Lab Quiz #8- 10.2, 10.3, 10.4 BIOL 124 GMU
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
cerebrum
Largest part of the brain; responsible for voluntary muscular activity, vision, speech, taste, hearing, thought, and memory.
Gyri (gyrus)
ridges of the cortex
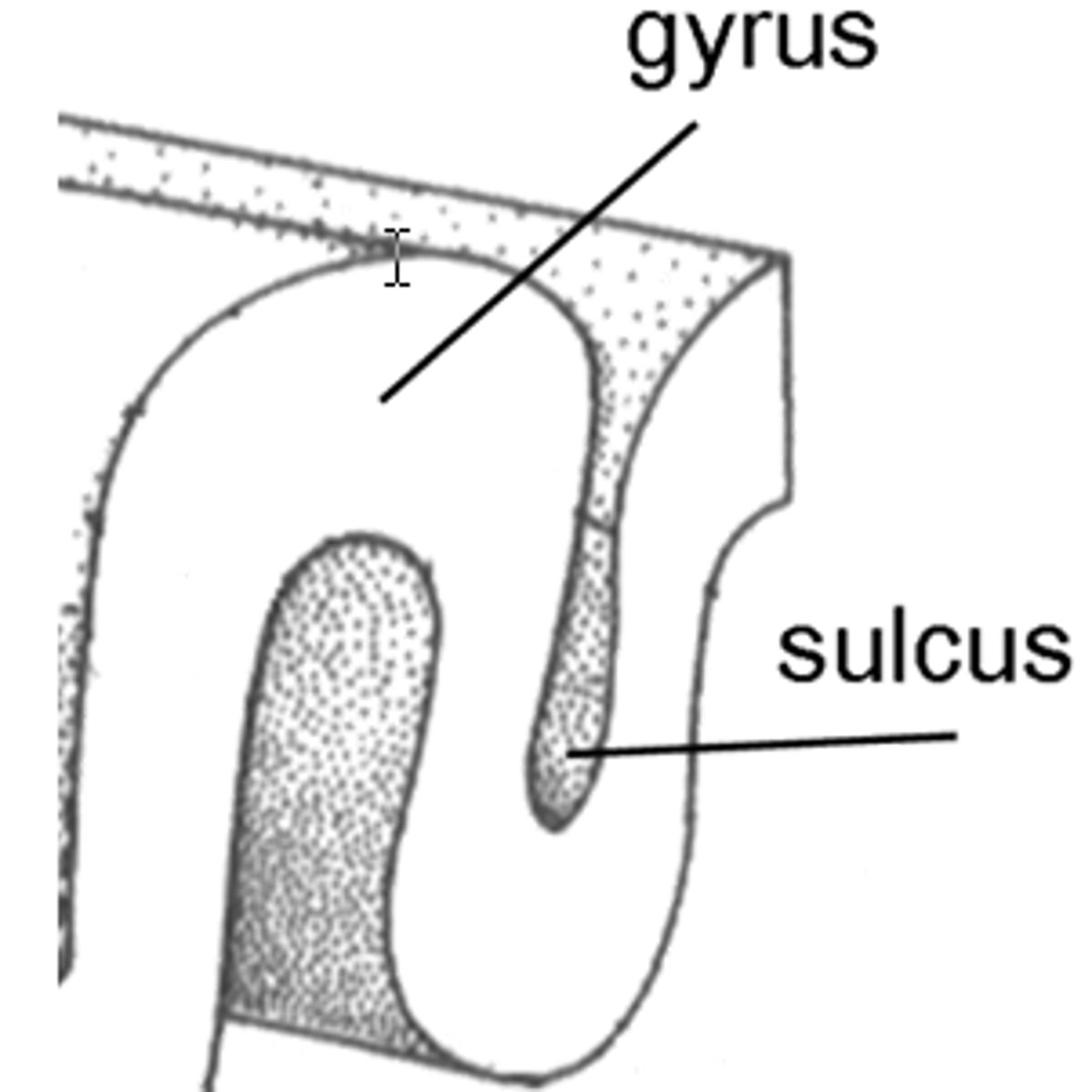
Sulci (sulcus)
shallow grooves

cerebral hemispheres
The right and left halves of the cerebrum, covered by the cerebral cortex and connected by the corpus callosum; they control movement and feeling on the opposing sides of the body.

cerebral cortex
outer gray matter of cerebrum
cerebral white matter
tracts to and from the cerebral cortex - projection fibers, commissural fibers, association fibers
protection fibers
connects the cortex with other areas in the CNS
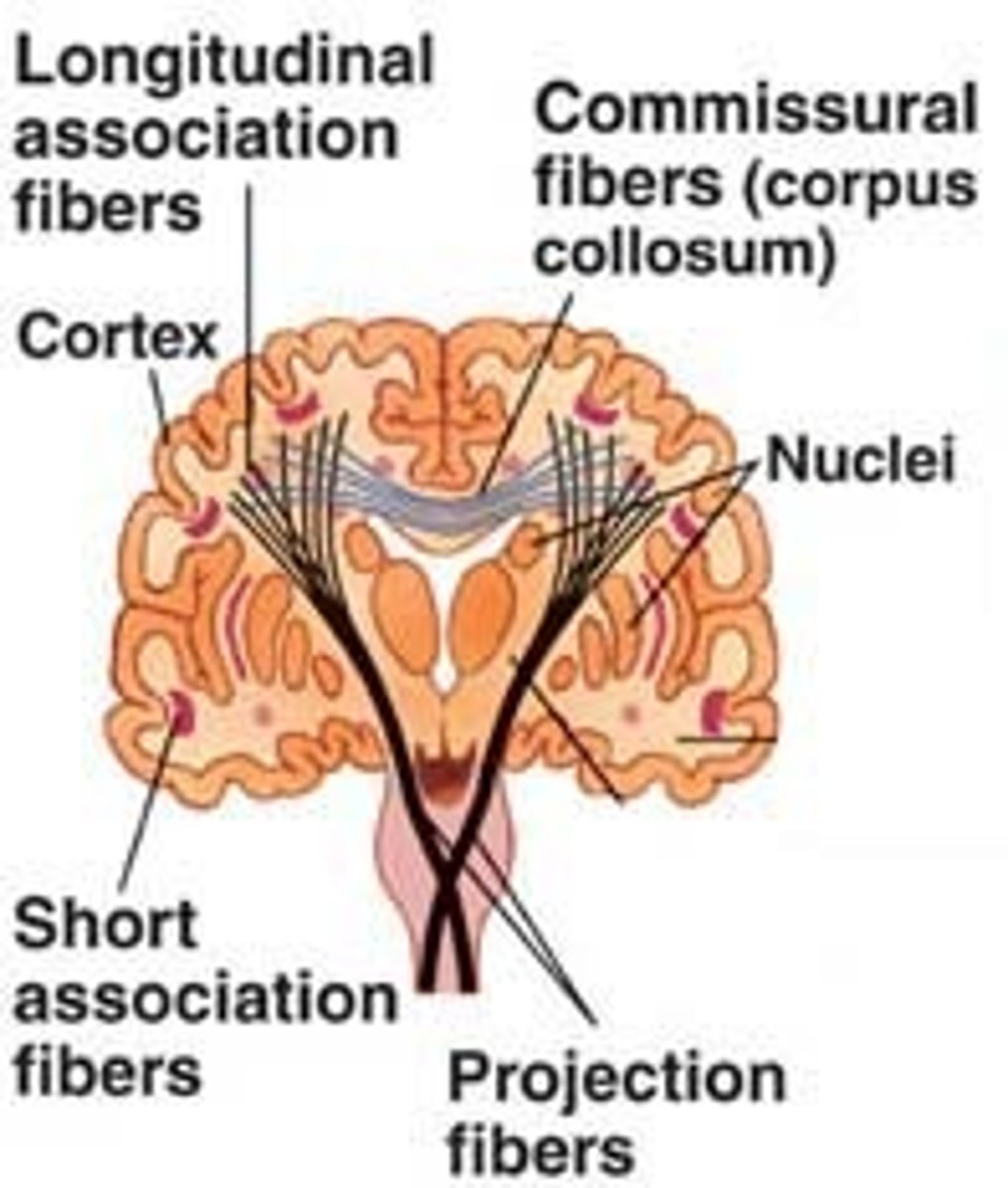
commissural fibers
the left and right hemisphere
e.g., the corpus callosum
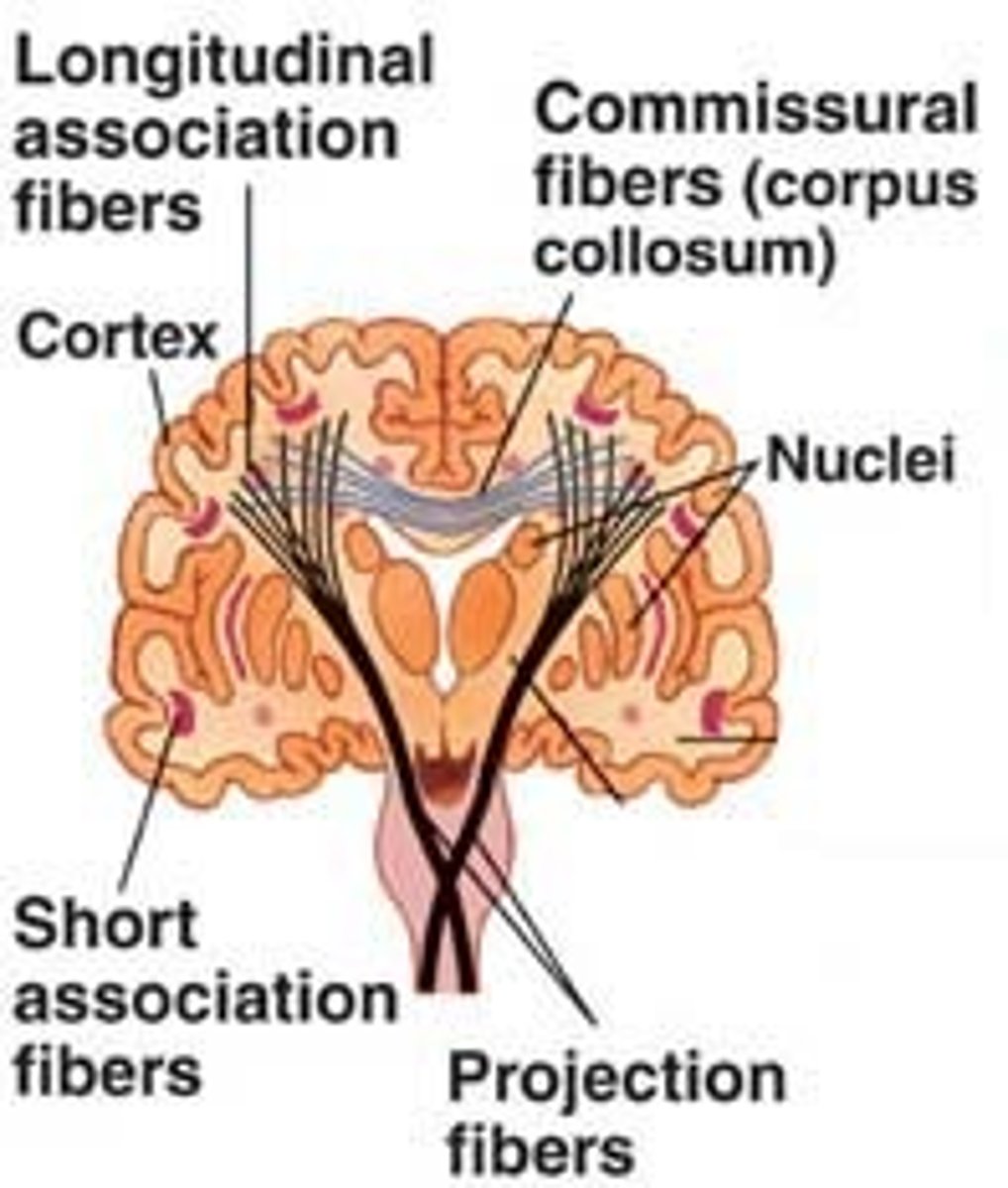
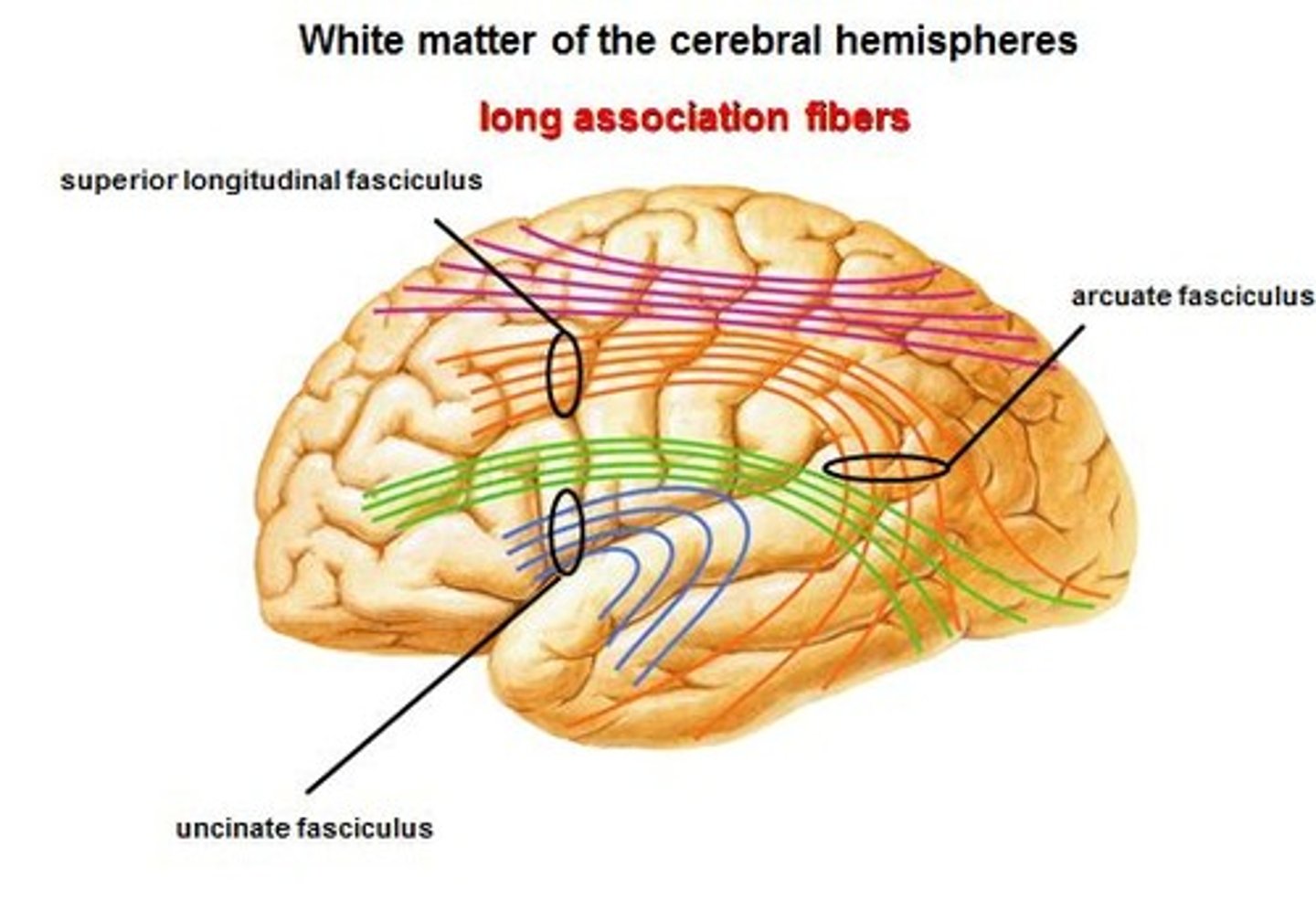
association fibers
connect different parts of the same hemisphere
Fissures
deep grooves in the brain

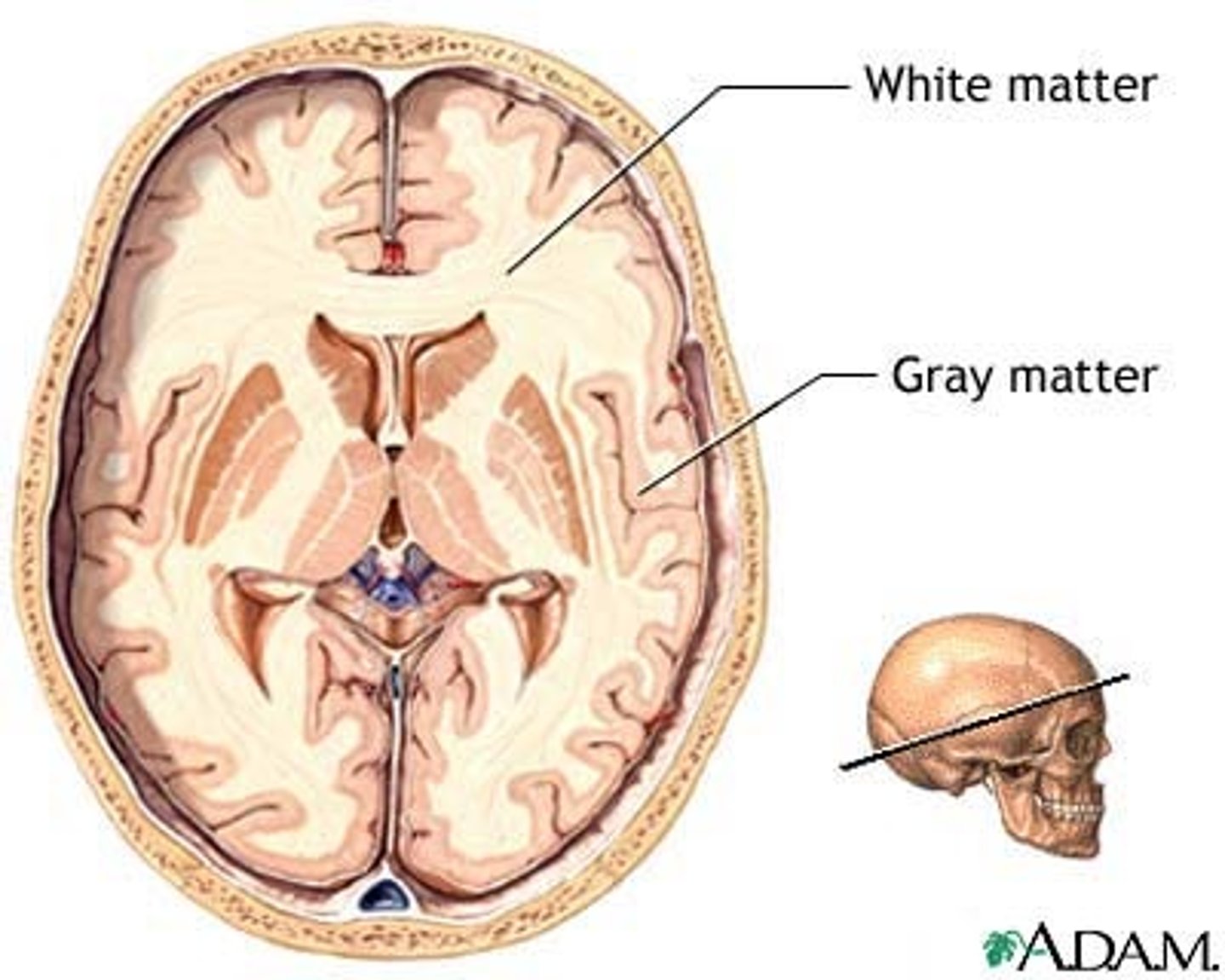
gray matter
a portion of the CNS consisting of cytons (cell bodies), their dendrites and synaptic connections
white matter
myelinated axons
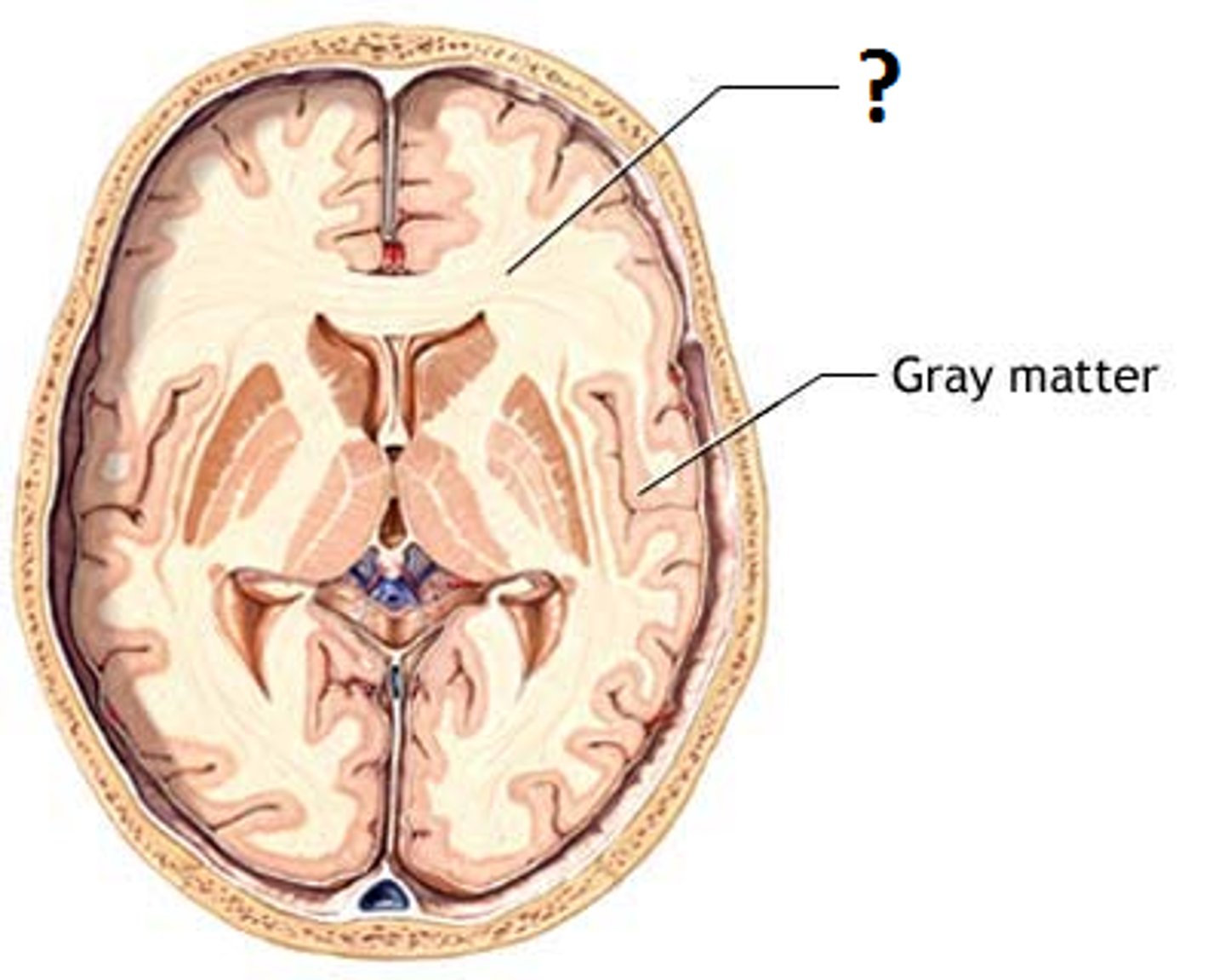
tentorium cerebelli
separates cerebrum from cerebellum

