Cell Structure and Function Terms (TEAS 7 Study Set)
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
mitosis
cell division in eukaryotes that produces two daughter cells, each with the same chromosome number as the parent cell. [produces body cells; makes identical cells]
![<p>cell division in eukaryotes that produces two daughter cells, each with the same chromosome number as the parent cell. [produces body cells; makes identical cells]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/2e5febeb-9ed0-4021-b220-86423c06e293.jpg)
meiosis
specialized cell division is used to create haploid gametes in diploid organisms. [makes sex cells; gametes: sperm cells and egg cells]
![<p>specialized cell division is used to create haploid gametes in diploid organisms. [makes sex cells; gametes: sperm cells and egg cells]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/f9076c3e-c858-4f77-81b0-77ec8535e4a6.png)
macromolecules
very large molecules, four major types of which are important to living things; carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids
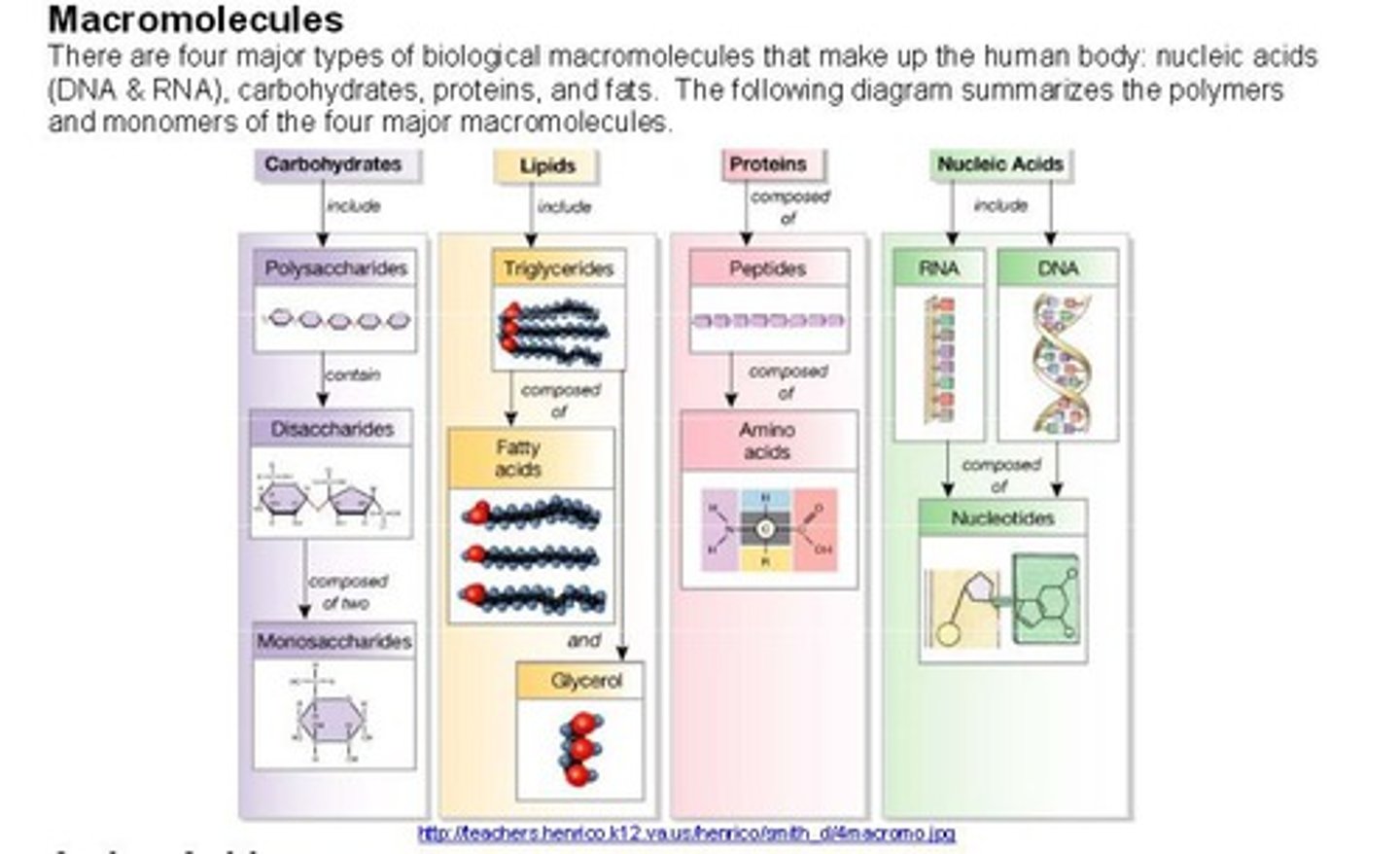
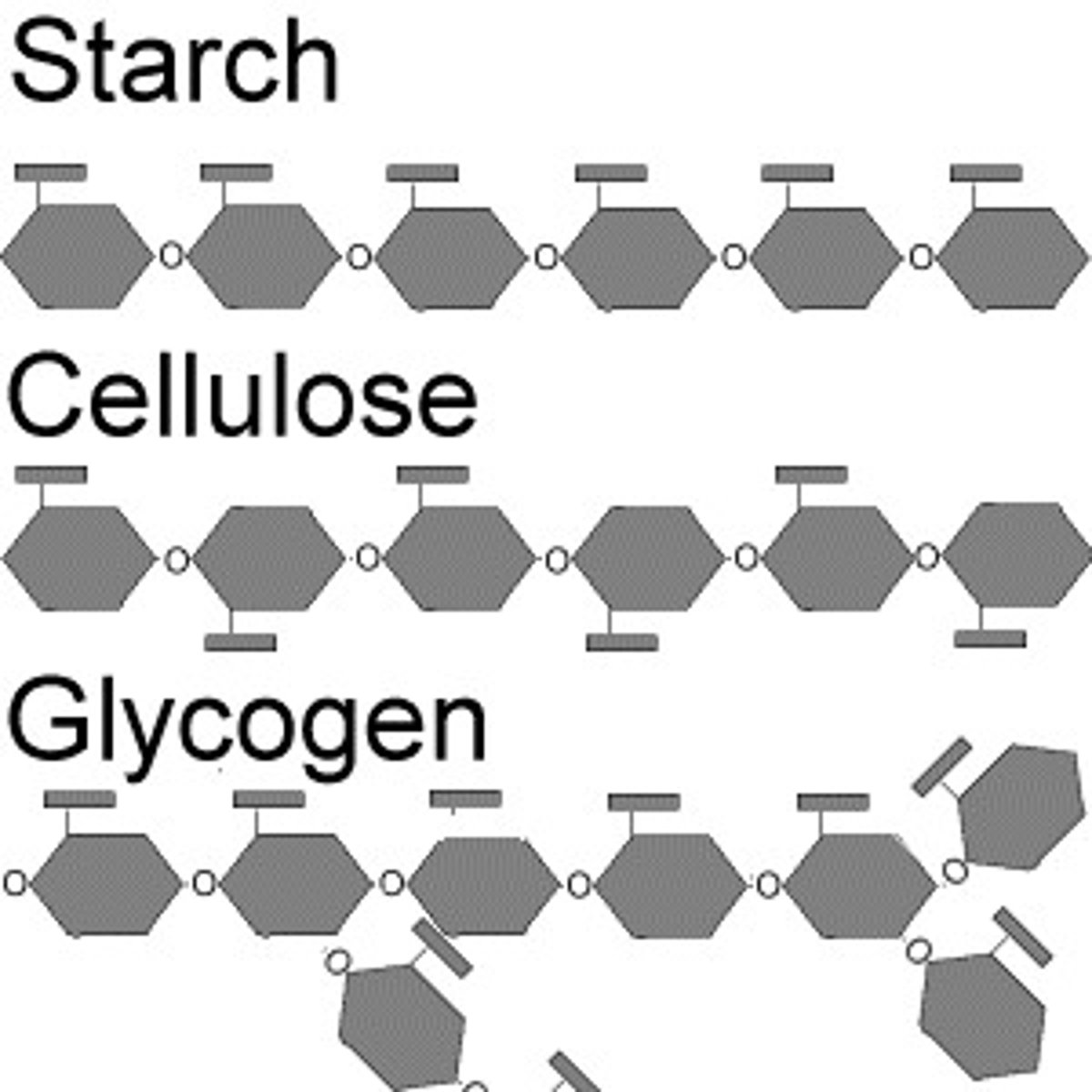
carbohydrates
Sugars and starches which the body breaks down into glucose
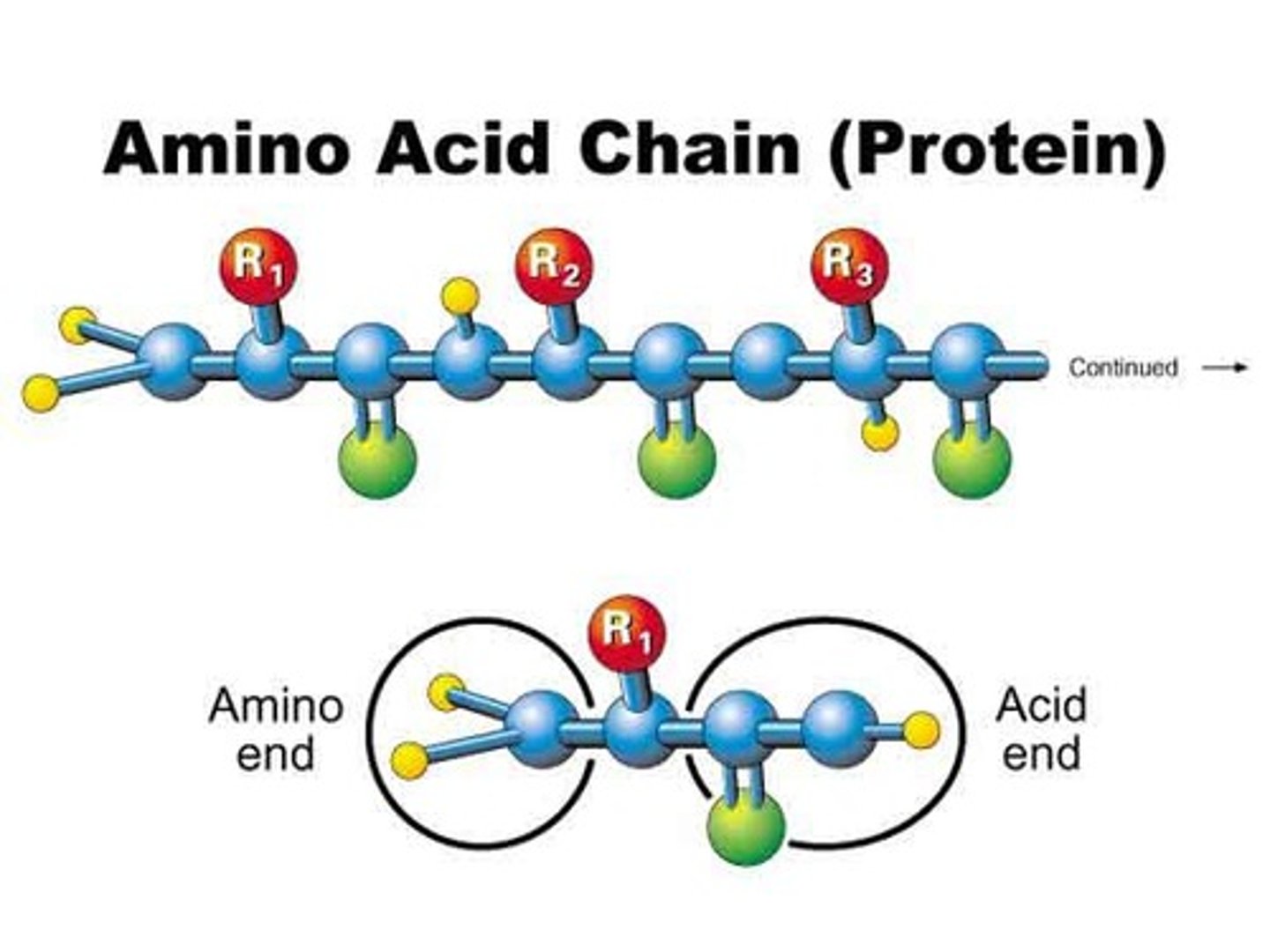
proteins
molecules composed of amino acids joined by peptide bonds
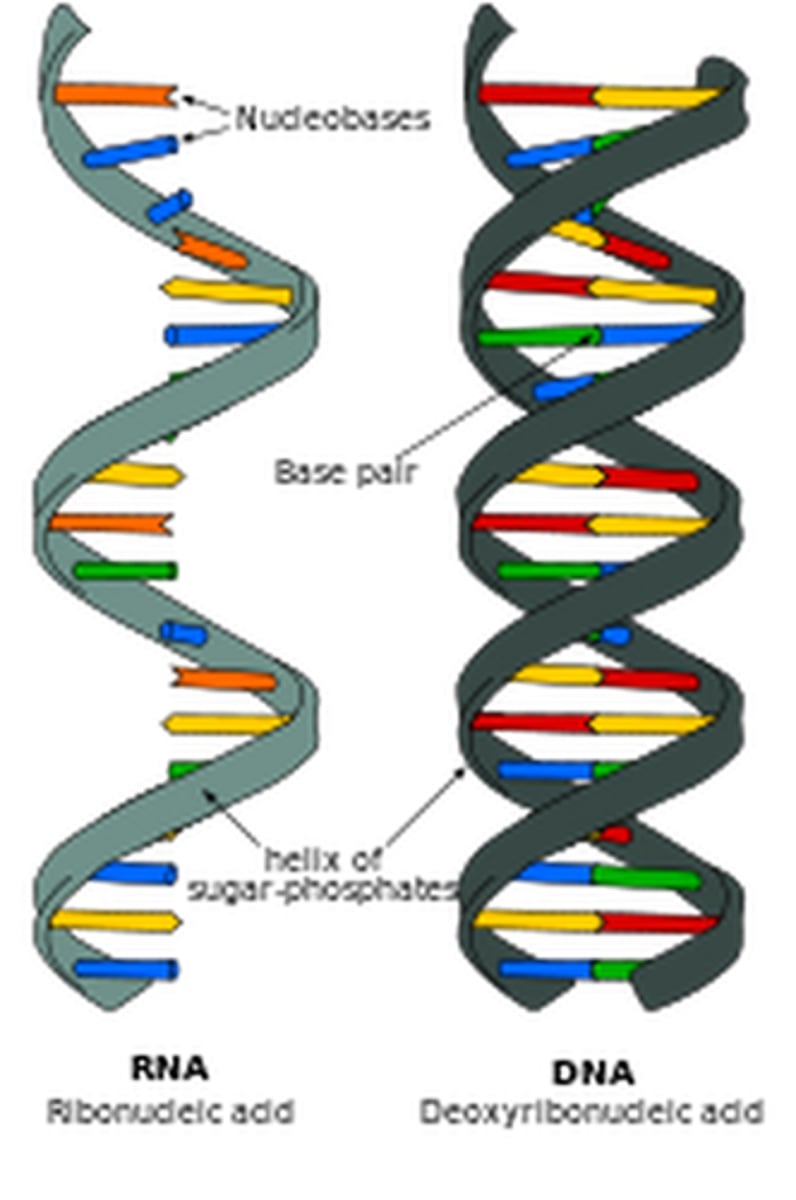
nucleic acids
Long molecules made of nucleotides; DNA and RNA
lipids
fats and oils

cells with shared functions form larger collective groups called
tissues
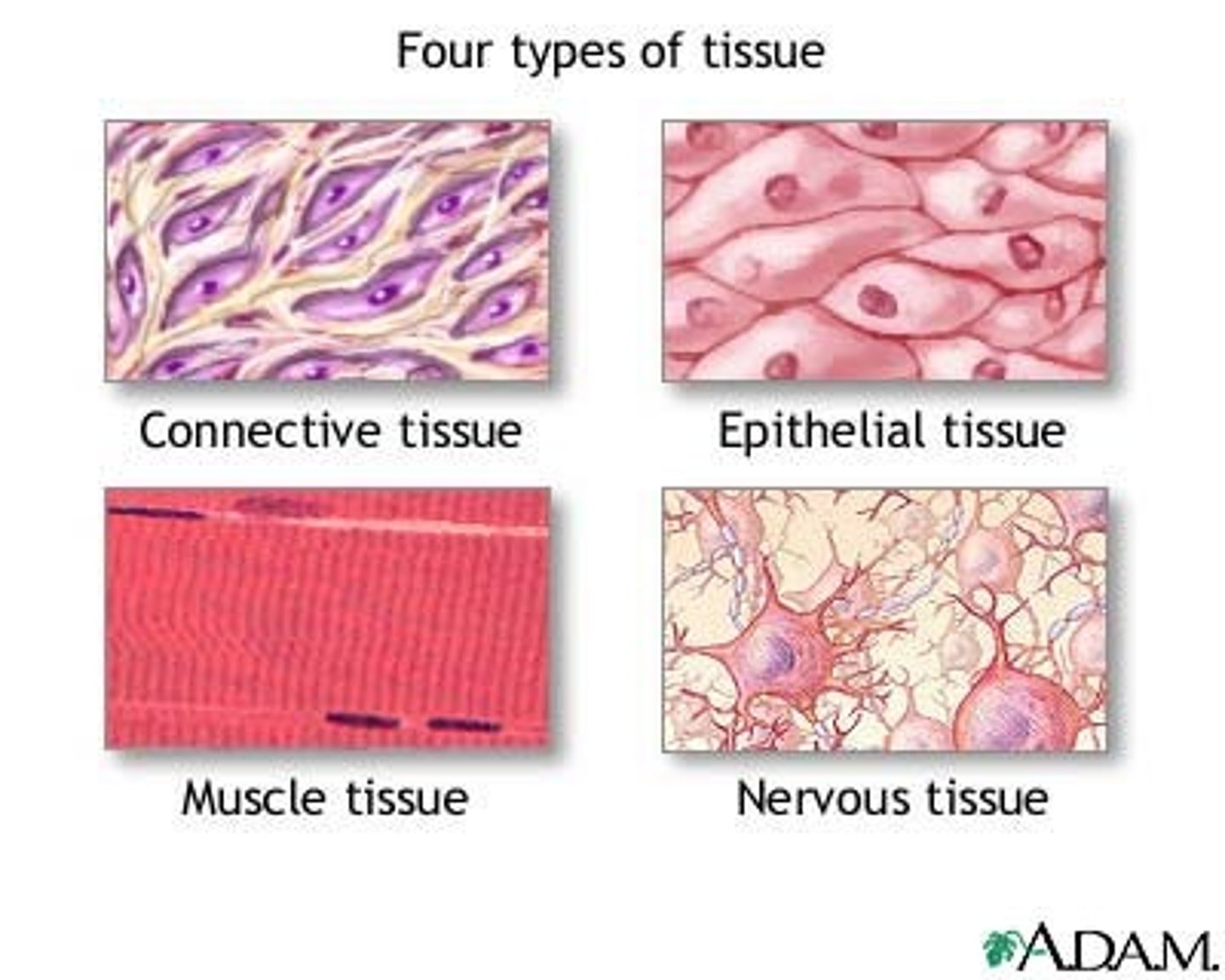
the four basics tissues are:
epithelial, connective, nervous, and muscular
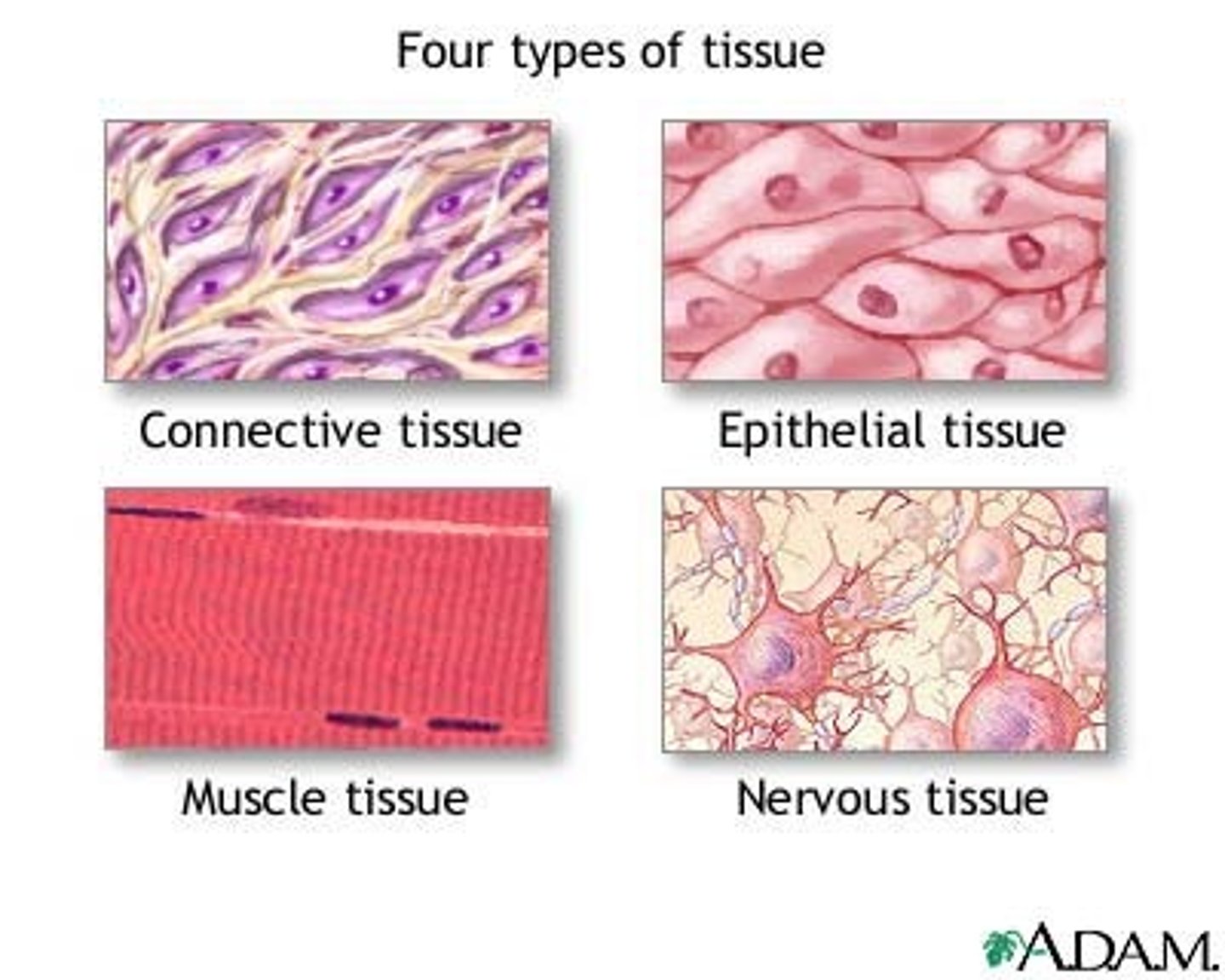
lungs are an organ whose task is to
deliver oxygen to the bloodstream.
