Geology final
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/158
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
159 Terms
1
New cards
what are the two ways that lava can errupt?
* lava (quietly)
* pyroclasts (violent)
* pyroclasts (violent)
2
New cards
what are the two main factors on how a volcano errupts?
* silica content
* viscosity
* viscosity
3
New cards
How do volcanoes erupt?
(gas content)
(gas content)
magma is filled with gas, deep within the crust the magma is under so much pressure it doesn’t expand. As the magma rises, the gas expands and creates pressure. Eventually, the gas overwhelms the magma causing it to fragment and explode as a gas jet.
4
New cards
Does silica increase the viscosity of magma?
yes, the more silica the greater the viscosity.
5
New cards
Silica % basalt
50% (gas poor)
6
New cards
silica % andesite:
60% (gas rich)
7
New cards
ryolite and granite
70% (gas rich)
8
New cards
How does baslat magma flow?
flows smooth and over long distances
9
New cards
How does andesite magma flow?
breaks up as it flows, does not cover long distances
10
New cards
How does ryolite magma flow?
piles up in a dome, very viscous
11
New cards
What is a caldera?
* a large depression created by the collapse of a volcano.
* primarly rhyolitic
* largest explosions are related to calderas.
* primarly rhyolitic
* largest explosions are related to calderas.
12
New cards
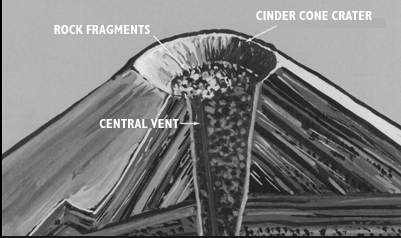
what is a cinder cone?
* a simple volcano built from blobs of lava ejected from a single vent.
* small but explosive
* erupts for only one episode
* is a pile of pyroclastic debris of the angle of repose.
* small but explosive
* erupts for only one episode
* is a pile of pyroclastic debris of the angle of repose.
13
New cards
what is a shield volcano?
* built from countless outpourings of fluid lava. (basaltic lava flows)
* calm erruptions
* flat
* little or no ash
* calm erruptions
* flat
* little or no ash
14
New cards
What is a stratovolcanoe?
* pointed
* lots of ash
* built up from lava, ash and volcanic debris. altering layers of lava and pyroclasts.
* dominantly andesitic in composition
* typical for subduction zones (where one plate slips below the other)
* lots of ash
* built up from lava, ash and volcanic debris. altering layers of lava and pyroclasts.
* dominantly andesitic in composition
* typical for subduction zones (where one plate slips below the other)
15
New cards
what is a lava dome?
mount formed when viscous lava piles up around vents
16
New cards
what is the tallest volcano on earth?
Muana Kea, measured from the sea floor (13,767 ft)
17
New cards
Do other planets have shield volcanoes?
Yes, mars has shield volcanoes, the largest in our solar system called Olympus mons. These volcanoes are massive in comparison to earth.
18
New cards
magma generation at hot spots
a hot spot is an area where the oceanic or continental lithosphere are able to melt where they would not normally be able to.
the lava comes from deep within the mantle and is fed up through plums,
the lava comes from deep within the mantle and is fed up through plums,
19
New cards
interplate volcanism
volcanoes that take place away from the tectonic plate margins
ex: hawaii is surrounded by hotspots
ex: hawaii is surrounded by hotspots
20
New cards
Magma generation at mid-oceanic ridges
* an oceanic ridge is formed by two tectonic plates
* in these zones, the mantle rises and melts
* produces magma if silicate composition
* when the lava rises it erupts as basaltic flows
* knows as a rifting product
* in these zones, the mantle rises and melts
* produces magma if silicate composition
* when the lava rises it erupts as basaltic flows
* knows as a rifting product
21
New cards
how is rifting affecting Iceland?
Iceland is being pulled apart by two plates however the center is renewed by new magma from the mantle.
