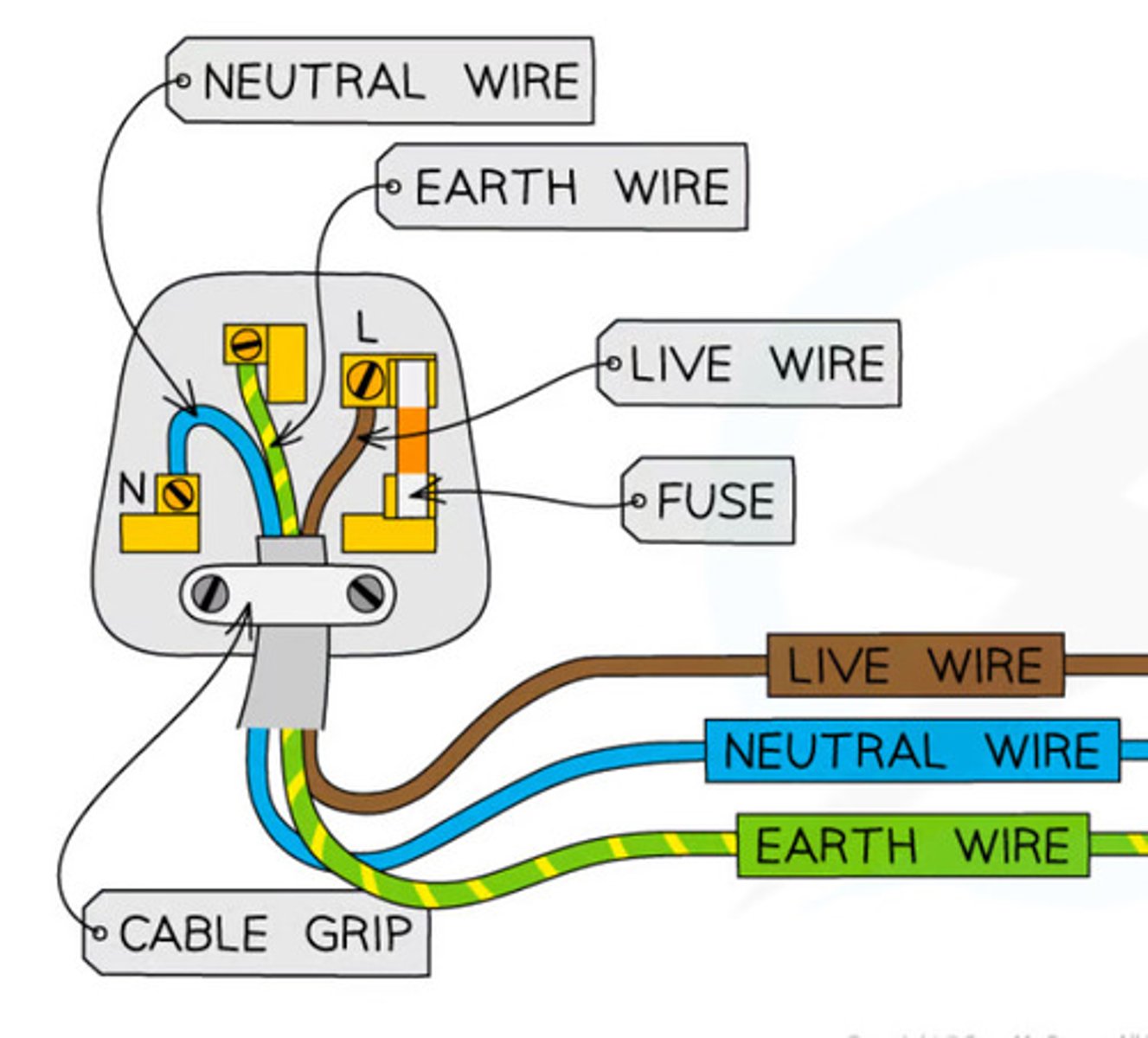
Mains electricity
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
What is power?
The rate of energy transfer
What two quantities does electrical power depend upon?
Current and voltage
What is power measured in?
Watts
What is the electrical power equation?
