tissue fluid and lymph
1/3
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
4 Terms
what is tissue fluid? what does it contain?
fluid which passes out of the blood and bathes the tissue cells
contains mostly water, glucose, amino acids, fatty acids, ions and oxygen
(virtually same composition as blood plasma, just w/o proteins and cells)
describe the process of tissue fluid formation:
at the arterial end of the capillary, there is a high hydrostatic pressure due to contraction of the ventricles
there is a Ψ gradient into the capillaries (due to the hydrophilic plasma proteins exerting an oncotic pressure), but the hydrostatic pressure is greater and so overcomes this
ultrafiltration - water and dissolved substances, e.g. glucose forced out through the gaps (fenestrations) between the capillary endothelial cells, forming tissue fluid
proteins and RBCs are too large to pass through so remain in the capillaries
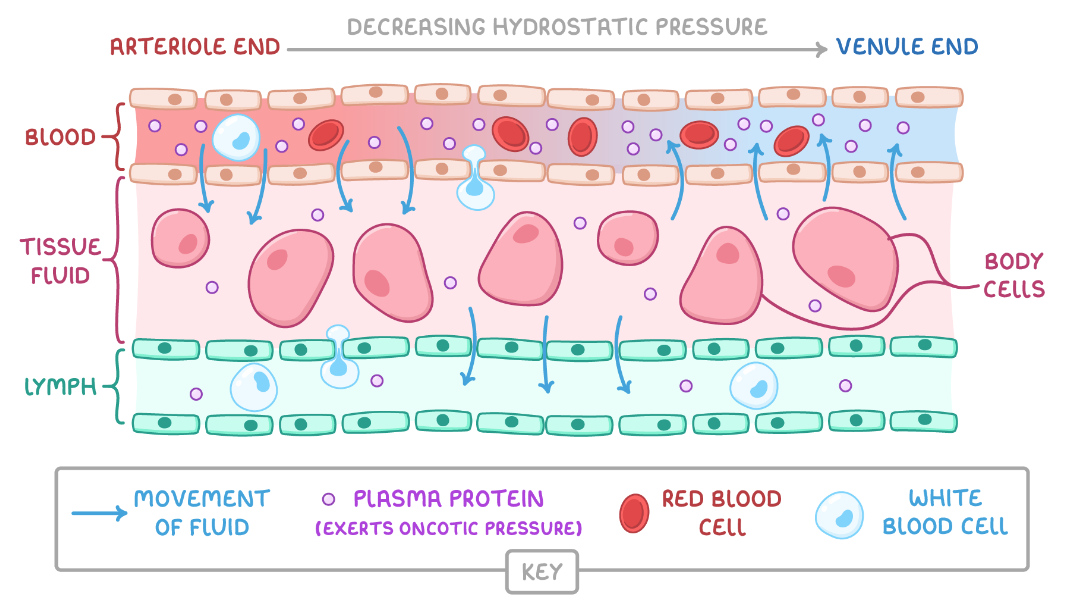
describe the process of tissue fluid reabsorption:
at the venule end of the capillary, the hydrostatic pressure is lower due to loss of water/fluid
Ψ in capillaries is lower than in the tissue fluid due to proteins remaining in the blood
water returns from tissue fluid to the venous end of the capillaries by osmosis down the Ψ gradient
the lymphatic system collects any XS tissue fluid which returns to the circulatory system
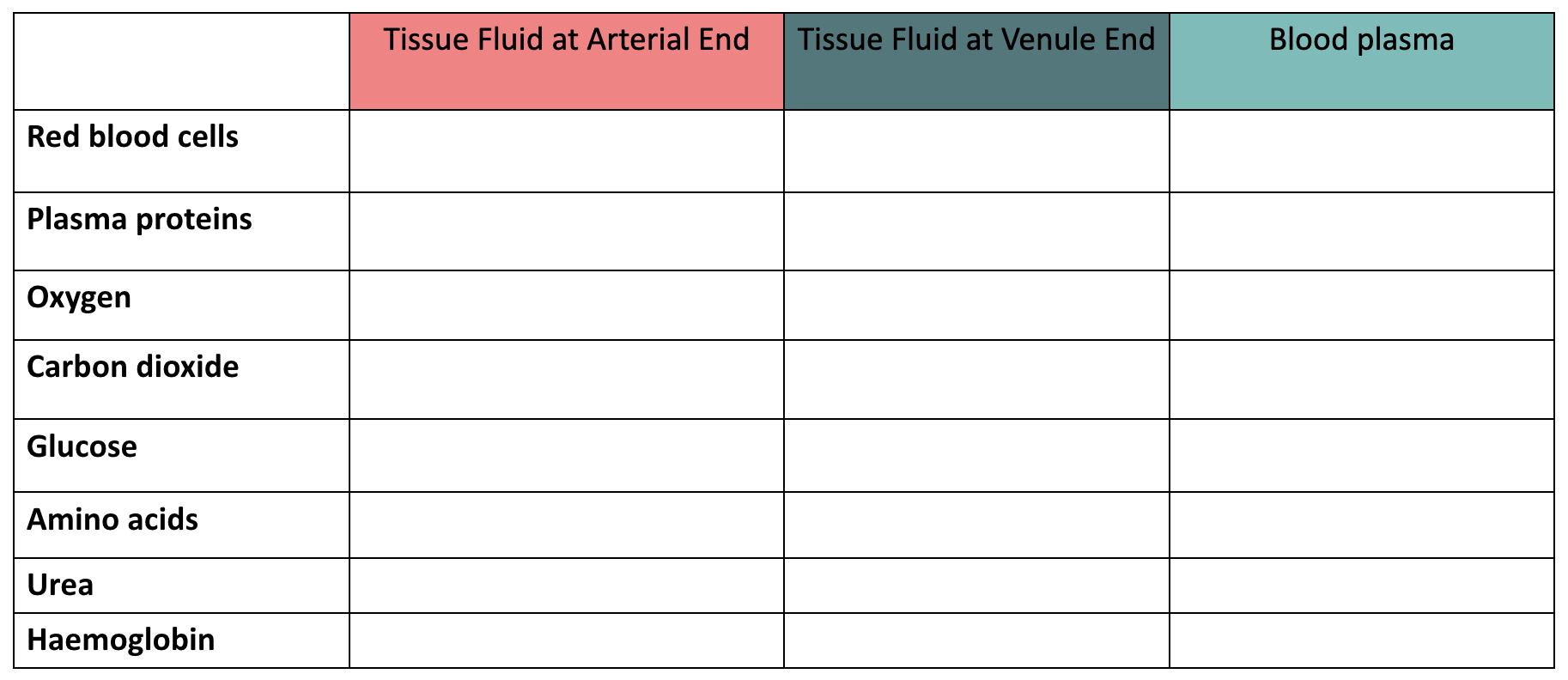
summarise the composition of tissue fluid surrounding the arterial and venule end of the capillaries and that of the blood plasma at the arterial end: