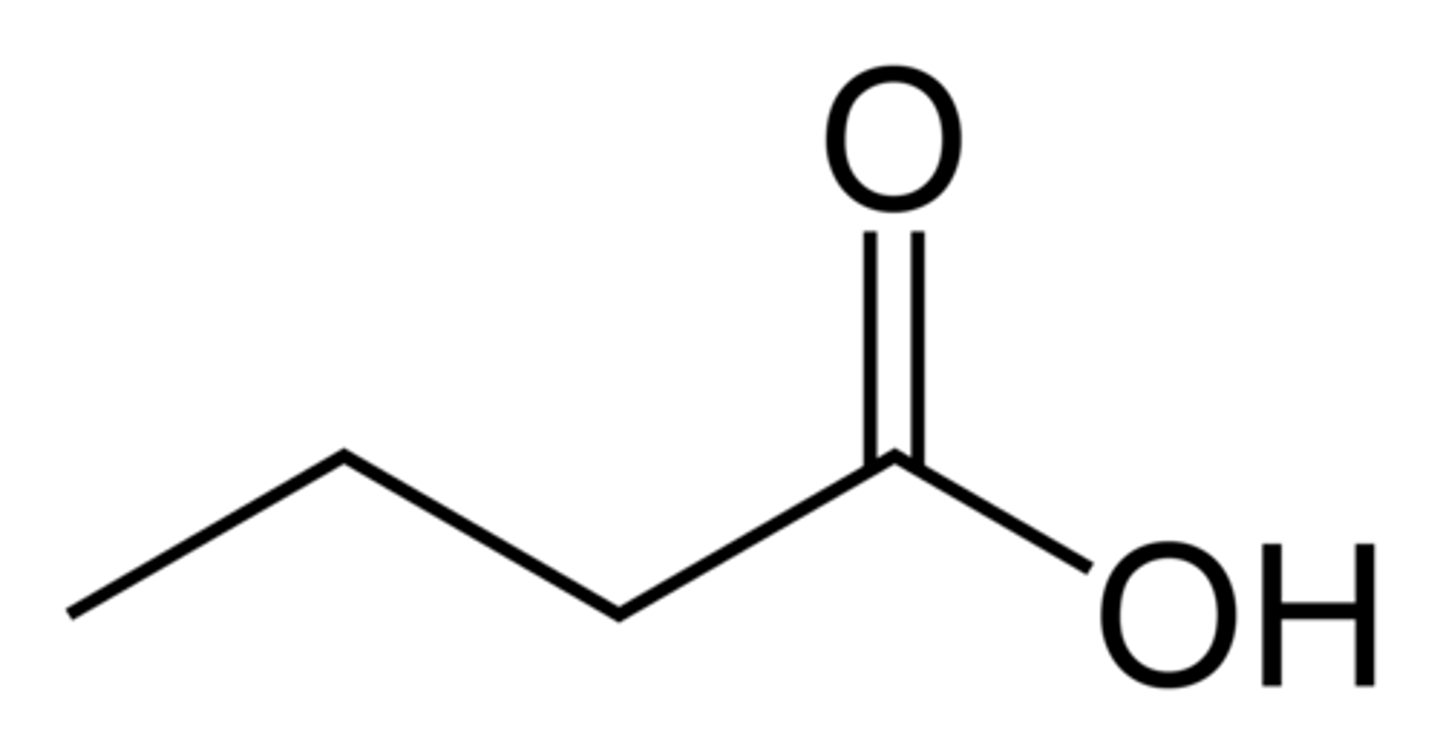
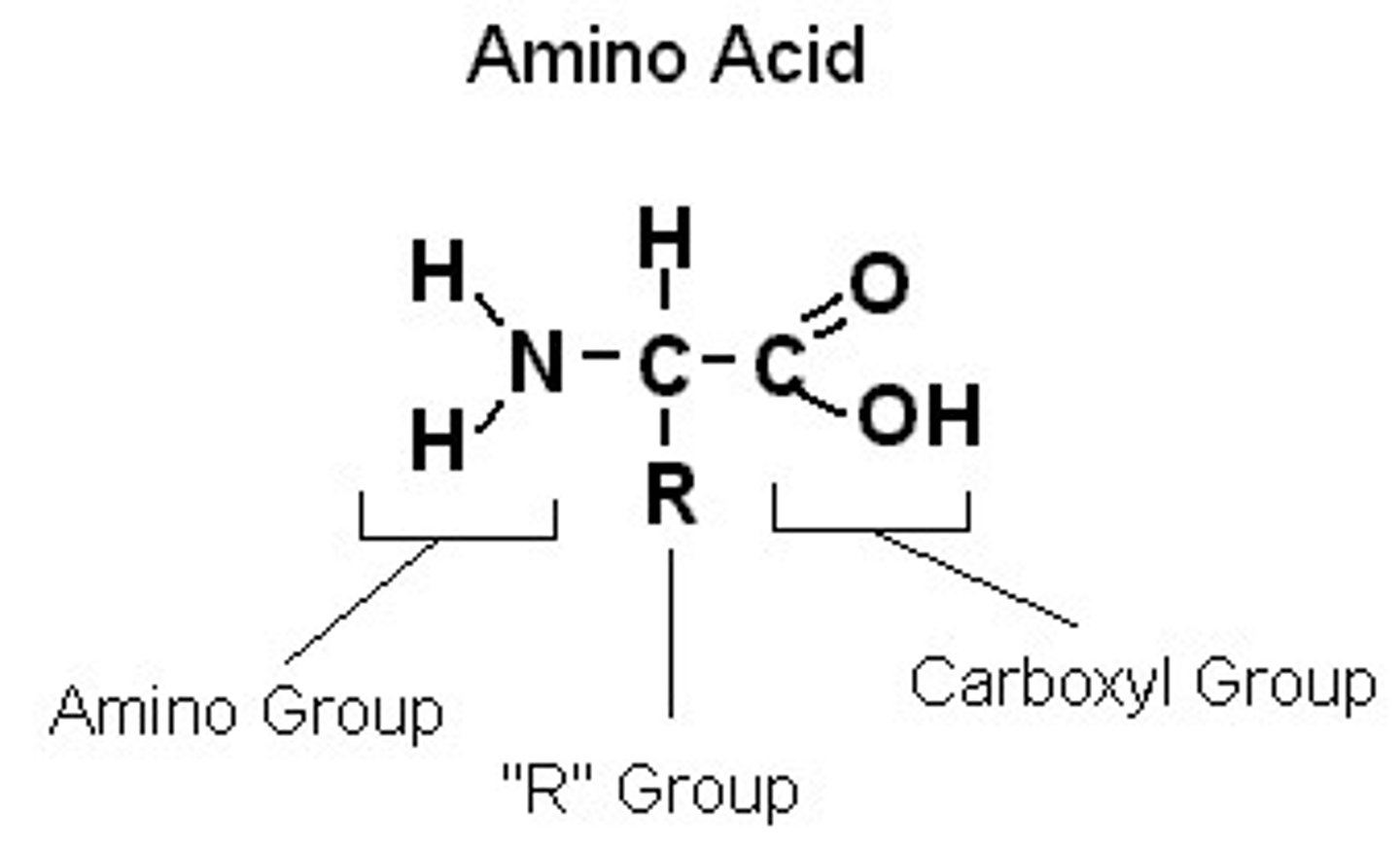
Amino acid
A molecule that contains both an amino group and carboxyl group