P = IV
Draw/Imagine a fuse symbol
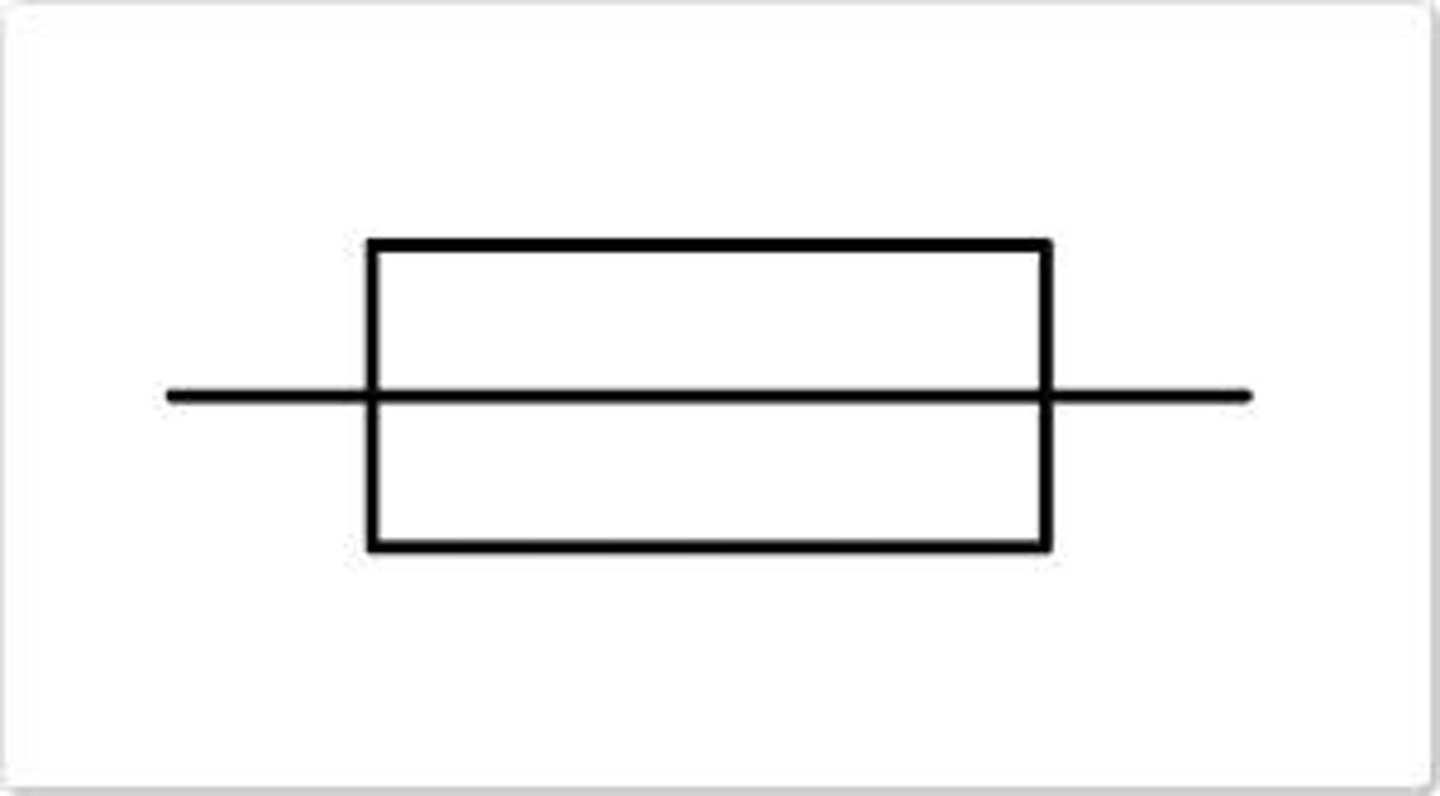
What is the purpose of a fuse in a circuit?
It is a safety device that cuts of the flow of electricity if the current is too large
What happens to the wire in a fuse when the current becomes too large (greater than the fuse rating)?
Wire melts, which breaks it, thus breaking the circuit and stopping the current
State the three fuse sizes
3A, 5A, 13A
What is the rule to determine a fuse size for a electrical component
Choose the next size up
State the correct fuse size for an appliance that requires a current of 4.5 A
5A
What is the equation for calculating energy transfers in terms of current, potential difference and time?
I X V x t
Which wire is the most dangerous?
Live wire
List 3 electrical common safety hazards
-Damp conditions
-Damaged insulation
-Overheating of cables
How are damp conditions a hazard?
Water can conduct electricity, causing a short circuit or posing an electrocution risk.
