GI - Histo: Images Only
1/116
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
117 Terms
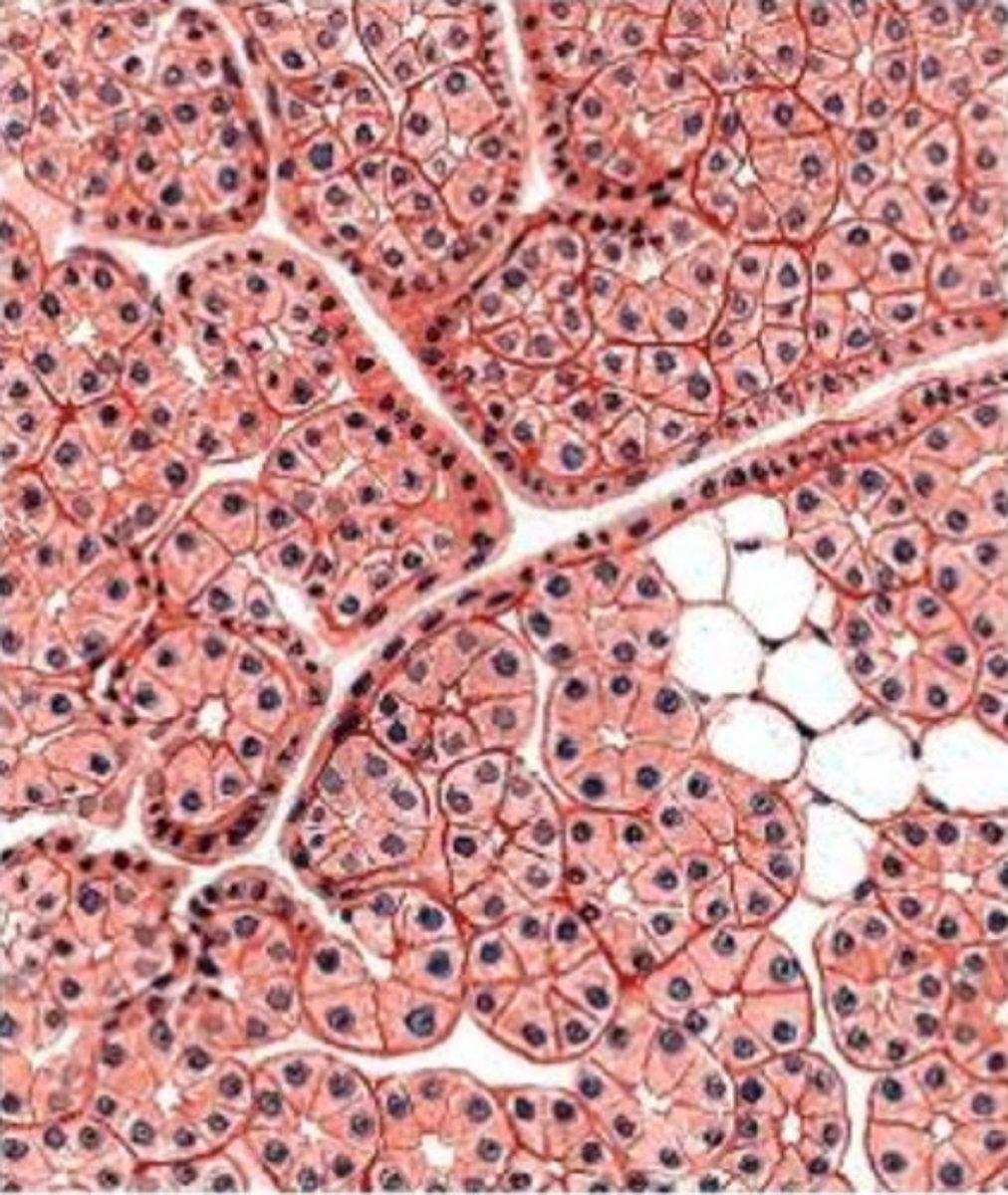
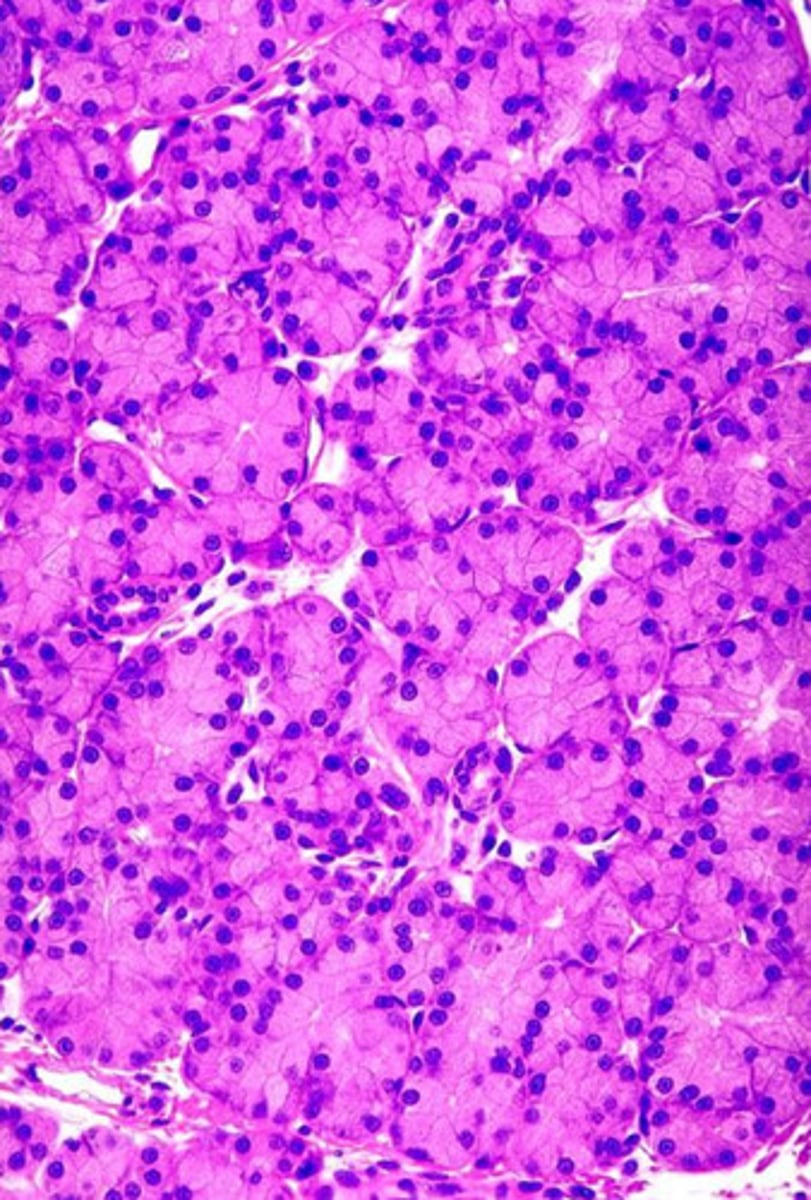
what gland is this from? how do you know?
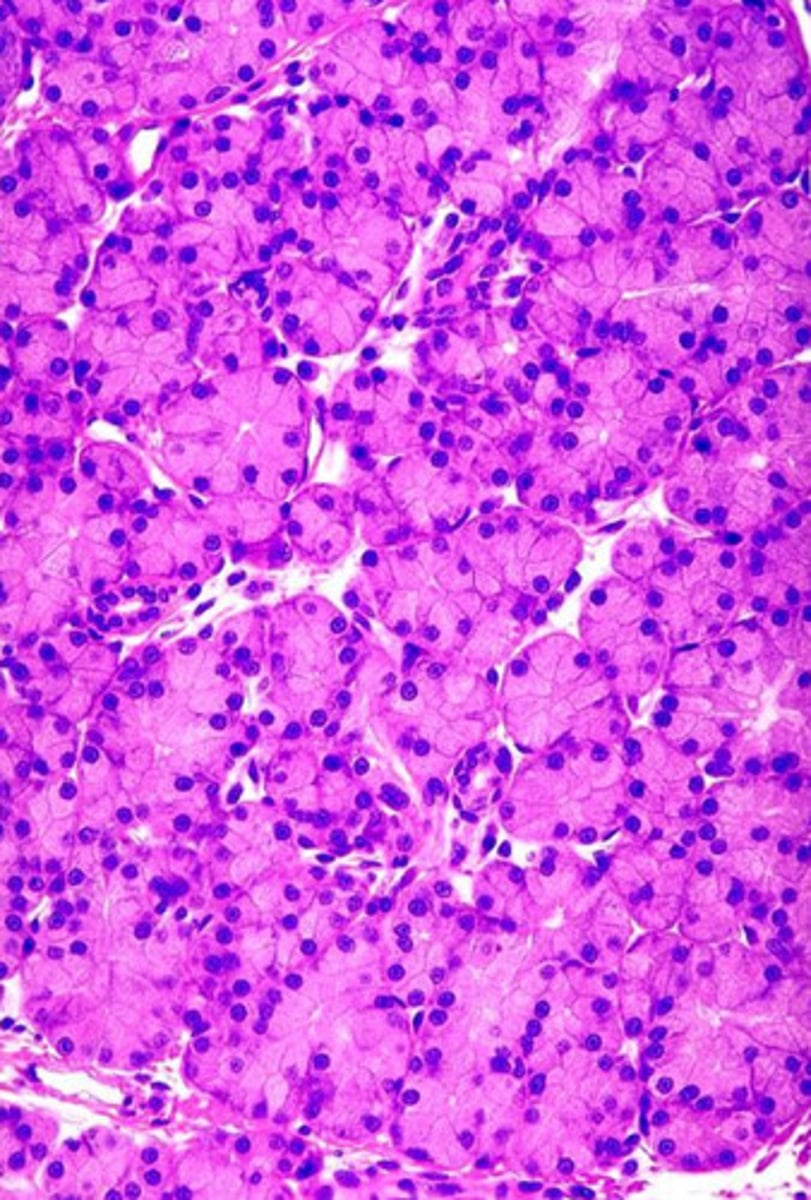
- parotid
- we see acinar cells with perfectly round nuclei
- serous secretions only, mucus is rare
- the unstained cells are adipose cells
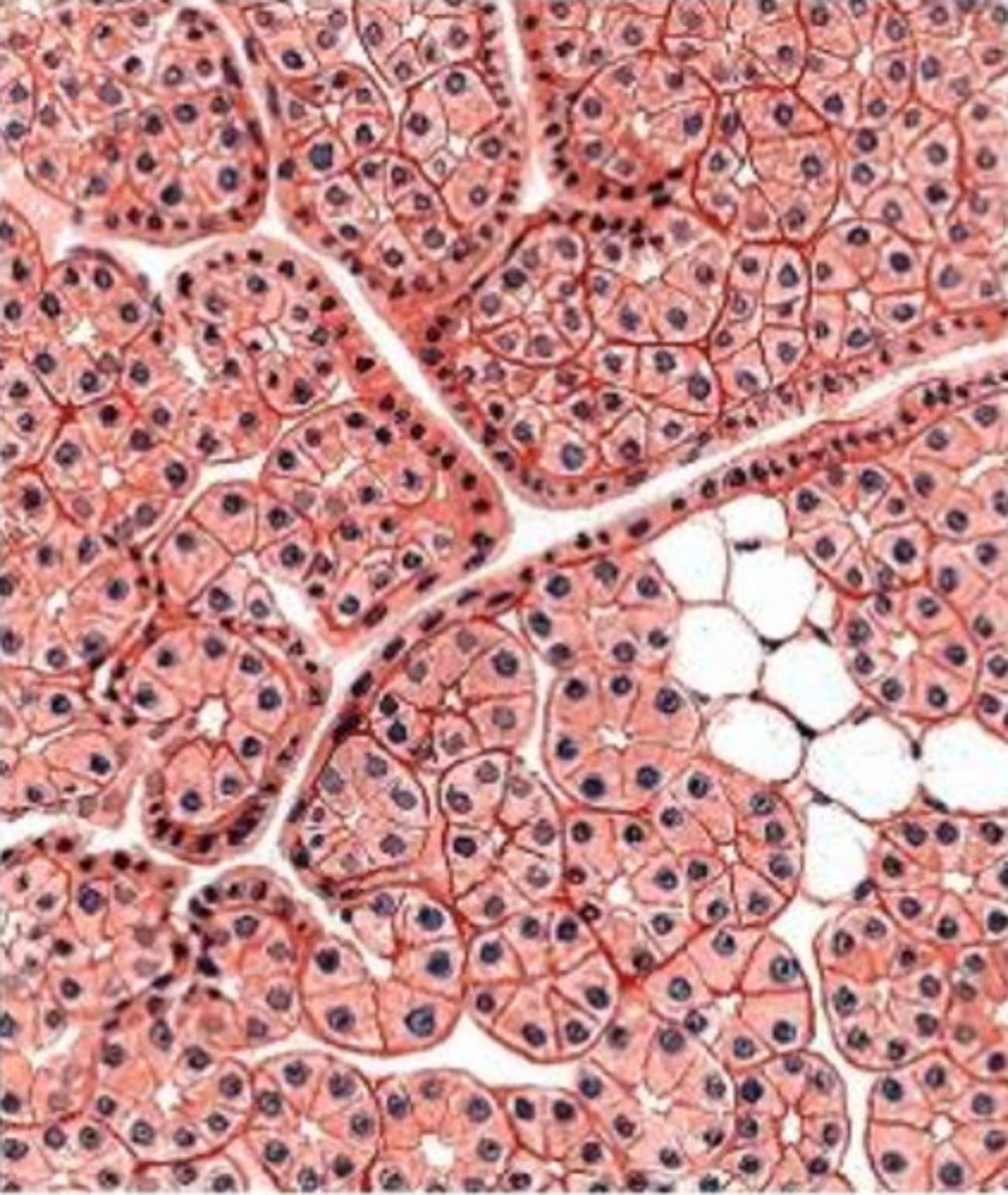
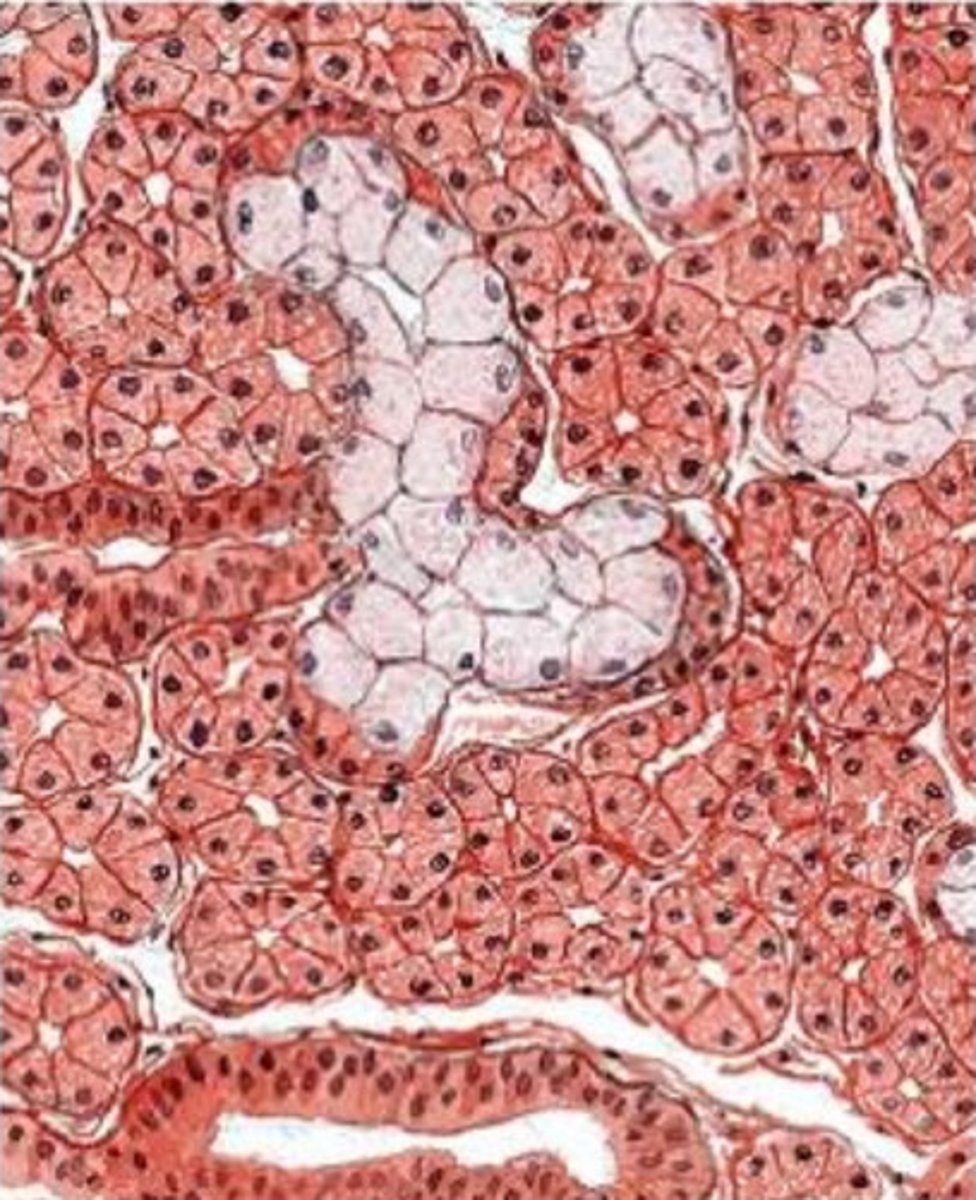
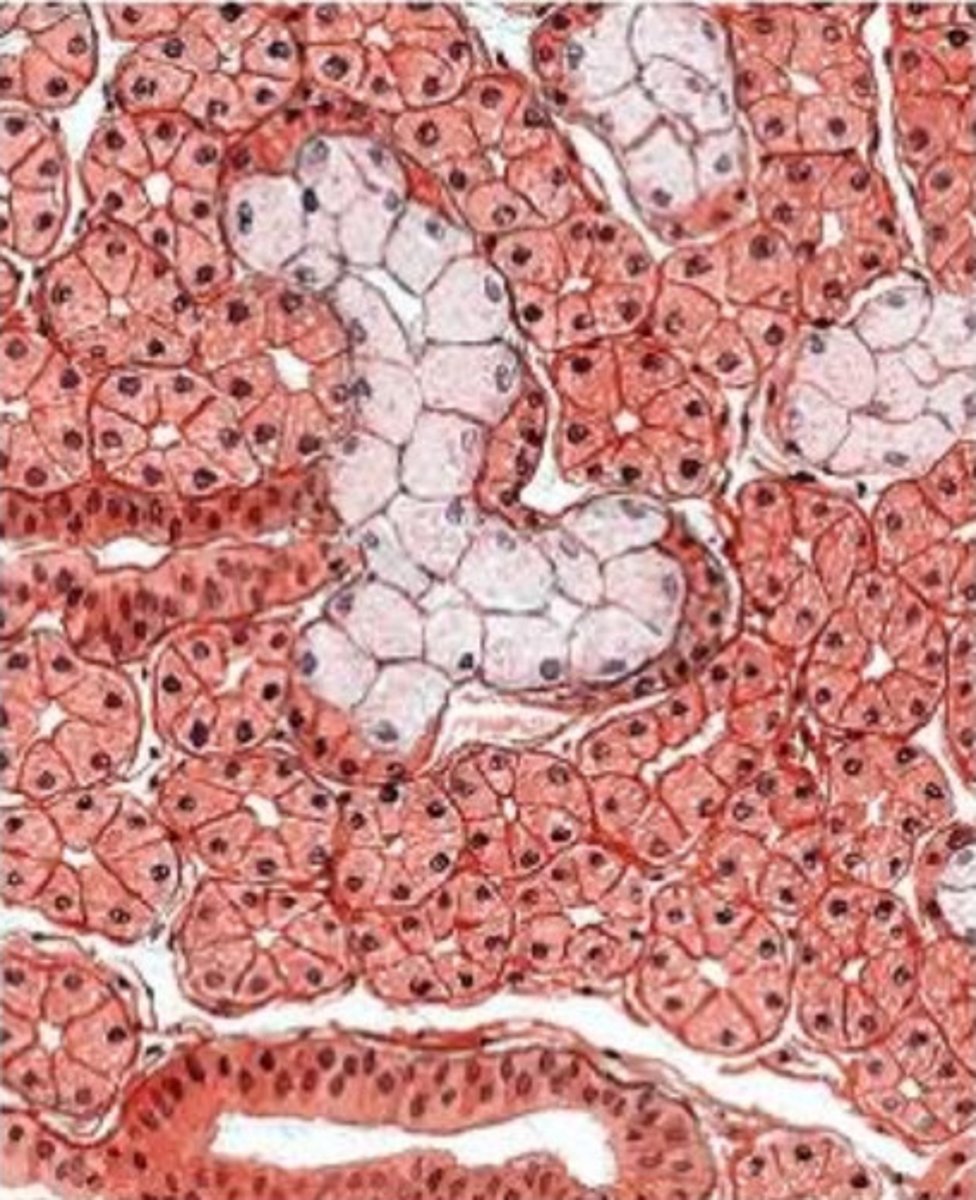
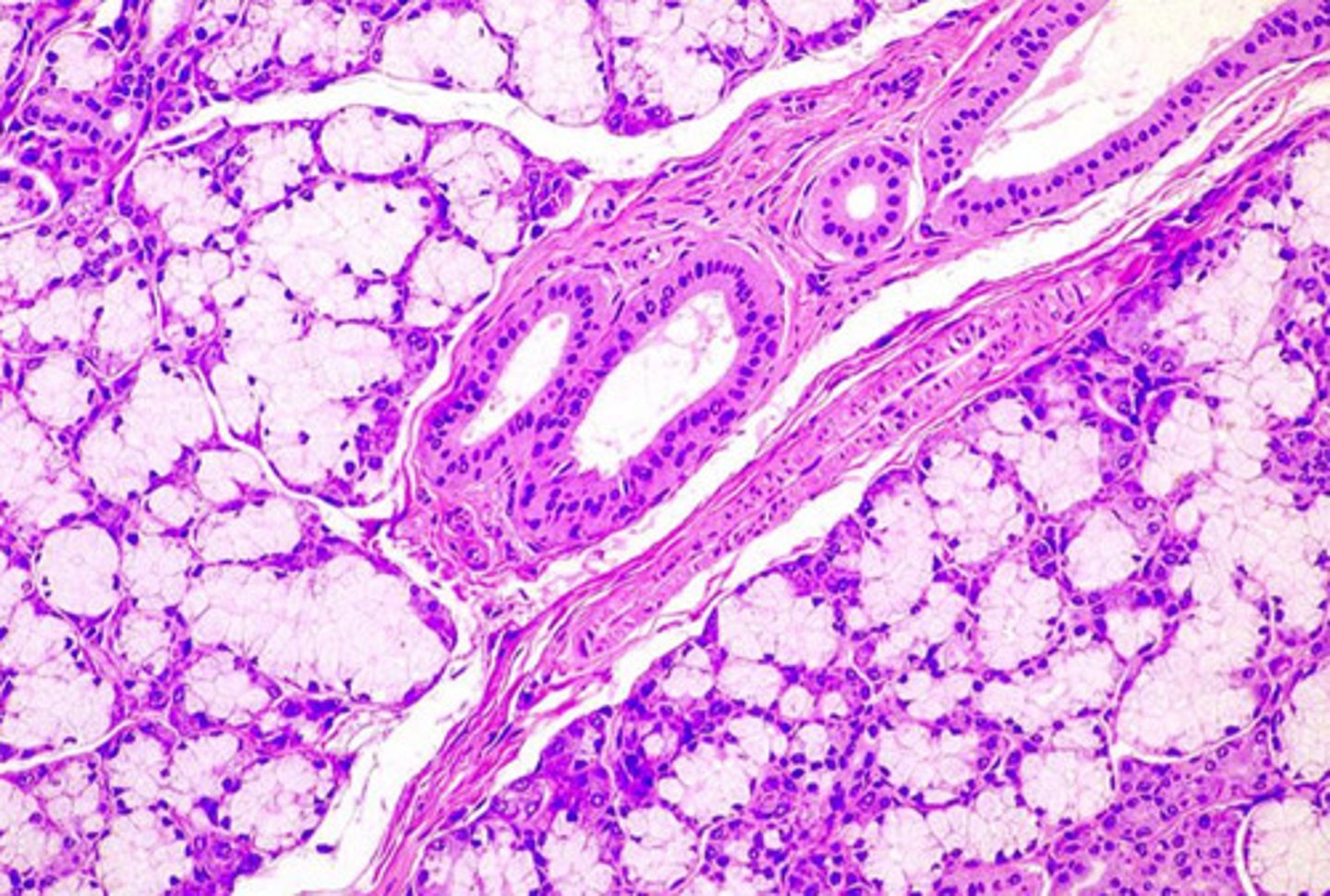
what gland is this from? how do you know?
- submandibular gland
- we see a mix of acinar cells (well-stained) with perfectly round nuclei and tubule cells with flattened nuclei
- although there is a mix of serous and mucous cells, there are more serous cells
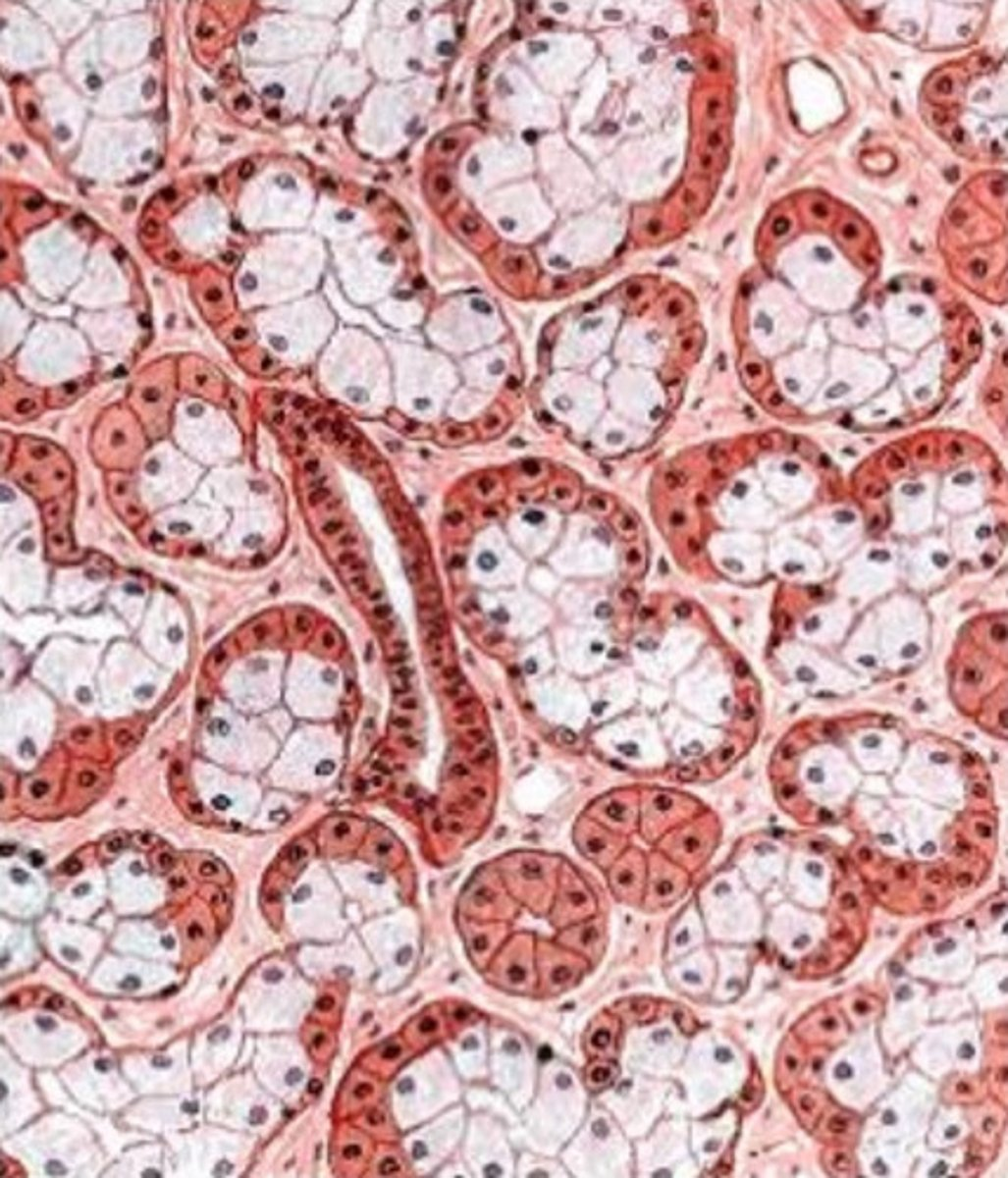
what gland is this from? how do you know?
- sublingual gland
- we see more mucus tubule cells (with flattened nucleus pushed to basal end of cell) than we do serous cells (round nucleus, well stained)
- mucous cells outnumber acinar cells and more mucus is produced in this gland
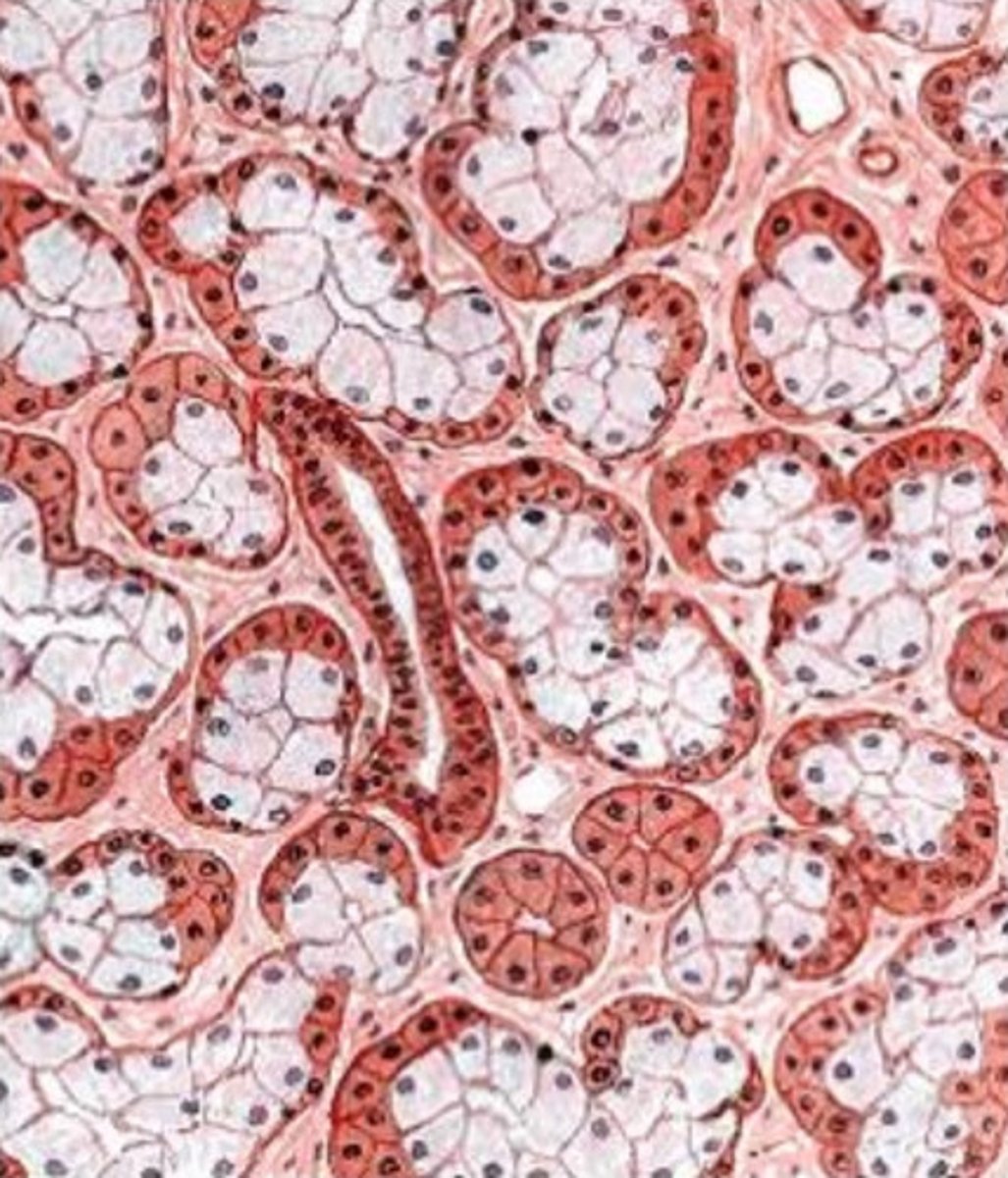
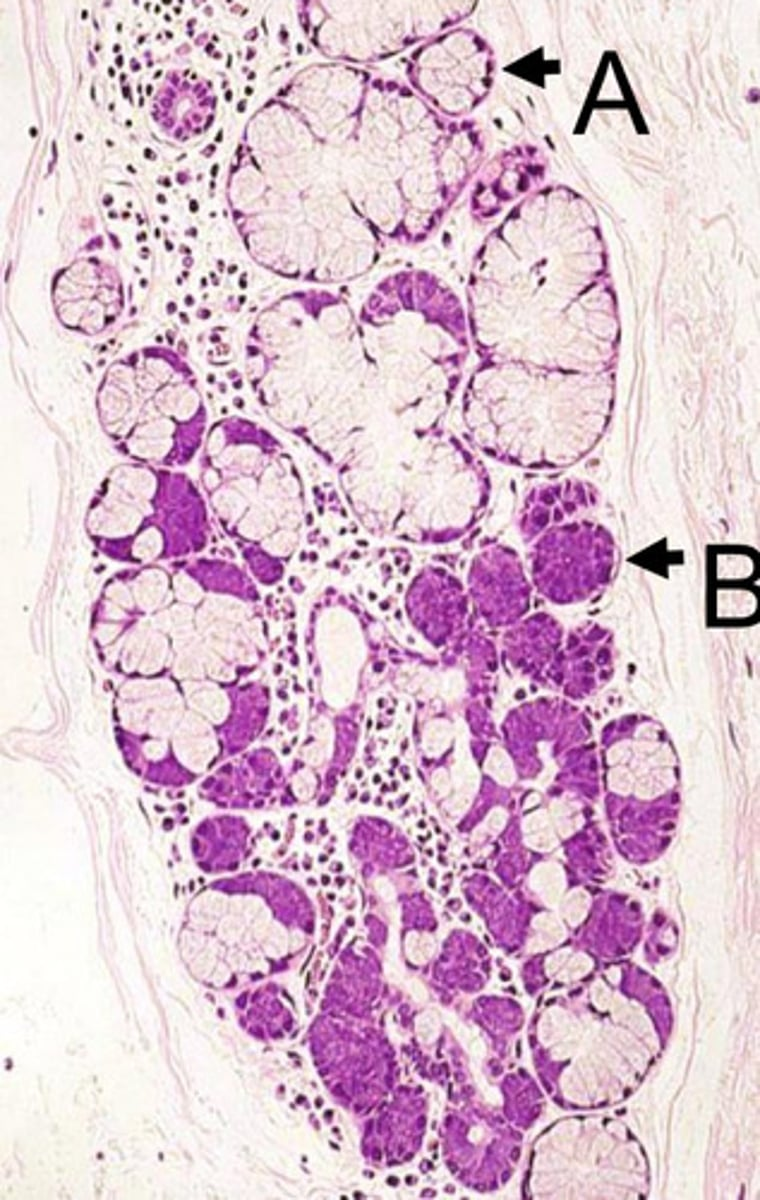
secretions from this gland will be serous or mucous?
serous
- this is from the parotid gland
- note: no mucous tubule cells (all cells are well-stained with perfectly round nuclei)
what type of secretions do you expect from this gland?
both serous and mucous
- contains both tubule mucous cells (poorly stained, nuclei pushed toward basal end of cell) and acinar cells (well stained cells w/ perfectly round nuclei)
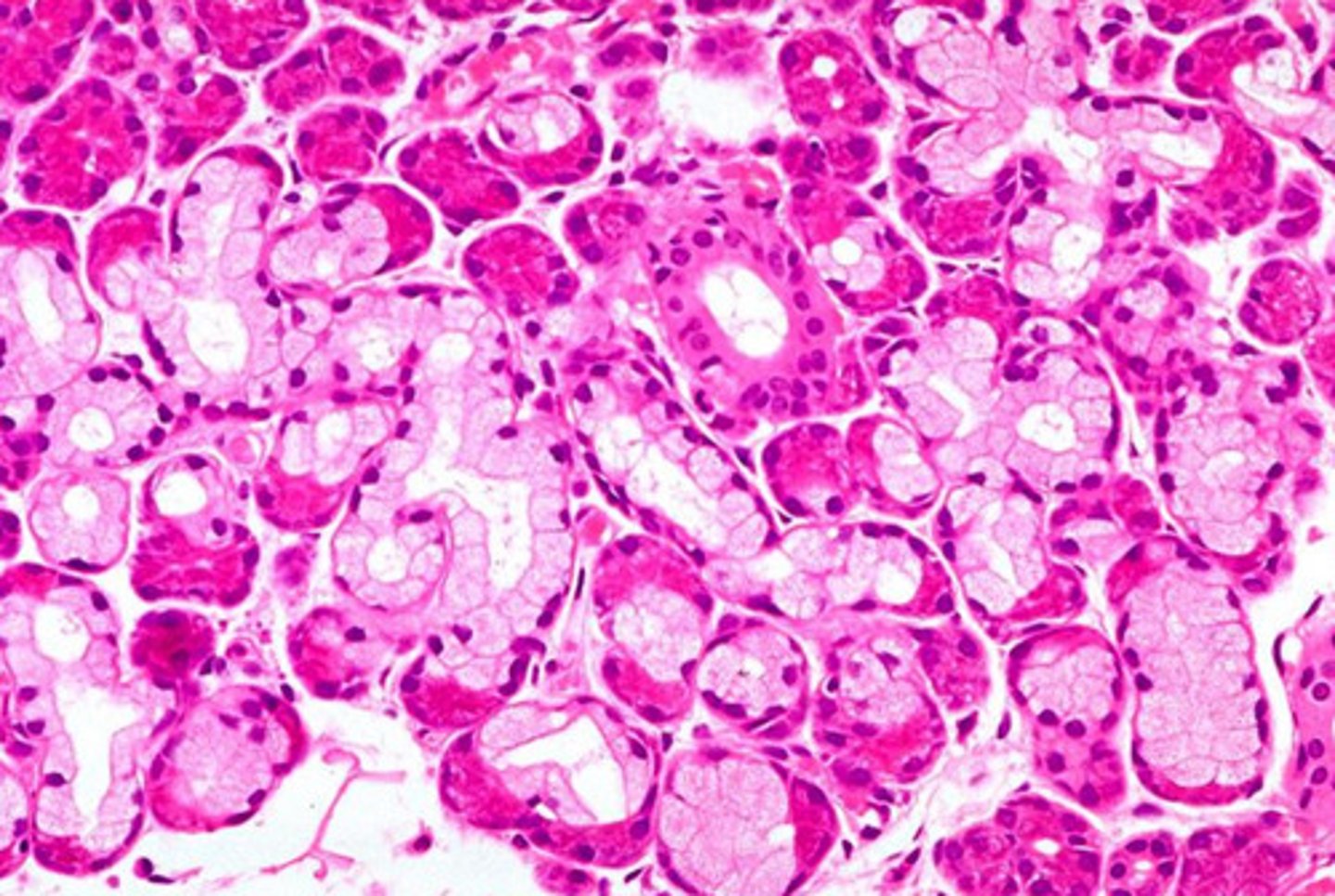
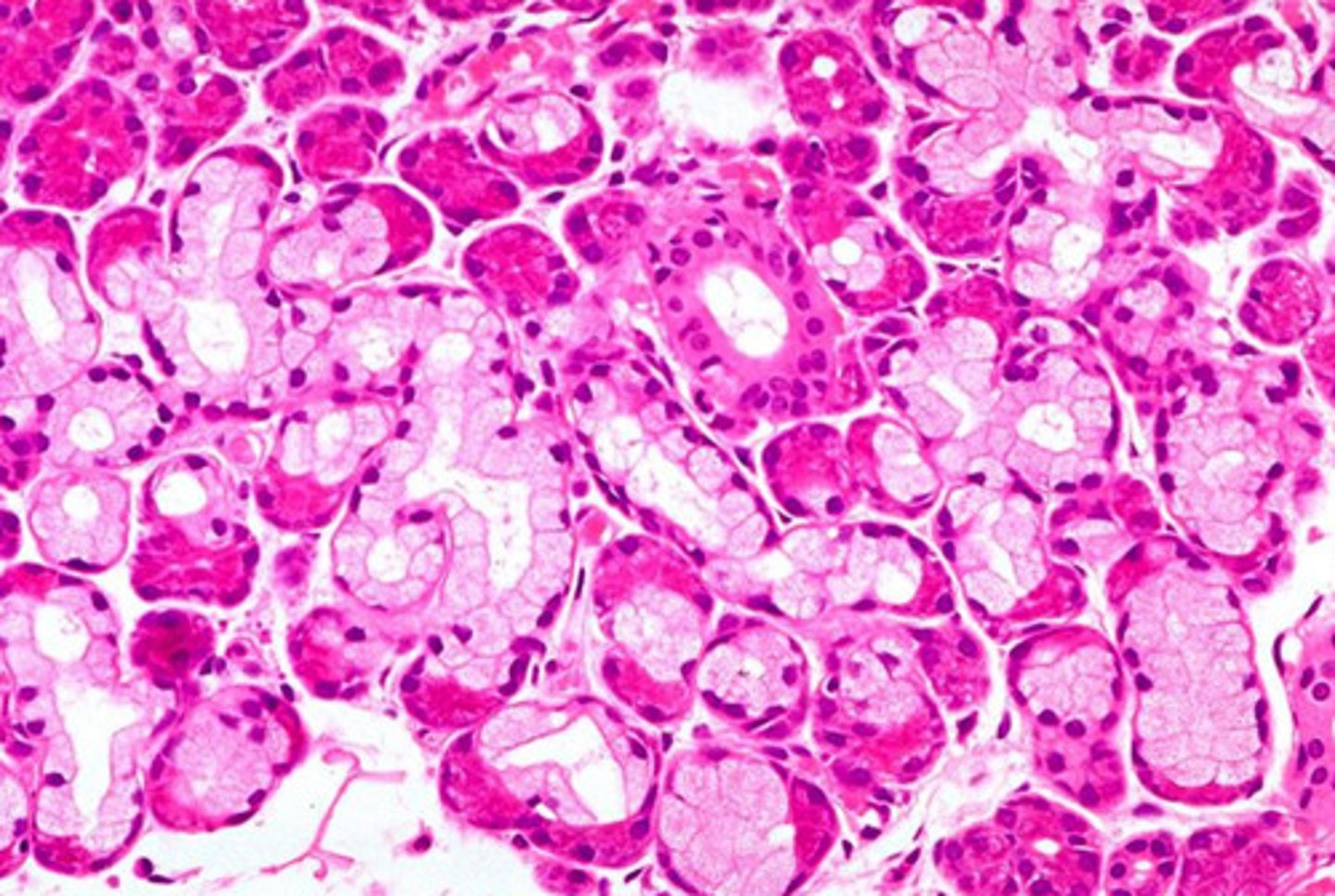
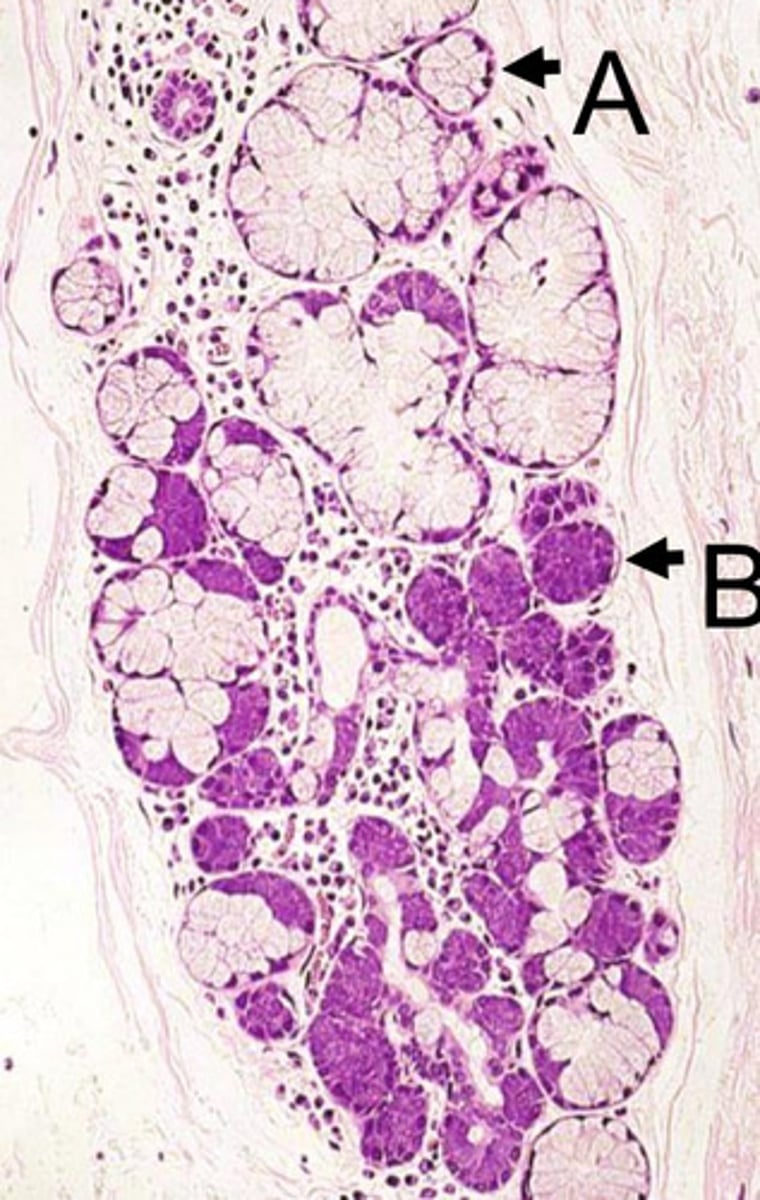
what gland is this from? how do you know?