the nervous system sends signals to the muscular system to
coordinate movement: together, coordinate organ systems allow an organism to function.
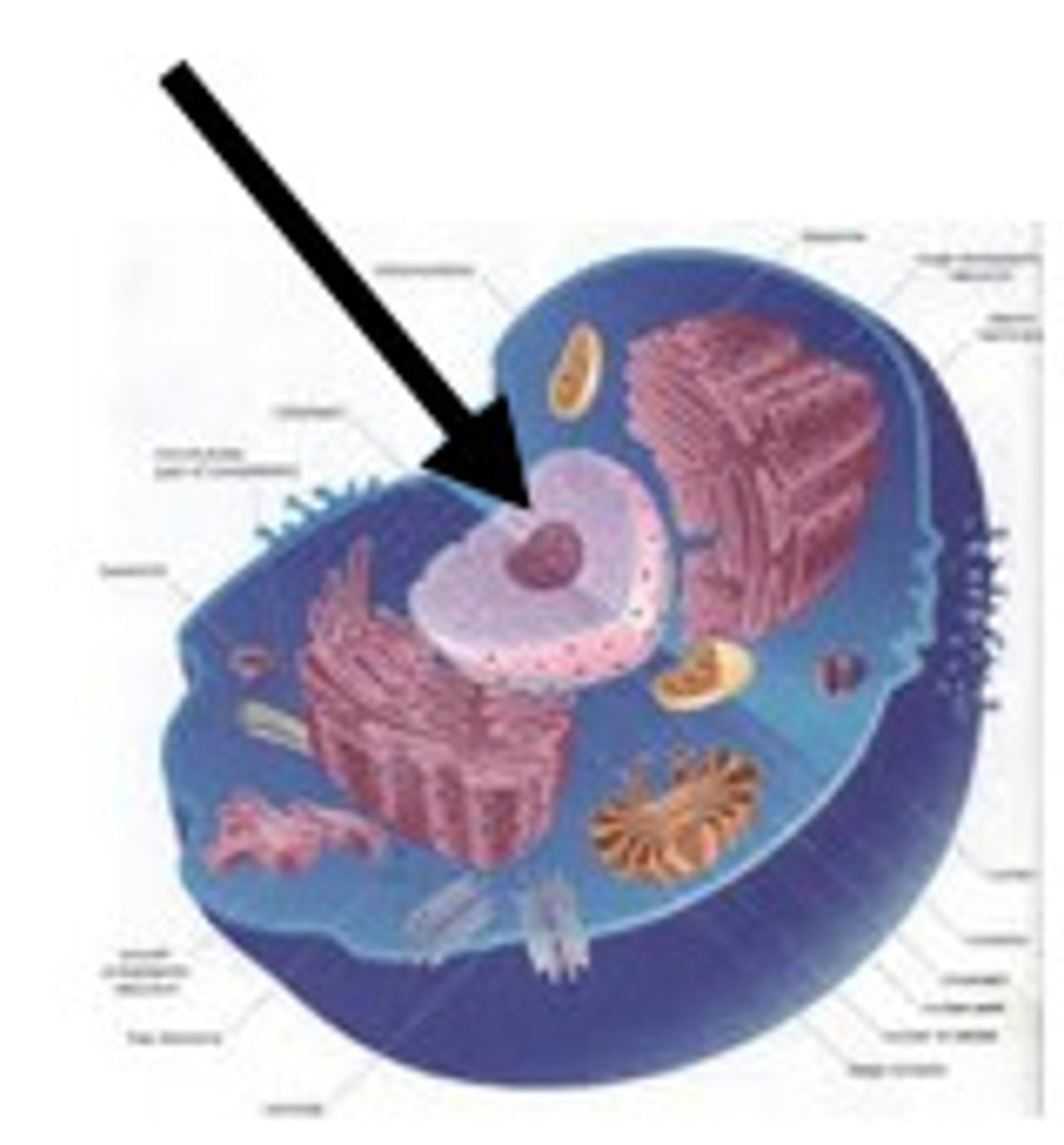
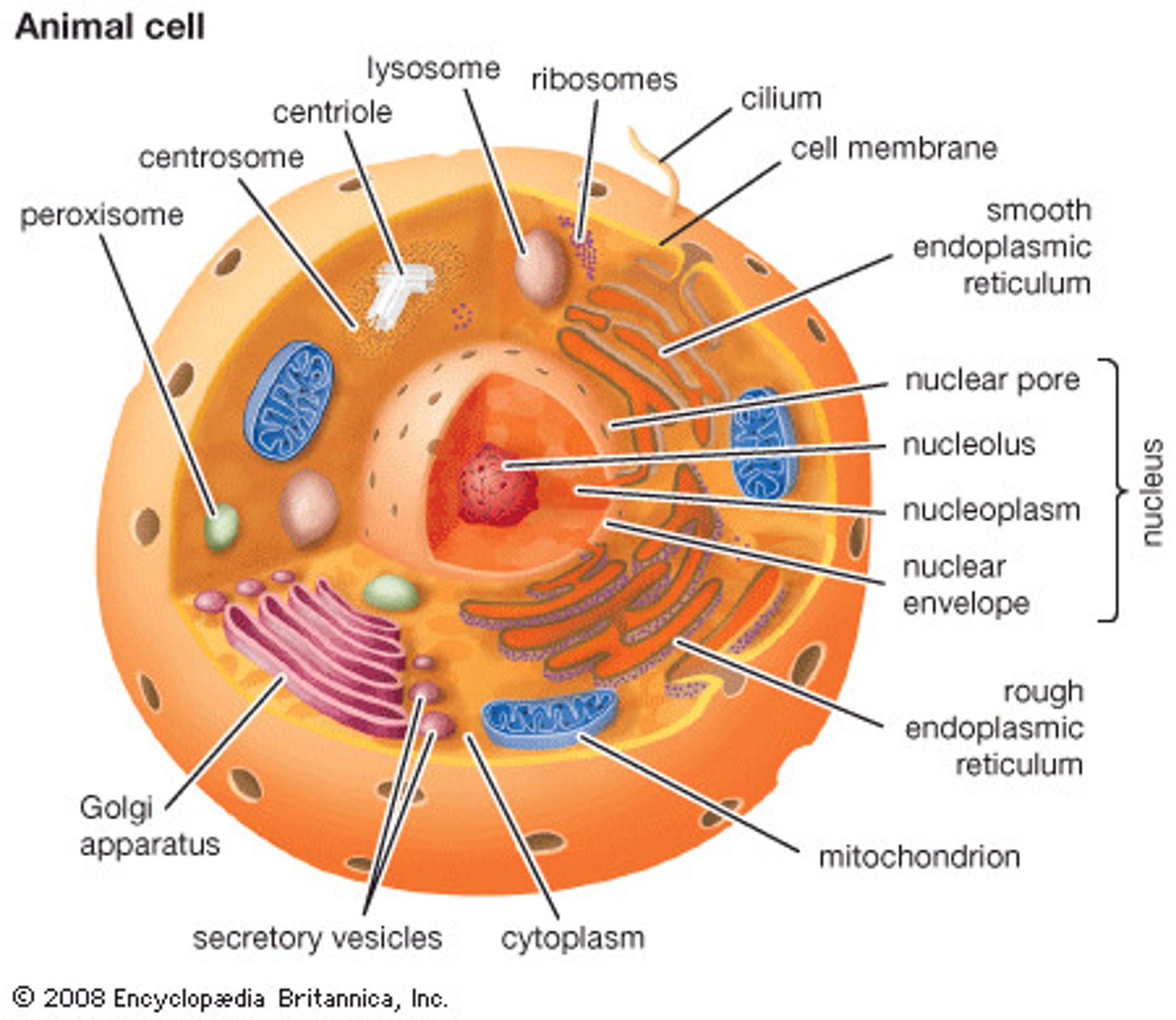
Nucleus
a large organelle within the cell that houses the chromosomes and regulates the activities of the cell.
cell (plasma) membrane
a cell organelle that maintains its environment through the property of selective permeability; controls entry into and out of the cell
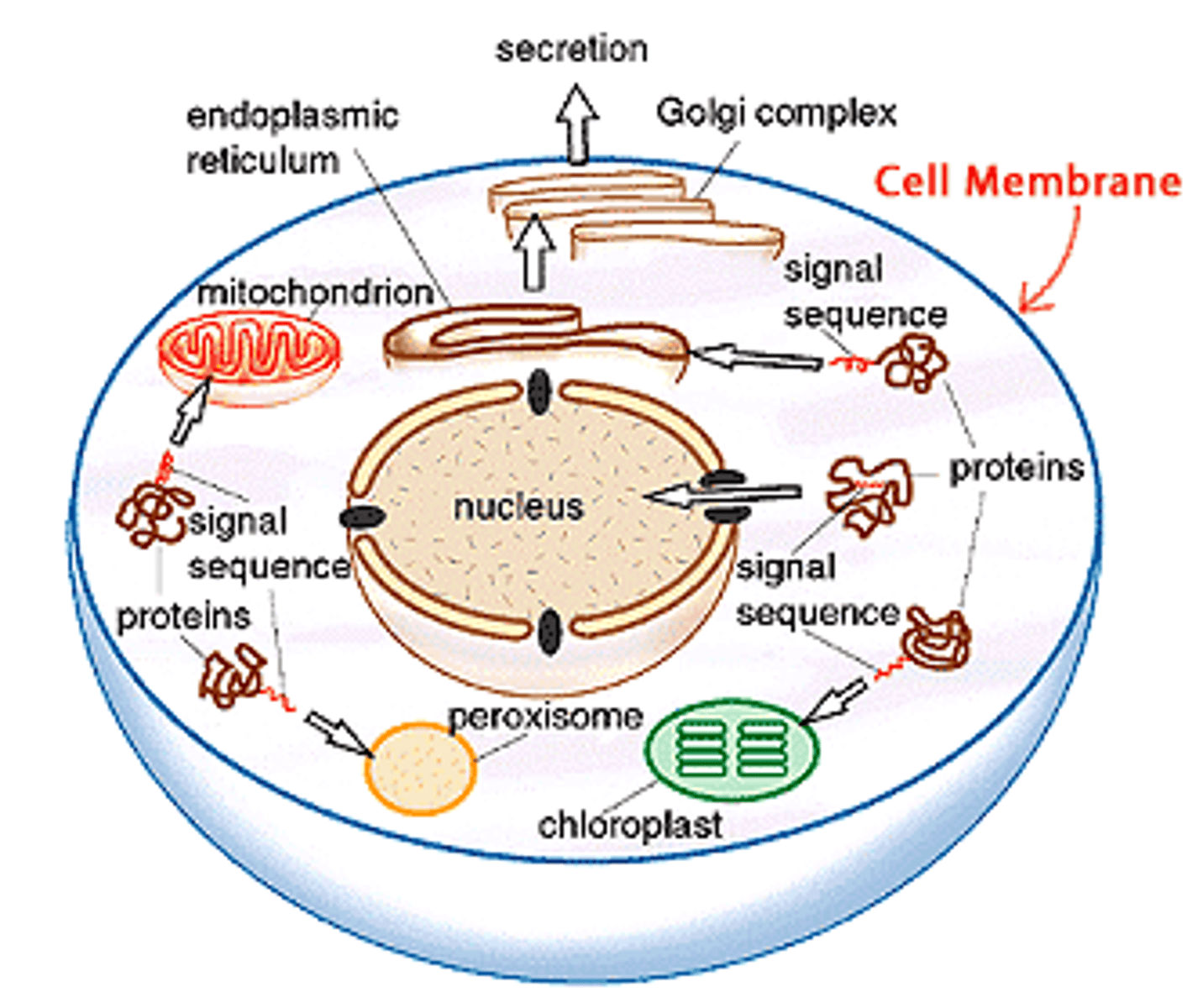
organelle
a specialized part of a cell that has specific functions and is found in the cell's cytoplasm organic molecule. a molecule found in a living thing that contains carbon.
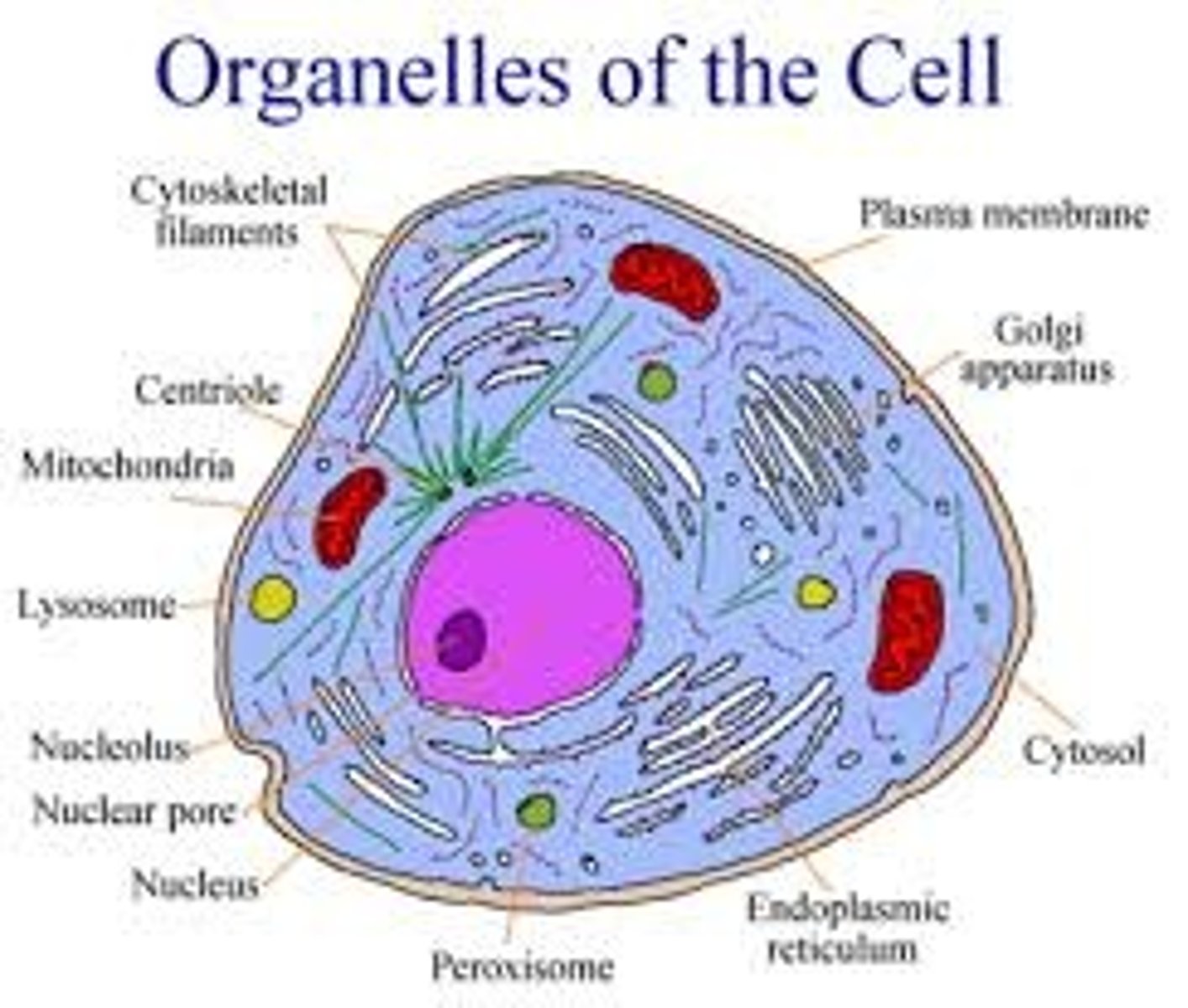
mitochondrion
the site of energy production in a cell