How can damaged insulation of a wire pose a threat?
Contact with an exposed piece of wire can cause an electric shock
How do cable overheating be dangerous?
Passing too much current through too small a wire (or leaving a long length of wire tightly coiled) can lead to the wire overheating. This could cause a fire or melt the insulation, exposing live wires
How is double insulation a safety feature?
Appliance has insulation around each of the wires and have a non-metallic case, eliminating the need for an earth wire.
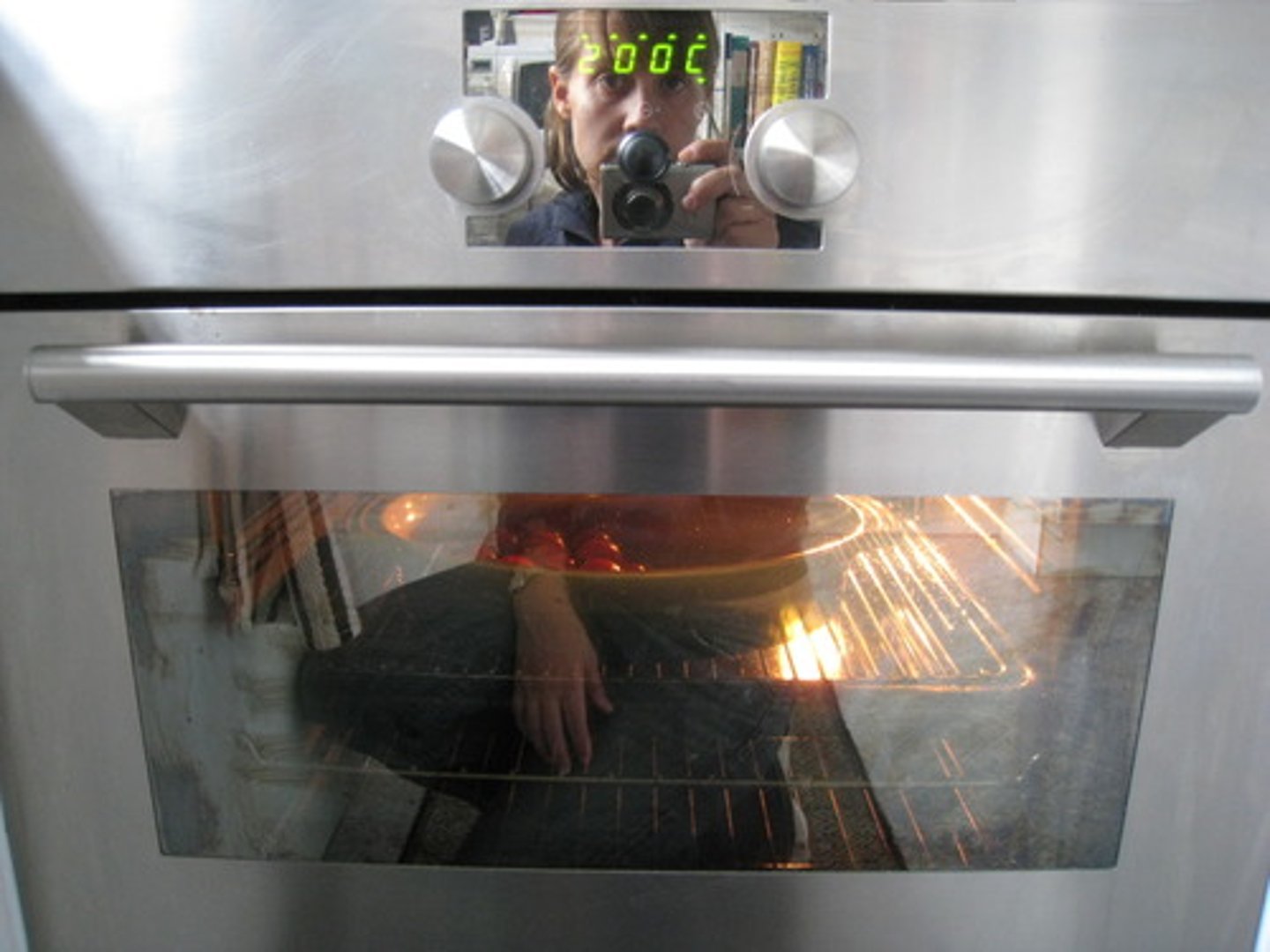
Some appliances have metal cases around them (e.g. oven)
Explain why this poses a potential electrical safety hazard?
If a live wire (inside the appliance) came into contact with the case, the case would become electrified (metal is a good conductor of electricity) and anyone who touched it would risk getting an electric shock

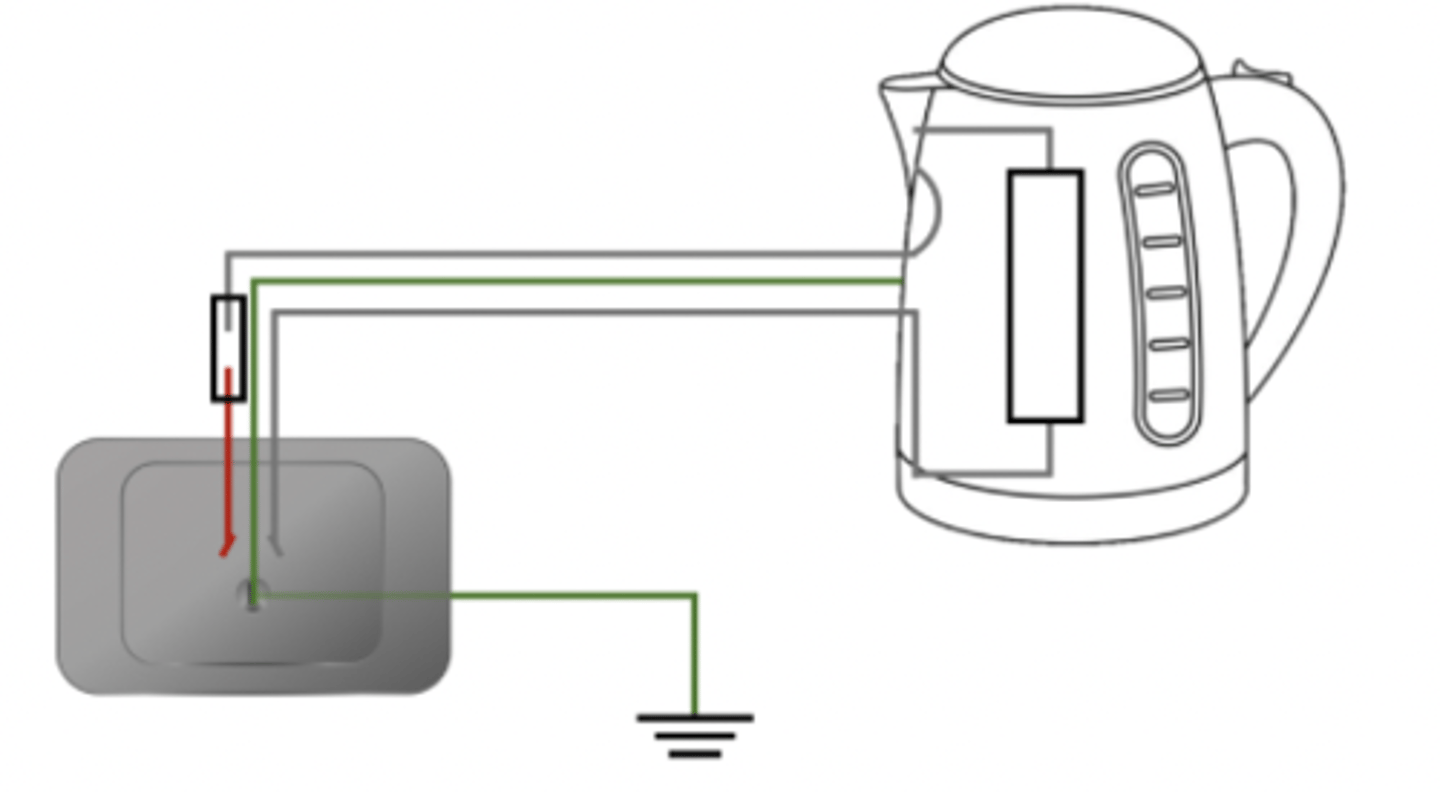
How do earth wires reduce the risk of people using appliances with metal casing?
Provides a low resistance path to the earth
which causes a surge of current in the earth wire
The high current through the fuse causes it to melt and break
This stops the current
How do circuit breakers prevent electric shock?
Consists of an automatic electromagnet switch that breaks the circuit if the current exceeds a certain value
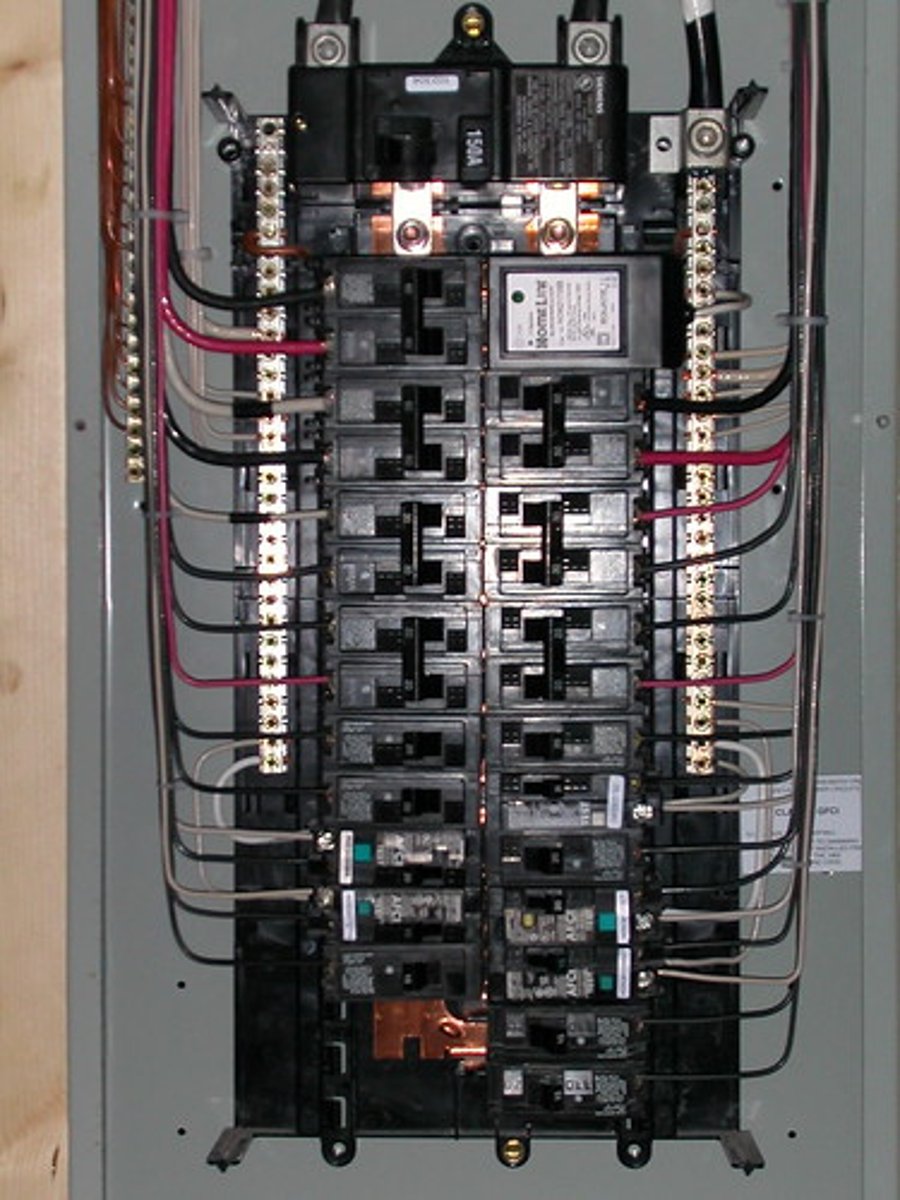
Why does a circuit breaker have a major advantage over a fuse as an electrical safety device?
It doesn't melt and break, hence it can be reset and used again
It works much faster
What do neutral wires do?
They complete the circuit
What is the heating effect of current
Current flows through a conductor (such as a wire), it encounters resistance, the energy gets dissipated in the form of heat to the surroundings by the electrons colliding with metal ions
Do wires in a toaster have a high or low resistance?
High resistance, so more heat energy can get dissipated.
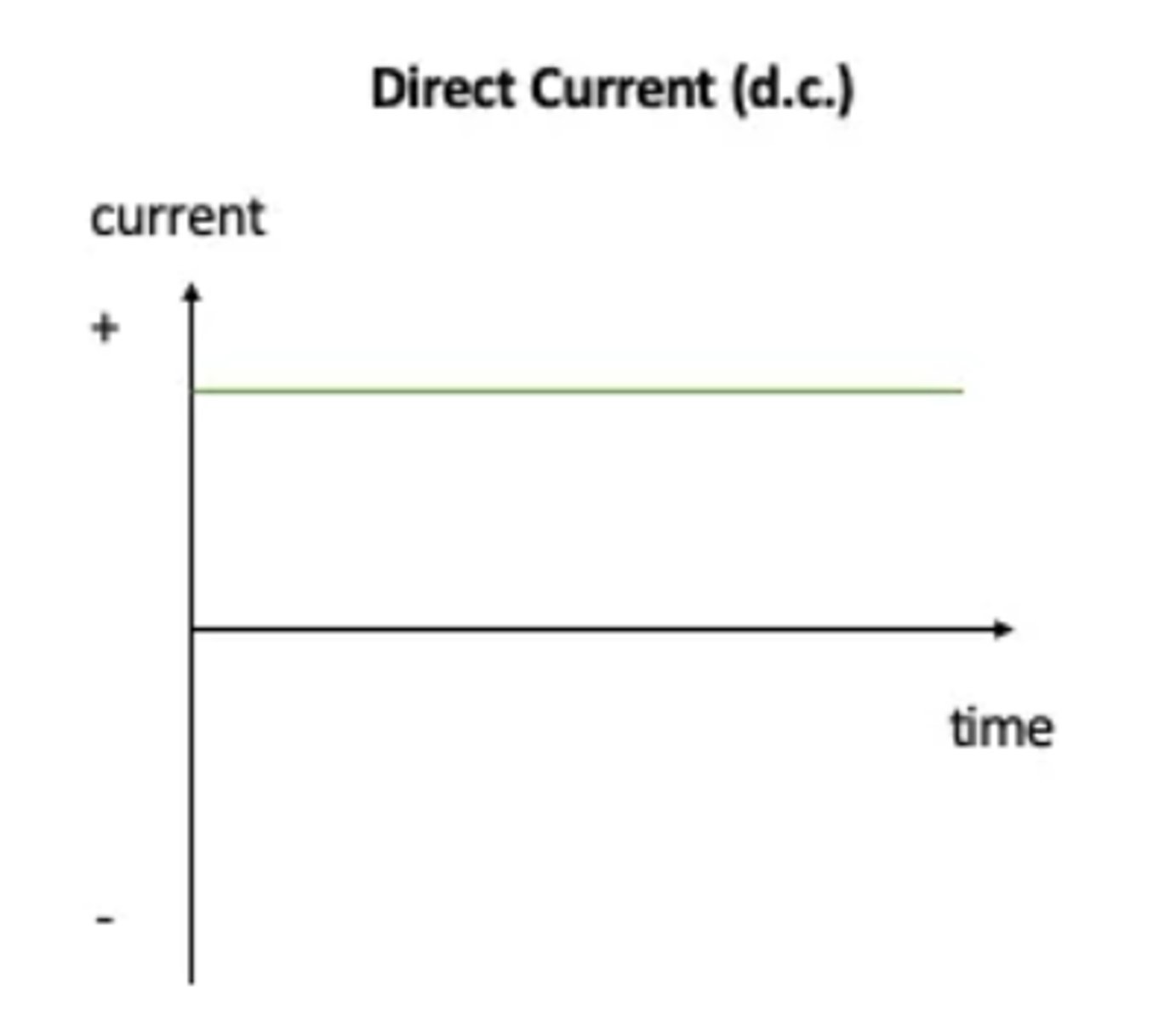
What is direct current?
Current flowing in one direction, that is, from positive and negative.
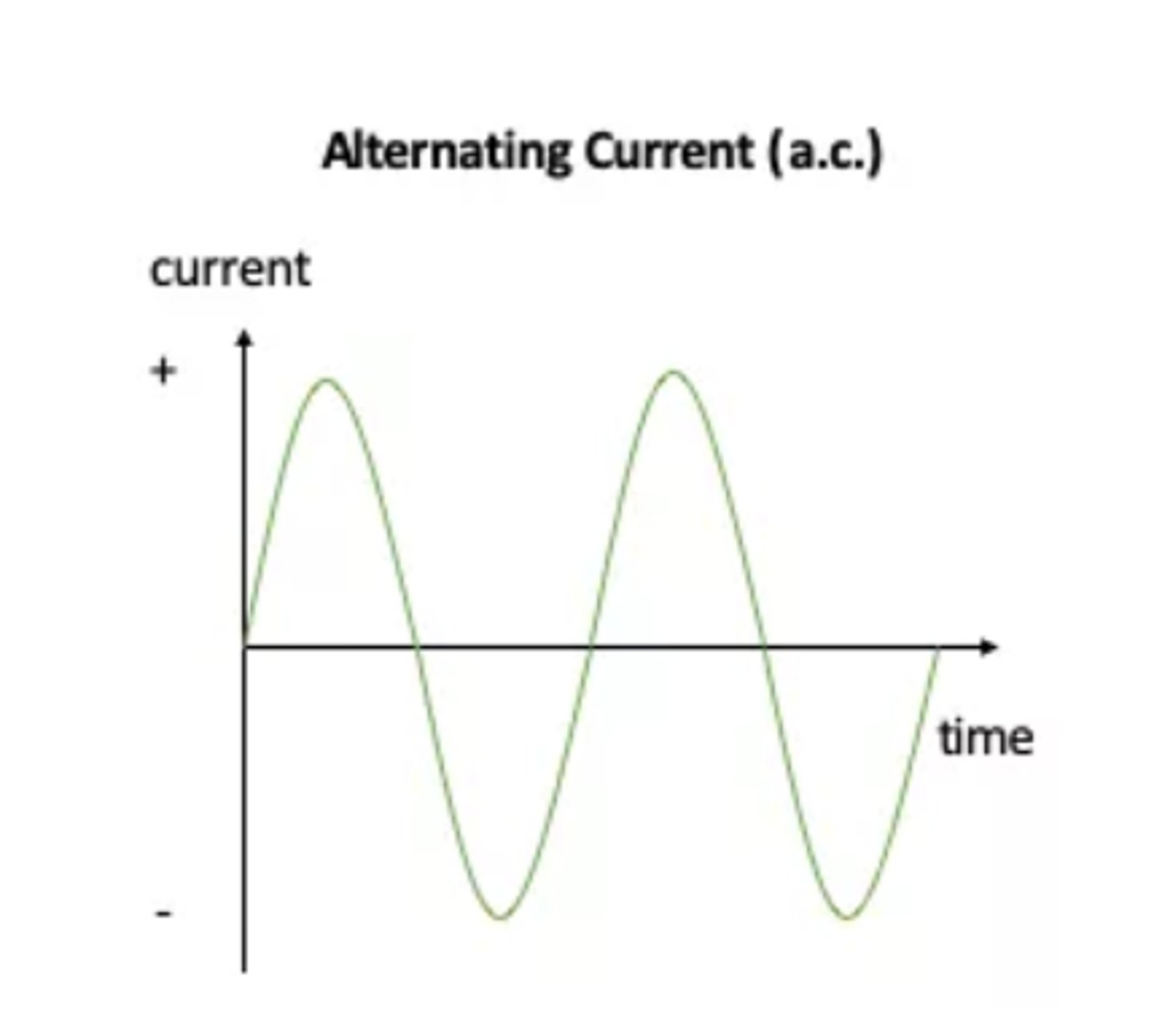
What is alternating current?
A current that continuously changes its direction
What is direct current produced by?
A cell or battery