nuclei
islands of gray matter, basal nuclei

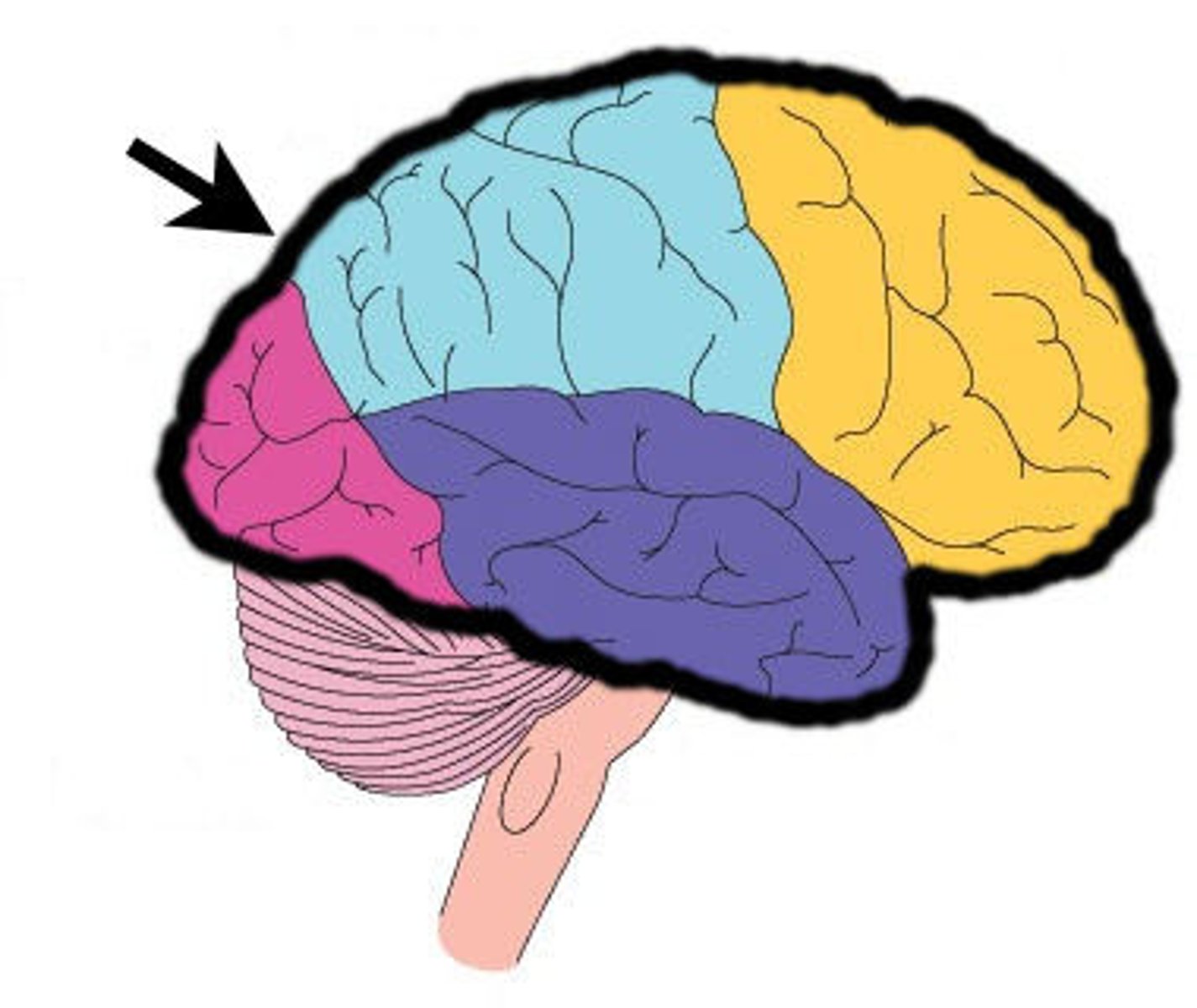
frontal lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex that has specialized areas for movement, abstract thinking, planning, memory, and judgement
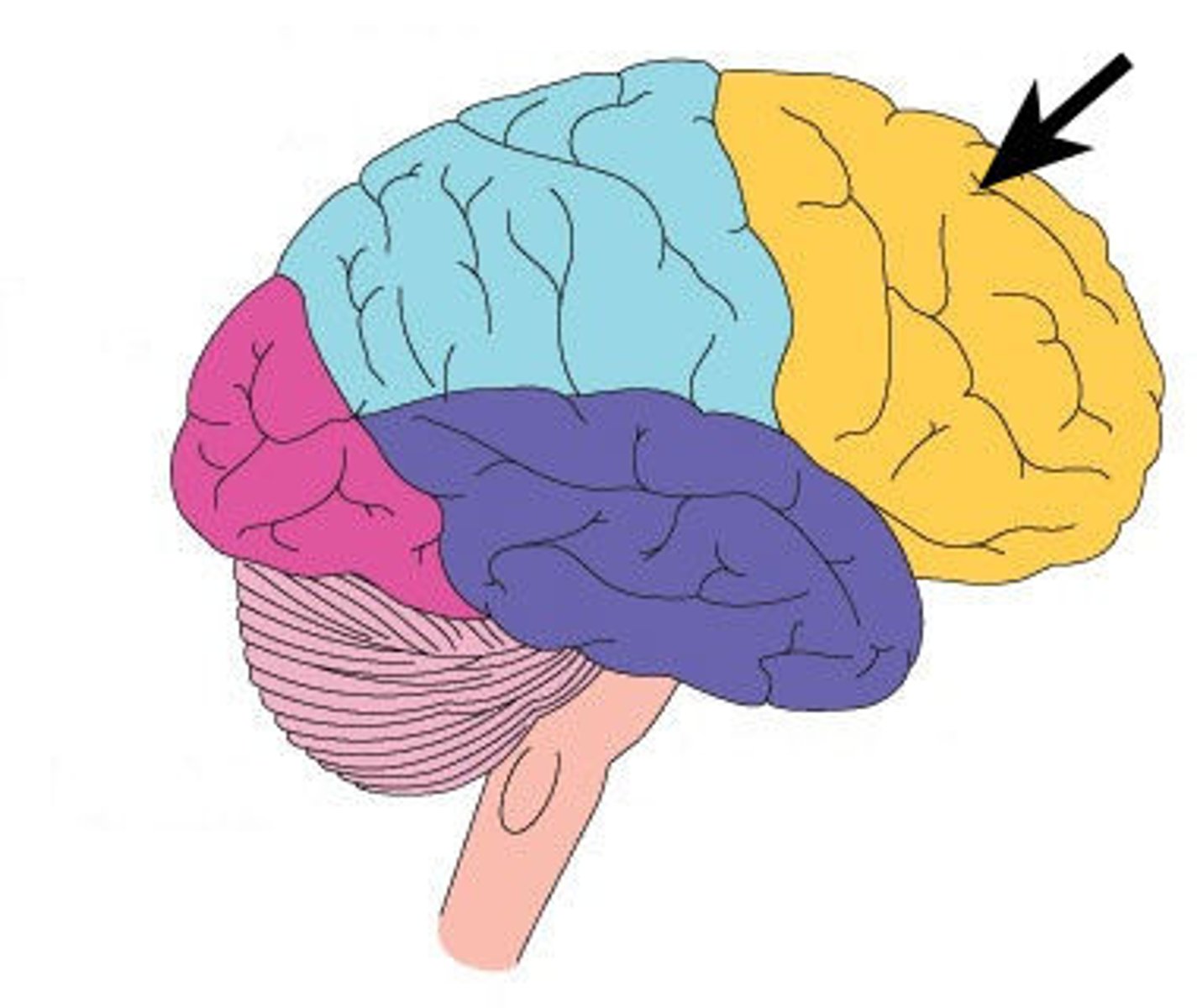
parietal lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex whose functions include processing information about touch.
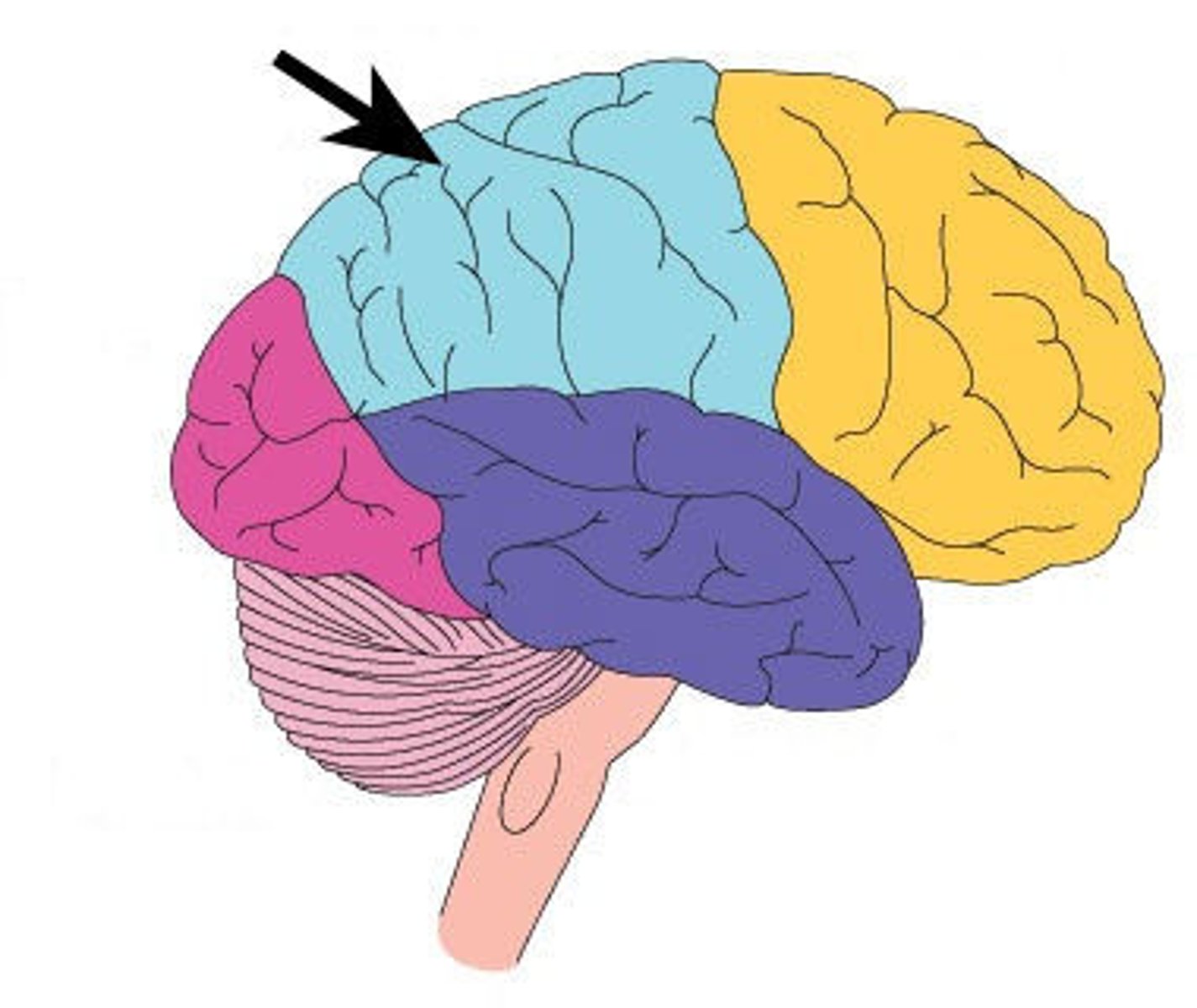
occipital lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex that processes visual information

temporal lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex responsible for hearing and language.

insula lobe
found deep beneath the lateral sulcus, associated with memory and interpretation of taste
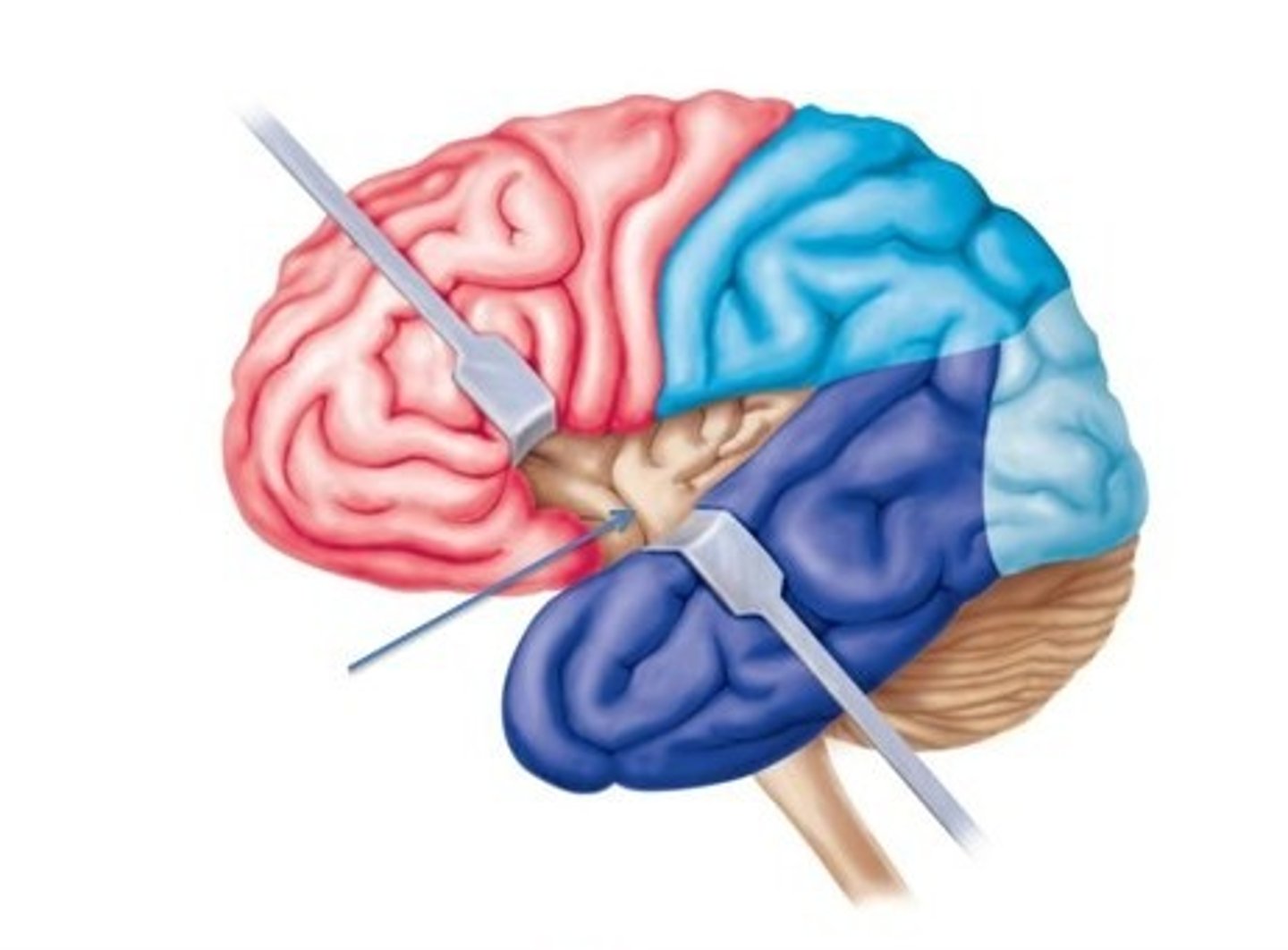
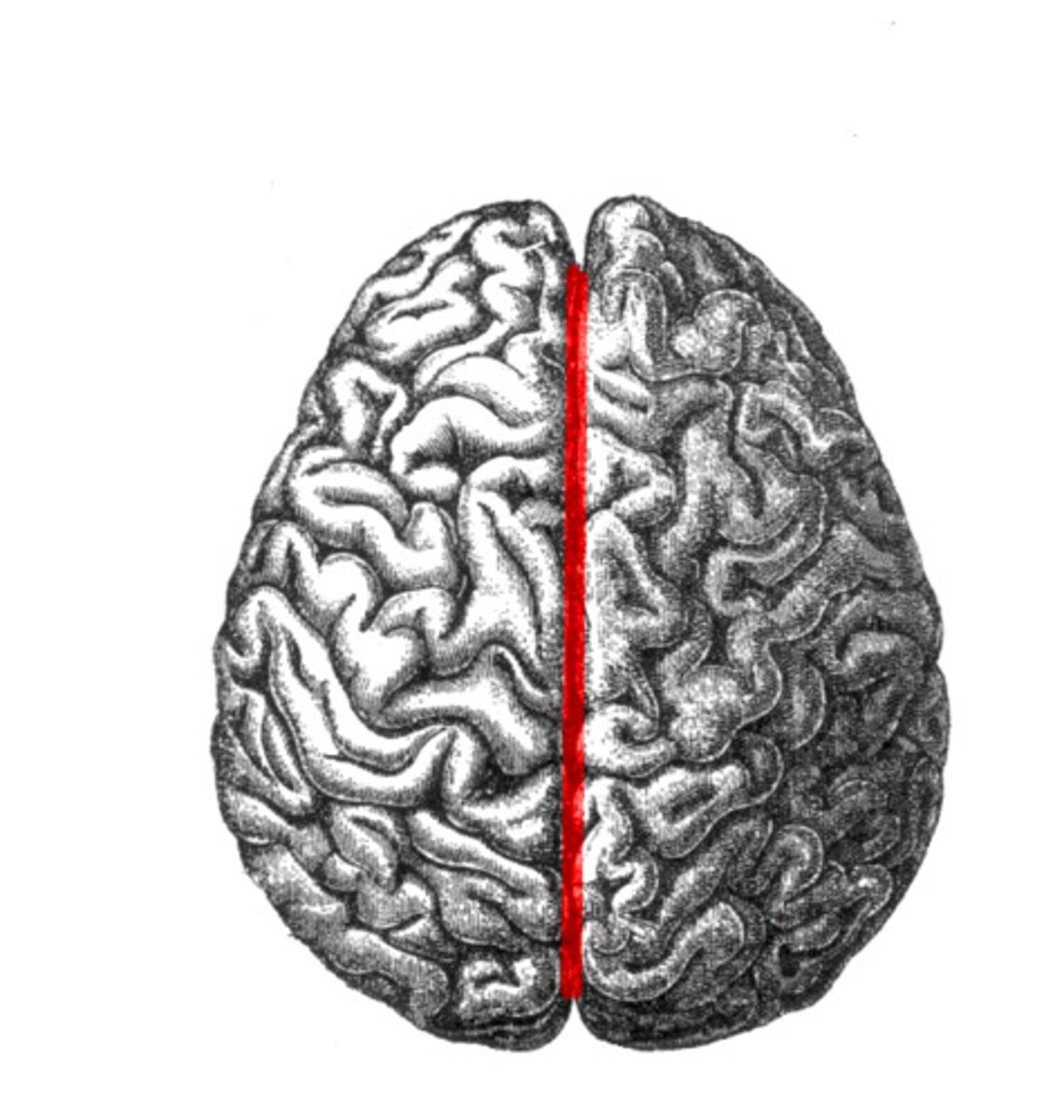
longitudinal fissure
separates cerebral hemispheres
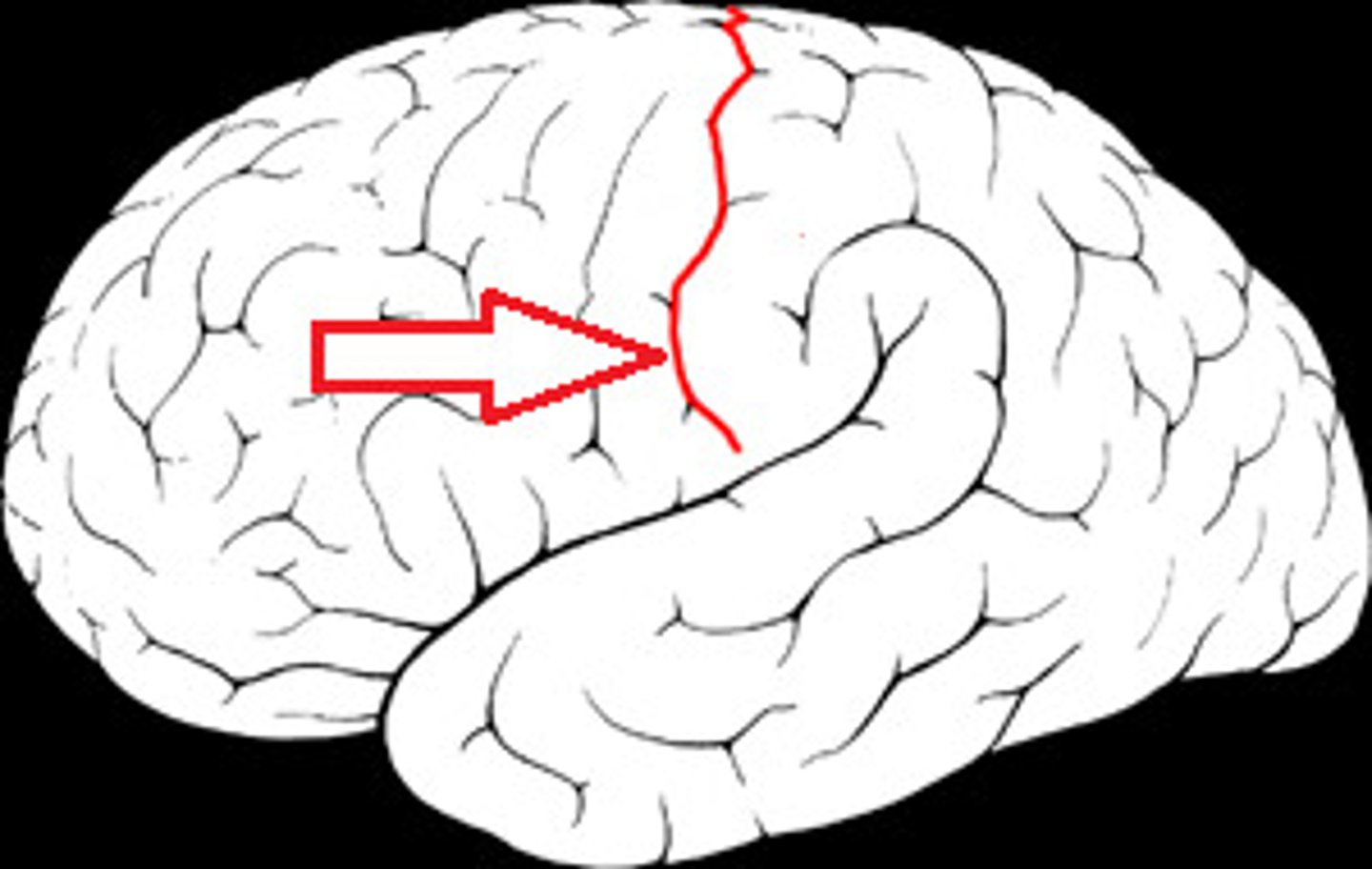
central sulcus
separates frontal and parietal lobes
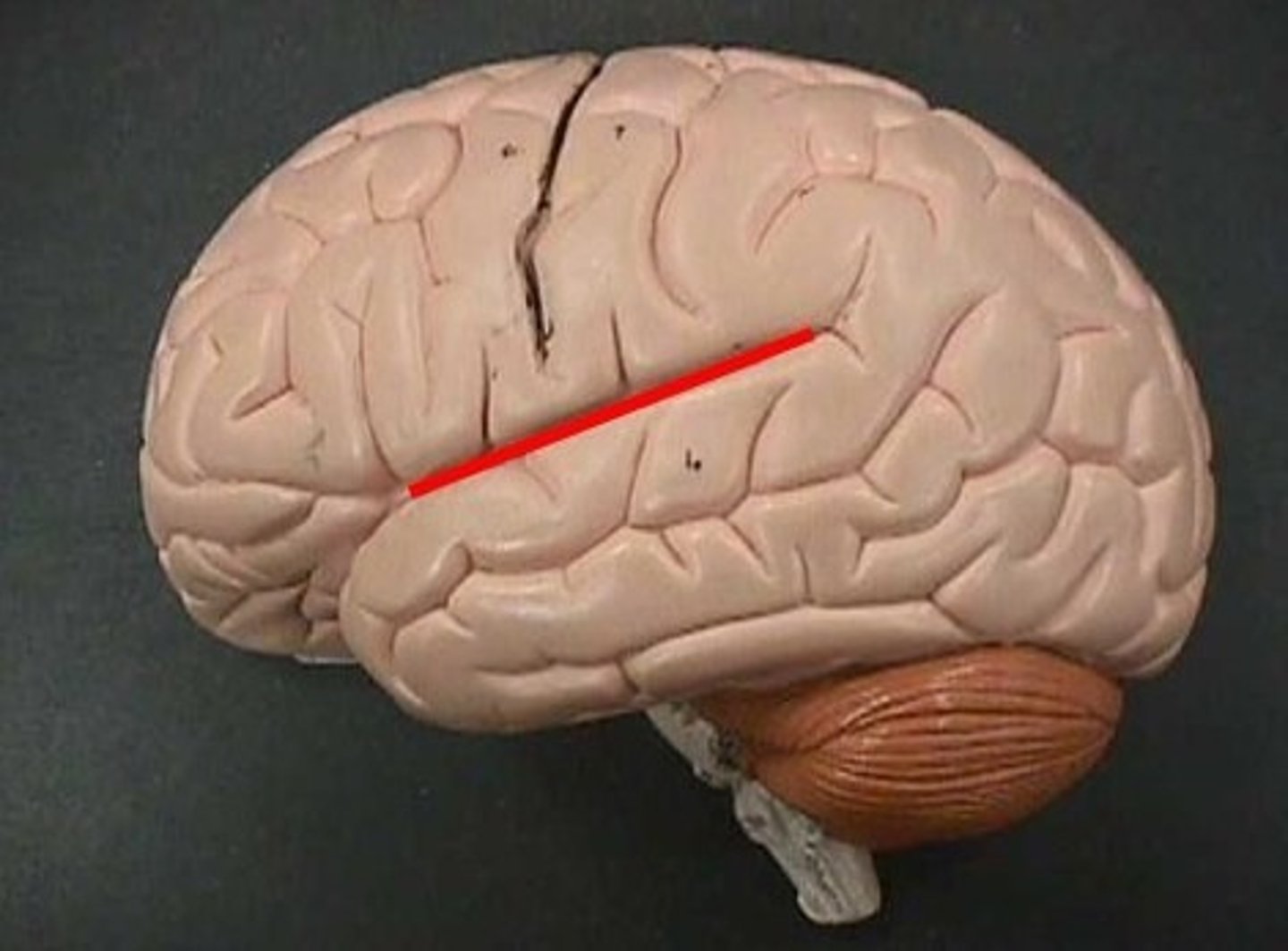
lateral sulcus
Separates temporal lobe from parietal and frontal lobes
Parietooccipital Sulcus
separates parietal and occipital lobes
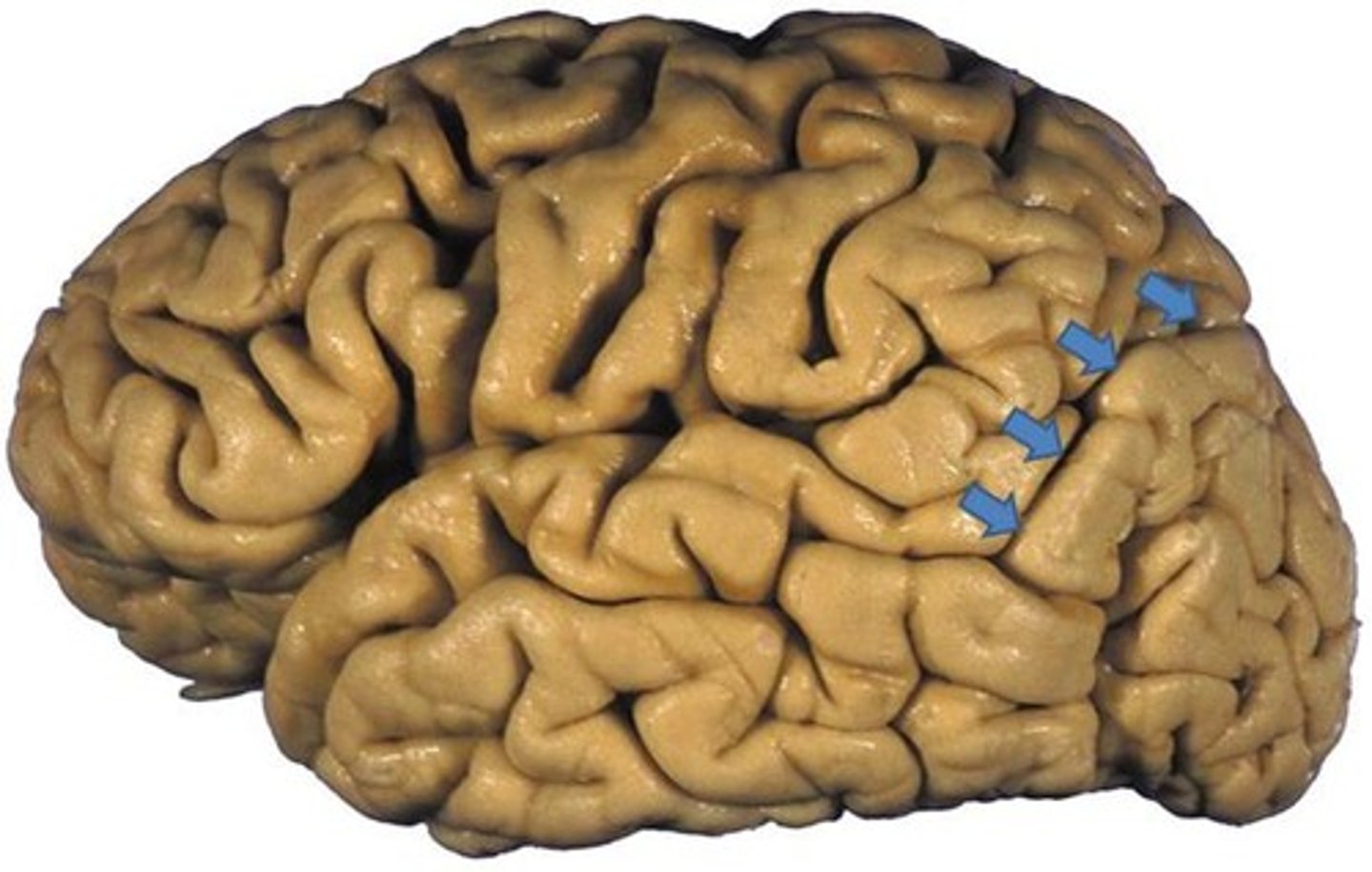
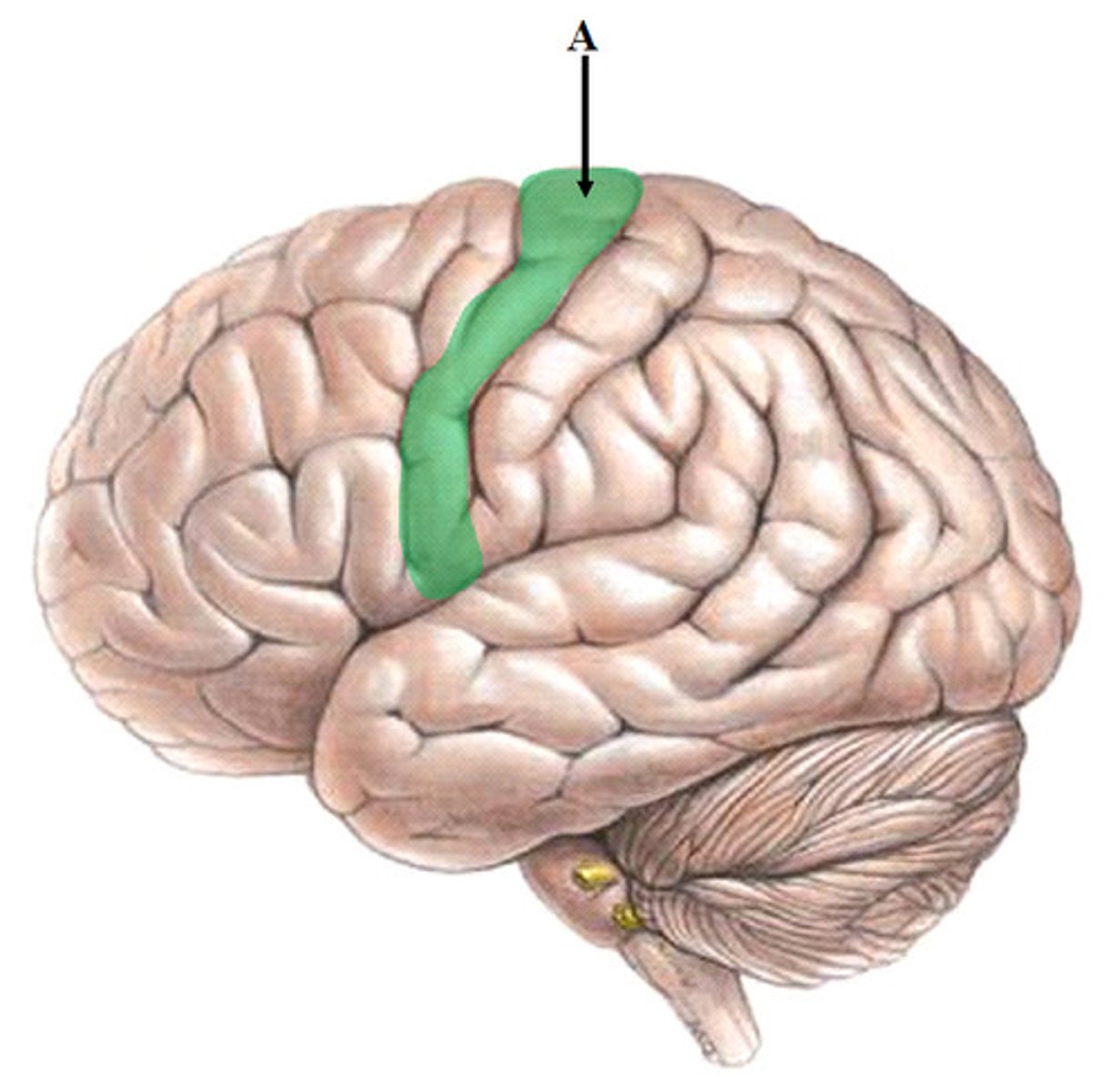
pre central gyrus
location of primary motor cortex
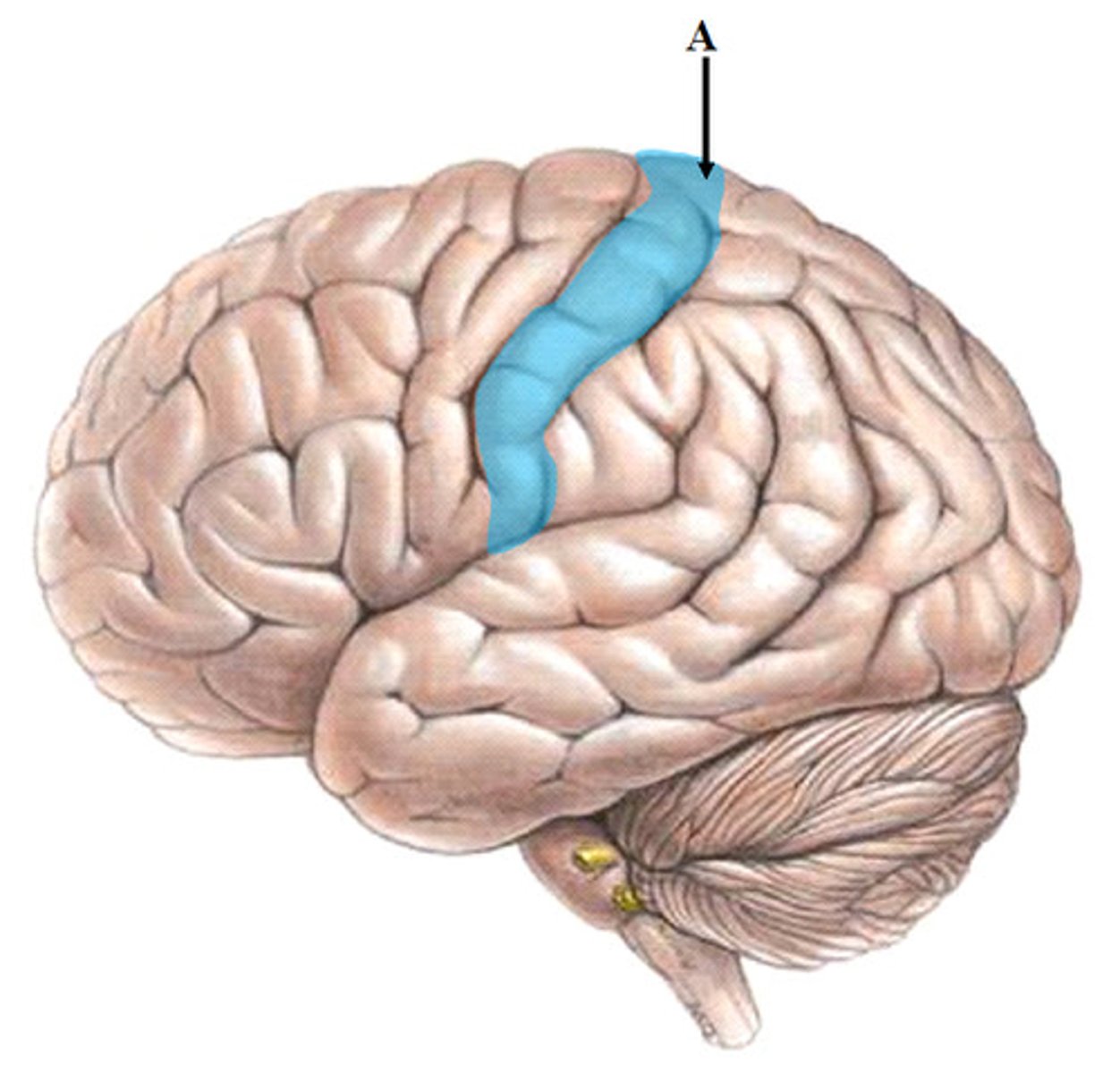
post central gyrus
primary somatosensory cortex
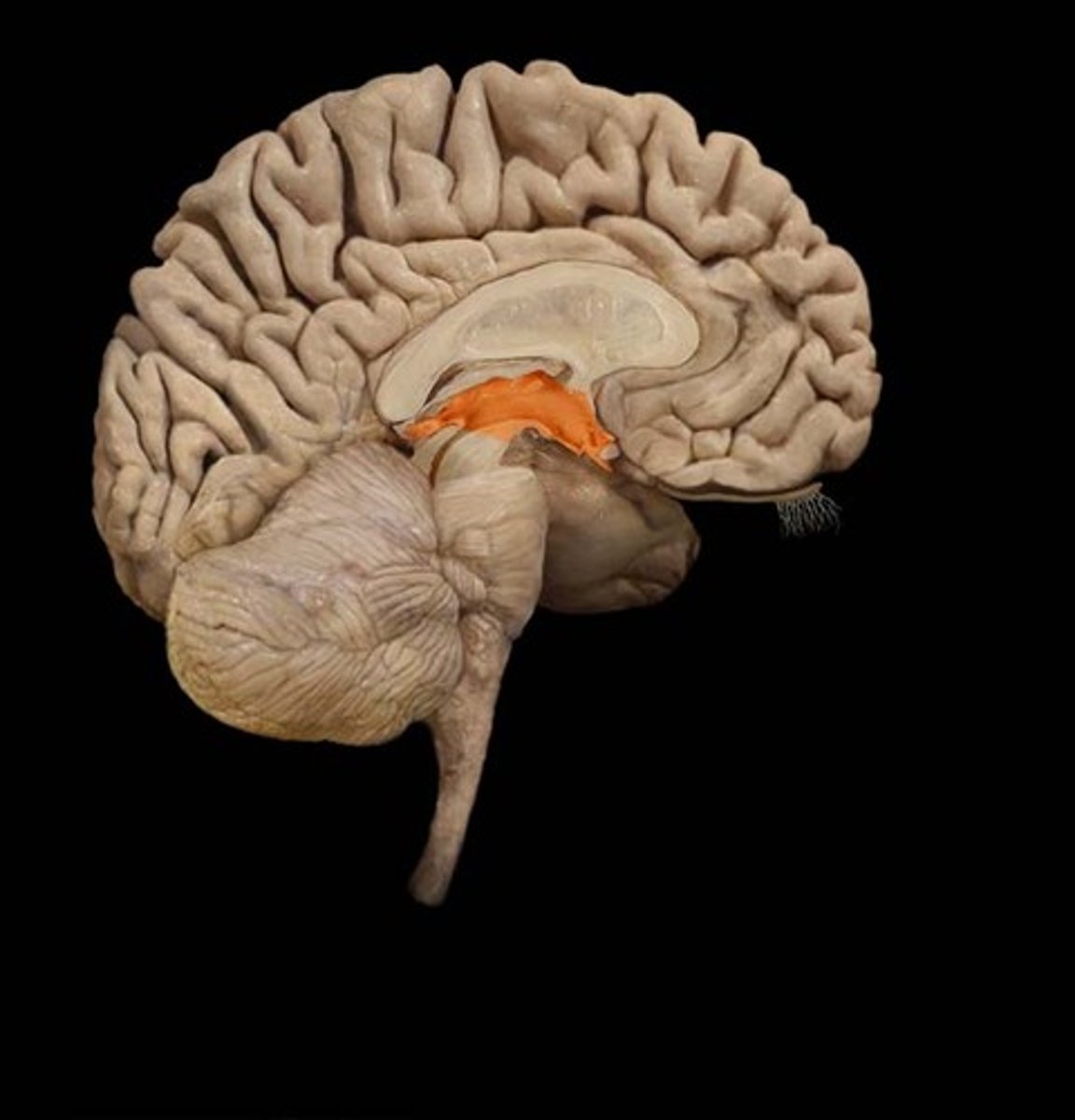
Diencephalon
thalamus, hypothalamus, epithalamus
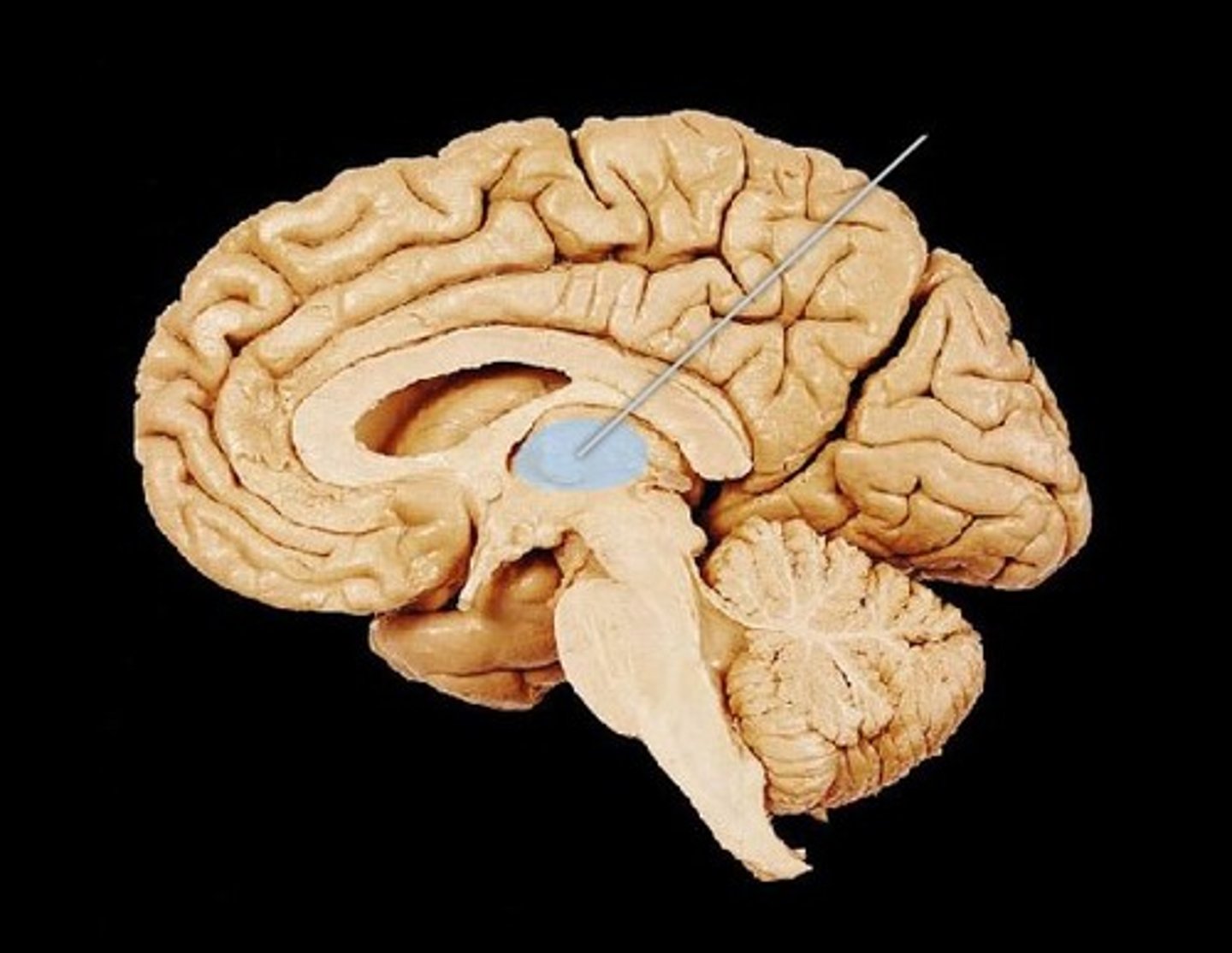
thalamus
the brain's sensory switchboard, located on top of the brainstem; it directs messages to the sensory receiving areas in the cortex and transmits replies to the cerebellum and medulla
hypothalamus
A neural structure lying below the thalamus; it directs several maintenance activities (eating, drinking, body temperature), helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland, and is linked to emotion and reward.