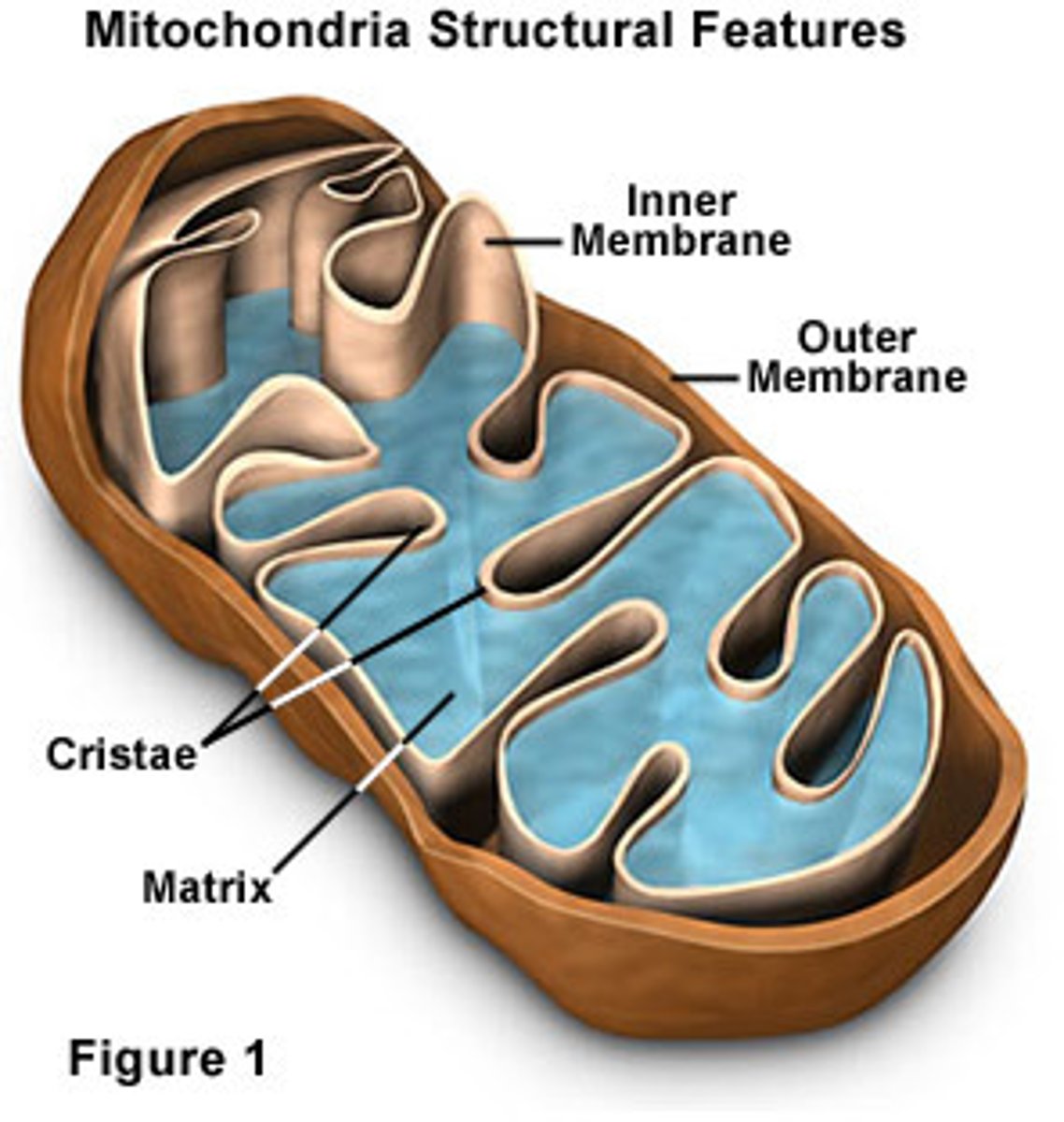
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER)
a cell organelle that synthesizes and concentrates lipids in the cell; does not contain ribosomes
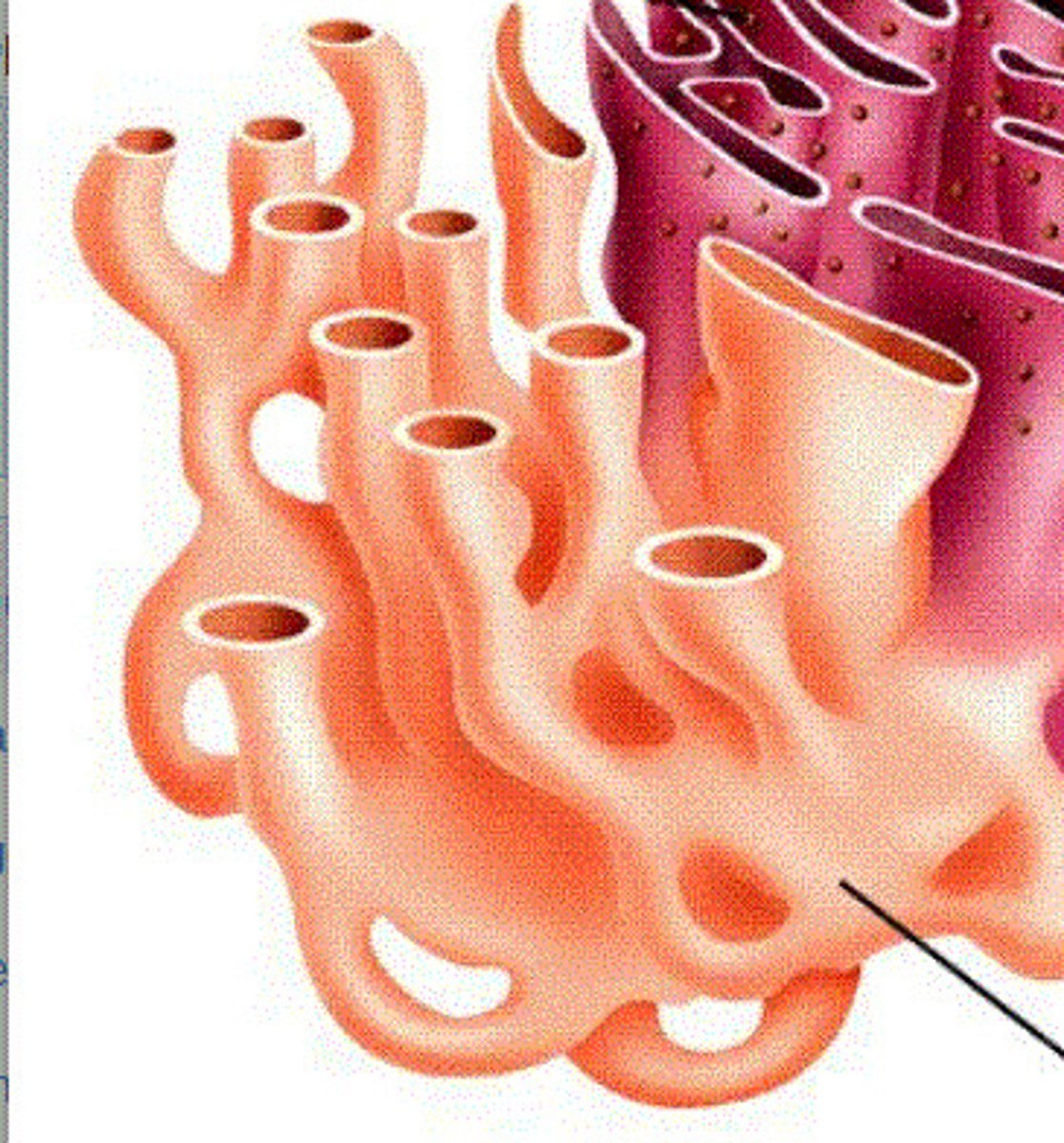
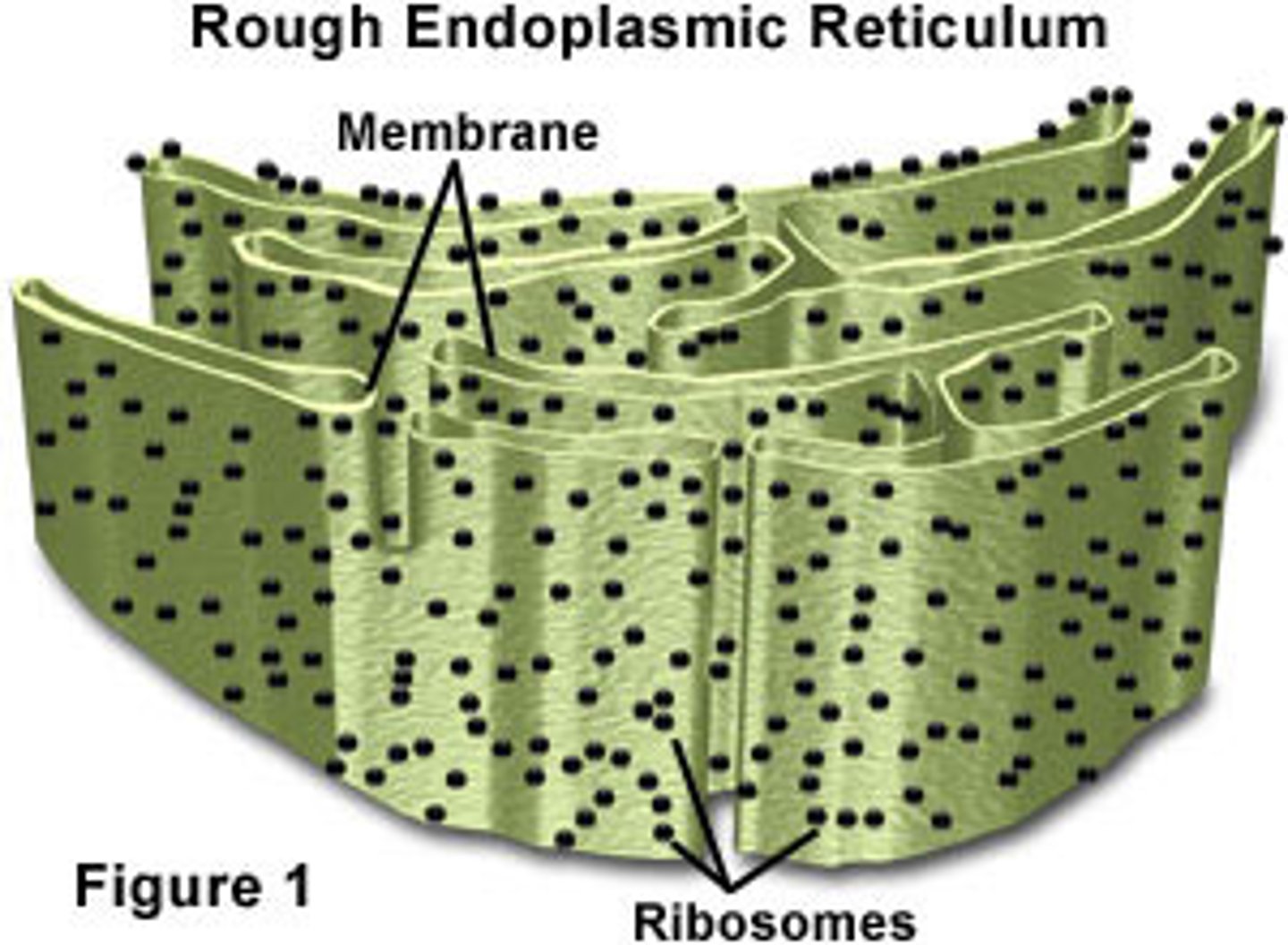
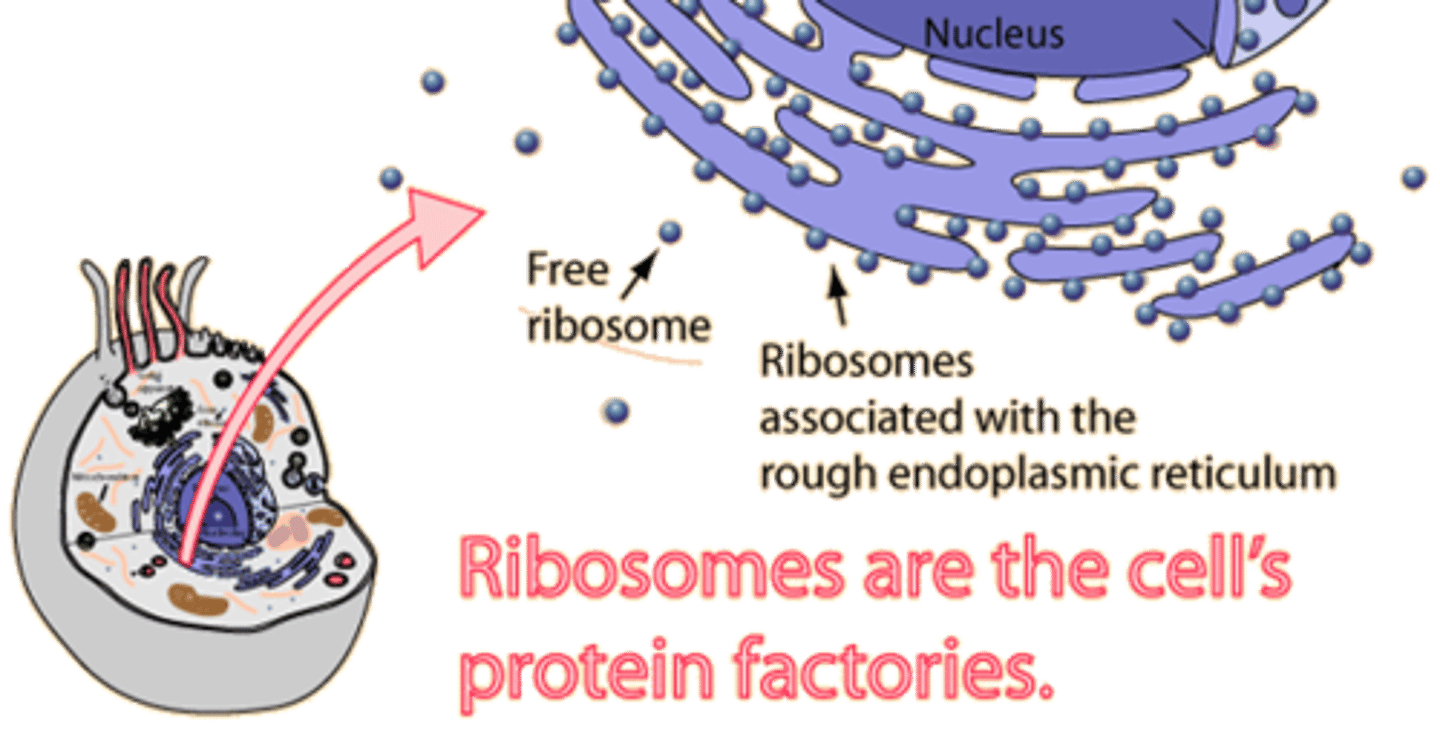
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER)
a cell organelle containing ribosomes that synthesizes proteins in the cell.