22
New cards
what is the result o rifting?
frequent eruptions that produce fountains of fluid lave
23
New cards
what are fountains of magma?
a result of when the gas cant escape fast enough ending ina jet-like propulsion of lava and gas.
24
New cards
subduction zone
Where the oceanic lithosphere of a tectonic plate converges with the less dense lithosphere of a second plate, the heavier plate dives beneath the second plate and sinks into the mantle
25
New cards
magma at subduction zones
* the subduction plate curves down into the mantle and heats up.
* around 80-120km down, the melting begins
* volcanoes are produced parallel to this zone
* usually produces andesitic and dacitic magmas.
* around 80-120km down, the melting begins
* volcanoes are produced parallel to this zone
* usually produces andesitic and dacitic magmas.
26
New cards
volcano explosion: Anak Krakatau Indonesea
* august 27,1883
* blew away 2/3 of the island
* follows by the collapse of the underground taverns and magma chambers creating an underwater caldera.
* blew away 2/3 of the island
* follows by the collapse of the underground taverns and magma chambers creating an underwater caldera.
27
New cards
why is rhyolite magma richer in H2O, what does it cause?
rhyolite magma is richer in CO2 because of the partial melting of the crust. The rich in H2O and silica allow for rapid expansion and runaway reactions
28
New cards
Yellow stone
yellow stone is a super volcano that has its magma chamber close to the surface. when a large portion of gas expands it will cause a runaway reaction and blow parts of the crust off. This will create a huge gas explosion.
29
New cards
volcanic threats to canada:
* there are many volcanoes in the west coast
* an explosion from the Washington area will create dust and ash to settle on parts of Canada (AB BC)
* an explosion from the Washington area will create dust and ash to settle on parts of Canada (AB BC)
30
New cards
Pahoehoe
* type of lava flow
* smooth ripply and ropy lava
* fluid like textures
* smooth ripply and ropy lava
* fluid like textures
31
New cards
Aa lava
* lava flow
* rocky surface but has a cool temp in comparisons to other lavas
* below the surface the temp is high
* rocky surface but has a cool temp in comparisons to other lavas
* below the surface the temp is high
32
New cards
can lava be managed?
cooling reductions can be used to manage lava
33
New cards
pyroclstic falls
* during explosive volcanic eruptions, ash falls down wind of the volcano
* can cover very large areas
* can cover very large areas
34
New cards
what are saftey concerns for pyroclastic falls?
* aviation saftey
* structure damage
* death
* climate change
* bad drinking water
* structure damage
* death
* climate change
* bad drinking water
35
New cards
pyroclastic flows
suspension of hot pyroclastic materials, air, and gases that decend due to gravity.
can reach 50-500km/hr
can reach 50-500km/hr
36
New cards
lahars
* volcanic debris flows (mudflows)
* flows of water and lose volcanic debris
* prevalent in snow and ice volcanoes
* flows of water and lose volcanic debris
* prevalent in snow and ice volcanoes
37
New cards
how are lahars triggered?
1. volcanic activity melting the snow and ice
2. torrential rainfall (rainwater mixes with the debris)
3. rocks and ash flow into existing drainage routes.
38
New cards
What is builking? (lahars)
when the lahar incorporates materials from the area they flow over
erodes away the area and existing drainage channel
erodes away the area and existing drainage channel
39
New cards
what are the impacts of bulking? (lahar)
* large objects can be picked up during bulking ( which can destroy infrastructure)
* people living in drainage valleys are at risk
* sediment loads can affect ecosystems
* people living in drainage valleys are at risk
* sediment loads can affect ecosystems
40
New cards
debris avalanches (VA)
* when a volcanoe erupts and weakens an area (ediface)
* collapse of the area will start an avalanche
* collapse of the area will start an avalanche
41
New cards
volcanic gases
* highly acidic
* affect vegetation and crops that we eat
* attacks respiratory systems
* corrodes metal and damages infrastructure
* gases react with the concrete to crumble it
* affect vegetation and crops that we eat
* attacks respiratory systems
* corrodes metal and damages infrastructure
* gases react with the concrete to crumble it
42
New cards
VEI
* volcanic explositivy index
* the logarithmic scale is used to tell us how explosive volcanoes are
* the logarithmic scale is used to tell us how explosive volcanoes are
43
New cards
what are the primary features of an earthquake?
ground shaking
44
New cards
what are the secondary features of an earthquake?