What is a alternating current produced by?
Electrical generators
What terminal does a direct current have?
A positive and negative terminal
What terminal does a alternating current have?
Has two identical terminals
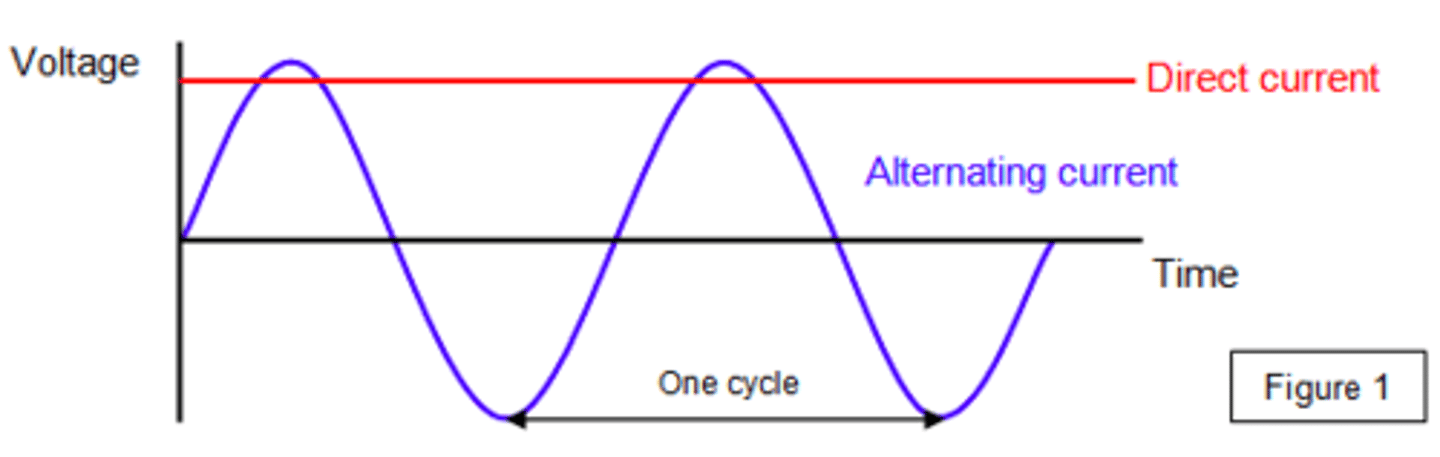
State the type of current used by a lamp plugged into a domestic plug socket.