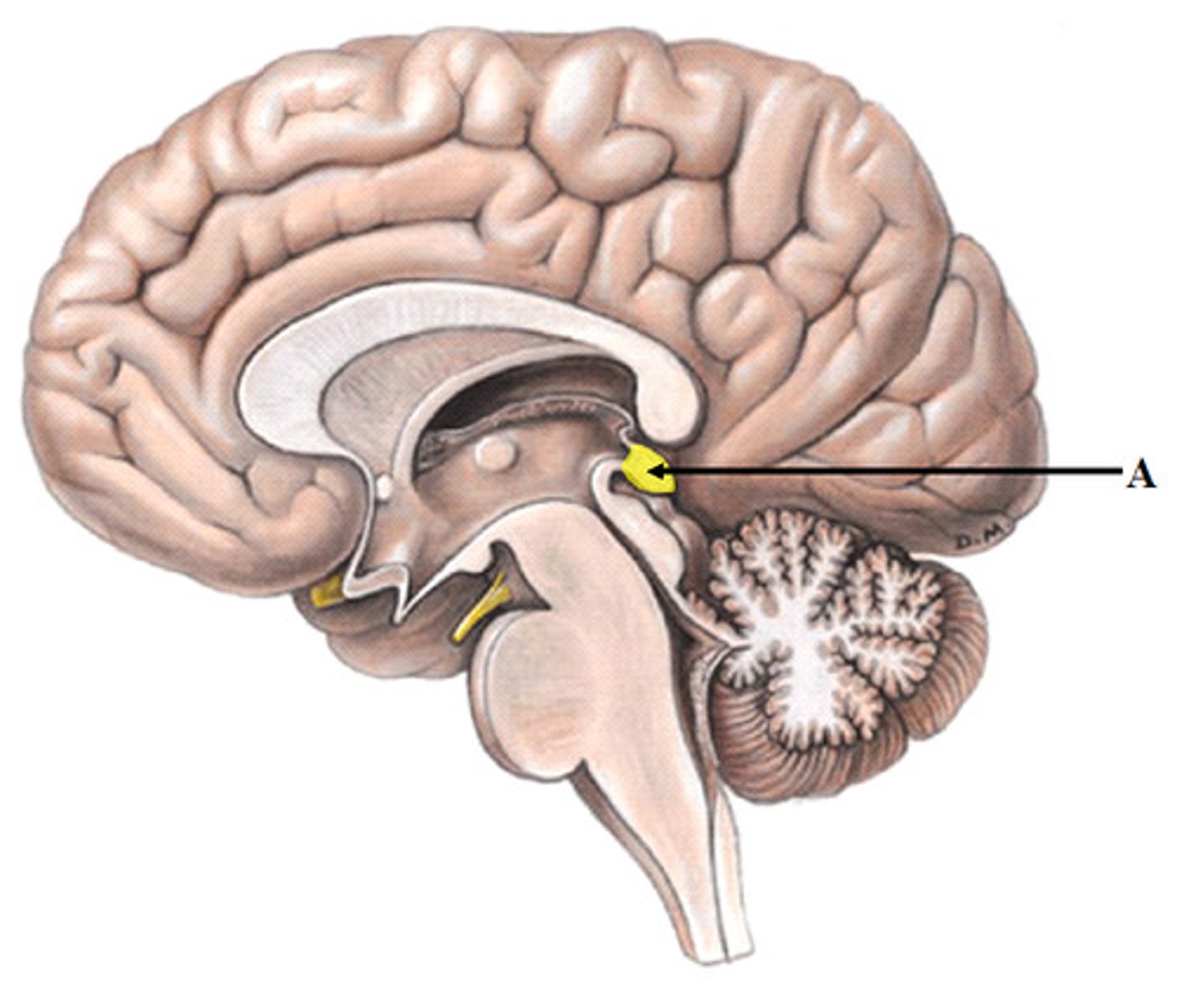
epithalamus
Contains pineal body. Involved in olfactory senses and sleep/wake cycle- melatonin
inner gray matter
basal nuclei - movement
middle white matter
myelinated axons, association fibers, projection fibers, comisseral fibers

outer gray matter
cerebral cortex, motor, sensory, visual, audio

cerebellum
the "little brain" at the rear of the brainstem; functions include processing sensory input and coordinating movement output and balance
arbor vitae
white matter of the cerebellum
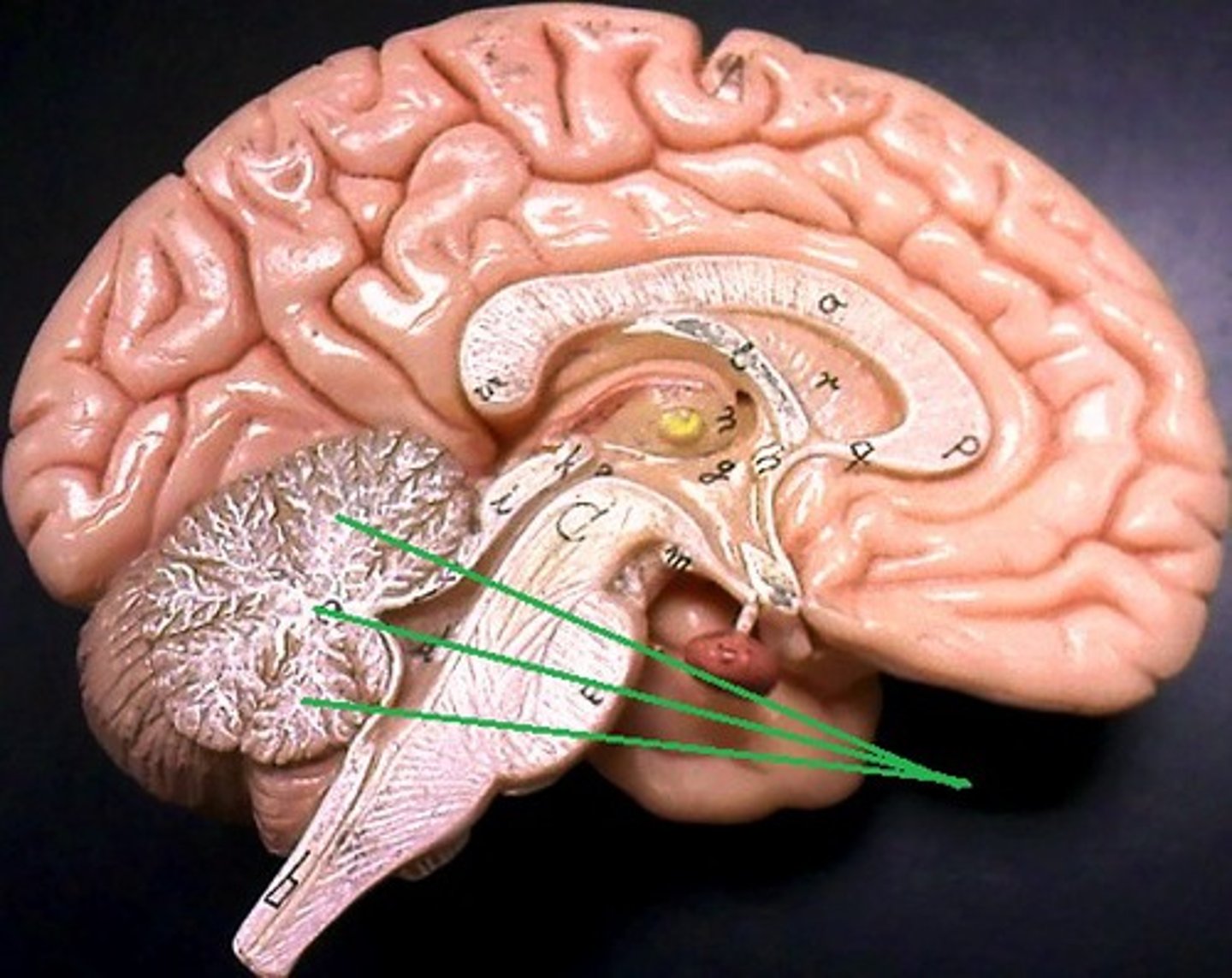
outer gray matter of cerebellum
cerebellar cortex

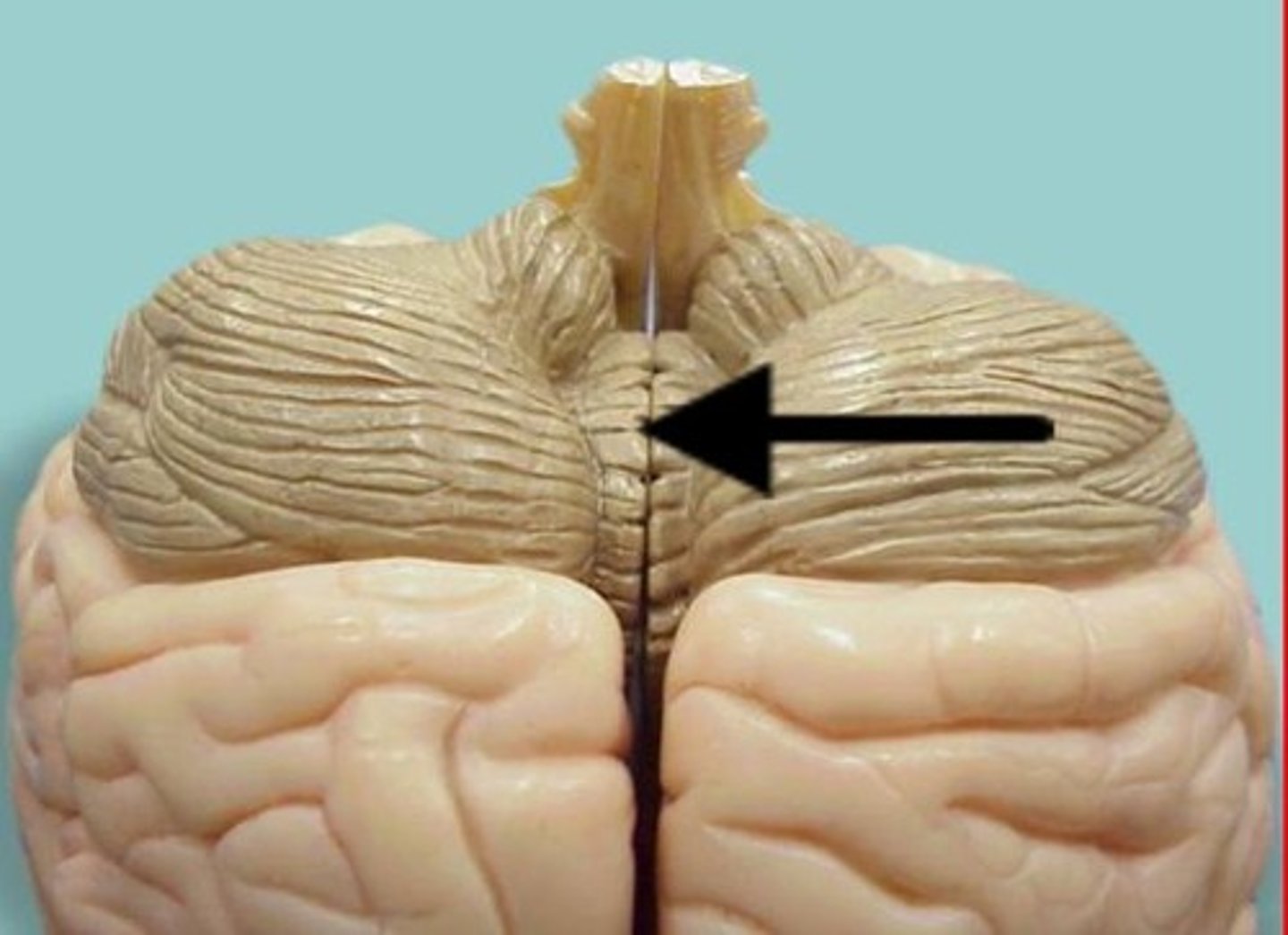
vermis
Connects the two hemispheres of the cerebellum
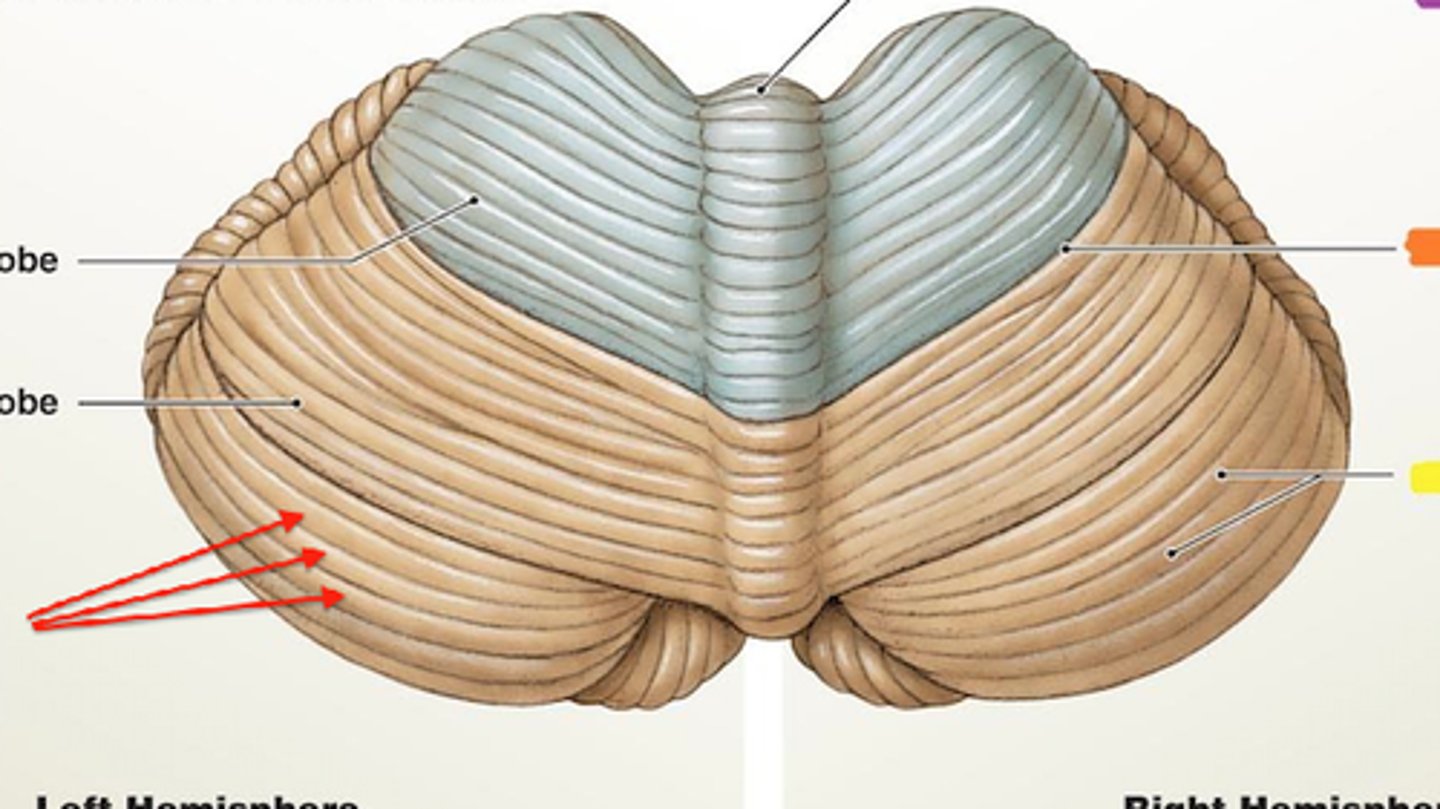
folia
folds of the cerebellum
falx cerebelli
separates the two hemispheres of the cerebellum

brainstem
the oldest part and central core of the brain, beginning where the spinal cord swells as it enters the skull; the brainstem is responsible for automatic survival functions
mid brain, pons, medulla oblongata
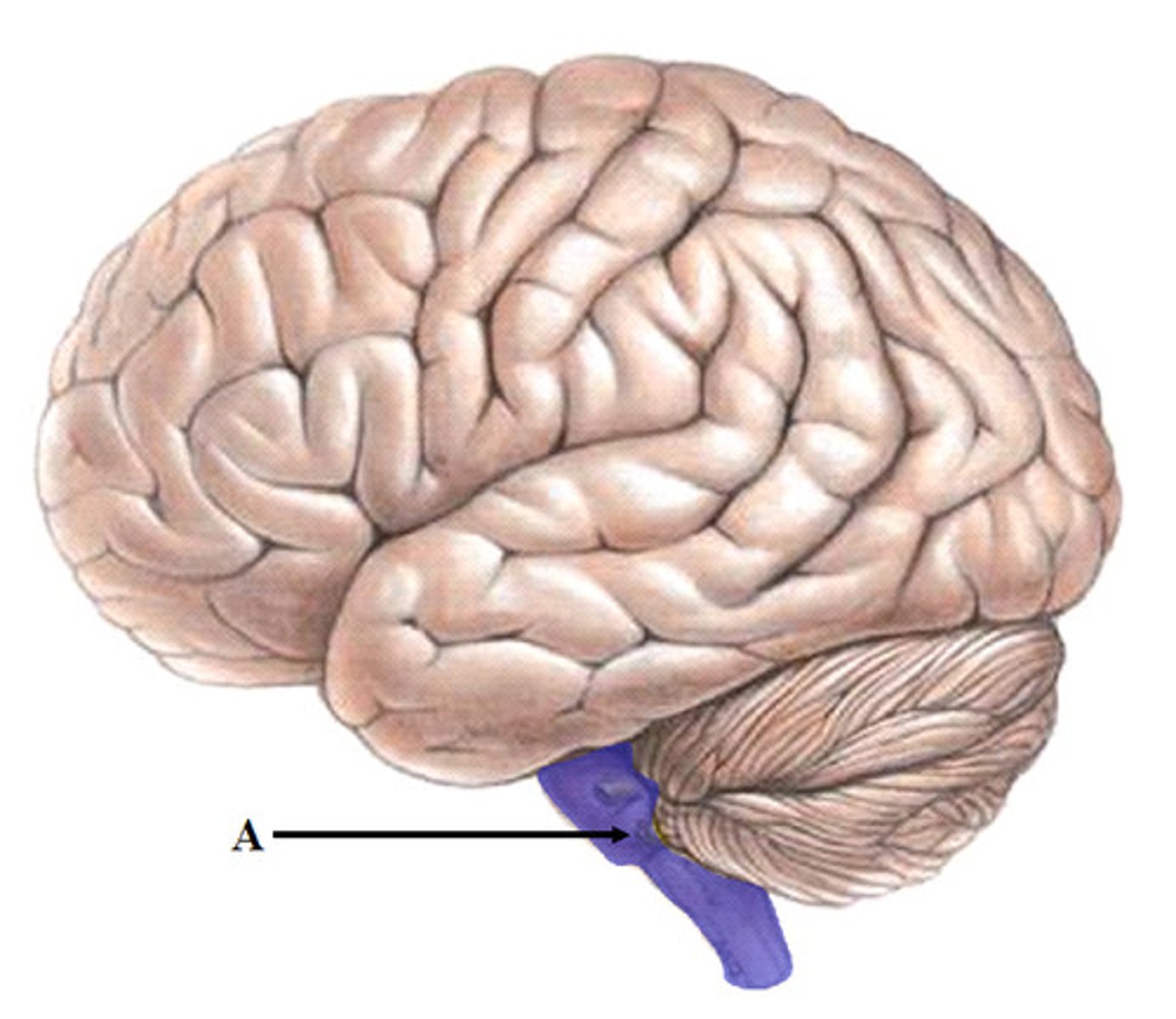
midbrain
A small part of the brain above the pons that integrates sensory information and relays it upward.

pons
A brain structure that relays information from the cerebellum to the rest of the brain
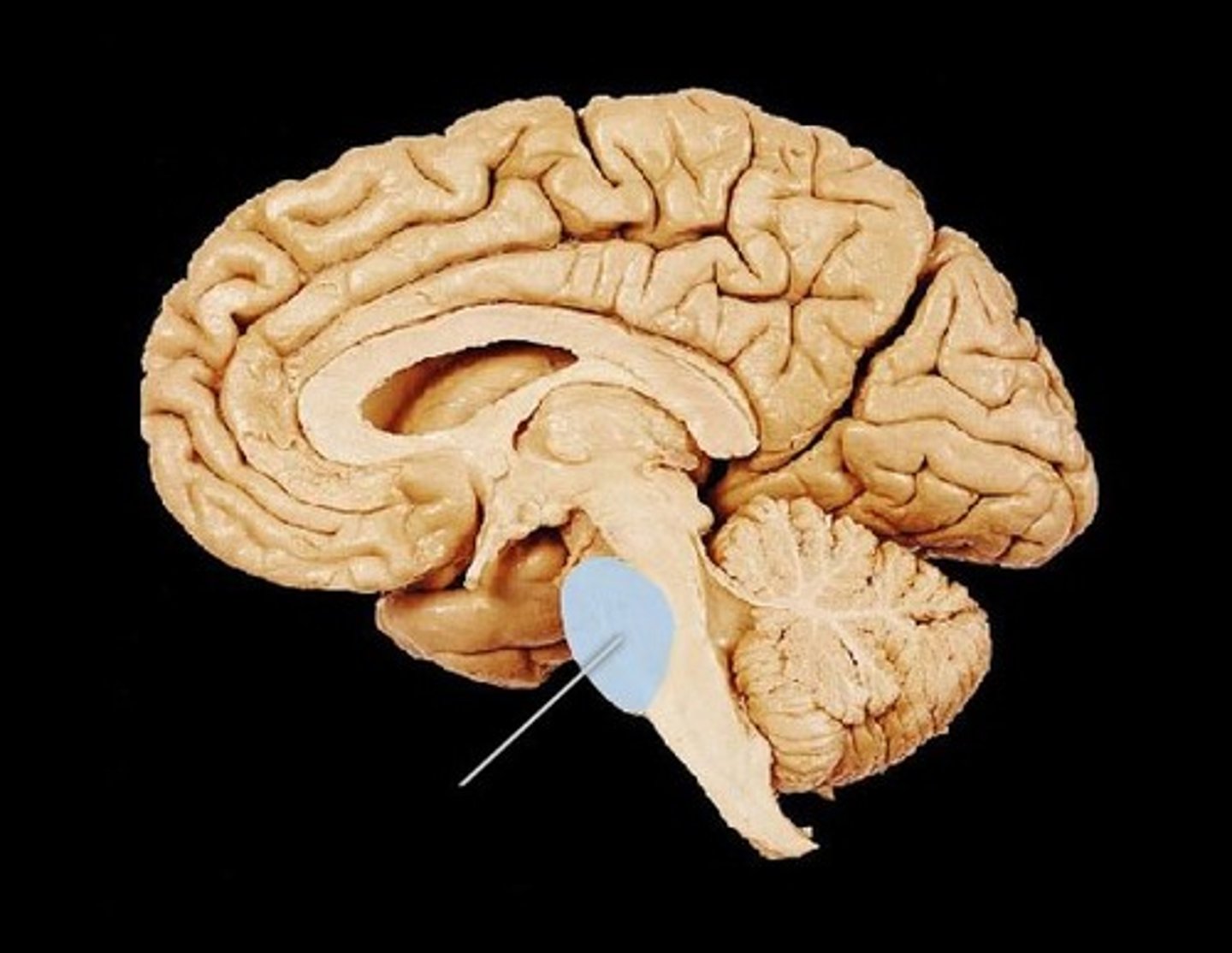
medulla oblongata
Part of the brainstem that controls vital life-sustaining functions such as heartbeat, breathing, blood pressure, and digestion.