sublingual
- mucous cells (poorly stained w/ flattened nucleus) outnumber acinar cells
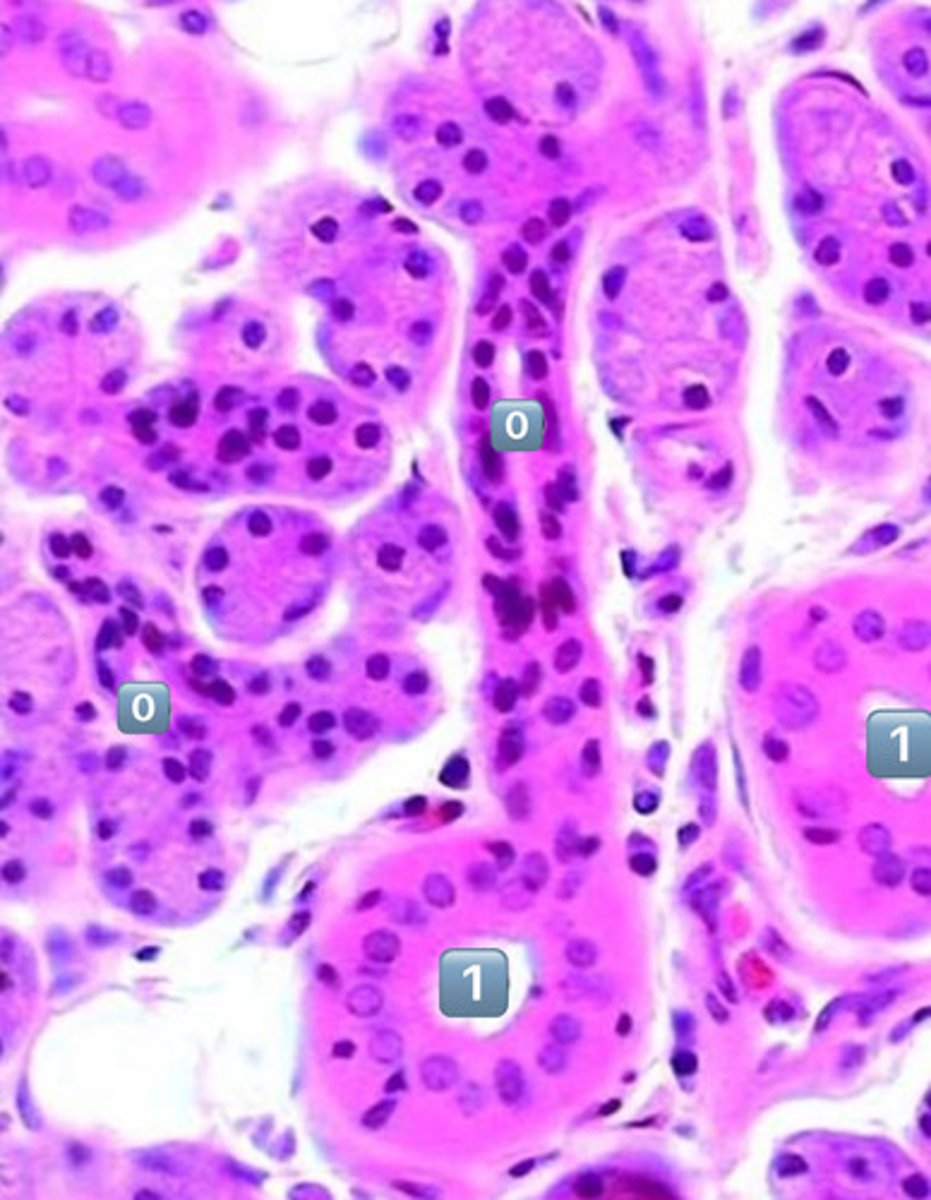
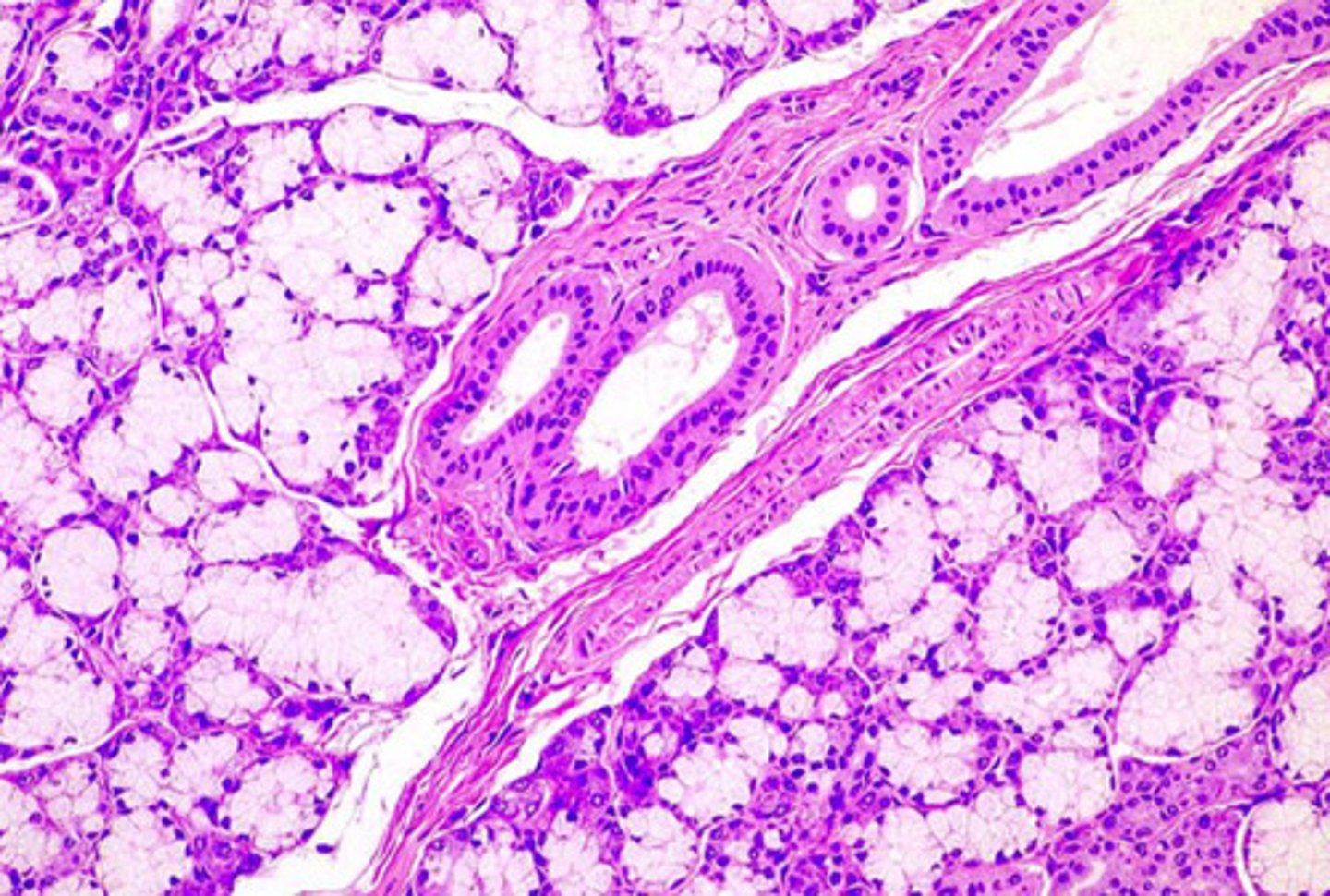
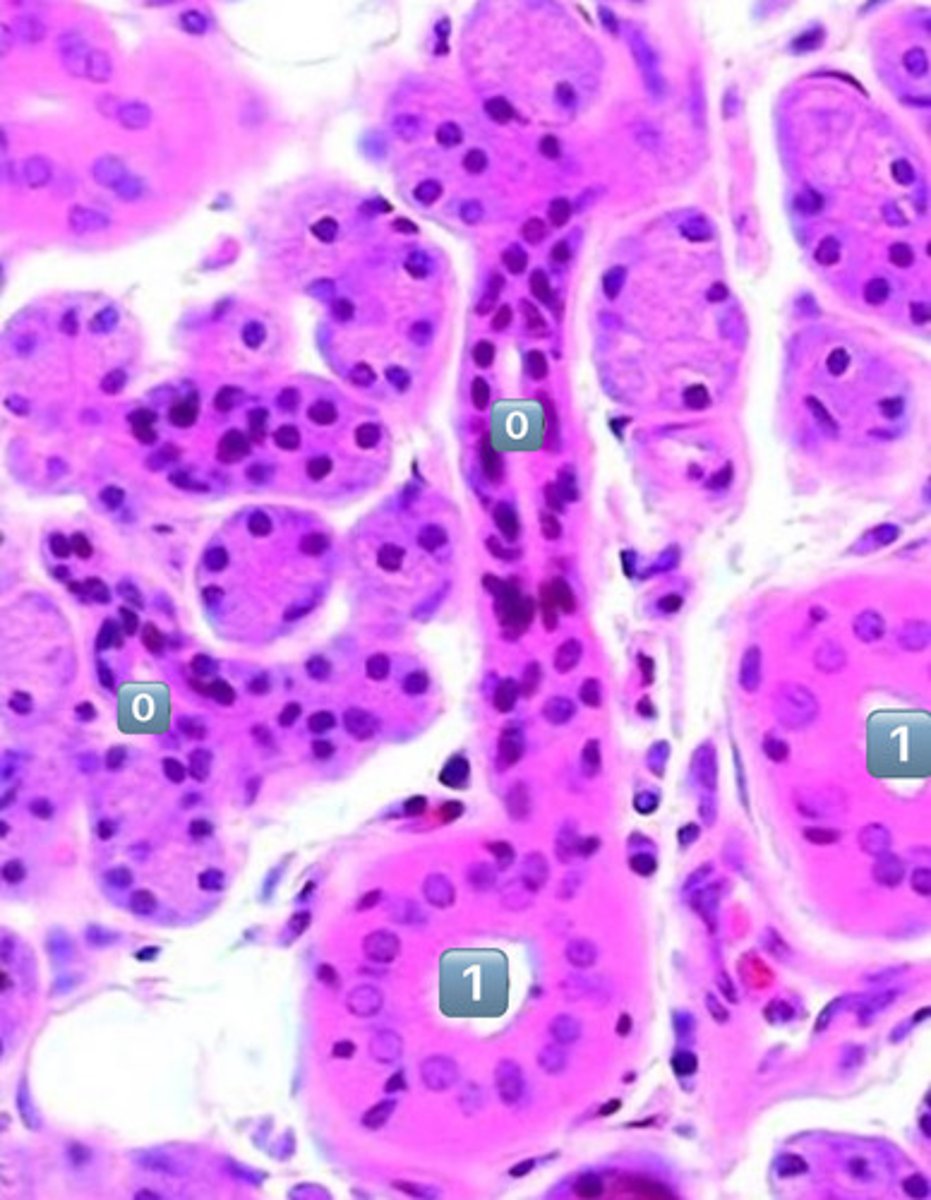
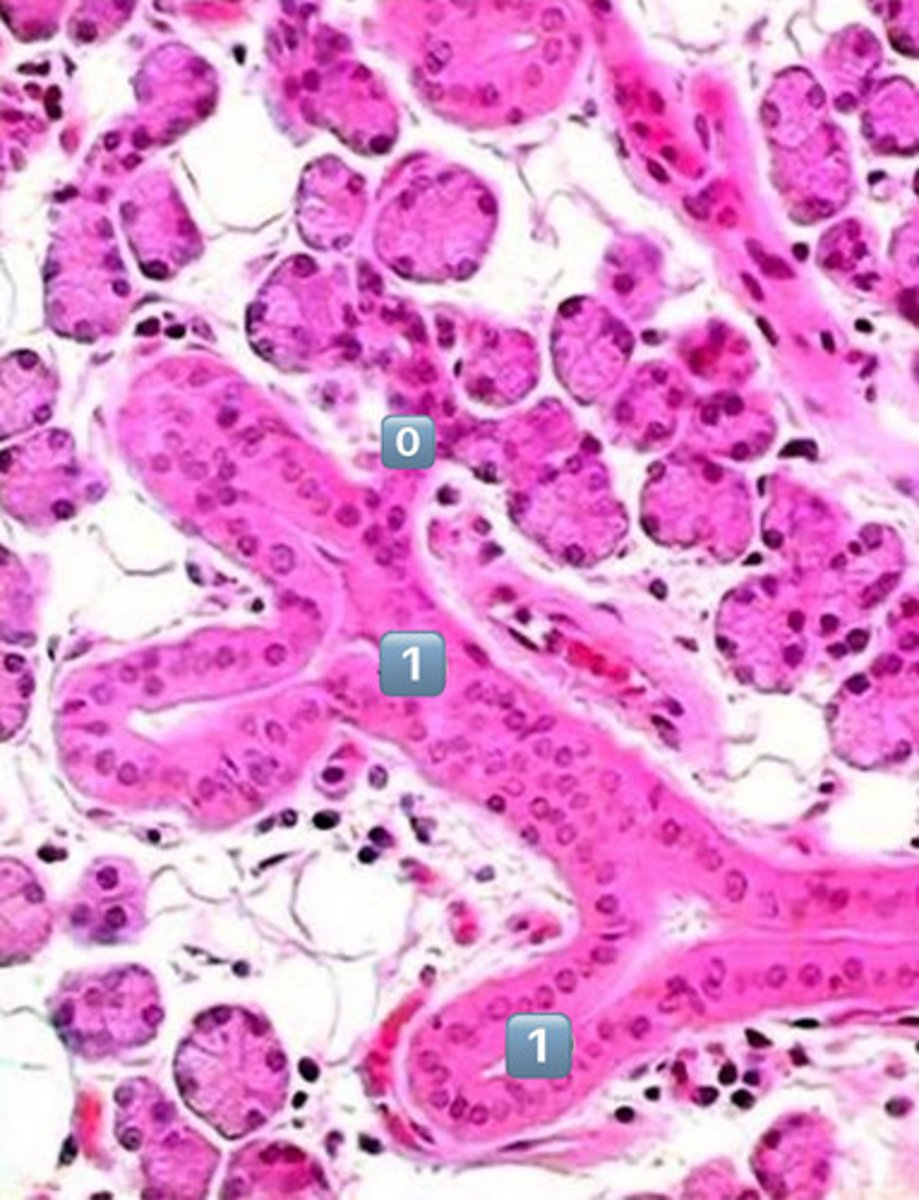
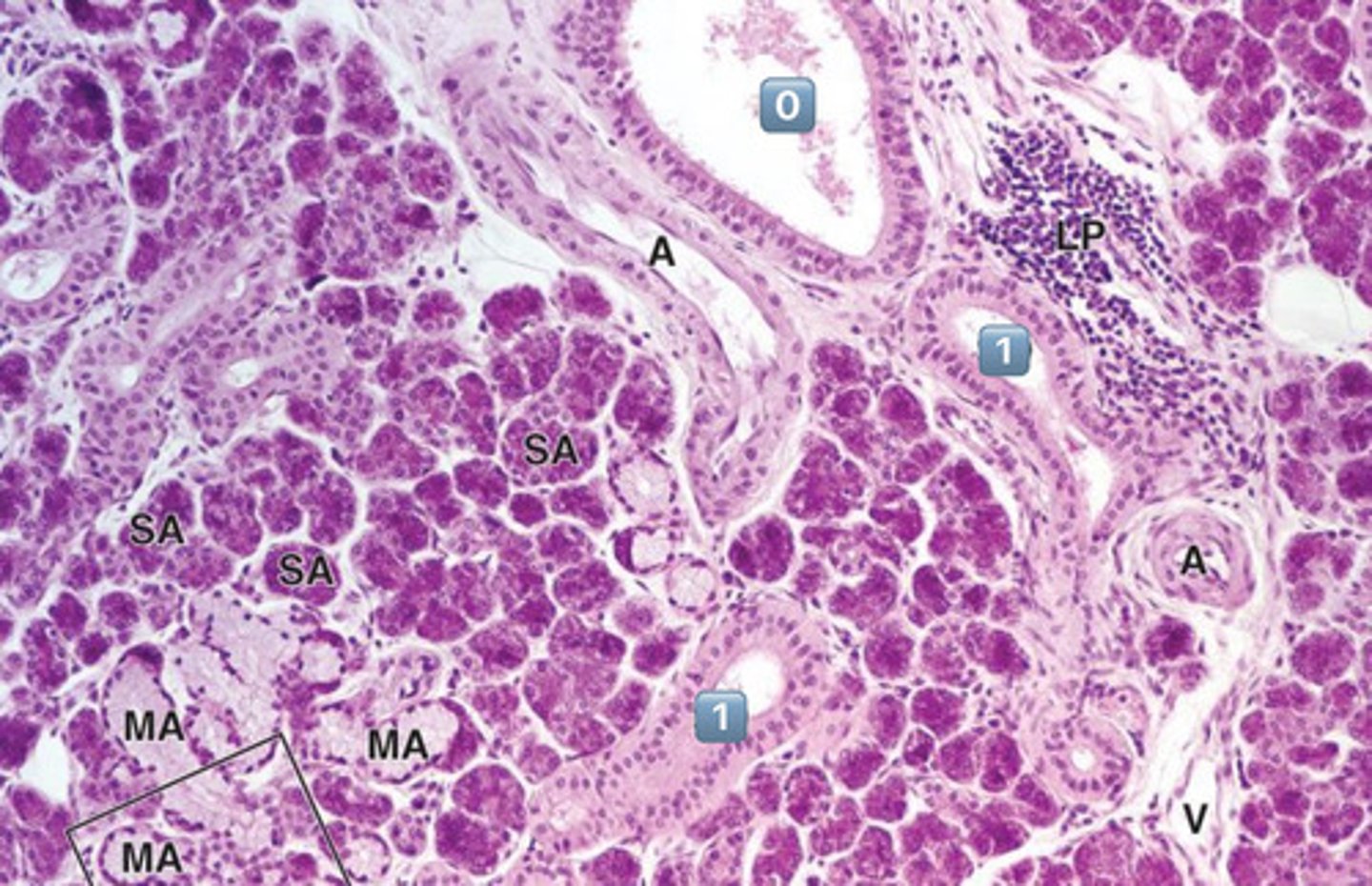
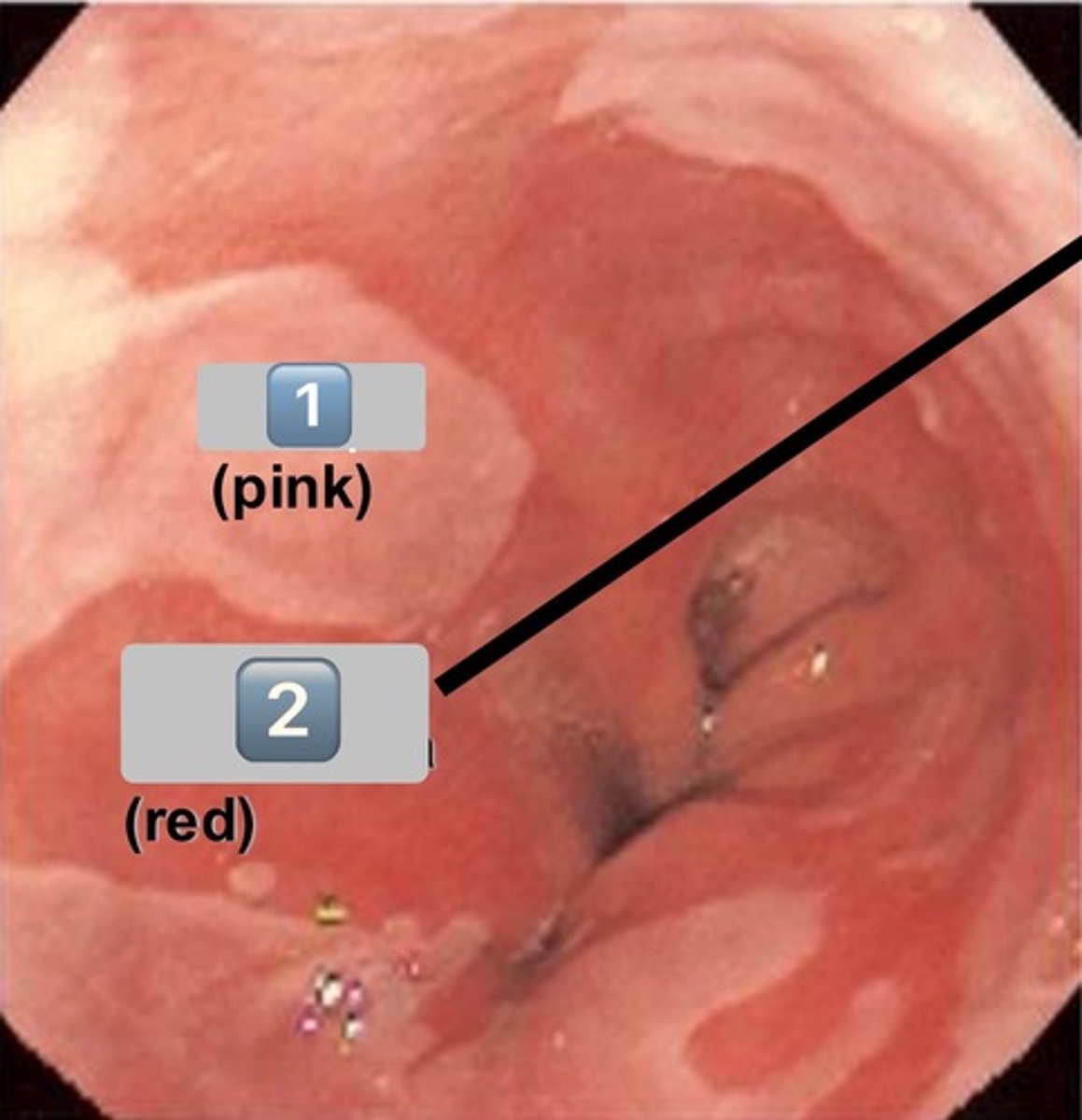
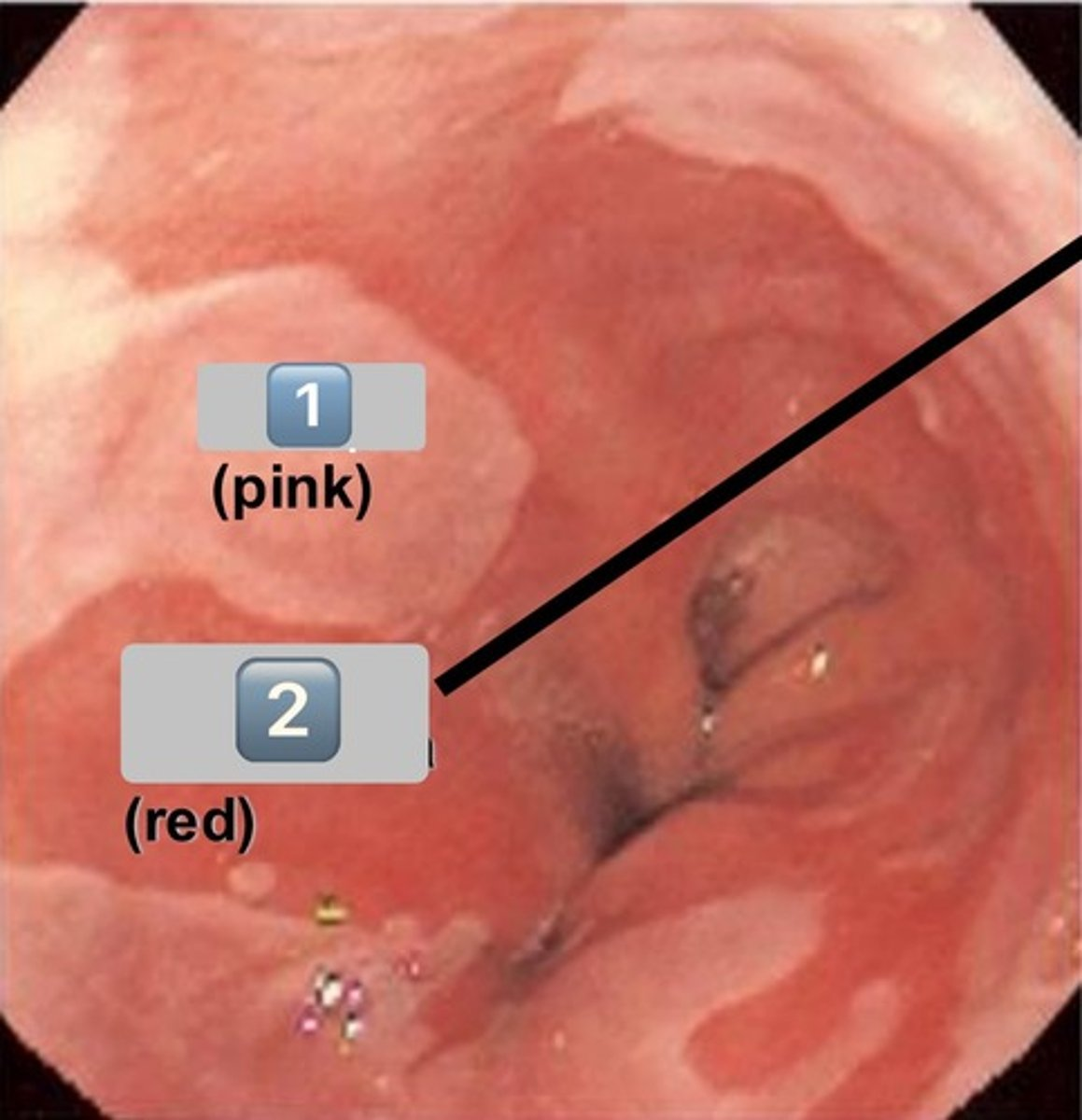
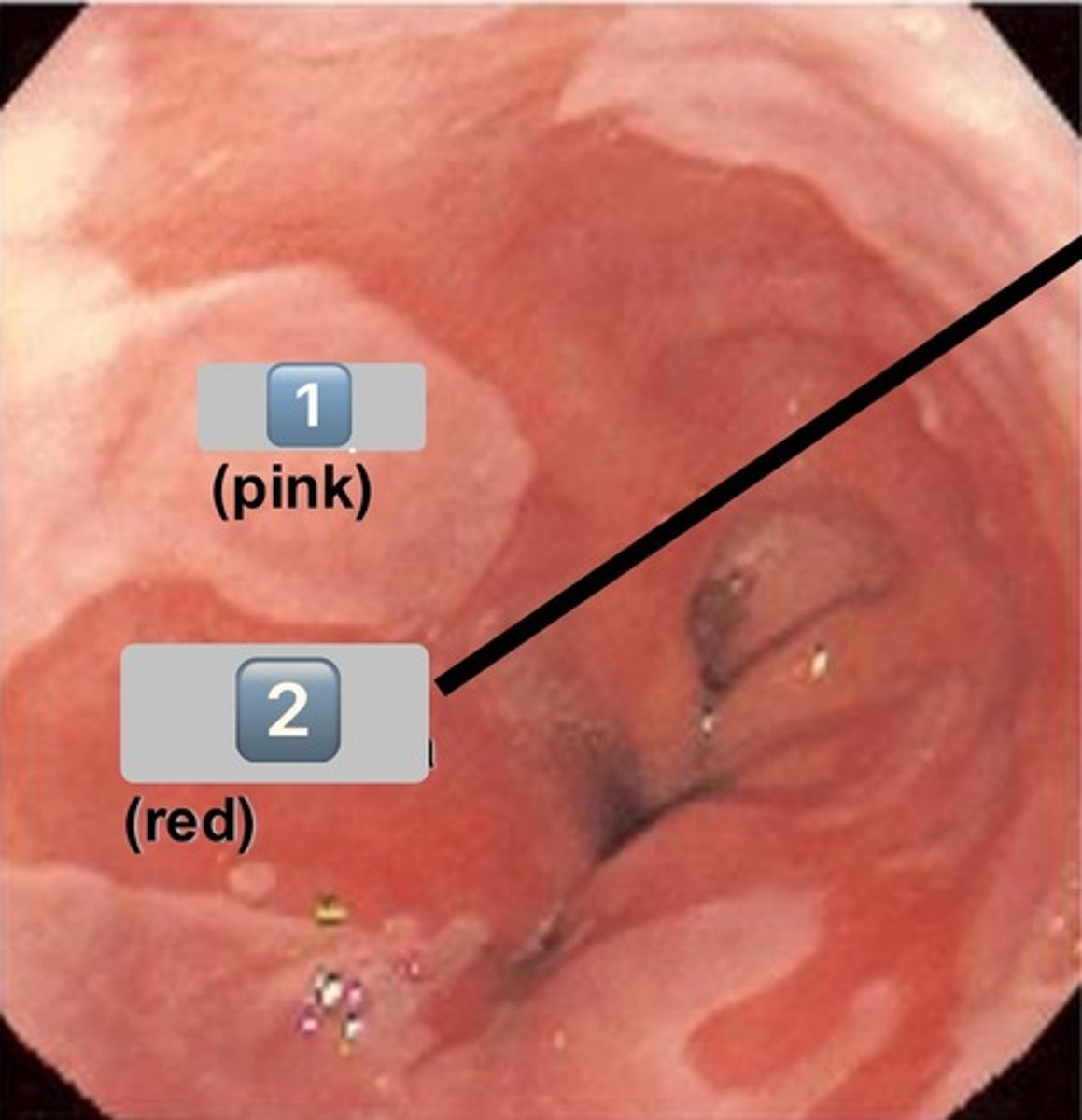
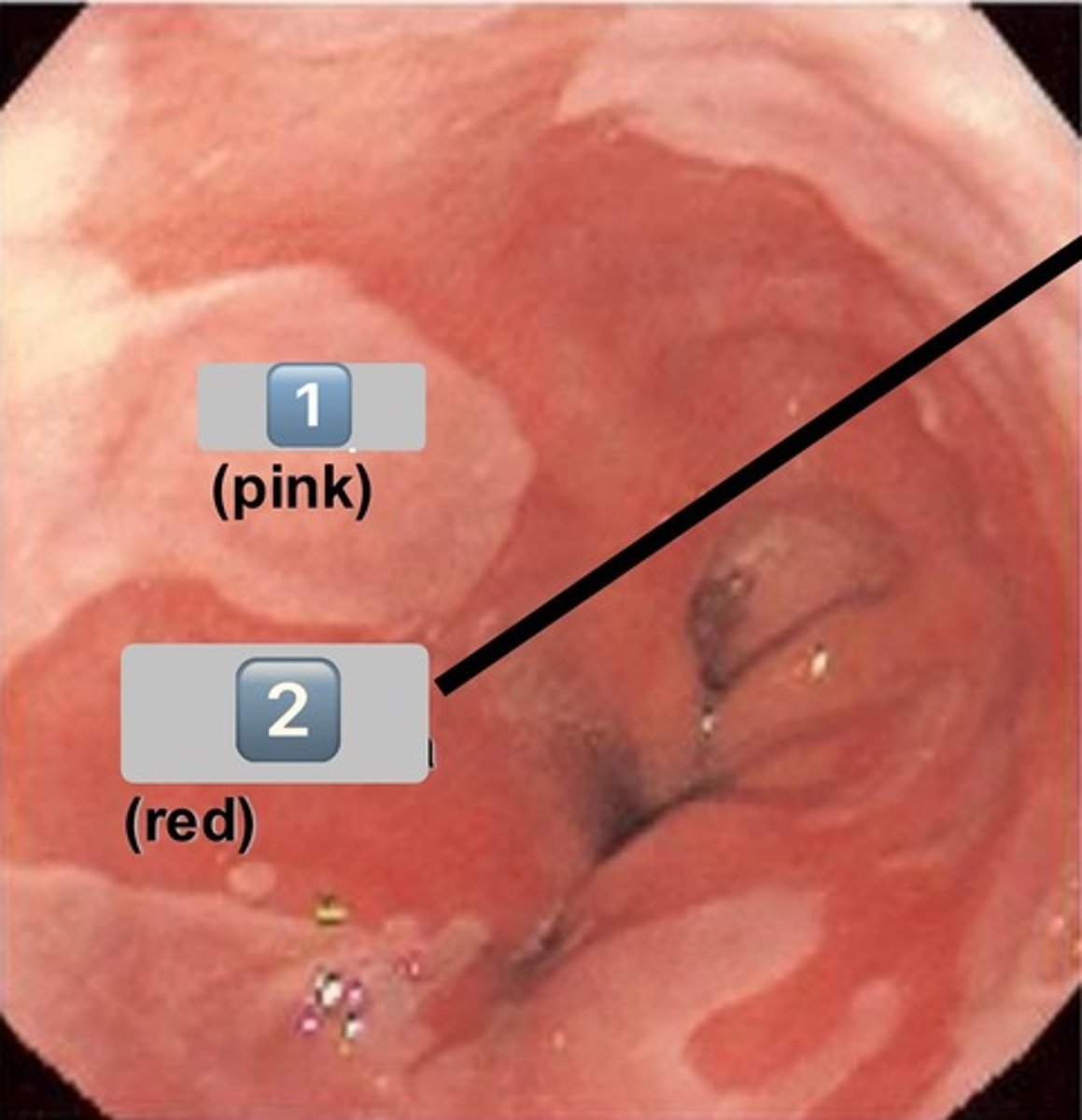
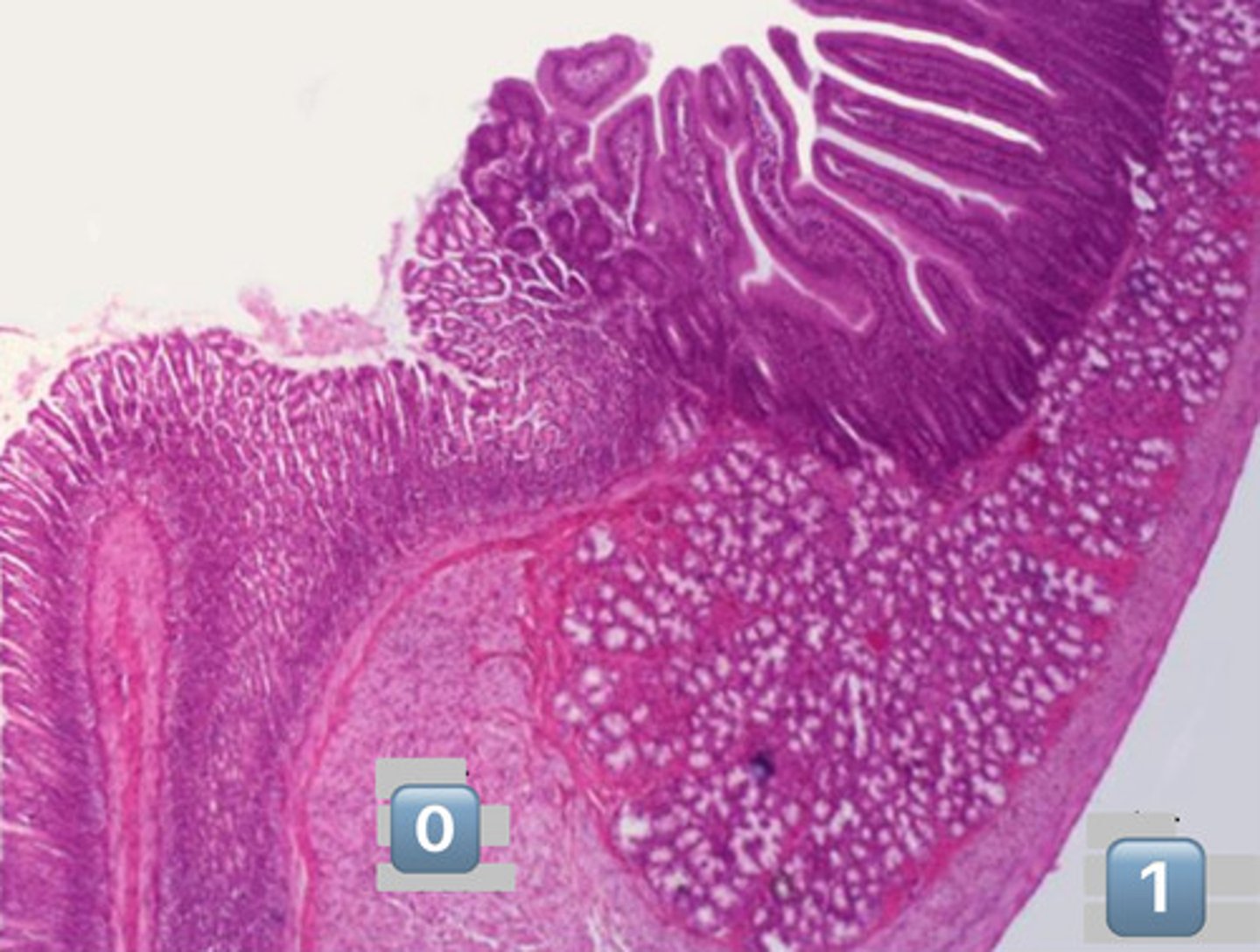
what epithelium type is found at the location labeled "0"
simple cuboidal
- cell is wider than it is tall
- intercalated duct
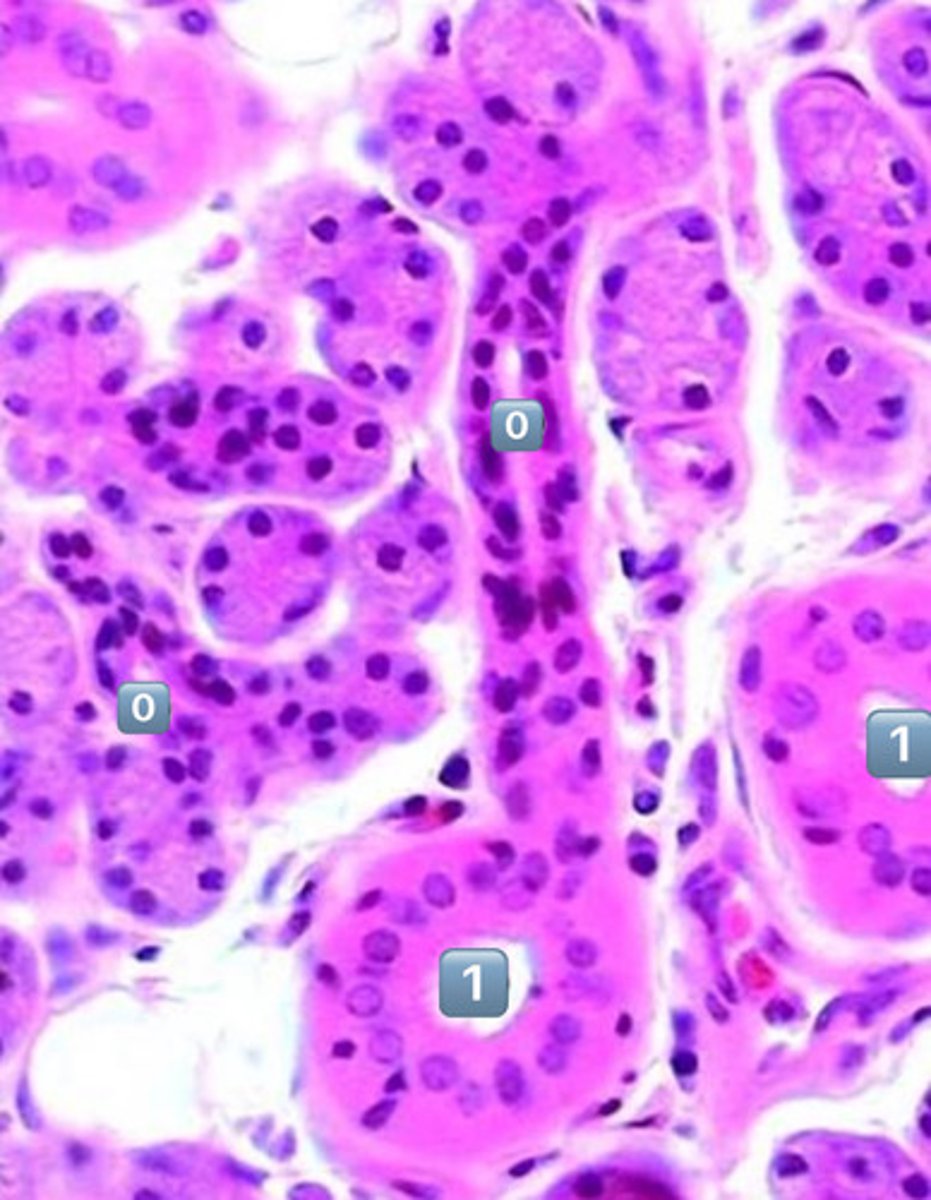
0
intercalated duct
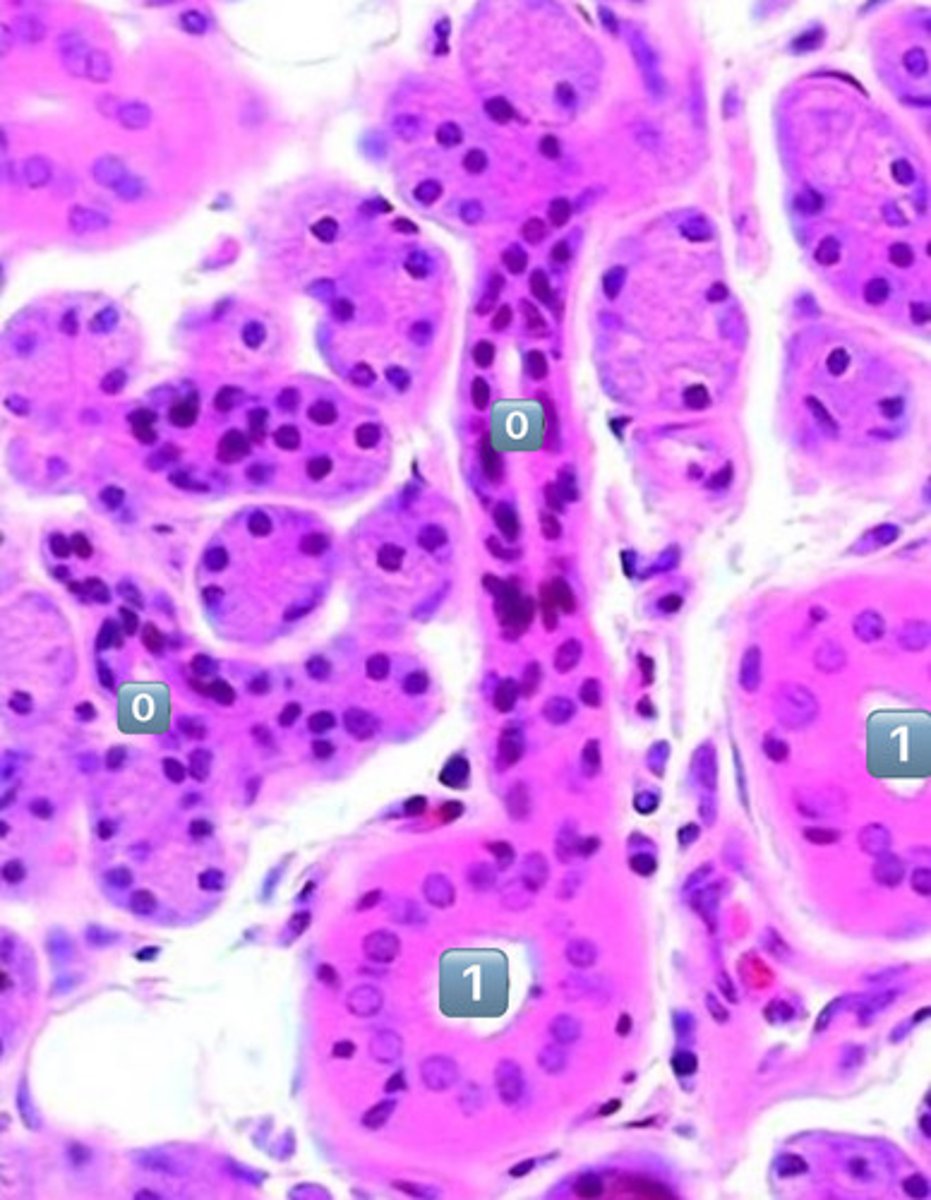
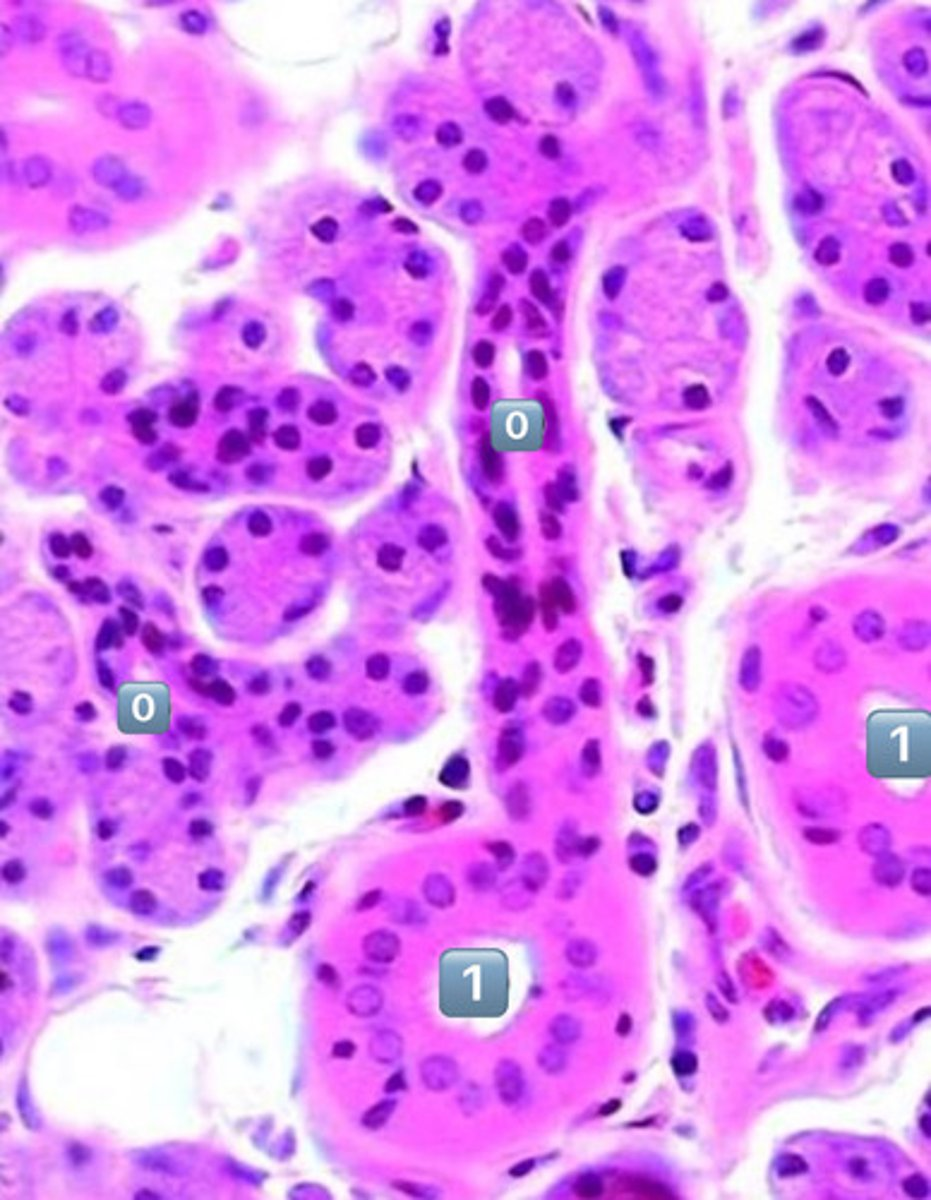
1
striated duct
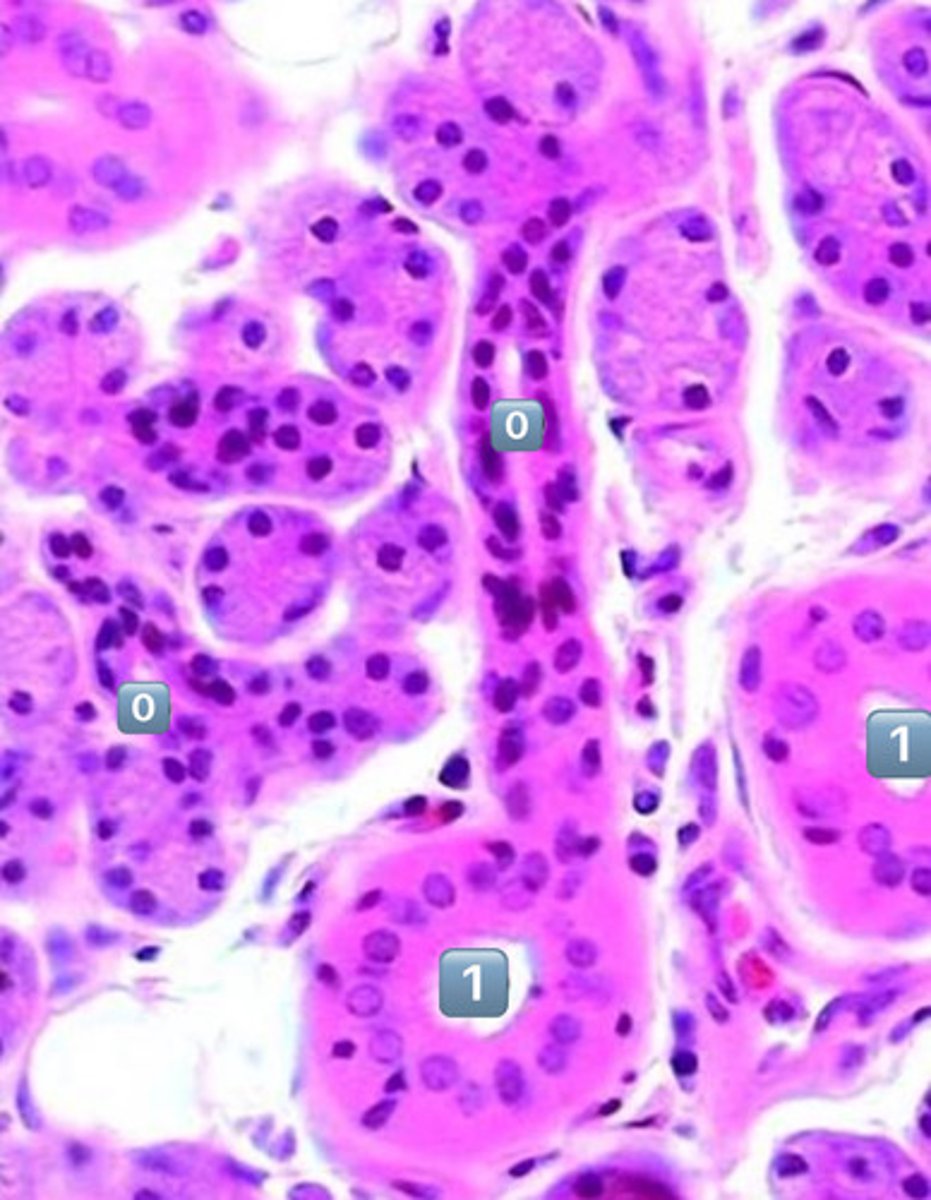
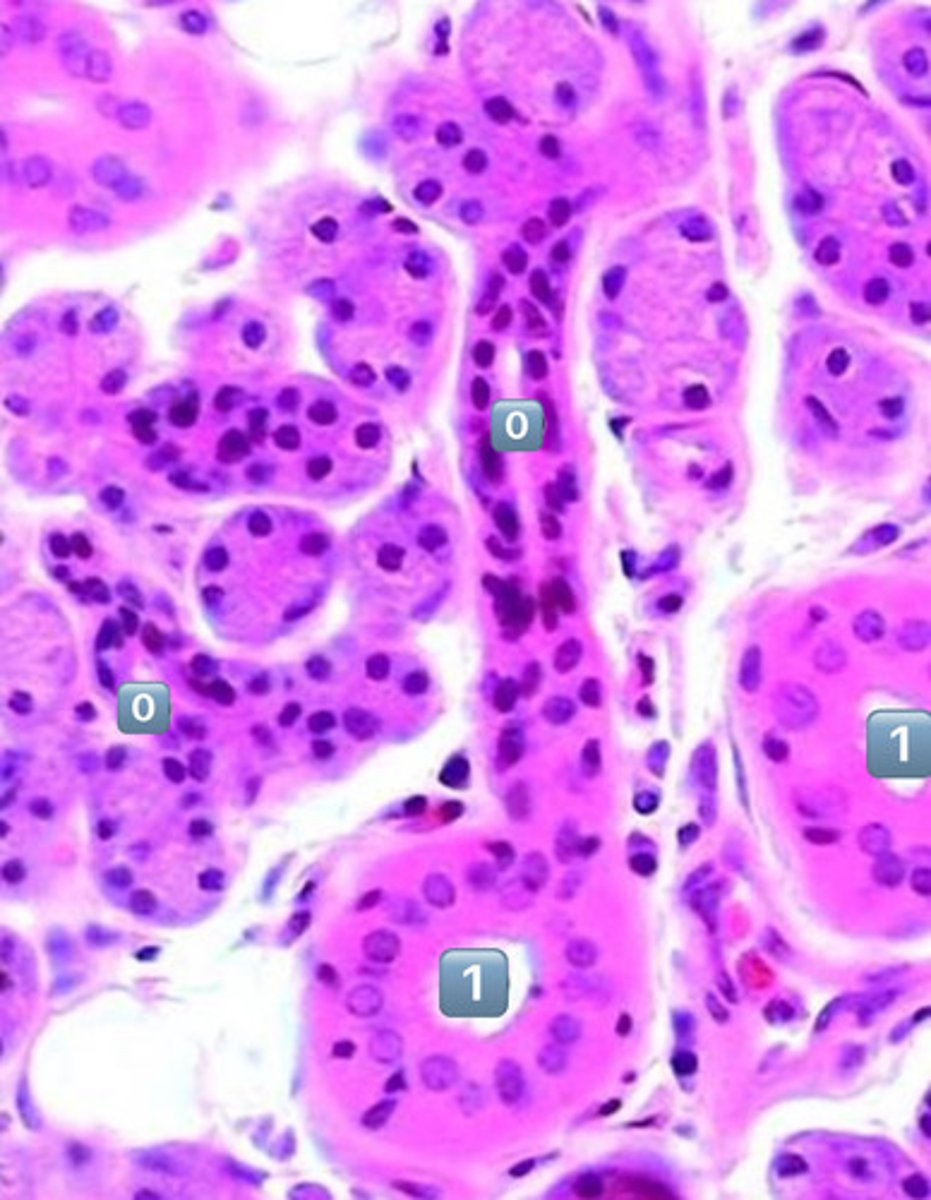
what epithelium is found in the location labeled with a 1
simple columnar
- cell is taller than it is wide
- striated duct
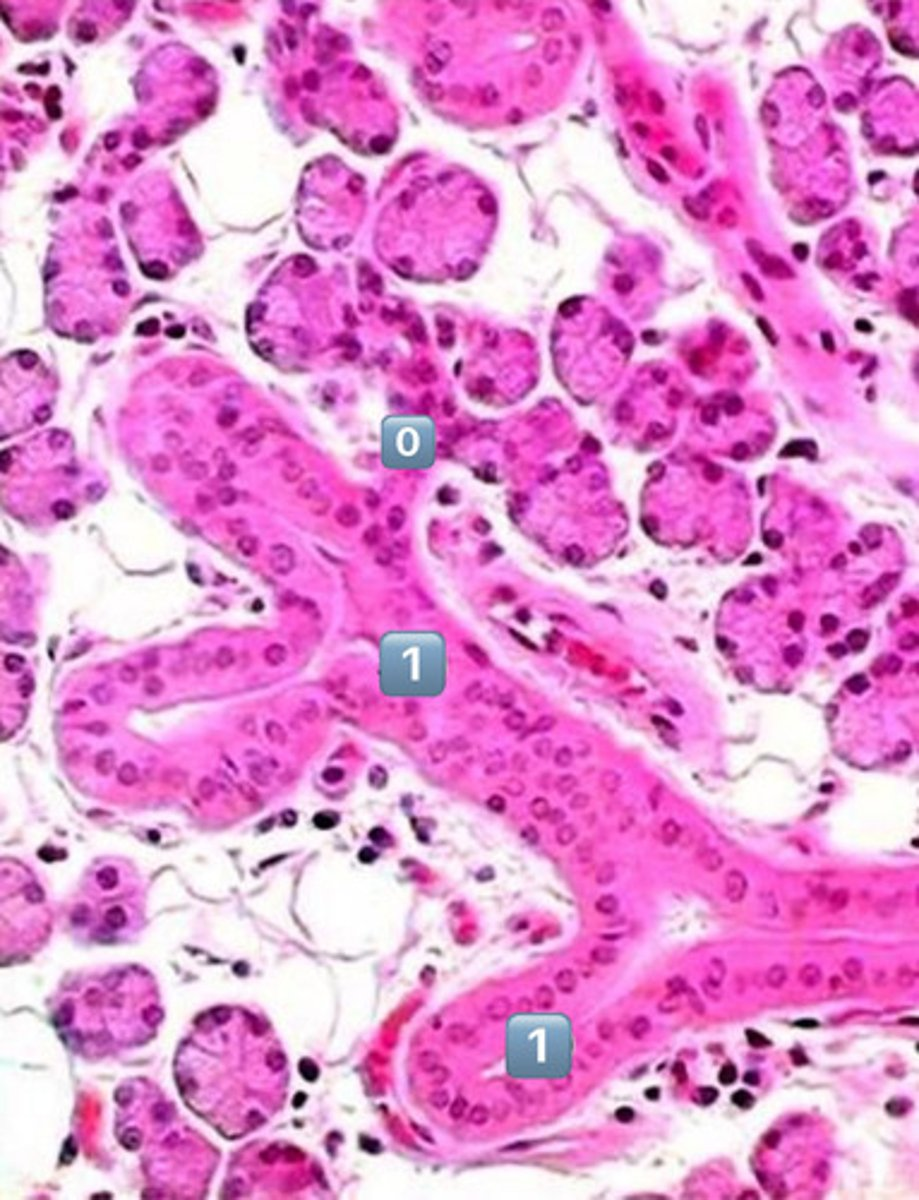
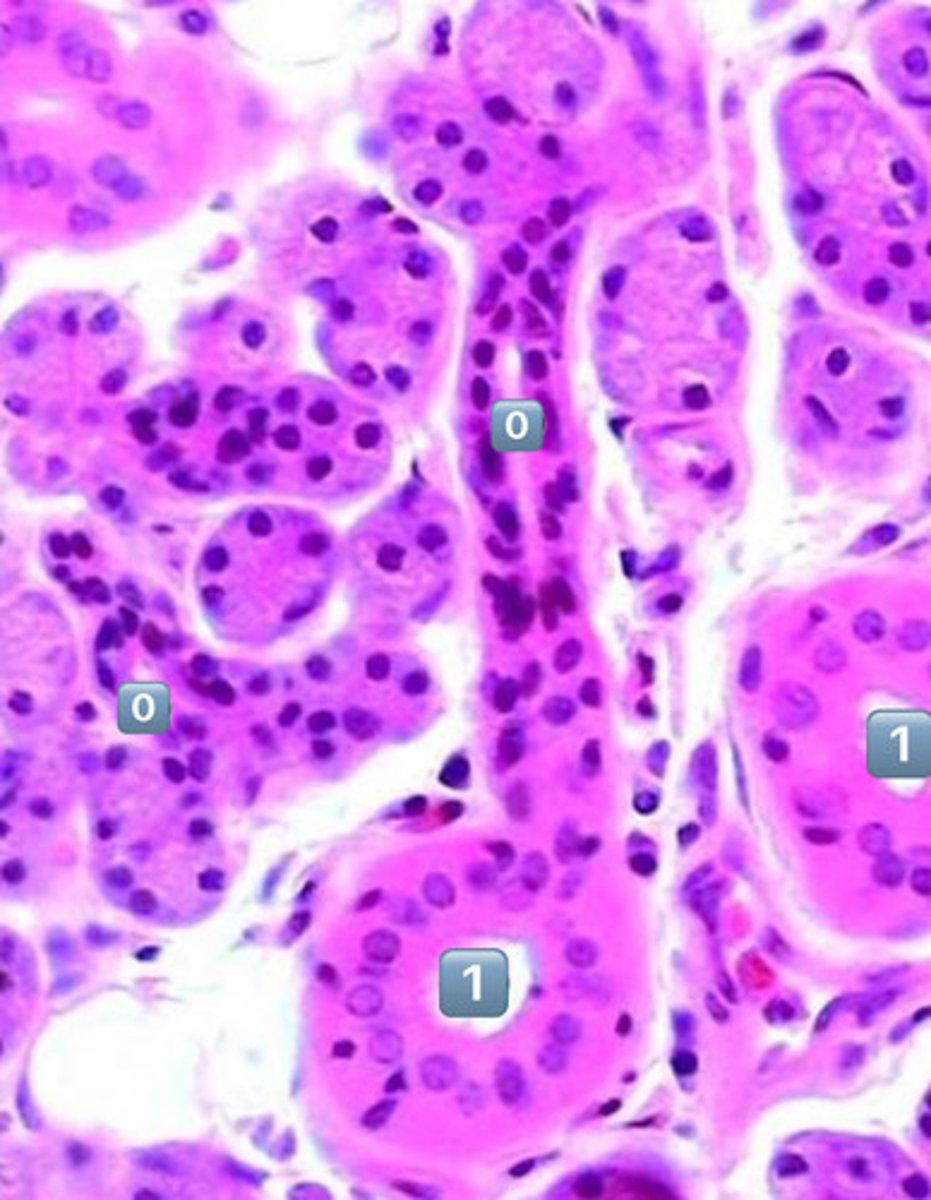
0
intercalated duct
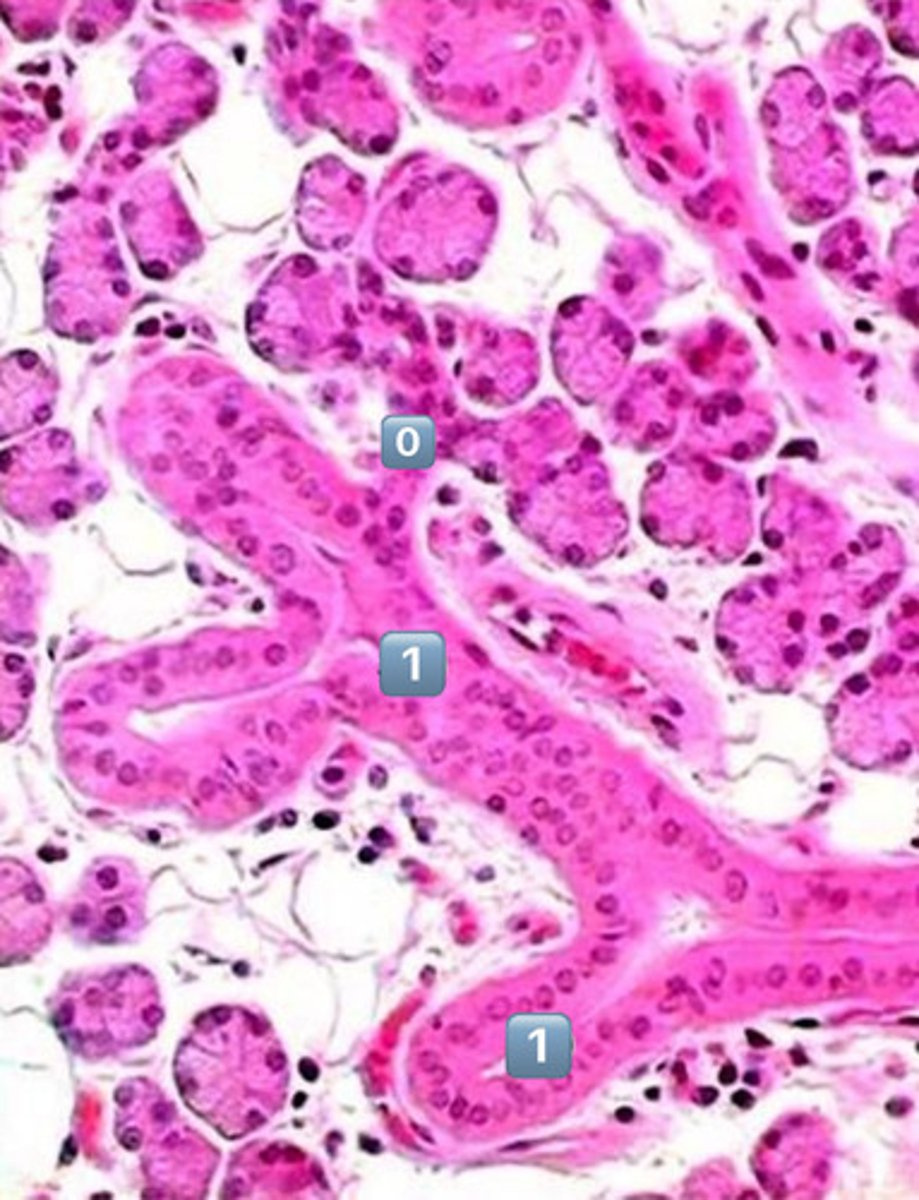
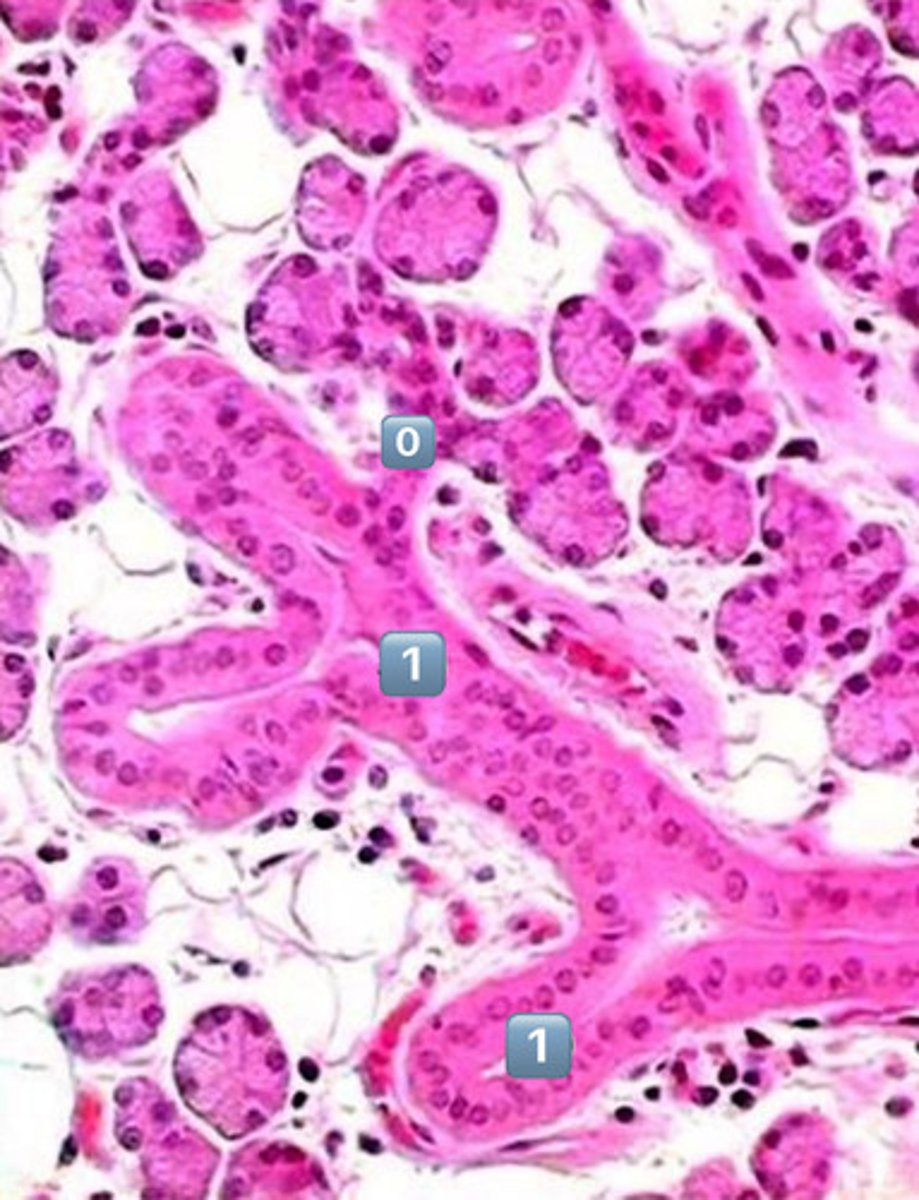
1
striated duct
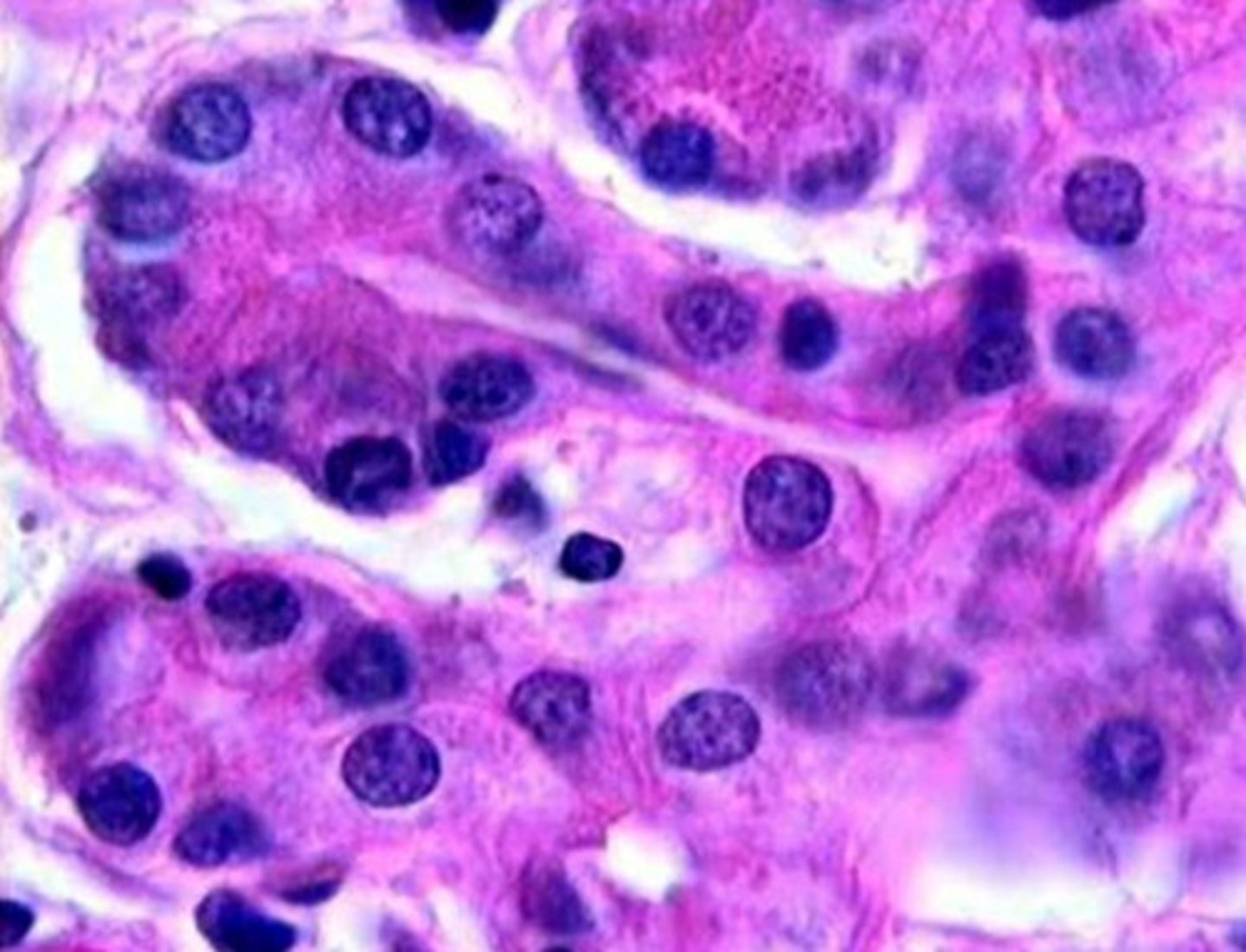
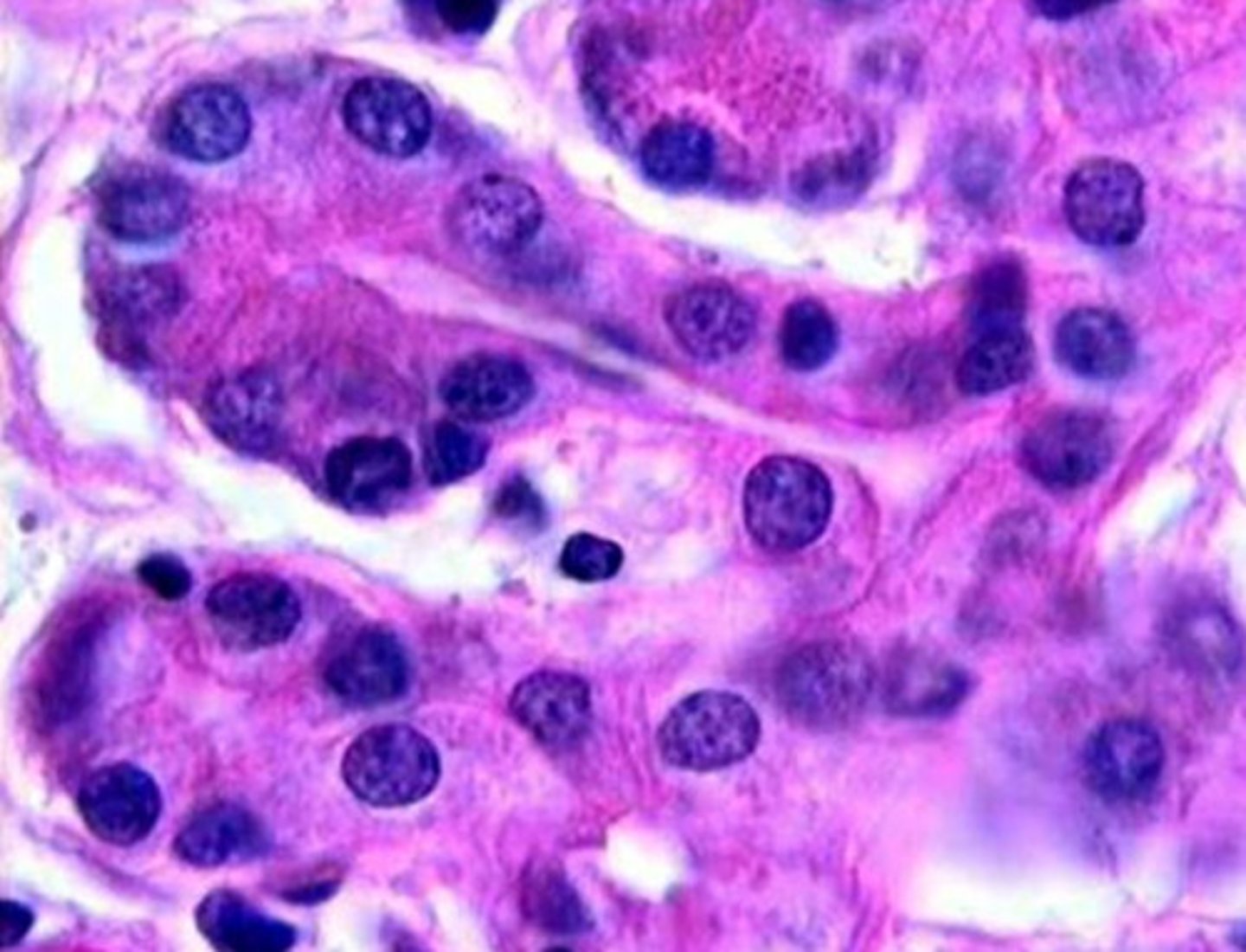
?
intercalated duct
- simple cuboidal
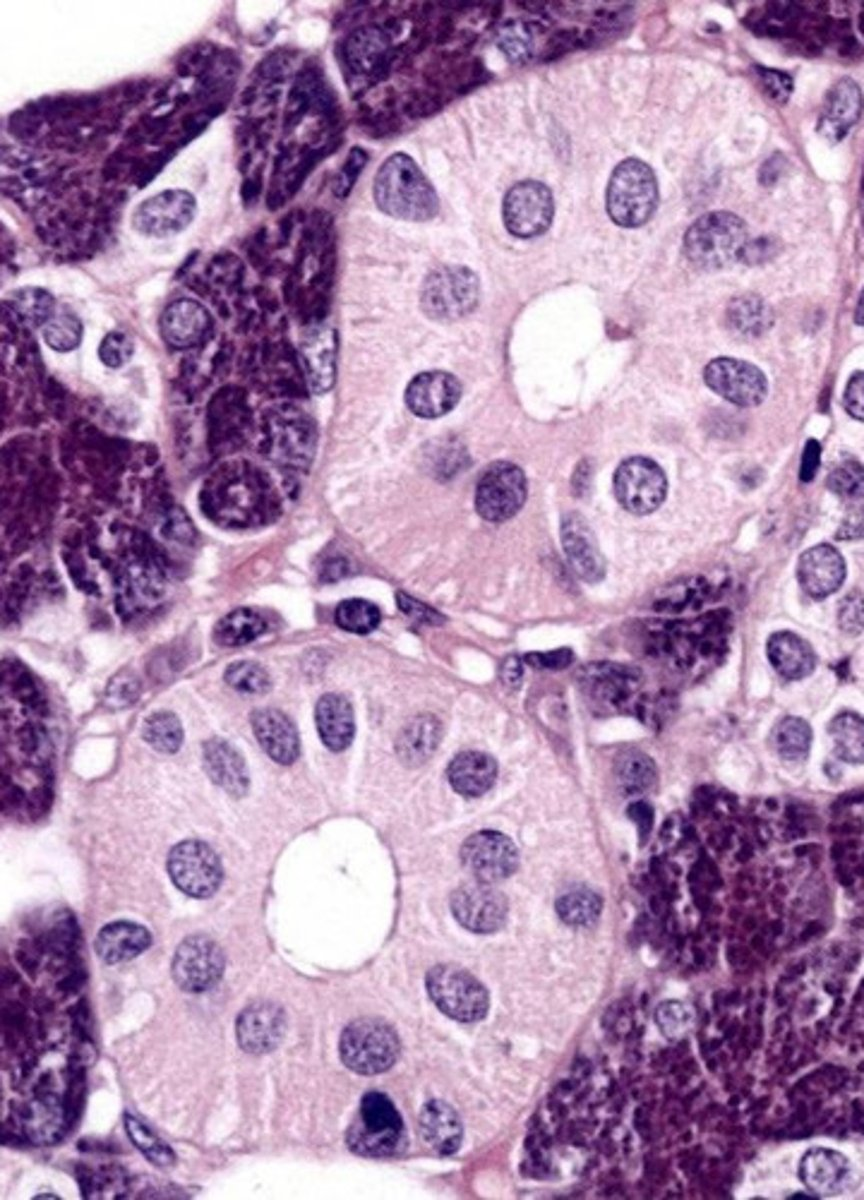
?
striated duct
- simple columnar
- note: striations
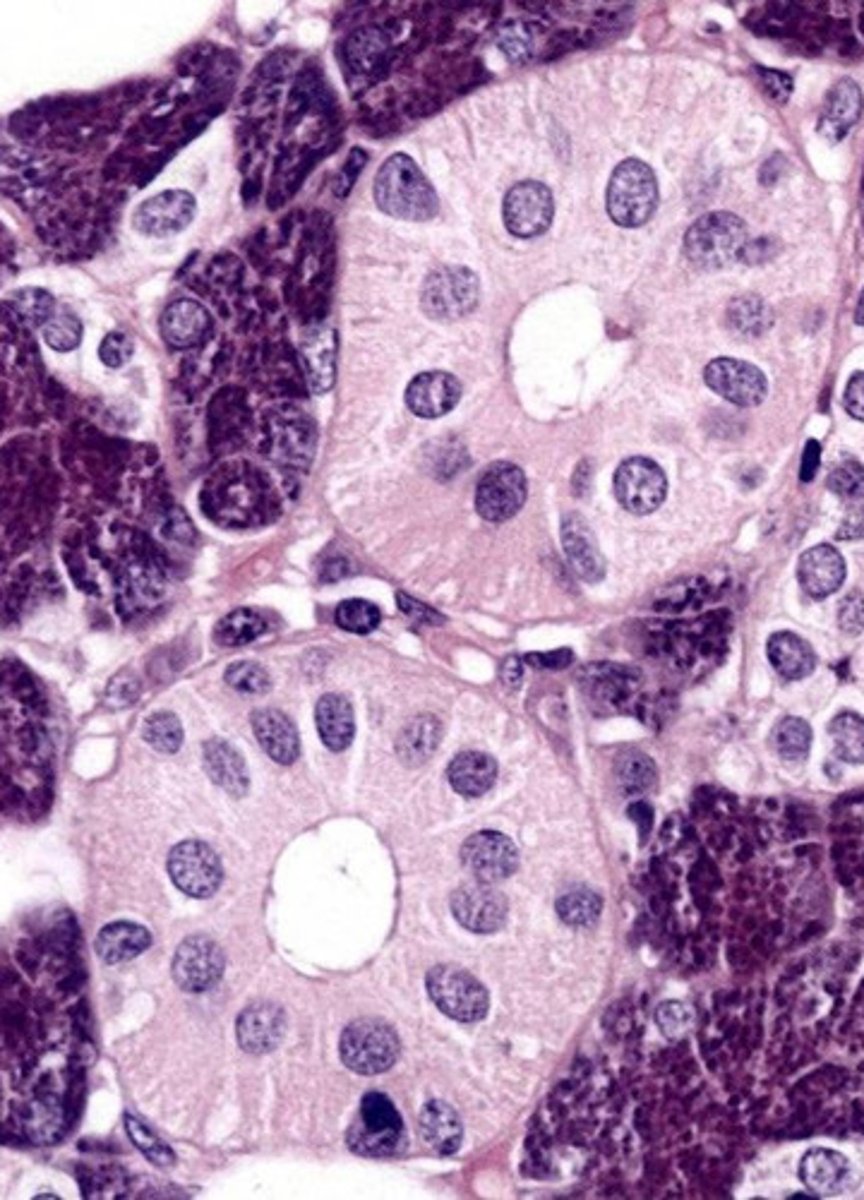
does modification of saliva happen at the location labeled "0"?
NO, this is an excretory duct, salivary modification only happens in the intercalated and striated ducts
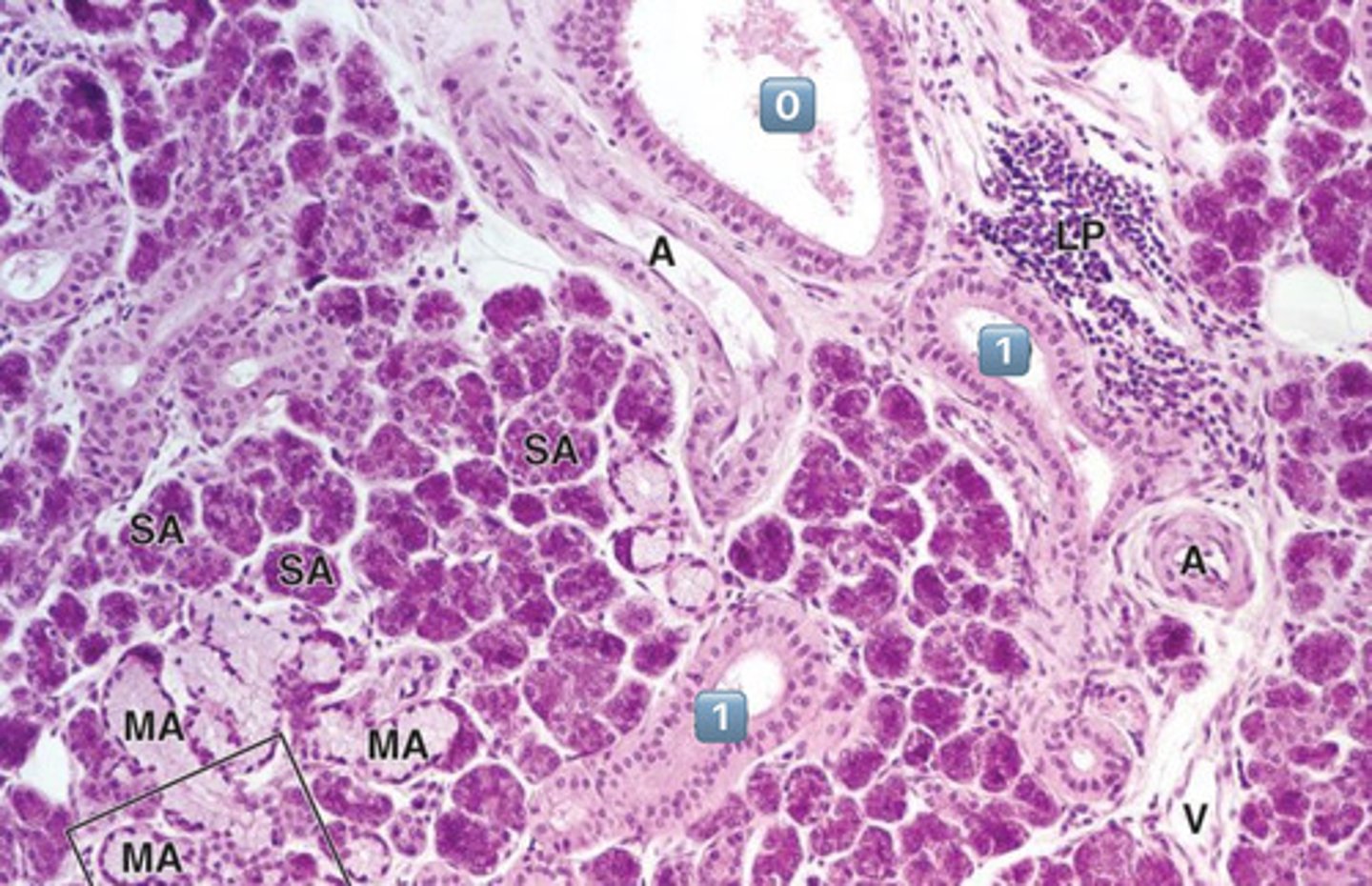
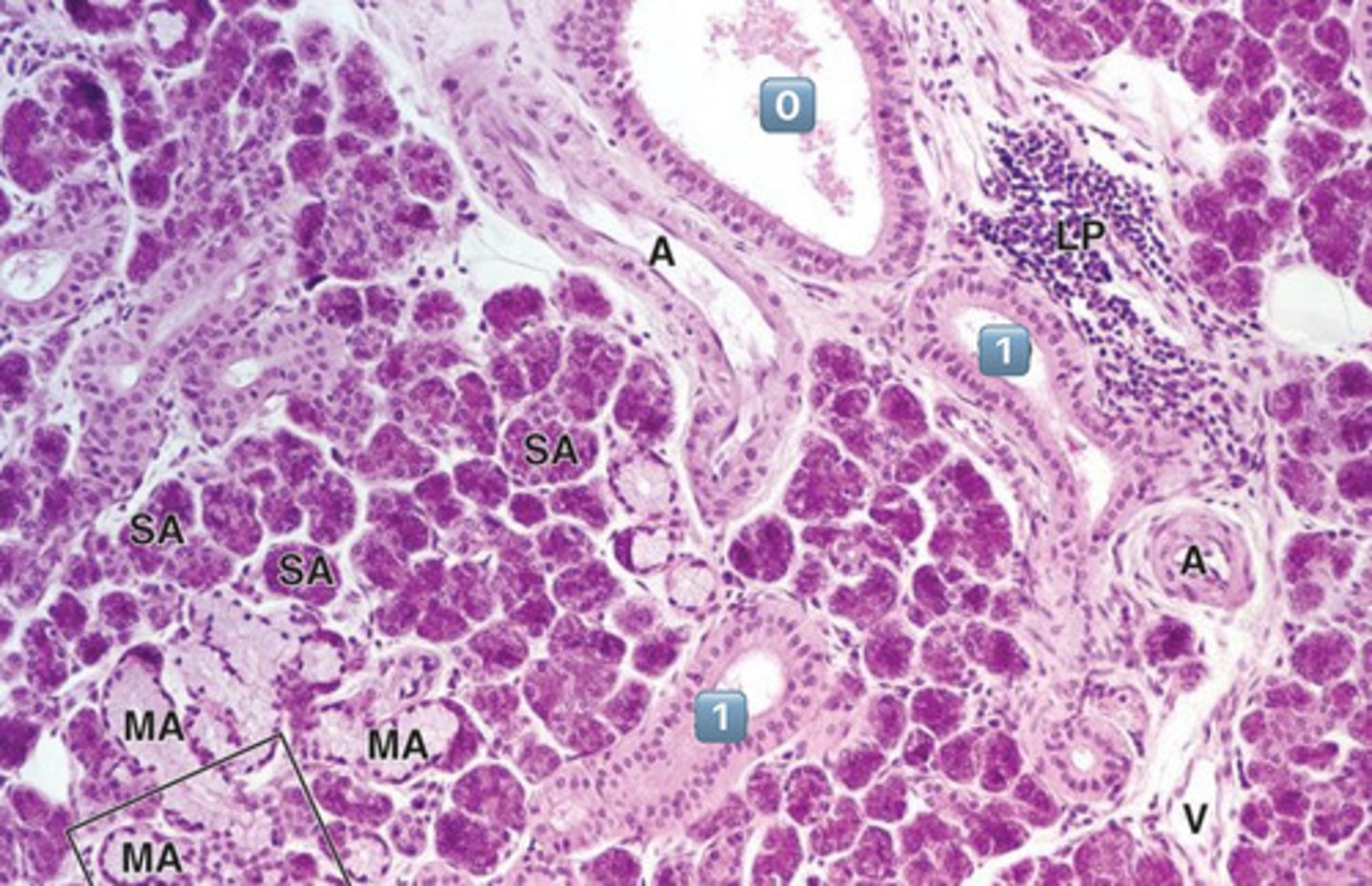
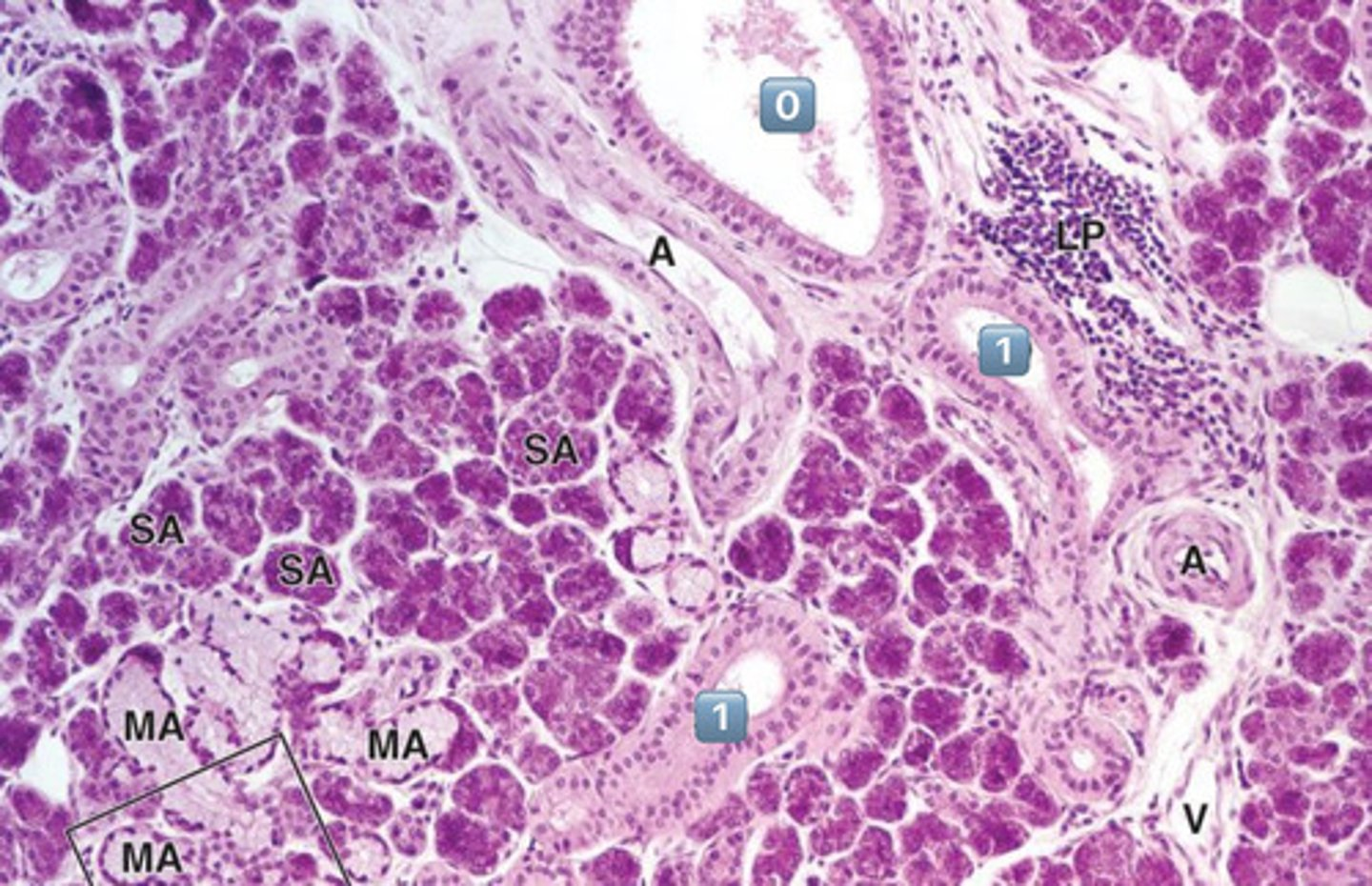
0
excretory duct
- no salivary modification happens here
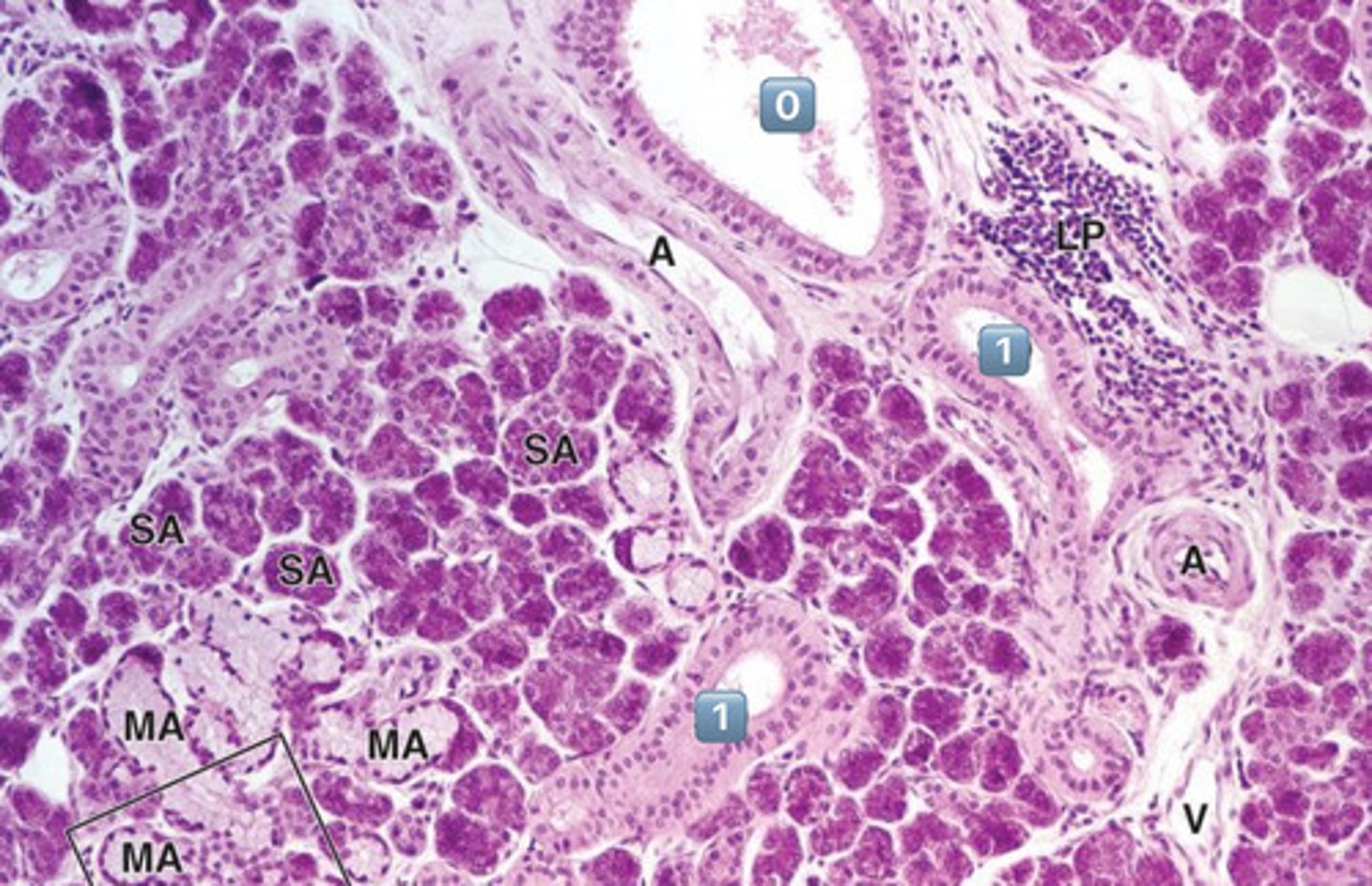
what epithelium is found in the location labeled "0"?
pseudostratified epithelium
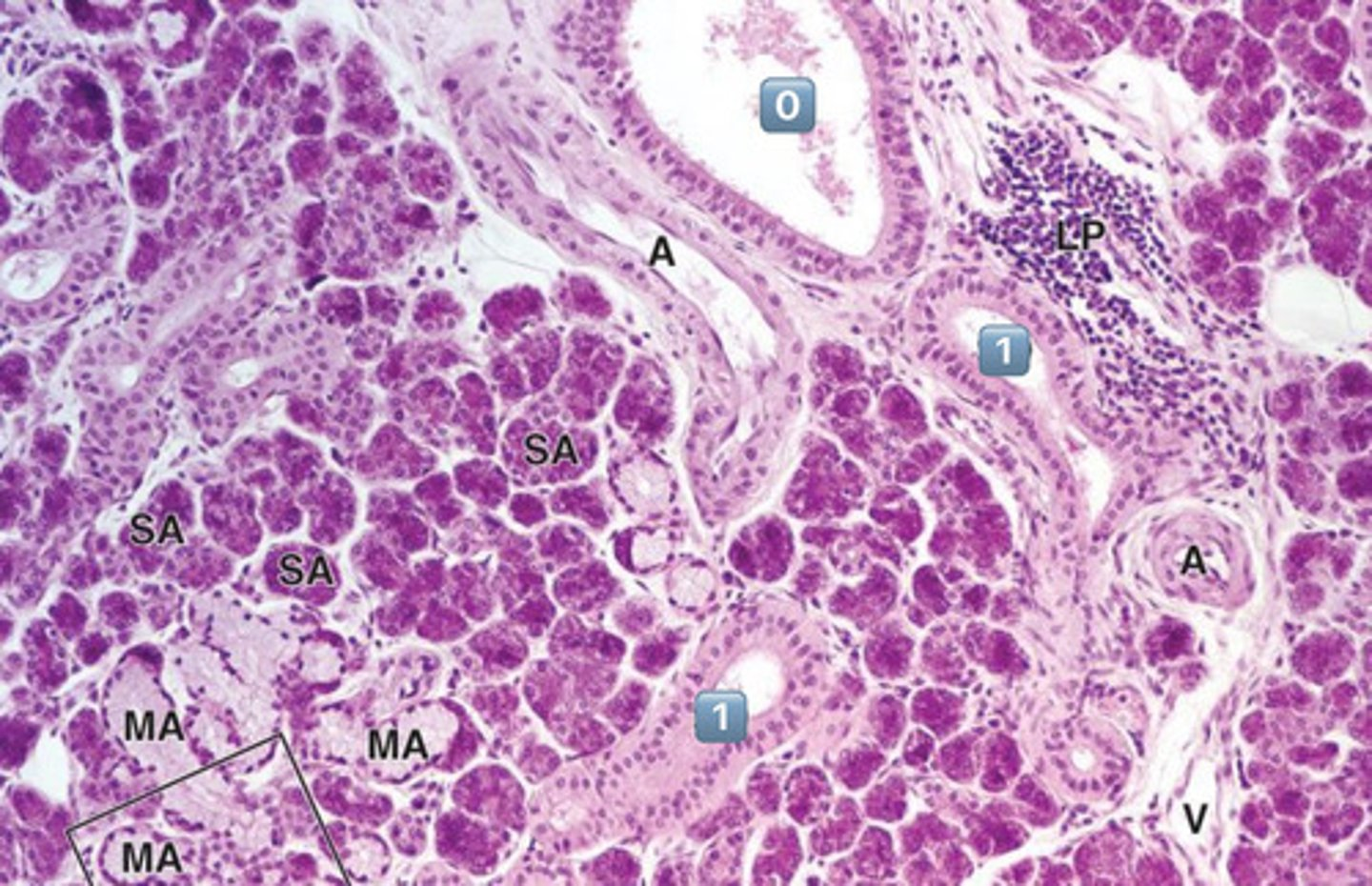
1
striated duct
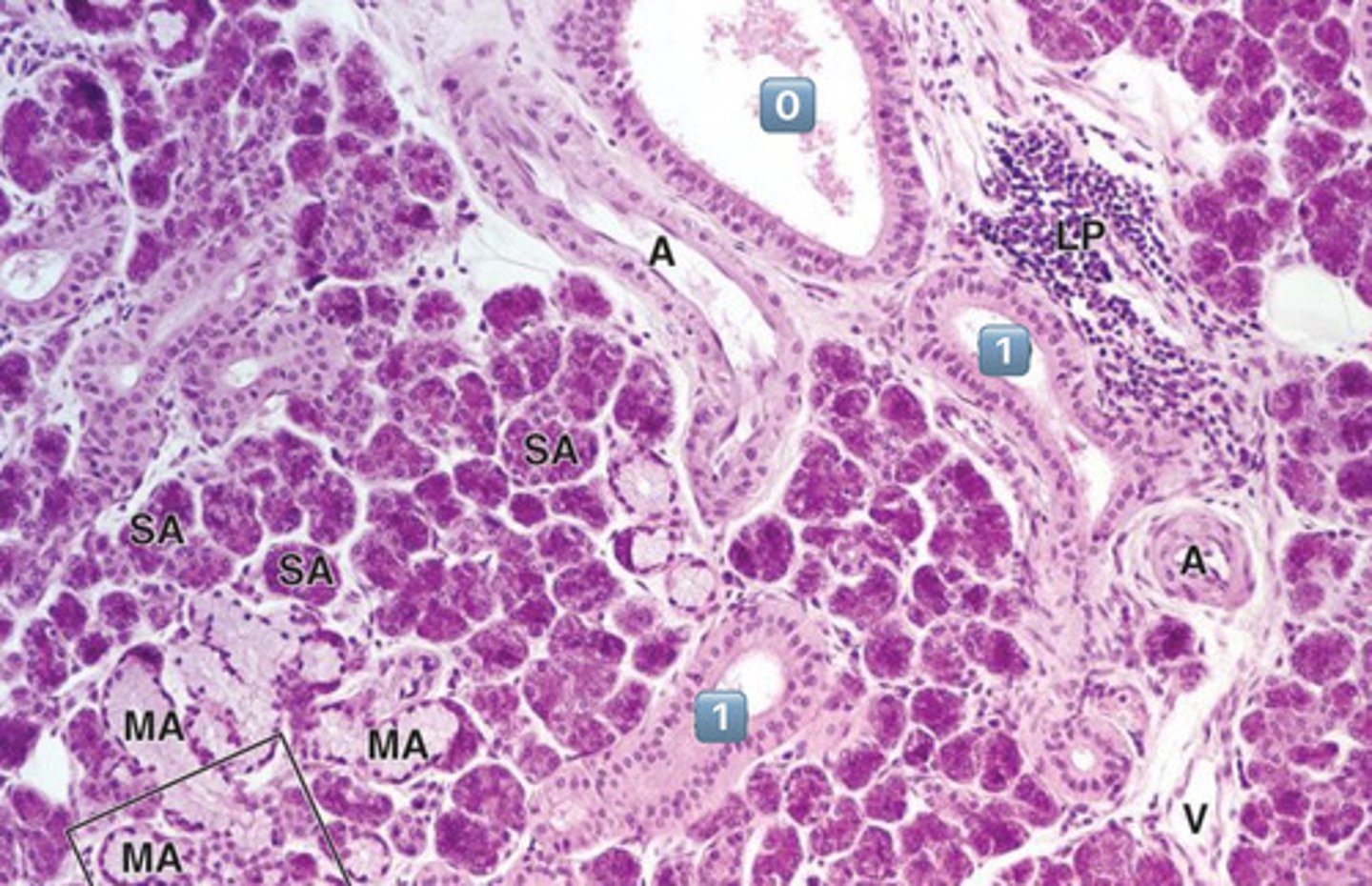
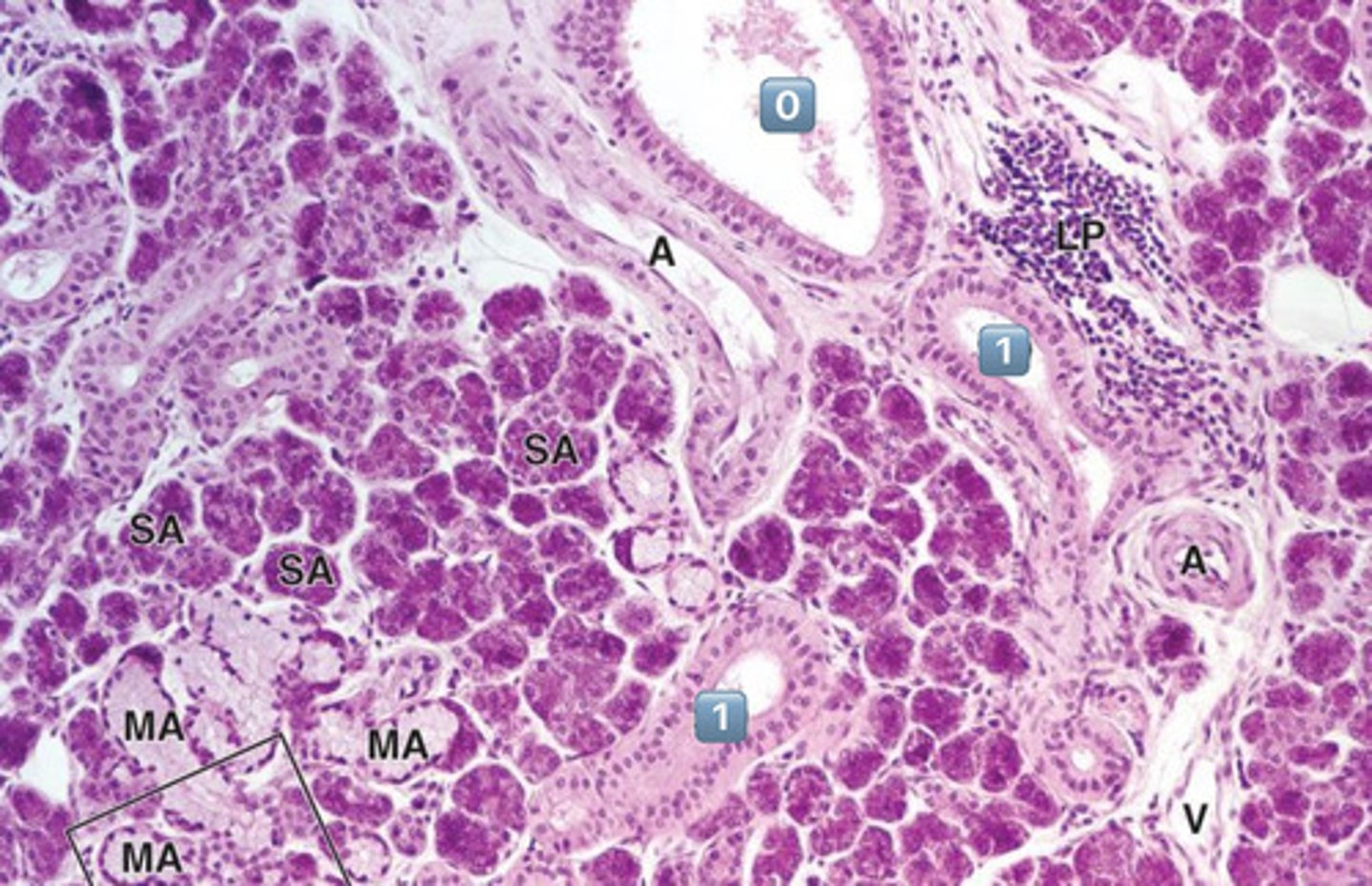
in which location, 0 or 1, do you expect salivary modification to occur?
1
- 1 is a striated duct
- 0 is an excretory duct, NO modification occurs here
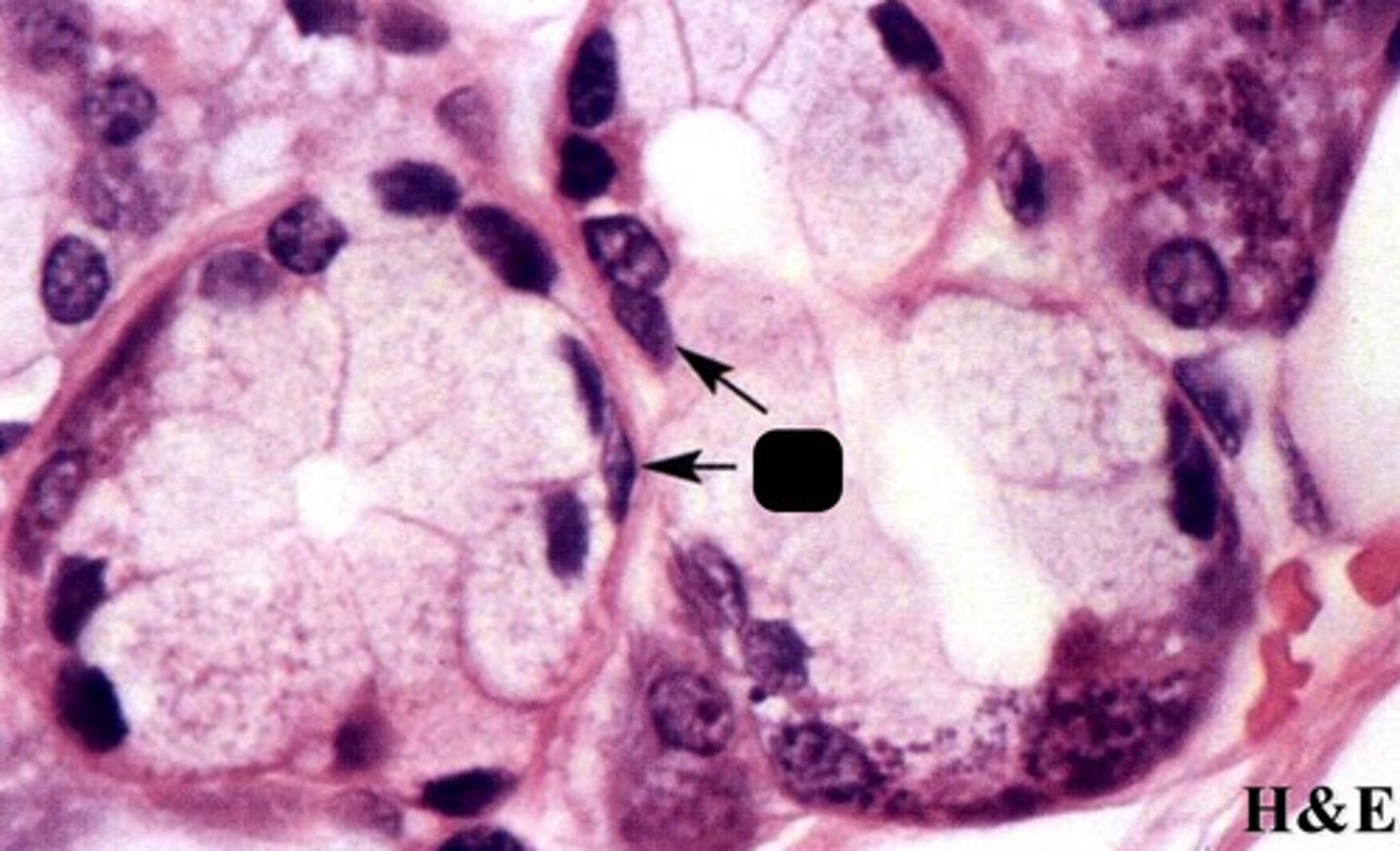
?
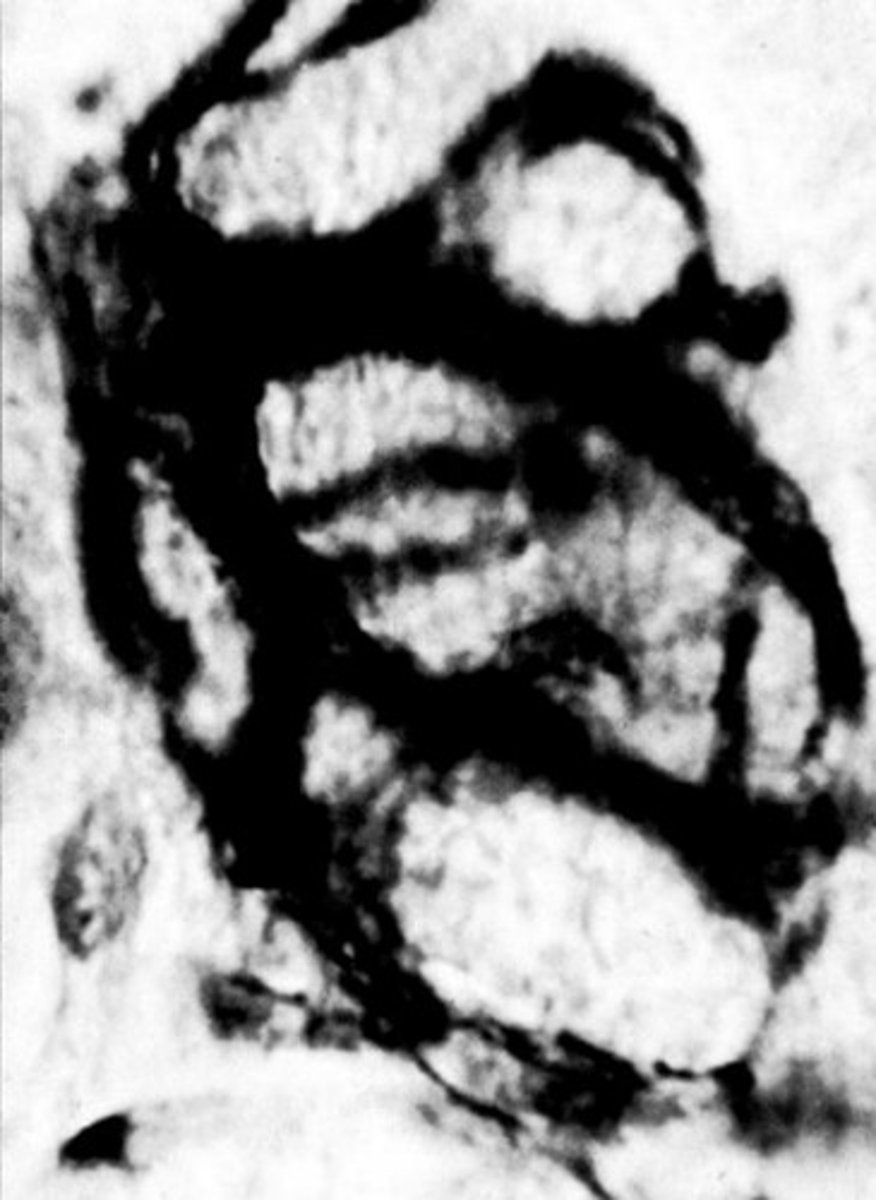
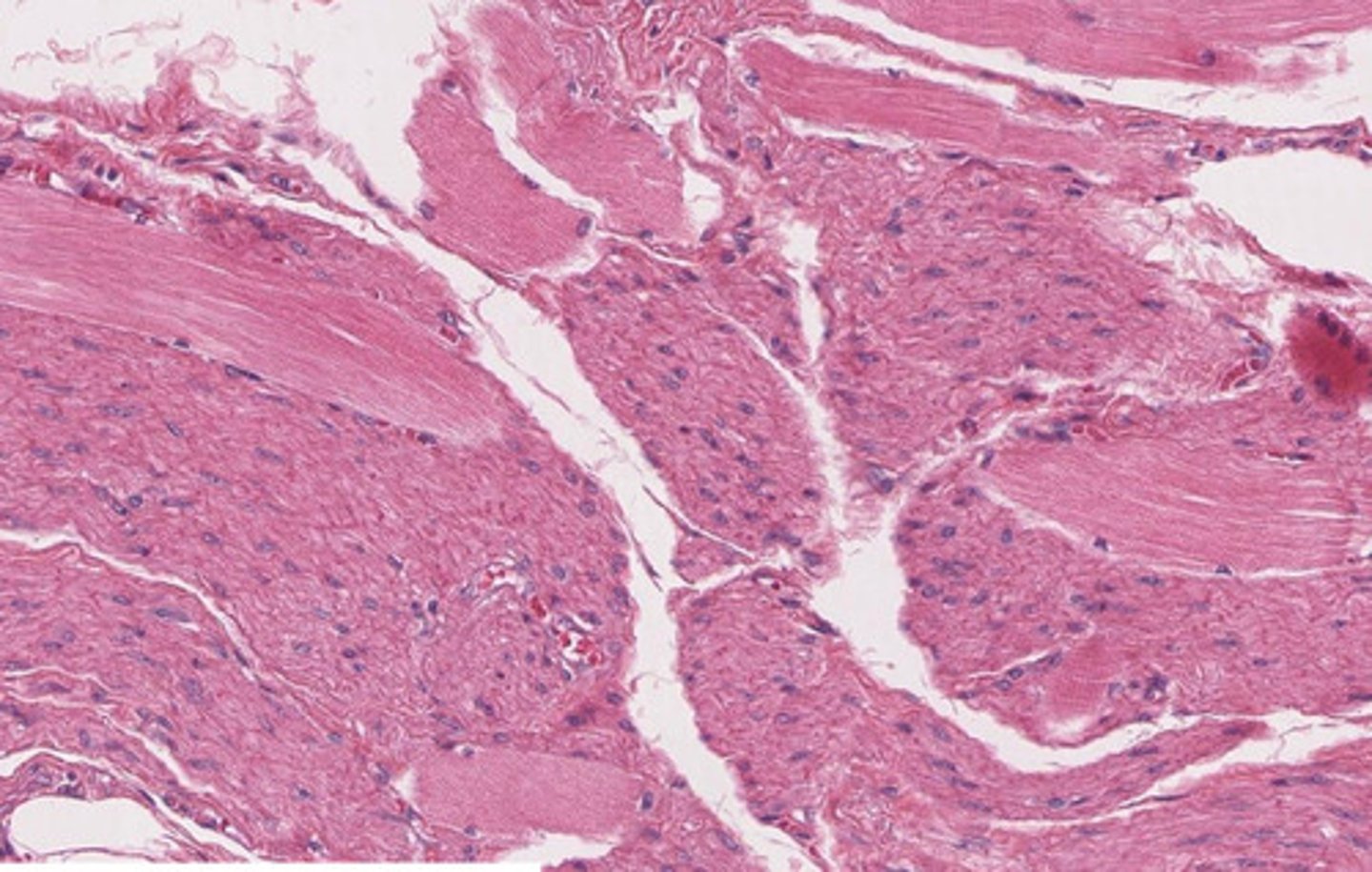
myoepithelial cells in salivary glands
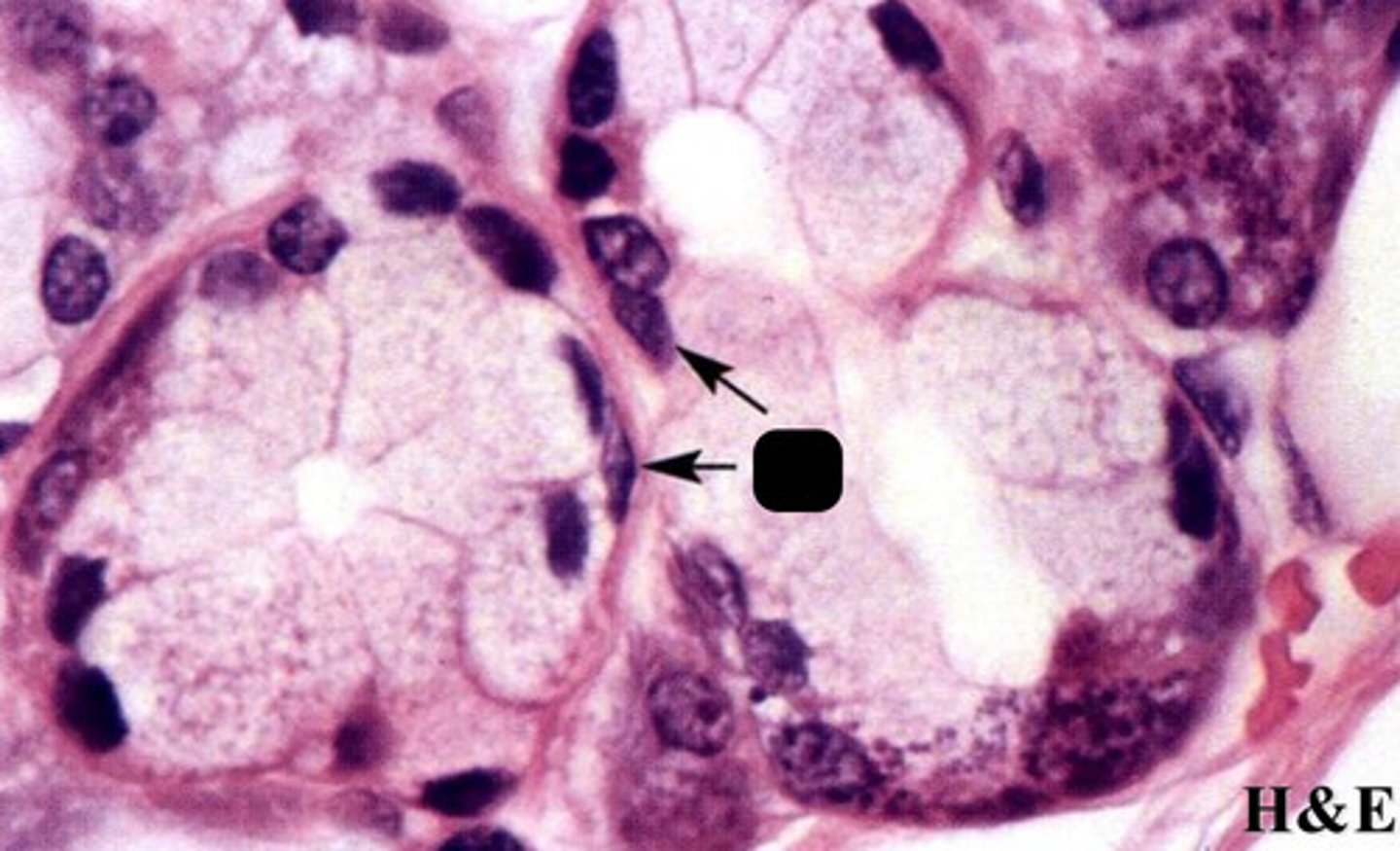
?
myoepithelial basket cell
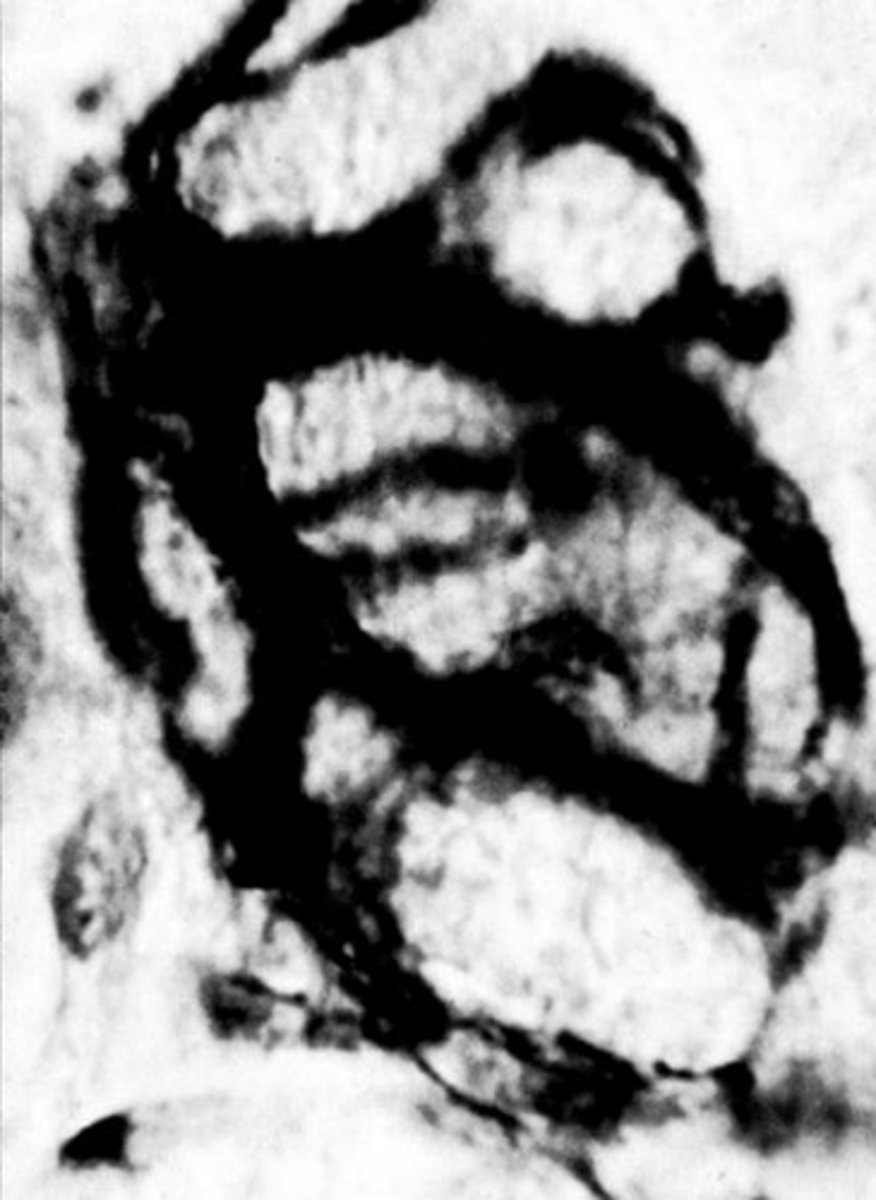
?
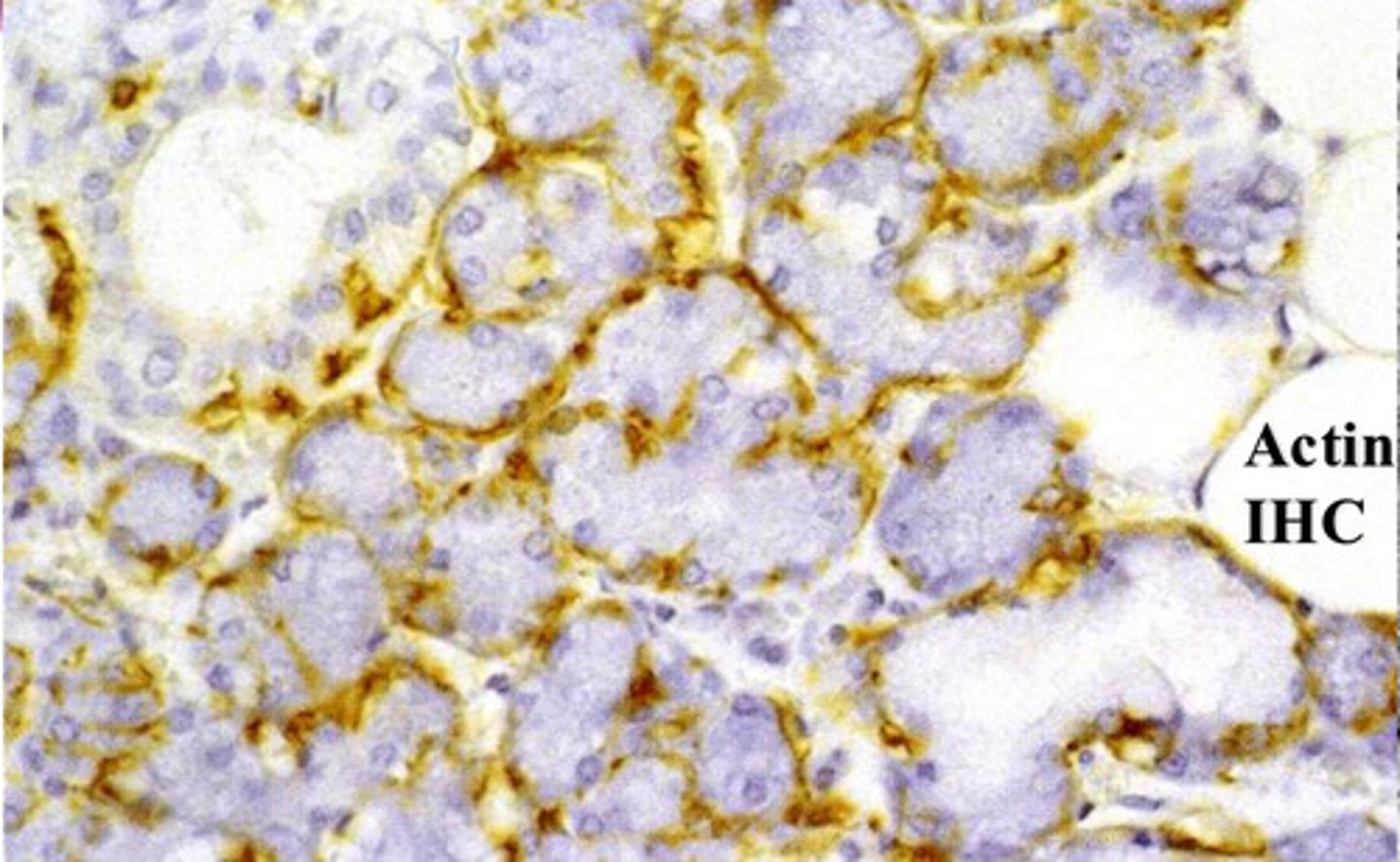
myoepithelial cells seen with Actin IHC staining
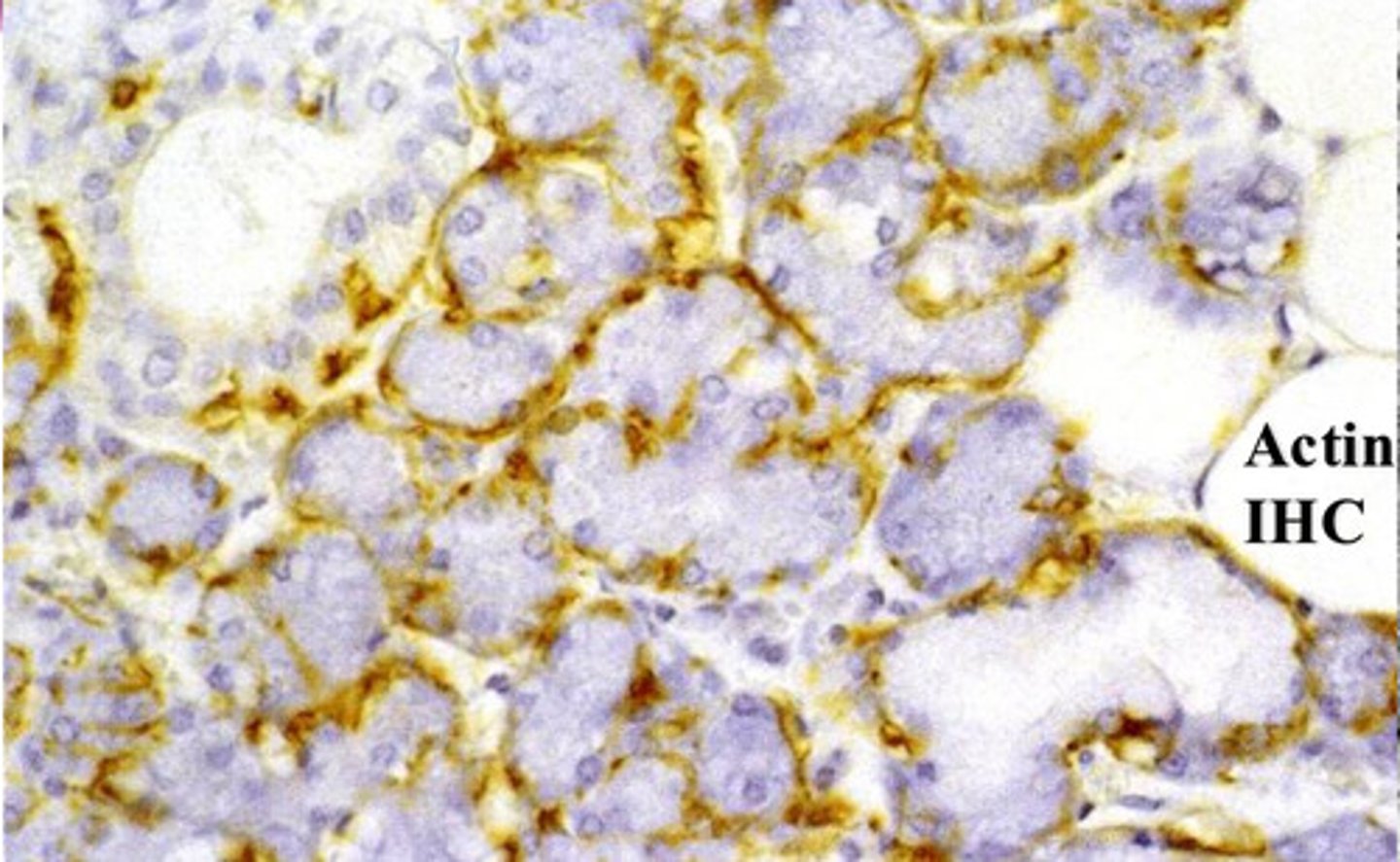
?
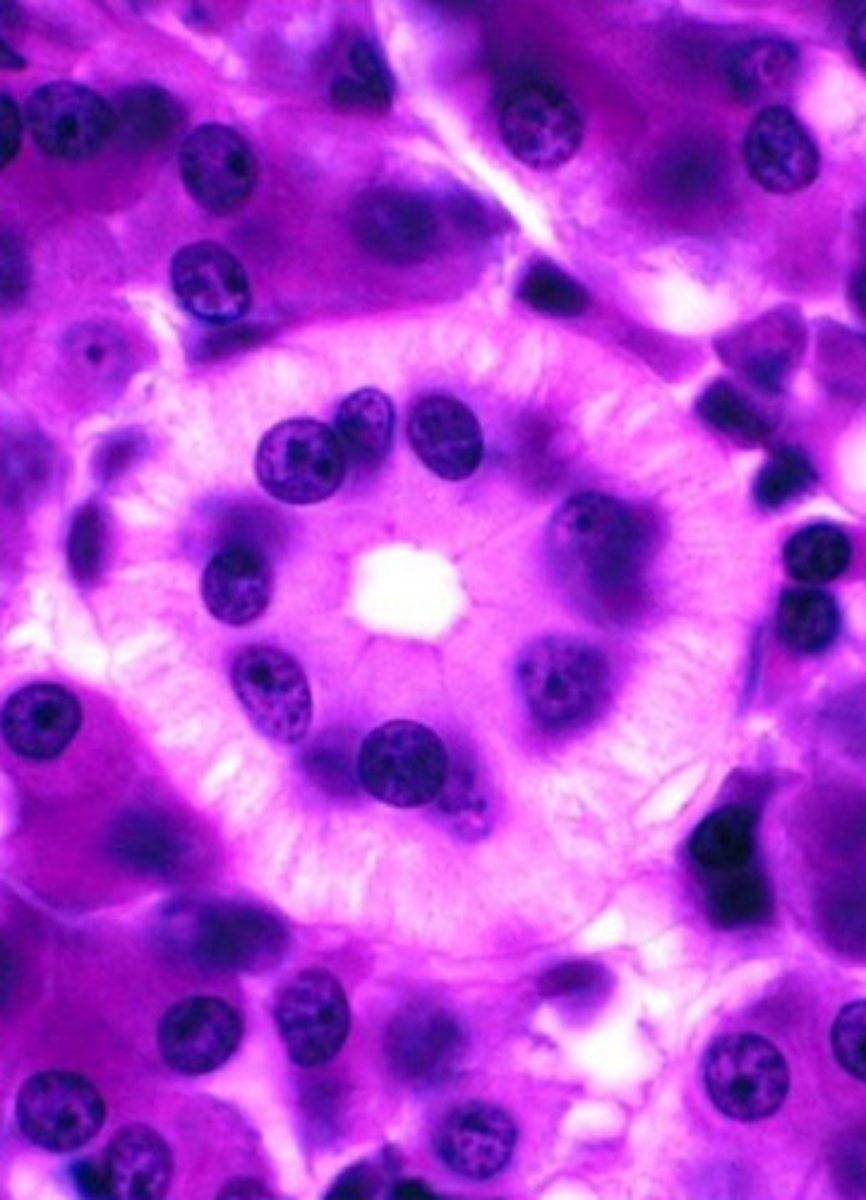
striated duct
note:
- striations (infolding of basement membrane with mitochondria in between)
- perfectly round nuclei pushed apically
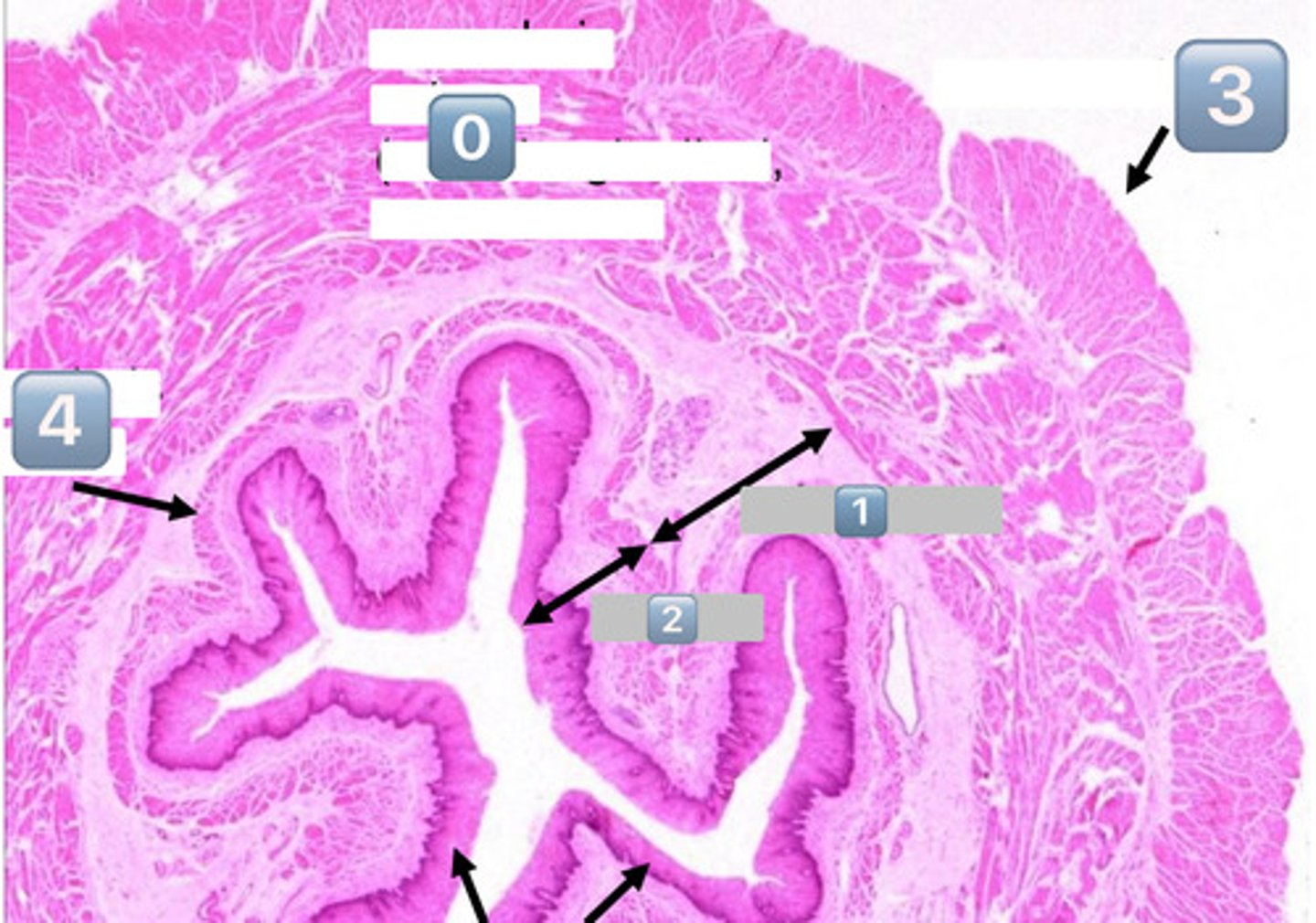
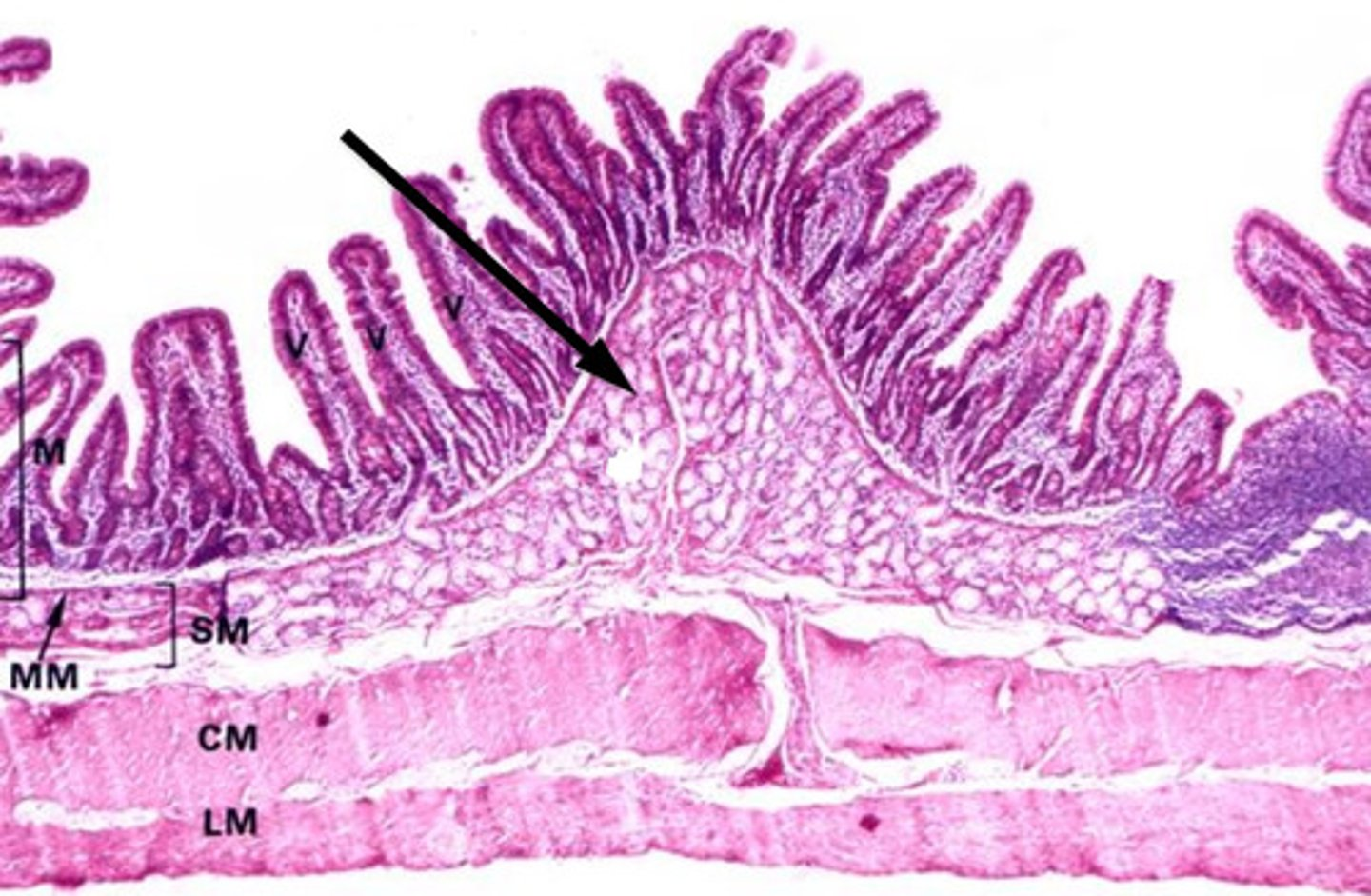
0
muscularis externa (outer longitudinal, inner circular)
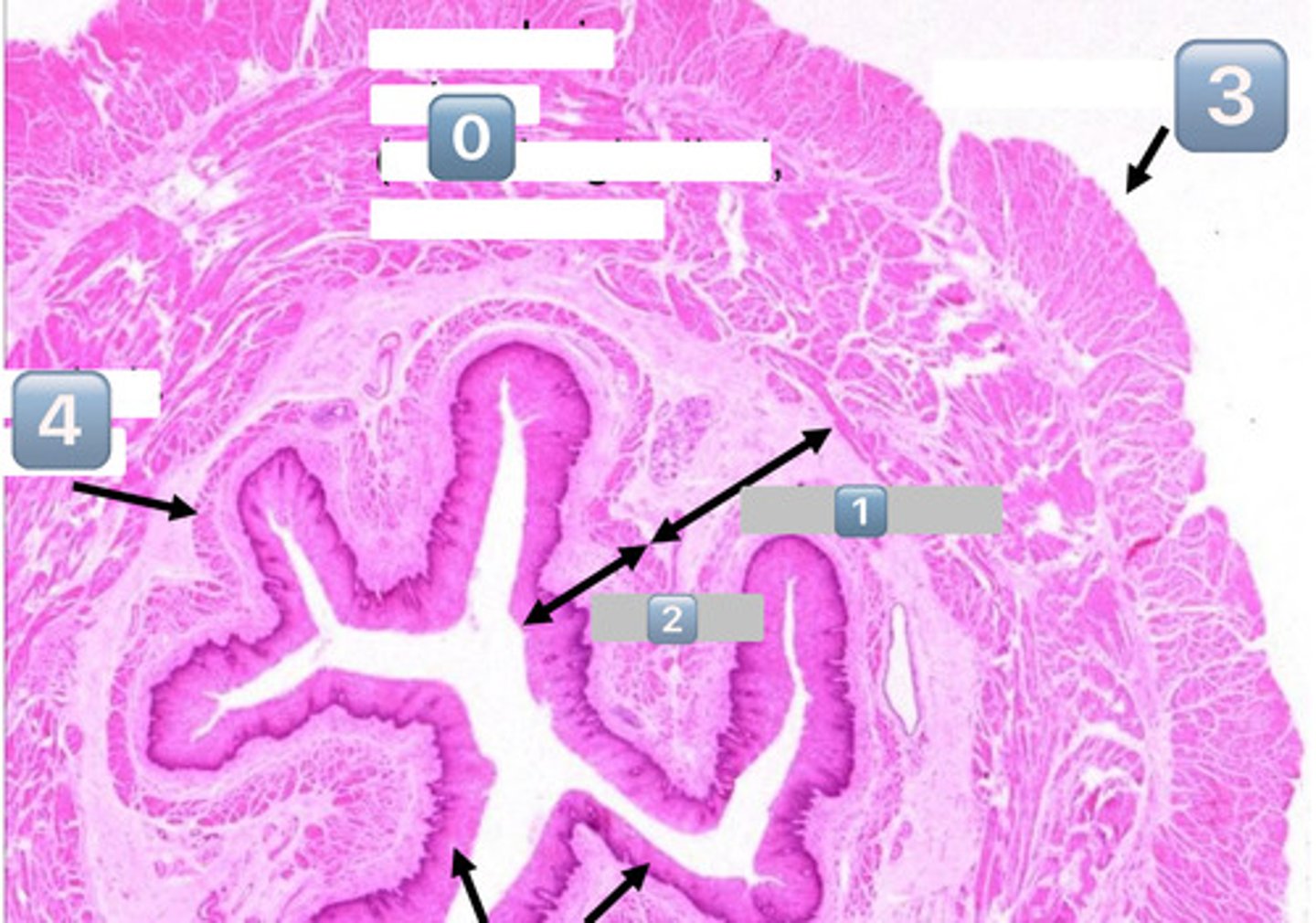
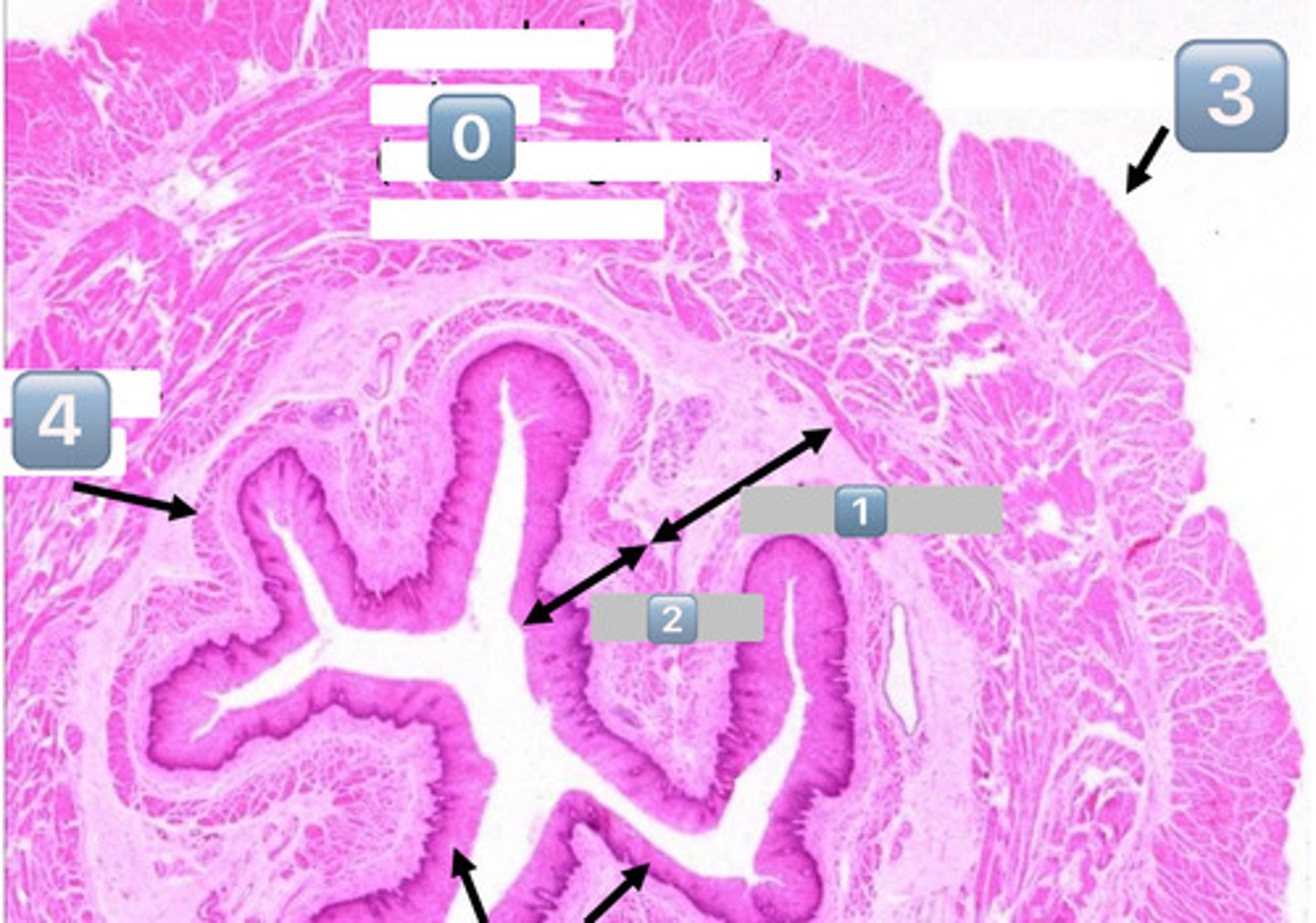
1
submucosa
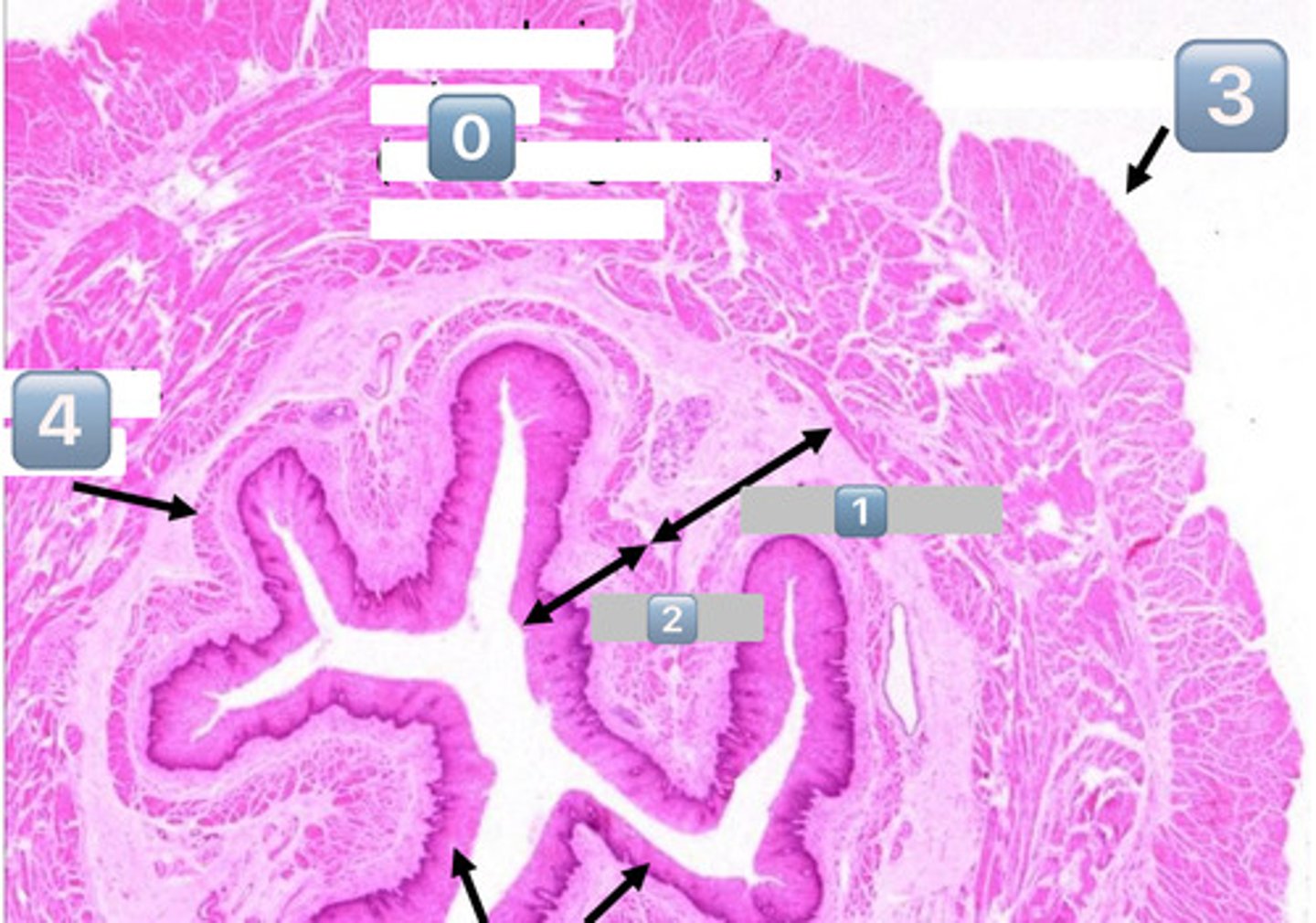
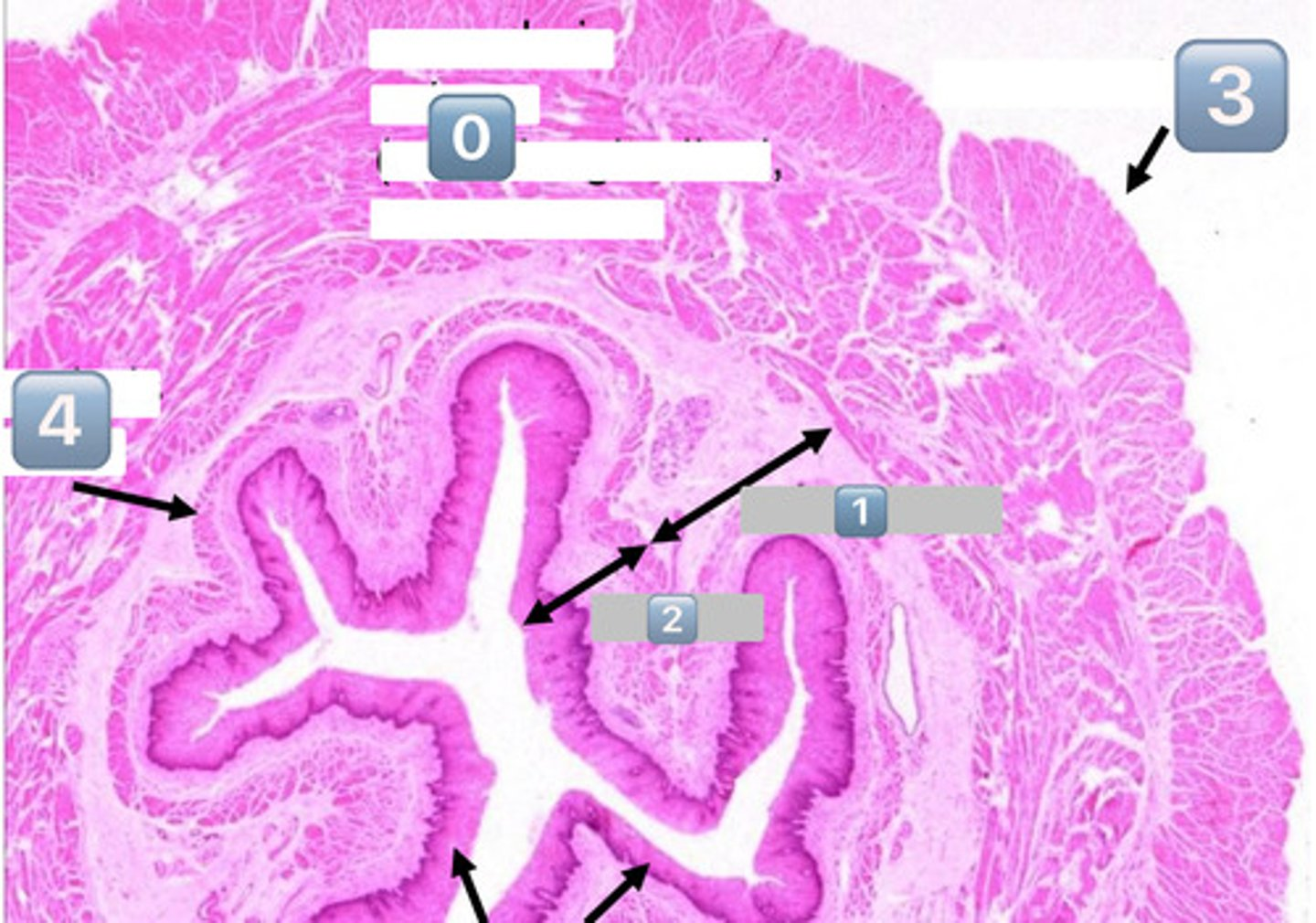
2
mucosa
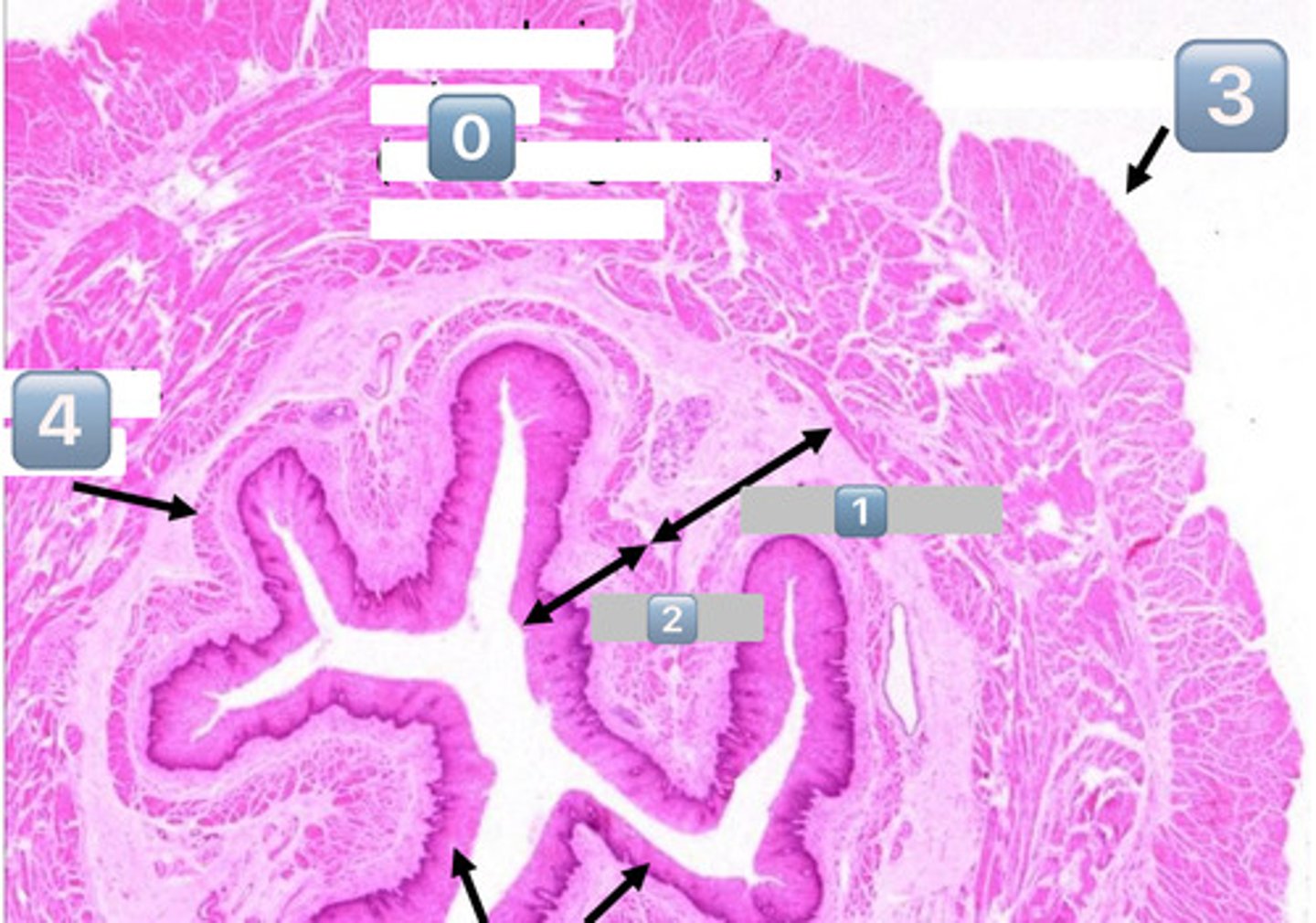
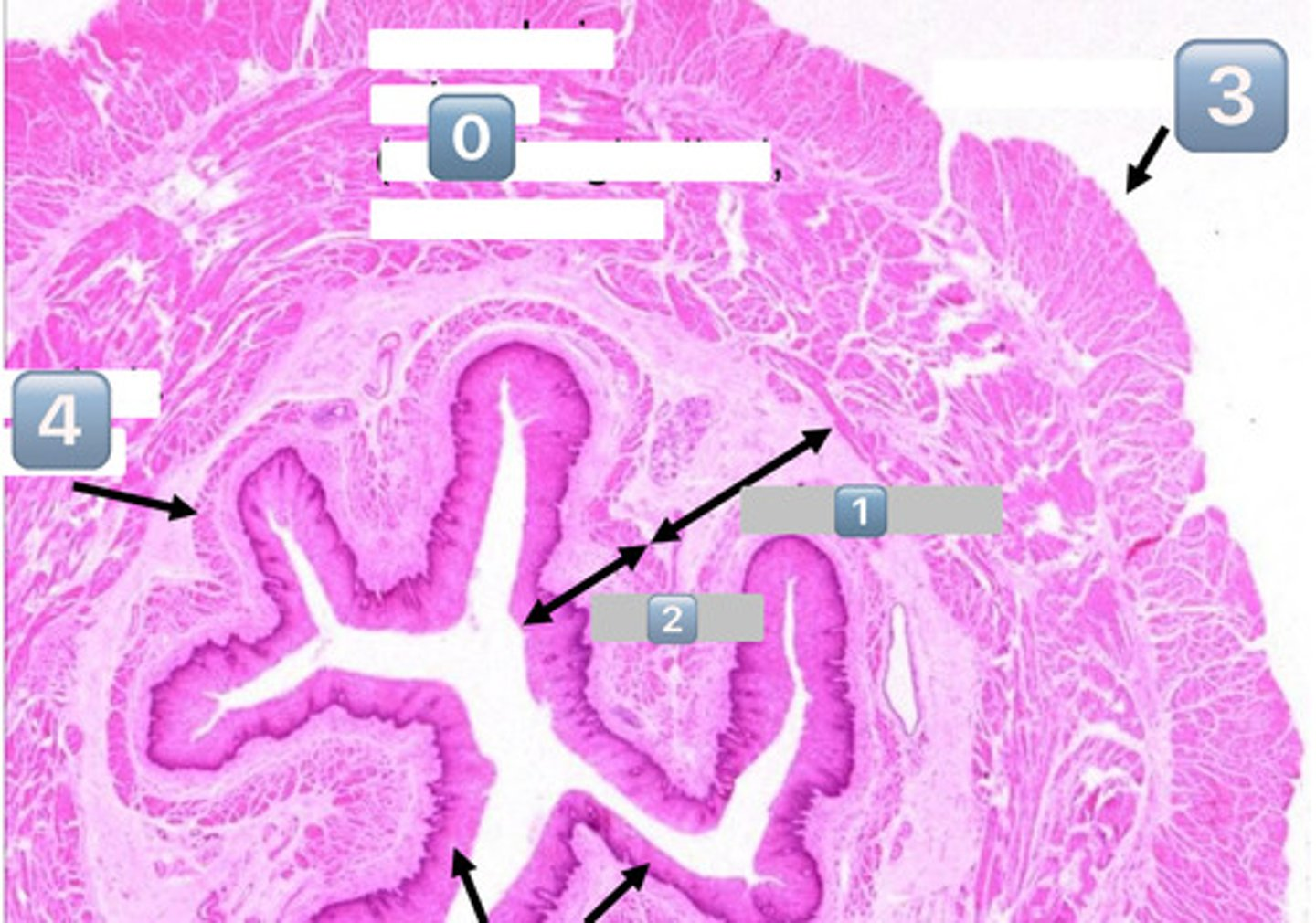
3
adventitia/serosa
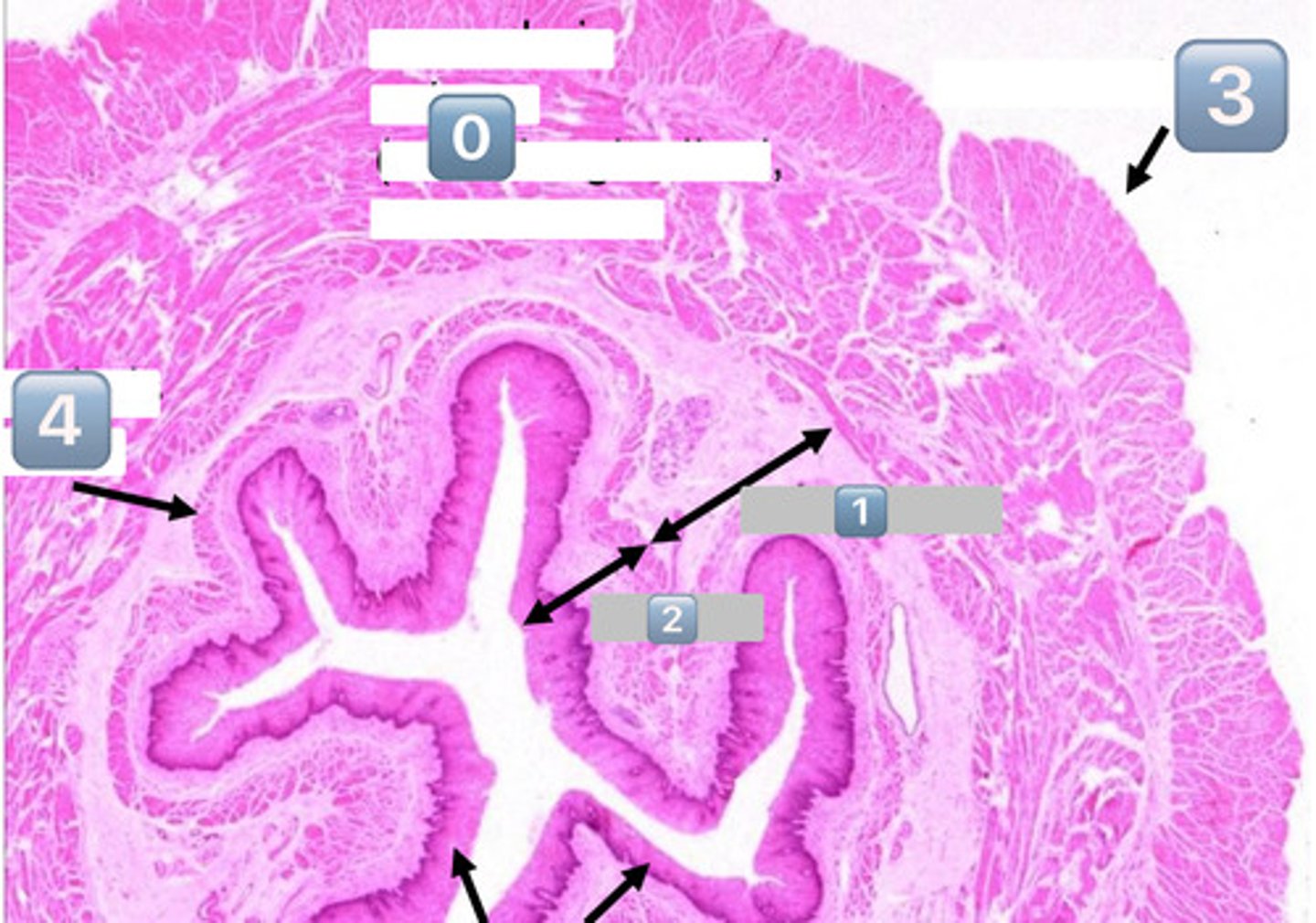
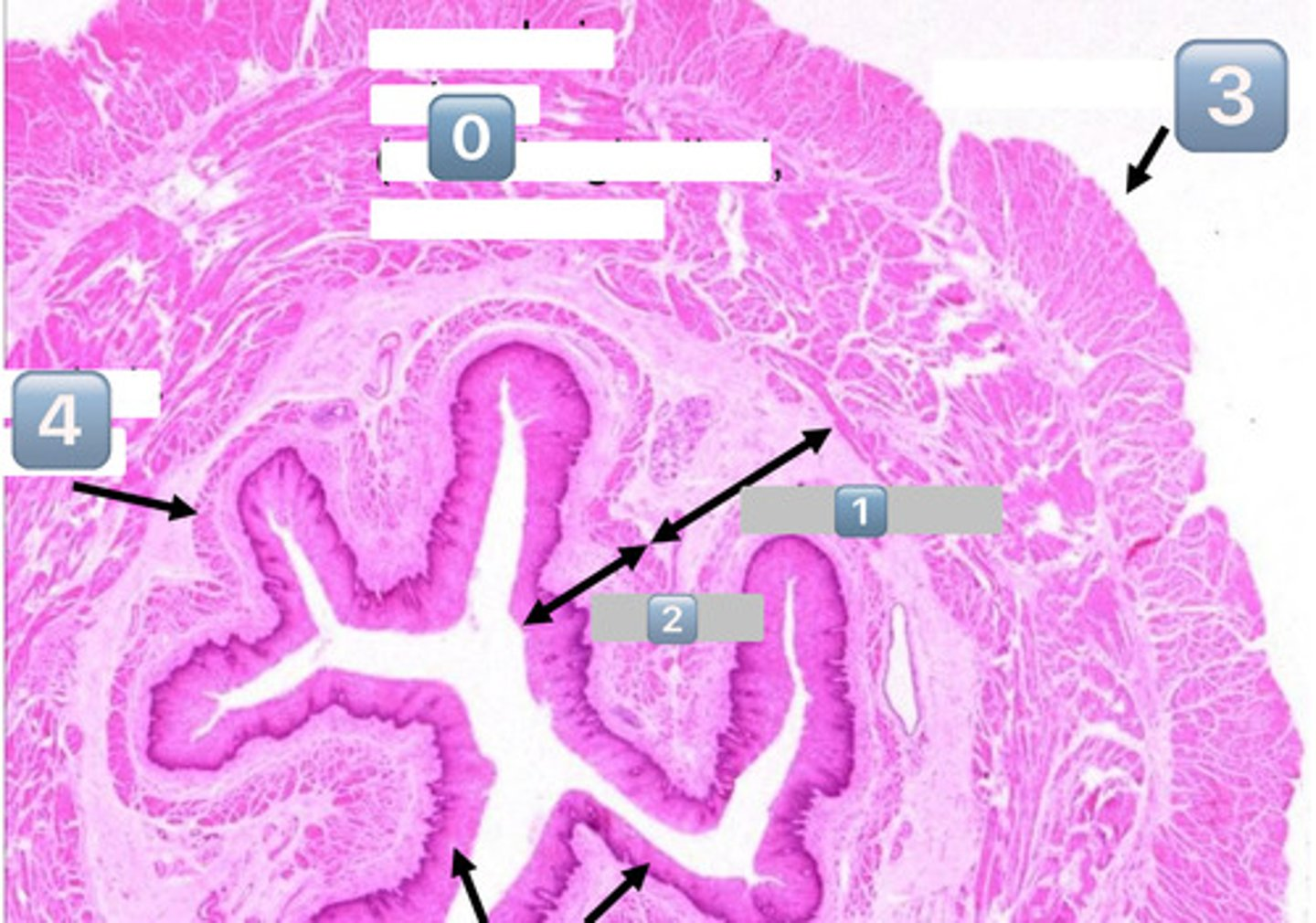
4
muscularis mucosae
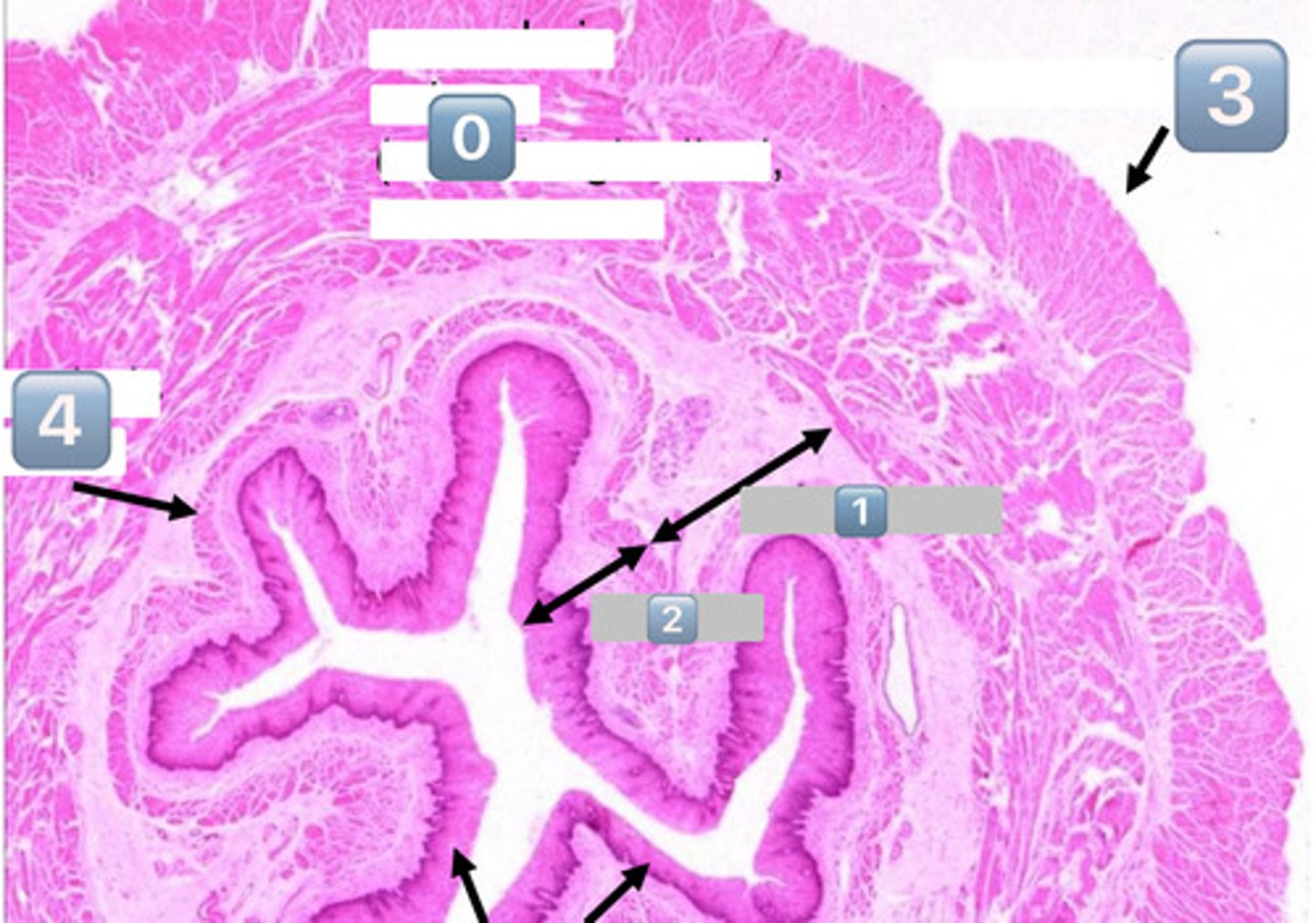
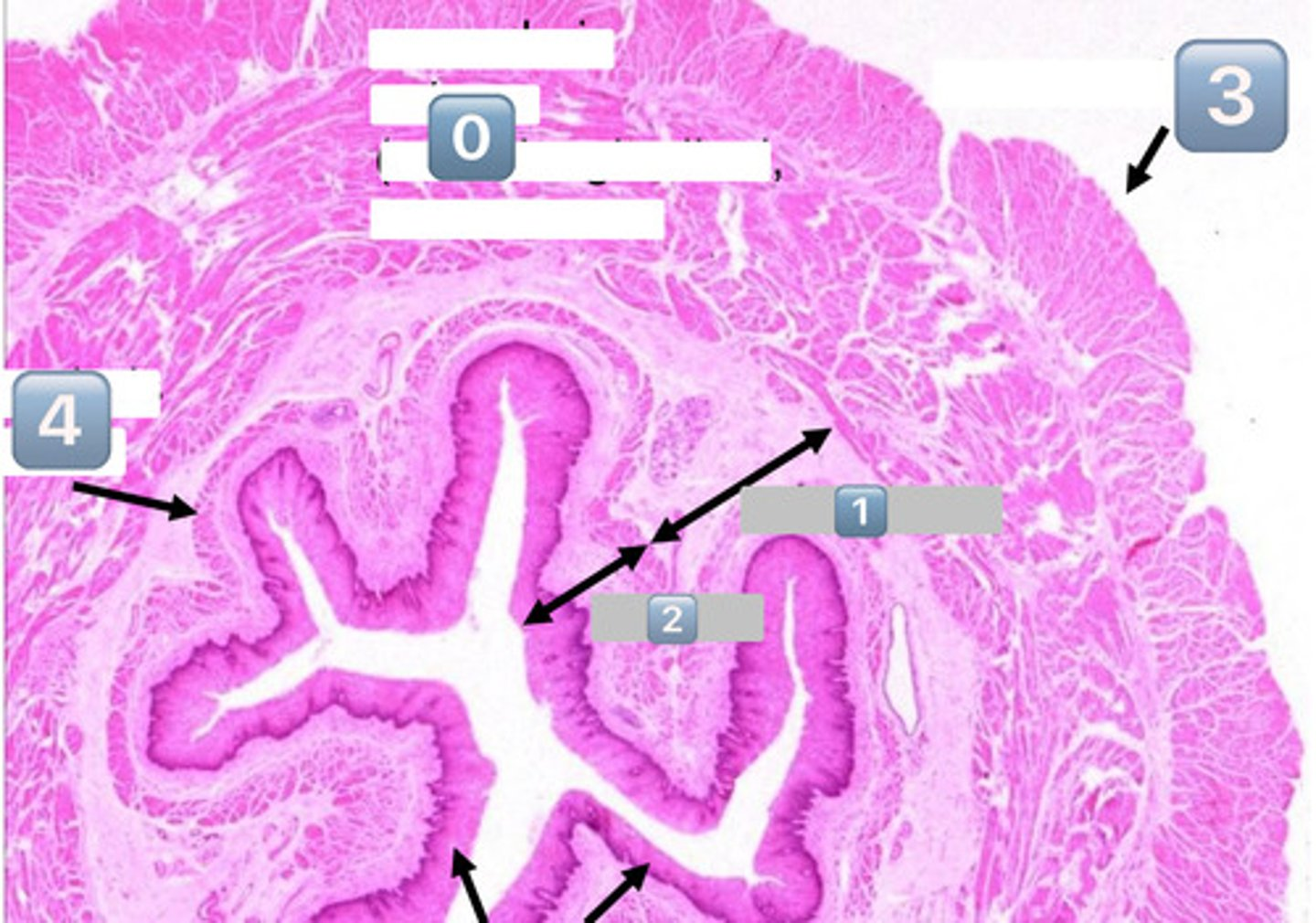
black arrows (at the bottom)?
lining epithelium (SSNKE)
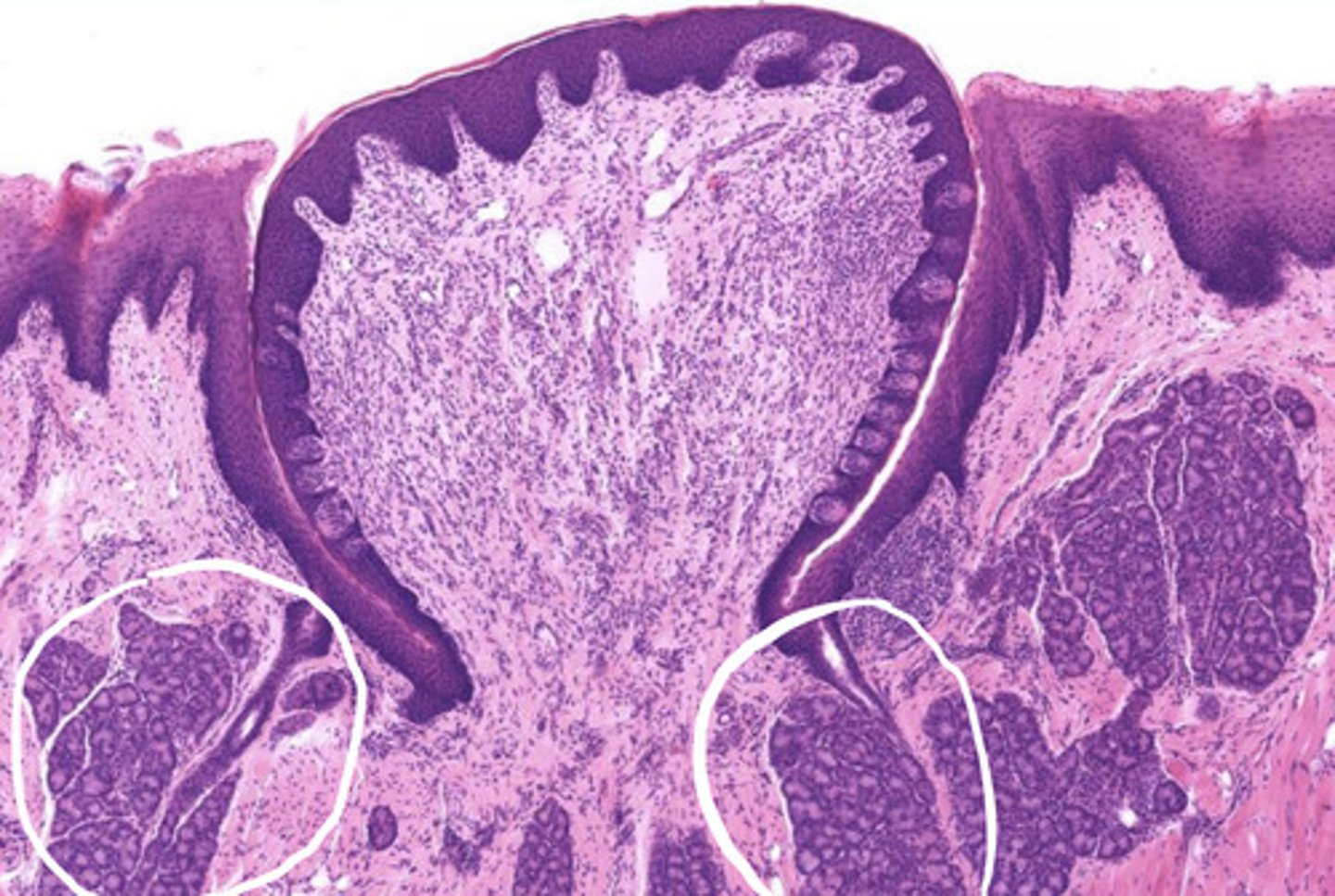
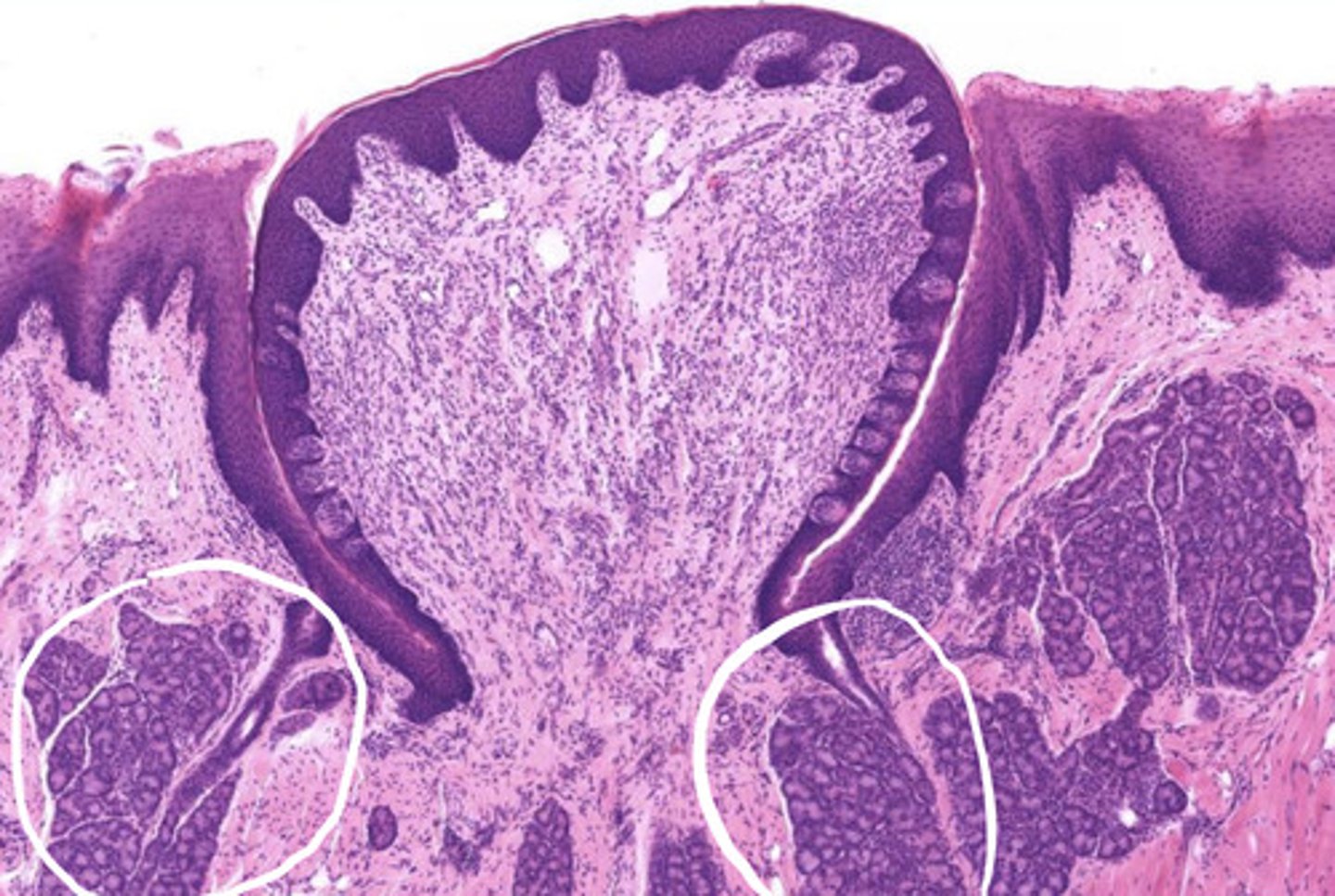
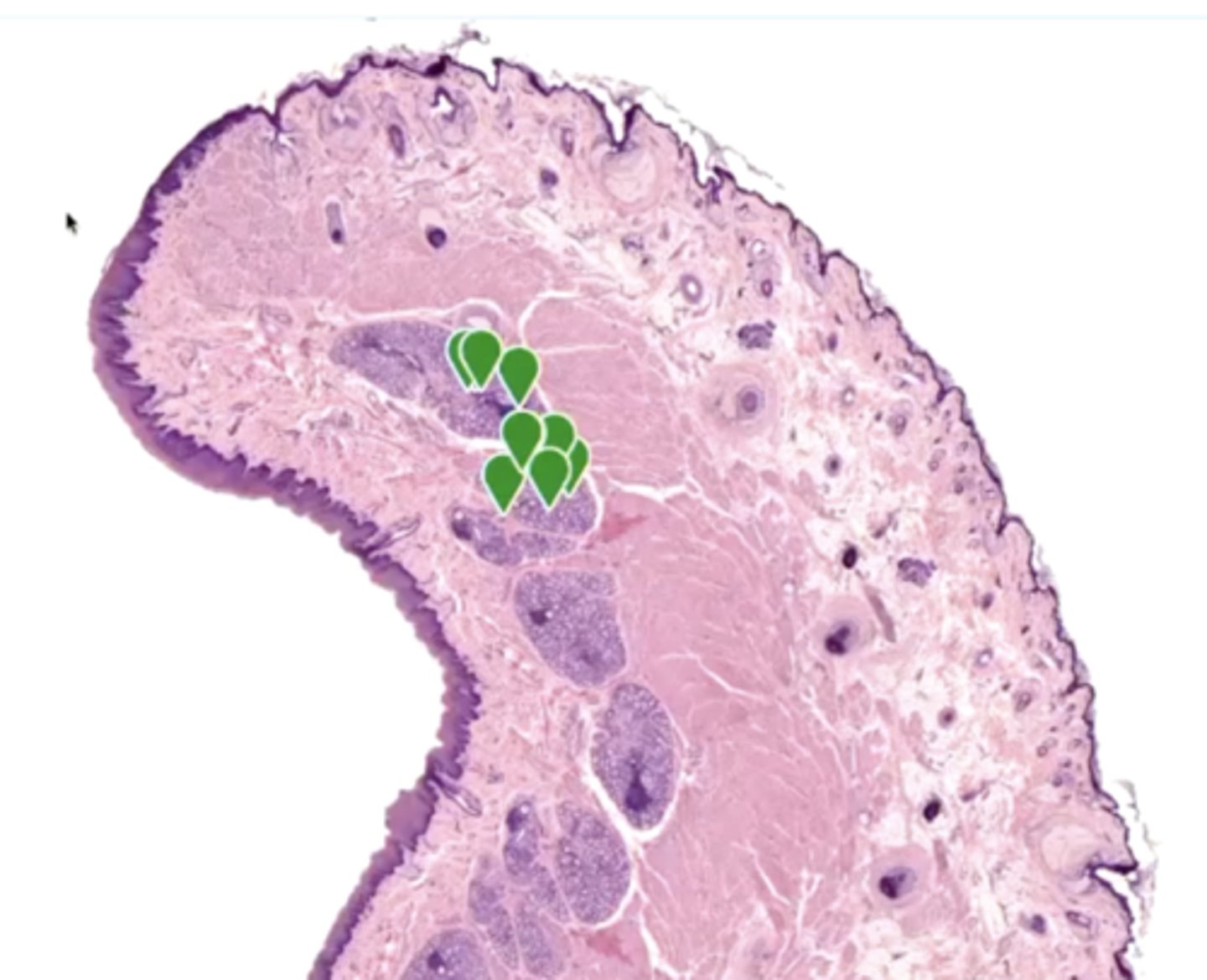
what is the function of the circled glands?
