Inherited Retinal Disease
1/129
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
130 Terms
flash ERG
mass retinal test
abnormal: ≥ 20% affected
multifocal ERG
test for small areas (100um) of retinal dysfunction
cones/rods
what does the a wave show on an ERG?
muller cells & bipolar cell region
what does the b wave show on ERG?
rod
____ response: stimulating dark-adapted eye
cone
____ response: stimulating light-adapted eye, w/ flickering light (30Hz)
no (not beneficial unless the condition is treatable)
do you repeat an ERG?
cones
waveform: photopic A
retinal component: _______
cone dystrophies
in what type of disorders is the photopic A waveform altered in?
rods
waveform: scotopic A
retinal component: _______
inner nuclear layer (cones)
waveform: photopic B
retinal component: _______
inner nuclear layer (rods)
waveform: scotopic B
retinal component: _______
cones
waveform: flicker ERG
retinal component: _______
macula
waveform: multifocal ERG
retinal component: _______
rod dystrophies
in what type of disorders is the scotopic A waveform altered in?
retinoschisis
in what type of disorders is the photopic B waveform altered in?
retinoschisis
in what type of disorders is the scotopic B waveform altered in?
cone dystrophies
in what type of disorders is the flicker ERG waveform altered in?
maculopathy
in what type of disorders is the multifocal ERG waveform altered in?
EOG
measures electrical potential generated by RPE/photoreceptor complex, produces square waves
positive
the cornea is electro ___
negative
the posterior pole is electro ____
light peak / dark trough
what is the arden ratio?
>1.80
what is a normal arden ratio?
dark adaptation
night blindness test: ability of retina & pupil to react to decreased illumination
Goldmann-Weekers adaptometer
cones: initial segment
rods: 2nd slower segment
rod-cone break @ 7min
autosomal dominant
every generation affected
males = females
transmission only by affected person
50% risk to offspring
variable expression
s/sx:
milder
later onset
autosomal recessive
same generation affected
transmission by asymptomatic
probability:
50% carrier
25% affected
25% neither carrier nor affected
every child of an affected person is a carrier
both members of the chromosome pair must be affected for expression of the trait
males = females
less variable expression
s/sx:
more severe than AD
earlier onset than AD
X-linked recessive
only males are affected
trait transmitted through mother (carrier) w/ abnormal gene on 1 of her X chromosomes
probability:
transmission from mother to daughter (carrier) or son (affected): 50%
transmission from affected father to daughter: 100%
transmission from affected father to son: 0%
less variable in expression than AD
s/sx:
more severe
earlier onset than AD
lyonization
random inactivation of 1 X-chromosome in every cell
carrier manifests s/sx depending on degree of predetermined inactivation
RP
CSNB
Best’s
dominant drusen
aniridia
Duane’s
Marfan’s
ptosis
neurofibromatosis
list AD diseases
RP
CSNB
Usher’s
gyrate atrophy
Stargardt’s
fundus flavimaculatus
rod monochromat
Sjogren’s
list AR diseases
RP
CSNB
choroideremia
ocular albinism
R-G color defects
Fabry’s
list X-linked diseases
RP
congenital stationary night blindness
fundus albipunctatus
choroideremia
gyrate atrophy of choroid & retina
list diseases that affect peripheral & night vision
Stargardt’s disease/FF
Best’s vitelliform dystrophy
pattern dystrophies of RPE
dominant drusen
central areolar choroidal dystrophy
rod monochromatism
progressive cone dystrophy
albinism
list diseases that affect central & color vision
bilateral, symmetrical
almost all hereditary disorders are ______(bilateral/unilateral) & ________(asymmetrical/symmetrical)
RP
group of heredofamilial diseases characterized by progressive VF loss, night blindness, & abnormal/non-recordable EG
primarily affects photoreceptors & RPE function
prevalence: ~2million worldwide
age of onset: 9-19yo
bilateral, symmetric, progressive but variable