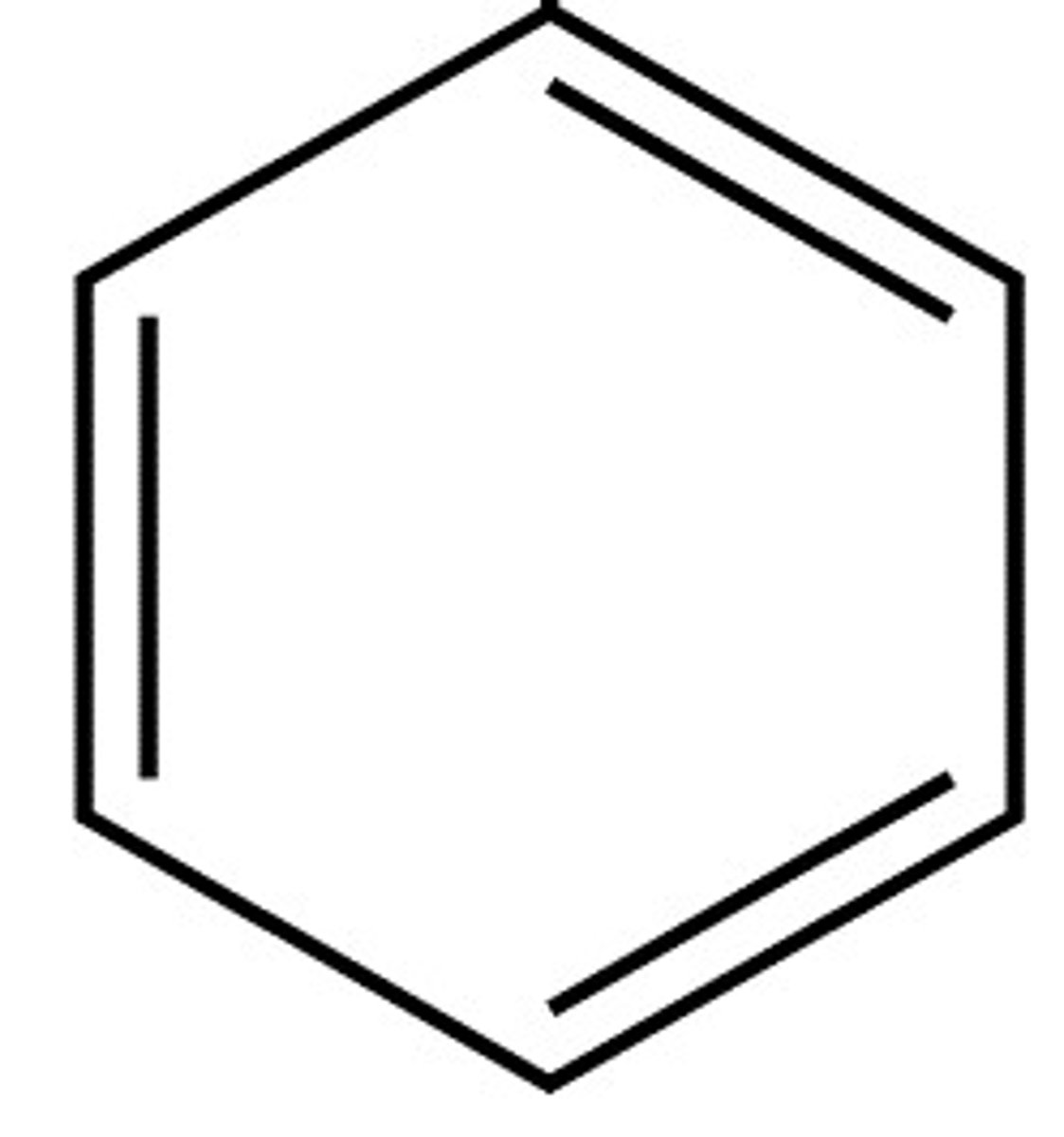
Arenes
Cyclic (ring-shaped) molecules in which electrons are delocalised around