secretes watery fluid into the sulcus of the taste bud to flush it so we can taste
- these are Ebner's glands
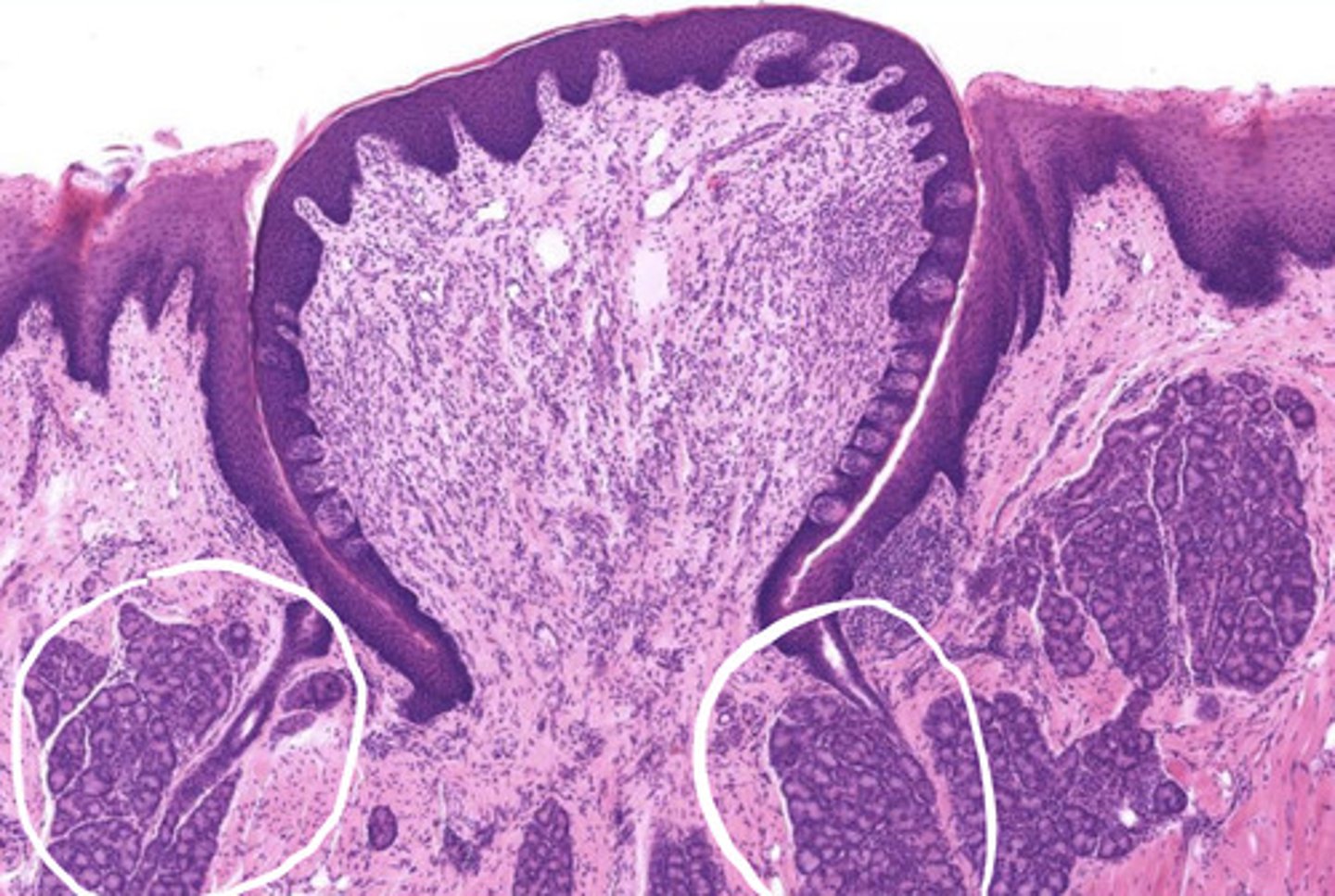
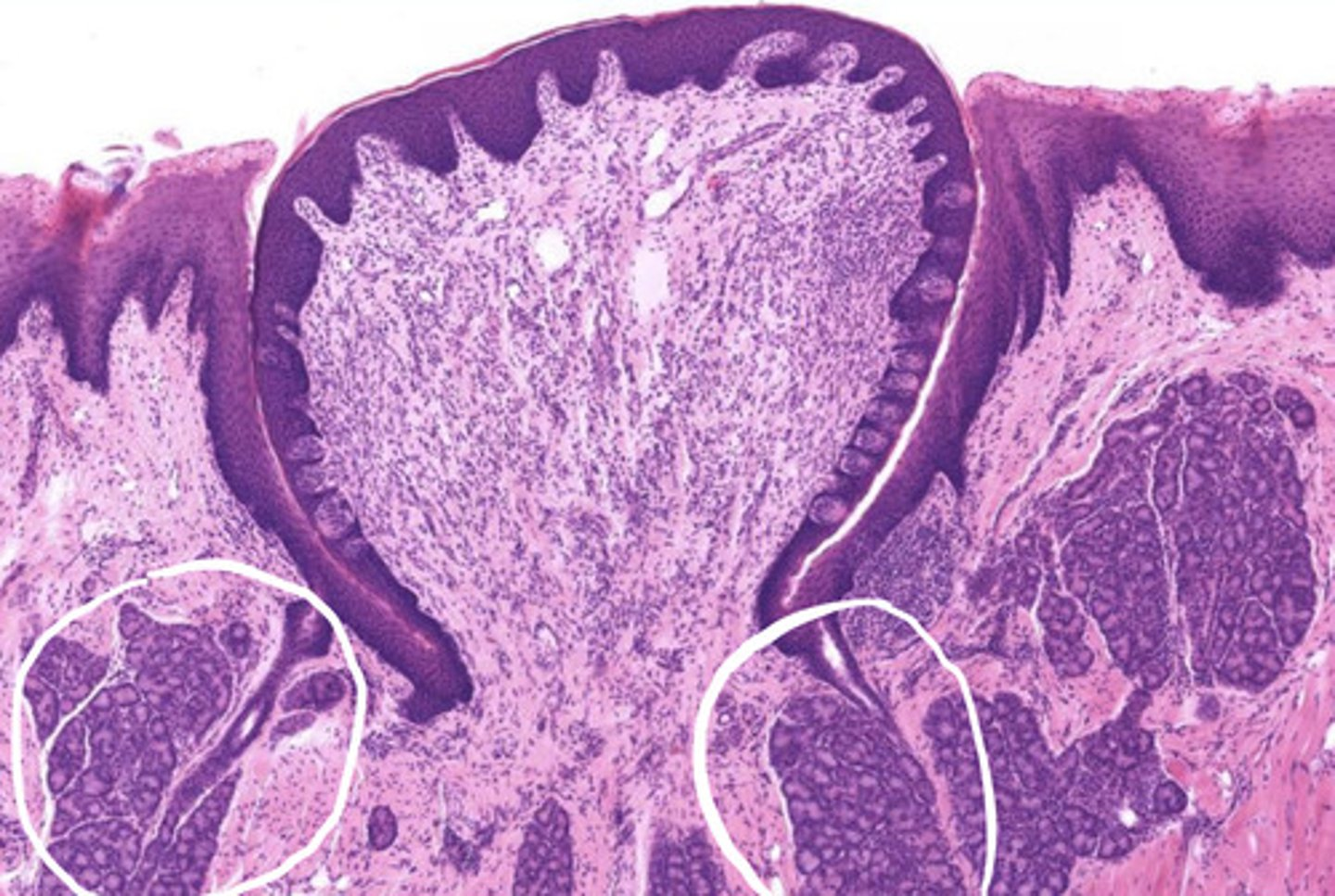
what is circled?
Ebner's glands
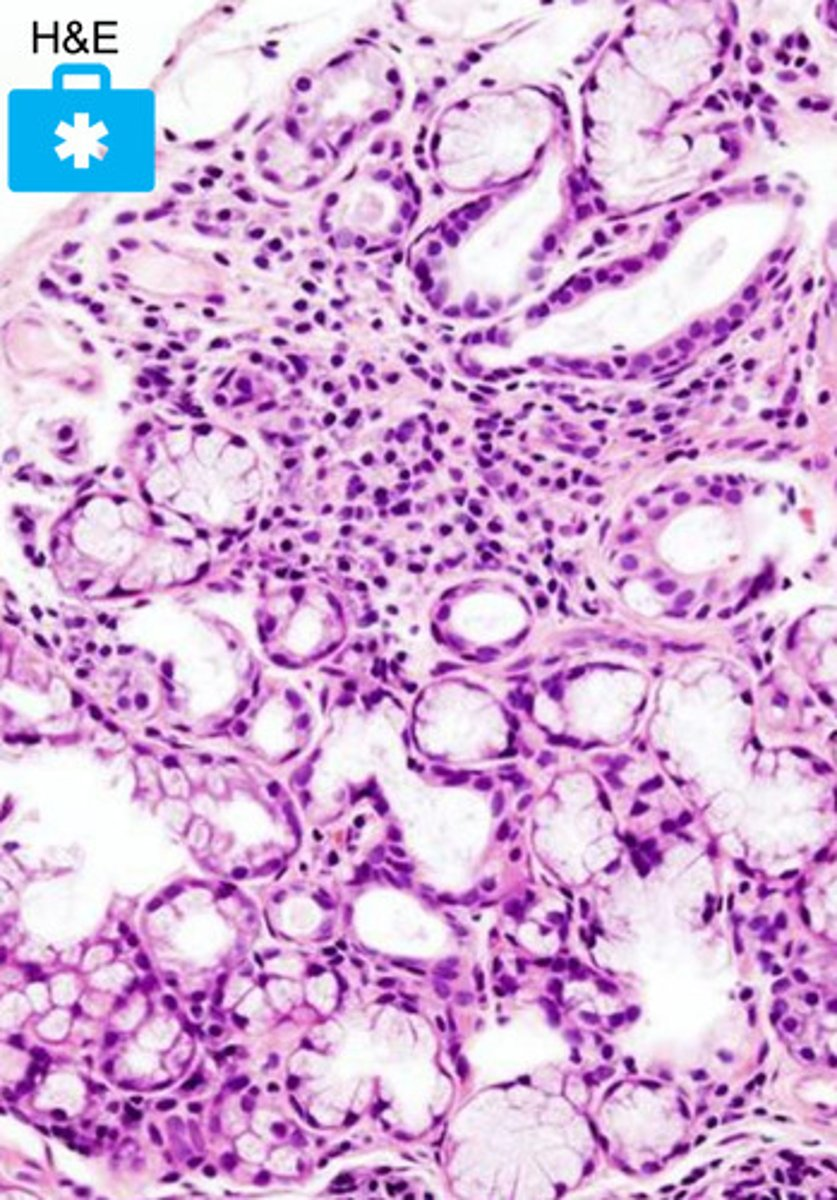
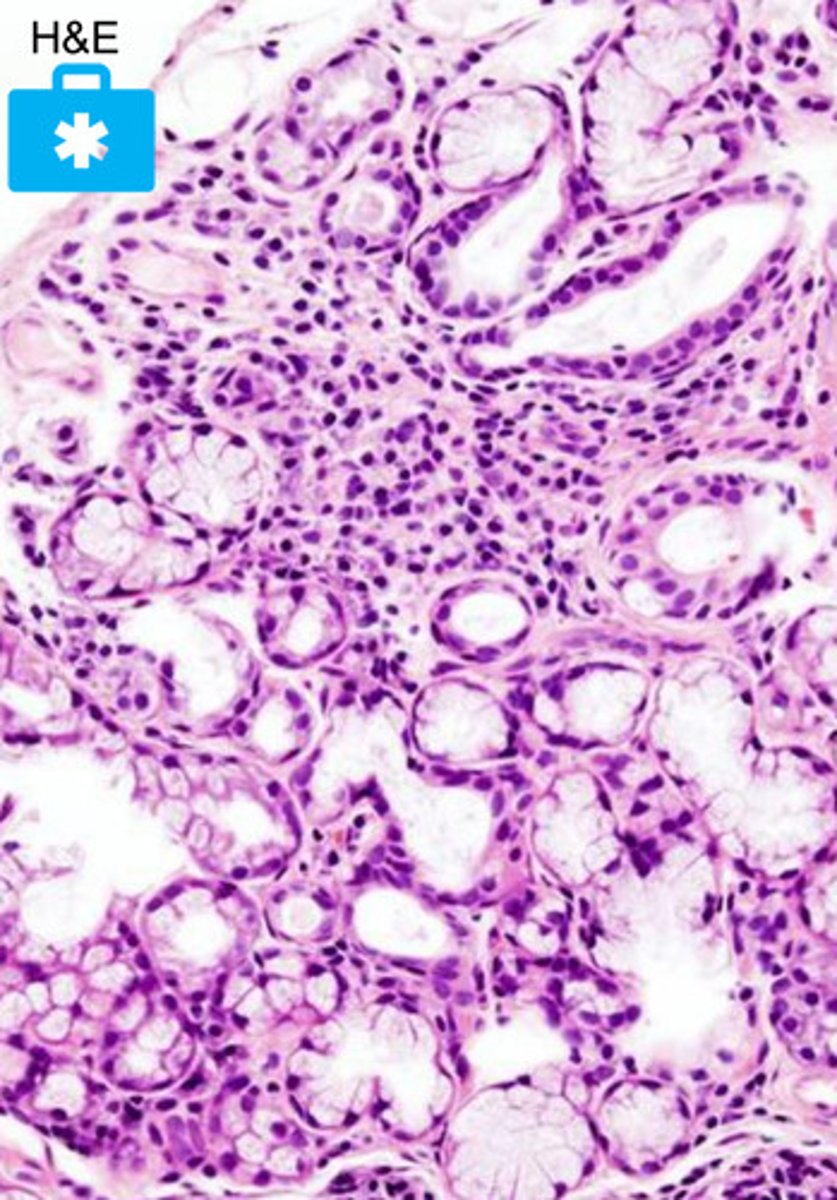
what pathology is pictured here?
Sjogren's syndrome
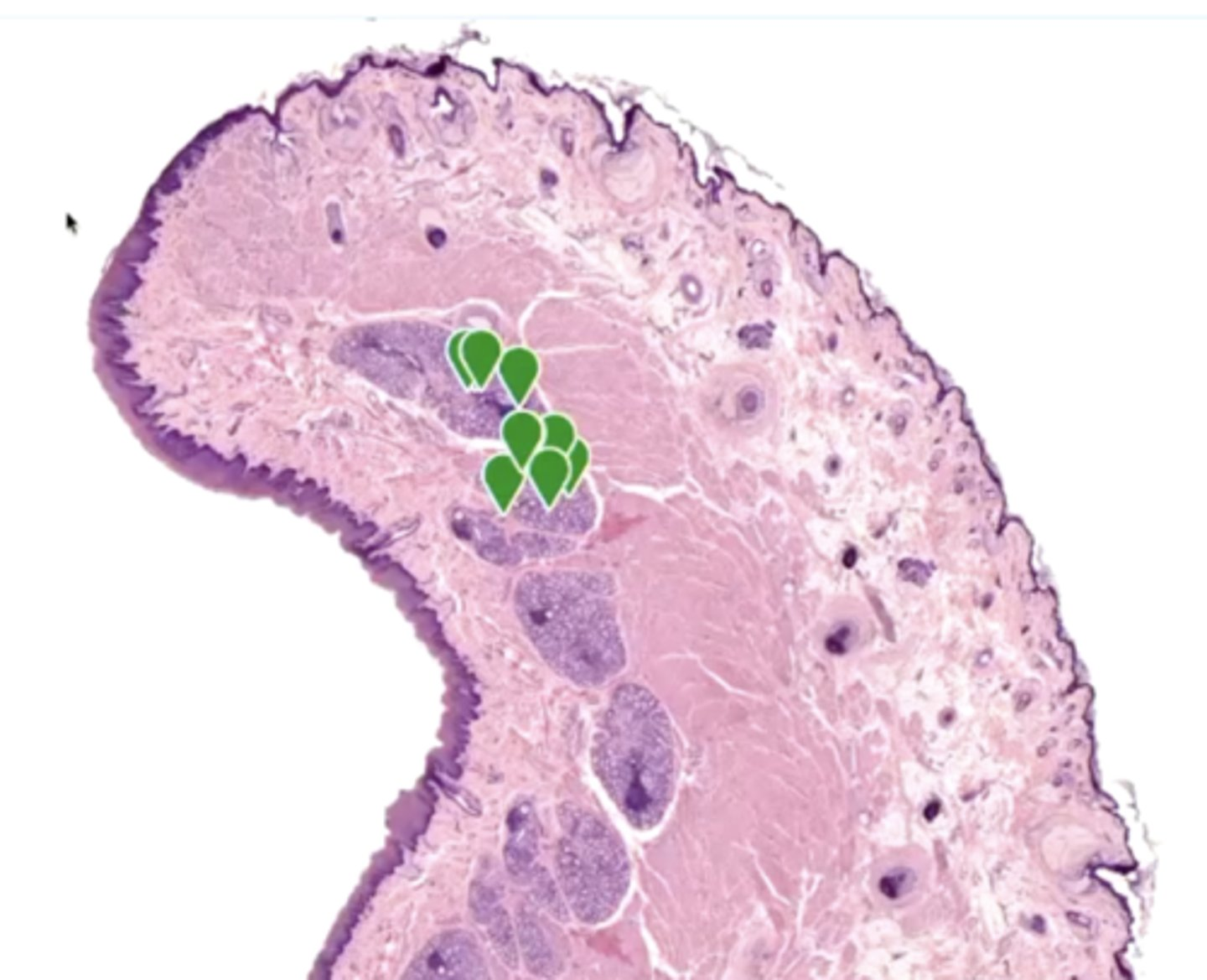
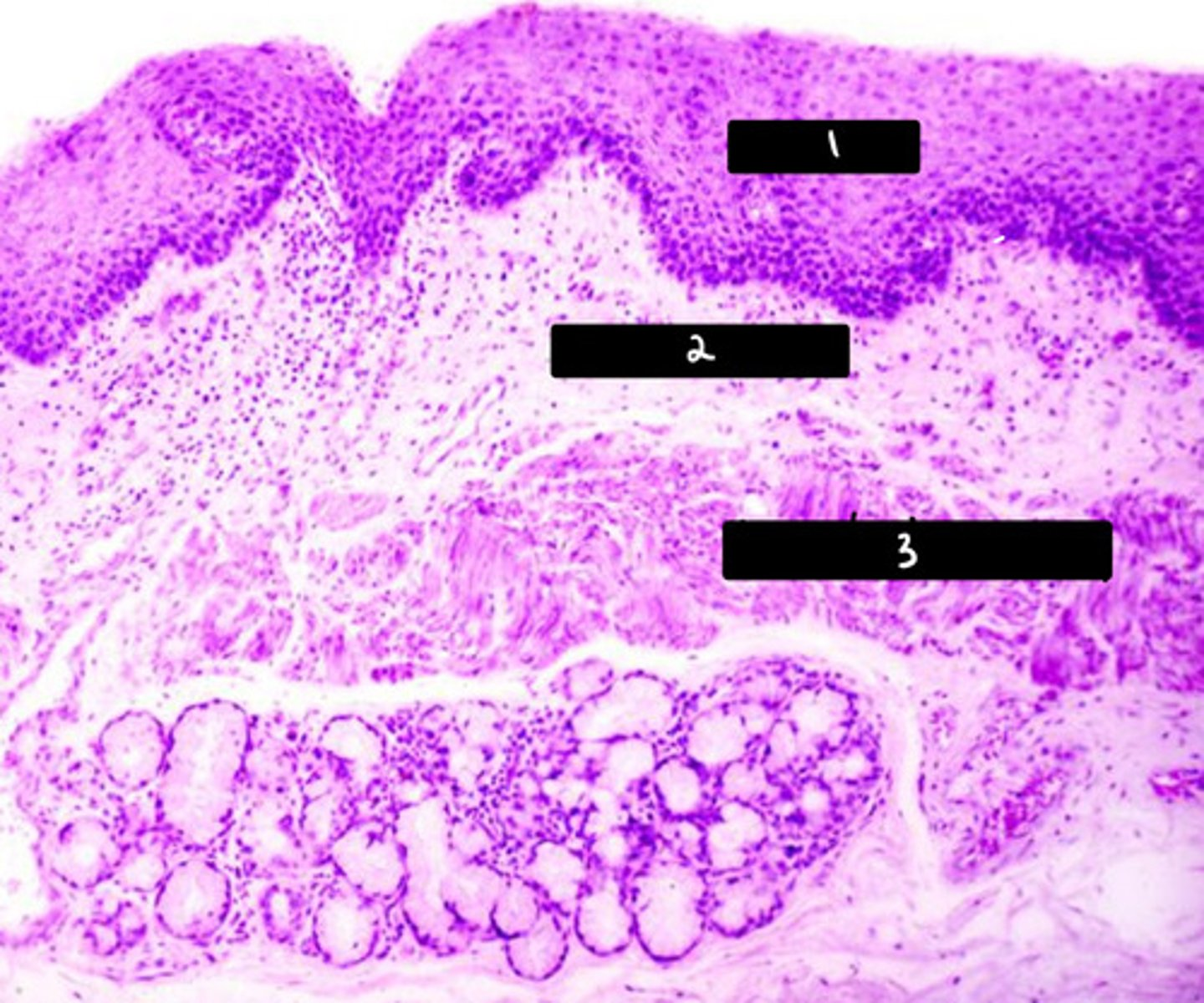
what is labeled in the image?
labial glands
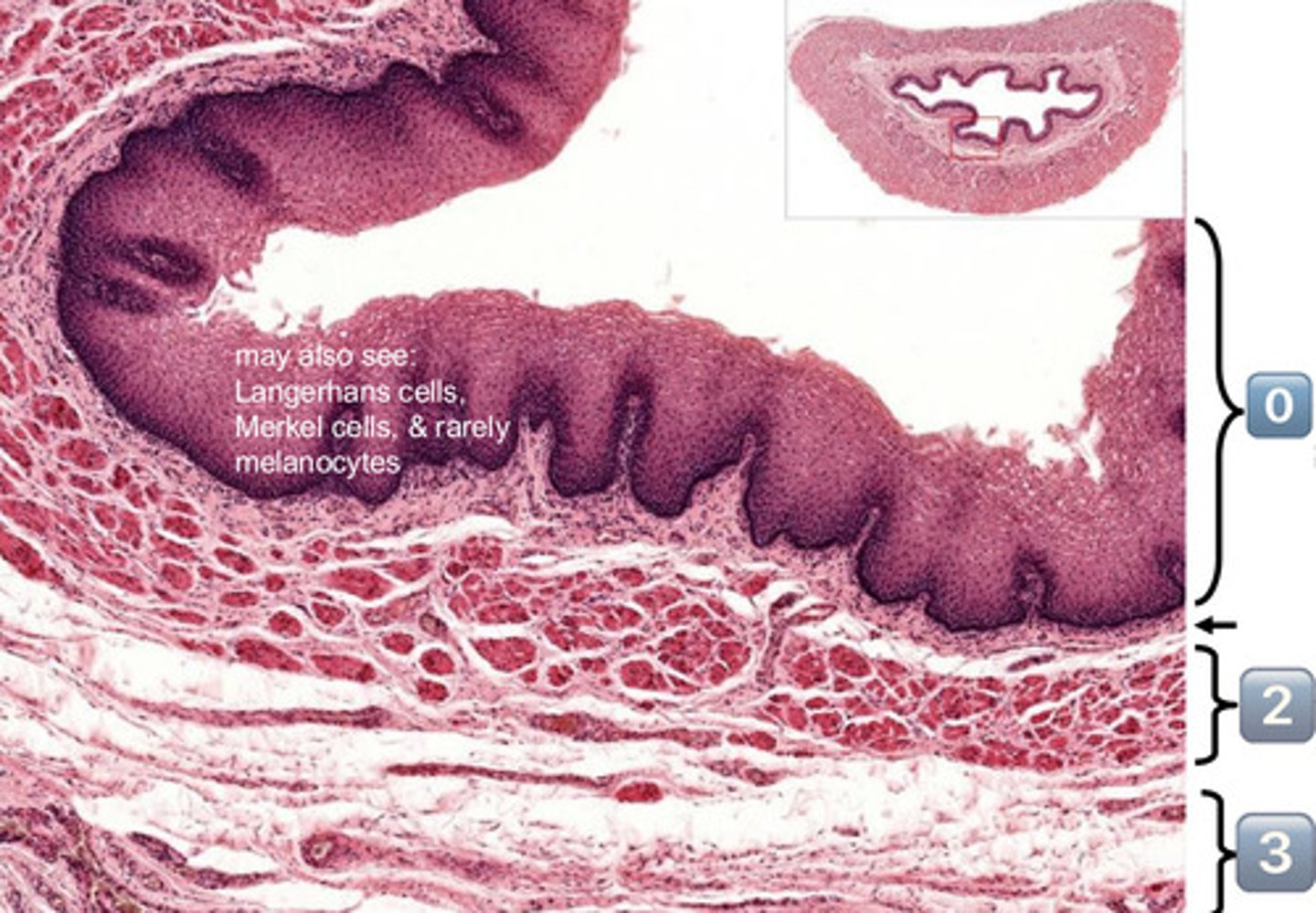
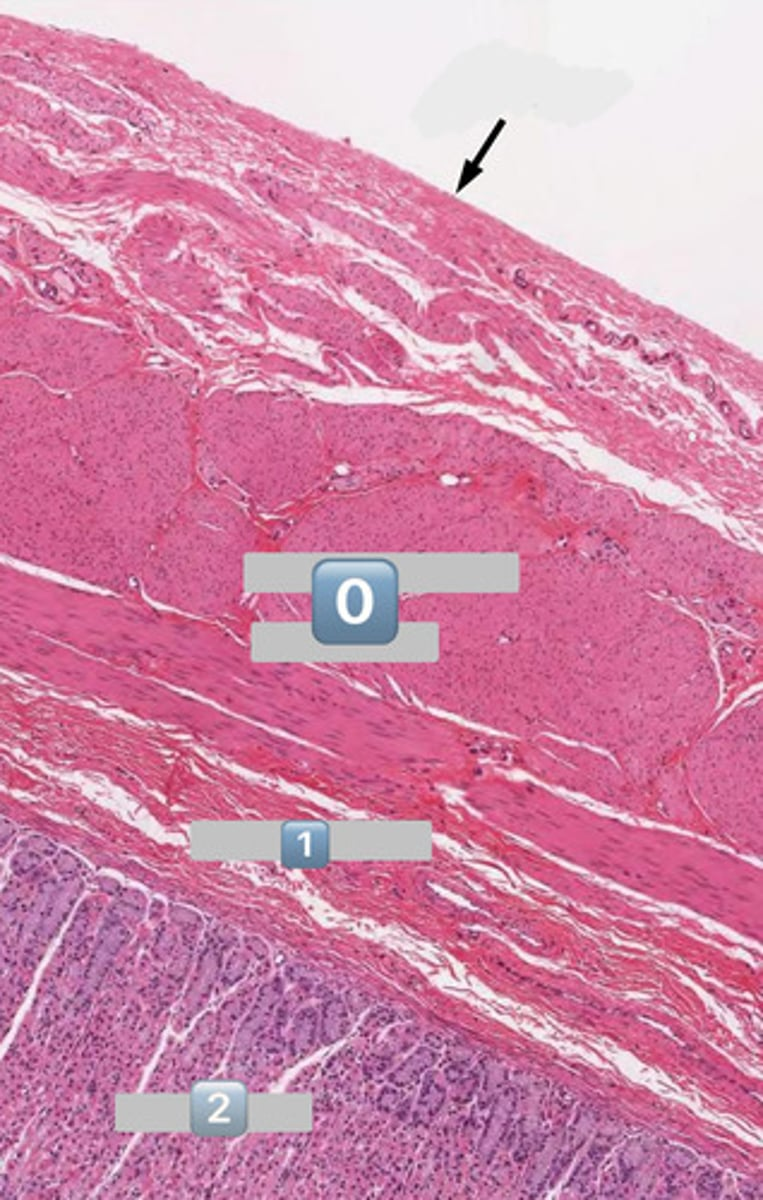
0
epithelium (SSNKE)
arrow
lamina propria
2
muscularis mucosae
3
submucosa
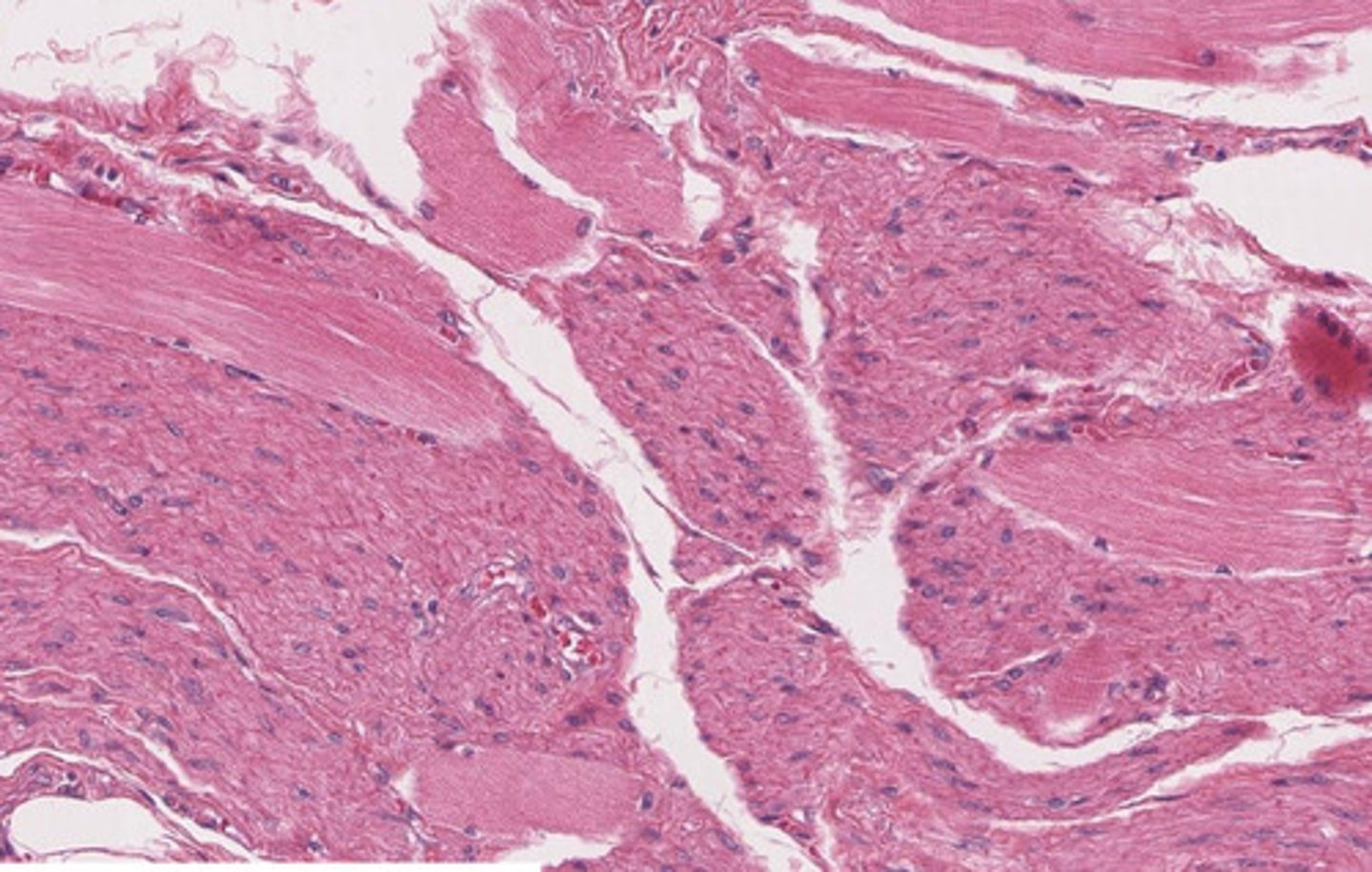
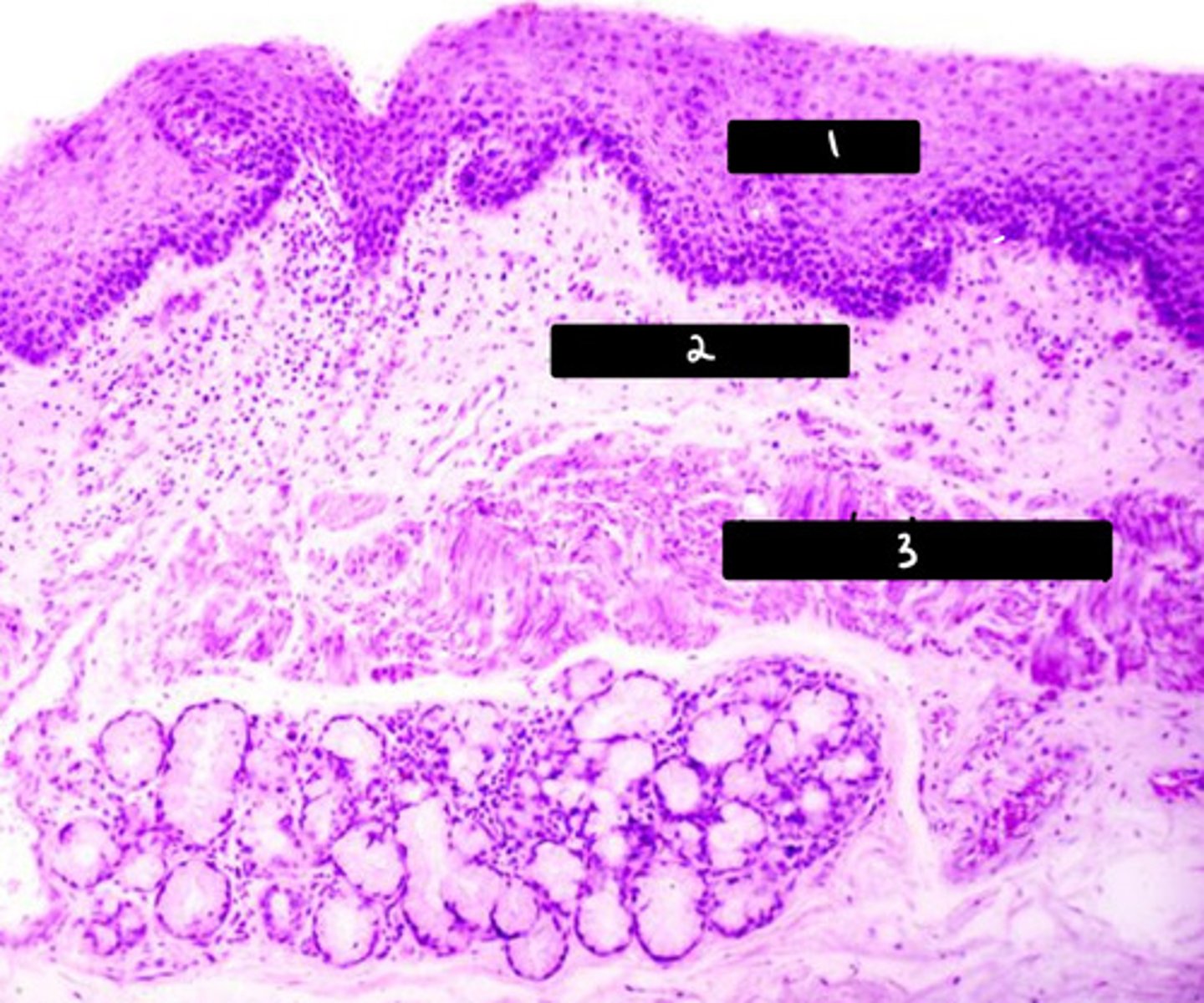
describe this image
this image is a histological section of the middle 1/3 of the esophagus
note: the mix of smooth and skeletal muscle representative of the partial voluntary, partial involuntary control of swallowing at this point in the esophagus
?
esophageal glands
- mucosal and serous
pictured are esophageal glands found in what layer?
submucosal
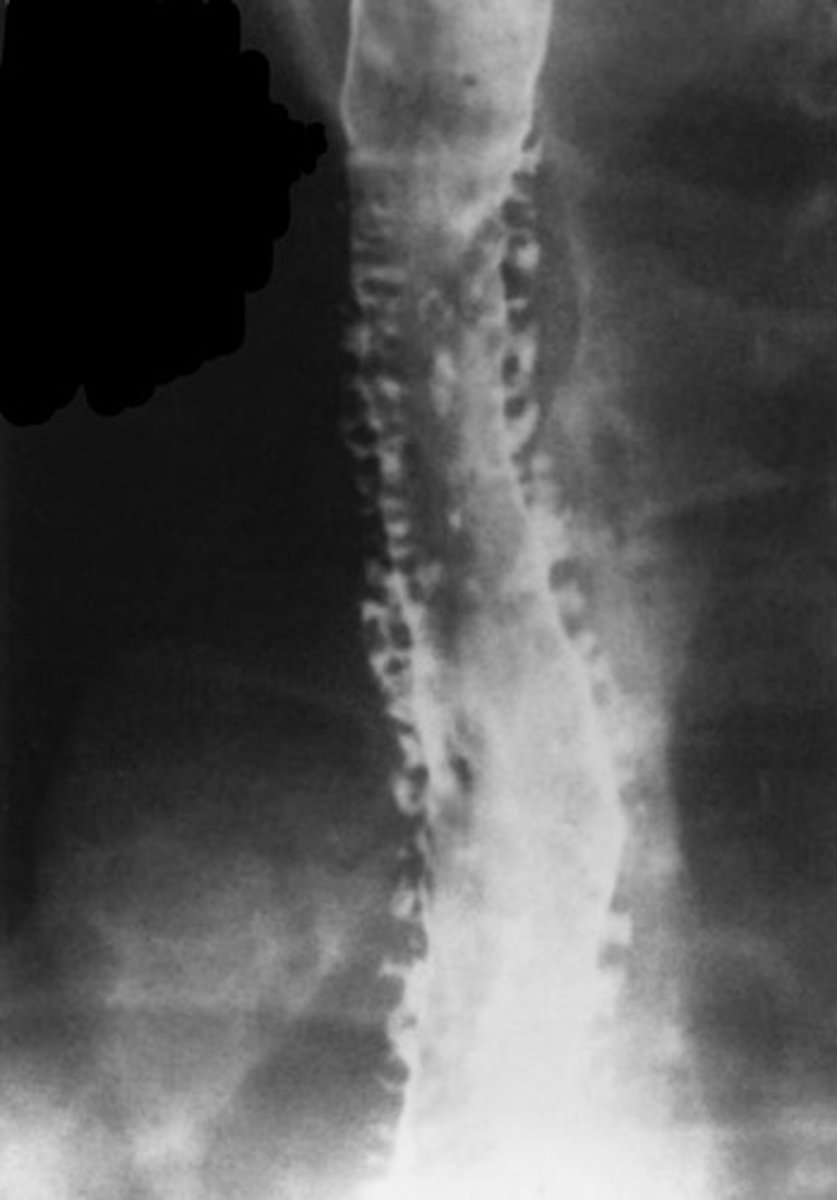
?
ducts in esophagus
- stratified cuboidal epithelium
- barium goes into ducts
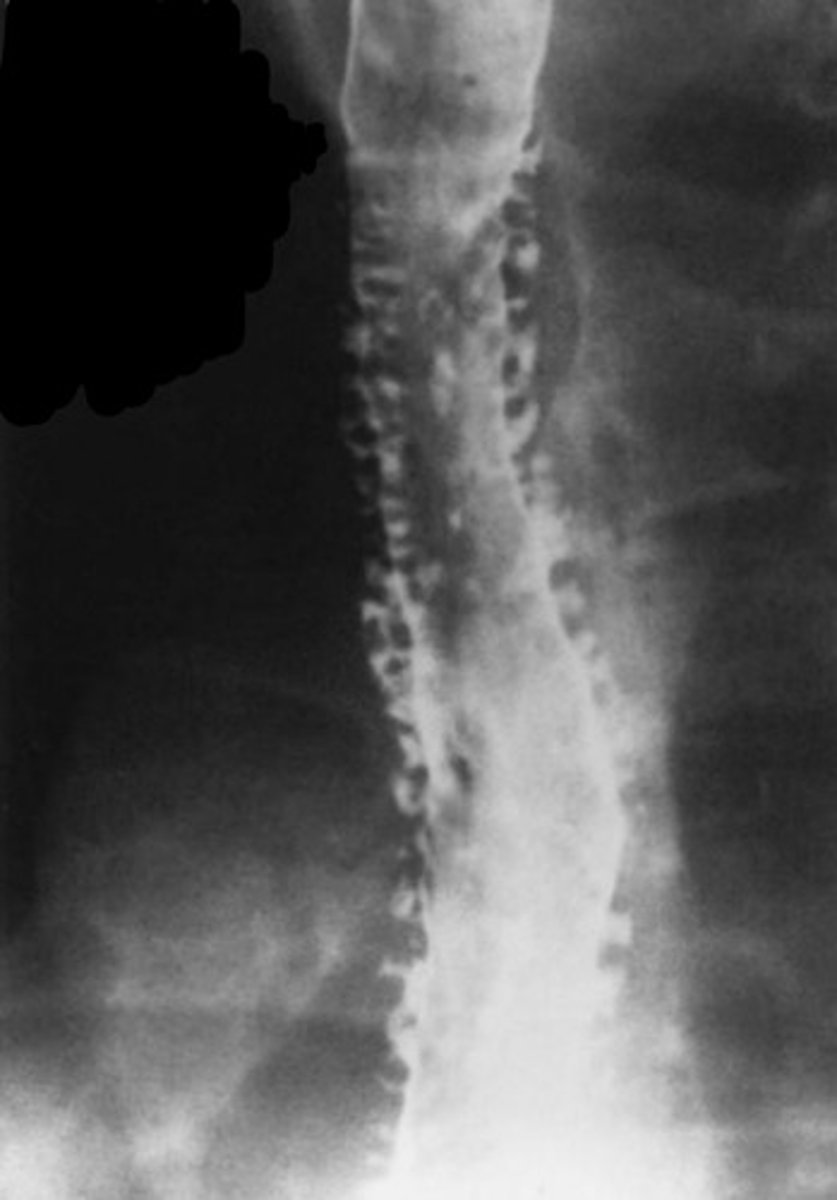
?
barium esophagram showing ducts of esophageal submucosal glands
?
squamocolumnar mucosal junction
- zig-zag line
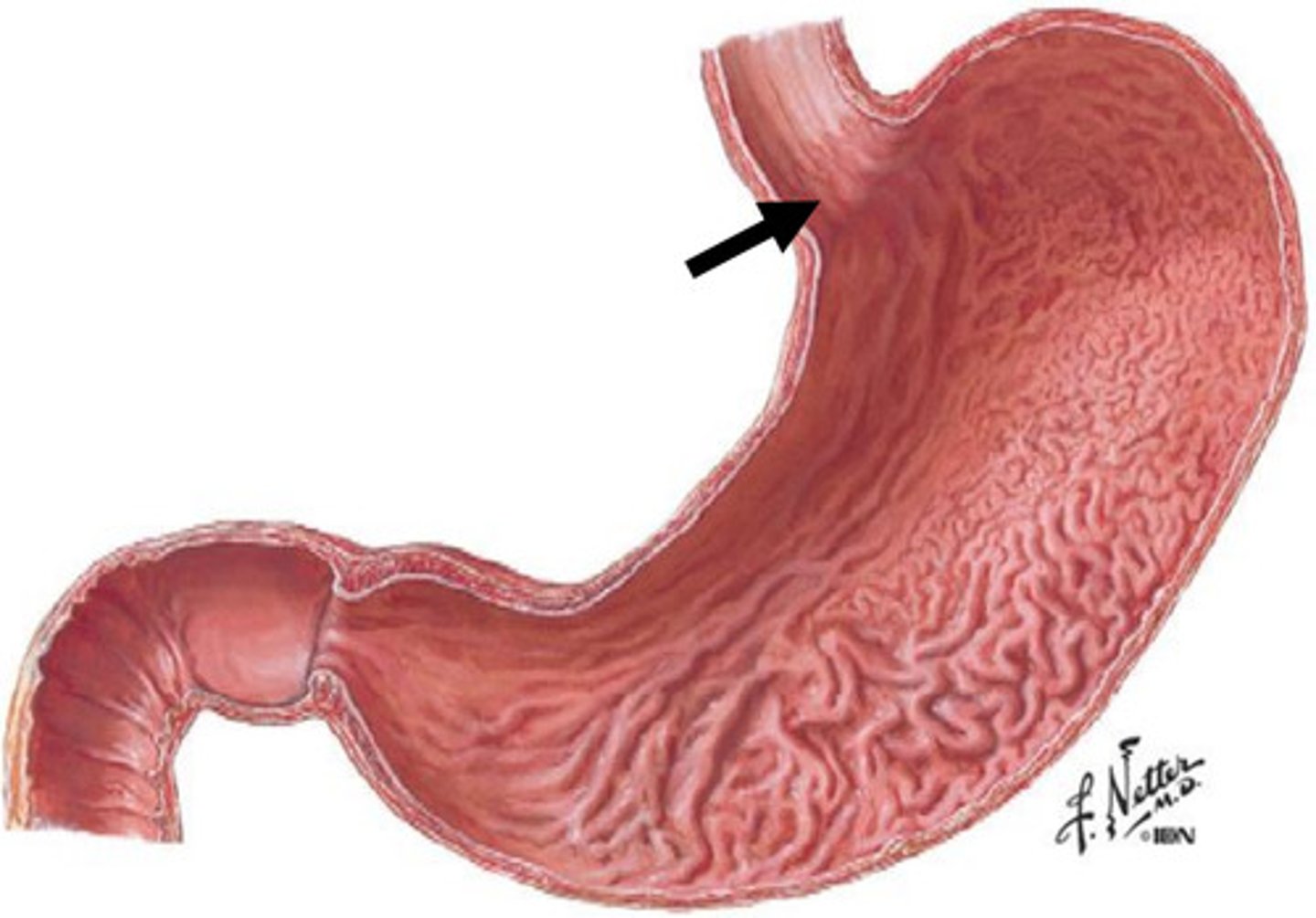
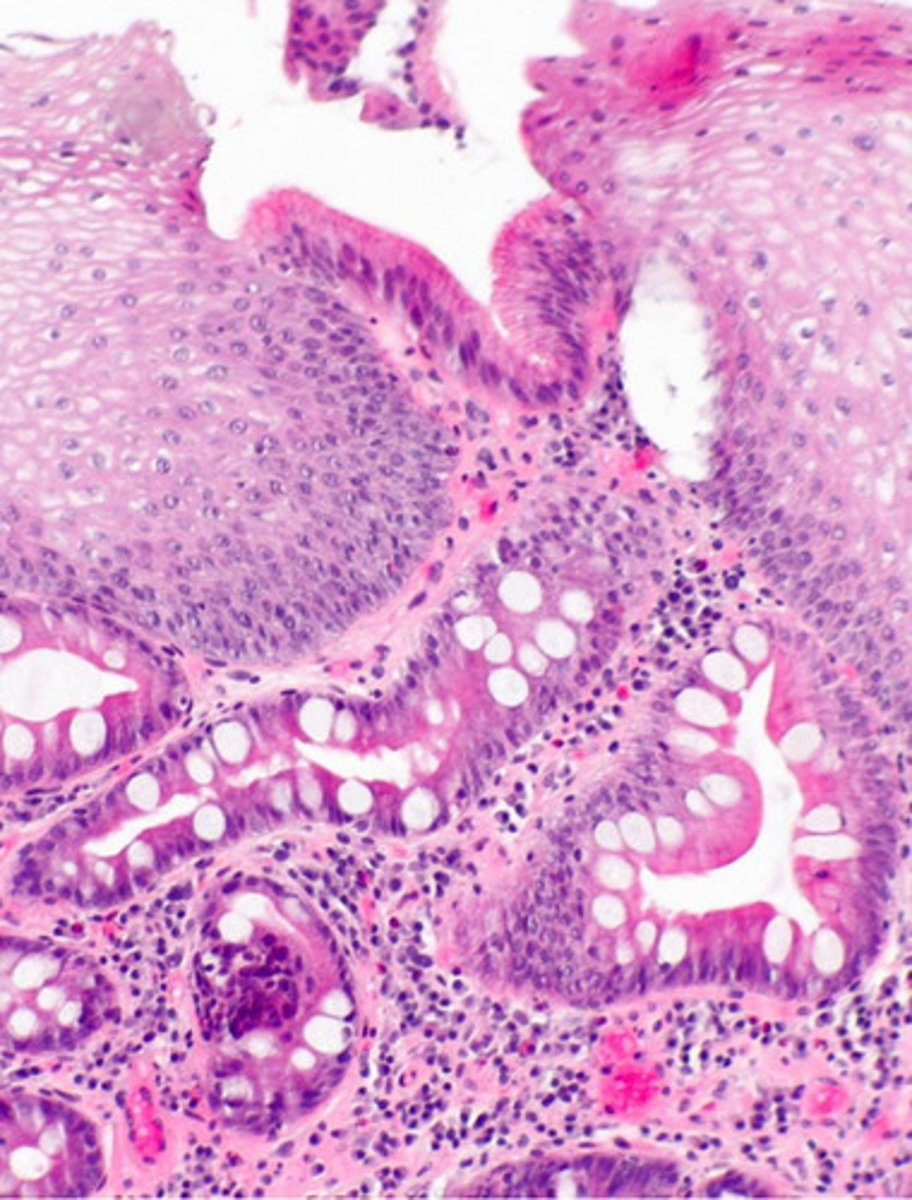
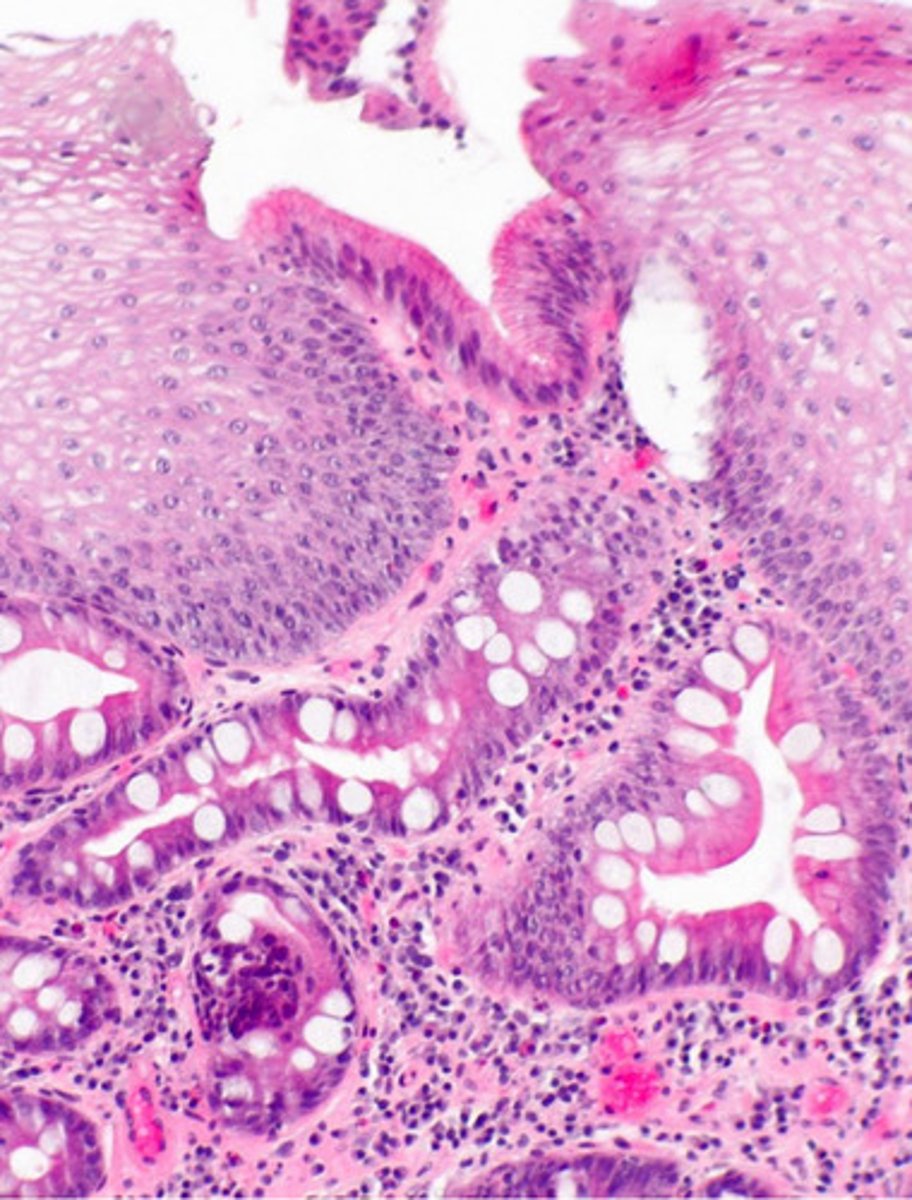
identify the pathology
Barrett's esophagus
- irregular squamocolumnar junction
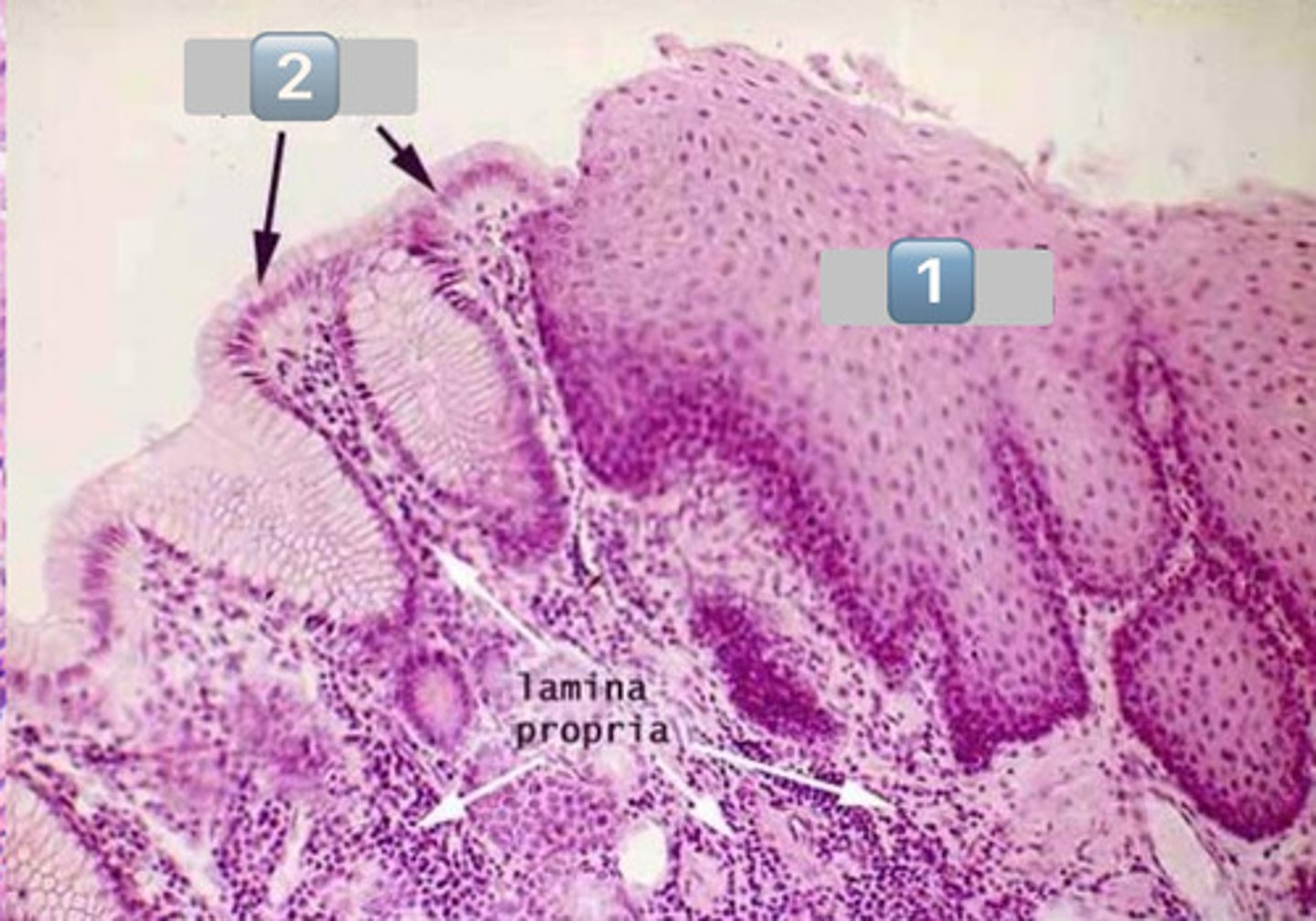
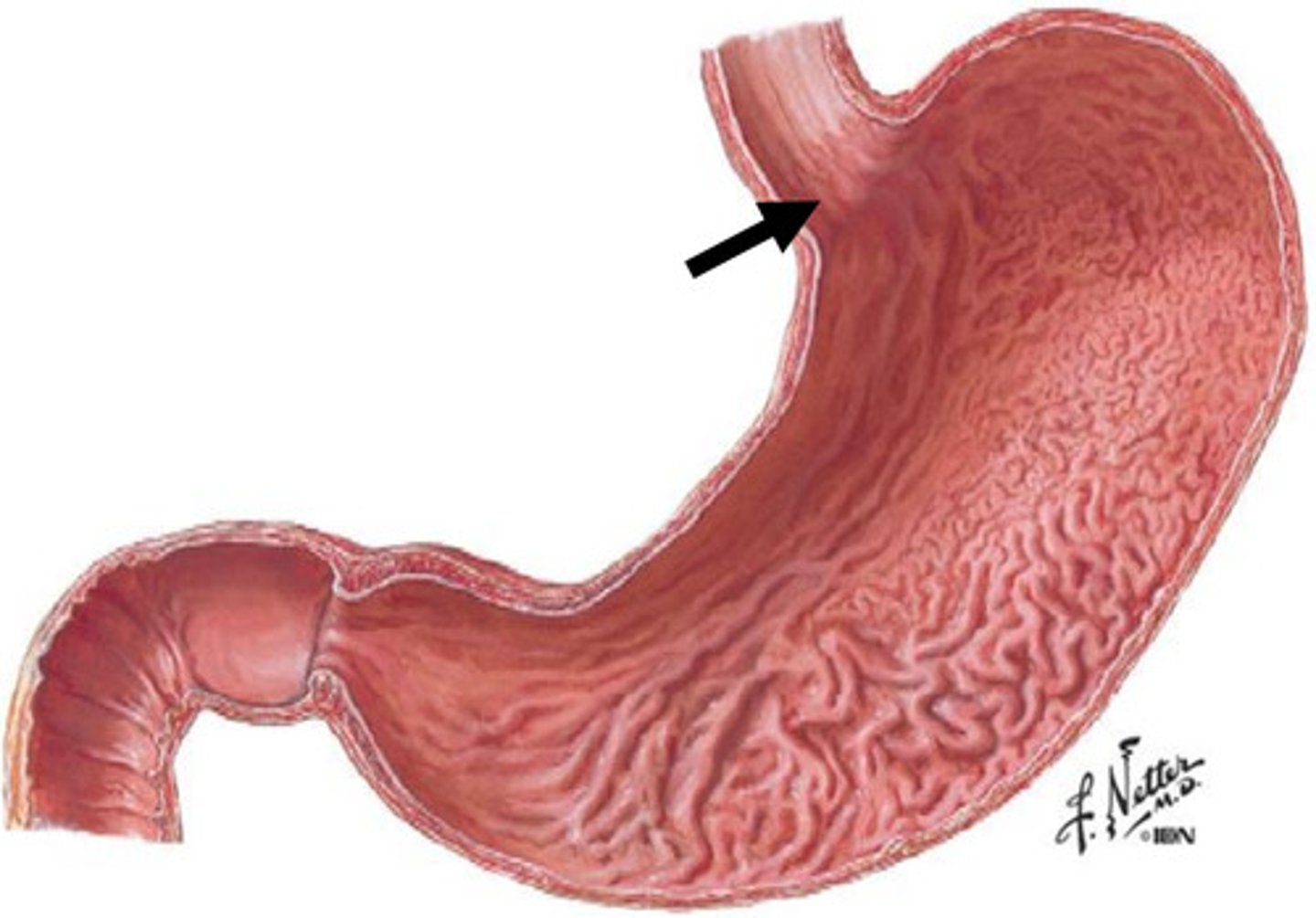
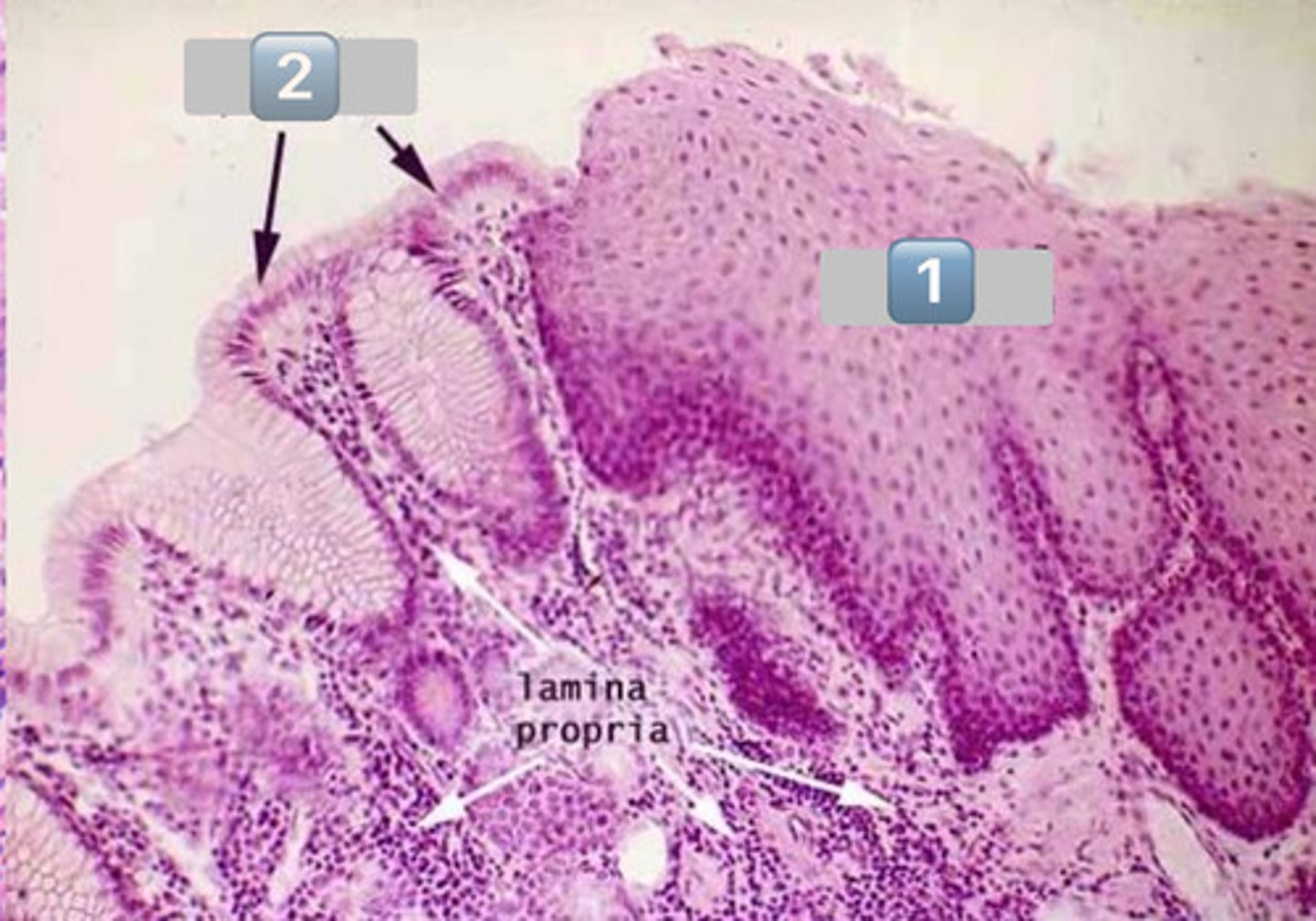
what is pictured here? (big picture)
normal squamocolumnar junction
1
esophageal epithelium
2
gastric epithelium
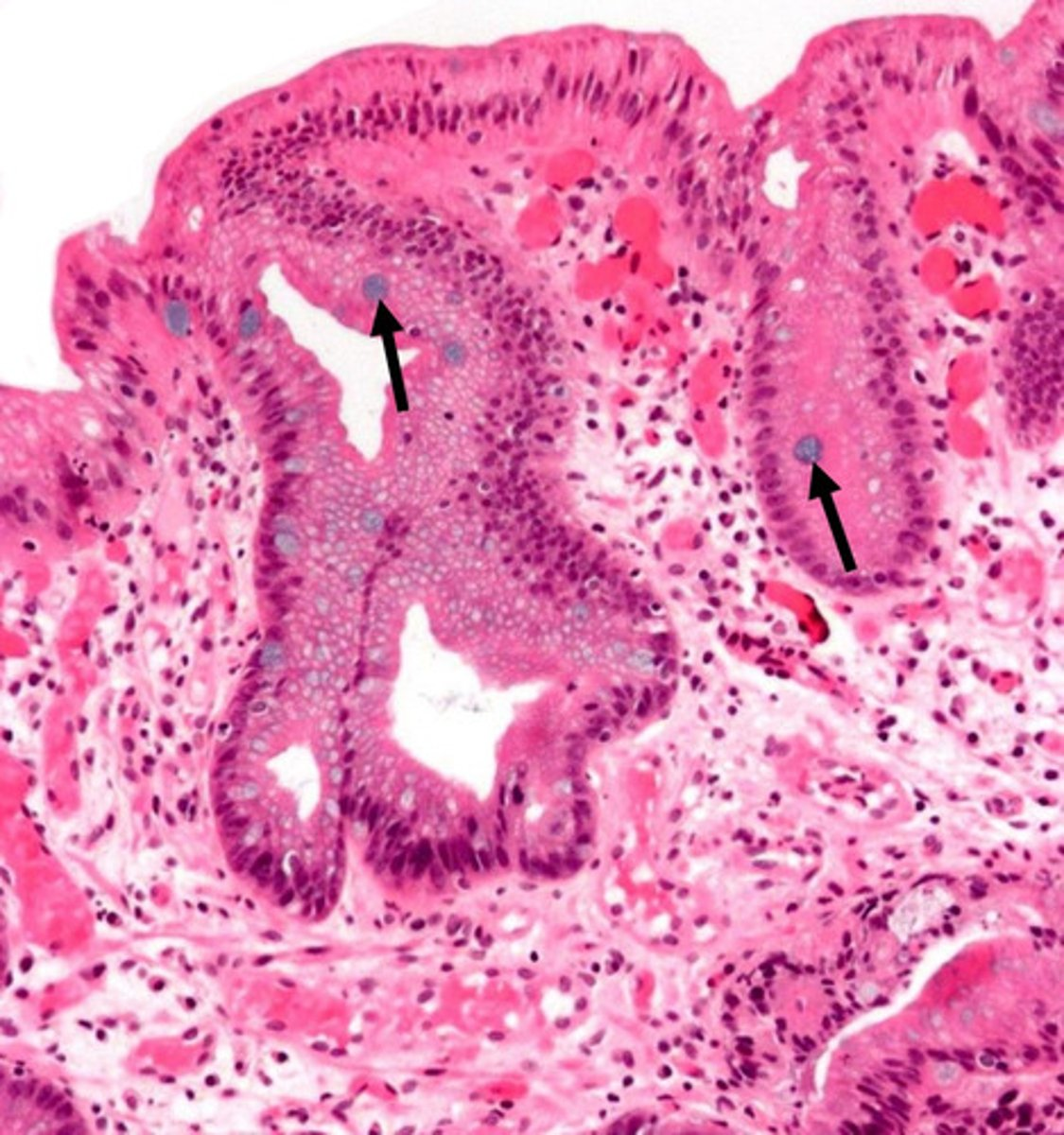
arrows?