* fire
* landslides
* ground subsidence
* snow and ice avalanches
* floods
* landslides
* ground subsidence
* snow and ice avalanches
* floods
45
New cards
what is stress?
force applied to a material that changes its dimensions
46
New cards
what are the types of stress?
1. compressed stress
1. non-rotational
1. forces directed toward on another
2. decreases the volume of material
2. rotational (shear)
1. parralel force in the opposite diractions
2. tension stress
1. stretching stress that tends to increase the volume of material.
47
New cards
what is strain?
the effects of stress shown on the material
48
New cards
what are the types of strain?
1. extensions
2. compression
49
New cards
what is strength?
limiting stress that a material can take without failing by rupture or continuous plastic flow
50
New cards
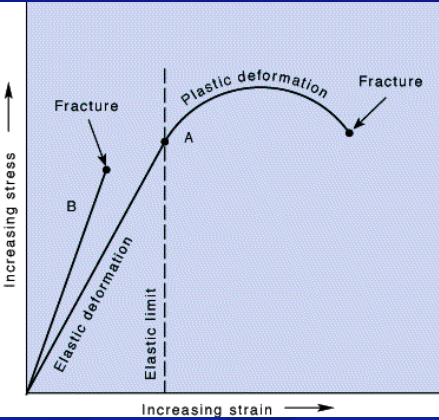
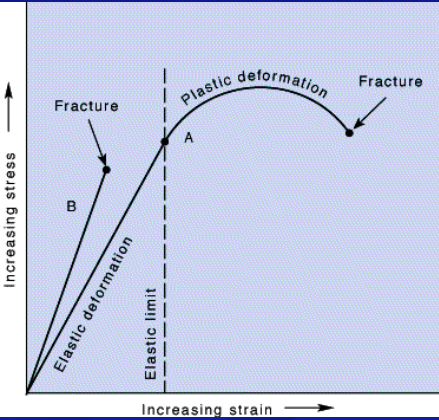
response to stress: elastic deformation
* strian is proportional to the stress
* rocks will return to their begininning state if stress is taken off
* absorb, store, release
* rocks will return to their begininning state if stress is taken off
* absorb, store, release
51
New cards
response to stress: plastic deformation
* permanent deformation caused by the flowing and folding at stress above the elastic limit
* high pressure and temp
* warm rocks tend to plastic deform
* absorb, internally consume energy, permanent deformation
* high pressure and temp
* warm rocks tend to plastic deform
* absorb, internally consume energy, permanent deformation
52
New cards
response to stress: brittle deformation
* rock breaks if stress is too great
* rocks near the surface tend to deform this way
* absorb, exceed and break, permanent deformation
* rocks near the surface tend to deform this way
* absorb, exceed and break, permanent deformation
53
New cards
what is an earthquake?
* shaking and vibration of the ground
* rocks undergoing deformation suddenly at a fault
* creates seismic waves
* rocks undergoing deformation suddenly at a fault
* creates seismic waves
54
New cards
where do the worlds earthquakes happen?
