B3 Movement into and out of cells
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
what is diffusion?
diffusion is the net movement of particles from a region of their higher concentration to a region of their lower concentration as a result of their random movement
what is the cell membrane’s rolel in osmosis?
some substances move into and out of cells by diffusion through the cell membrane
What is the importance of diffusion of gases and solutes in living organisms?
Gases and solutes such as carbon dioxide and oxygen are able to diffuse in and out of cells across the cell membrane. This is important as these are used in metabolic reactions.
Animals-Respiration
Plants-photosyhthesis
What are the factors affecting the rate of diffusion
surface area, temperature, concentration gradient and distance
How does surface area affect the rate of diffusion?
As the surface area increases, the rate of diffusion increases. This is because there is more space available for substance to diffuse through
How does temperature affect the rate of diffusion?
As the temperature increases, the rate of diffusion increases. This is because the molecules gain kinetic energy and move fasters
How does the concentration gradient affect the rate of diffusion?
As the concentration gradient increases, the rate of diffusion increases. This is because there is a bigger difference so particles will naturally move faster to even out
How does the diffusion distancet affect the rate of diffusion?
As the diffusion distance increases, the rate of diffusion decreases. This is because molecules must travel faster.
What is osmosis?
Osmosis is the net movement of water molecules from a region of higher water potential (dilute solution) to a region of lower water potential (concentrated solution), through a partially permeable membrane
What is a partially permeable membrane?
a membrane that lets some substances in and not others
How does water move in and out of cells?
water moves into and out of cells by osmosis through the cell membrane
Osmosis effect on plant tissue when immersing them in solutions of different concentration? (explanation)
In a dilute solution, water moves into plant cells causing them to swell and gain mass and length.
In a concentrated solution, water moves out the cell causing them to lose mass and length
At the isotonic point, the solute concentration inside the cells is equal to the solution concentration outside so there is no movement of water, therefore mass and length stays the same.
What is turgor pressure?
The water pressure inside a plant cell that presses against the cell wall.
What is turgid?
A plant cell with a high turgor pressure, it’s stiff, tight and firm
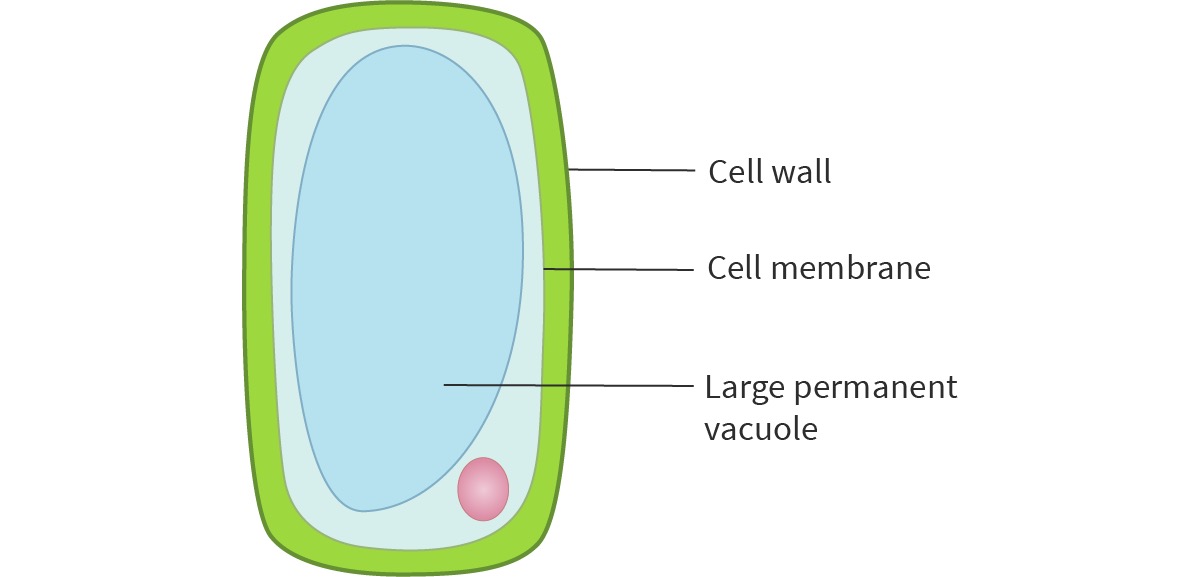
What is flaccid?