history: age of onset of sx, FHx, associated systemic issues
hereditary pattern: >100 gene loci have been mapped or identified
PSC, PCO, & CME more common
early phase RP
nyctalopia & photophobia
spreading ring scotomas: 30-50deg
RPE grey-green discoloration
diffuse RPE depigmentation & migration of pigment into sensory retina
reduced ERG (scotopic moreso than photopic)
ERM
PVD
vitreous condensation by 10yo
mid phase RP
moth-eaten RPE loss mid-periphery
bone spicule pigmentation
arteriolar attenuation
waxy pallor of ONH
PSC
CME
vitreous opacities & cells (free melanin pigment granules, uveal melanocytes, macrophage-like cells) evenly distributed throughout vitreous
late phase RP
choroidal vessels yellow-white w/ RPE loss
optic nerve pallor
VF reduction to small central & temporal island
non-recordable ERG
FA: diffuse hyperfluorescence due to RPE defects, hypofluorescence due to pigment clumping & choriocapillaris/RPE atrophy
focal degeneration
describe the histopathology of rods & cones w/ RP
depigmentation, atrophy, proliferation w/ pigment clumping & migration around vessels, accumulation of degraded phagosomal material
describe the histopathology of the RPE w/ RP
total loss of all retinal neurons, replaced w/ glial tissue
describe the histopathology of inner retina w/ RP
ERM, gliosis of optic disc, hyalinization/thickening of vessel wall
describe the histopathology of RP besides rods/cones/RPE/inner retina changes
scotopic ERG diminished to absent
abnormal/absence of light rise
dark adaptation: increased R-C thresholds
photopic gradual reduction to absent
30Hz flicker cone responses last to be reduced
less amplitude variability than dark or light-adapted flash stimuli
what are the ERG/EOG changes associated with RP?
genetic counseling
low vision & spectacle tints
cataract extraction
vitamin A + lutein, DHA may delay disease progression
avoid vitamin E
gene therapy, stem cell therapy, transplantation, artificial vision
what are the tx/management strategies for RP?
luxturna
approved for tx of confirmed biallelic RPE65 mutation-associated retinal dystrophy (Leber’s Congenital Amaurosis & some RP)
delivers normal copy of RPE65 gene directly to retinal cells
cells then produce normal protein that converts light to an electrical signal in retina to restore pt’s vision loss
subretinal injection
given w/ oral prednisone to limit potential immune rxn
retinitis sine pigmento
unilateral RP
sector RP
retinitis punctata albescens
Leber’s congenital amaurosis
what are the atypical RPs?
retinitis sine pigmento
AD, AR
onset: 1st-2nd decades
probable variation of RP
less severe s/sx
slight attenuation
waxy pallor
ERM
monitor x5y for dx
unilateral RP
rare
onset: 3rd-4th decades
prognosis similar to RP
carefully ddx (blunt trauma, resolved RD, IOFB, choroidal vascular occlusions, inflammation)
sector RP
AD
onset: <20yo
bilateral & symmetrical
inferior or inferior nasal
attenuated arterioles
RPE changes
corresponding VF defect
slow progression
DDx: retinal trauma, inflammation, RD
retinitis punctata albescens
AR
onset: 1st decade
fundus:
discrete whitish dots w/ subsequent bone spicules
vessel attenuation
ONH pallor
abnormal ERG
may improve w/ dark adaptation but will not normalize
slow progression
DDx: other white dot syndromes
Leber’s congenital amaurosis
congenital RP
AR form onset: 1st yr
AD form onset: 1st decade
s/sx:
profound visual impairment at birth
searching nystagmus
photophobia
oculo-digital sign
sluggish pupillary rxn
cataracts (50%)
keratoconus
glaucoma
extinguished ERG
fundus
progressive chorioretinal degeneration w/ optic atrophy
arteriolar attenuation
poor prognosis
tx: genetic testing, Luxturna for RPE65
loss of outer segments of PR w/ progressive degeneration of all retinal layers & RPE
describe the pathology of Leber’s Congenital Amaurosis
Usher’s Syndrome
AR
10% of all RP pts
congenital non-progressive deafness
Usher’s Syndrome
Bardet-Biedl Syndrome
Refsum’s Syndrome
Bassen-Kornzweig Syndrome
Batten’s Disease
what are some RP-associated systemic diseases?