* the majority occur at plate argins
* ring of fire
* ring of fire
55
New cards
what are the forces that cause earthquakes? (6)
1. volcanic activity
2. meteorite and asteroid impacts
1. kinetic energy is transferred from impact to waves
3. landslides
1. kinetic energy from the moving mass of material is transmitted through waves
4. nuclear explosions
1. can be used to catch illegal nuclear tests
5. collapse of underground caverns
6. movement on faults
1. when a fault breaks
56
New cards
joints
* fractures in the earth’s crust
* no appreciable movement occurs
* happen in grounds and run parallel to each other
* result of brittle fracturing
* no appreciable movement occurs
* happen in grounds and run parallel to each other
* result of brittle fracturing
57
New cards
faults
* fractures where movement has occurred
* sudden movement along faults causes earthquakes
* most faults are inactive
* sudden movement along faults causes earthquakes
* most faults are inactive
58
New cards
what do faults produce? (not earthquakes)
* fualt scarps
* cliff formed by vertical motions
* fault brecca
* angular rocks along a fault
* cliff formed by vertical motions
* fault brecca
* angular rocks along a fault
59
New cards
what are the three types of vertical faults
1. normal fault: result of tension forces.
1. bottom plate moves up and top plate moves down
2. reverse fault: horizontal compression
1. bottom plate moves down, top moves up
3. thrust fault: horizontal compression
1. bottom moves down, top moves up
2. happens inside the lithospere and does not break surface
60
New cards
strike-slip faults
when one block slides past another
* left lateral
* right lateral
* left lateral
* right lateral
61
New cards
elastic rebound theory
* the theory explains how energy is released during an earthquake
* rocks on opposite sides are subjected to force
* they slowly accumulate energy and deform until their internal strength is exceeded
* at this time, a sudden movement occurs along the fault releasing accumulated energy
* the rocks will snap back into shape afterwards
* rocks on opposite sides are subjected to force
* they slowly accumulate energy and deform until their internal strength is exceeded
* at this time, a sudden movement occurs along the fault releasing accumulated energy
* the rocks will snap back into shape afterwards
62
New cards
what is an earthquakes epicenter
the vertical projection of the focus of the surface
63
New cards
how are earthquakes classified by depth?
* 0-70km (shallow)
* 70-300km (intermediate)
* 300-700+ (deep)
* 70-300km (intermediate)
* 300-700+ (deep)
64
New cards
what are the two types of waves produced by earthquakes?
1. body waves
1. travel through the earth
2. p, s waves
2. surface waves
1. travel along the surface
2. rayleigh
3. love
65
New cards
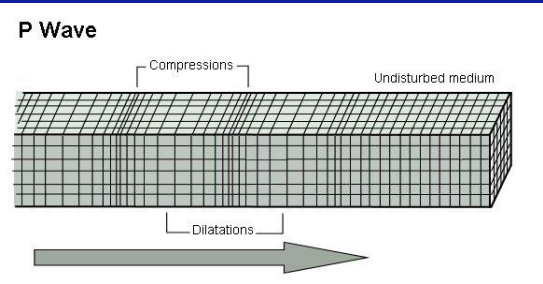
What are P waves?
* primary waves
* travel through solid, liquid and fas
* 5 km/s
* alternately compressive and expansive
* travel through solid, liquid and fas
* 5 km/s
* alternately compressive and expansive
66
New cards
what are S waves?
* shear waves
* travel only through solids
* push material at right angle to their travel paths
* travel only through solids
* push material at right angle to their travel paths
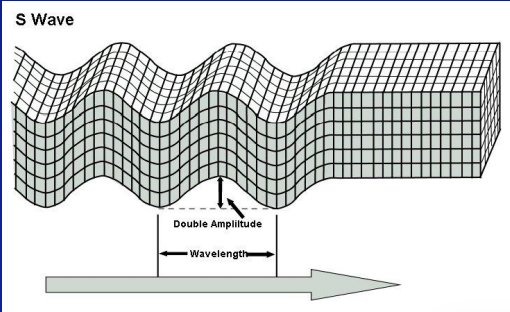
67
New cards
what are love waves?
* surface waves
* restricted to earths surface
* cause sideway shaking of the ground
* cause the most damage
* restricted to earths surface
* cause sideway shaking of the ground
* cause the most damage
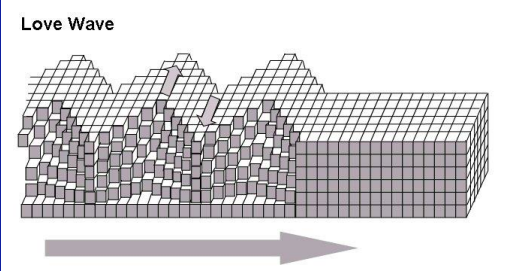
68
New cards
what are rayleigh waves?
* surface waves
* produce a rolling motion
* produce a rolling motion
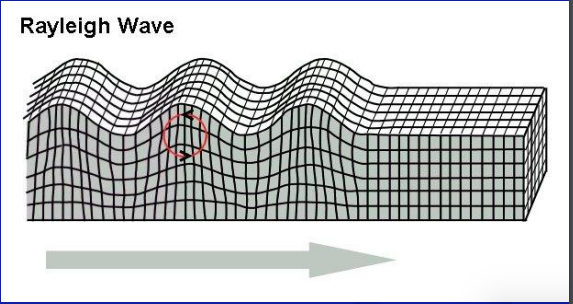
69
New cards
Mercalli scale
* assigns a measure of destructiveness to an earthquake
* qualitative and is based on observed effects on people and damages to buildings
* Mercalli I
* weak
* Mercalli XII
* total destruction
* qualitative and is based on observed effects on people and damages to buildings
* Mercalli I
* weak
* Mercalli XII
* total destruction
70
New cards
richer magnitudes
* measures the maximum amplitude of ground shaking
* logarithmic scale
* 1 richer unit = 10x ground motion, 33x energy
* small earthquakes are common and large earthquakes only happen every 5-10 years
* starts at 2.5 and increases over time
* the highest number is 8.0 and up
* logarithmic scale
* 1 richer unit = 10x ground motion, 33x energy
* small earthquakes are common and large earthquakes only happen every 5-10 years
* starts at 2.5 and increases over time
* the highest number is 8.0 and up
71
New cards
graph of waves
* surface waves have higher amplitudes
* 1st wave to hit the graph is the p waves
* s-p interval is the time between the two
* 1st wave to hit the graph is the p waves
* s-p interval is the time between the two
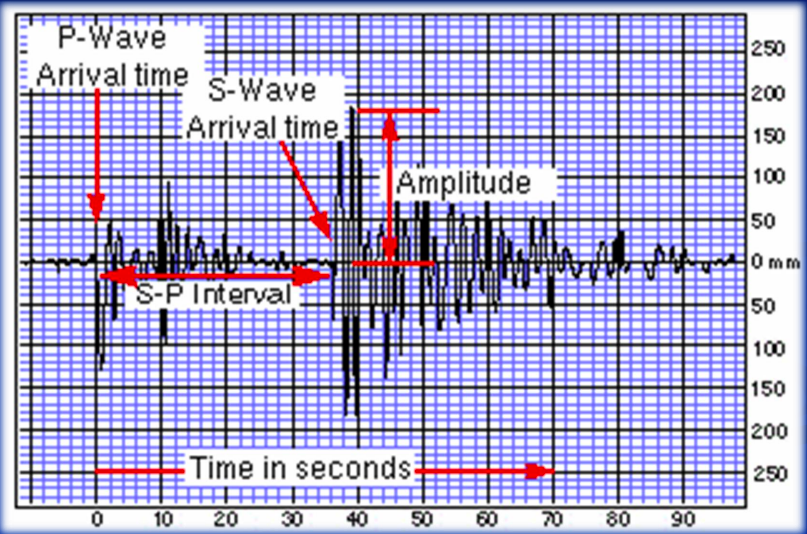
72
New cards
explain how to find the location based on the graph:
* in notes
73
New cards
The San Andreas Fault
* along west coast
* strike-slip fault
* transform boundry between the pacific plate and north American plate
* pacific plate moves northwest
* north American plate moves southeast
* some parts move smoothly while other parts lock up and produce energy
* 1,200 km long and 16 km deep in some areas
* strike-slip fault
* transform boundry between the pacific plate and north American plate
* pacific plate moves northwest
* north American plate moves southeast
* some parts move smoothly while other parts lock up and produce energy
* 1,200 km long and 16 km deep in some areas
74
New cards
1906 san fran
* earthquake caused by san Andreas fault
* M7.7-7.9
* 3000 dead
* 225,000 out of 400,000 homeless
* M7.7-7.9
* 3000 dead
* 225,000 out of 400,000 homeless
75
New cards
1989 loma prieta quake
* the earthquake caused by the san Andreas fault
* M 6.9
* 57 dead