goblet cell mucins stained with alcian blue
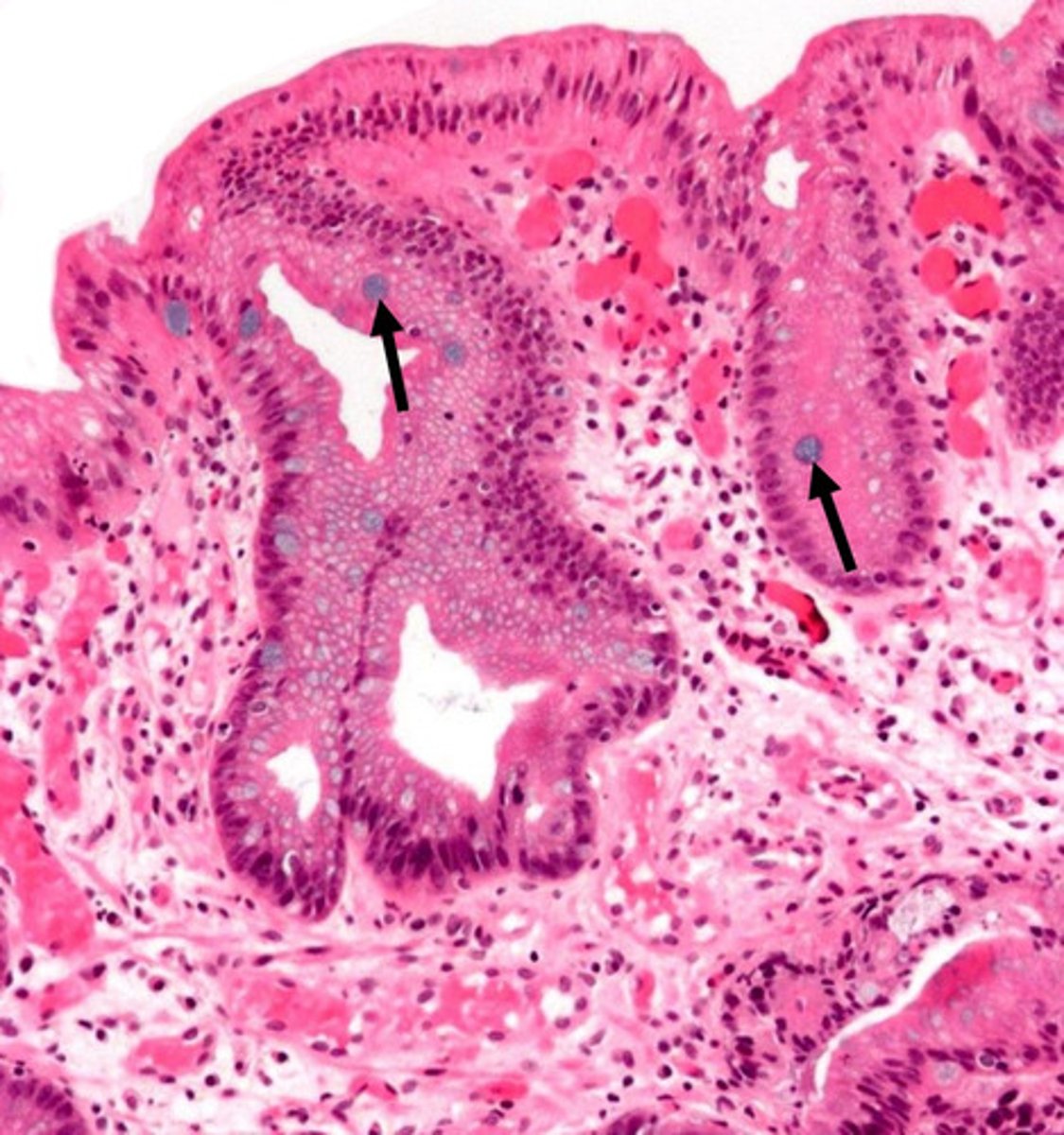
what pathology?
Barrett's esophagus
1
SSNKE (esophagus epithleium)
2
columnar epithelium (metaplasia)
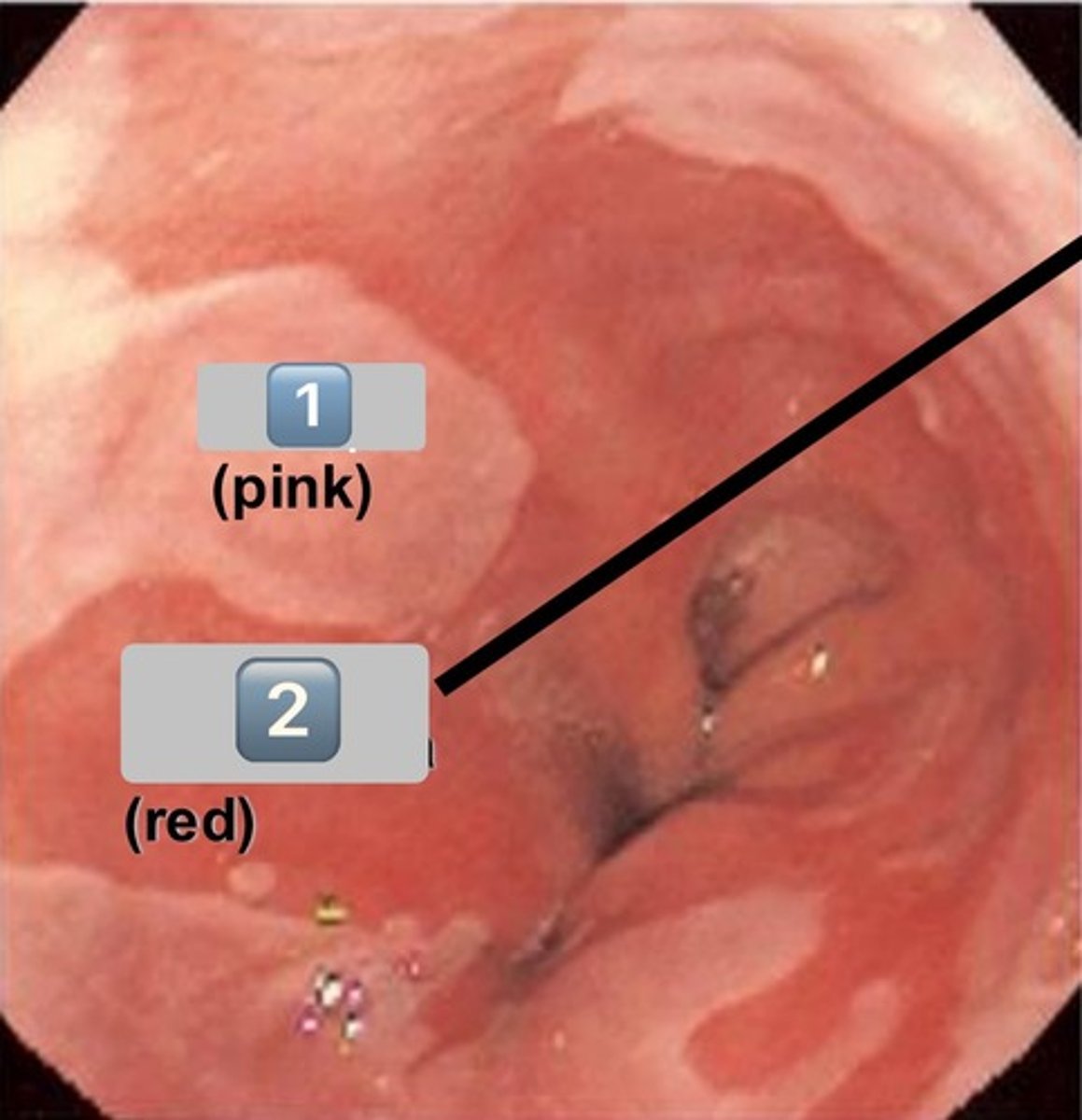
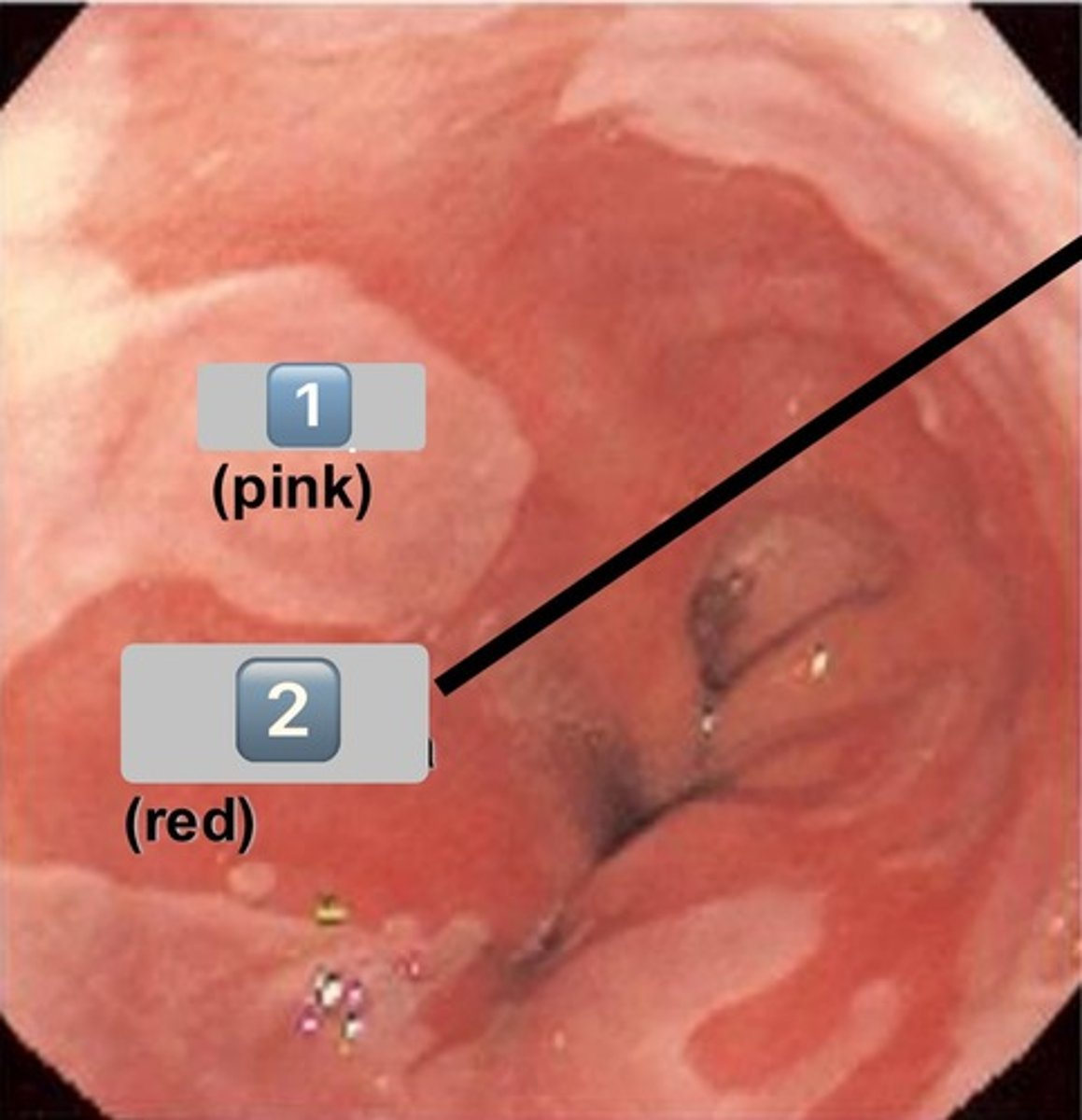
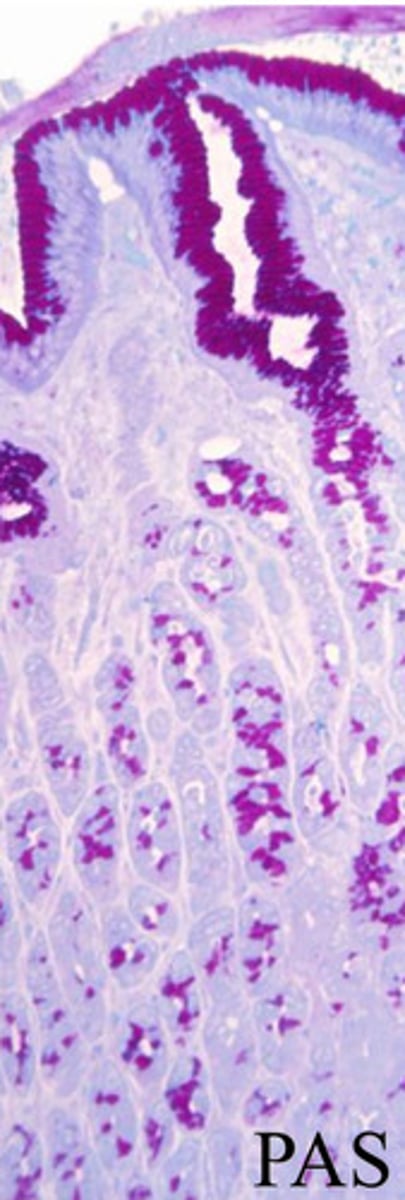
what is shown in the image?
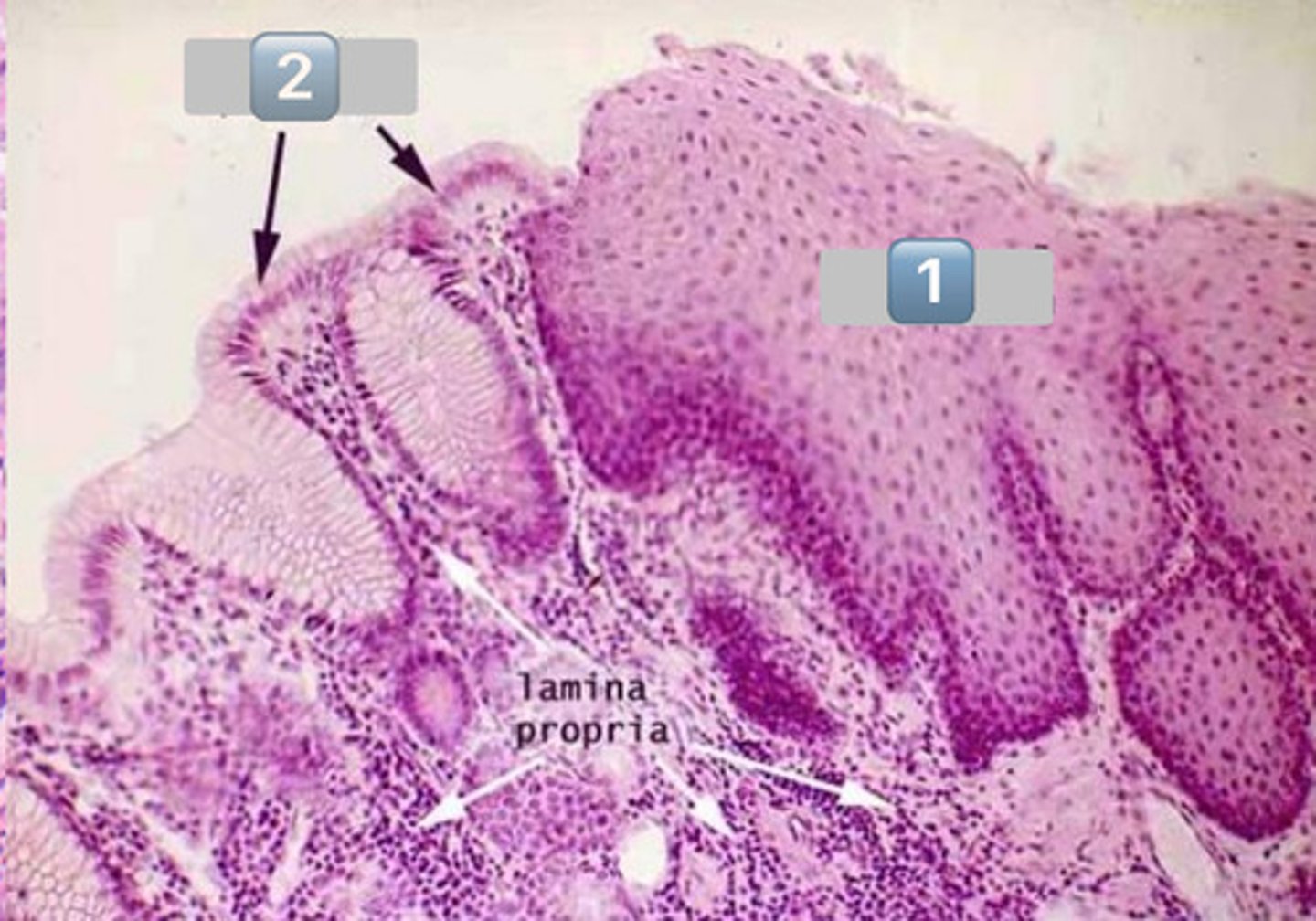
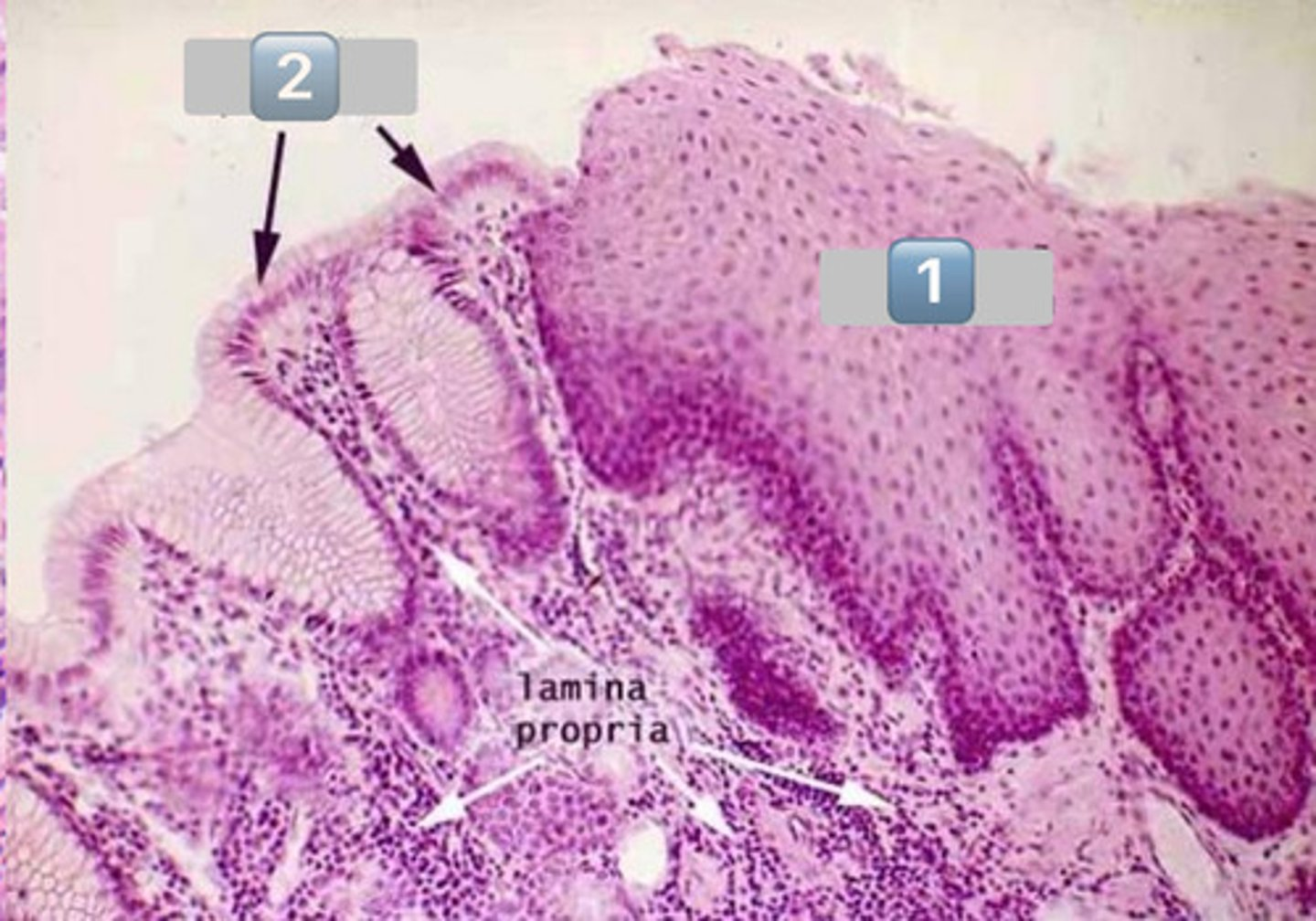
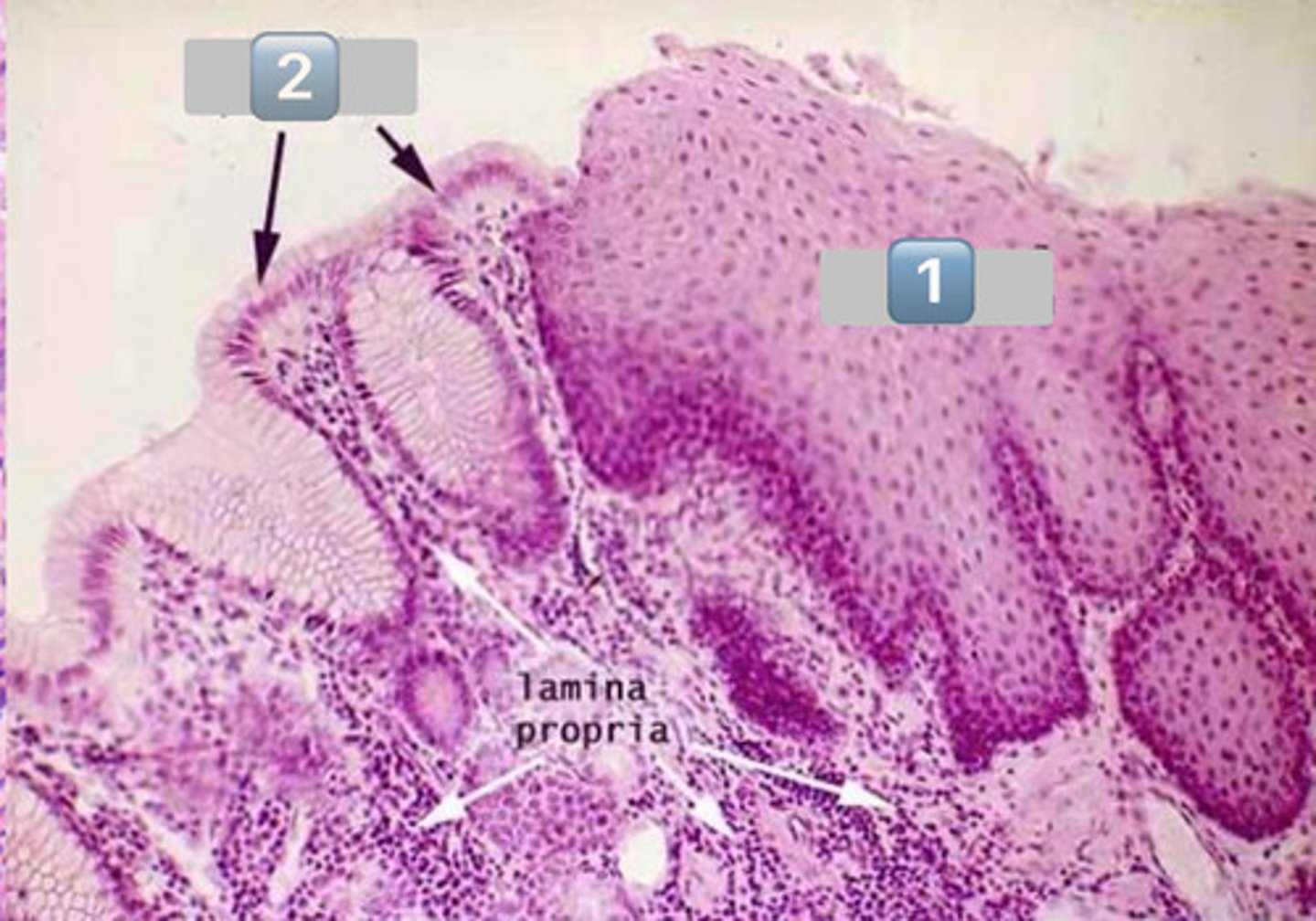
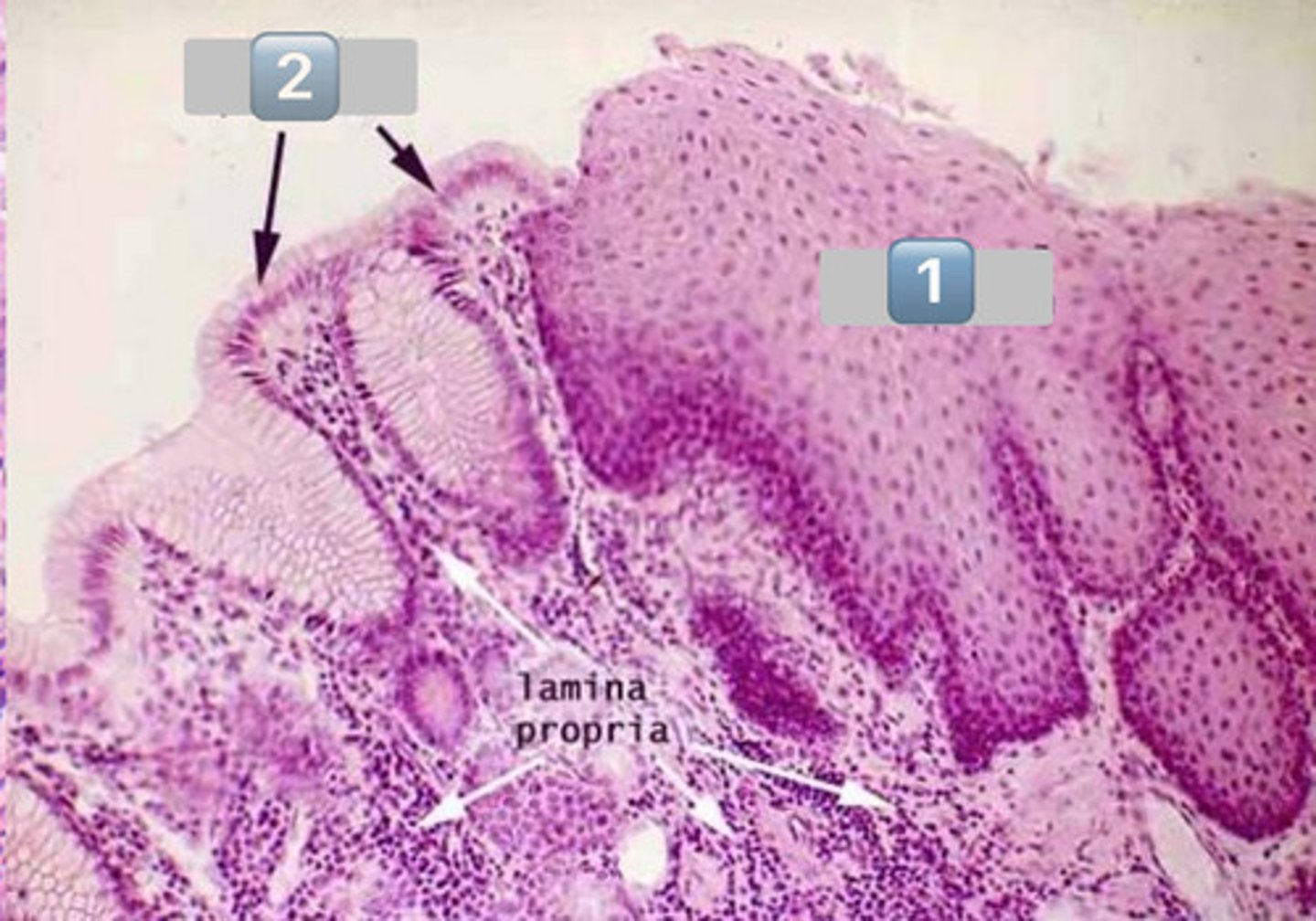
gastroesophageal junction
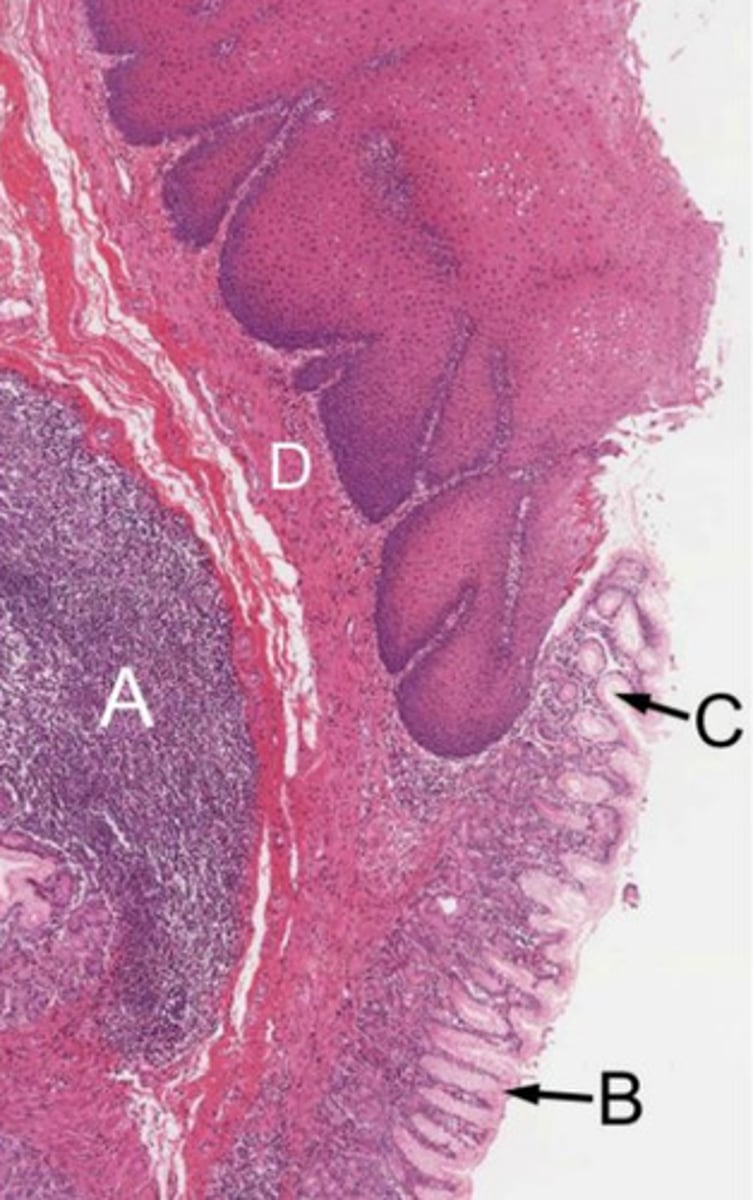
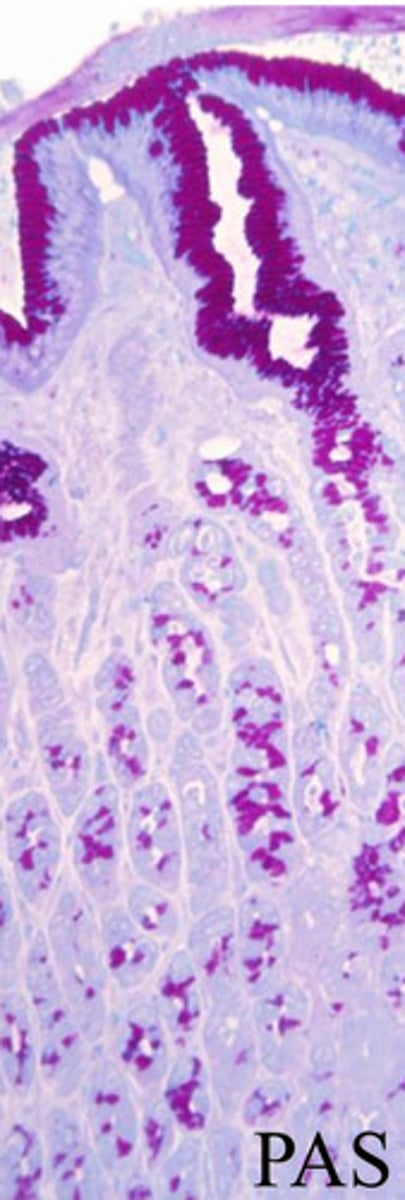
surface mucous cells
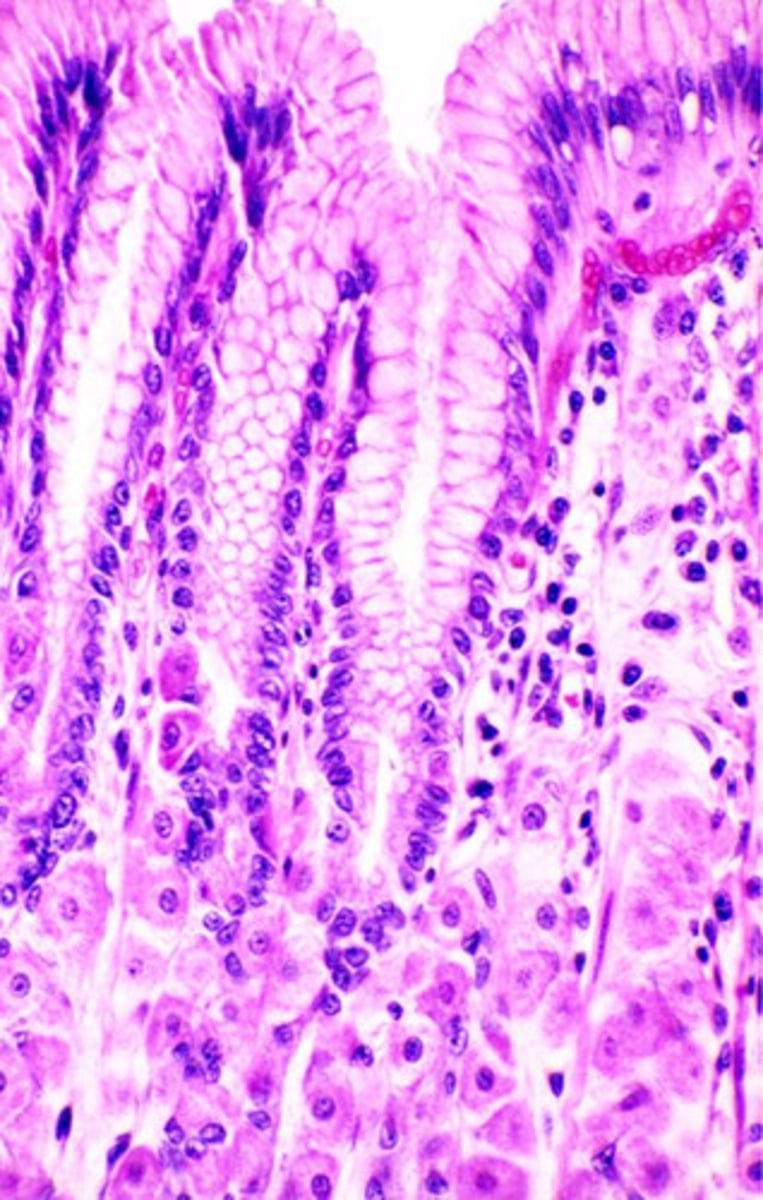
surface mucous cells
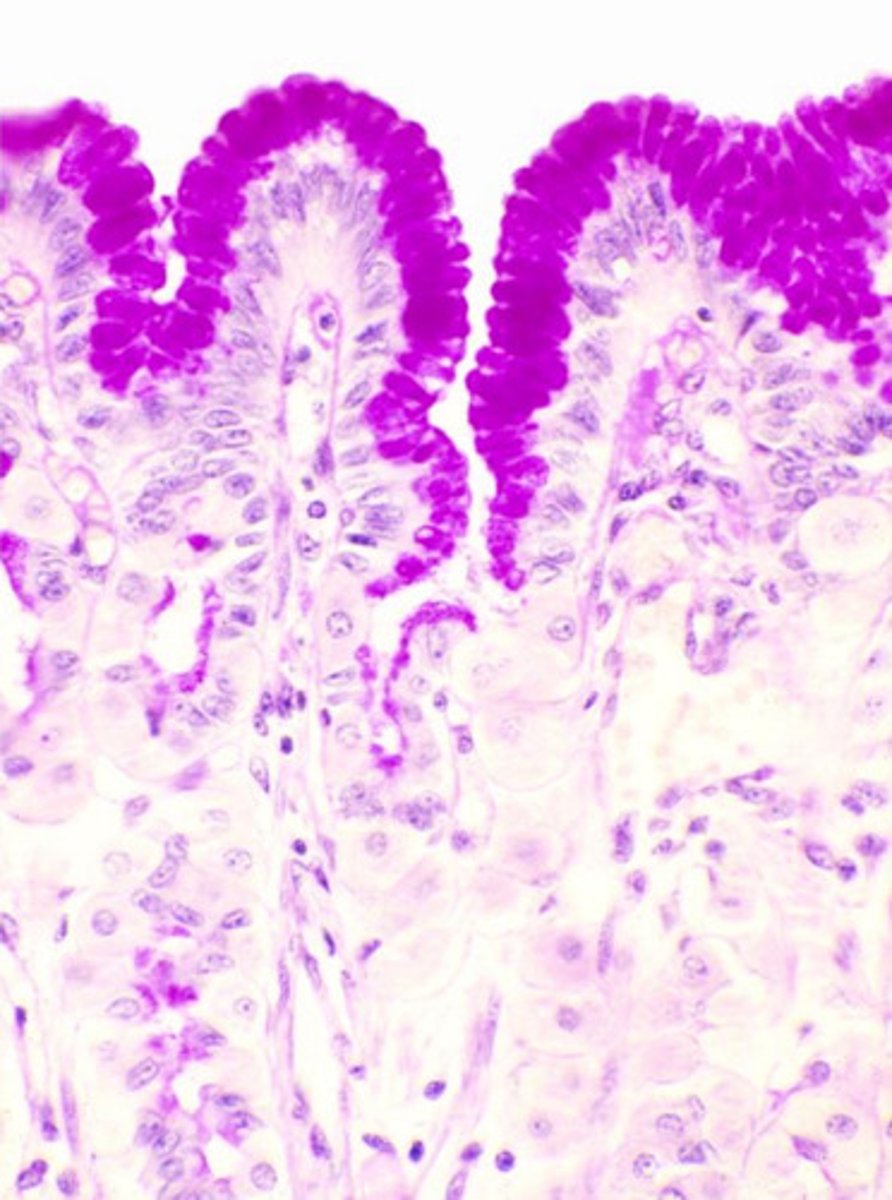
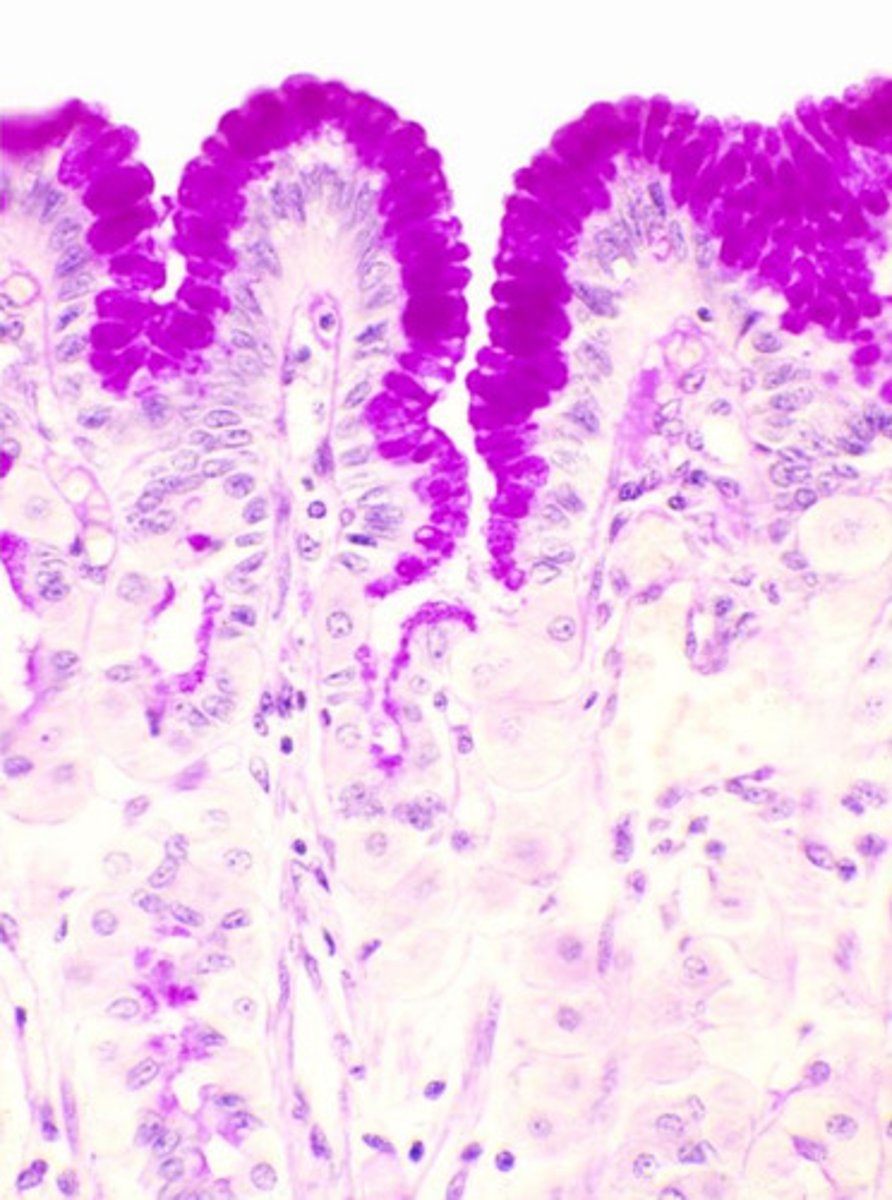
mucous neck cells
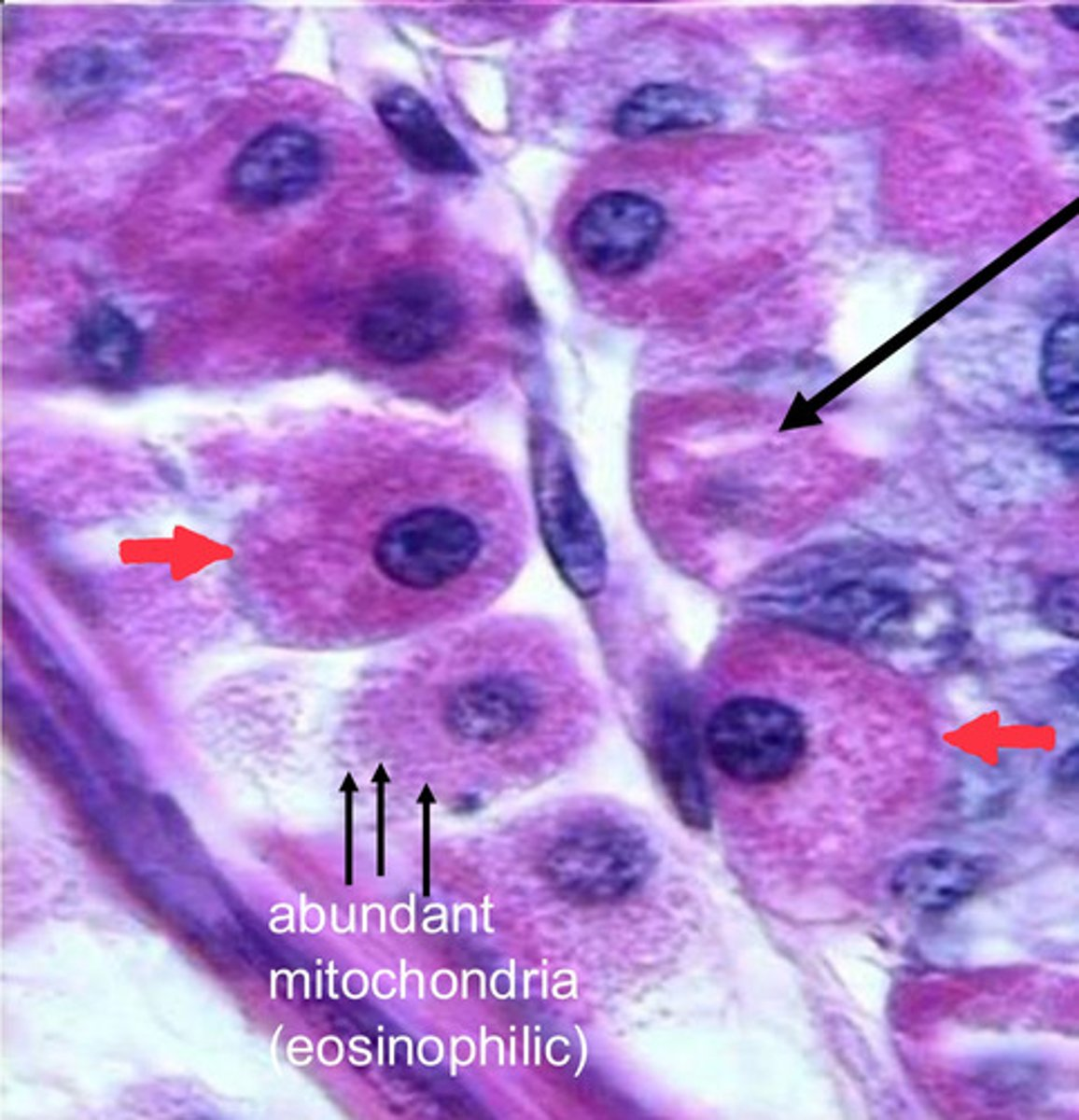
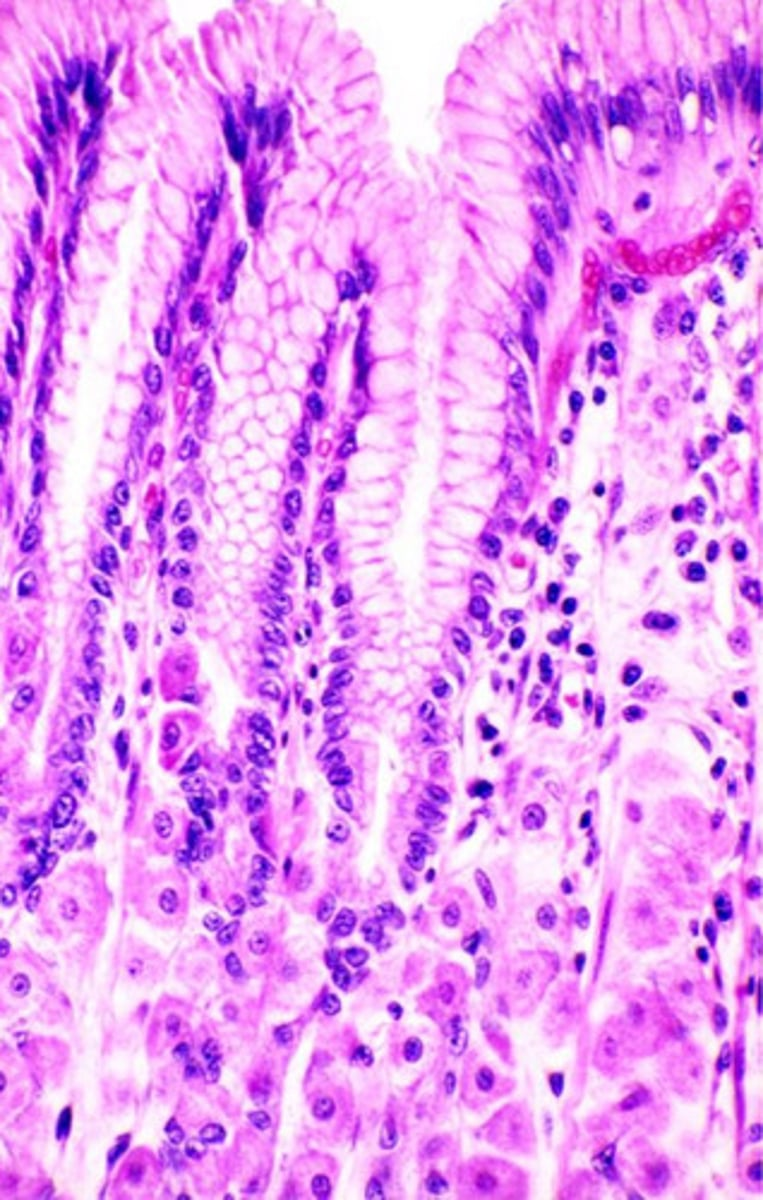
single black arrow?
