AP NSL Unit 2: Interactions Among Branches of Government
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/108
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
109 Terms
1
New cards
bicameralism
Type of legislature that is divided into two separate houses, (Our case is House of representatives and the senate)
2
New cards
House constituency
a body of citizens entitled to elect a representative (people in individual districts)
3
New cards
Senate constituency
2 for each state
4
New cards
Senate’s chamber size and formality of debate
100 people
Any representative can hold a filibuster for a bill (holds the bill) only thing that can end a filibuster is a vote for cloture (60 Senators) or an agreement is made
\
Informal action where any senator can stop floor consideration of measures or matters that are available to be scheduled by the Senate.
Any representative can hold a filibuster for a bill (holds the bill) only thing that can end a filibuster is a vote for cloture (60 Senators) or an agreement is made
\
Informal action where any senator can stop floor consideration of measures or matters that are available to be scheduled by the Senate.
5
New cards
House’s chamber size and formality of debate
435 people
\
The rules committee is responsible for the rules under which bills will be presented to the House of Representatives.
\
A discharge petition is where any house member can have a bill discharges from consideration by the committee (Needs majority vote) (also can only be used after 30 days of the bill being in a standing committee)
\
The rules committee is responsible for the rules under which bills will be presented to the House of Representatives.
\
A discharge petition is where any house member can have a bill discharges from consideration by the committee (Needs majority vote) (also can only be used after 30 days of the bill being in a standing committee)
6
New cards
Senate Leadership
\
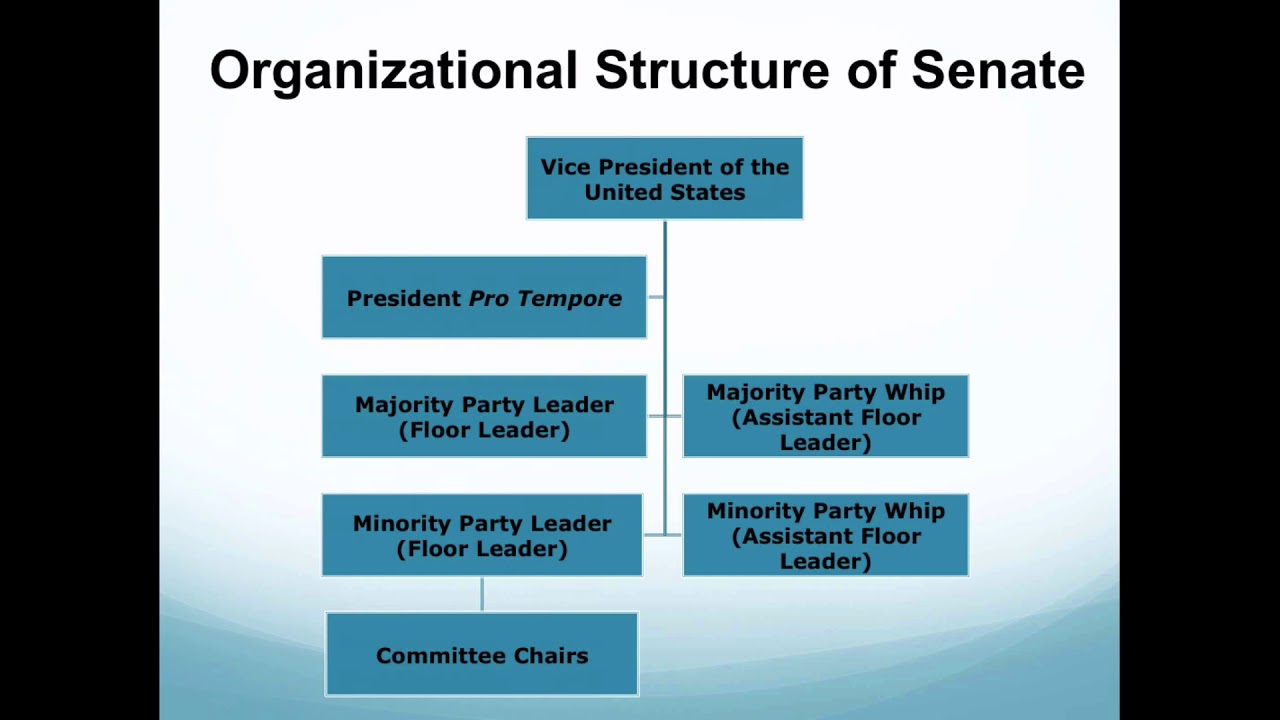
7
New cards
House Leadership
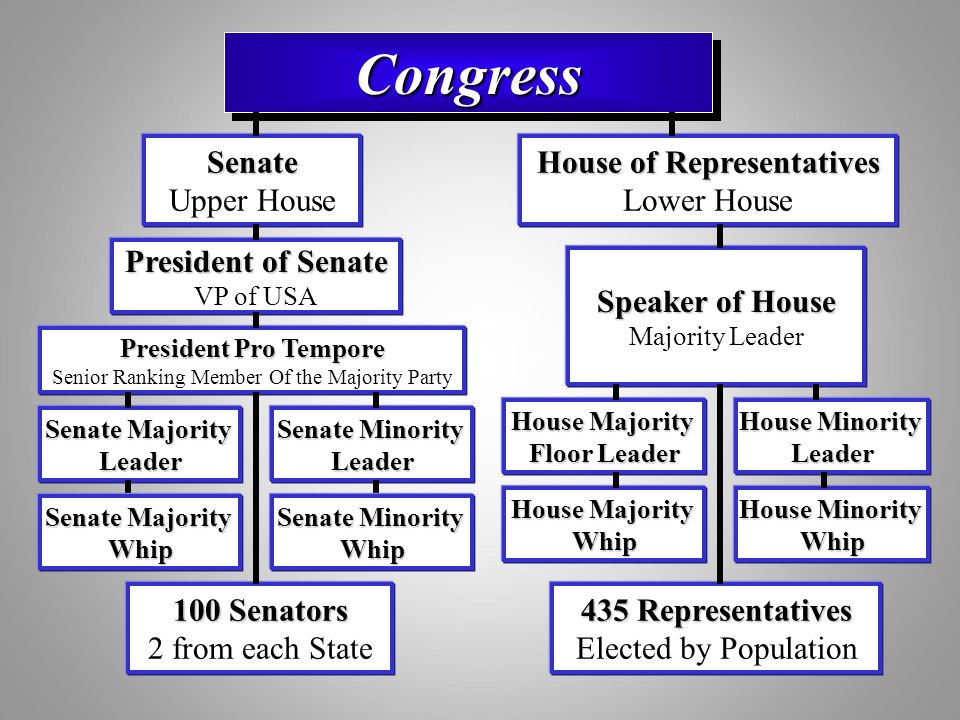
8
New cards
Powers specific to the Senate **Article I**
Power to confirm those of the President's appointments that require consent, and to provide advice and consent to ratify treaties, power to remove prez from office
9
New cards
Powers specific to the House **Article I**
