Biology 1.6 Ecosystems, Nutrients Cycles and the Environment
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
What is a producer?
An organism that makes its own food.
What types of organisms are primary producers?
Photosynthetic organisms like green plants and algae that trap energy from the sun.
What is a primary consumer?
An organism that feeds on producers.
What is a secondary consumer?
An organism that feeds on primary consumers.
What is a tertiary consumer?
An organism that feeds on secondary consumers.
What are herbivores?
Animals that only eat plants.
What are carnivores?
Organisms that mainly eat animals.
What are decomposers?
Organisms that break down dead matter.
What do food chains show?
Food chains show the feeding relationships of different organisms and the flow of energy between them.
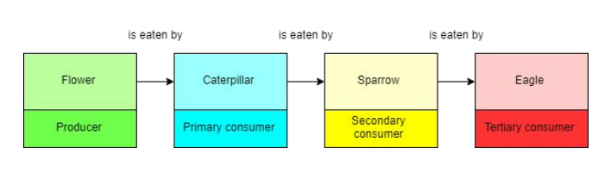
What is the difference between a food web and a food chain?
Food webs show the interactions of multiple different food chains. Food chains show one path of food dependencies.
Why are biomass transfers not 100% efficient?
Energy is lost through: Egestion (removal of faeces). Excretion (removal of waste products, e.g., urine). Respiration. The production of inedible bones and shells.
What is biomass?
The dry mass of all of the living organisms in an area.
Why is dry mass used for biomass?
Because the wet mass varies as the volume of water in the organism varies.
What is a biomass pyramid?
A pyramid that shows the total dry mass of organisms at each trophic level.
What is a pyramid of numbers?
A pyramid of numbers shows the number of organisms at each trophic level.
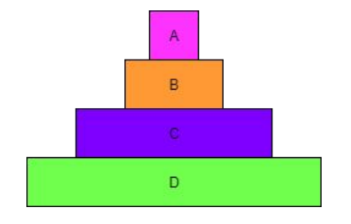
Identify the producer in this pyramid of biomass.
D is the producer.
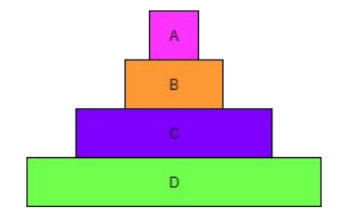
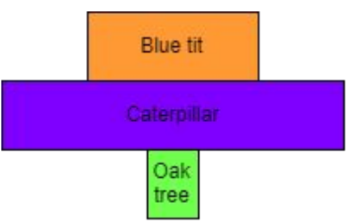
Why is this pyramid of numbers not pyramid-shaped?
Pyramids of numbers don’t take size and mass of organisms into account.
How do you calculate the efficiency of biomass transfer? (Higher)
Efficiency = (energy transferred / total energy available) × 100.
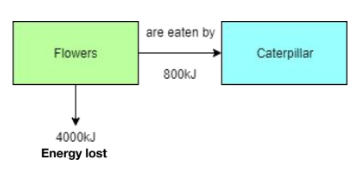
Calculate the efficiency of the biomass transfer from the flowers to the caterpillar (Higher).
Total energy available = 800 kJ + 4000 kJ = 4800 kJ. Energy transferred = 800 kJ. Efficiency = (800 / 4800) × 100 = 16.67%.
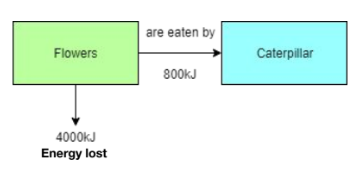
How does the efficiency of biomass transfers affect the number of trophic levels in a biomass pyramid?
The less efficient the transfers, the fewer trophic levels and the fewer organisms in higher trophic levels.
Name 2 different types of decomposer.
Bacteria and fungi.
What are nutrient cycles?
Processes by which molecules and ions are transferred between dead and living organisms.
Give 4 examples of nutrient cycles.
Carbon cycle. Nitrogen cycle. Phosphorus cycle. Water cycle.
Describe the carbon cycle.
Plants fix carbon dioxide into organic molecules during photosynthesis. The organic carbon-containing molecules are passed onto organisms that eat the plants. Carbon dioxide is released back into the atmosphere by respiration from animals and plants. Burning fossil fuels also releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
Describe the water cycle.
Water from lakes and oceans evaporates. The evaporated water condenses into clouds and returns to earth as precipitation. The water from precipitation is useful for life on land. The water then returns to rivers and oceans through surface runoff.
Why is the water cycle important?
Living organisms require water. The water cycle provides organisms on land with a continuous supply of water.
What are the two types of decomposition?
Aerobic decomposition (with oxygen). Anaerobic decomposition (without oxygen).
Which type of decomposition is faster?
Aerobic decomposition is faster than anaerobic decomposition.
How would a decrease in water availability affect the rate of decomposition?
Decomposing microorganisms need water for chemical processes. The less water available, the slower the rate of these processes.
How does the presence of too much water affect decomposition?
Waterlogged soil prevents oxygen from reaching the decomposers, so anaerobic decomposition must occur, which is slower.
How would a change in temperature affect the rate of decomposition?
A decrease in temperature slows the rate of decomposition reactions. A large increase in temperature will denature enzymes, slowing or even stopping decomposition.
Where does mummification happen instead of decomposition?
In places where the climate is too harsh for decomposition to take place (e.g., too dry or too hot).
Briefly describe how nitrogen is cycled through an ecosystem (Higher).
Nitrogen is fixed by lightning, the Haber process, and bacteria. Decomposers break dead matter down into ammonia. Nitrifying bacteria convert ammonia into nitrites and nitrates. Denitrifying bacteria release nitrogen back to the atmosphere.
How is a rising human population negatively impacting the environment?
More space is needed for housing, work, and leisure, which leads to the destruction of habitats and threatens organisms that live there.
What are intensive farming methods?
Ways of farming to maximise the potential yield (e.g., by using fertilisers, pesticides, or battery farming).
How can fertilisers and pesticides help agriculture?
Fertilisers provide the plant with all the nutrients it needs so that it can grow more quickly. Pesticides kill pests that could harm the growth of the plant.
State 2 methods of pest control.
Biological control. Pesticides.
What is biological control?
A method of controlling plant pests by deliberately introducing organisms that feed on the pests to decrease their numbers.
Give 3 disadvantages of pesticides.
They are not specific and can kill other insects that are not pests. They can contaminate water sources. They have to be applied more than once.
What methods are used in battery farming to maximise yield?
Animals are given antibiotics so that less energy is spent fighting disease. Animals are kept in small spaces so that movement is restricted. The temperature of the pens is regulated so that the animals do not use energy keeping themselves warm. Animals are fed high-protein food to maximise growth.
What is an indicator species?
Any species that can be used to measure conditions in an environment, often by the presence or absence of that species.
What does a decrease in water pH suggest about pollution levels?
A lower pH (more acidic) suggests pollution levels are increasing, as many gases in pollutants are acidic in solution (e.g., CO2 makes carbonic acid).
Describe how sewage in waterways can affect aquatic life.
Microorganisms that decompose sewage will use up the oxygen in the water, leaving insufficient oxygen for respiration in other aquatic organisms.
What is eutrophication?
An excess of nutrients in a body of water, often due to fertilisers in the water source.
Why is eutrophication bad for aquatic life?
It causes an ‘algal bloom,’ which decreases oxygen supplies in the water and degrades water quality.
Why are heavy metals in industrial waste and pesticides bad for the environment?
They can enter food sources and build up to toxic levels, harming or killing animals that consume the contaminated food. This process is called bioaccumulation.