the ring E.g. benzene
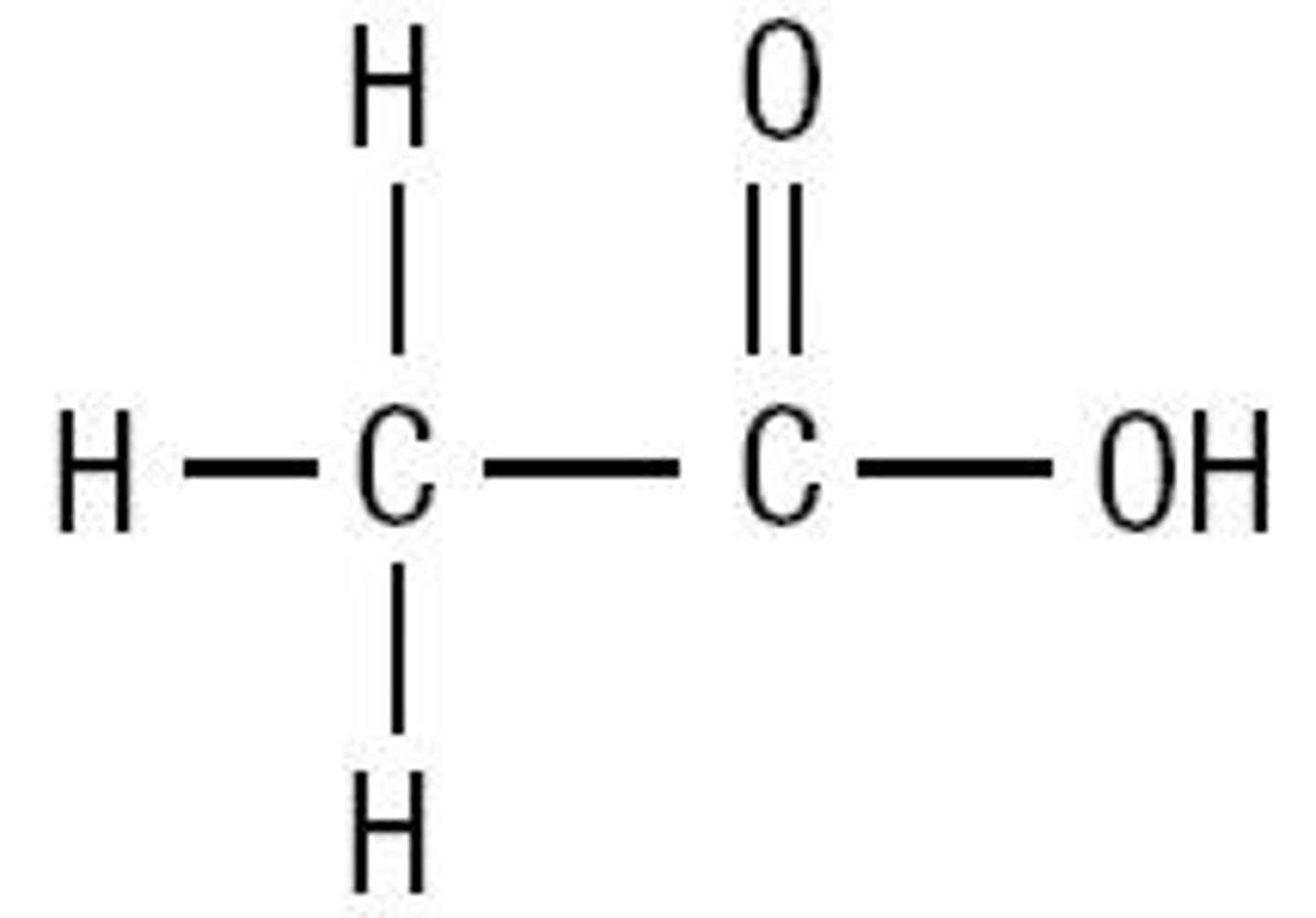
Carboxyilic Acid
An organic molecule containing the carboxyl (-COOH) functional group.