intracellular cannaliculus
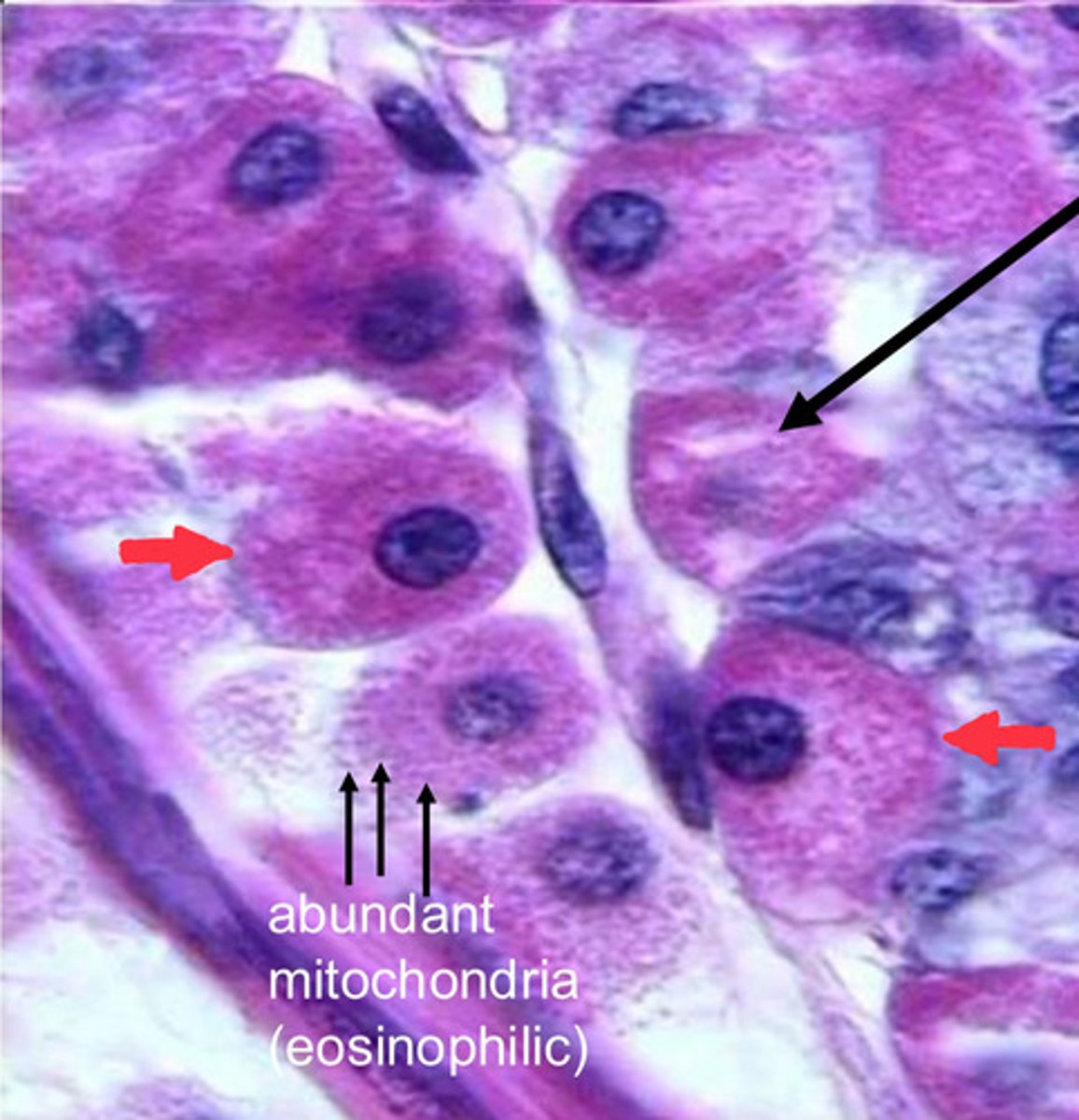
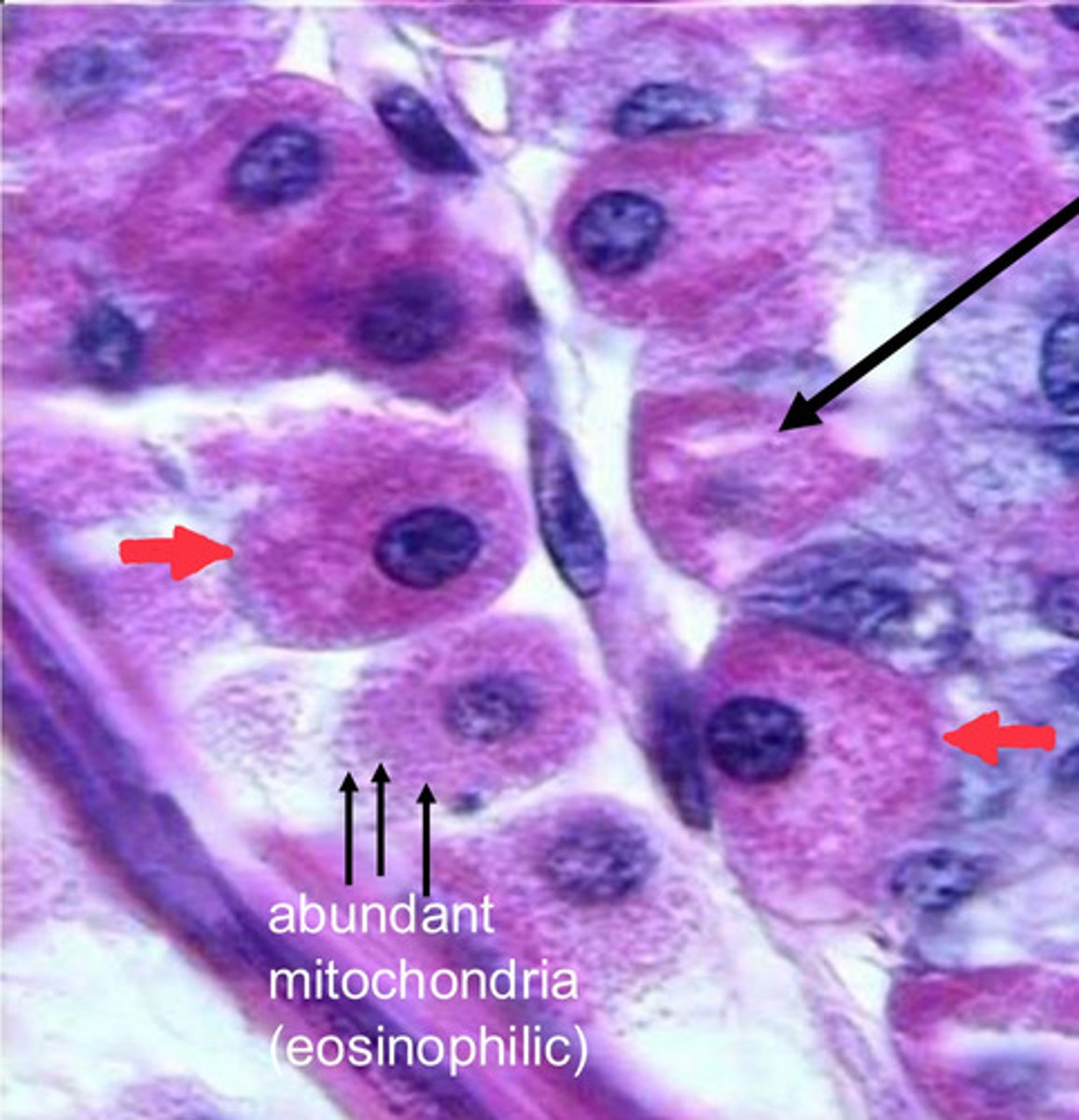
red arrows?
parietal cells
note:
- eosinophilic staining due to abundance of mitochondria
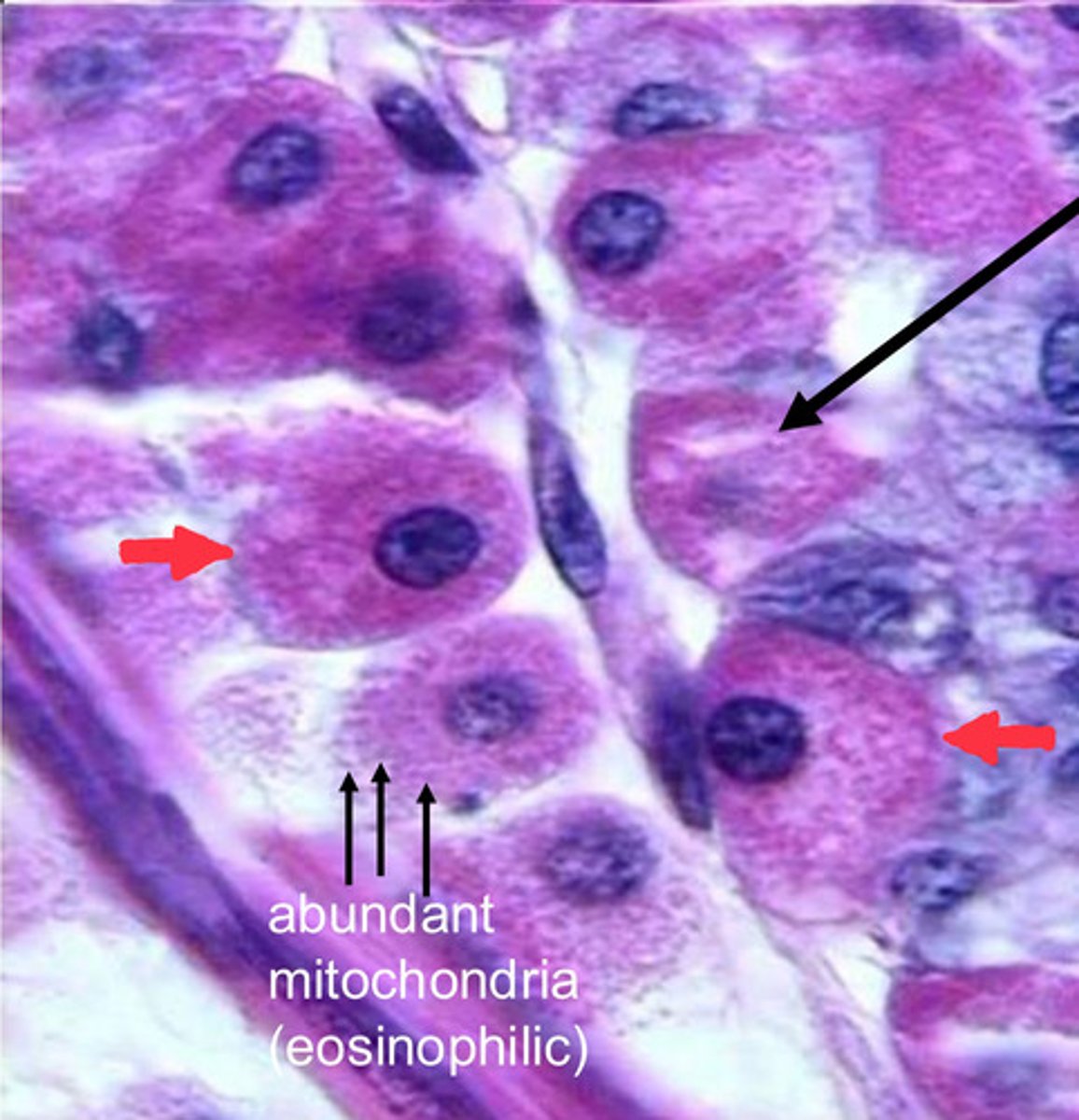
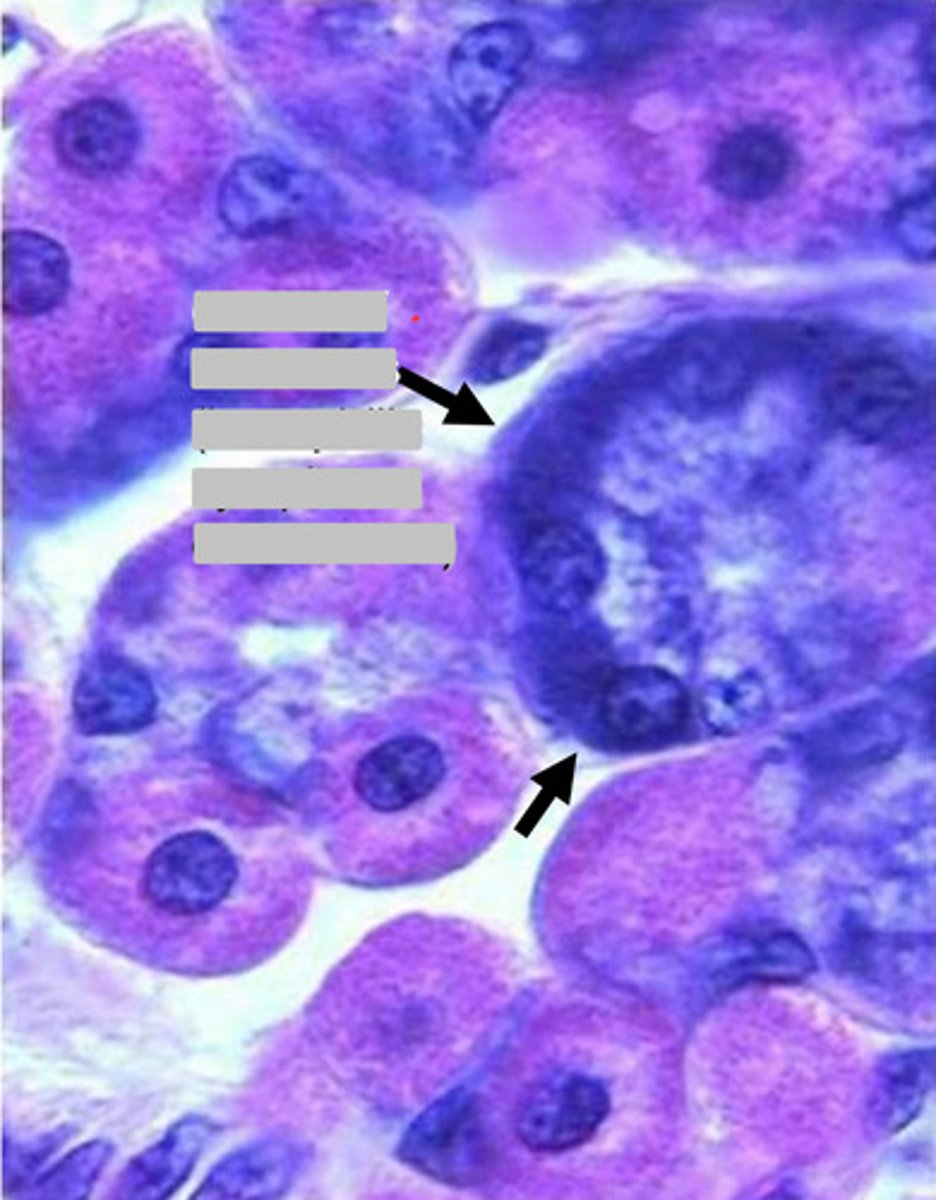
chief cells
note:
- basophilic cytoplasm due to RER
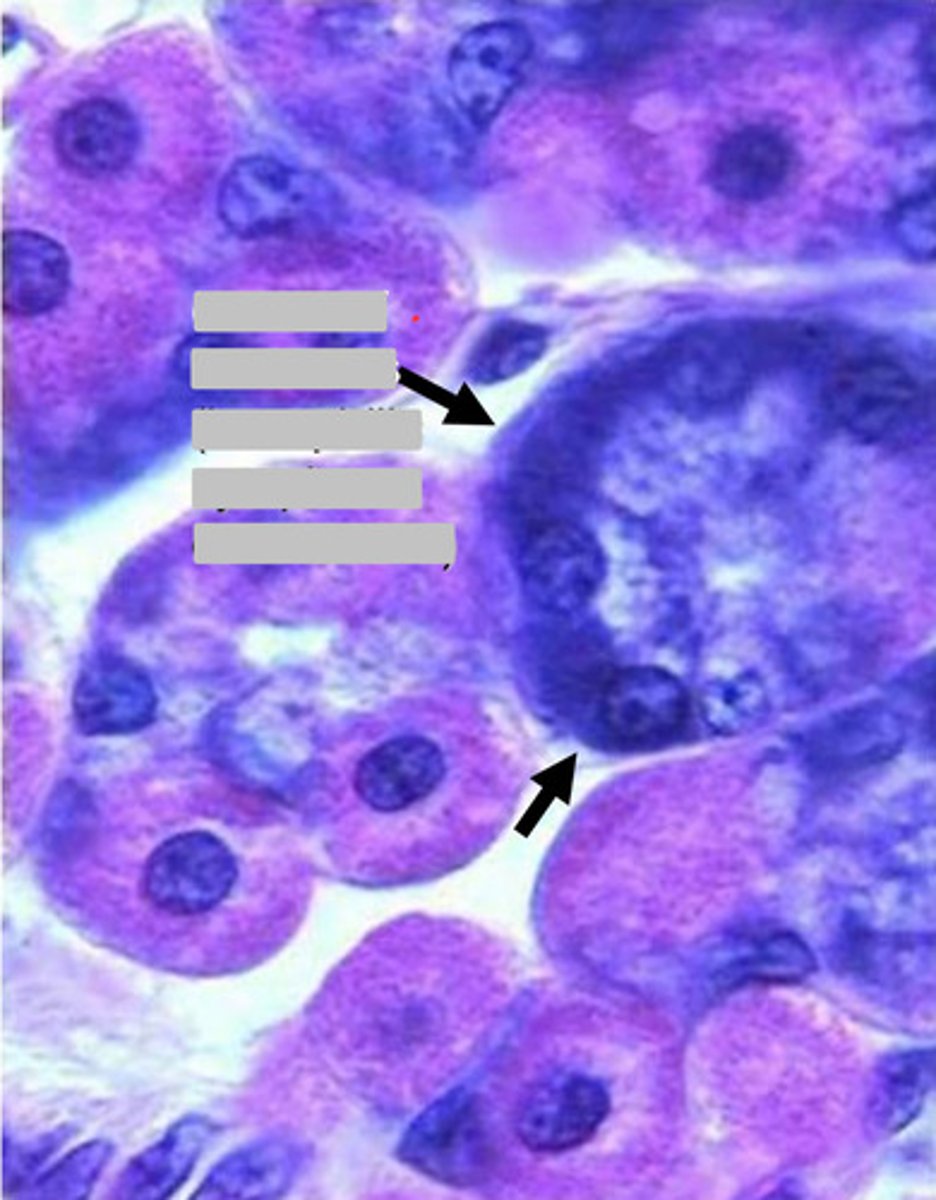
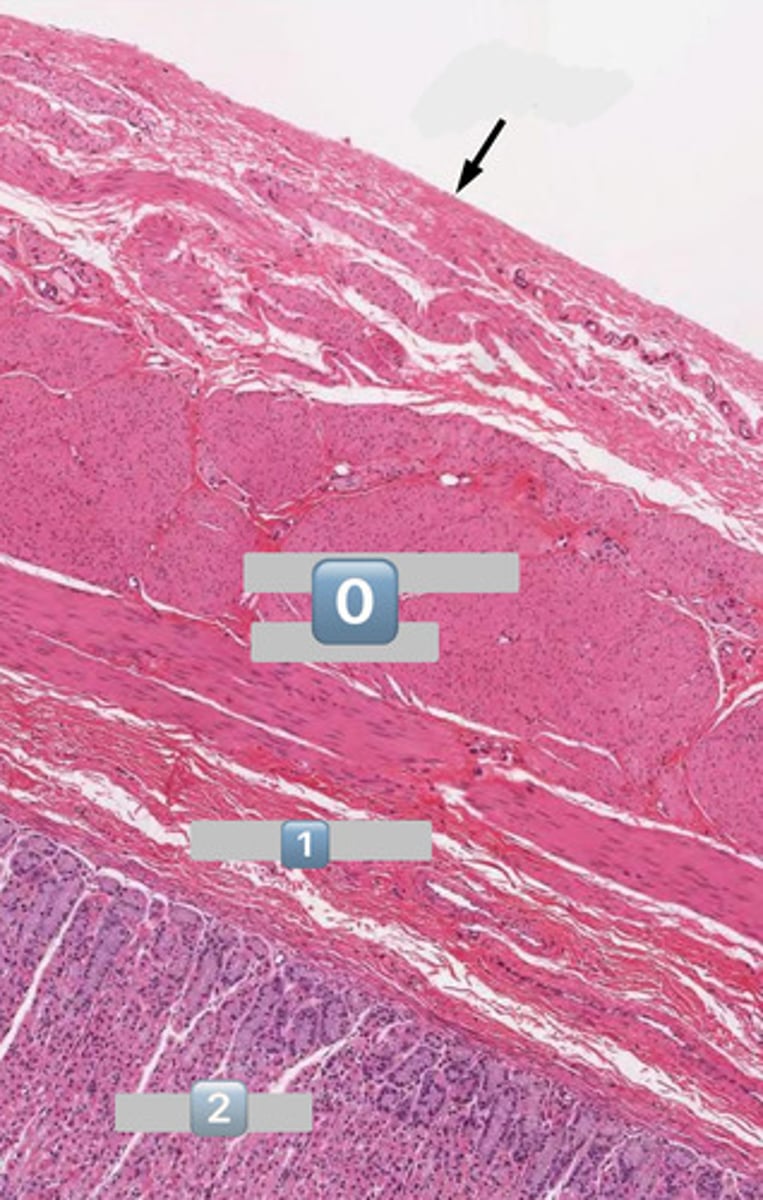
arrow
serosa
0
muscularis externa
1
submucosa
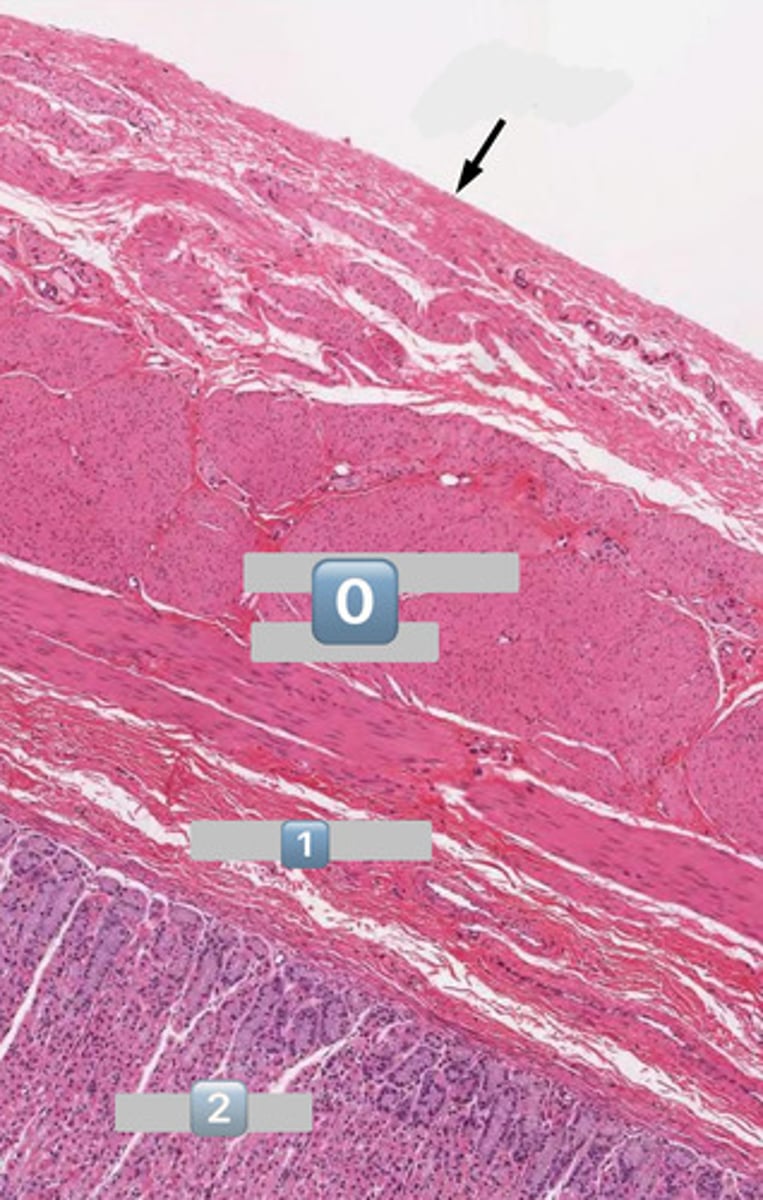
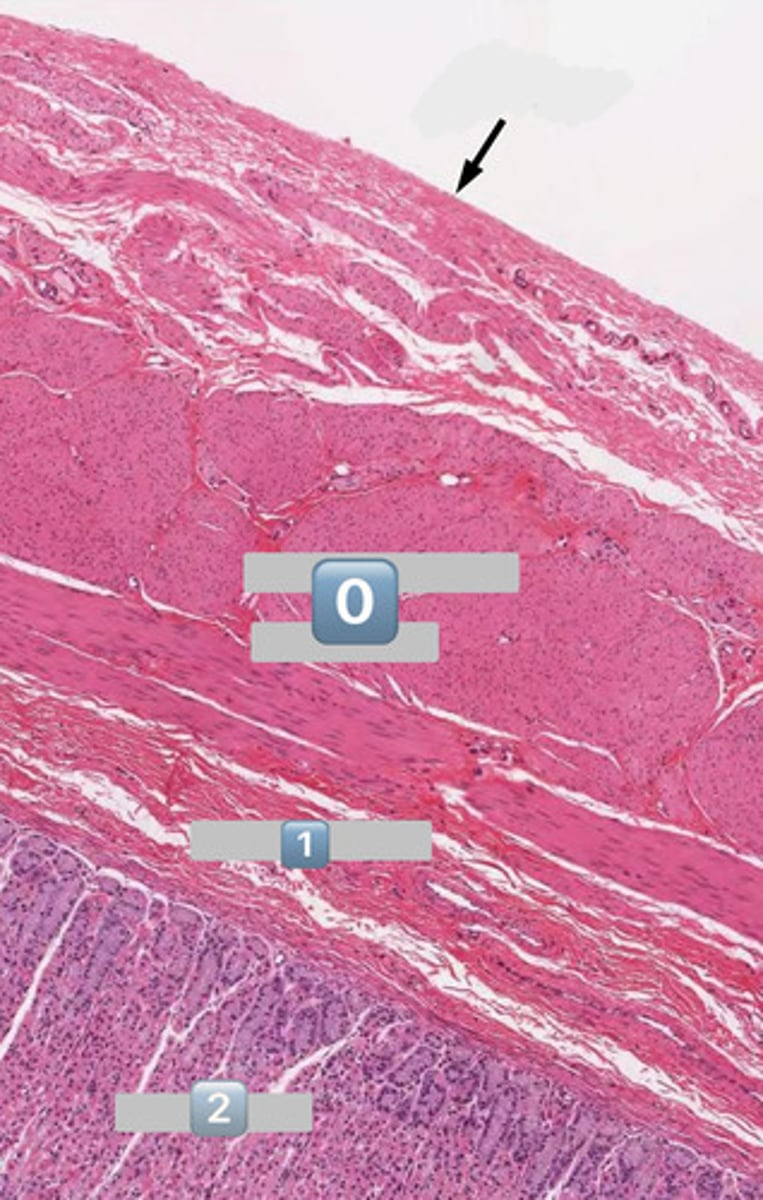
2
mucosa
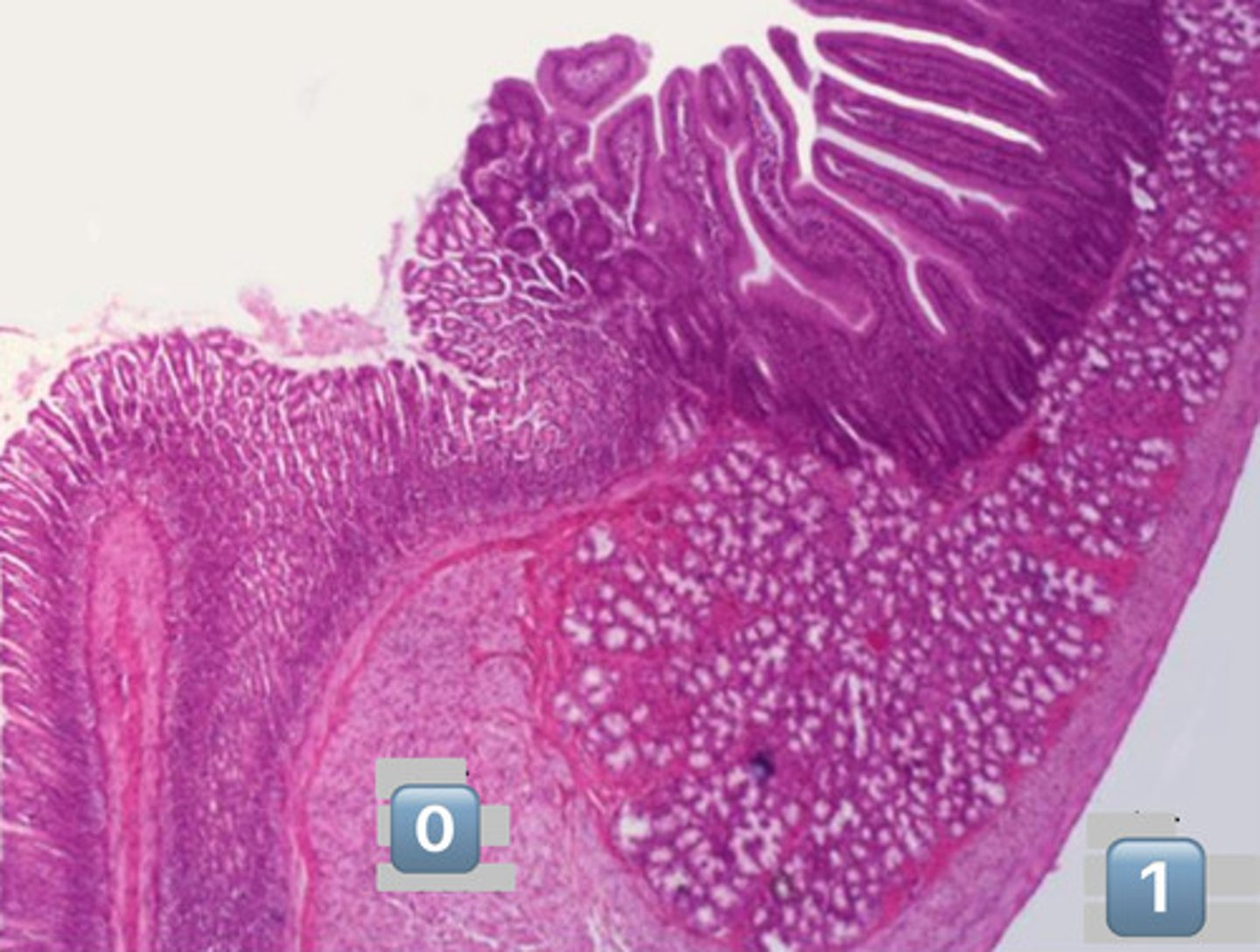
what is pictured here?
gastroduodenal junction
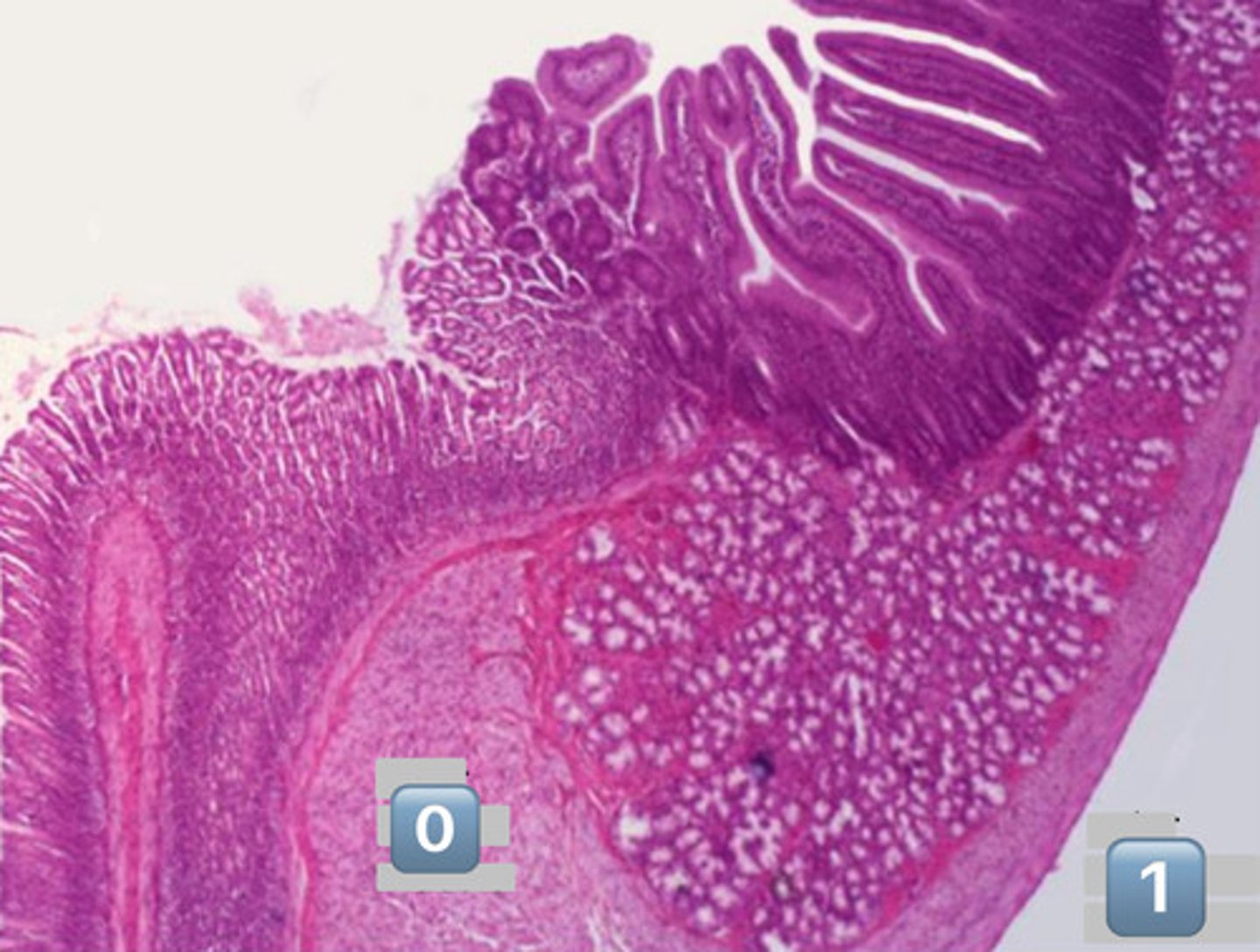
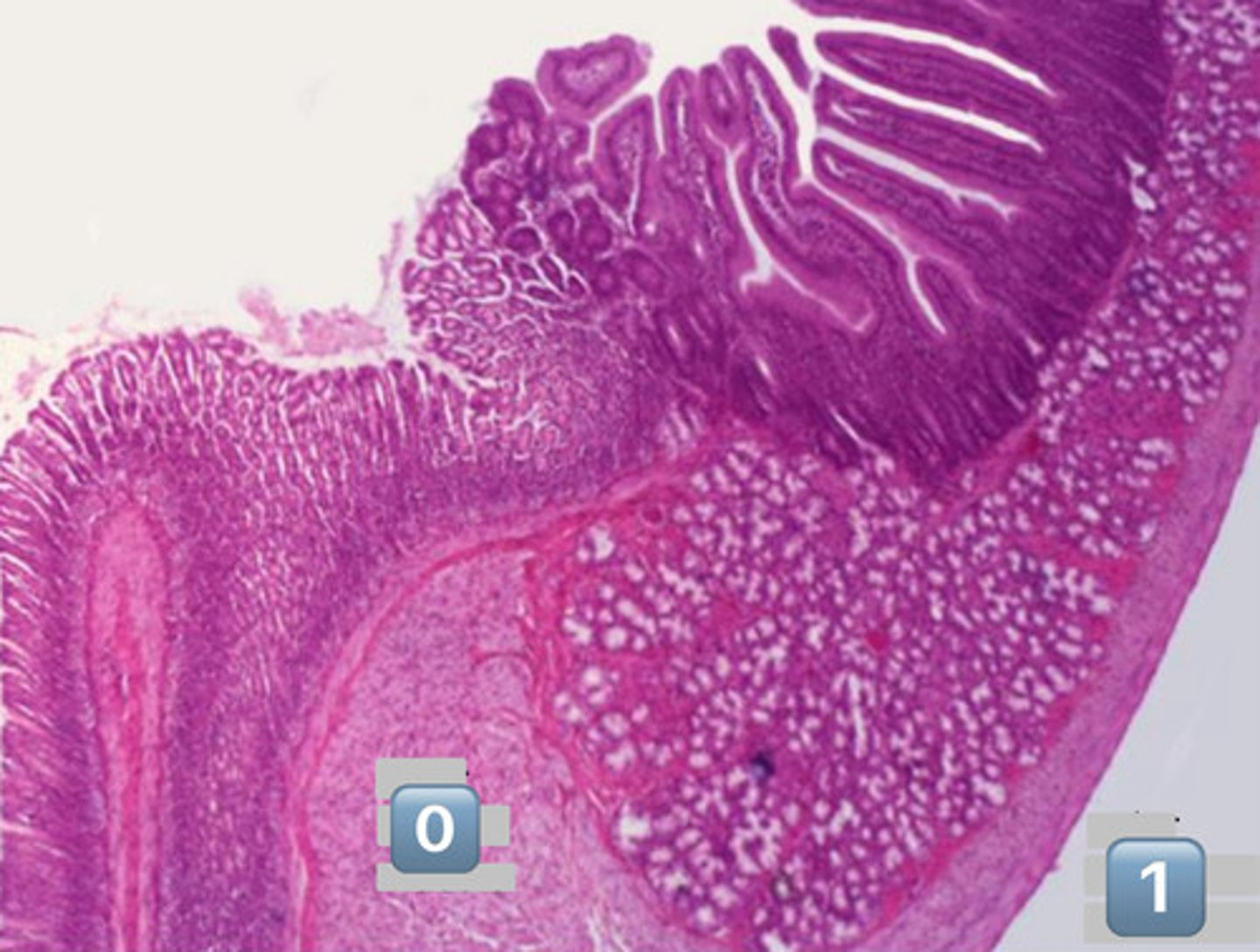
0
inner circular muscle
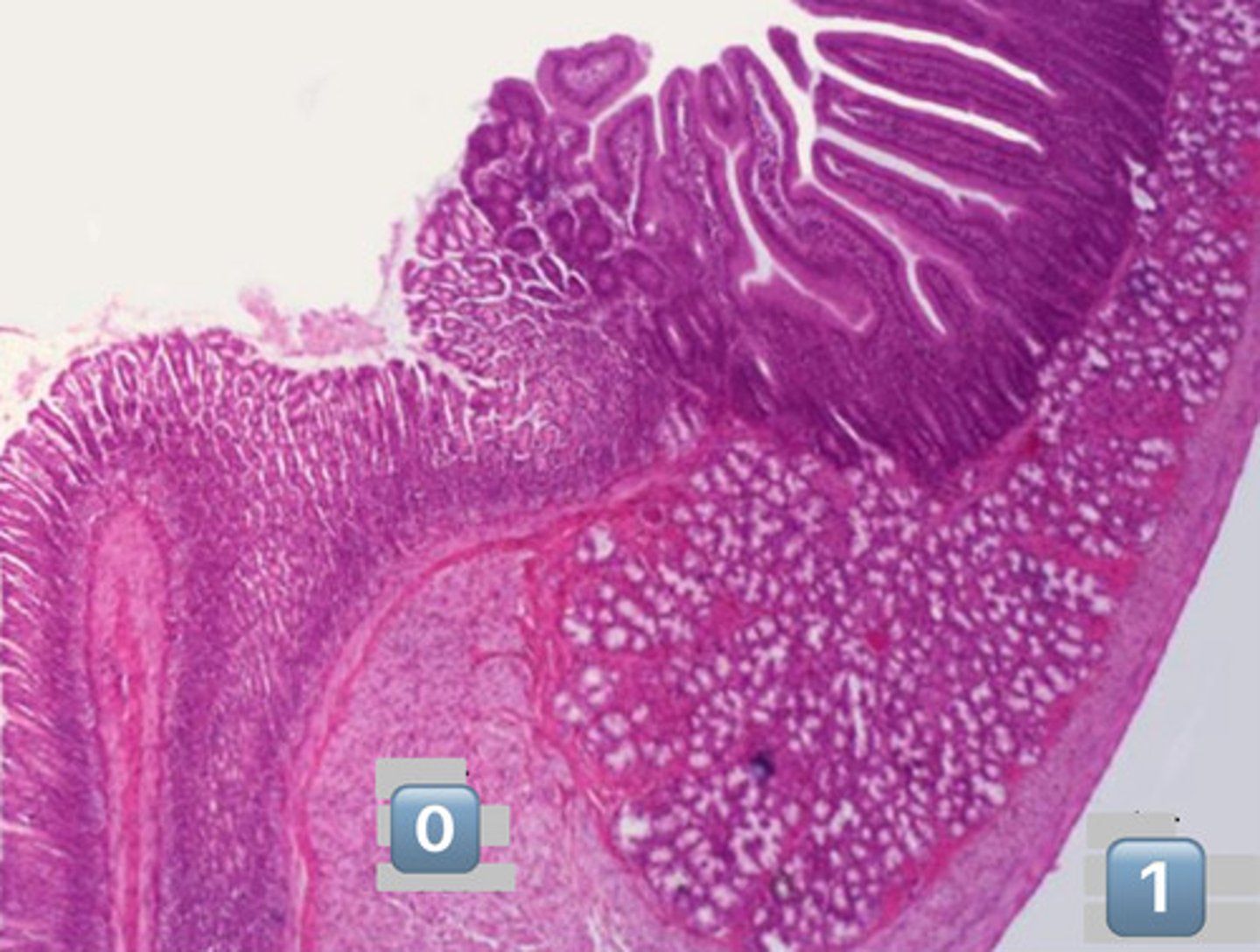
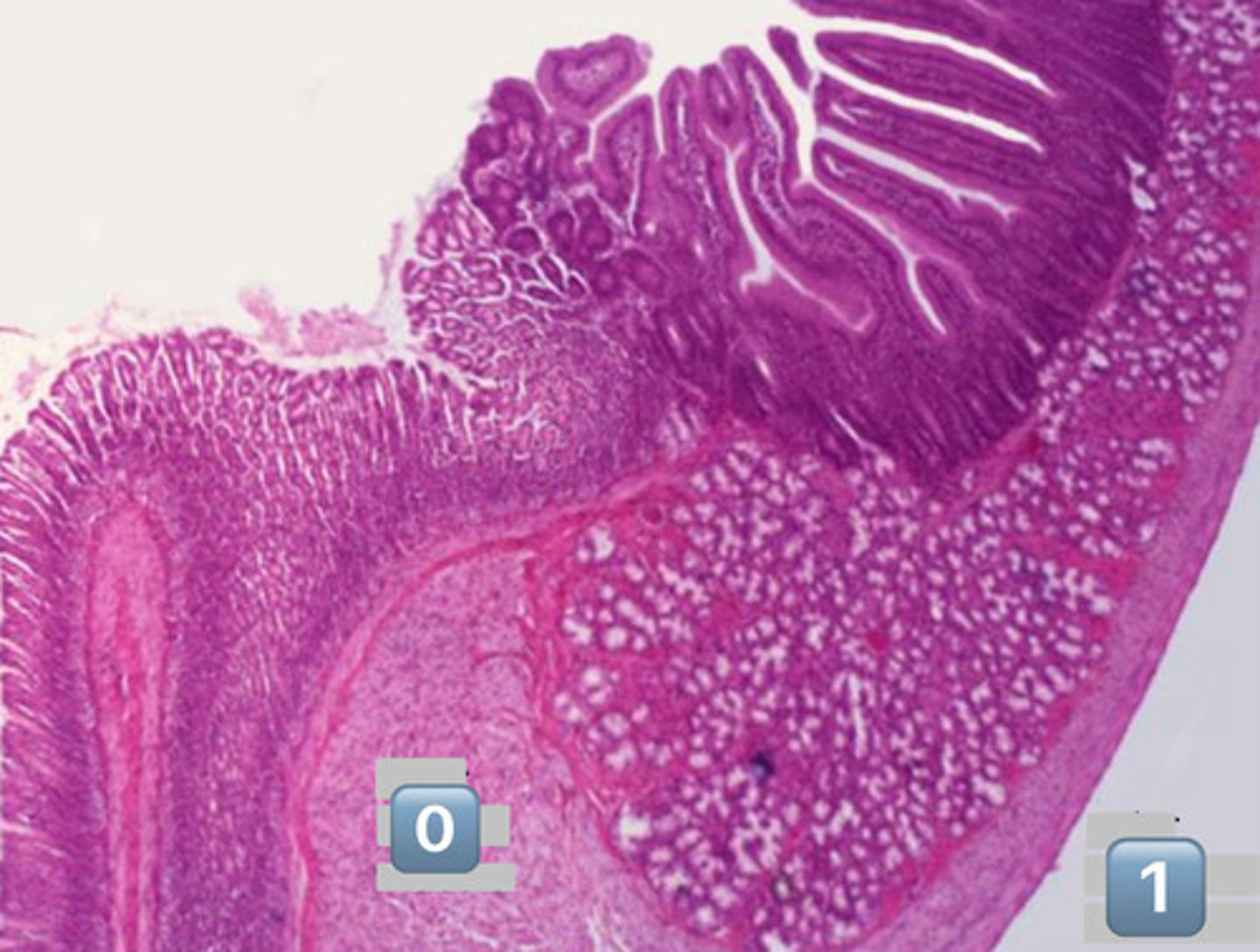
1
outer longitudinal muscle
arrow?
Duodenal submucosal Brunner's Glands
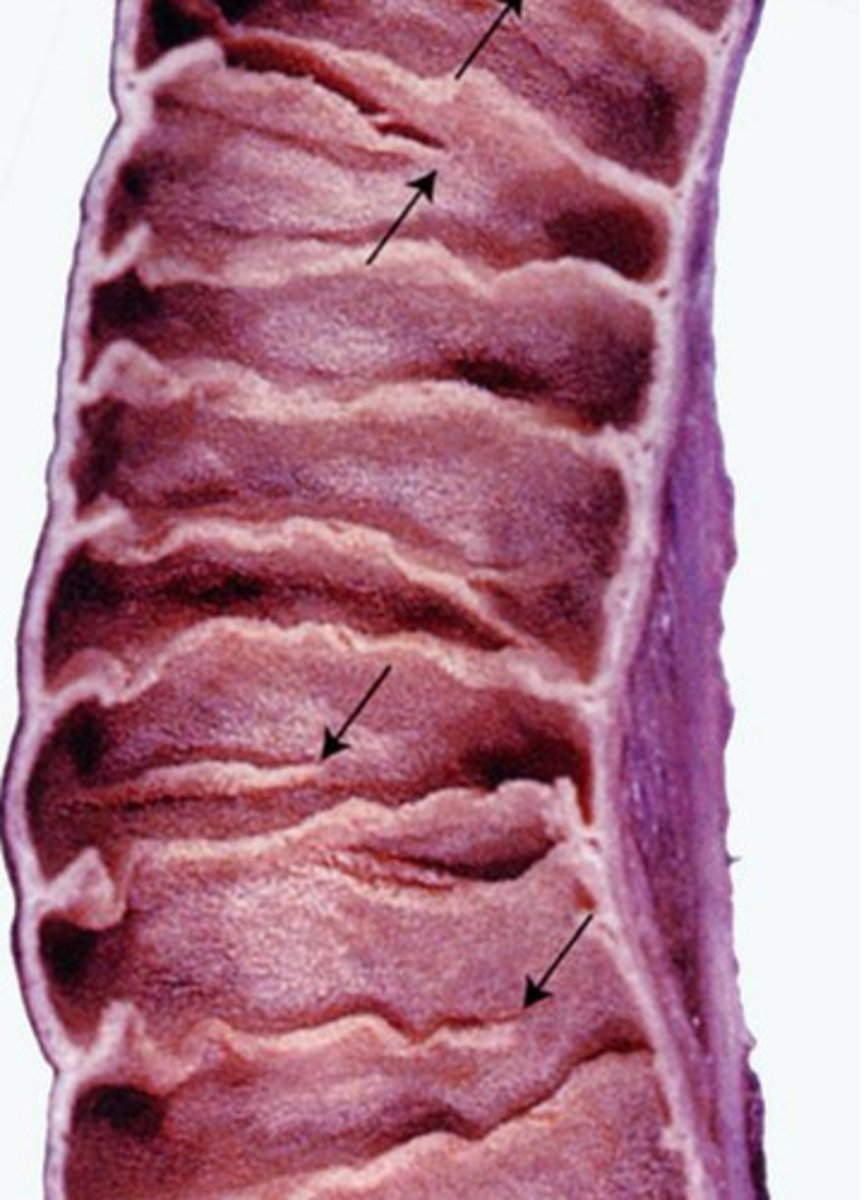
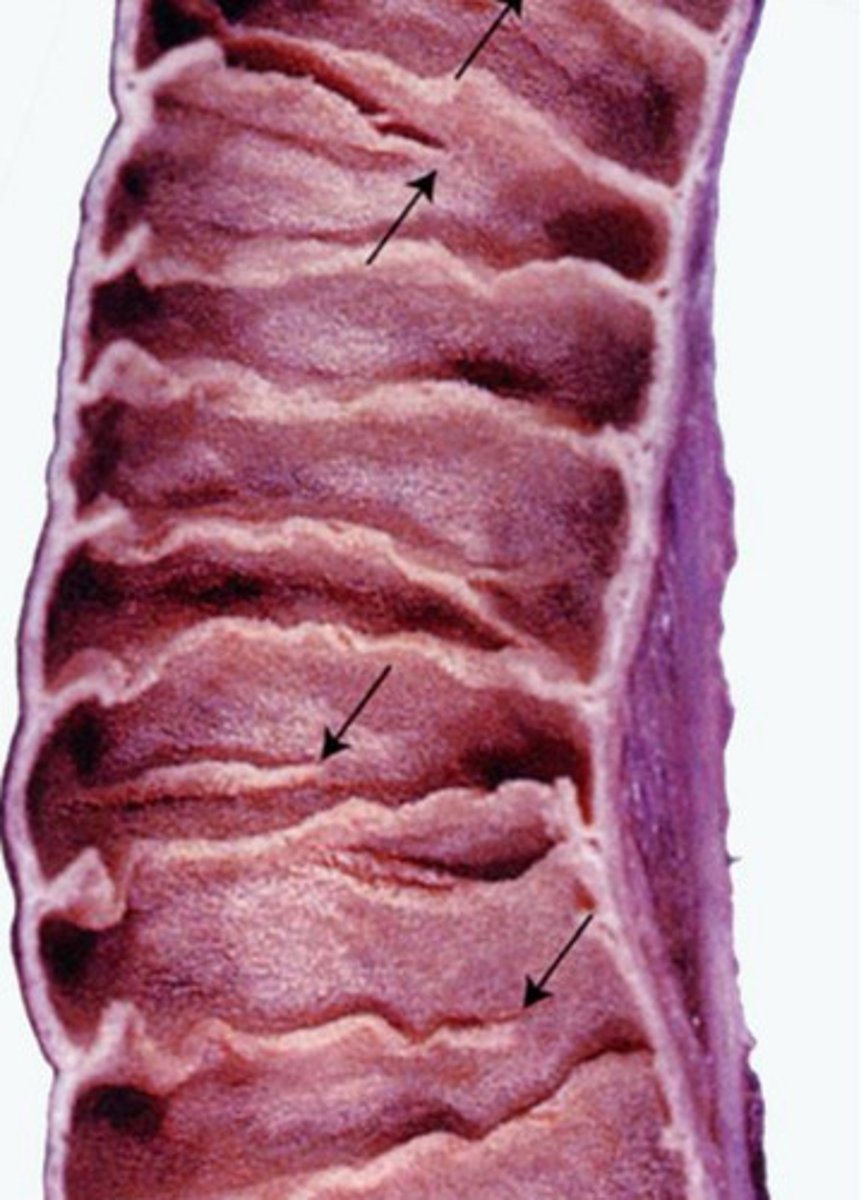
plicae circulares
- infolding of submucosa
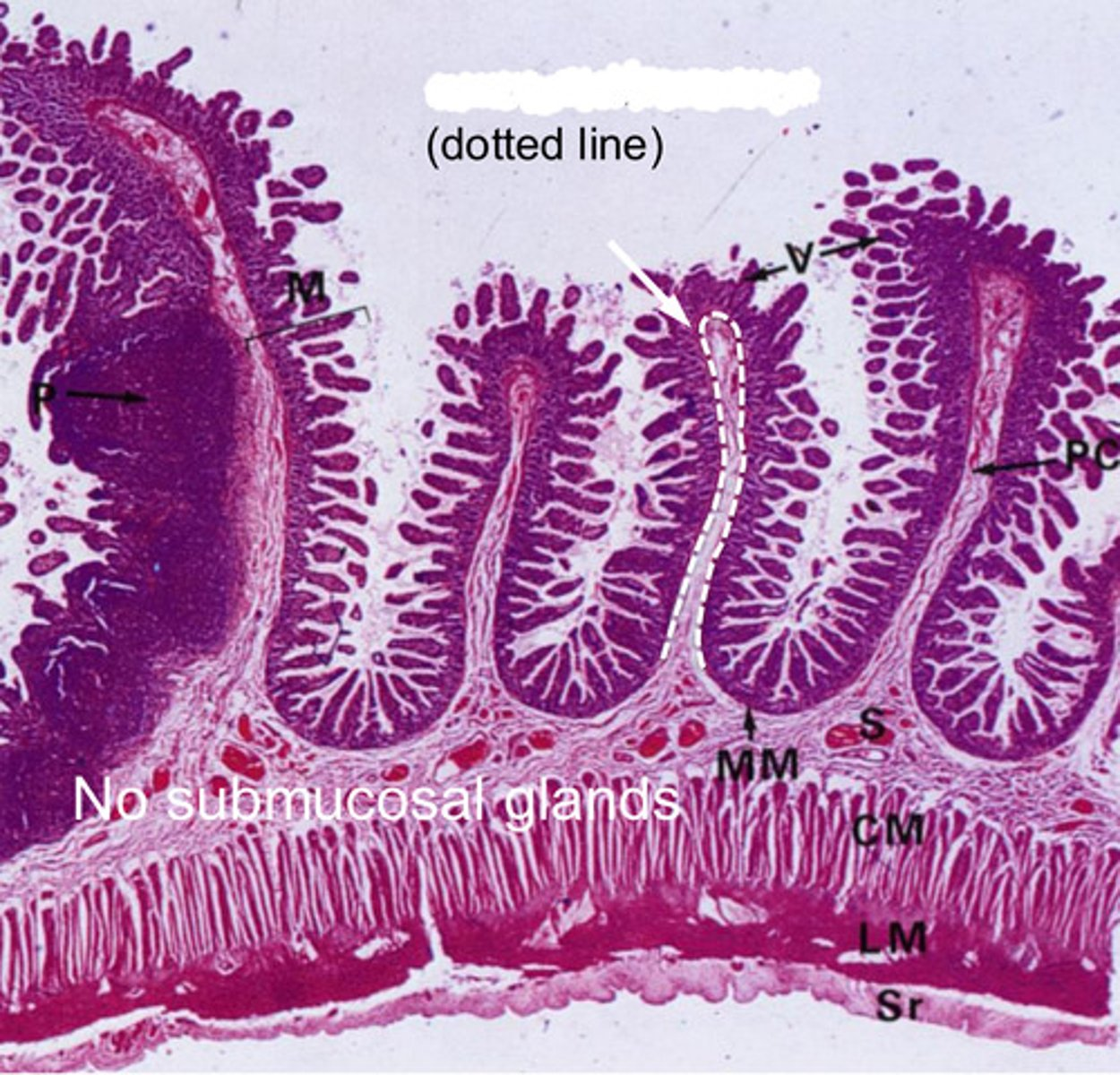
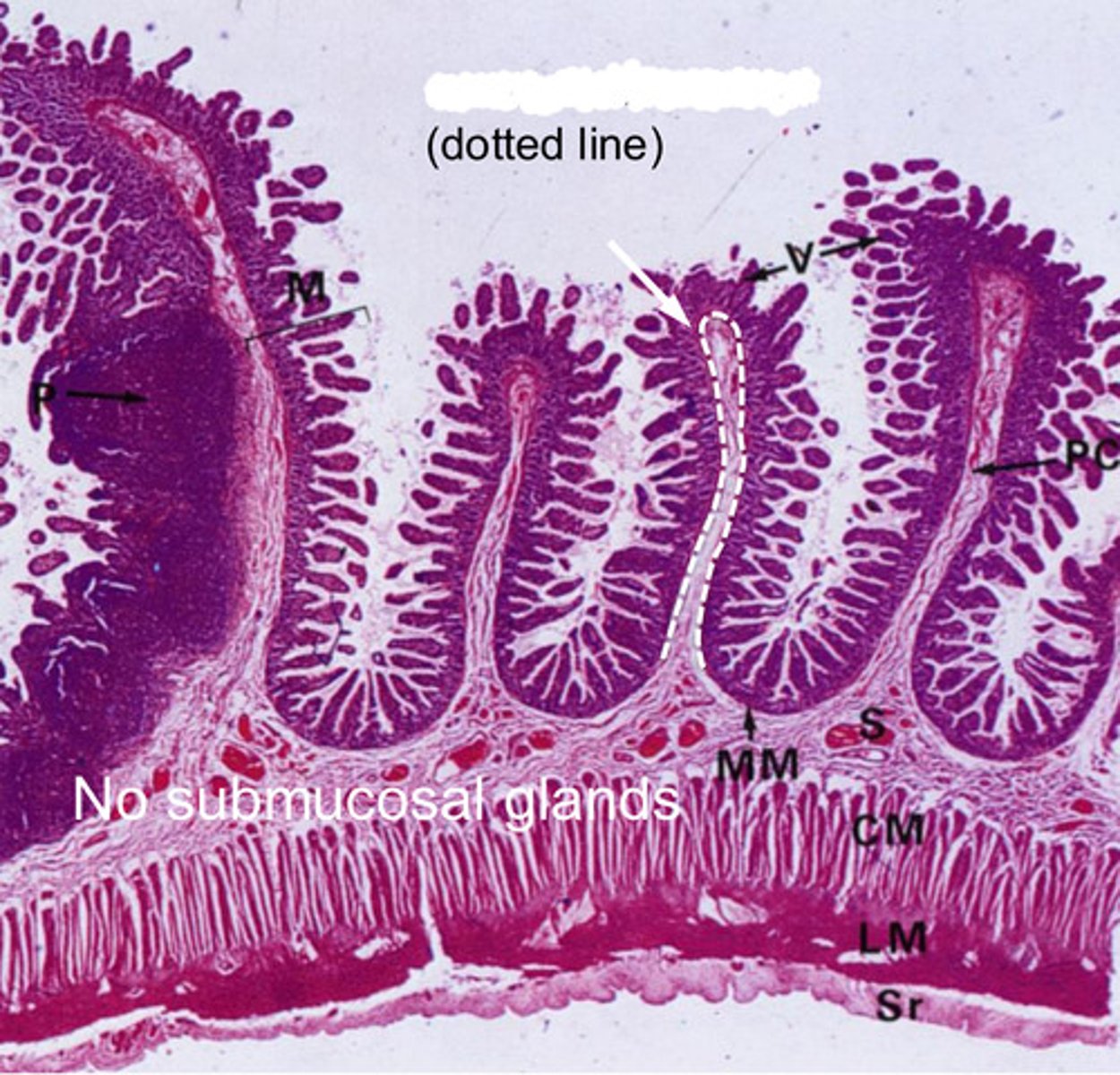
dotted line?
