Crude oil
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Crude oil
A mixture of hydrocarbons with different boiling points
Fractional distillation
A physical process used to separate the molecules in crude oil into fractions based on their different boiling points
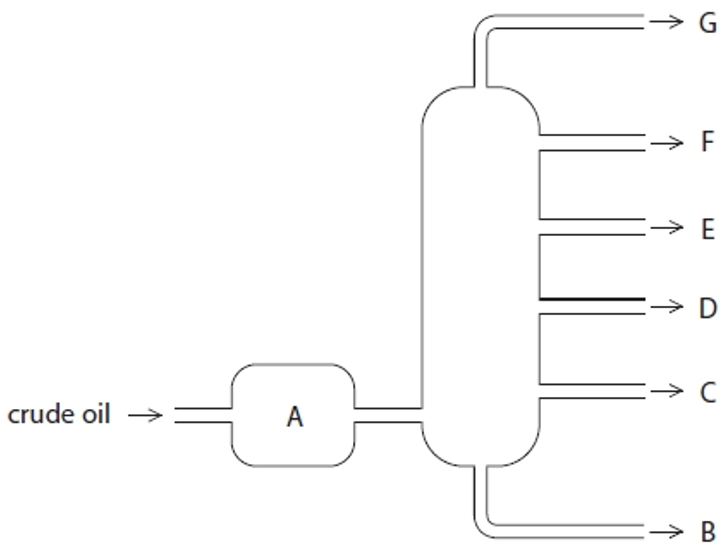
Structure G
Gases- Bottled gas
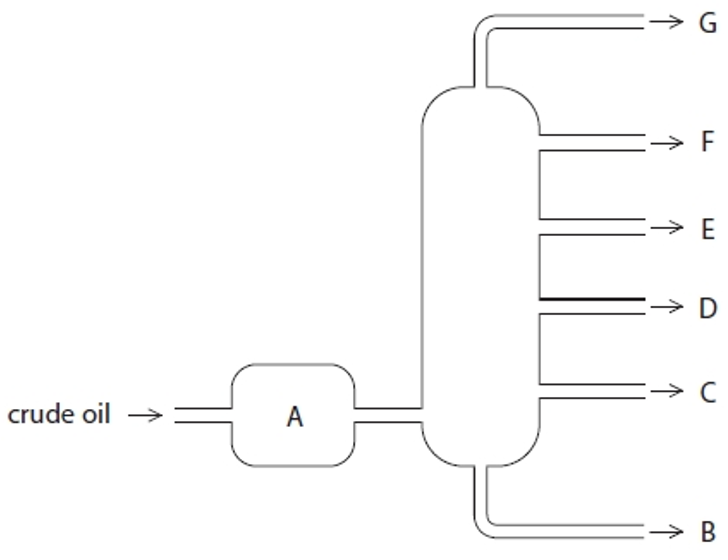
Structure F
Gasoline- Cars
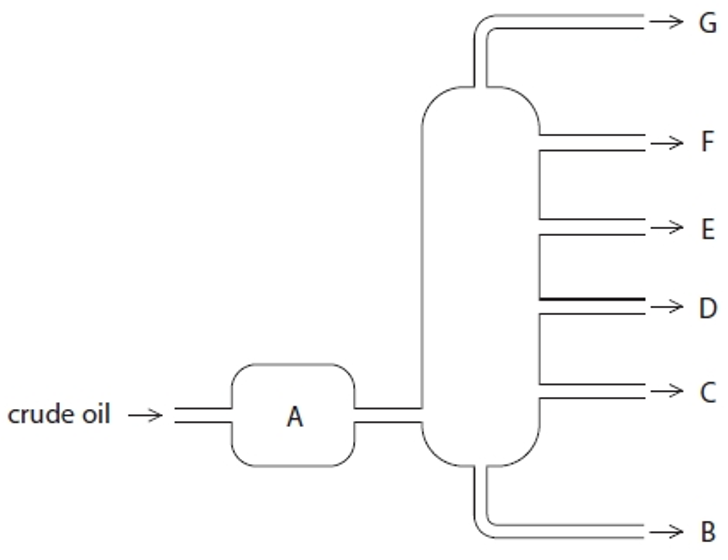
Structure E
Kerosene- Aircraft fuel
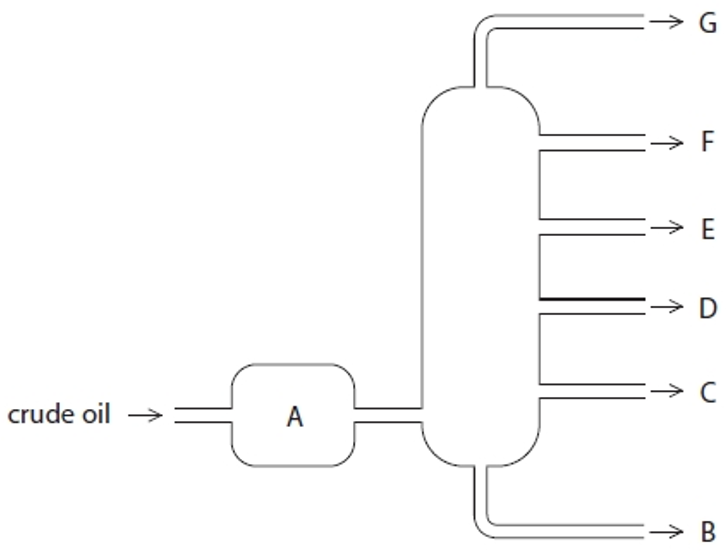
Structure D
Diesel- Trucks & Buses
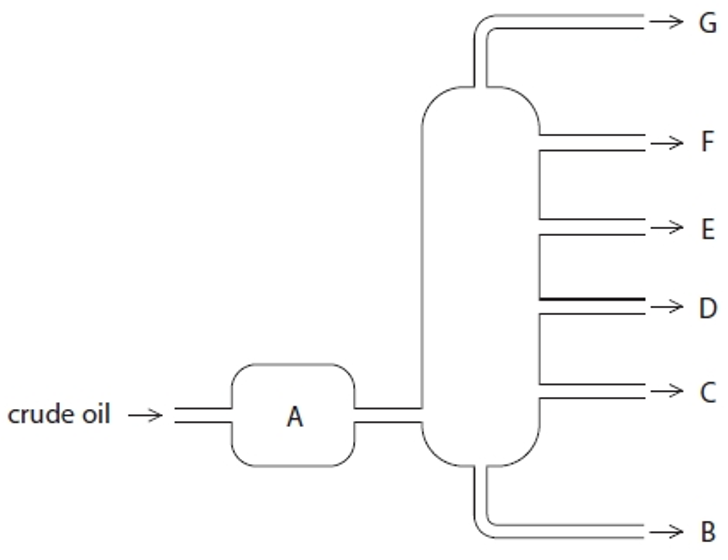
Structure C
Fuel oil- Ships
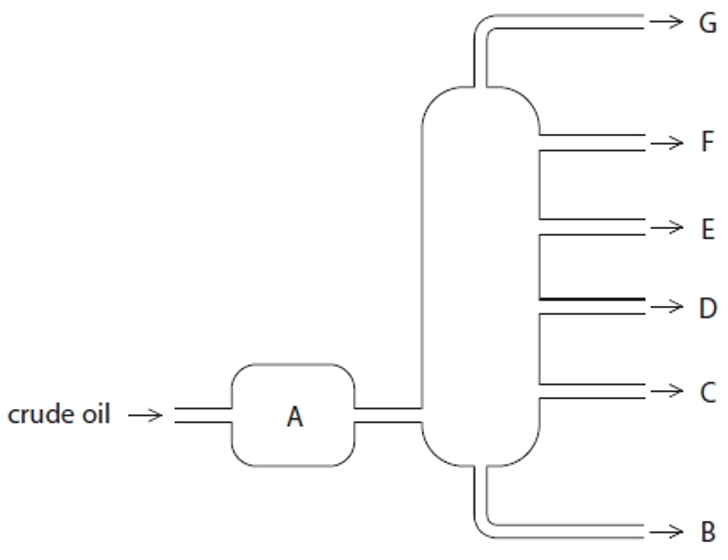
Structure B
Bitumen- Roads and rooftops
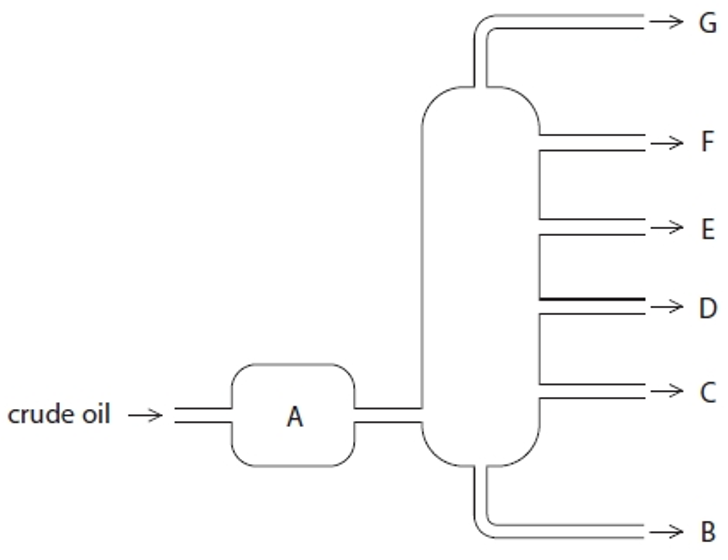
Structure A
Heated crude oil
Process of fractional distillation
The crude oil is heated/vaporised.
The vapours enter the lower part of the column.
There is a temperature gradient up the column (it is hotter at the bottom and cooler at the top).