Initiate revenue bills, impeach federal officials, and elect the President in the case of an Electoral College tie
10
New cards
Power of the Purse
The ability to tax and spend public money for the national government
11
New cards
Declaring war
Congress
12
New cards
Necessary and proper clause
Under Article I, Section 8 of the Constitution, Congress can do whatever they want they helps them carry out there powers
13
New cards
casework
social work directly concerned with individuals (done by people that you elect in Congress)
14
New cards
Mandatory spending
the payments established by existing laws and made for schemes such as Medicare and Social Security (also pays people in the gov)
15
New cards
Discretionary spending
a non-essential expense that is incurred by an individual, household, or business.
16
New cards
entitlements
the fact of having a right to something
17
New cards
Pork barrel legislation
Legislation that allocates government money to projects in a certain district (localized projects) (may not be helpful to everyone)
18
New cards
Logrolling
he practice of exchanging favors (I vote for your bill, you vote for mine)
19
New cards
seniority
The practice of ranking senators based on length of service (Typically these people get more benefits)
20
New cards
earmarks
Funds provided by Congress for projects or programs that reduce the ability of the Executive Branch (setting aside money as well)
21
New cards
divided government
control of the executive branch and the legislative branch is split between two political parties resulting in gridlock (ratio between bills passed and the agenda of the legislature decreases.)
22
New cards
apportionment/ redistricting
Process of dividing the 435 memberships, or seats, in the U.S. House of Representatives among the 50 states
23
New cards
gerrymandering
practice of setting boundaries of electoral districts to favor specific political interests/ certain groups
24
New cards
standing committees
permanent committees in Congress that specialize in the consideration of particular subject areas
25
New cards
select committees
a group set up for a specific and usually temporary purpose, such as an investigation
26
New cards
joint committees
Made of five Representatives and five Senator appointed by the respective presiding officers that debate and report on matters concerning the Congress rather than issues of public policy.