Alternating current
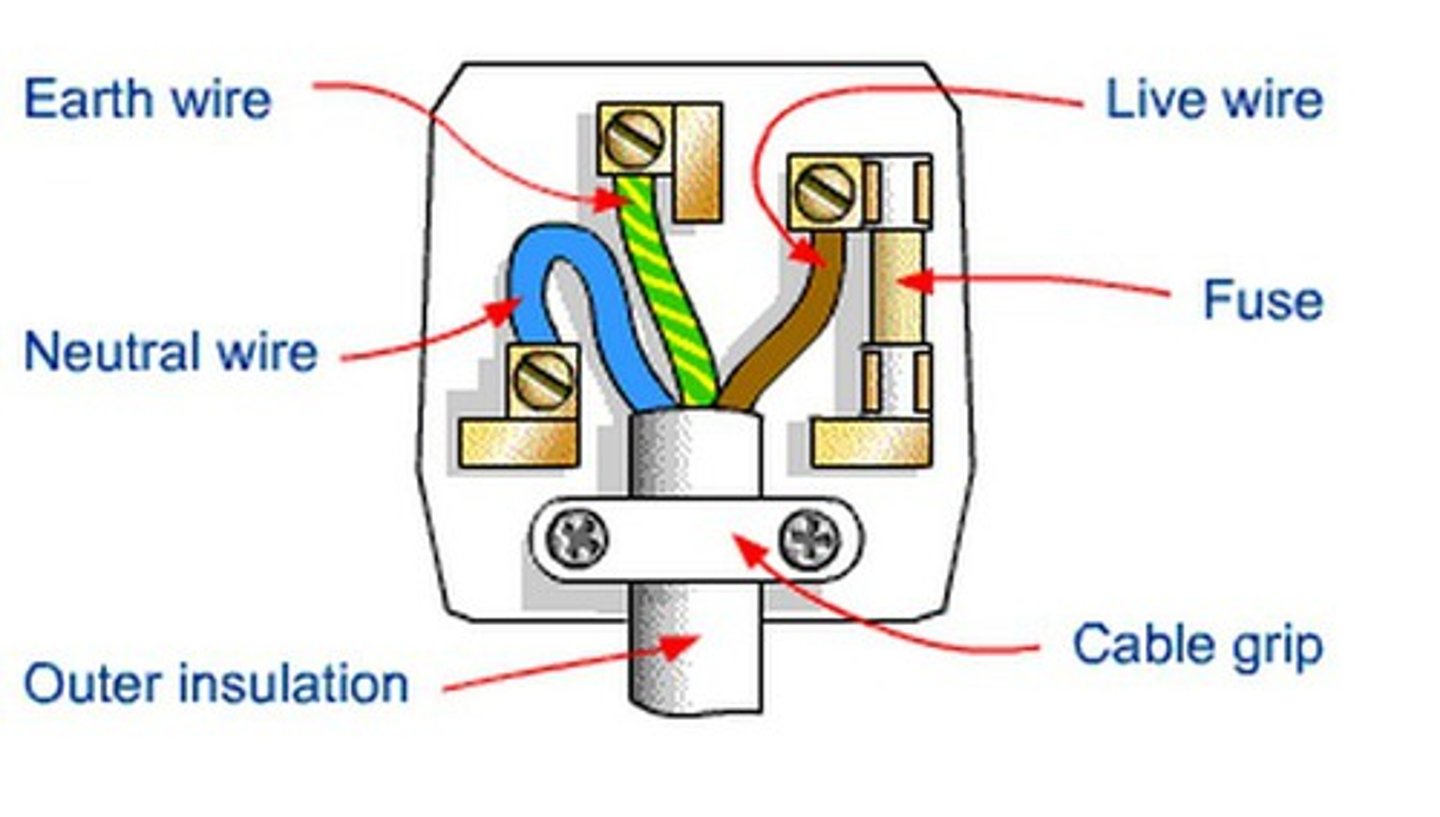
Where is the live wire in a plug?
On the right
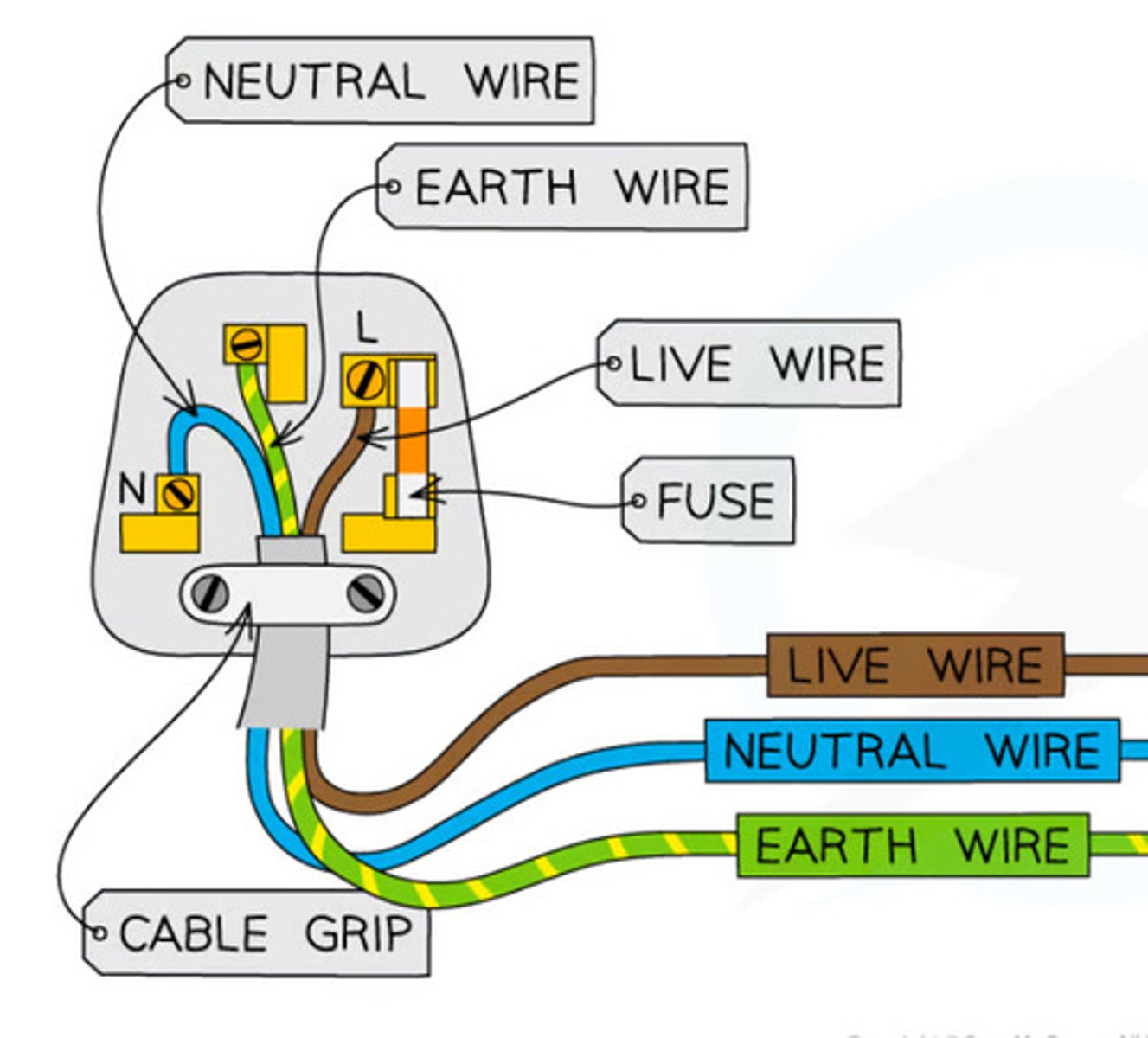
Where is the neutral wire on a plug?