congenital stationary night blindness
X-linked > AR > AD
s/sx:
night blindness
possible VA reduction
high myopia
essentially normal retina but may have loss of foveal reflex
VF constricted in mesopic conditions but normal in photopic
dark adaptation abnormal
etiology:
defect in light-activated enzymatic process involved in normal rod functioning
defect in synaptic transfer of message
complete or incomplete
severe nightblindness
scotopic normal a-wave, severely reduced/absent b-wave
EOG normal
what are the s/sx of complete CSNB?
do not uniformly report severe nightblindness
scotopic a & b waves reduced but measurable
EOG abnormal
what are the s/sx of CSNB?
fundus albipunctatus
CSNB variant
AR, AD
s/sx:
dull white dots midperiphery & perimacular
normalization w/ prolonged dark adaptation
slow adaptation of cones & rods
ERG is abnormal but normal after 3hrs of dark adaptation
choroideremia
X-linked
mutation in Rab escort protein 1 → degeneration of RPE then choroid & PR
onset: 1st-2nd decades
s/sx:
night blindness
peripheral VF constriction
eventual loss of central vision
ERG: photopic severely reduced, scotopic non-recordable
EOG abnormal
fundus
initial midperipheral RPE stippling
confluent areas of atrophy of RPE & choriocapillaris, vessel attenuation
preserved large choroidal vessels
OCT: thinning of RPE w/ attenuation of interdigitation zone
FA: early diffuse hyperfluorescence then later stages have hypofluorescence secondary to choroidal atrophy
prognosis: poor, slowly progressive
onset in 2nd decade
asymptomatic but some individuals have night blindness, chorioretinal degeneration, patchy granularity of RPE, decreased VA to 20/32
describe the appearance of chorioideremia in a female carrier
gyrate atrophy
AR
deficient OAT activity → increased ornithine levels in plasma/urine/CSF/aqueous
onset: 1st-2nd grade
s/sx:
myopia
night blindness
peripheral VF constriction
PSC
ERG: severely abnormal to non-recordable
abnormal EOG
systemic: seizure disorders, intellectual disability, muscle weakness
fundus:
mid-peripheral geographic RPE & choroidal atrophy coalesce to form scalloped borders w/ progression
macular degeneration
optic atrophy
vessel attenuation
poor prognosis w/o tx
tx: reduce serum ornithine levels when young, supplement w/ B6
Stargardt’s disease
AR (rarely AD)
enlargement of RPE cells in zones of flecks w/ total disappearance of cones, rods, & RPE in circumfoveal zone
s/sx:
bilateral
color vision loss
reduced VA
central scotoma
peripheral vision remains intact
normal-abnormal ERG/EOG
FA: hypofluorescence but becomes hyper as atrophy progresses
fundus
initial loss of FLR
RPE granularity
Bull’s eye maculopathy: zone of normal retina at macula, surrounded by grayish yellow depigmentation, pigment stippling
beaten-bronze, metallic appearance
fundus flavimaculatus
AR (rarely AD)
enlargement of RPE cells in zones of flecks w/ total disappearance of cones, rods, & RPE in circumfoveal zone
s/sx:
bilateral
color vision loss
reduced VA
central scotoma
peripheral vision remains intact
normal-abnormal ERG/EOG
FA: hypofluorescence but becomes hyper as atrophy progresses
fundus:
midperipheral yellowish-white flecks progressing toward macula
regions of RPE cells engorged w/ abnormal lipofuscin-like material
what are the flecks that appear in Stargardt’s & fundus flavimaculatus?