* marina district was liquified due to shaking
* M 6.9
* 57 dead
* marina district was liquified due to shaking
76
New cards
cascadia
* pacific northwest subduction zone
* evidence for very large earthquakes
* evidence for very large earthquakes
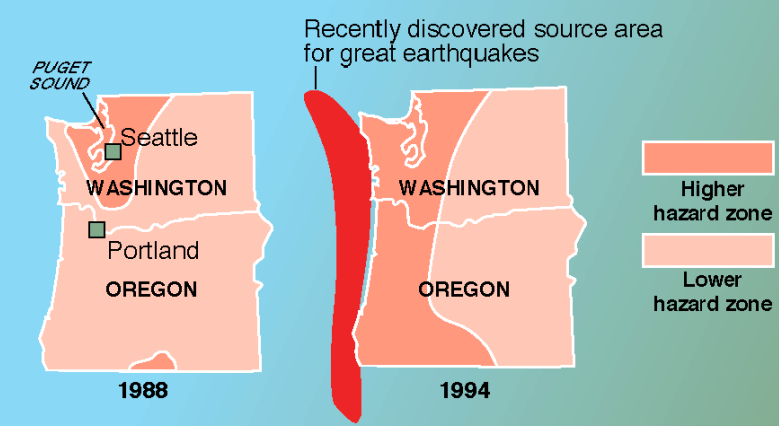
77
New cards
Quebec
* st. lawrence has high seismicity for a zone in the interior plate
78
New cards
Earthquake effects: liquefaction
* occurs within sediments during earthquakes
* groundwater moves up due to shaking and lubricates the sediments
* it amplified the shaking and causes structures to sink.
* groundwater moves up due to shaking and lubricates the sediments
* it amplified the shaking and causes structures to sink.
79
New cards
Earthquake effects: aftershocks
* normally occur after major earthquakes
* can span over the space of months or even years
* can cause damage to already weakened materials
* can span over the space of months or even years
* can cause damage to already weakened materials
80
New cards
Earthquake effects: landslides
* shaking can induce landslides in mountainous areas
81
New cards
Earthquake effects: Tsunamis
* ocean waves caused by the displacement from earthquakes.
82
New cards
Earthquake effects: building destruction
* damaged or destryed by ground vibrations
* can be increased by liquification
* Masonry (bricks): not capable of withstanding stress
* wood: can withstand stress but not fires
* can be increased by liquification
* Masonry (bricks): not capable of withstanding stress
* wood: can withstand stress but not fires
83
New cards
Earthquake effects: fires
* ground shaking can rupture gas lines and water lines.
84
New cards
Earthquake effects: personal loss
self explanatory
85
New cards
mitigating earthquakes
* seismic hazard maps can be used to help use decide where and how to build
* avoid unstable soils
* avoid mountainous areas for avalanches
* avoid fracture faults
* building codes
* bedrock foundations
* avoid asymmetrical builds
* flexible gas lines
* avoid unstable soils
* avoid mountainous areas for avalanches
* avoid fracture faults
* building codes
* bedrock foundations
* avoid asymmetrical builds
* flexible gas lines
86
New cards
short term forecasting for earthquakes
* ground deformation
* foreshocks
* changes in water table
* changes in the electrical conductivity of rocks
* strange animal behaviour
* increased radon gas emmison
* foreshocks
* changes in water table
* changes in the electrical conductivity of rocks
* strange animal behaviour
* increased radon gas emmison
87
New cards
what is a tsunami?