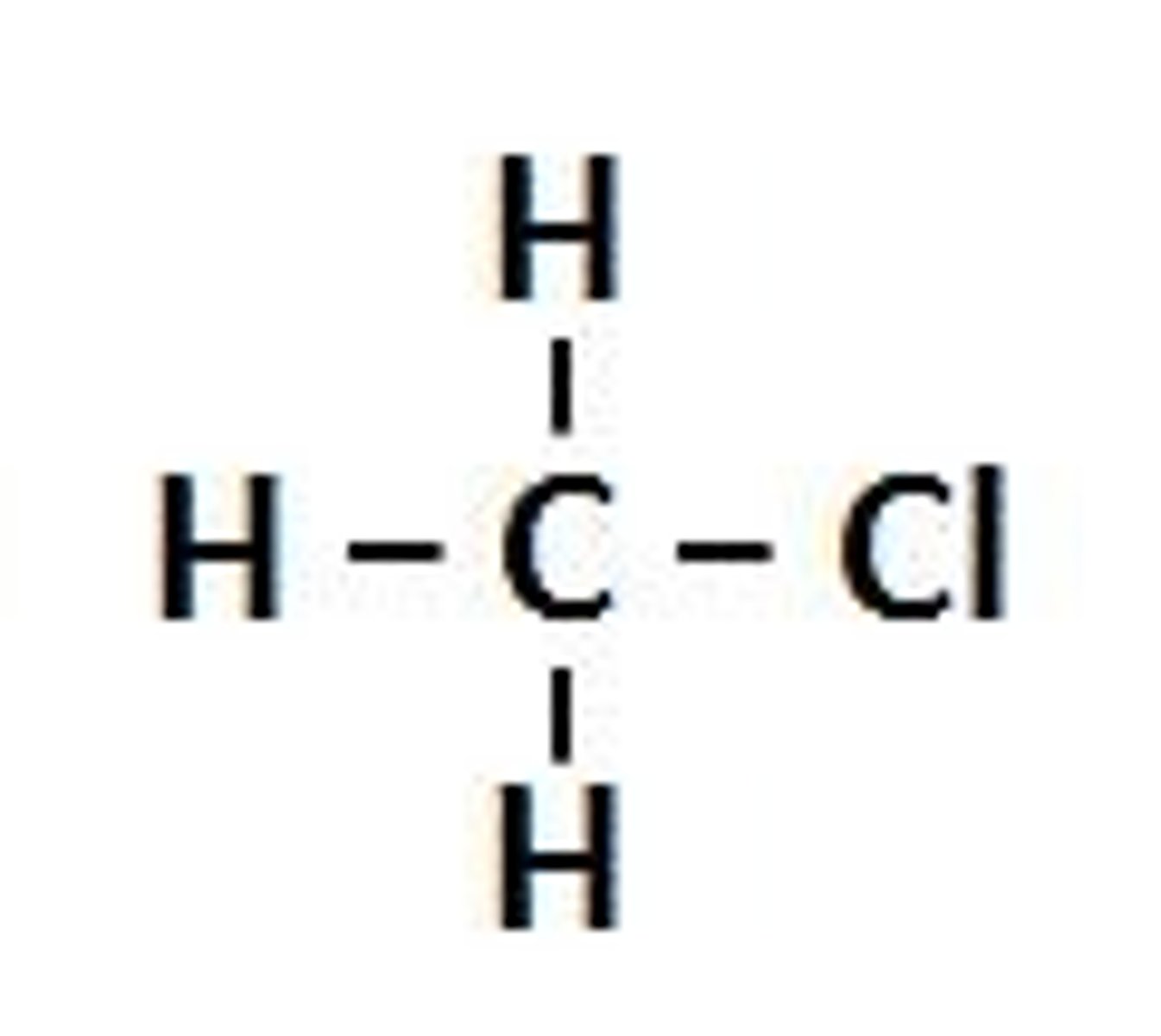
Chloroalkane
A molecule derived from an alkane, containing a -Cl functional group.