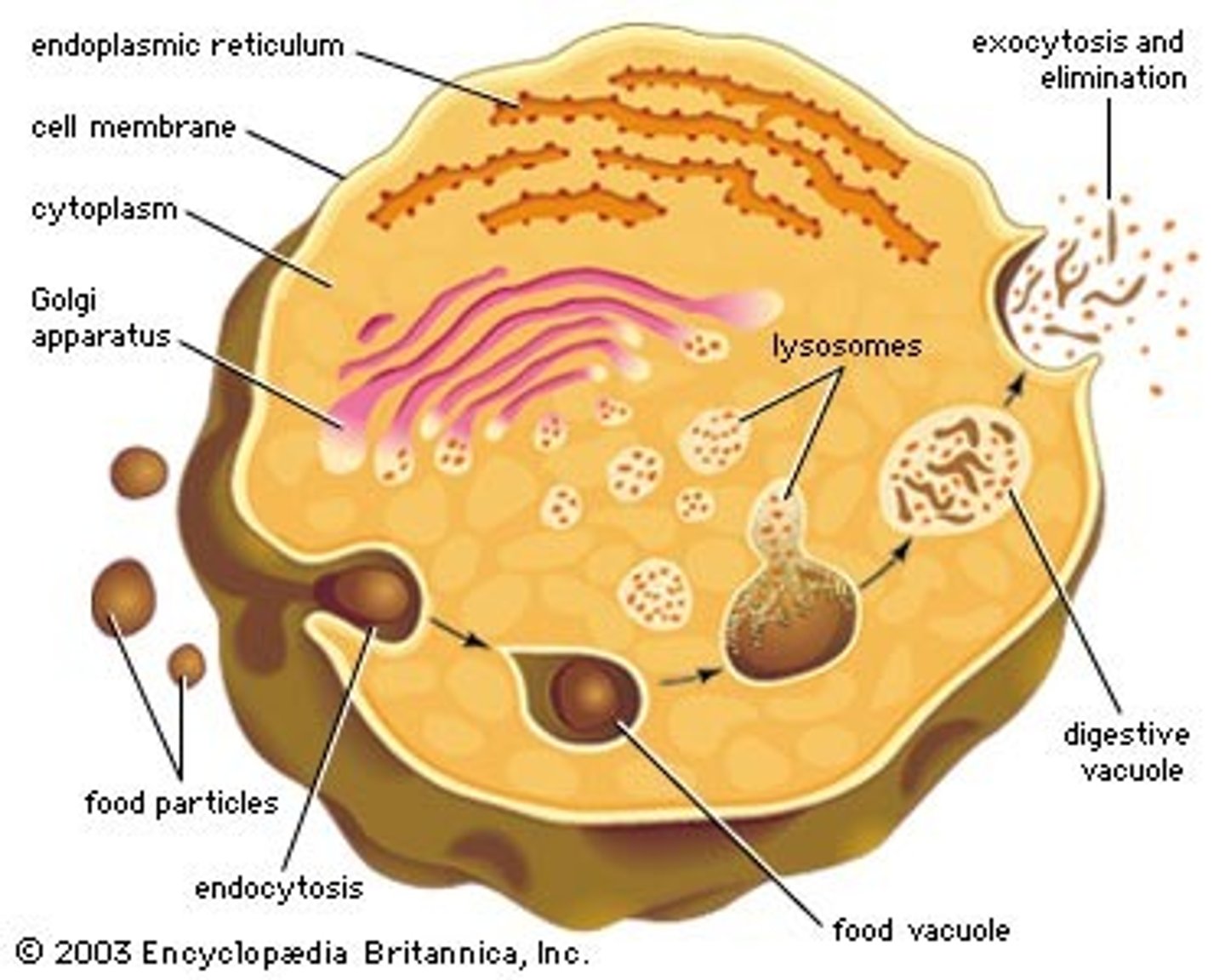
Golgi apparatus
a cell organelle that processes proteins and lipid molecules
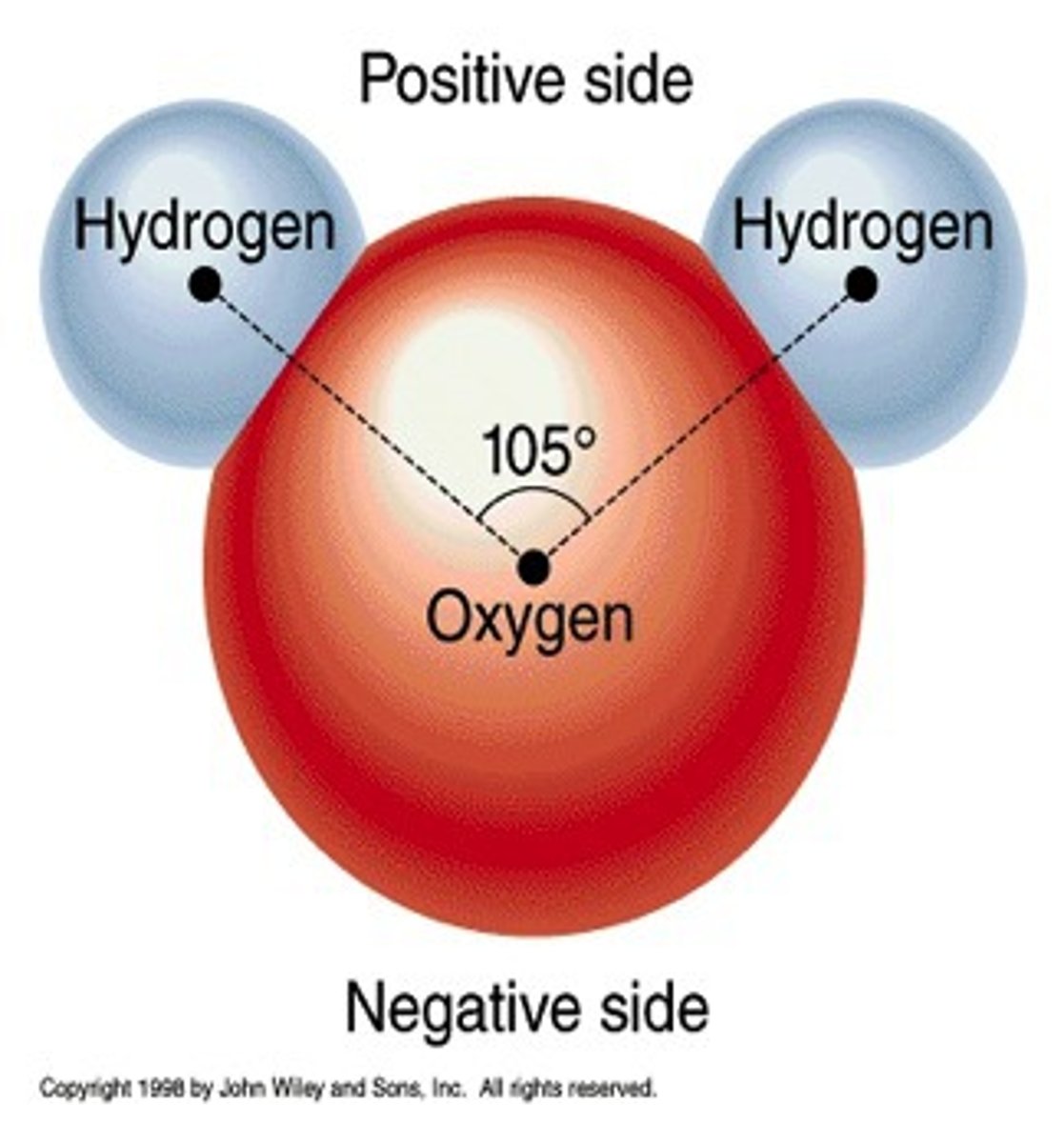
Molecule
an arrangement of two or more atoms bonded together
lysosome
a cell organelle that aids in digestion and the recycling of old cell materials
Ribosomes
a protein-RNA complex that is the site of protein synthesis
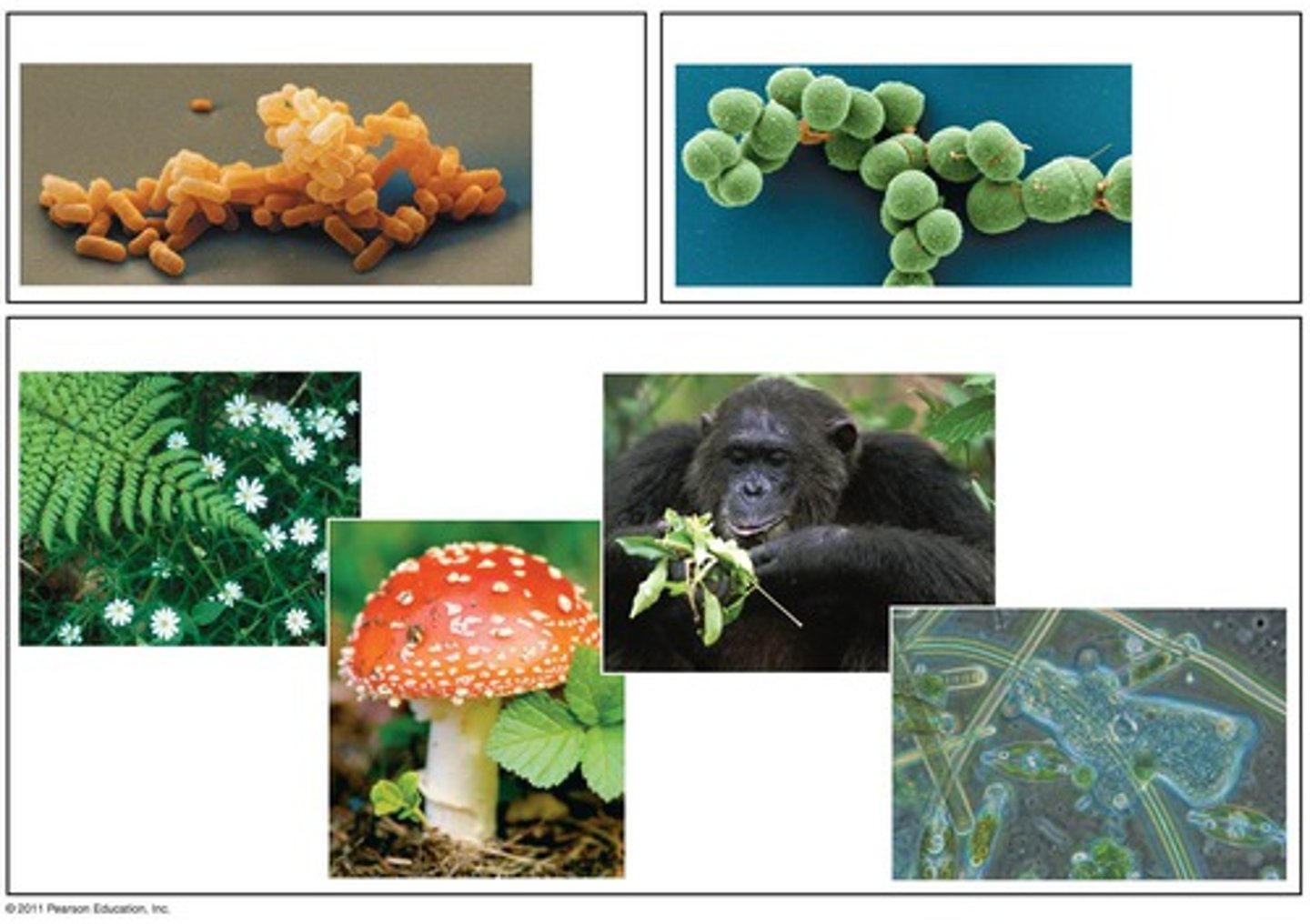
the cell is a building block of
all living organisms
skeletal muscle cells contains high number of
mitochondria because of the energy needed for movement.