The vapours rise up the column and are cooled until they condense
At a height where the temperature is below their boiling point.
The fractions are removed.
Cracking
Used to break down long-chained hydrocarbons to shorter-chained alkanes and alkenes.
Conditions required for cracking
Temperature- 600-700oc
Catalyst- Zeolite
Why is cracking important
Crude oil has a surplus of long-chain molecules.
Cracking produces shorter-chain alkanes and alkenes.
Shorter chain molecules are more useful and have a greater demand.
Shorter chain alkanes are used to make petrol.
Shorter chain alkenes are used to make polymers/plastics.
3 main pollutant gasses produced when burning fossil fuels
Carbon Monoxide
Sulfur Dioxide
Nitrogen oxides
Carbon monoxide
Produced through incomplete combustion- not enough oxygen
Colourless, odourless gas
Prevents red blood cells from carrying oxygen
Sulfur dioxide
Produced when a fuel that contains sulfur impurities is burned
Acid rain
Sulfur dioxide is released into the atmosphere and it dissolves in the water droplets in the clouds to form sulfourous acid
How does acid rain damage the environment
pH in lakes decrease- kills fish
Damages trees
Corrodes limestone buildings and statues
Nitrogen dioxide
Produced when nitrogen in the air reacts with oxygen in the air- Takes place in car engines
How does nitrogen dioxide cause acid rain
Nitrogen dioxide reacts with water in the atmosphere to form nitric acid
Cracking
An industrial process used to break low demand, long chain hydrocarbon molecules into more useful, small chain hydrocarbon molecules
Process of catalytic cracking
Heat the hydrocarbon molecules to 600-700°c to vaporise them
Vapours then pass over a hot powdered catalyst of aluminium oxide
Covalent bonds are broken as they come into contact with the catalyst → thermal decomposition reactions
Products of cracking
A mixture of shorter alkanes and alkenes