Saturated hydrocarbon
Hydrocarbons composed of molecules with only carbon to carbon single bonds
semi-structural formula
A formula that summarises the structural formula without giving the arrangement of atoms in space.
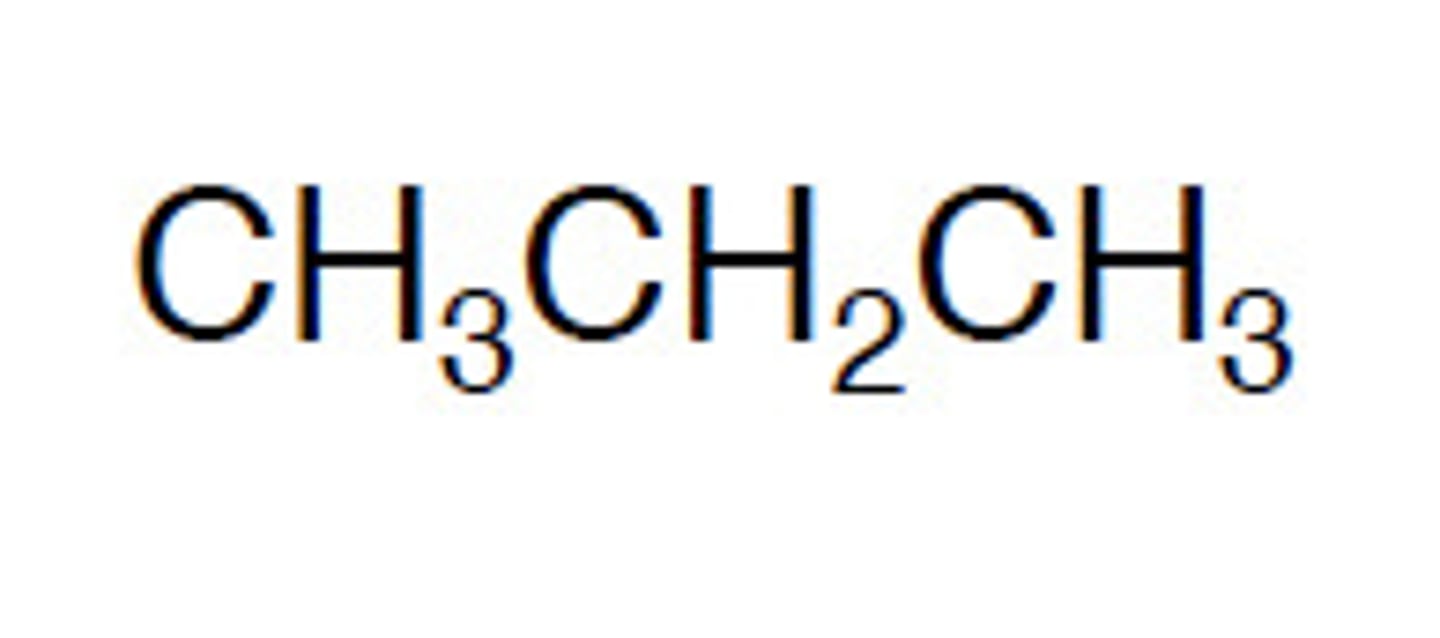
primary alcohol
an alcohol in which the hydroxyl (-OH) group is attached to a carbon that is attached to no more than one other alkyl group
secondary alcohol
An alcohol in which the hydroxyl (-OH) group is attached a carbon that is attached to two other alkyl groups
tertiary alcohol
An alcohol in which the -OH group is attached to a carbon atom that is attached to three alkyl groups
physical property
a quality or condition of a substance that can be observed or measured without changing the substance's composition. e.g. Boiling point, flashpoint, viscosity
boiling point
the temperature at which a substance changes from a liquid to a gas
Flashpoint
The lowest temperature at which a combustible material will produce an ignitable vapor.