27
New cards
conference committees
A temporary panel(created when necessary composed of House and Senate conferees formed for the purpose of reconciling differences in legislation that has passed both chambers.
28
New cards
committees
monitor on-going governmental operations, identify issues suitable for legislative review, gather and evaluate information, and recommend courses of action
29
New cards
**Baker v. Carr**
Baker and other Tennessee citizens alleged that a 1901 law designed to apportion the seats for the state's General Assembly was virtually ignored.
Court could intervene of cases considered "political questions".
the Fourteenth Amendment equal protection issues which Baker and others raised in this case merited judicial evaluation.
Court could intervene of cases considered "political questions".
the Fourteenth Amendment equal protection issues which Baker and others raised in this case merited judicial evaluation.
30
New cards
**Shaw v. Reno**
The U.S. Attorney General rejected a North Carolina congressional reapportionment plan because the plan created only one black-majority district
\
although North Carolina's reapportionment plan was racially neutral on its face, the resulting district shape was bizarre enough to suggest that it constituted an effort to separate voters into different districts based on race
\
although North Carolina's reapportionment plan was racially neutral on its face, the resulting district shape was bizarre enough to suggest that it constituted an effort to separate voters into different districts based on race
31
New cards
lame duck
A time during the end of a term typically when transition of power is happening, where the person has some to no power
32
New cards
delegate
They vote on what their constituents want
33
New cards
politico
Combo of delegates and trustees (delegate when their constituents care about the impact)
34
New cards
filibuster
a prolonged speech that obstructs progress in a legislative assembly
35
New cards
\
cloture
cloture
Stops a filibuster (60 people)
36
New cards
hold
An informal practice by which a senator informs Senate leadership that he or she does not wish a particular measure or nomination to reach the floor for consideration.
37
New cards
\
Speaker of House
Speaker of House
the House's presiding officer, party leader, and the institution's administrative head, among other duties.
\
“administering the oath of office to the Members of the U.S. House of Representatives, giving Members permission to speak on the House floor, designating Members to serve as Speaker pro tempore, counting and declaring all votes, appointing Members to committees, sending bills to committees, and signing bills and resolutions that pass in the House.”
\
“administering the oath of office to the Members of the U.S. House of Representatives, giving Members permission to speak on the House floor, designating Members to serve as Speaker pro tempore, counting and declaring all votes, appointing Members to committees, sending bills to committees, and signing bills and resolutions that pass in the House.”
38
New cards
\
Pres.ProTemp
Pres.ProTemp
preside over the Senate in the absence of the vice preside
39
New cards
Majority leader
schedules legislation to be considered on the House floor; organizes daily, weekly, and yearly legislative plans; consults with Members to understand how party members feel about issues; and works to advance the goals of the party.
40
New cards
Minority leader
promote and publicize the party's agenda. The minority leader, if their party controls the White House, confers regularly with the Preside
41
New cards
Whips
whips are mainly responsible for counting heads and rounding up party members for votes and quorum calls, and they occasionally stand in for the majority or minority leaders in their absence.
42
New cards
President’s formal powers
* make treaties with the approval of the Senate.
* veto bills and sign bills.
* represent our nation in talks with foreign countries.
* enforce the laws that Congress passes.
* act as Commander-in-Chief during a war.
* call out troops to protect our nation against an attack.
* make suggestions about things that should be new laws.
* lead his political party.
* entertain foreign guests.
* recognize foreign countries.
* grant pardons.
* nominate Cabinet members and Supreme Court Justices and other high officials.
* appoint ambassadors.
* talk directly to the people about problems.
* represent the best interest of all the people
* \
* veto bills and sign bills.
* represent our nation in talks with foreign countries.
* enforce the laws that Congress passes.
* act as Commander-in-Chief during a war.
* call out troops to protect our nation against an attack.
* make suggestions about things that should be new laws.
* lead his political party.
* entertain foreign guests.
* recognize foreign countries.
* grant pardons.
* nominate Cabinet members and Supreme Court Justices and other high officials.
* appoint ambassadors.
* talk directly to the people about problems.
* represent the best interest of all the people
* \
43
New cards
Vesting clause
a constitutional law that vests legislative power in Congress, executive power in the President, and judicial power in the federal courts.