Best’s vitelliform dystrophy
AD
abnormal accumulation of materials in RPE resulting in dysfunction, atrophy, & eventual loss of PR function
onset: 4-10yo
bilateral, asymmetrical
s/sx:
initially slight VA reduction
later on, severe VA loss, color vision loss, central scotoma
normal ERG
abnormal EOG, even prior to fundus change
fundus:
macular egg yolk 0.5-2DD in size
progress to scrambled egg & VA loss
adult form: polymorphic
FA: hypofluorescent egg yolk followed by hyperfluorescence w/ RPE breakdown
0: normal macula, abnormal EOG
1: pre-vitelliform
2: vitelliform
3: pseudohypopyon
4: vitelliruptive
5: atrophy & fibrotic scar tissue
6: choroidal neovascularization
list the stages of Best’s vitelliform macular dystrophy
dominant drusen
AD
inherited malfunction of metabolic process in RPE
onset: w/in first 3 decades
s/sx:
metamorphopsia
VA loss
color vision loss
central scotomas
normal to minimally abnormal ERG
subnormal EOG in late stages
fundus:
macular drusen
confluent
eventual calcification
RPE atrophy
low risk of CNVM
FA: early hyperfluorescence of RPE & late staining
management: PRP/anti-VEGF for CNVM, low vision aids
retinitis punctata albescens
fundus albipunctatus
fundus flavimaculatas
Stargardt’s disease
dominant drusen
talc retinopathy
tamoxifen retinopathy
what are the white-dot syndromes?
central areolar choroidal dystrophy
AD, AR
choriocapillaris atrophy w/ subsequent loss of RPE & sensory retina
onset: after age 40
s/sx:
slowly progressive VA loss to <20/200
color vision loss
central scotoma
normal to minimally abnormal ERG/EOG
fundus:
initial macular RPE stippling
progressing to RPE & choriocapillaris atrophy w/ sharply defined borders
FA: early hyperfluorescence w/ eventual loss of choriocapillaris flow
poor prognosis w/ VA loss but peripheral vision intact
complete rod monochromatism
AR
congenital absence of cones
s/sx:
severe photophobia
pendular nystagmus
decreased vision, <20/200
color vision absent
ERG: photopic non-recordable, scotopic normal
fundus:
normal
loss of FLR
incomplete rod monochromatism
AR
congenital marked deficiency of cones
s/sx:
less severe photophobia
less severe pendular nystagmus
decreased vision, 20/40-20/100
color vision subnormal
ERG: minimal photopic waveform, scotopic normal
fundus:
normal
loss of FLR
progressive cone dystrophy
AD (possibly AR & X-linked)
onset: 1st-2nd decade
s/sx:
VA 20/60-20/200
photophobia
color vision loss
fine nystagmus
central scotoma
fundus:
bulls eye zone of RPE mottling & atrophy
diffuse pigment stippling, loss of foveal reflex & VA
RPE/choriocapillaris atrophy, optic atrophy, attenuated vessels
FA: bulls eye hyperfluorescent ring w/ fine areas of leakage
ERG: photopic abnormal to non-recordable, scotopic normal
EOG: usually normal
poor prognosis
Stargardt’s disease
progressive cone dystrophy
plaquenil toxicity
thioridazine/mellaril toxicity
what are the bull’s eye maculopathies?
usage >5y
cumulative dose of HCQ>1000g or CQ>460g
daily dose of HCQ>400mg/day or CQ>250mg/day
older age
kidney or liver dysfunction
retinal disease or maculopathy
what are the factors increasing the risk of CQ or HCQ retinopathy?
oculocutaneous albinism
AR, AD
congenital hypopigmentation of skin & eyes
s/sx:
nystagmus
photo-refractive error
reduced VA
strabismus
normal color vision
fundus:
foveal hypoplasia
retinal hypopigmentation
iris transillumination
ERG/EOG: supernormal due to light scatter
nystagmus & VA may improve w/ age
management: spec tints, UV protection
negative
the complete form of oculocutaneous albinism is tyrosinase _____, the pt is incapable of synthesizing melanin
positive
the incomplete form of oculocutaneous albinism is tyrosinase _____, the pt synthesizes variable amounts of melanin & varies in complexion, iris, & fundus pigmentation
ocular albinism
X-linked, AR
hypopigmentation limited to ocular structures
iris transillumination
scattered fundus depigmentation & granularity
what are the signs that asymptomatic female carriers of ocular albinism can show?