Viscosity
a liquid's resistance to flow
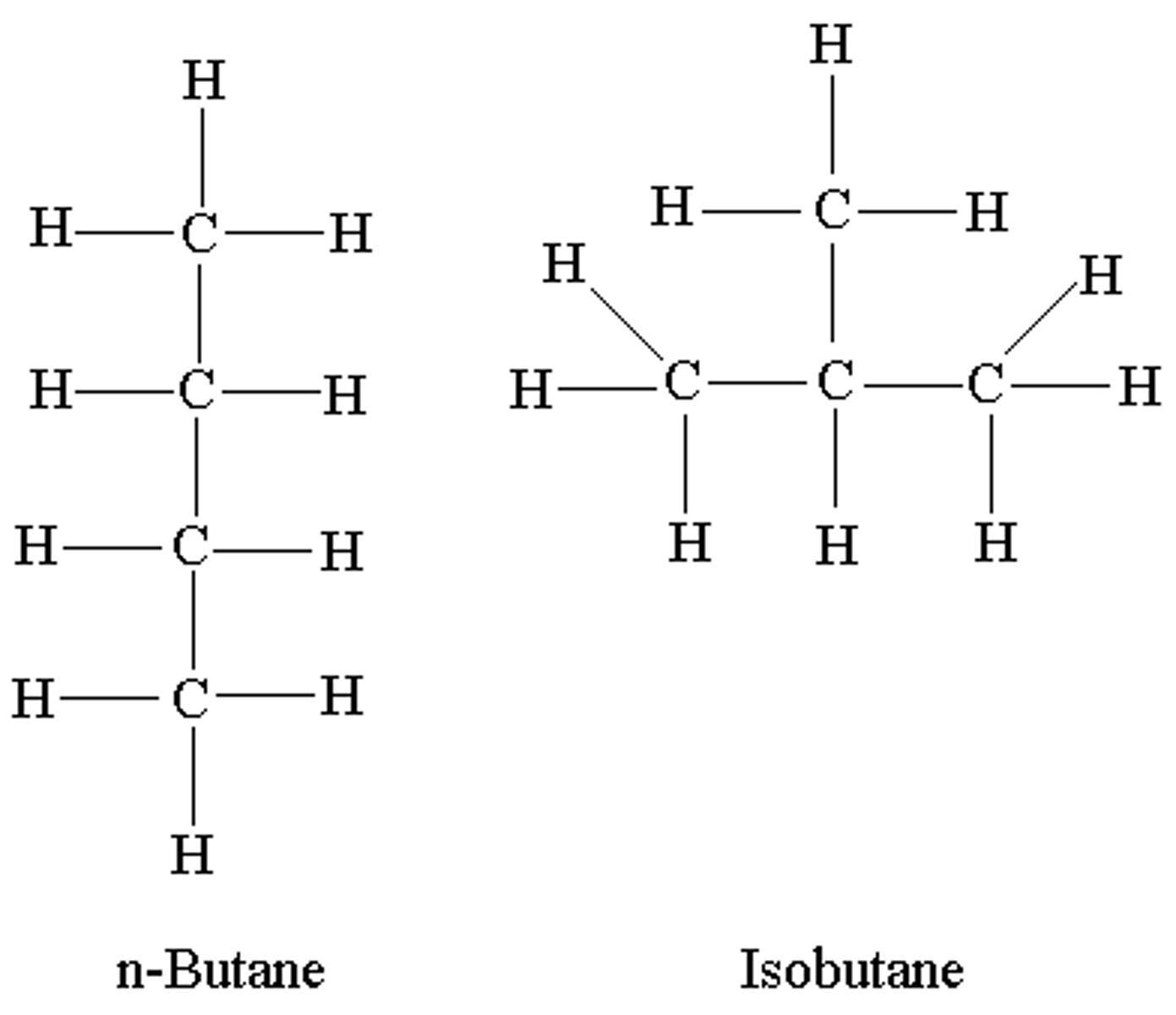
Isomer
each of two or more compounds with the same formula but a different arrangement of atoms in the molecule and different properties.