cranial meninges outer to inner
connective tissue around brain, dura mater, arachnoid mater, Pia mater
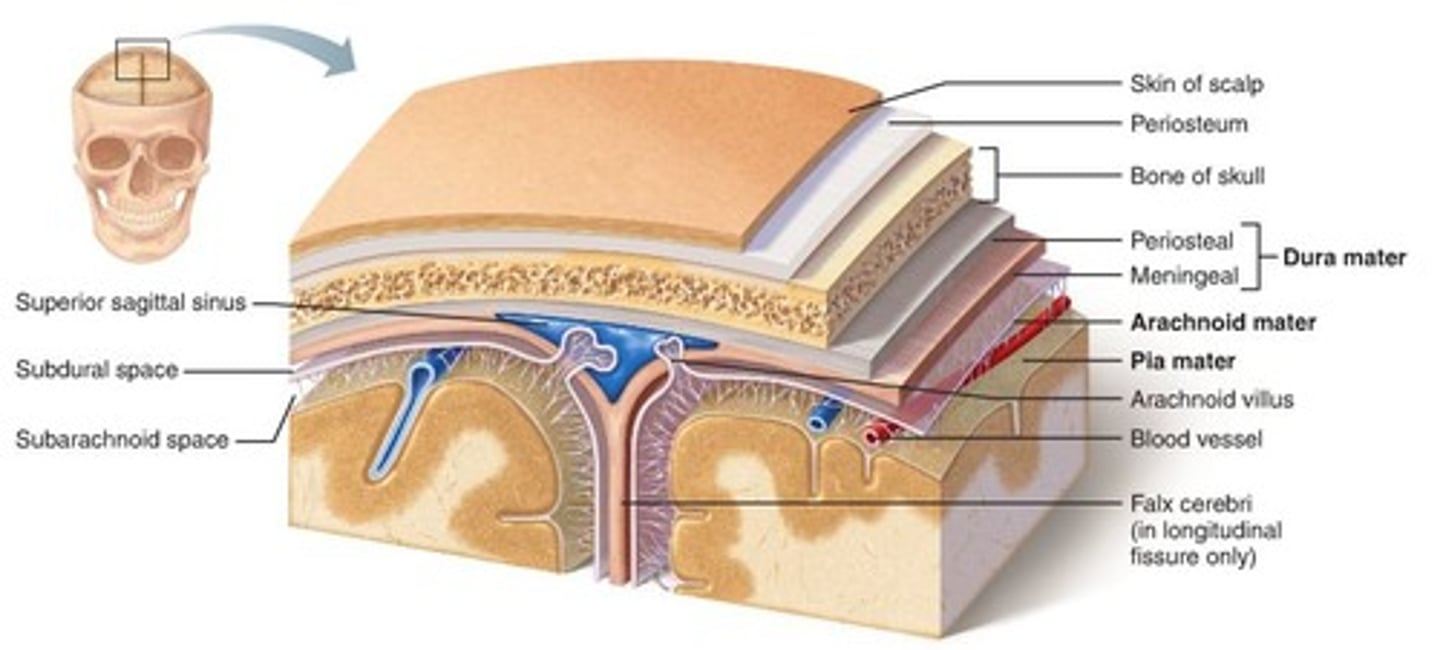
dura mater of brain
two parts:
periosteal and meningeal layer
made of dense irregular connective tissue
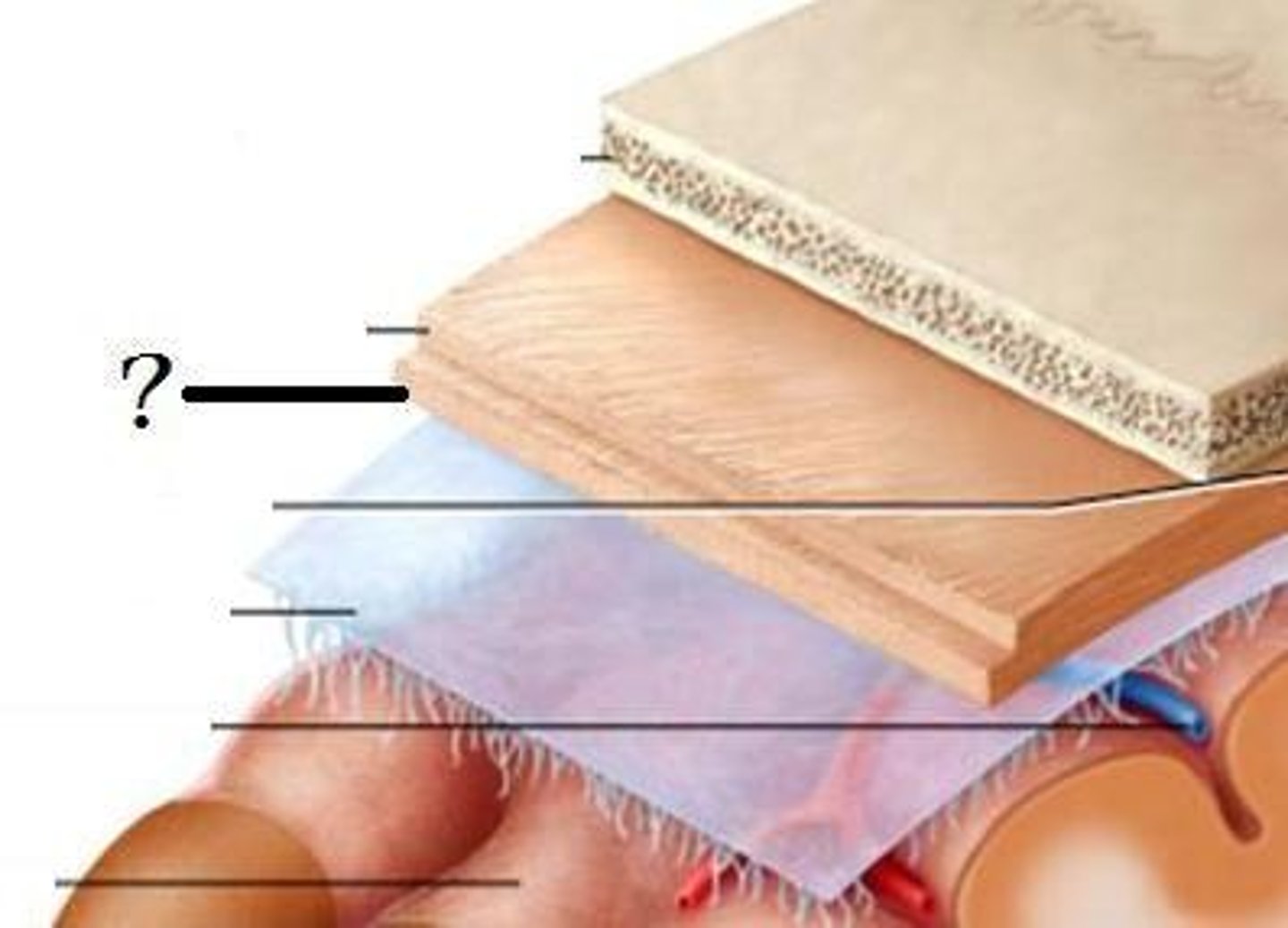
arachnoid mater of brain
subarachnoid space (CSF) and arachnoid villus/granulation (CSF draining into sinus)
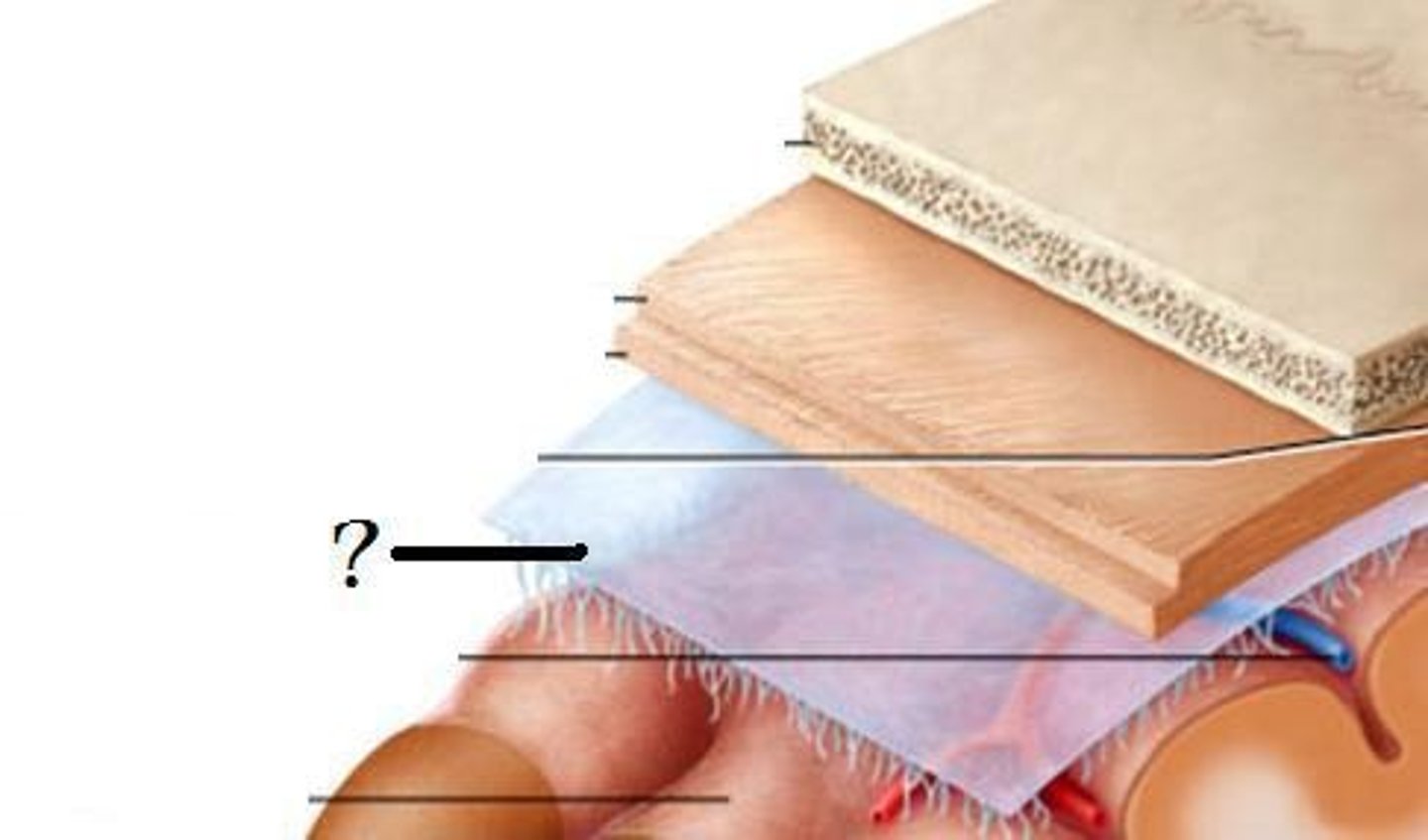
subarachnoid space
a space in the meninges beneath the arachnoid membrane and above the pia mater that contains the cerebrospinal fluid
loose fibrous connective tissue

arachnoid villus/granulations
drainage of CSF into dural sinuses

pia mater
thin, delicate inner membrane of the meninges

cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
plasma-like clear fluid circulating in and around the brain and spinal cord

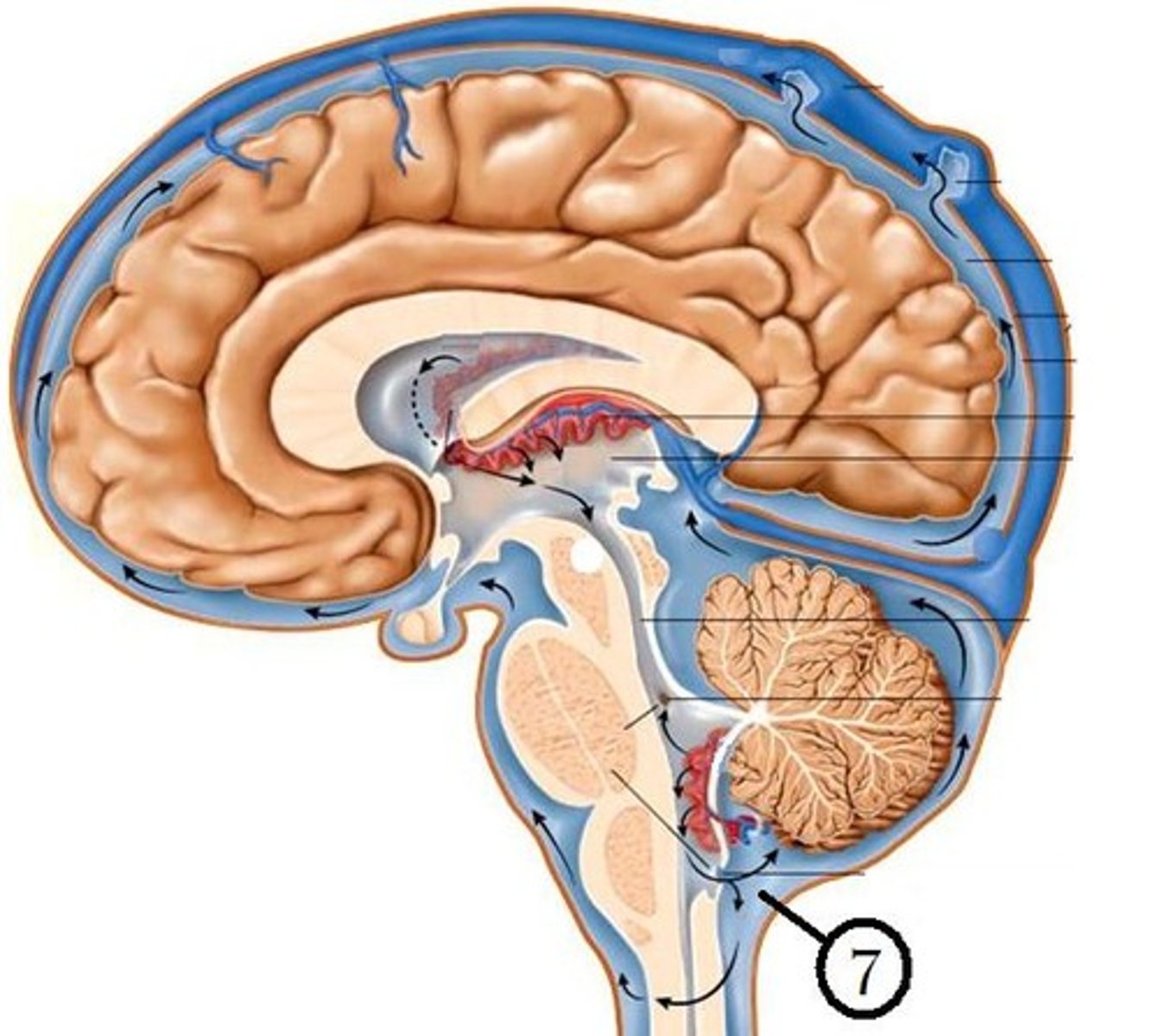
Production of CSF
begins with the filtration of blood plasma through the capillaries of the brain
Ependymal cells modify the filtrate, so CSF has more sodium and chloride than plasma, but less potassium, calcium, glucose, and very little protein
HAPPENS IN ALL VENTRICLES

CSF circulates through
lateral ventricles to third ventricle to cerebral aqueduct to fourth ventricle to subarachnoid space and central canal of spinal cord
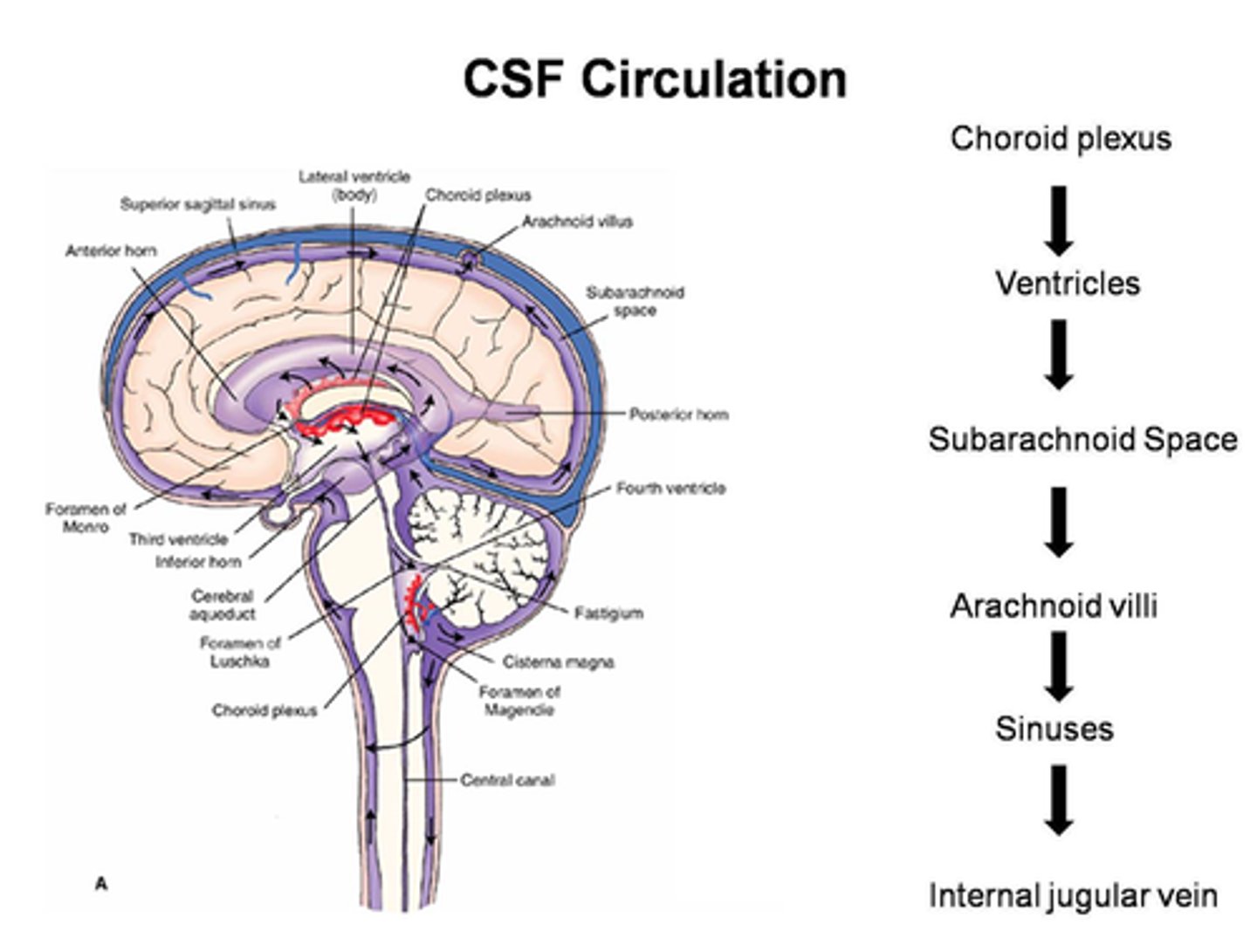
choroid plexus
A highly vascular portion of the lining of the ventricles that secretes cerebrospinal fluid.

lateral ventricle
one of the two ventricles located in the center of the telencephalon
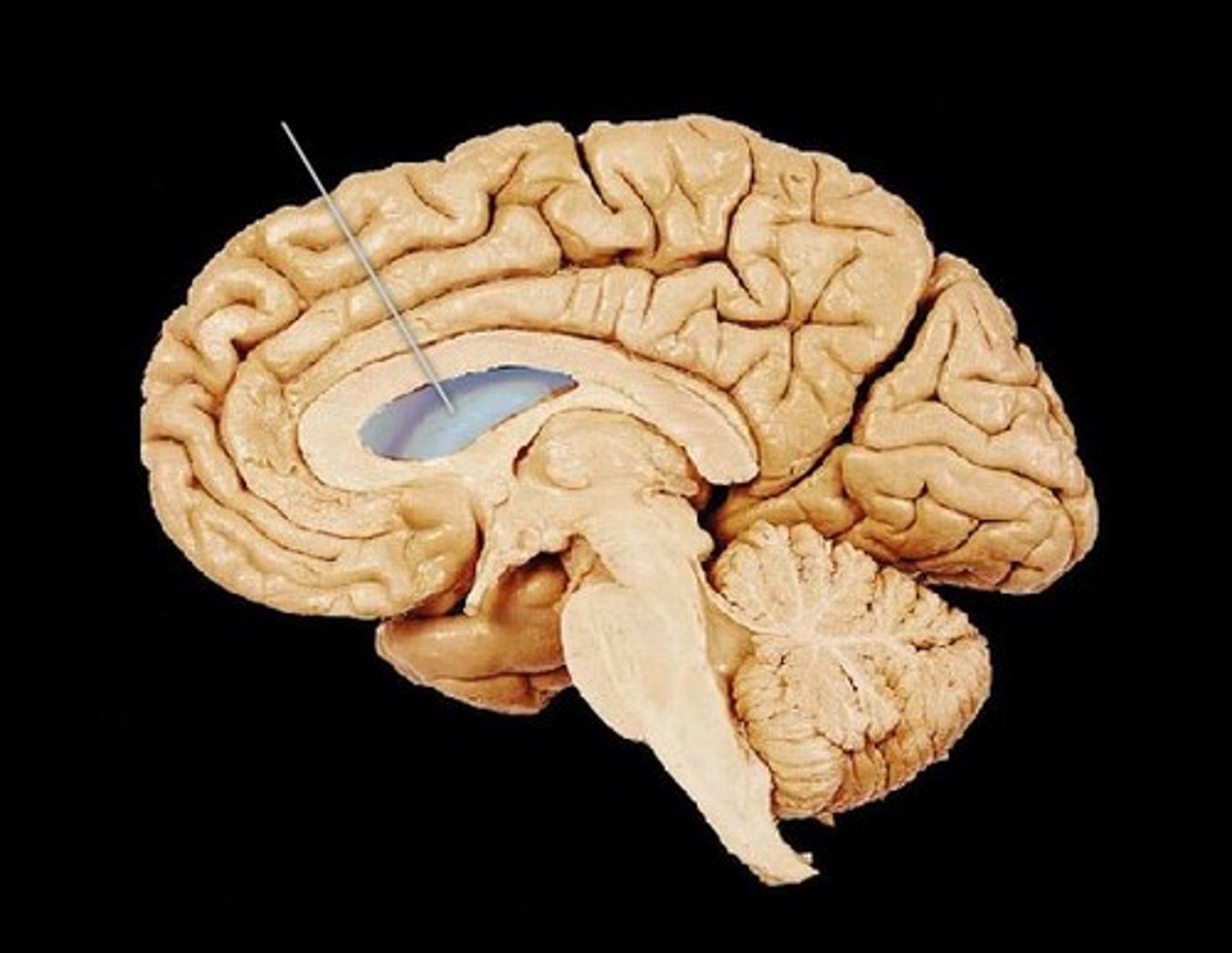
third ventricle
the ventricle located in the center of the diencephalon
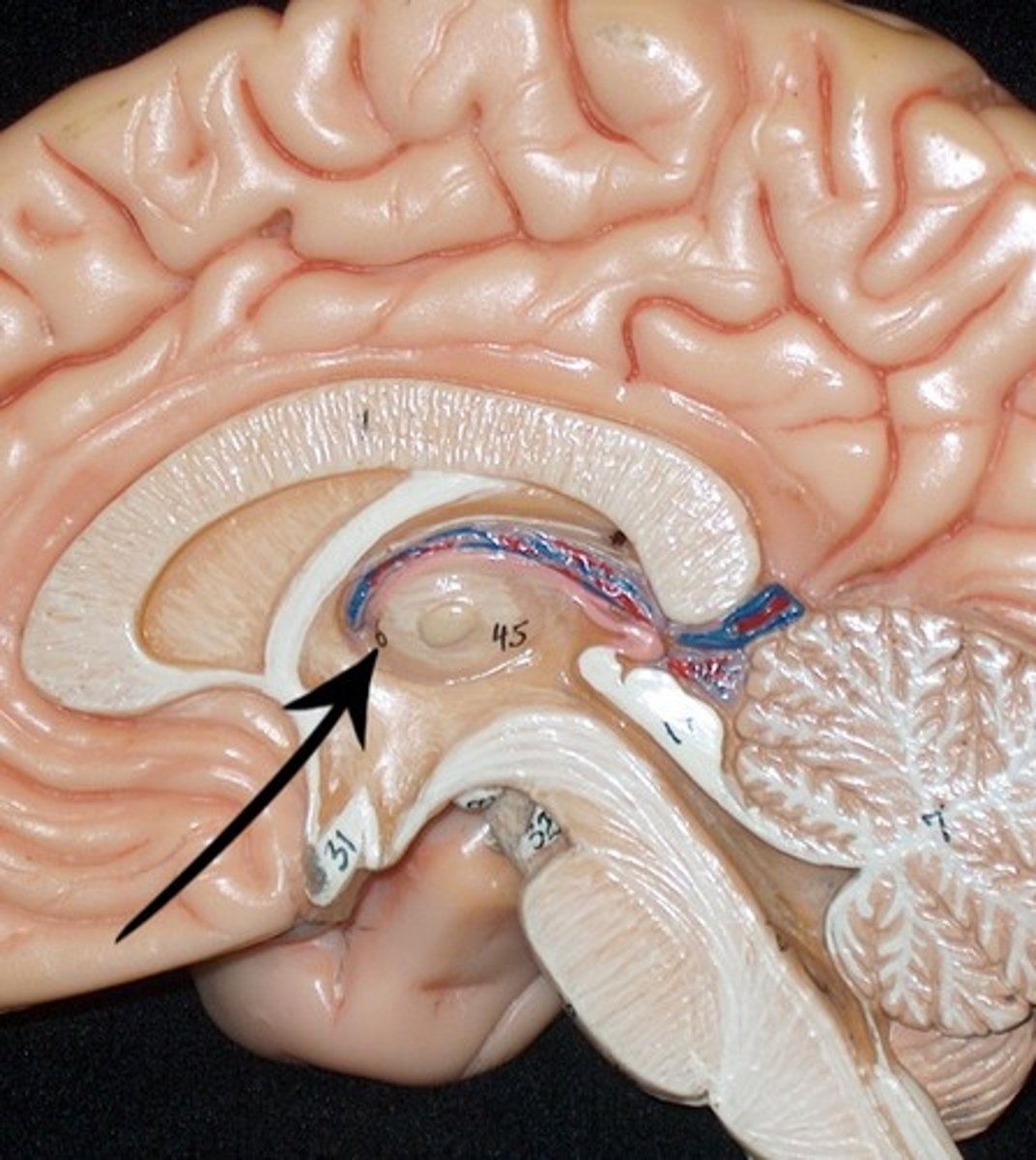
cerebral aqueduct
connects the third and fourth ventricles
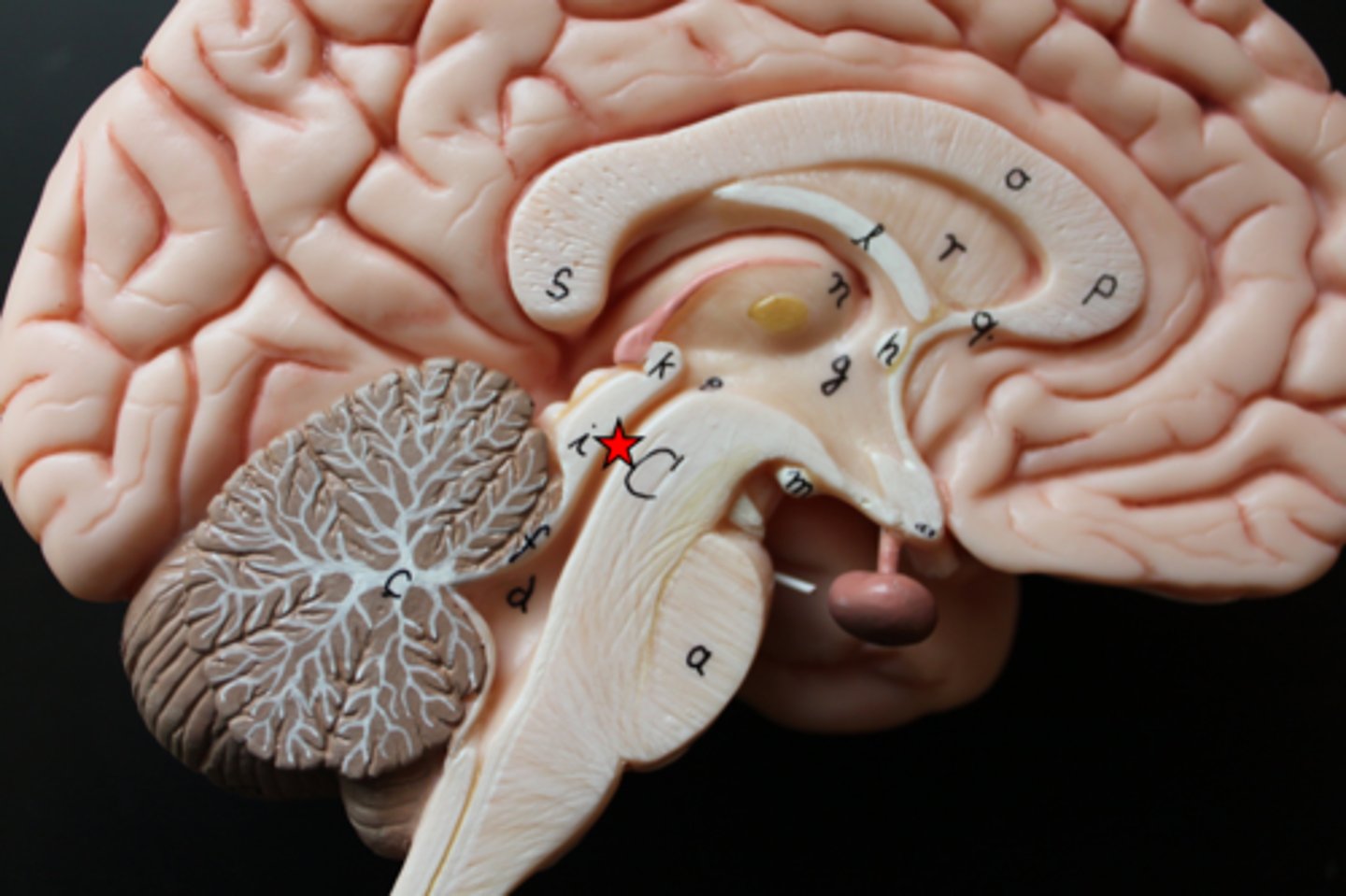
fourth ventricle
the ventricle located between the cerebellum and the dorsal pons, in the center of the metencephalon