Interphase
the stage in mitosis or meiosis in which [DNA replicates; growing]
![<p>the stage in mitosis or meiosis in which [DNA replicates; growing]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/358e34a1-8f10-4738-aa84-c0205c5e5a55.jpg)
prophase
the state in mitosis in which chromosomes condense in preparation for being pulled apart. [condense and visible chromosomes appear]
![<p>the state in mitosis in which chromosomes condense in preparation for being pulled apart. [condense and visible chromosomes appear]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/49413133-5062-4a23-9aad-68d0dca16941.jpg)
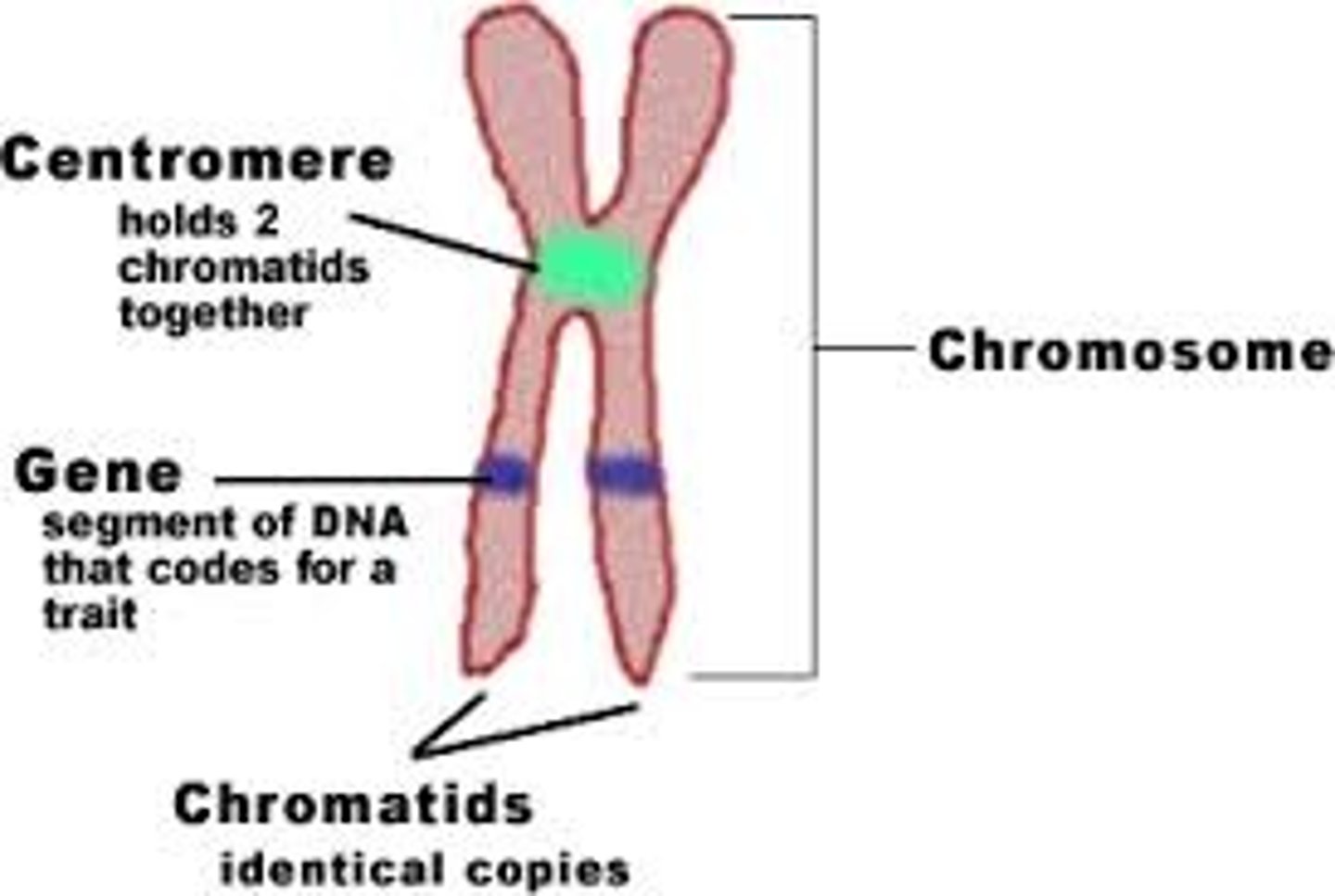
chromosomes
a structure made of proteins and one molecule of DNA that contains genetic information
metaphase
the stage in mitosis in which chromosomes align. [chromosomes line up in the middle of cell]
![<p>the stage in mitosis in which chromosomes align. [chromosomes line up in the middle of cell]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/3706da41-57dc-4dc5-b83d-77242a6f00ef.jpg)
anaphase
the stage in mitosis in which the [chromosomes are pulled apart to the poles and cell division begins]
![<p>the stage in mitosis in which the [chromosomes are pulled apart to the poles and cell division begins]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/42346d5f-3959-4c91-85e3-8962570683e5.jpg)
telophase
the stage in mitosis in which [two nuclei form and the daughter cell separates.]
![<p>the stage in mitosis in which [two nuclei form and the daughter cell separates.]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/95b61c59-e525-4d22-8a5f-a3fc760e82ff.jpg)
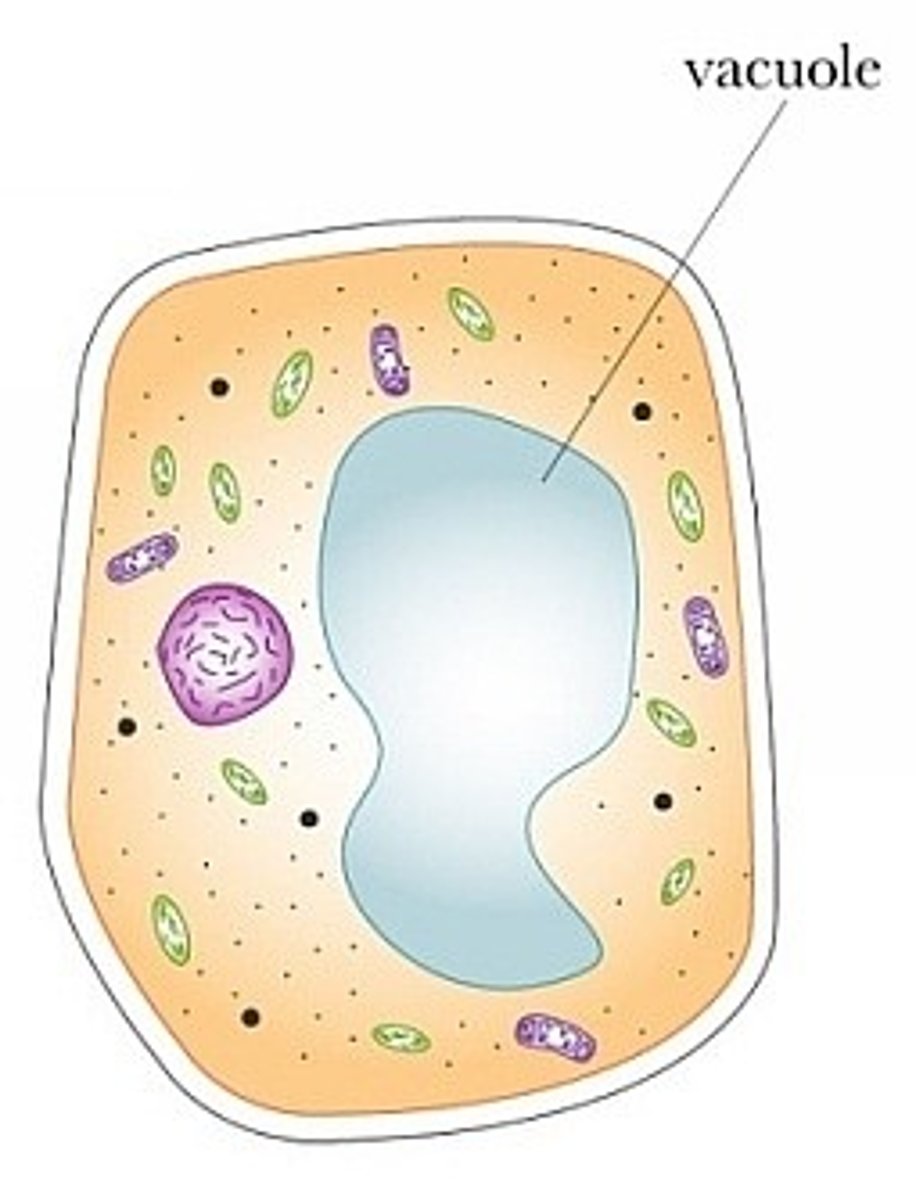
vacuole
a cell organelle that serves as storage for a variety of substances, including water, toxins and carbohydrates
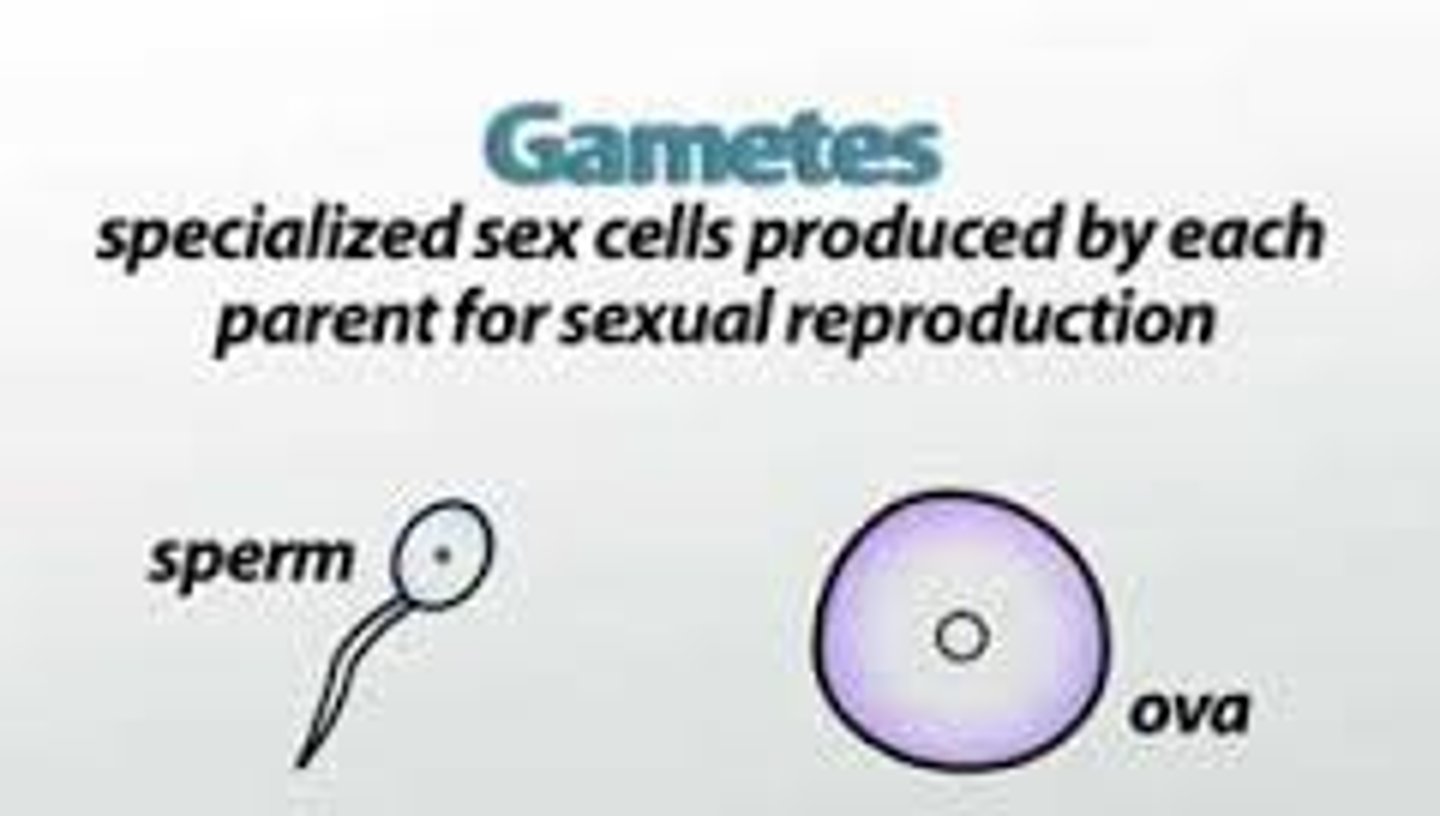
gamete
sex cell; in males the sperm, in females the eggs.
Prophase I [Meiosis]
the stage in meiosis I in which chromosomes condense and form homologous pairs. [homologous pairs and cross over]
![<p>the stage in meiosis I in which chromosomes condense and form homologous pairs. [homologous pairs and cross over]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/f7b7c39c-69a0-41c5-96e1-559ec22775f6.png)
Metaphase I [Meiosis]
the stage in meiosis I in which [pairs of homologous chromosomes align in the middle]
![<p>the stage in meiosis I in which [pairs of homologous chromosomes align in the middle]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/38925206-6807-4cd9-89dd-94061ccd5d91.jpg)
Anaphase I [Meiosis]
the stage in meiosis I in which homologous chromosomes move to opposite ends of the cell. [one chromosomes from each homologous pair is pulled towards each pole]