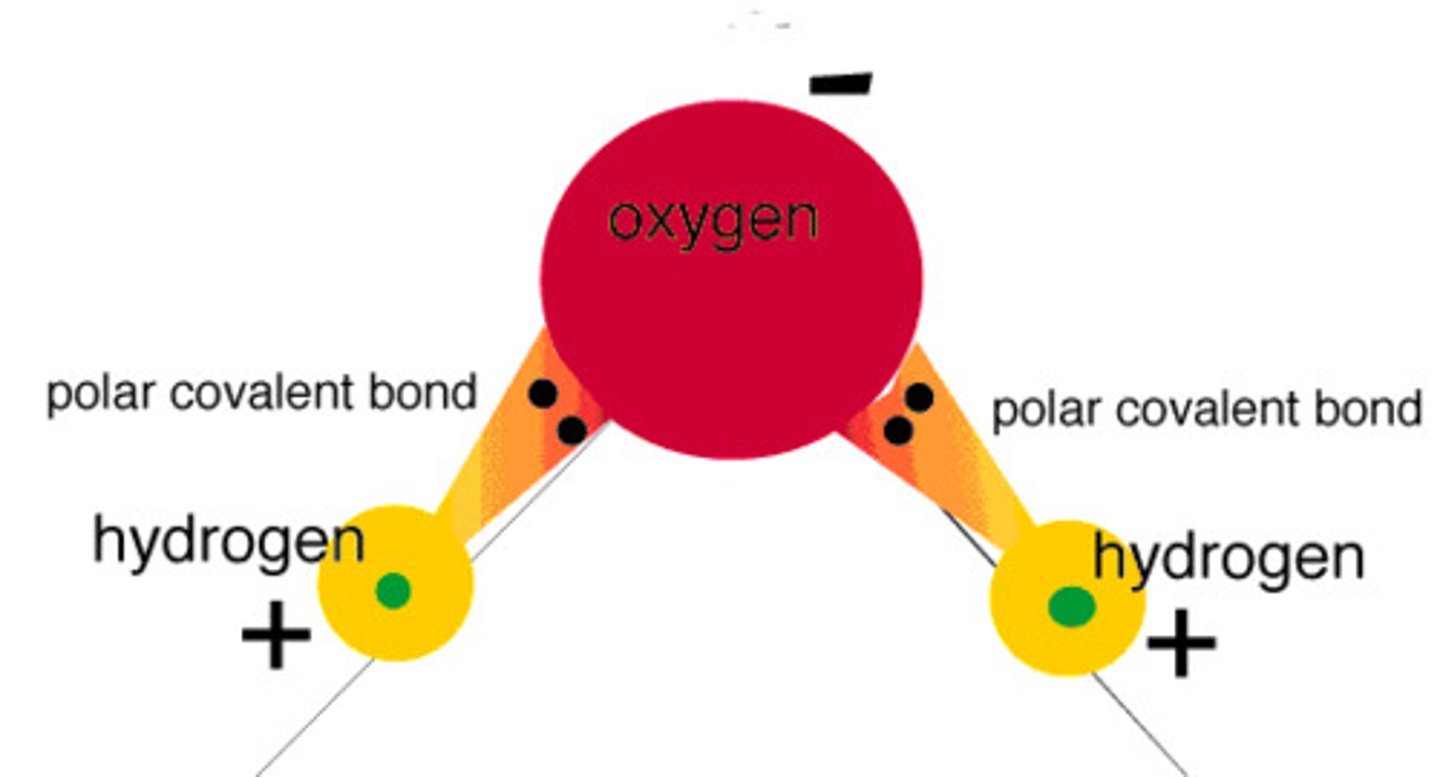
polar bond
A covalent bond between atoms that differ in electronegativity. The shared electrons are pulled closer to the more electronegative atom, making it slightly negative and the other atom slightly positive.