A plant cell with a low turgor pressure, it’s floppy, less stiff and less firm
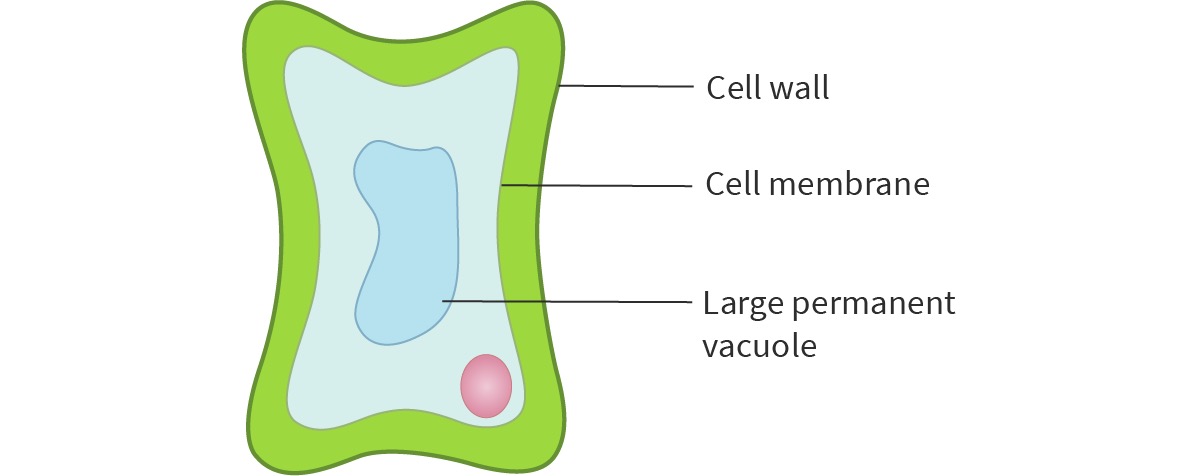
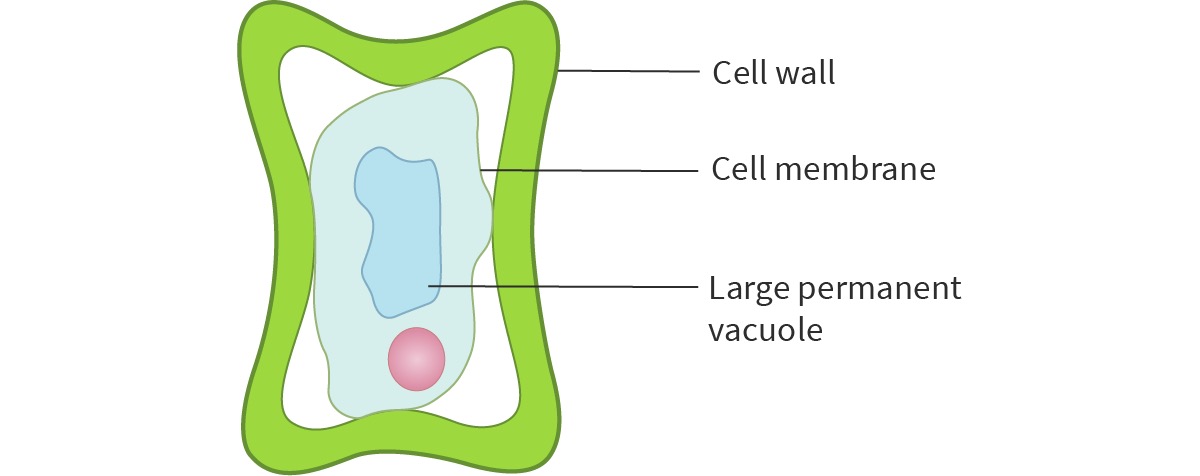
What is plasmolysed?
A plant cell with such a low turgor pressure that the cytoplasm and vacuole pull away from the cell wall.
Effect on plant cell in pure water(analysis)
When plant cells gain water by osmosis, the cytoplasm and vacuole will swell. Turgor pressure will press against the cell wall. The cell wall will stop the cell from bursting.
A plant with a high turgor pressure is called turgid.
Effect on plant cell in a concentrated solution(analysis)
When plant cells lose water by osmosis, the cytoplasm and vacuole will shrink. Turgor pressure will stop pressing outwards against the cell wall. Its turgor pressure decreases , the cell becomes flaccid.
Effect on plant cell in a very concentrated solution(analysis)
When plant cells lose a lot of water by osmosis, the cytoplasm and vacuole will shrink so much that it pulls away from the cell wall. The cell wall is left behind since it’s too stiff. This is called plasmolysed.
Osmosis plant cell practical
Importance of water potential and osmosis in the uptake of water in plants
Water uptake in plants occurs due to the water potential gradient between the soil and root hair cells. Water moves from the soil (region of higher water potential) into the root hair cells (region of lower water potential) by osmosis. This maintains turgor pressure helping plant stay and upright, also used for photosyhthesis.
Importance of water potential and osmosis in the loss of water in plants
During transpiration, water evaporates from the leaves This creates a lower water potential in the leaf compared to the roots. This causes more water to be pulled up from the roots, allowing continuous water movement
What is active transport?
Active transport is the movement of particles through a cell membrane from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration against a concentration gradient, using energy from respiration
What are carrier proteins?
Carrier proteins facilitate active transport. They are embedded in the cell membrane and allow passage through it. Molecules from the side with lower concentration bind to the carrier protein. The carrier protein then changes shape using energy from respiration. This forces the molecule to move through the membrane to the side with high concentration, where it is released.
Active transport in the uptake of ions by root hair cells
Root hair cells take in ions from the soil. The carrier proteins binds to the nitrate ions from outside the cell with lower concentration and then changes shape so that the ions is pushed through the cell membrane and into the cell with higher concentration. Energy is need to change shape of protein.
Active transport in the uptake of glucose.
Glucose is taken up in the small intestine and kidney tubules. Glucose moves against the concentration gradient through carrier proteins.