44
New cards
“take care” clause
requiring the President to “take Care that the Laws be faithfully executed.”
45
New cards
veto
President can stop any legislation from becoming a law (can be overruled by 2/3 majority vote in each house)
46
New cards
pocket veto
an indirect veto of a legislative bill by the president or a governor by retaining the bill unsigned until it is too late for it to be dealt with during the legislative session.
47
New cards
Executive privilege
the privilege, claimed by the president for the executive branch of the US government, of withholding information in the public interest.
48
New cards
pardons
use of executive power that exempts the individual to whom it was given from punishment
49
New cards
formal foreign policy powers
power to nominate ambassadors and appointments are made with the advice and consent of the Senate. Issue executive orders and negotiate and sign treaties with advice and consent of the Senate
50
New cards
executive agreements
an international agreement entered into by the President, pursuant to the President's constitutional or statutory authority, without the Senate's advice or consent.
51
New cards
bargaining and persuasion
**Setting priorities for Congress and attempting to get majorities to put through the president's legislative agenda**.
52
New cards
unilateral action
any policy decision made and acted upon by the president and his staff without the explicit approval or consent of Congress.
53
New cards
executive orders
declaration by the president or a governor which has the force of law, usually based on existing statutory powers
54
New cards
\
signing statements
signing statements
a written pronouncement issued by the President of the United States upon the signing of a bill into law. (something he says)
55
New cards
Cabinet members and EOP
includes the Vice President and the heads of 15 executive departments they advise the President on any subject he or she may require relating to the duties of each member's respective office.
To provide the President with the support that he or she needs to govern effectively, the Executive Office of the President (EOP)
To provide the President with the support that he or she needs to govern effectively, the Executive Office of the President (EOP)
56
New cards
Ambassadors
Directing and coordinating all executive branch offices and personnel in other places
57
New cards
White House staff
Ensure that the administration's policies are coherent – that initiatives of one department are not undercutting those of other departments. Ensure that the system for advising the president produces informed decisions. Ensure that decisions are implemented consistent with the intent of the President.
58
New cards
Senate confirmation
Senate approval of a president nominating someone through a long process of hearings
59
New cards
judicial appointments
The President of the United States appoints Supreme Court justices and federal judges to be approved by the Senate
60
New cards
**Federalist 70**
Alexander Hamilton argues for a strong executive lead
61
New cards
**22nd Amendment**
President can only serve two terms
62
New cards
Increased presidential power
**increase whenever there is a national crisis, or other need for strong, immediate action from the government**.
63
New cards
**25th Amendment**
In case of the removal of the President from office or of his death or resignation, the Vice President shall become President.
64
New cards
bully pulpit
a conspicuous position that provides an opportunity to speak out and be listened to. Having an agenda/ platform to force other people to do things
65
New cards
going public
a new style of presidential leadership in which the president sells his programs directly to the American public (appealing to the public to make them pressure Congress) especially through social media
66
New cards
\
The SCOTUS **Article III**
The SCOTUS **Article III**
The Court has original jurisdiction and appellate jurisdiction. It can hear certain cases, e.g., suits between two or more states and/or cases involving ambassadors and other public ministers.
67
New cards
Judiciary Act of 1789
established the structure and jurisdiction of the federal court system and created the position of attorney general.
68
New cards
**Federalist 78**
judicial branch as the “least dangerous” branch of the new national government
69
New cards
***Marbury v. Madison*** **(1803)**
Marbury had been appointed Justice of the Peace in the District of Columbia, but his commission was not delivered. Marbury petitioned the Supreme Court to compel the new Secretary of State, James Madison, to deliver the documents
\
The Court held that the provision of the Judiciary Act of 1789 enabling Marbury to bring his claim to the Supreme Court was itself unconstitutional. Said the court could not do anything.
\
Chief Justice John Marshall established the principle of judicial review, through this
\
The Court held that the provision of the Judiciary Act of 1789 enabling Marbury to bring his claim to the Supreme Court was itself unconstitutional. Said the court could not do anything.