dispersion forces
the weakest of all molecular interactions, are found between non-polar molecules
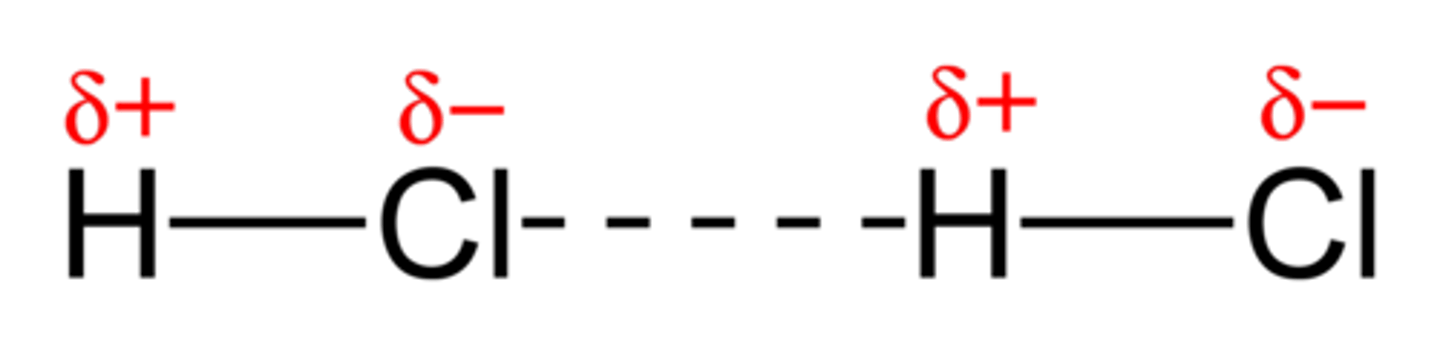
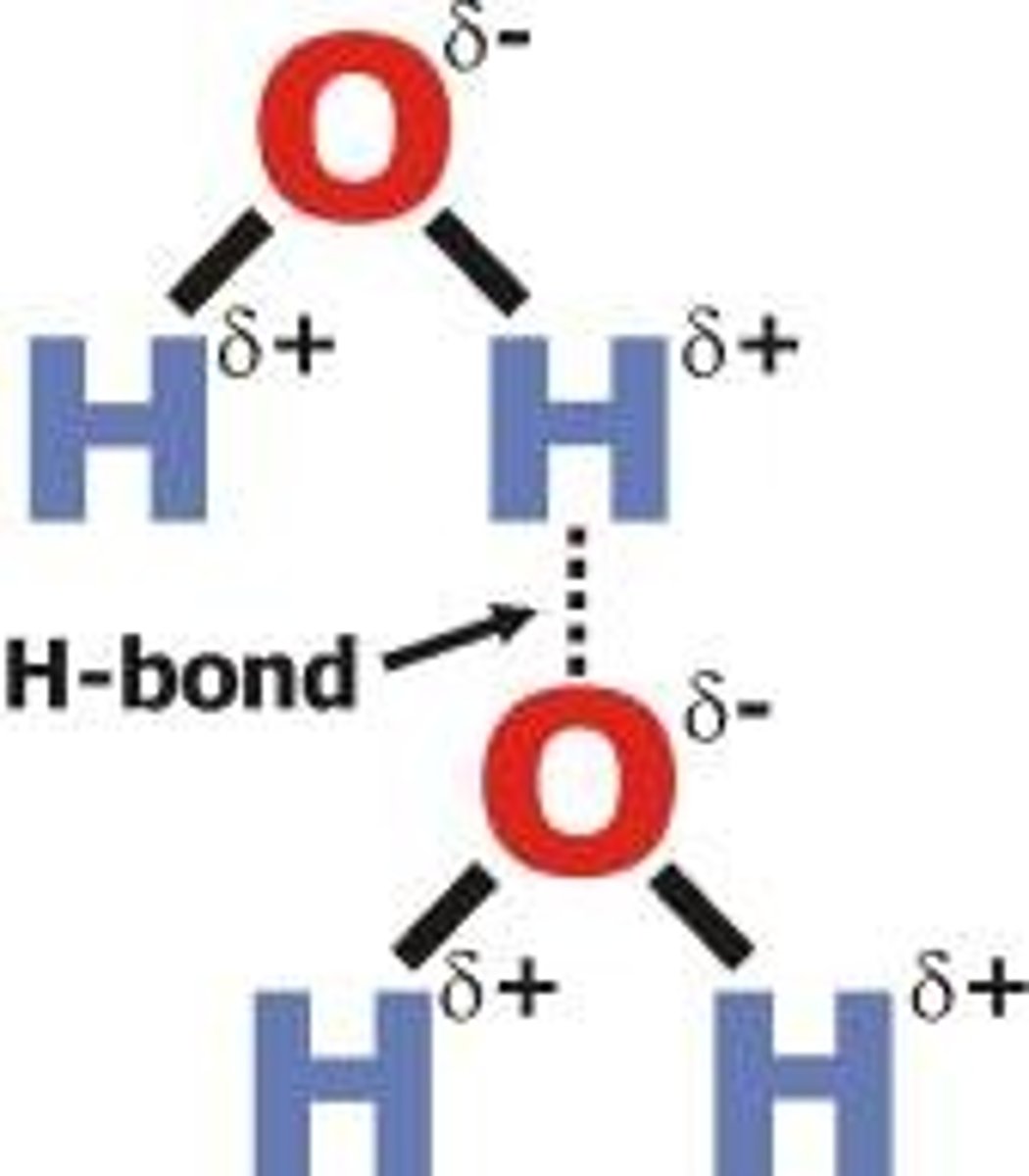
hydrogen bond
A type of weak chemical bond formed when the slightly positive hydrogen atom of a polar covalent bond in one molecule is attracted to the slightly negative atom of a polar covalent bond in another molecule. (H,N,O,F)
dipole-dipole forces
intermolecular forces that exist between polar molecules. Active only when the molecules are close together. The strengths of intermolecular attractions increase when polarity increases