Lecture 24 (Fleas and Lice)
1/49
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
Control and treatment of what is the single largest small animal health issue?
Fleas
T or F: Fleas are an irritating and embarrassing household nuisance.
True
What accounts for approximately $1 billion in annual sales in the U.S. alone?
Flea control products
What is Ctenocephalides felis known as?
The “Cat Flea”
What are the following describing?
Laterally compressed body
Adults are parasitic on the host
Larvae feed on defecated blood & organic debris in environment
“Cat Flea” - Ctenocephalides felis
What are the flea species of minor importance?
Ctenocephalides canis & Pulex simulans
What is Ctenocephalides canis known as?
The “Dog Flea”
What is the comparison of Ctenocephalides canis and C. felis on a dog infested with fleas?
C. canis → 12 to 20%
C. felis → ~80%
What is Pulex simulans known as?
The “False Human Flea”
What are Pulex simulans typically found on?
Wild canids (particularly coyotes), Rodents, Opossums, other wildlife
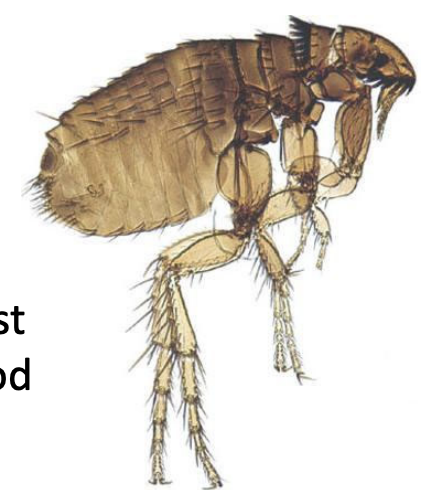
What is seen in the following image?
C. felis
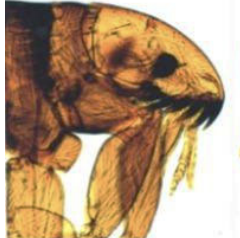
What is seen in the following image?
C. felis

What is seen in the following image?
C. canis

What is seen in the following image?
Pulex simulans
What accounts for over 50% of all dermatologic cases seen in the South East?
Flea related health problems
T or F: Fleas are a significant source of discomfort for animals and humans.
True
What are Fleas biologic vectors and intermediate hosts for?
Parasites, Viruses and Bacteria
Fleas are biologic vectors and intermediate hosts for parasites, viruses, and bacteria such as what?
Dipylidium caninum
Acanthocheilonema reconditum
Plague (Yersinia pestis)
Bartonella henselae (cat scratch)
Suspected vector competence for transmission of FeLV
Transmission by blood meal
Transmission through feces
Adults fleas are what, which is required for maturation and reproduction?
Obligate Blood Suckers
Will adult fleas feed on any warm-blooded host?
Yes
What do larval stages of fleas feed on?
Digested blood and organic debris (dander, dried feces, etc.)
What is true for newly hatched adult fleas?
They are able to survive long periods of starvation
How long does it take for the life cycle of a flea to be complete under optimal conditions?
3 weeks
What is the primary source of flea egg and flea larvae infesting companion animals?
Wildlife visiting yards of pet owners
What may be the primary vector for introducing fleas to the hyper sensitive dog?
The asymptomatic cat
What is adverse to flea survival outdoors?
Cooler weather (< 40*F) — (5 days at 34*F)
What must successful control of flea infestations be directed at?
All stages of life cycle
Fleas on primary host, fleas on secondary (asymptomatic) hosts, larval/pupal stages off of the host in residential environment
What is failure to treat any stage the basis of?
Perceived treatment failure
Products that kill fleas on the host, prevent re-infestation of the host (repellent properties) and prevent eggs from hatching or larvae from developing (growth regulators) are key for what?
Successful control of flea infestations
Successful mitigation of all Flea related infestations are based on what 4 activities?
Killing fleas on the primary host (Dog affected by flea bite dermatitis)
Killing adult fleas on reservoir hosts (Asymptomatic cohorts of the affected animal)
Preventing fleas from immediate re-infestation
Elimination of larval stages in the environment (Bedding, Carpets, Habitual Hangouts)
Failure to follow-thru on any single activity results in a perception of treatment failure
What type of life cycle do chewing and sucking lice have?
Direct Life Cycle
Chewing and Sucking Lice are dorso-ventrally flattened - do they have wings?
No - wingless
Chewing and Sucking Lice are poorly adapted for life off the host and are what?
Highly host specific
How can chewing and sucking lice be controlled?
By Tx and nit removal
When comparing lice - what is the following describing?
Head wider than thorax
Bites skin, chews feather, & feeds on sloughed dermis, oozing blood/serum
Host specific, only lice on birds and cats
Chewing Lice
When comparing lice - what is the following describing?
Head more narrow than thorax
Pierces skin, sucks blood, hypoprotinemia
Host specific, dogs, goats, horses, cows, etc.
Sucking Lice

What is seen in the following image?
Sucking Louse b/c head is smaller than thorax
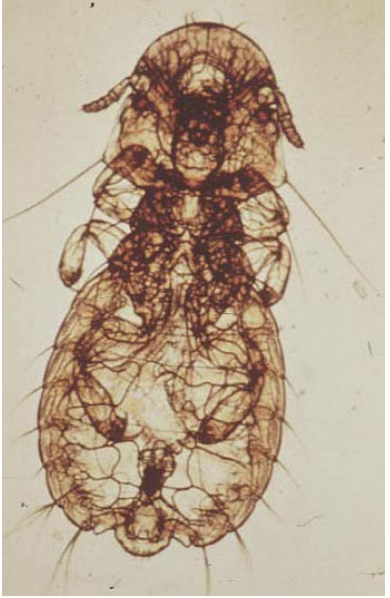
What is seen in the following image?
Chewing Louse b/c head is larger than thorax
What is the general term for louse infestation?
Pediculosis
Who is Pediculosis (louse infestation) often associated with?
Young animals
Human Pediculosis is exclusively host specific - what 3 species infest people?
Pediculus humanus capitis
P. humanus humanus
Pthiris pubis
What is the treatment/control for Pediculosis in companion animals?
Fipronil
Imidacloprid
Selamectin
What is the treatment/control for Pediculosis in Livestock?
Macrocyclic lactones (Pour-on & oral formulations)
Attention to other factors affecting herd health
What are considered True Bugs (Hemiptera)?
Reduviid bugs and Bedbugs (Cimex lectularius)
What are Reduviid bugs also known as?
Kissing Bugs or Assassin Bugs
What are Reduviid Bugs the intermediate host for?
Trypanosoma cruzi
Who are hosts for Reduviid Bugs?
Dogs and Cats
What is the common name for Cimex lectularius?
Bedbugs
Who are hosts for Bedbugs?
Rabbits, Poultry, and Pigeon Colonies — exsanguination of young & neonates
What is the clinical significance and pathogenic potential of fleas and lice?
Source of discomfort
Dermatologic issues
Vector potential