\
Chief Justice John Marshall established the principle of judicial review, through this
70
New cards
Rule of Four
e Supreme Court's practice of granting a petition for review only if there are at least four votes to do so
71
New cards
Writ of Cert
a request that the Supreme Court order a lower court to send up the record of the case for review
72
New cards
Precedent/Stare Decisis
**holds that courts and judges should honor “precedent”—or the decisions, rulings, and opinions from prior cases**
73
New cards
Impact of judicial appointments
deteriorates the rule of law
74
New cards
judicial activism
describes how a justice approaches judicial review, where judicial activists abandon their responsibility to interpret the Constitution and instead decide cases to advance their preferred policies/ beliefs
75
New cards
self-restraint
restraint imposed by oneself on one's own action. Going strictly by the constitution
76
New cards
original jurisdiction
the Supreme Court is the first, and only, Court to hear a case (disputes between the states or disputes arising among ambassadors and other high-ranking ministers.)
77
New cards
jurisdiction appellate
the power to reverse or modify the the lower court's decision
78
New cards
Constitutional Amendments
Amends the constitution, changes what it says or adds on to it
79
New cards
Presidents or states ignoring or evading SCOTUS decisions
they do not face any consequences
80
New cards
Bureaucracy
institution that is hierarchical in nature and exists to formulate, enact, and enforce public policy in an efficient and equitable manner.
81
New cards
Writing regulations/ enforcing/adjudicating
This phrase refers to the three main functions of government agencies responsible for implementing laws and policies. "Writing regulations" involves creating rules and guidelines that interpret and clarify the intent of laws. "Enforcing" refers to the process of ensuring compliance with these regulations through inspections, investigations, and penalties. "Adjudicating" involves resolving disputes and making decisions in legal cases related to the regulations.
82
New cards
Red tape
excessive bureaucracy or adherence to rules and formalities, makes work go slow/ stop it
83
New cards
Testifying before Congress/expertise
testify regularly before congressional committees on both legislative and oversight matters to see what the bureaucracies are doing
84
New cards
Issue networks and Iron triangles
\
an alliance of various interest groups and individuals who unite in order to promote a common cause or agenda in a way that influences government policy. (Bureaucracy, intrest groups, Congress)
an alliance of various interest groups and individuals who unite in order to promote a common cause or agenda in a way that influences government policy. (Bureaucracy, intrest groups, Congress)
85
New cards
\
merit system
merit system
the process of promoting and hiring government employees based on their ability to perform a job, rather than on their political connections.
86
New cards
patronage
a spoils system (also known as a patronage system) is a practice in which a political party, after winning an election, gives government jobs to its supporters,
87
New cards
civil servants
a person employed in the public sector by a government department or agency for public sector undertakings
88
New cards
political appointees
any employee who is appointed by the President, the Vice President, or agency head
89
New cards
Oversight
holding hearings and conducts oversight of agency enforcement operations, functions and policies.
90
New cards
police patrol
members of congress constantly monitor the bureaucracy to make sure that laws are implemented corectly
91
New cards
fire alarm
selective monitoring, triggered by complaints from citizens and interest groups who bring potential problems. to legislators' attention.
92
New cards
Notice and comment procedure
an agency (Like EPA) must first issue a notice of proposed rulemaking (NPRM) and provide an opportunity for public comment on the proposal before it can issue a final rule.
93
New cards
committee hearings
a method by which committee members gather information.
94
New cards
appropriations
A law of Congress that provides an agency with budget authority. An appropriation allows the agency to incur obligations and to make payments from the U.S. Treasury for specified purposes
95
New cards
Problem of control/checks on the bureaucracy
Hard to fire, Red tape, Conflicts between similar bureaucracies (who does what), external forces, they hire people to do what they don’t want to do
96
New cards
checks on the president
Judicial declares laws unconstitutional
\
Legislative rejects appointments, reject treaties, withhold funding, impeach and override veto
\
Legislative rejects appointments, reject treaties, withhold funding, impeach and override veto
97
New cards
checks on Congress
Executive can veto bills and adjourn Congress in certain situations
\
Judicial can declare laws unconstitutional
\
Judicial can declare laws unconstitutional
98
New cards
checks on the judiciary
Executive appoints judges
\
Legislative can propose amendments, impeach people, not enforce ruling, and reject appointments
\
Legislative can propose amendments, impeach people, not enforce ruling, and reject appointments
99
New cards
OMB
Office of Management and Budget (OMB) serves the President of the United States in overseeing the implementation of his or her vision across the Executive Branch.
100
New cards
Committee of the whole
a committee of the House on which all Representatives serve and which meets in the House Chamber for the consideration of measures from the Union calendar (moves bills to the floor faster because needs less votes)