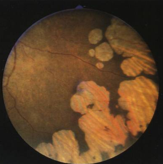
early phase RP
early phase RP
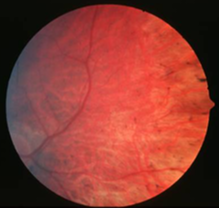
mid-phase RP
mid-phase RP
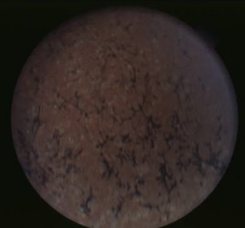
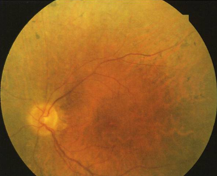
RP
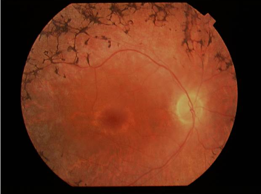
RP
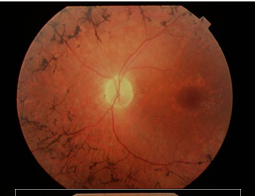
RP
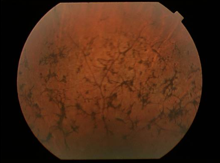
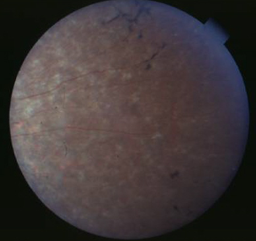
late phase RP
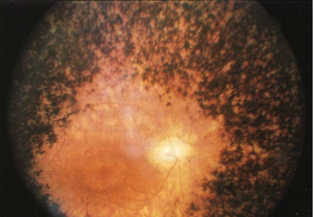
late phase RP
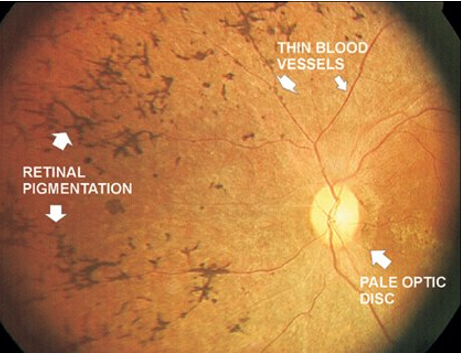
sector RP
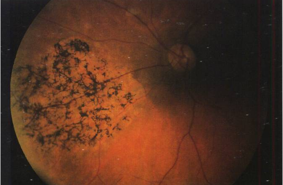
retinitis punctata albescens
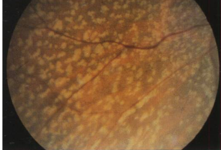
retinitis punctata albescens
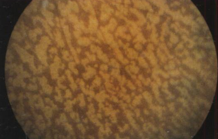
fundus albipunctatus
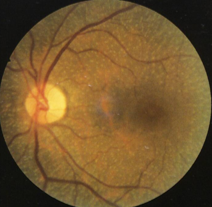
choroideremia
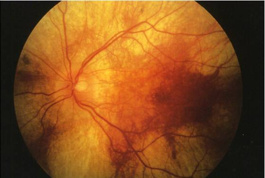
choroideremia
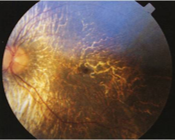
choroideremia
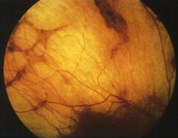
choroideremia
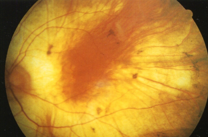
choroideremia
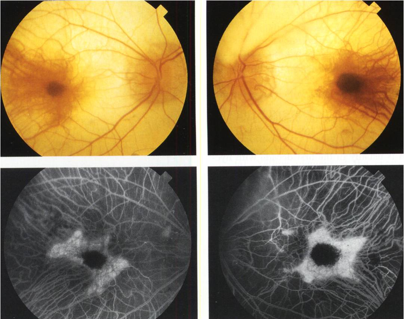
choroideremia
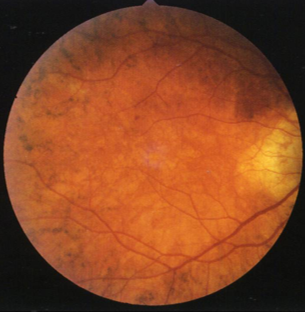
gyrate atrophy