On the left
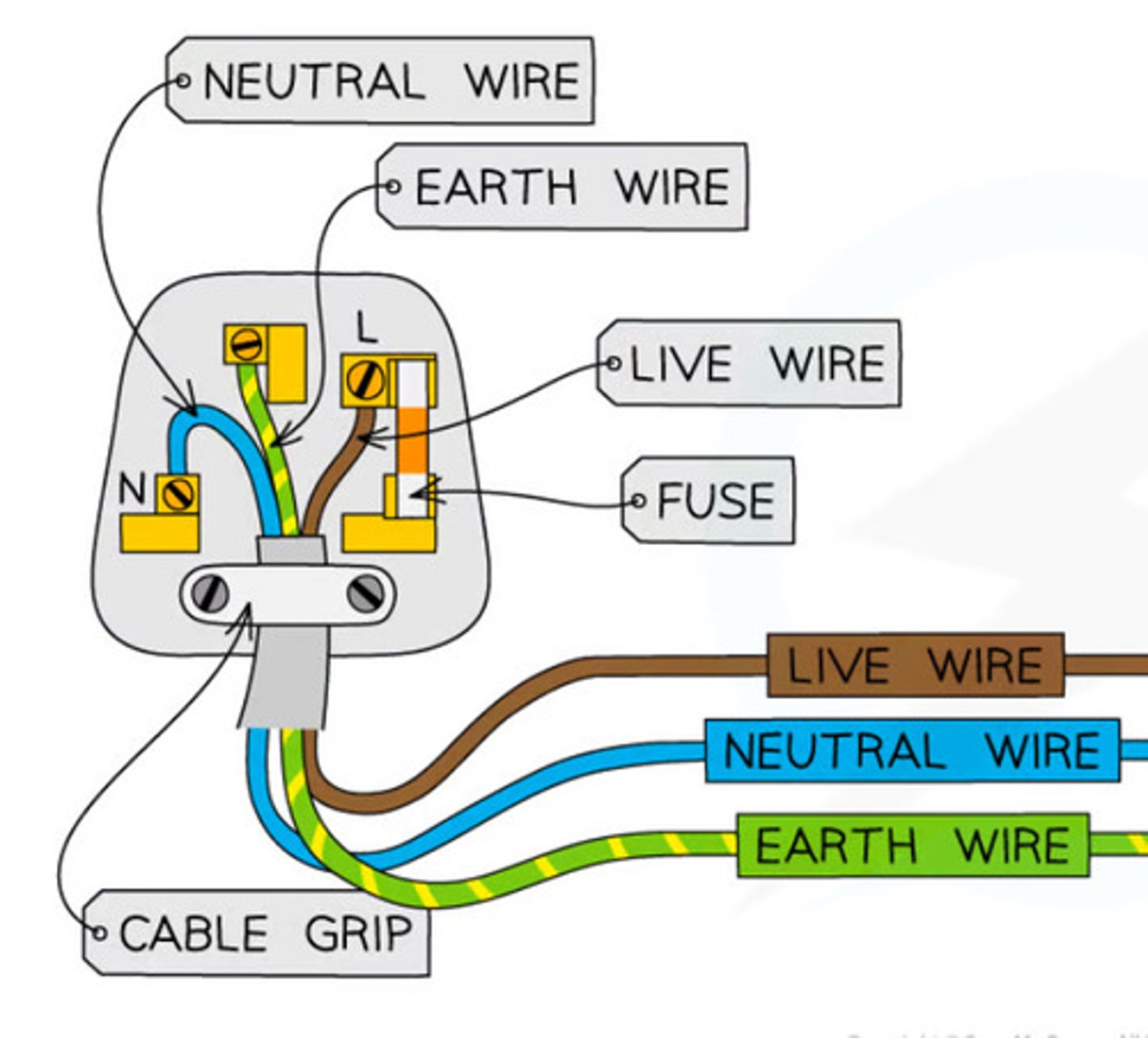
Where is the earth wire on a plug?
Middle