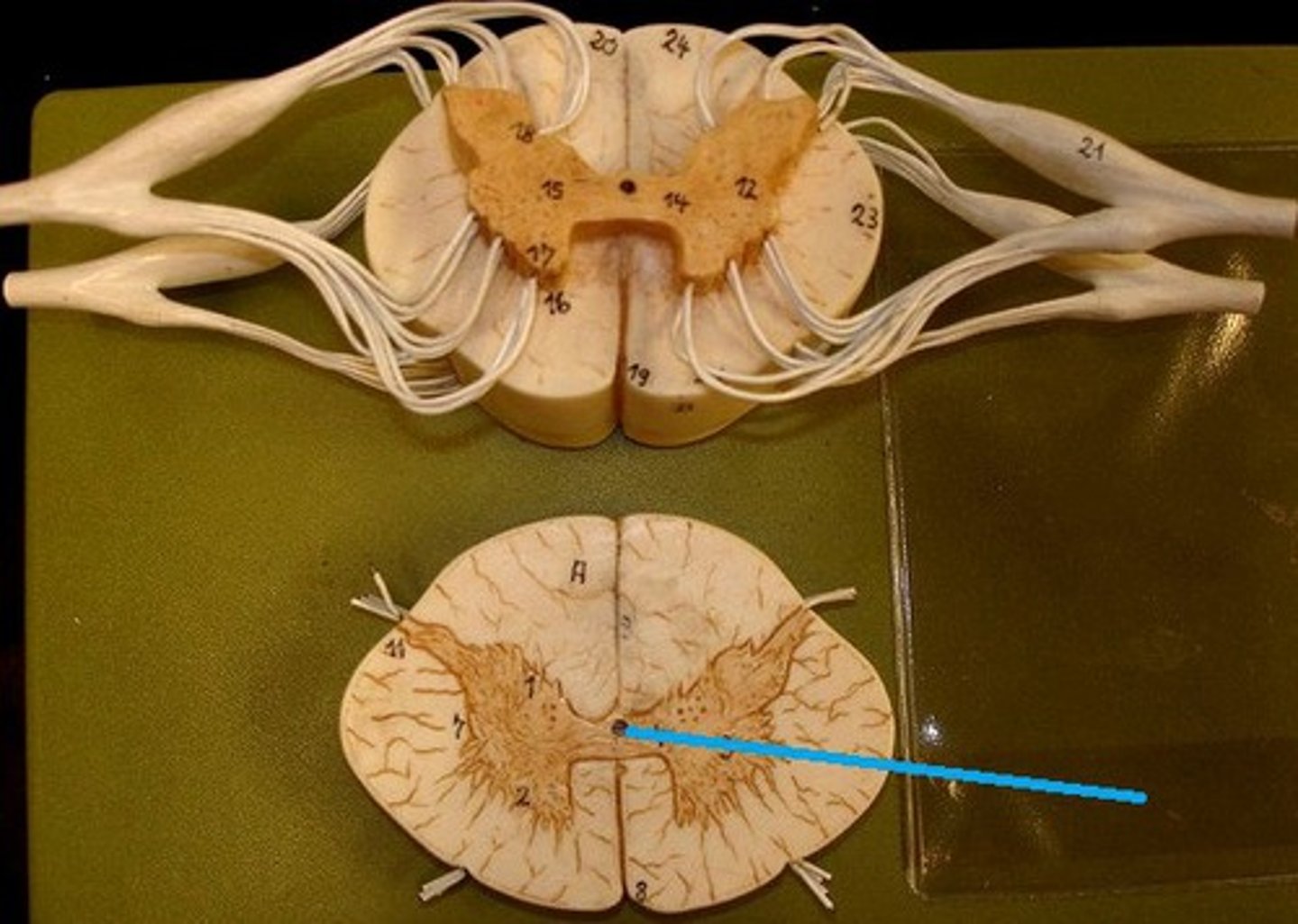
central canal of spinal cord
center of spinal cord which contains cerebrospinal fluid
continuous with 4th ventricle
Drainage of CSF
into dural sinuses via arachnoid granulations

spinal cord
exits via foramen magnum
contained in ventral foramen of vertebrae and ends at the cons medullar is (L2)
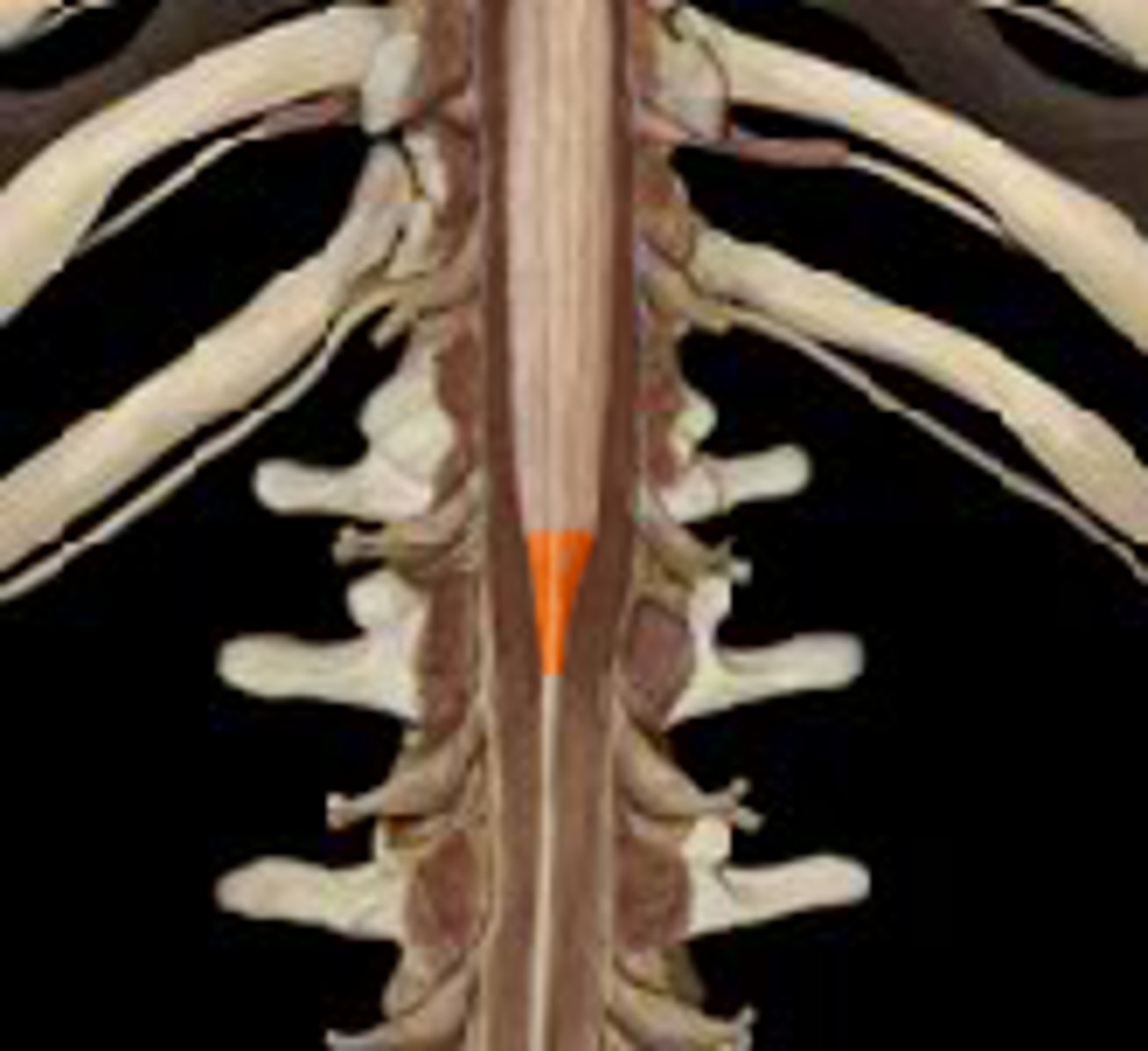
Cons medullaris
terminal end of spinal cord
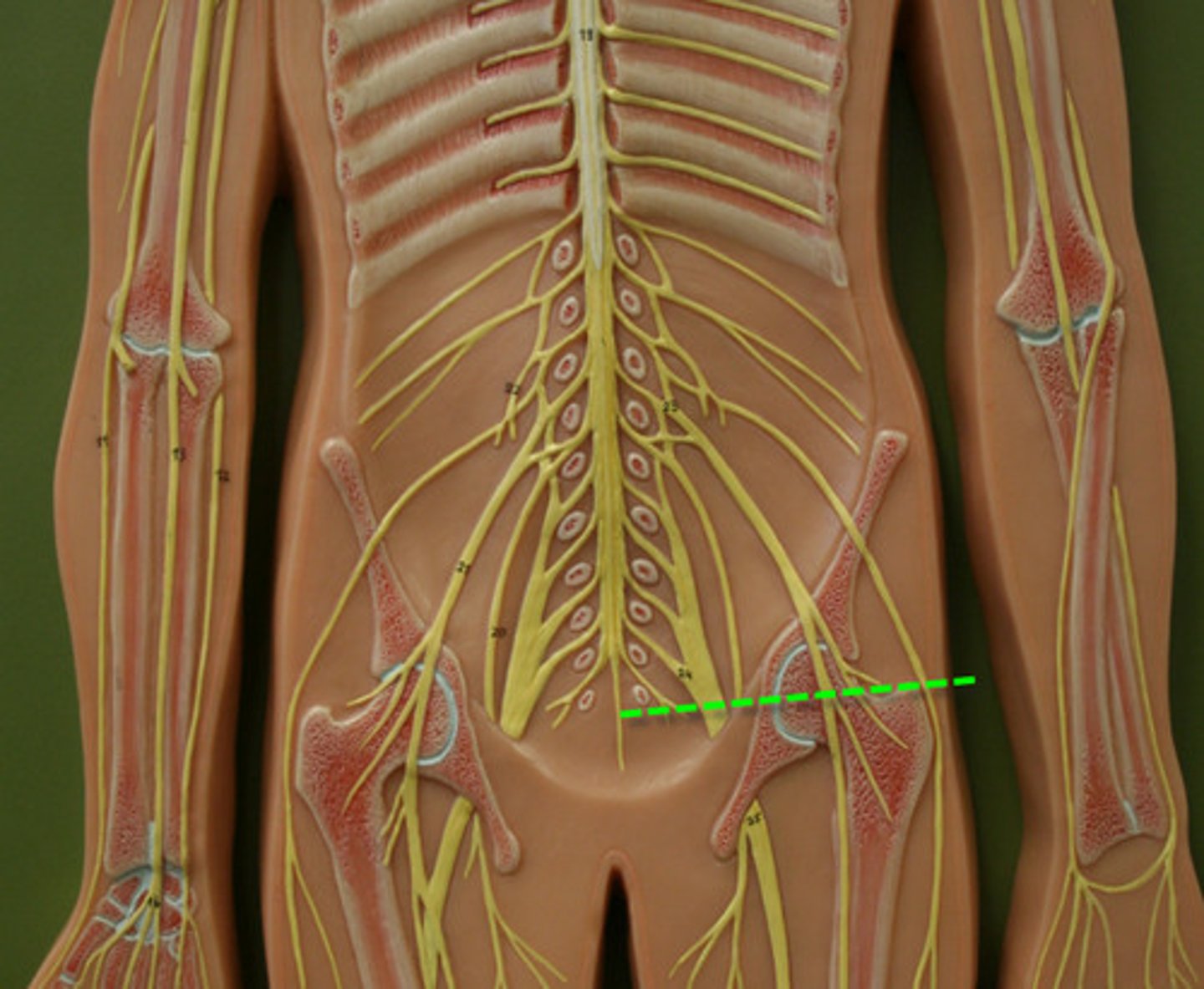
cervical and lumbar enlargements
sites where nerves serving the upper and lower limbs emerge
Cervical- upper limbs
Lumbar-Lower limbs

cauda equina
collection of spinal nerves below the end of the spinal cord- extends from cons medullaris

film terminale
posterior anchor to coccyx-fibrous connective tissue secures cons medullaris
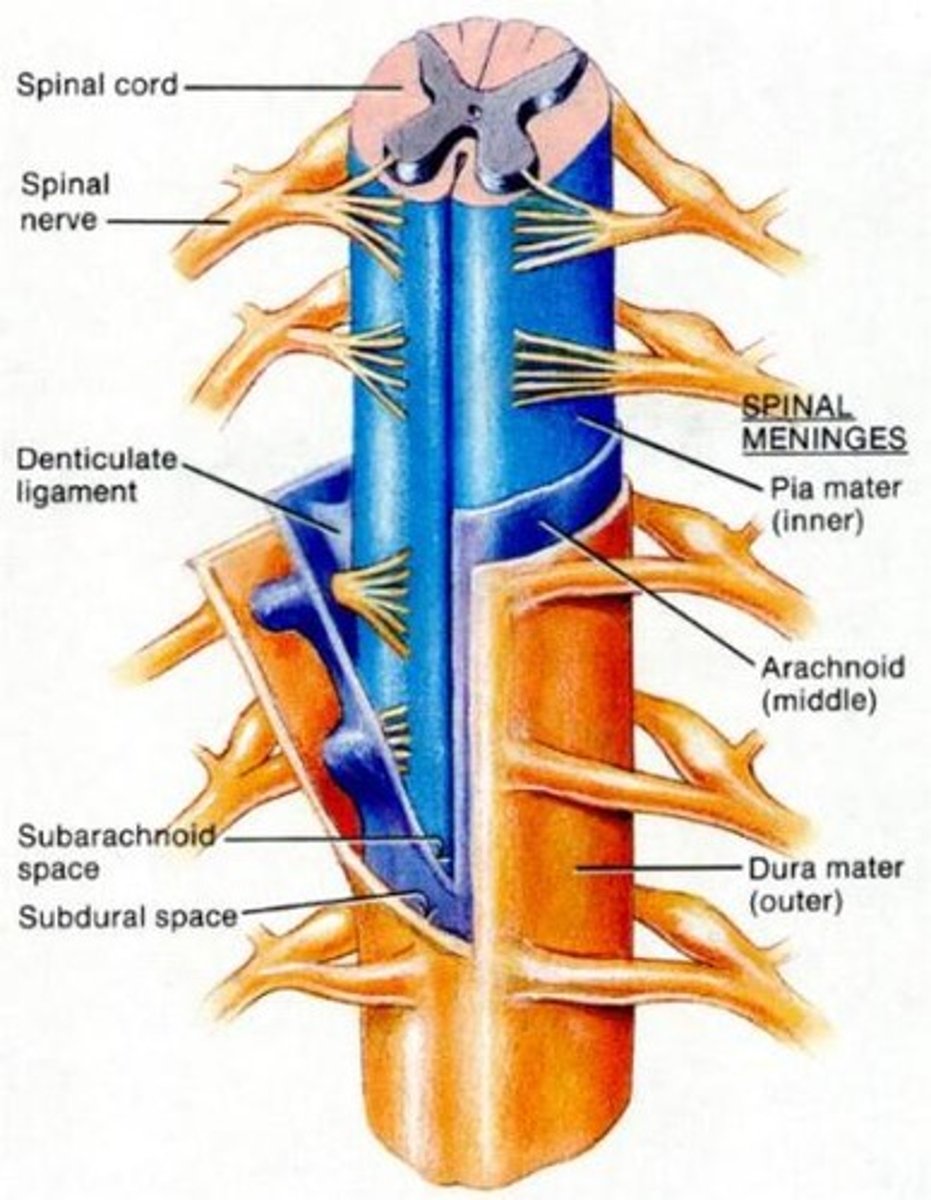
denticulate ligaments
delicate shelves of pia mater; attach the spinal cord to the vertebrae

differences between brain and spinal cord
dura mater is only one layer in spinal cord- it has no granulations for drainage
the spinal cord has an epidural space that has adipose tissue and blood vessels