![<p>the stage in meiosis I in which homologous chromosomes move to opposite ends of the cell. [one chromosomes from each homologous pair is pulled towards each pole]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/c80ceba5-5fc0-43c6-b79b-39e3595aaba4.jpg)
Telophase I [Meiosis]
the stage in meiosis I in which nuclear membranes form as the cell separates into two haploid daughter cells with chromosomes consisting of two sister chromatids. [nuclear membranes form as the cell separates into two]
![<p>the stage in meiosis I in which nuclear membranes form as the cell separates into two haploid daughter cells with chromosomes consisting of two sister chromatids. [nuclear membranes form as the cell separates into two]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/5a0d9780-d71b-4139-8235-0521933583ce.png)
prophase II
the stage in meiosis II in which chromosomes in the haploid daughter cells condense. [daughter cells contain half the chromosomes of the original cell]
![<p>the stage in meiosis II in which chromosomes in the haploid daughter cells condense. [daughter cells contain half the chromosomes of the original cell]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/a49b9c69-f890-4bcf-8260-01e256b4b50f.jpg)
metaphase II
the stage in meiosis II in which individual [chromosomes align in the middle; not in pairs like prophase I]
![<p>the stage in meiosis II in which individual [chromosomes align in the middle; not in pairs like prophase I]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/ac5d37e0-56d4-4ab1-bb5d-abbb13c0a550.jpg)
anaphase II
the stage in meiosis in which [sister chromatids separate and move to opposite ends of the cells]
![<p>the stage in meiosis in which [sister chromatids separate and move to opposite ends of the cells]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/289d8b8e-3012-487c-a29b-9098cdcab60c.jpg)
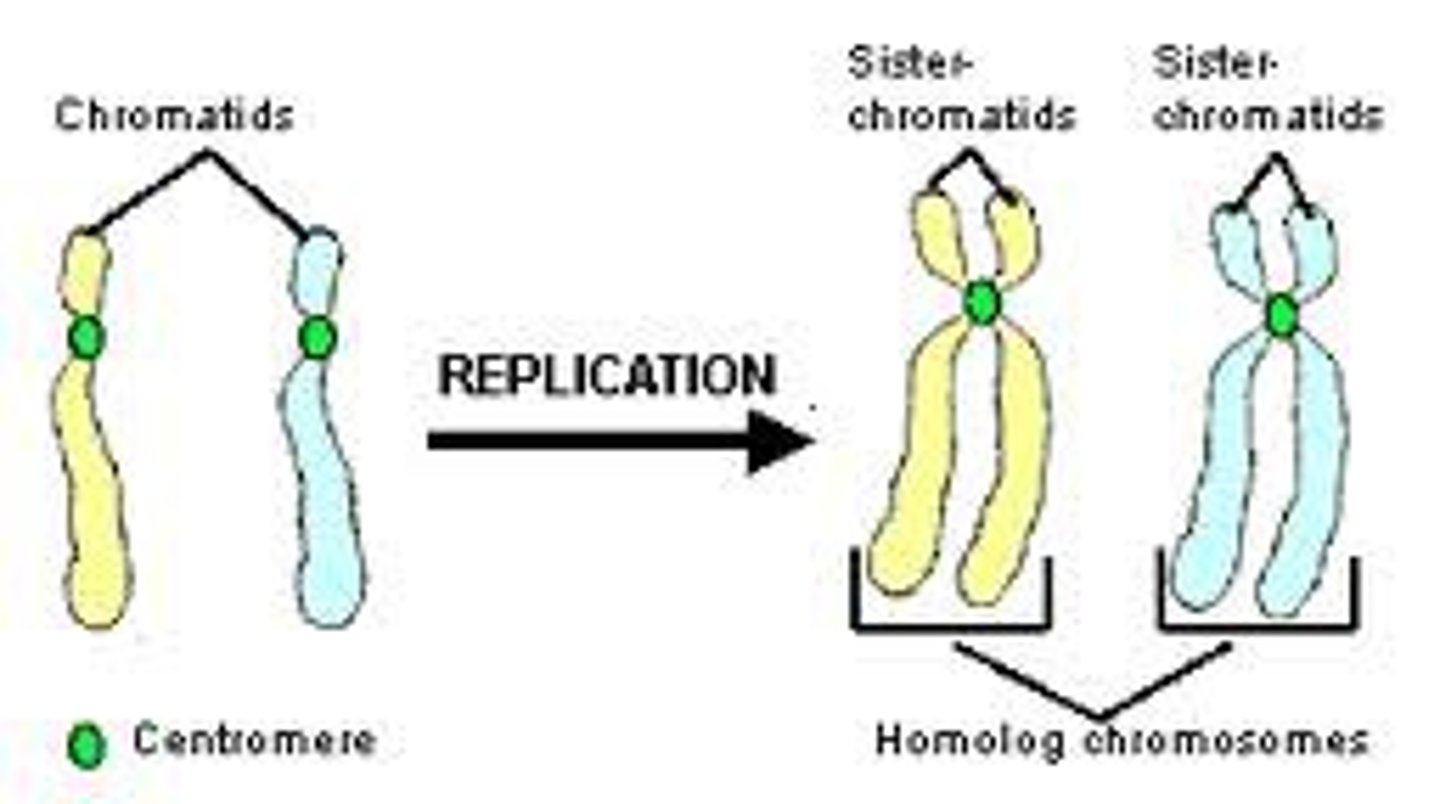
chromatid
one of the two duplicates of a chromosome formed during the cell cycle
telophase II
the stage in meiosis II in which nuclear membranes form as the two daughter cells from meiosis I separate into four haploid daughter cells with chromosomes consisting of a single cell. [nuclear membranes form as the two cells separate into four haploid daughter cells]
![<p>the stage in meiosis II in which nuclear membranes form as the two daughter cells from meiosis I separate into four haploid daughter cells with chromosomes consisting of a single cell. [nuclear membranes form as the two cells separate into four haploid daughter cells]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/64cd1778-d940-4cd8-9e39-6271f8a3d528.jpg)