* very large ocean wave that is generated by a sudden displacement of the seafloor or other mass
* tsunami is a Japanese word meaning harbour wave
* tsunami is a Japanese word meaning harbour wave
88
New cards
where are most the tsunamis produced?
75% of tsunamis are produced in the Pacific ocean
89
New cards
structure of a tsunami
pic
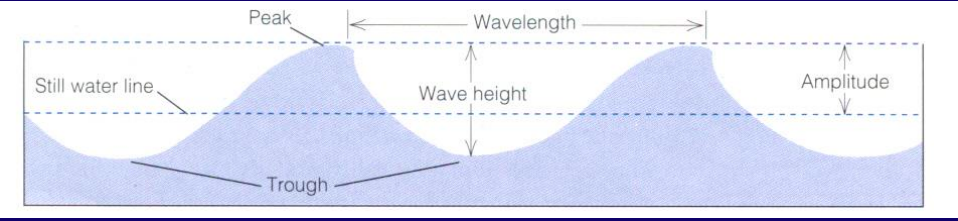
90
New cards
velocity of a tsunami
* tsunamis have very high velocity in the open ocean
* 1000 km/hr
* they lose velocity as it gets more shallow
* however the amplitude is increased
* 1000 km/hr
* they lose velocity as it gets more shallow
* however the amplitude is increased
91
New cards
amplitude of a Tsunami
* in deep water the amplitude is small (1m)
* shallow water has greater amplitude (40m)
* shallow water has greater amplitude (40m)
92
New cards
Tsunami generation: earthquakes
* vertical movements cause tsunamis, due to this strike-slip faults are less dangerous
* the magnitude of the earthquake is directly correlated
* the magnitude of the earthquake is directly correlated
93
New cards
locally generated tsunamis
* more dangerous due to less reaction time
* happen very fast and have great velocities
* the subduction zone of cascadia has great potential for tsunamis
* happen very fast and have great velocities
* the subduction zone of cascadia has great potential for tsunamis
94
New cards
Tsunami generation: volcanic activity
* displacement of rocks
* submarine caldra collapse
* avalanches caused by volcanoes can flow into the water
* submarine caldra collapse
* avalanches caused by volcanoes can flow into the water
95
New cards
Tsunami generation: landslides
* can occur in closed bodies of water creating a large wave
* enormous submarine landslides can occur off the flanks of oceanic cliffs
* step 1: Material slides
* step 2: water is sucked down
* step 3: water rebounds creating a tsunami
\
* enormous submarine landslides can occur off the flanks of oceanic cliffs
* step 1: Material slides
* step 2: water is sucked down
* step 3: water rebounds creating a tsunami
\
96
New cards
mitigation efforts:
1. warning times
1. every 750km is 1hr warning time
2. response
1. planning and preparation
2. access to information for educated and trained public
3. effieicnt and relable info
97
New cards
where do landslide occur?
* can occur anywhere, that’s why they are so dangerous
* happen due to slope instability from factors such as volcanic eruption, earthquakes, storms, ect.
* happen due to slope instability from factors such as volcanic eruption, earthquakes, storms, ect.
98
New cards
what is mass wasting
* slope failure
* the failure and downslope of rock or unconsolidated material in response to gravity
* the failure and downslope of rock or unconsolidated material in response to gravity
99
New cards
impacts of mass wasting in developed countries
lots of property damage
100
New cards
impacts of mass wasting in non-developed countries
damage is extensive due to population density and less prepared infrastructure and awareness.