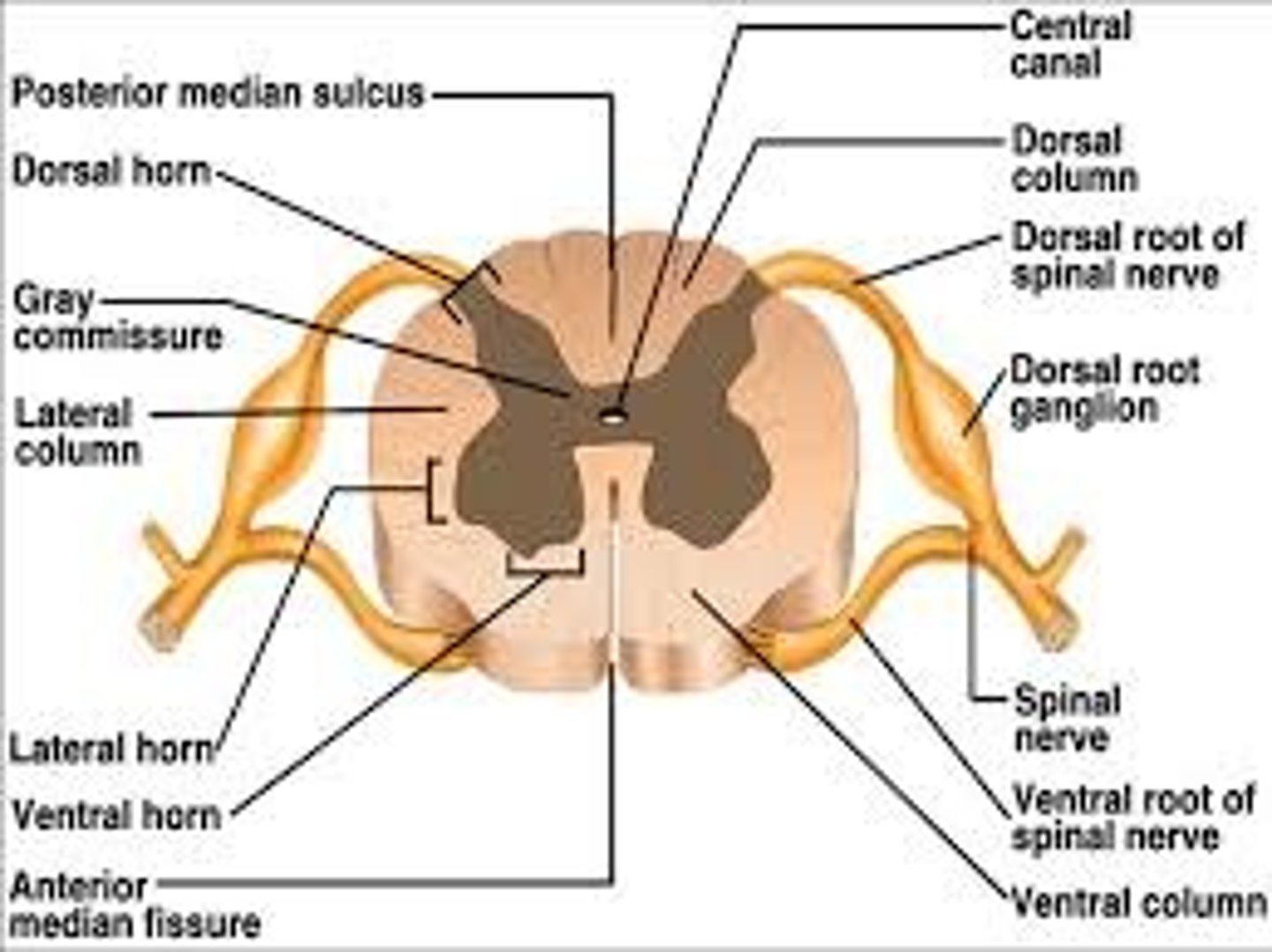
anterior median fissure and posterior median sulcus
fissures and sulcus in spinal cord to tell front from back
spinal meninges
epidural space, dura mater, arachnoid mater, pia mater
CSF spinal cord
central canal in center of spinal cord
subarachnoid space found between arachnoid mater and pia mater
gray matter of spinal cord: horns
dorsal (posterior) horn
Ventral (anterior) horn
lateral horn
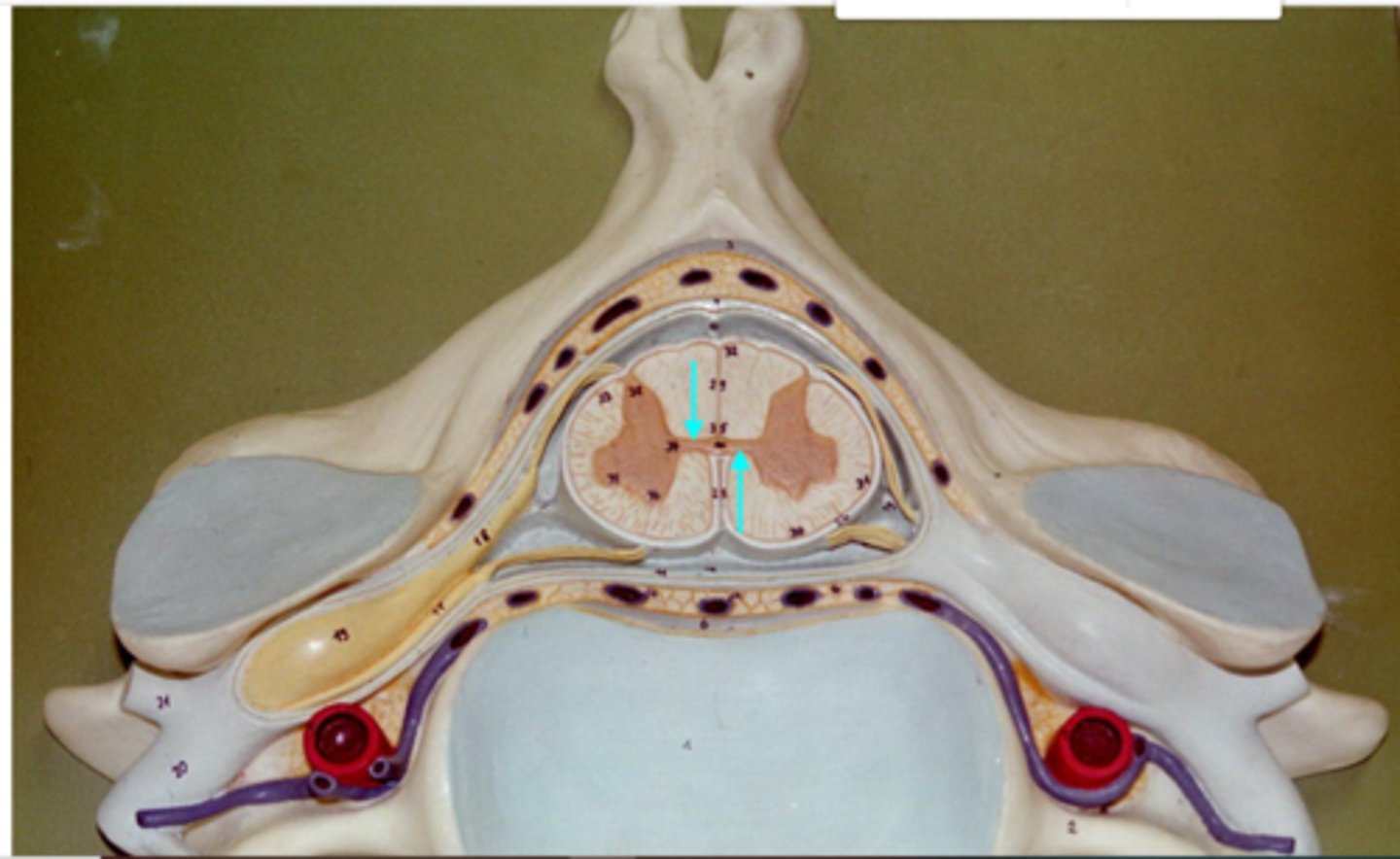
butterfly shape internal gray matter
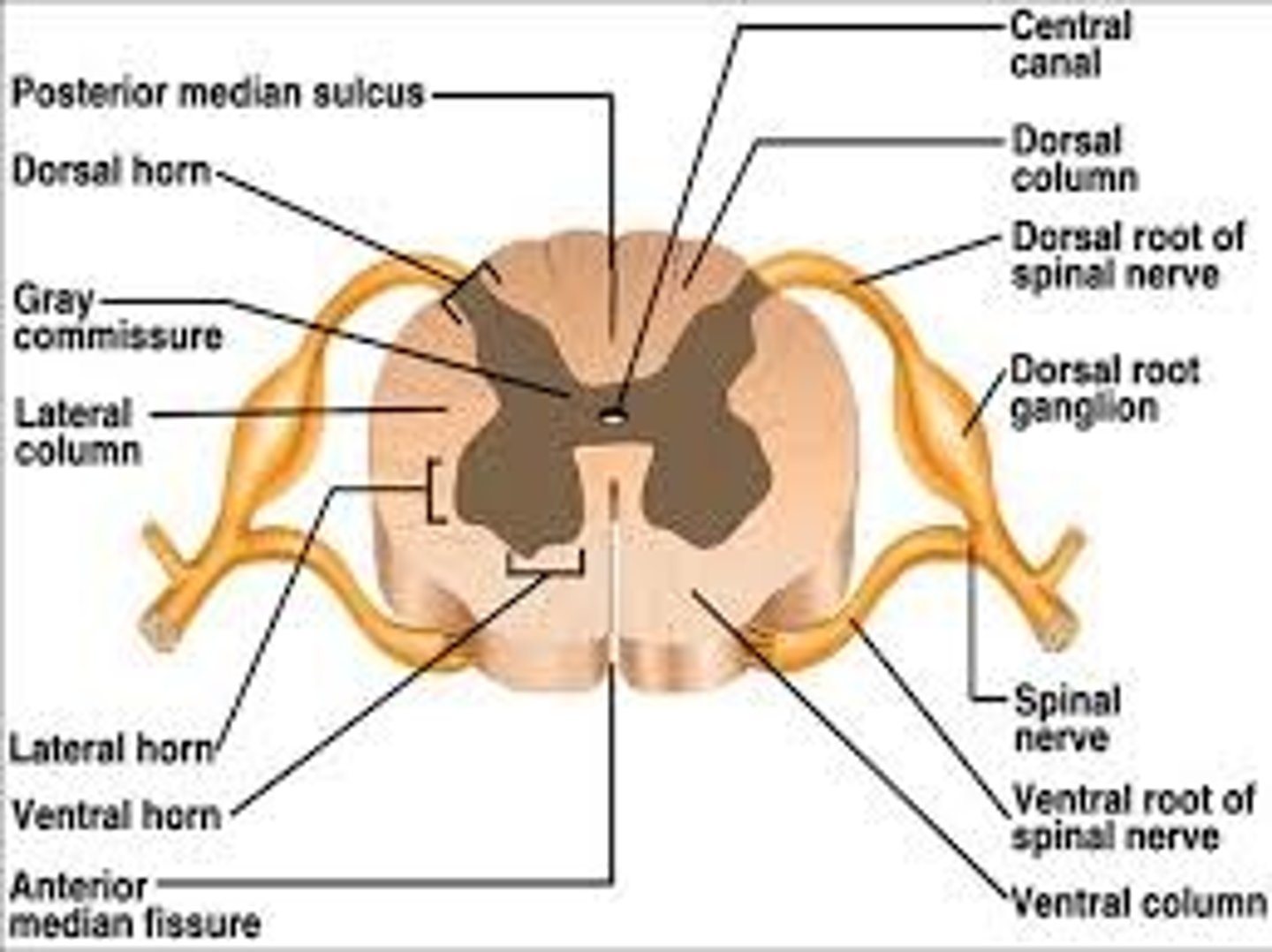
Gray Comissure of Spinal Cord
middle portion of butterfly of gray matter
root of spinal cord
where a nerve root attaches to spinal cord
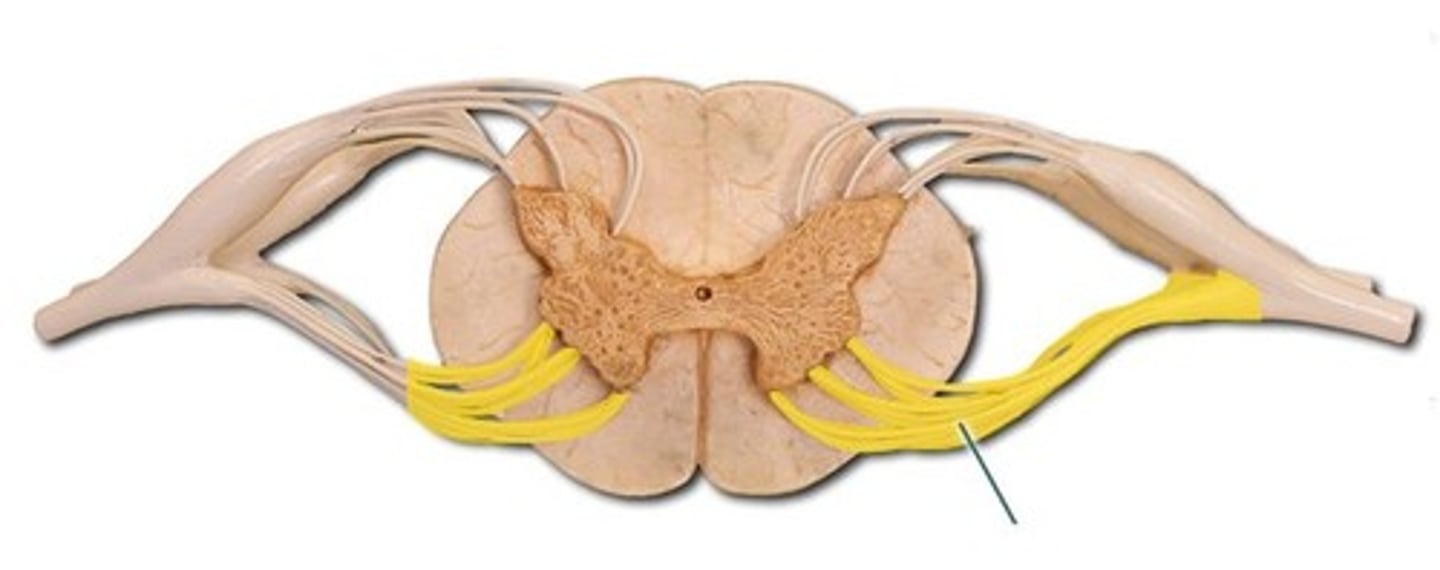
root ganglion
enlarged section of posterior spinal nerve root that contains cell bodies of sensory neurons
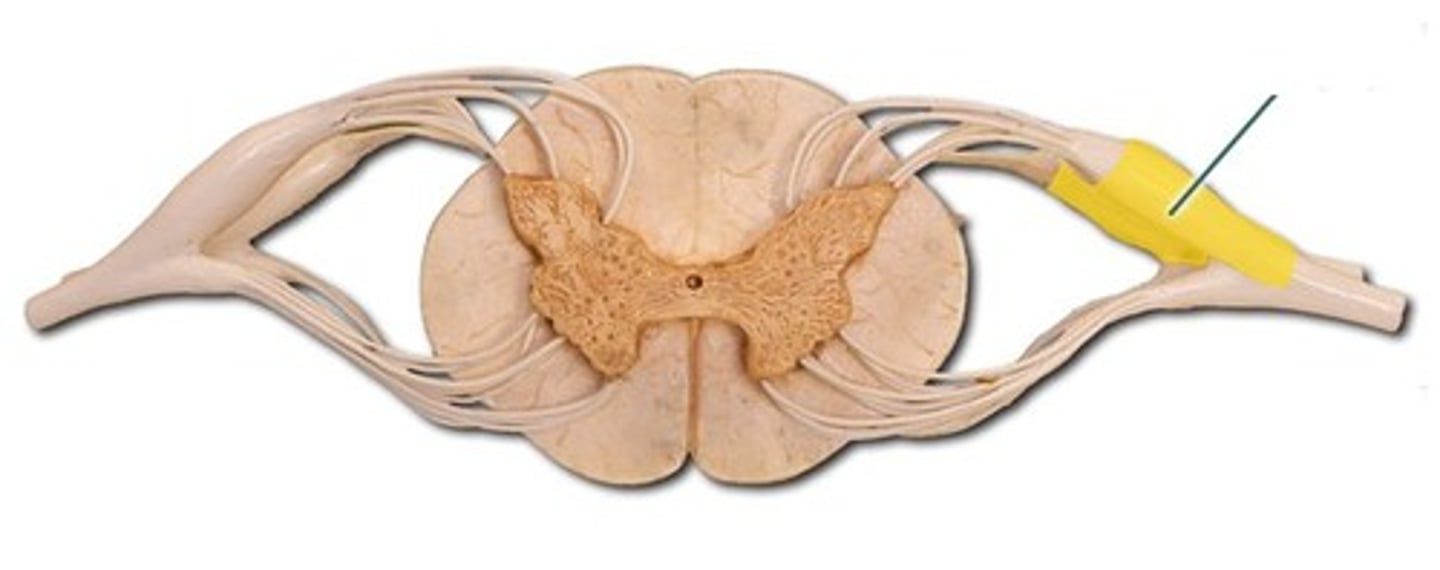
white matter columns (funiliculi)
ascending (sensory) and descending (motor tracts)
dorsal funiculus
ventral funiculus
lateral funiculus

I olfactory
Sensory, smell
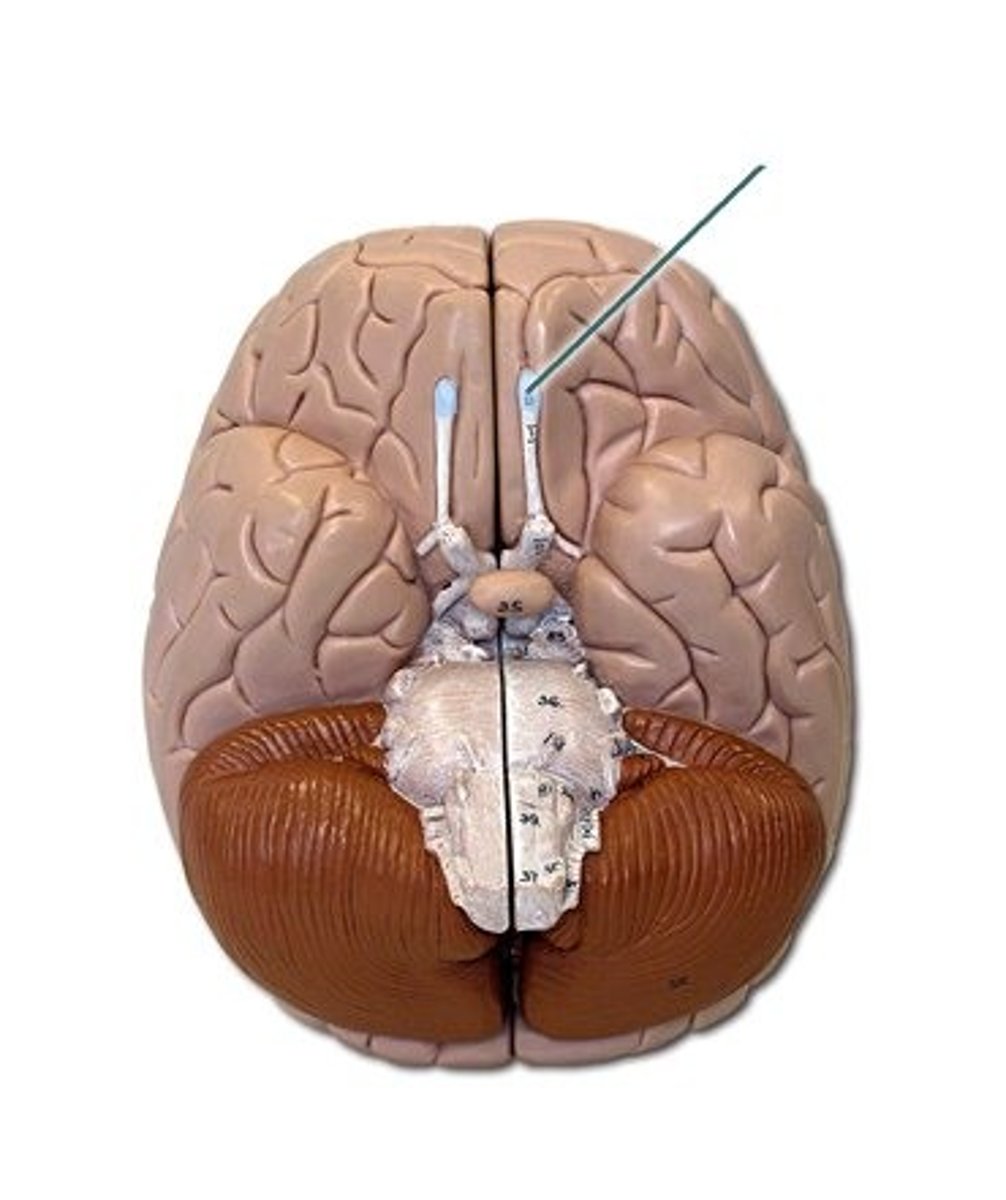
II Optic
sensory, vision
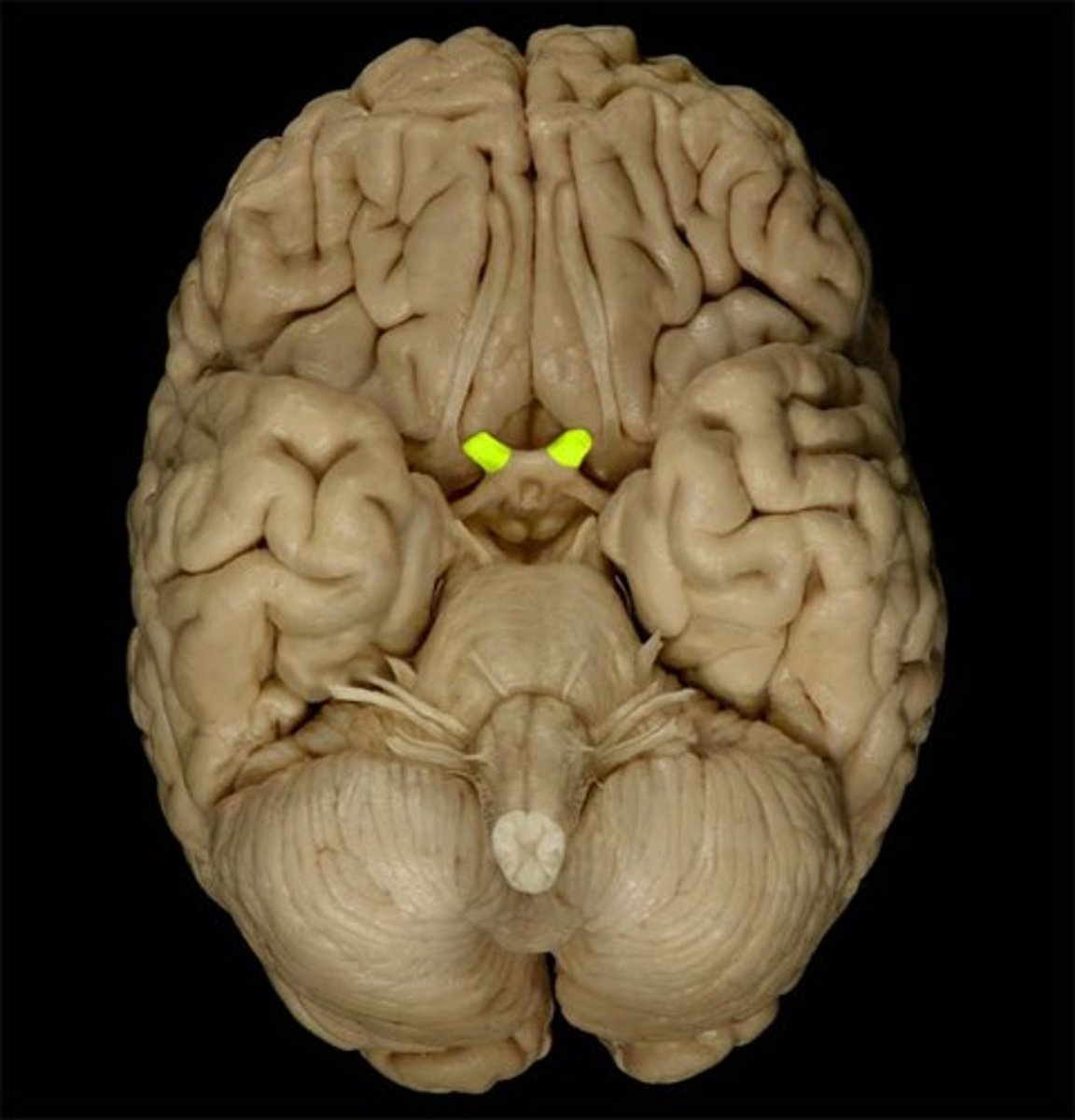
III Oculomotor
motor, eyelid, eyeball movement, pupil contraction
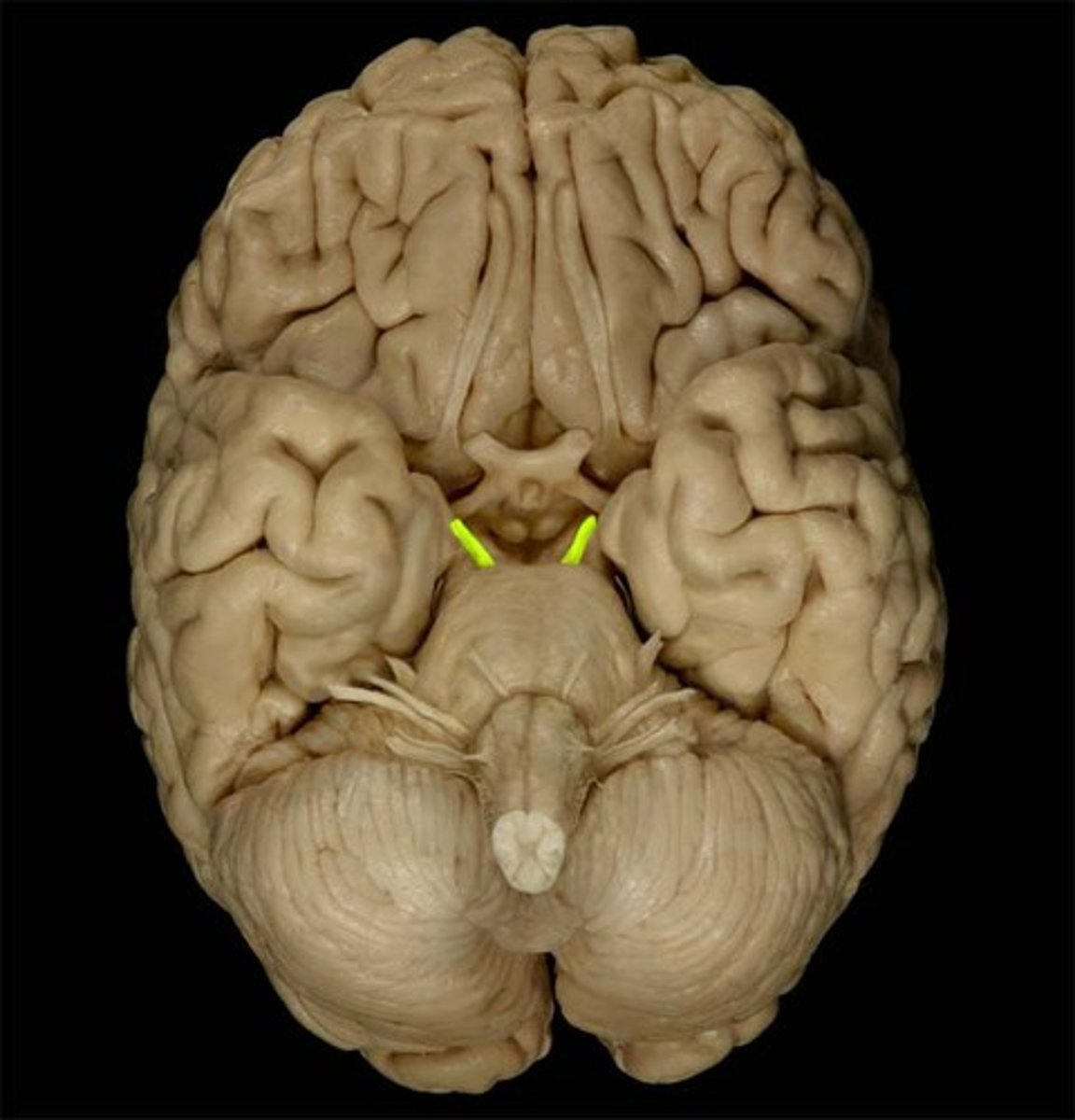
IV Trochlear
motor eye movement
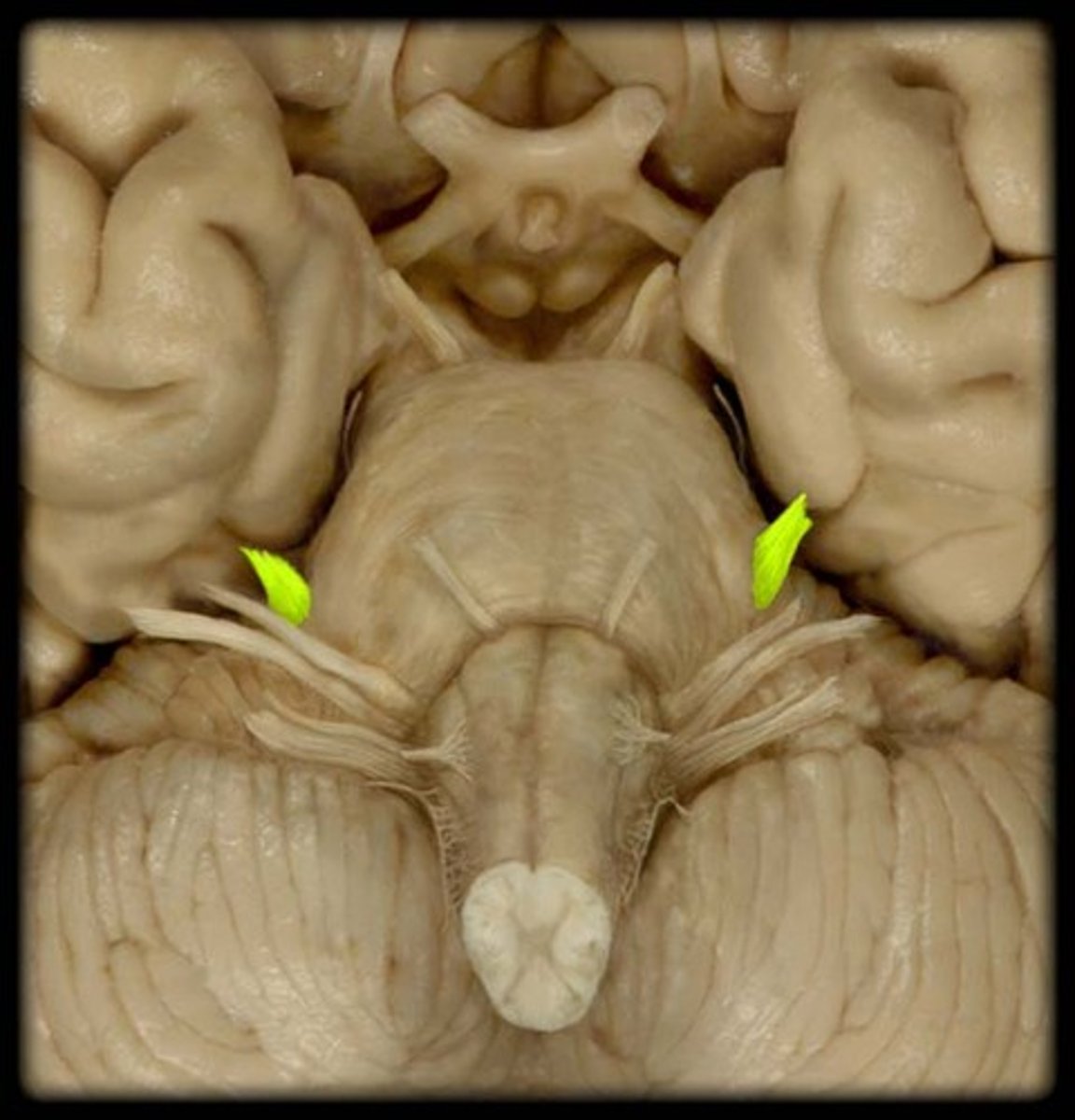
V Trigeminal
mixed, sensory for face, motor for chewing
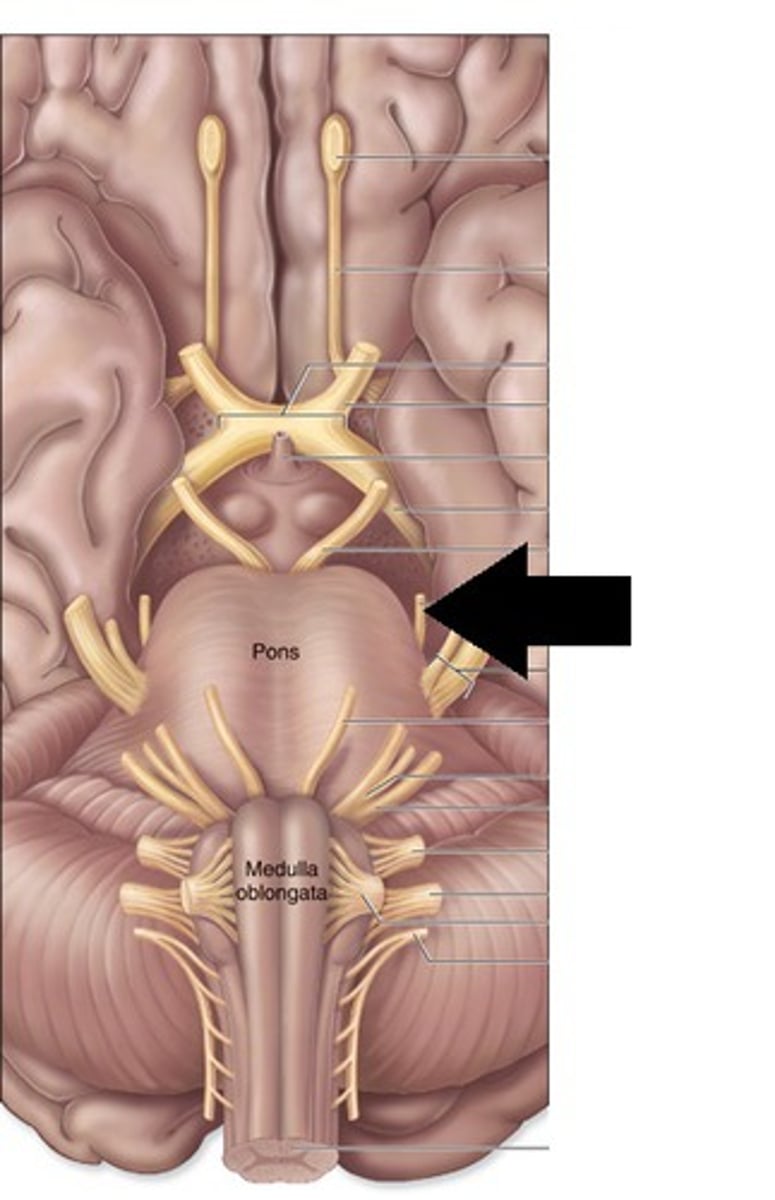
VI Abducens
motor; lateral movement of eye
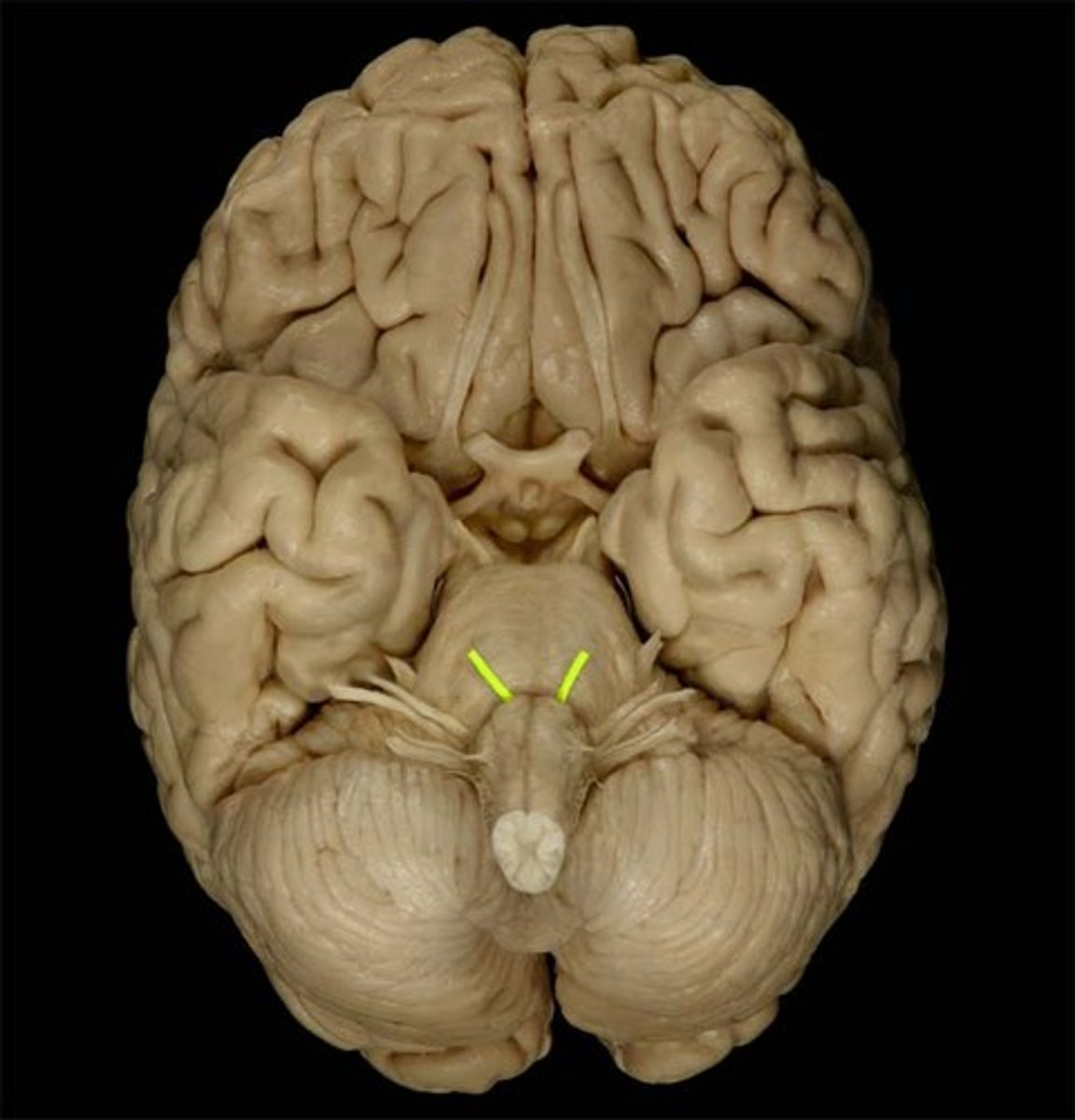
VII Facial
mixed, taste, facial expression, tears, saliva
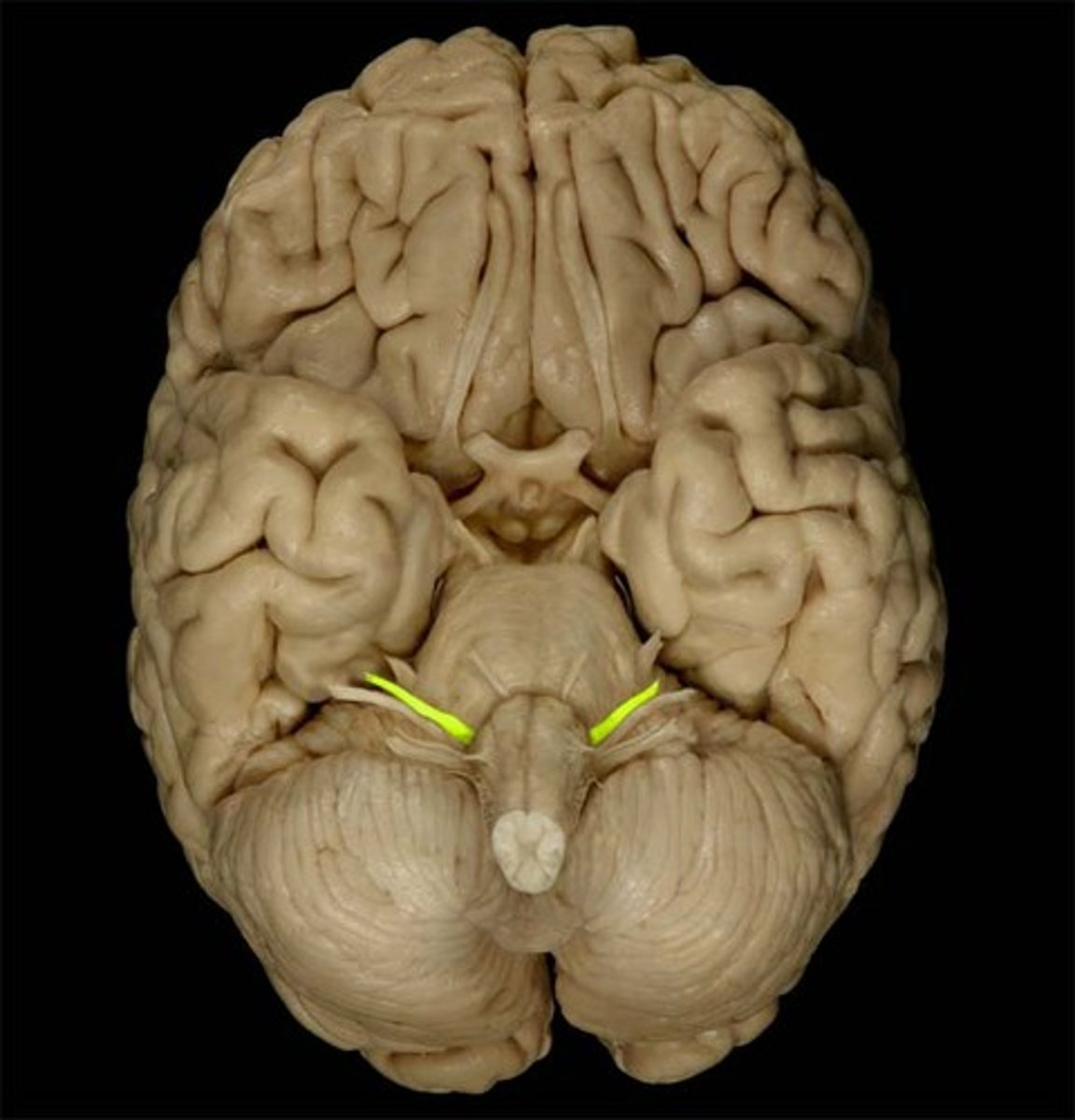
VIII Vestibulocochlear
Sensory: hearing and equilibrium
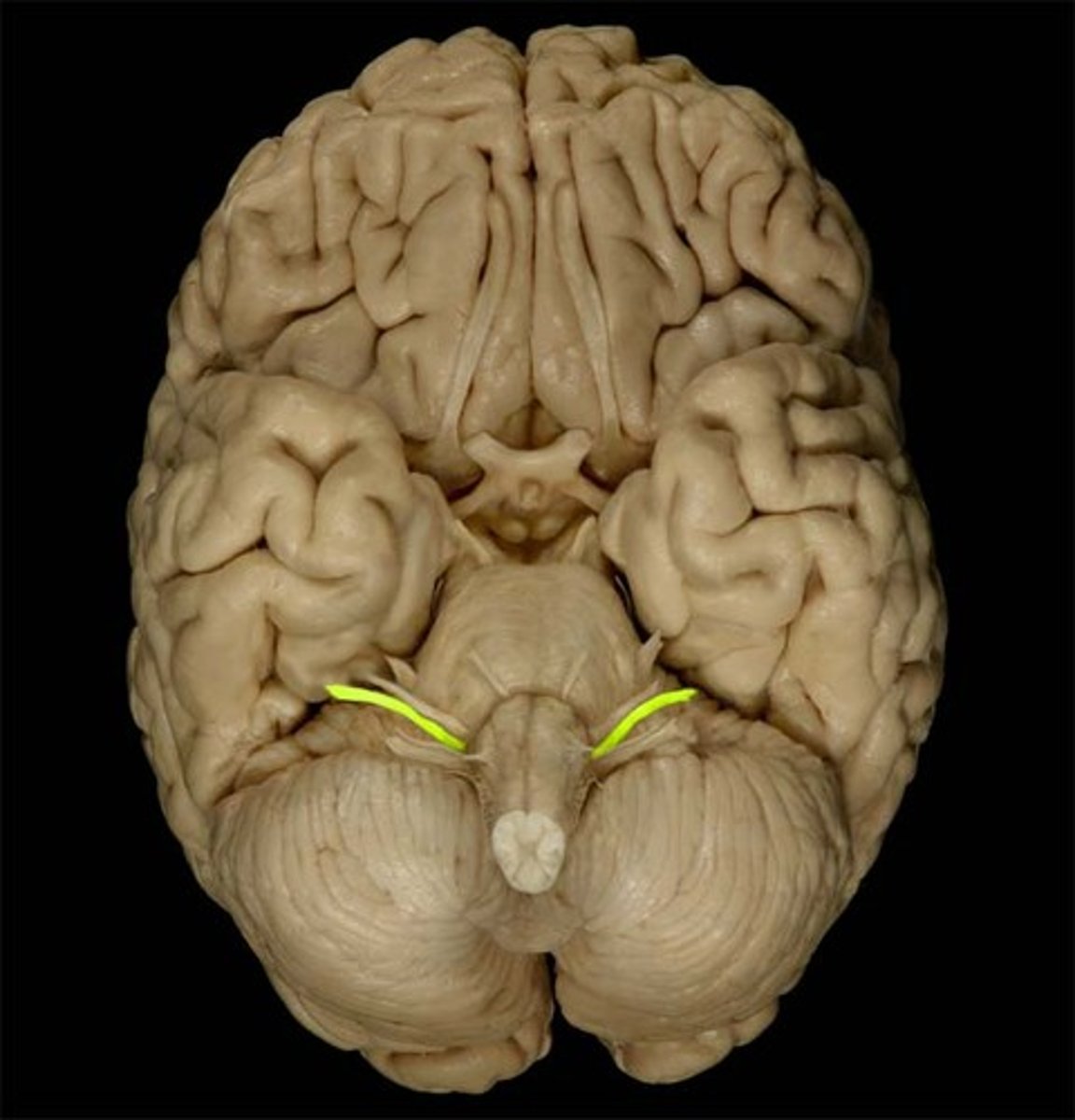
IX Glossopharyngeal
mixed, taste, swallow, saliva glands, respiration, blood pressure

X Vagus
mixed, cardiac and smooth muscle tissue
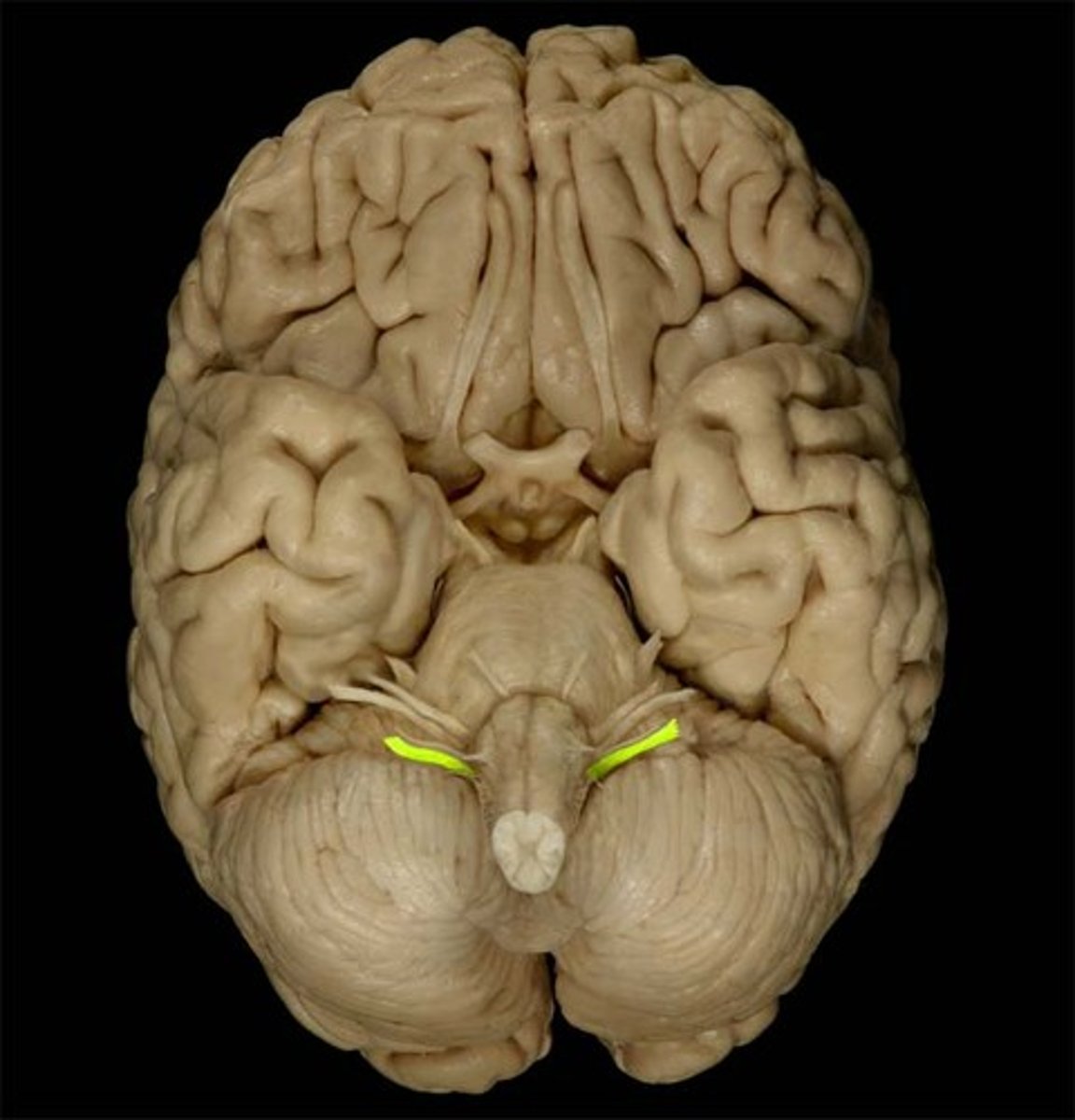
XI Accessory
motor: sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles
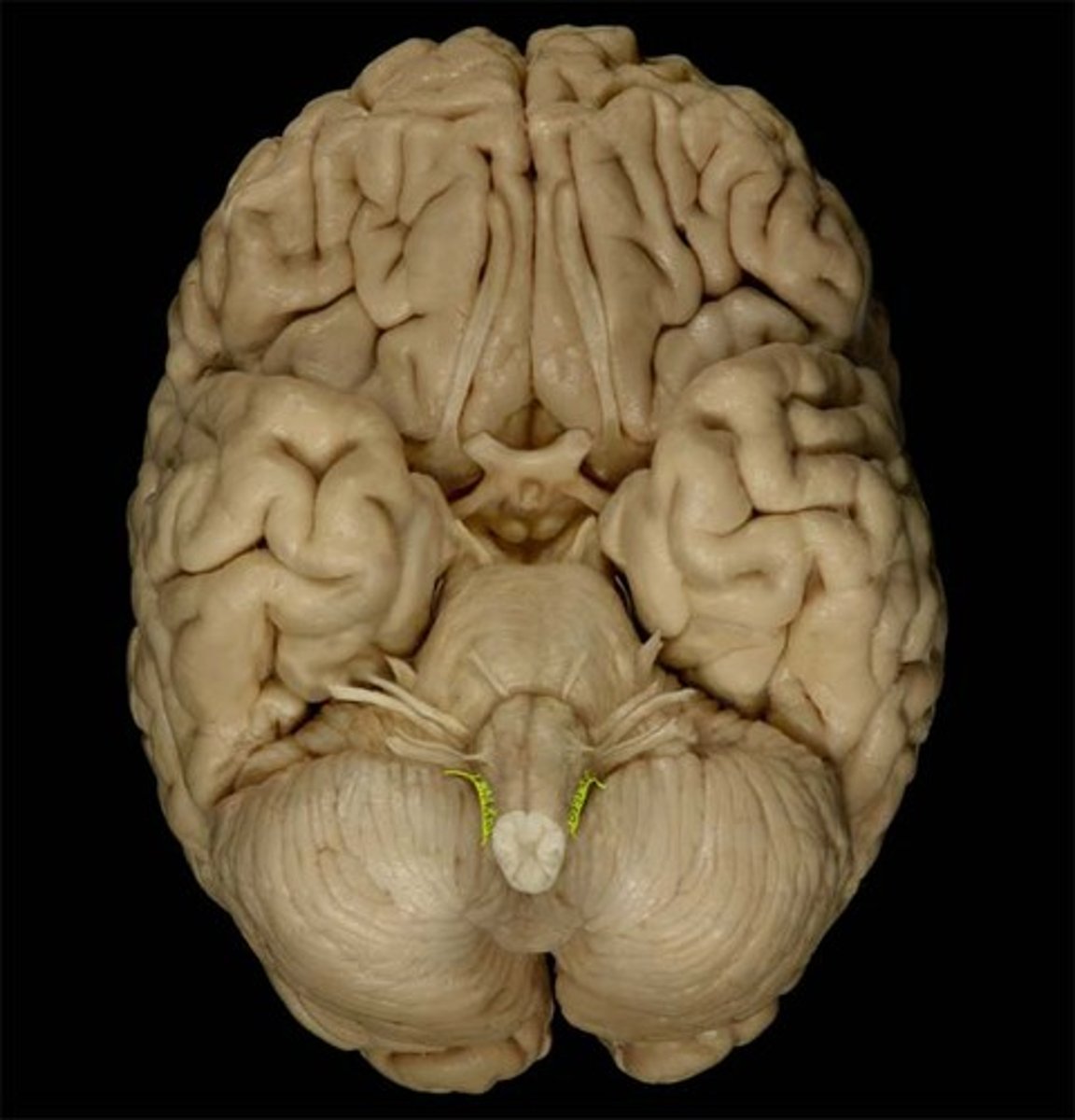
XII Hypoglossal
motor, tongue movement