muscularis mucosa
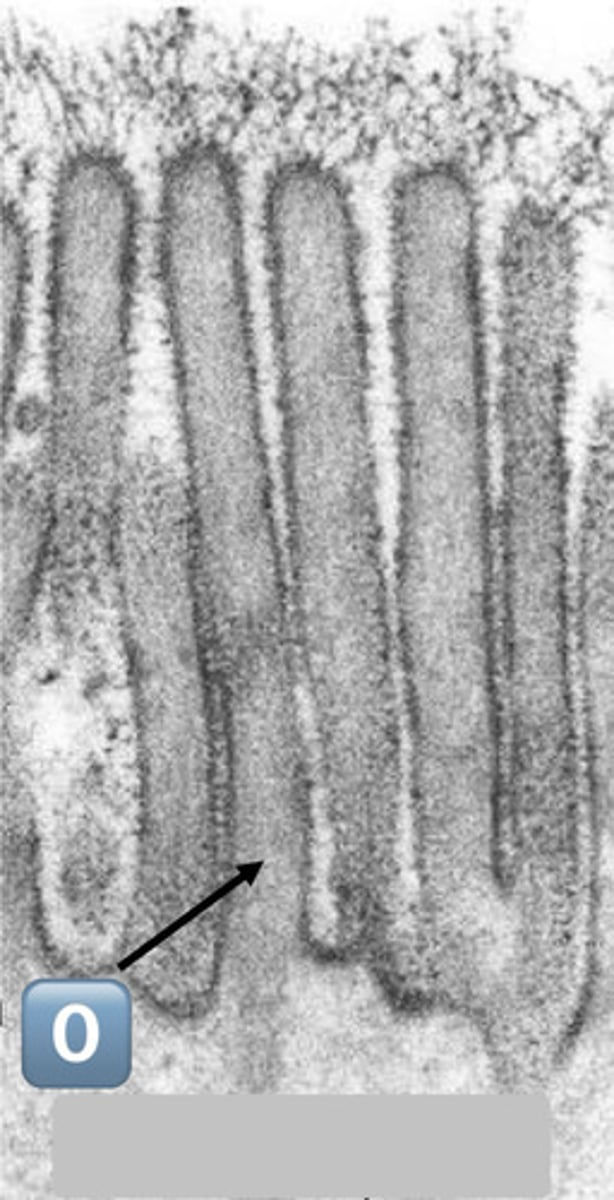
gray square?
epithelial surface cell: enterocyte
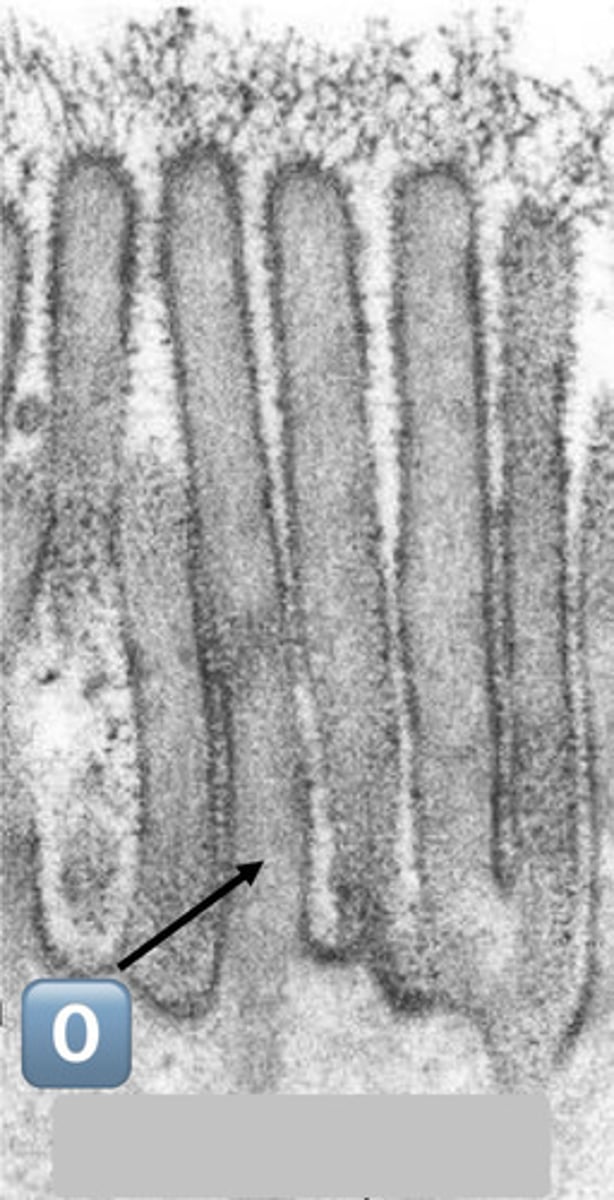
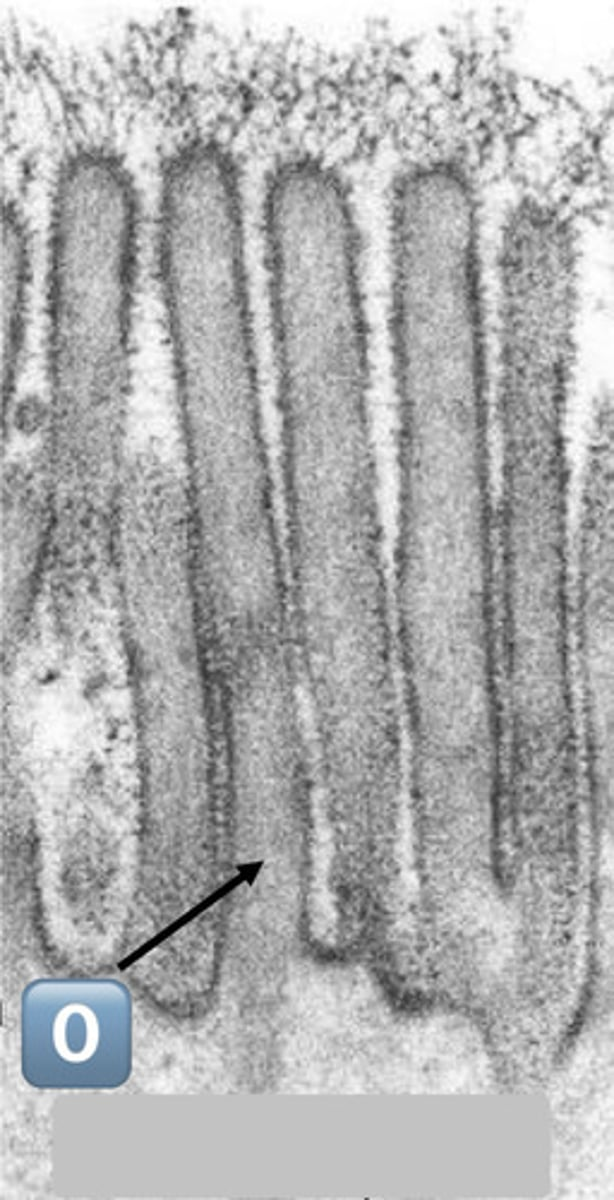
0
actin core
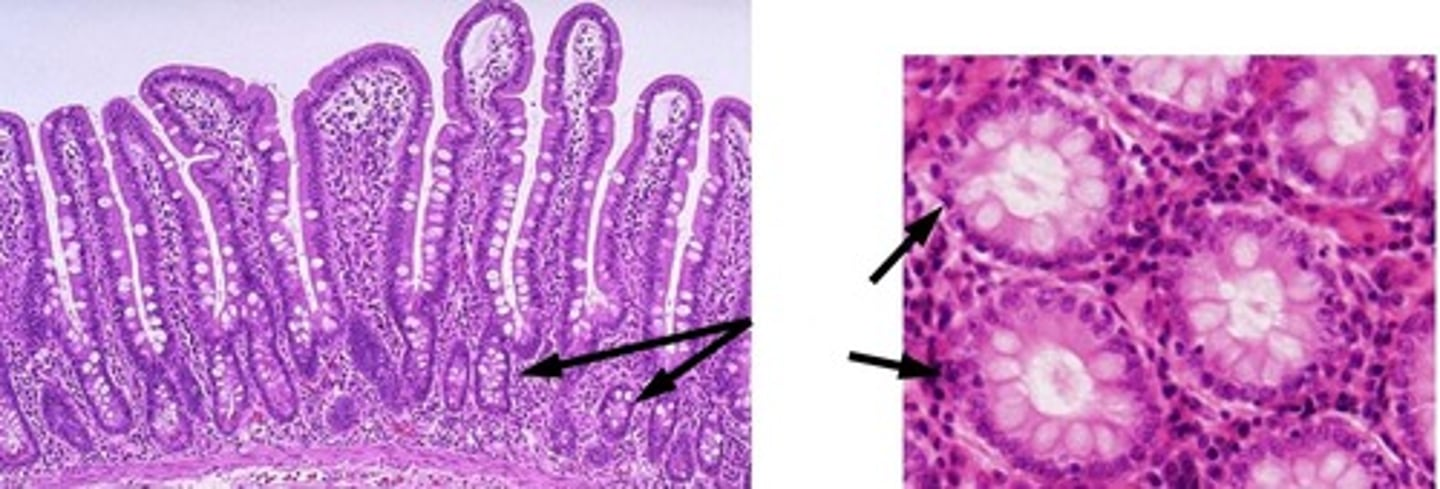
crypts
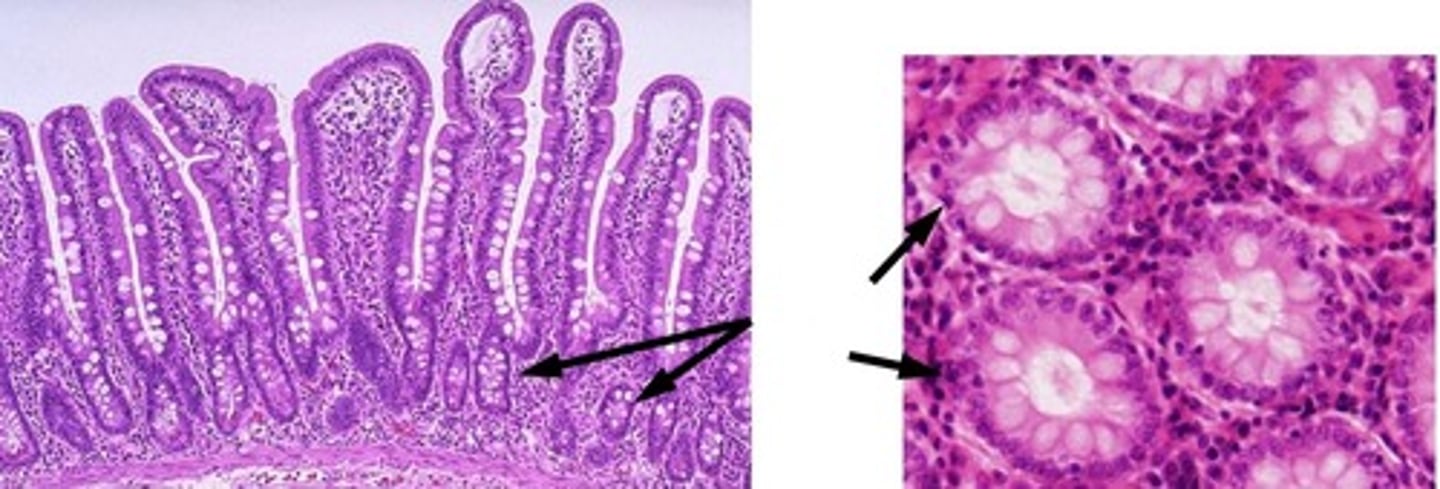
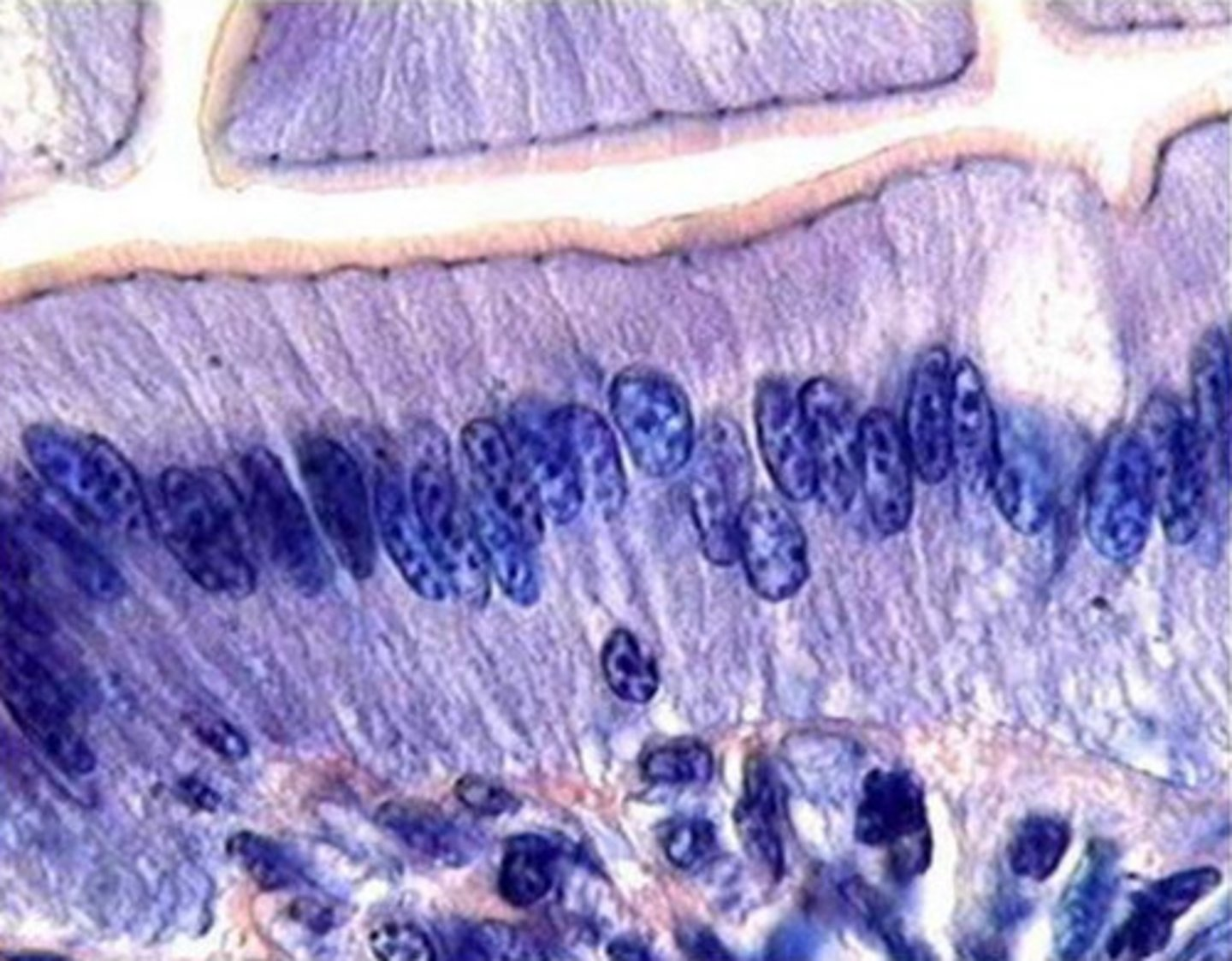
what is the function of the cells pictured?
controlled absorption
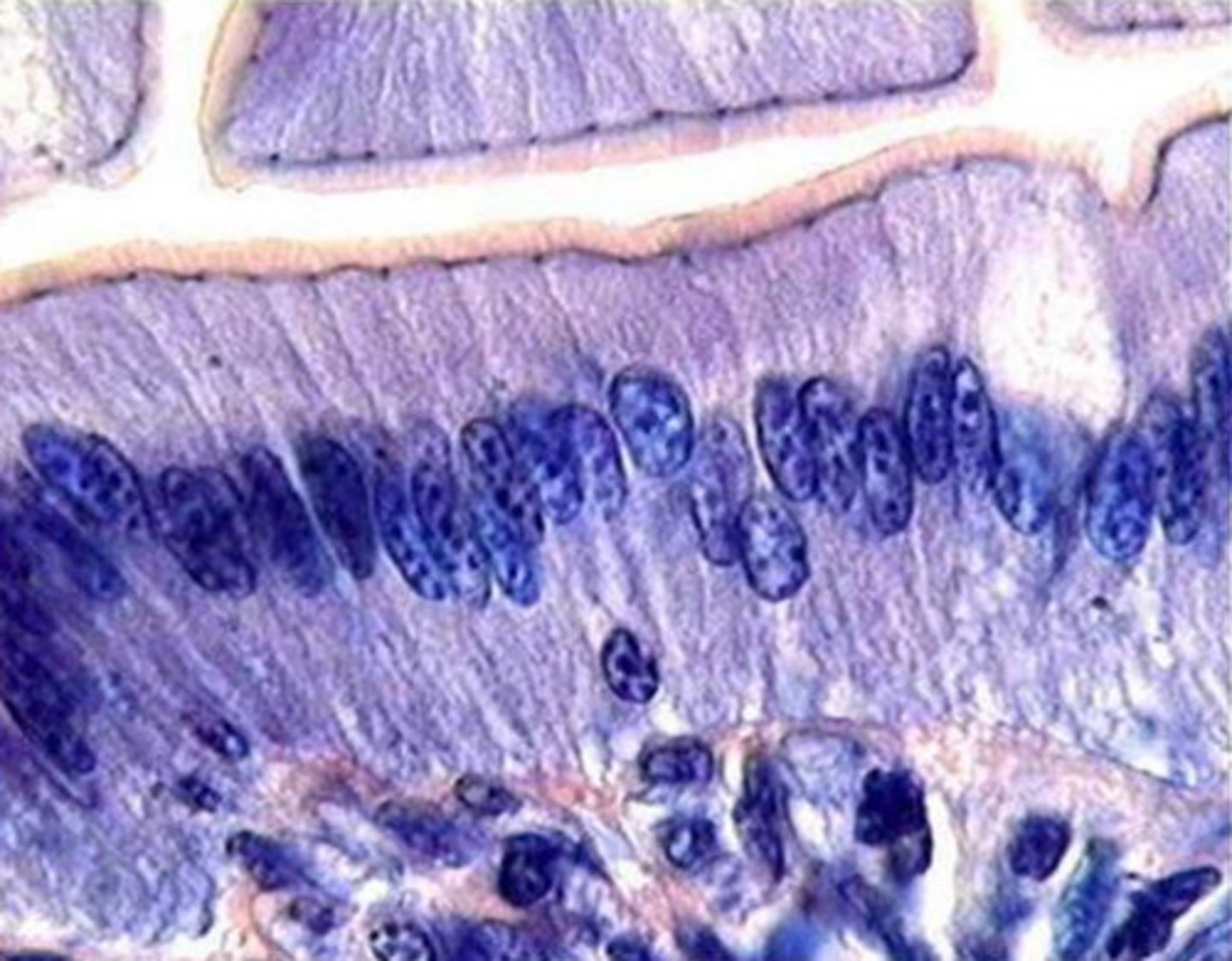
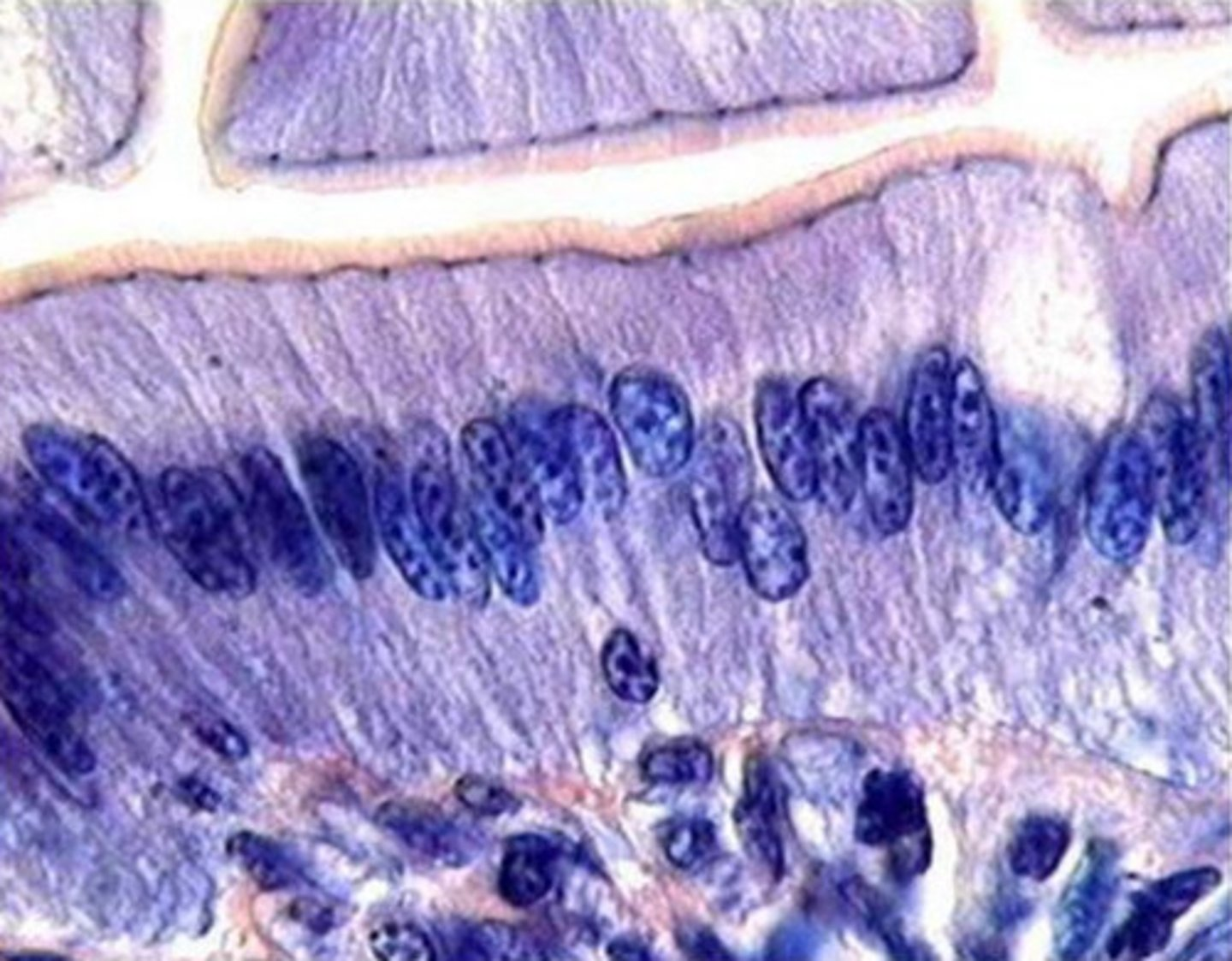
what is pictured?
enterocytes in small intestine
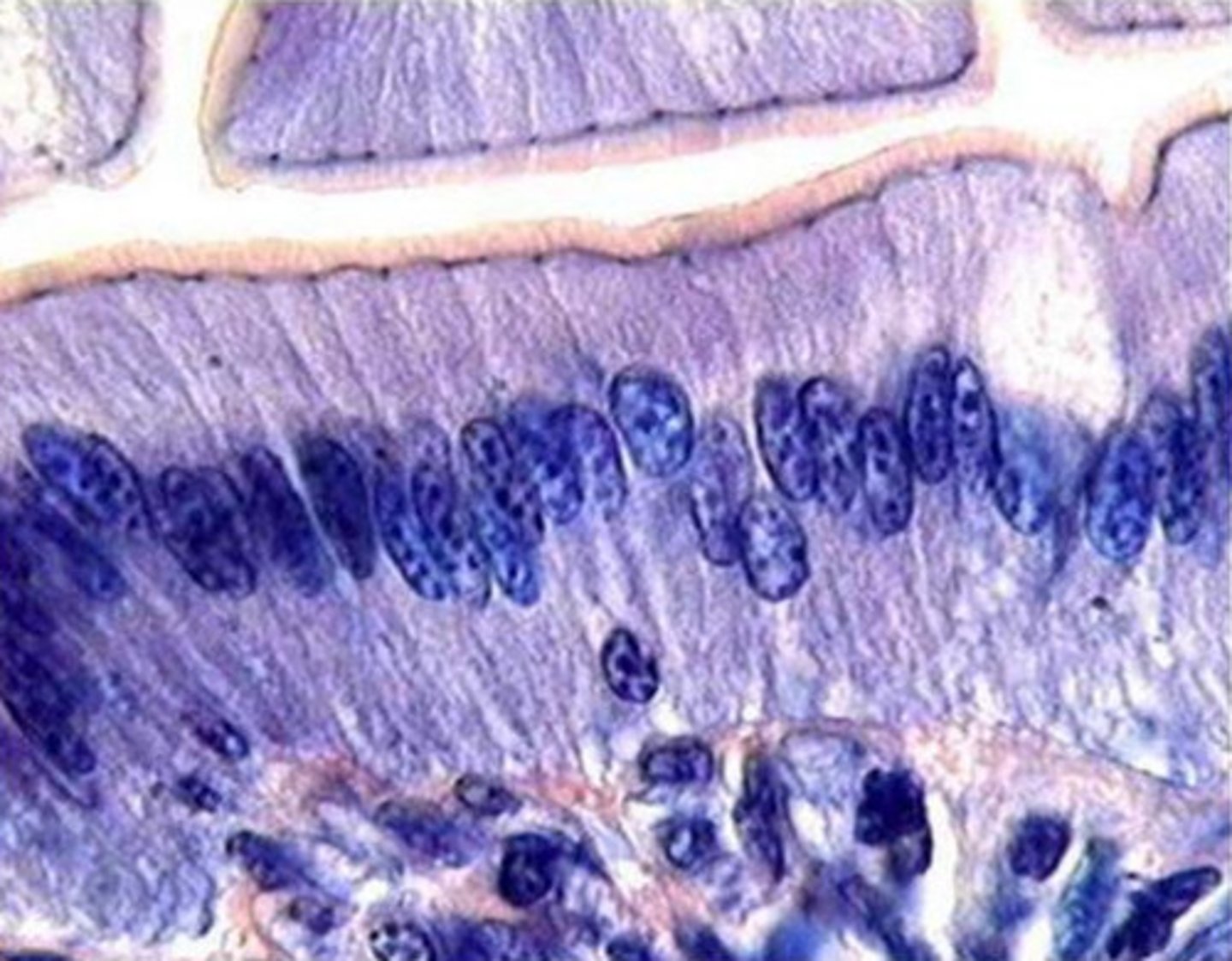
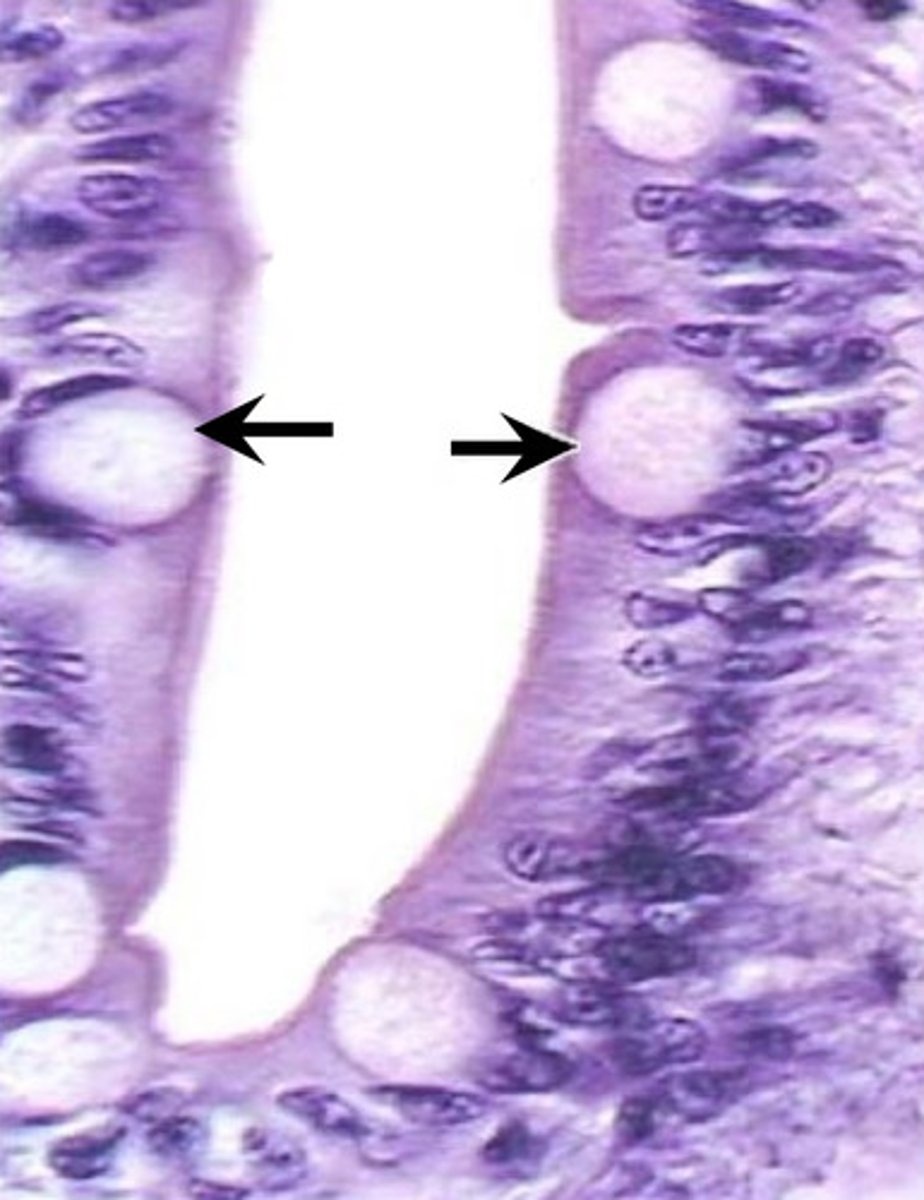
what is the function of the cell labeled?
produce mucin to protect and lubricate the inner surface of the small intestine
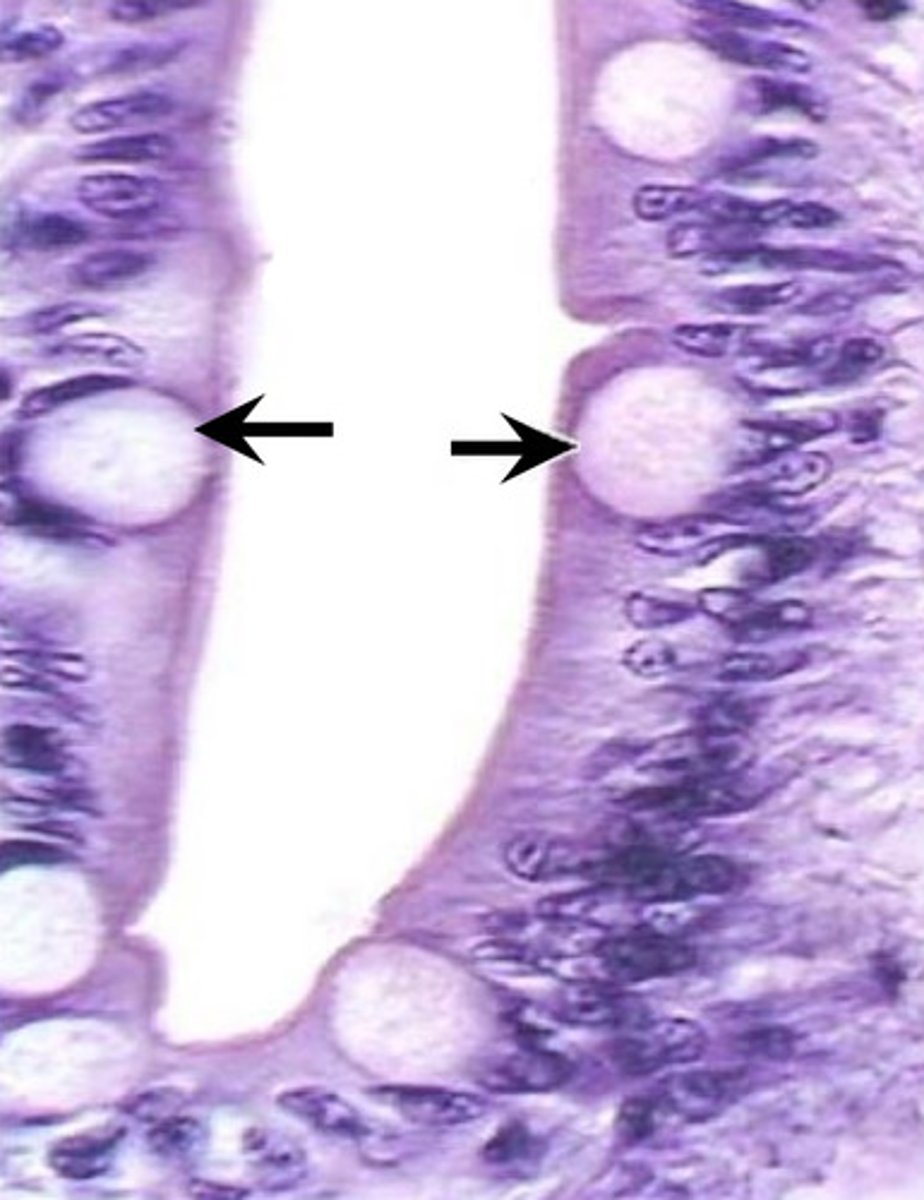
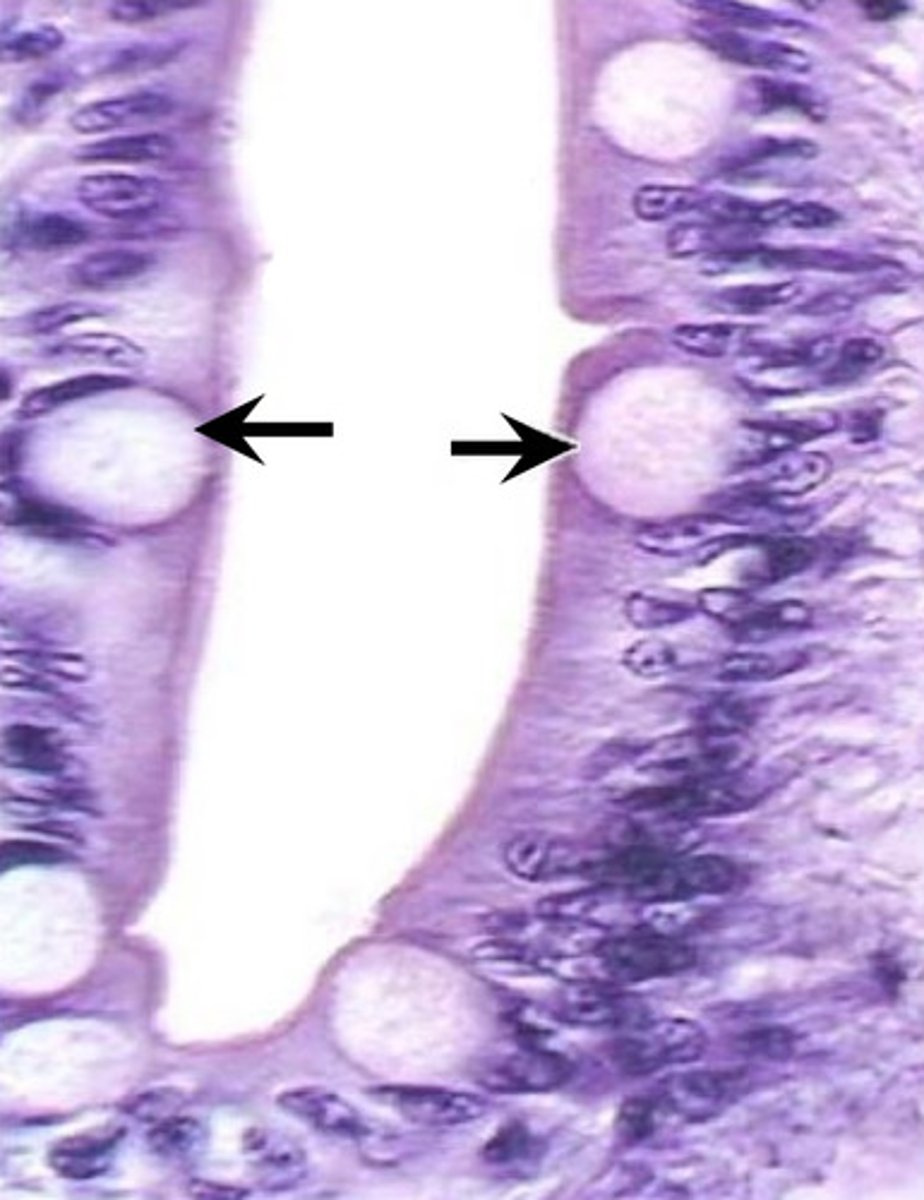
goblet cells of the small intestine
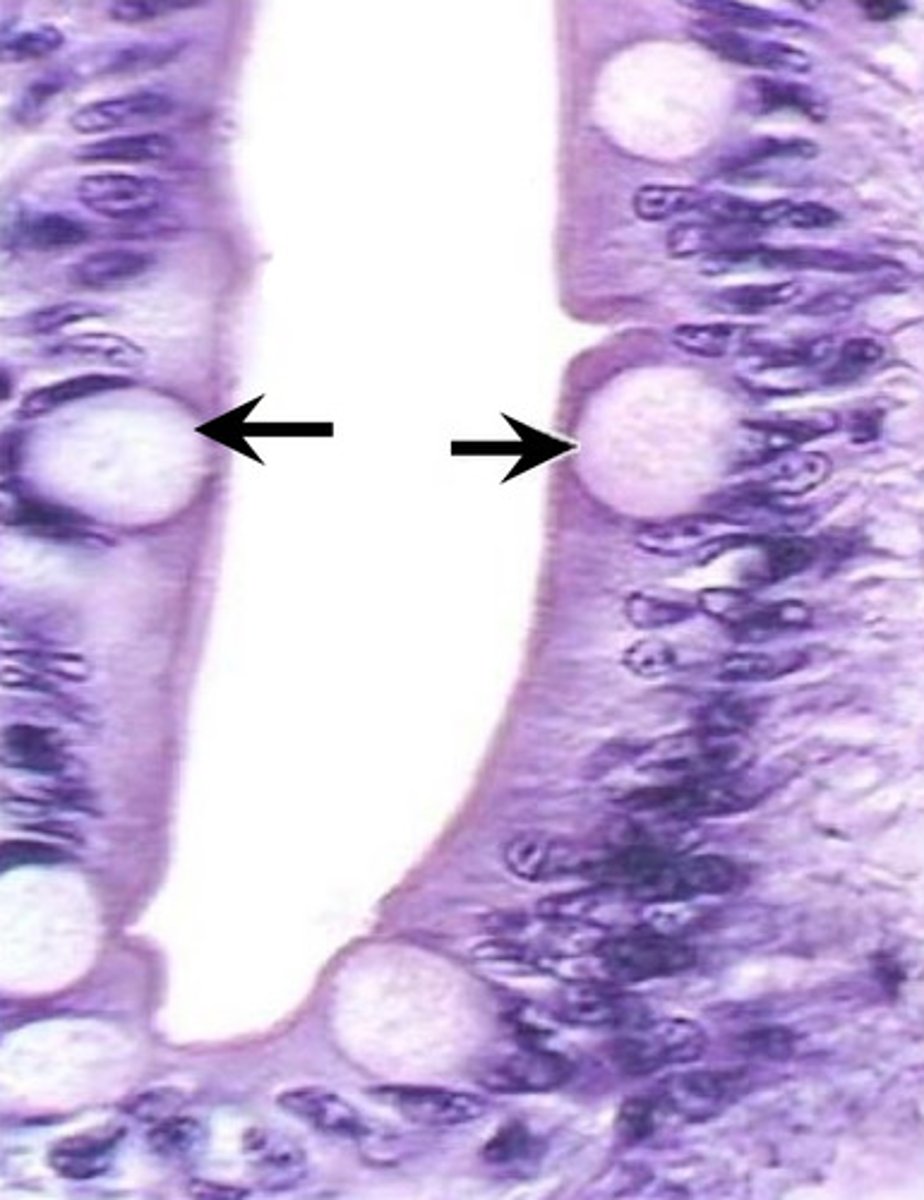
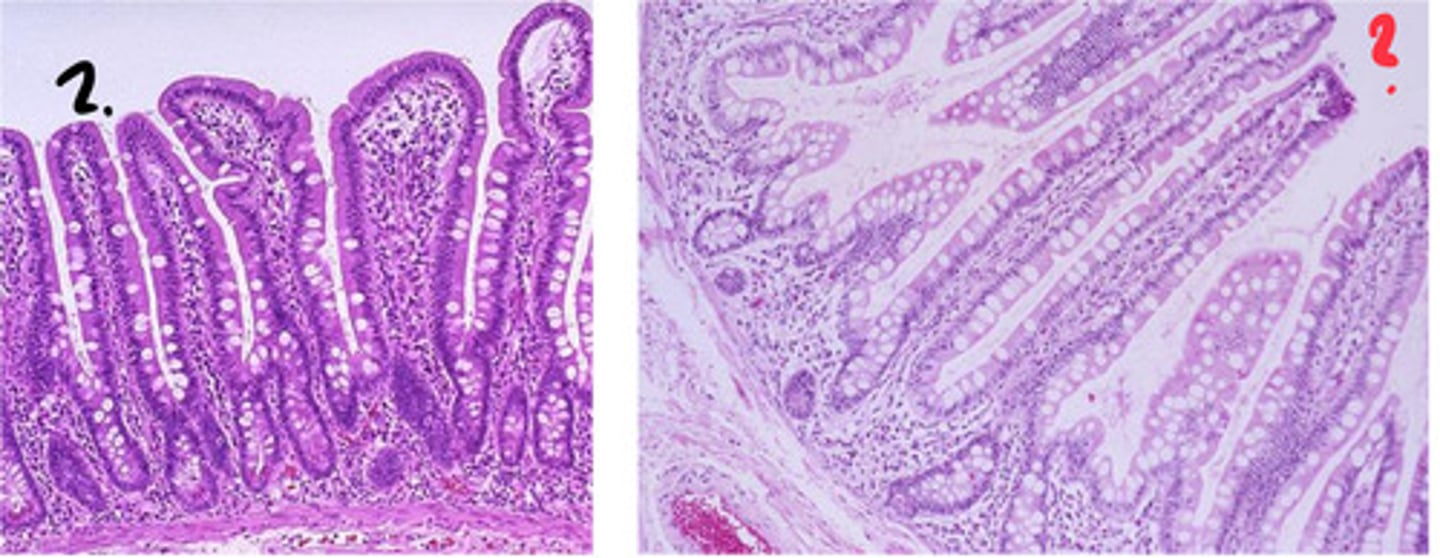
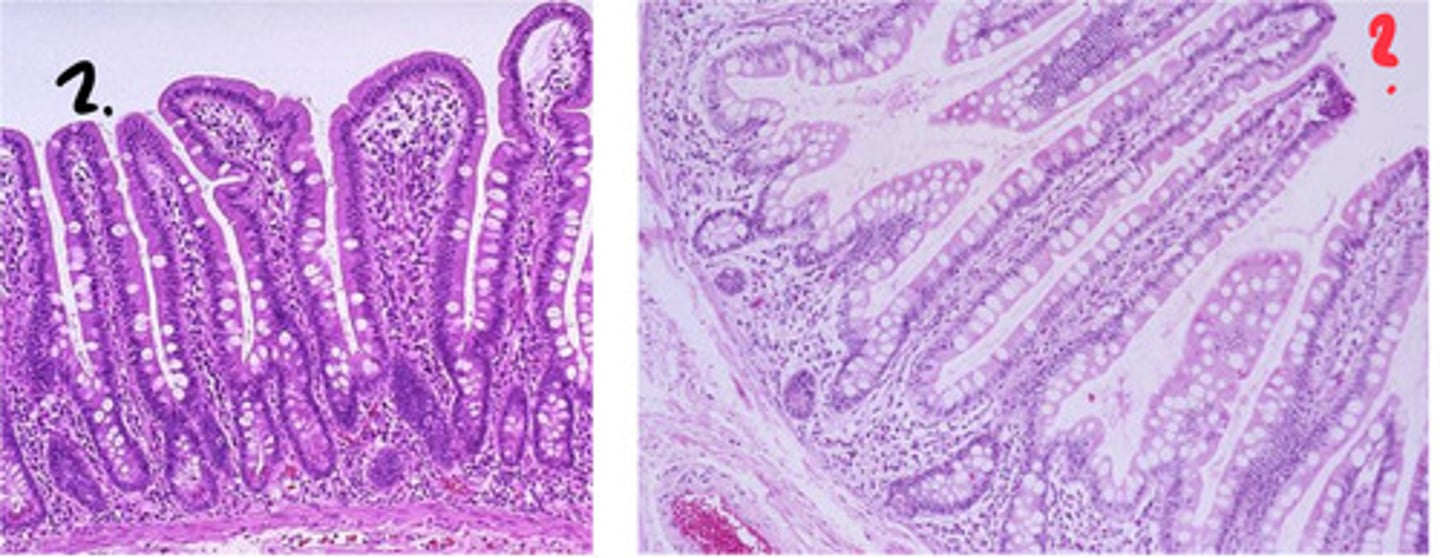
which of these is the duodenum? which is the ileum? how can you tell?
left = duodenum
right = ilium
- goblet cell number increases from proximal to distal
enteroendocrine cells in intestinal crypts
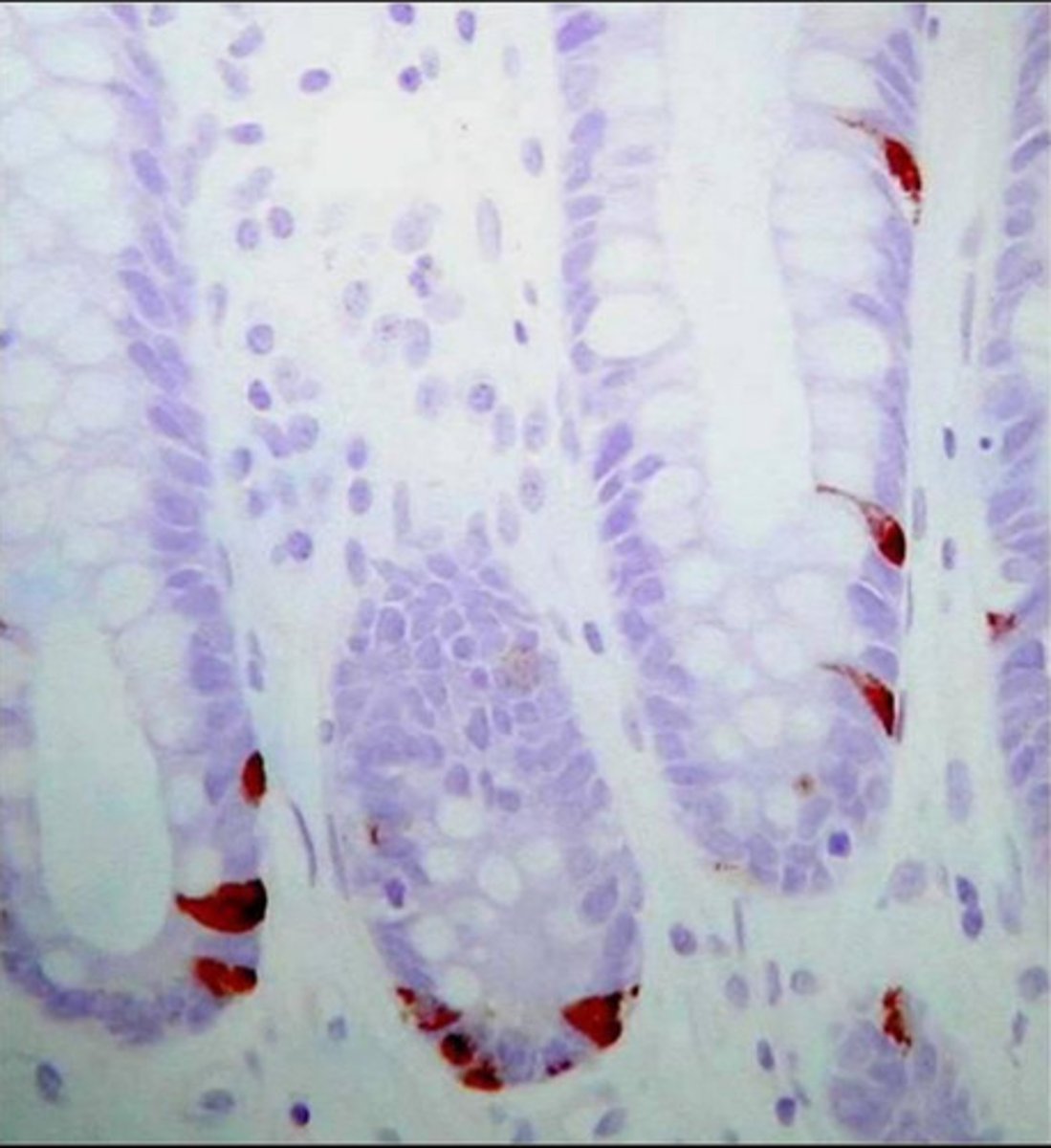
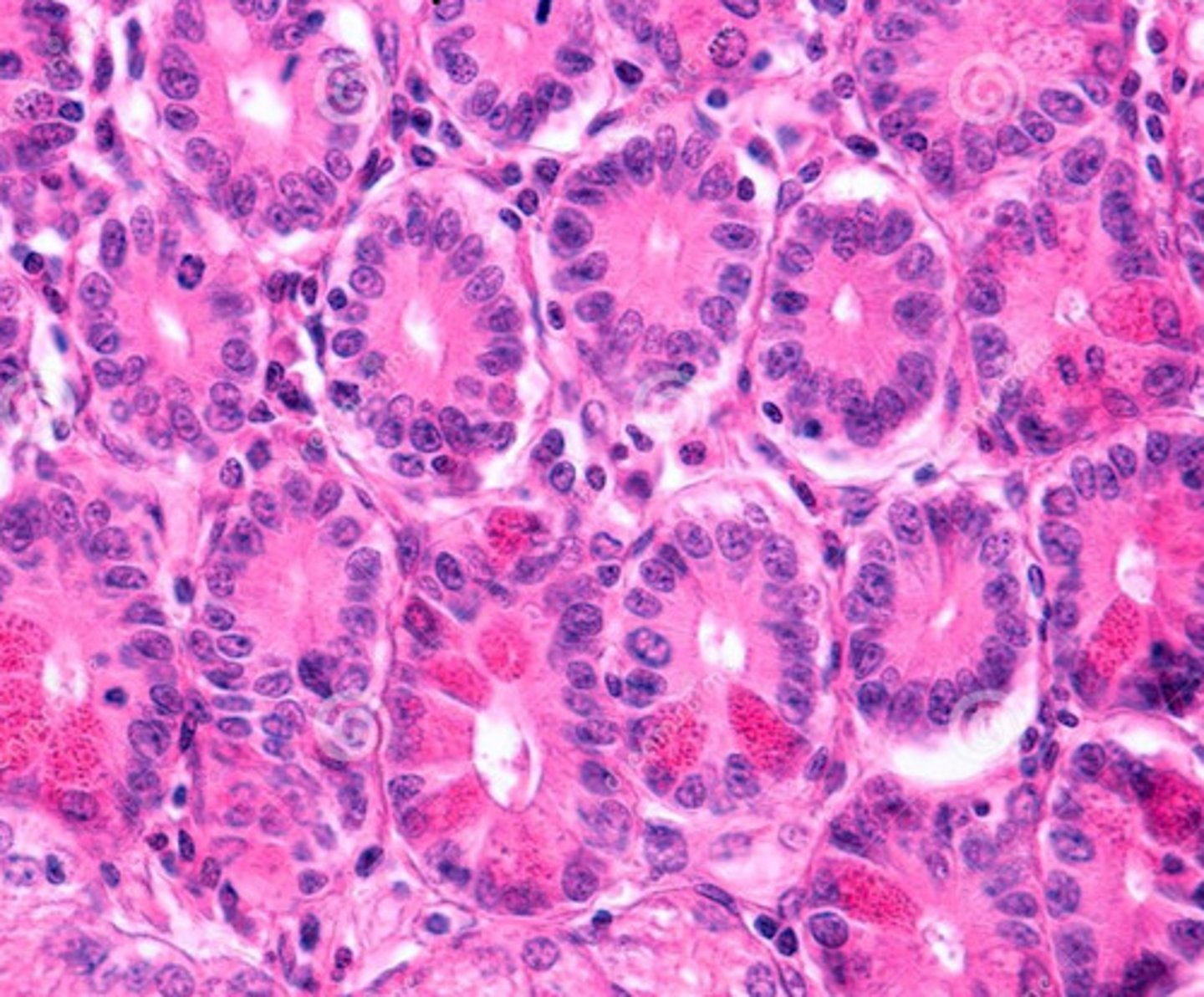
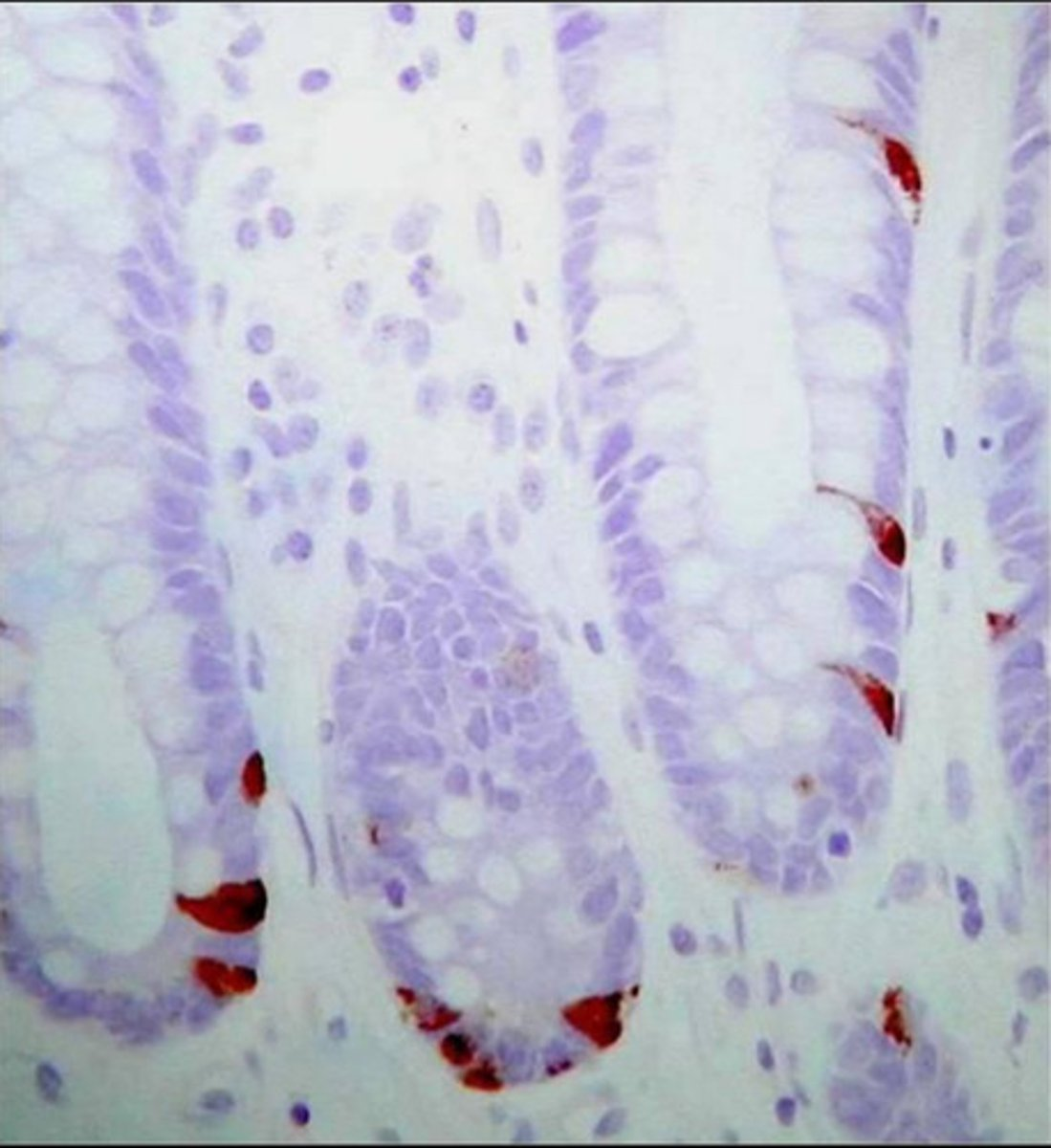
paneth cells
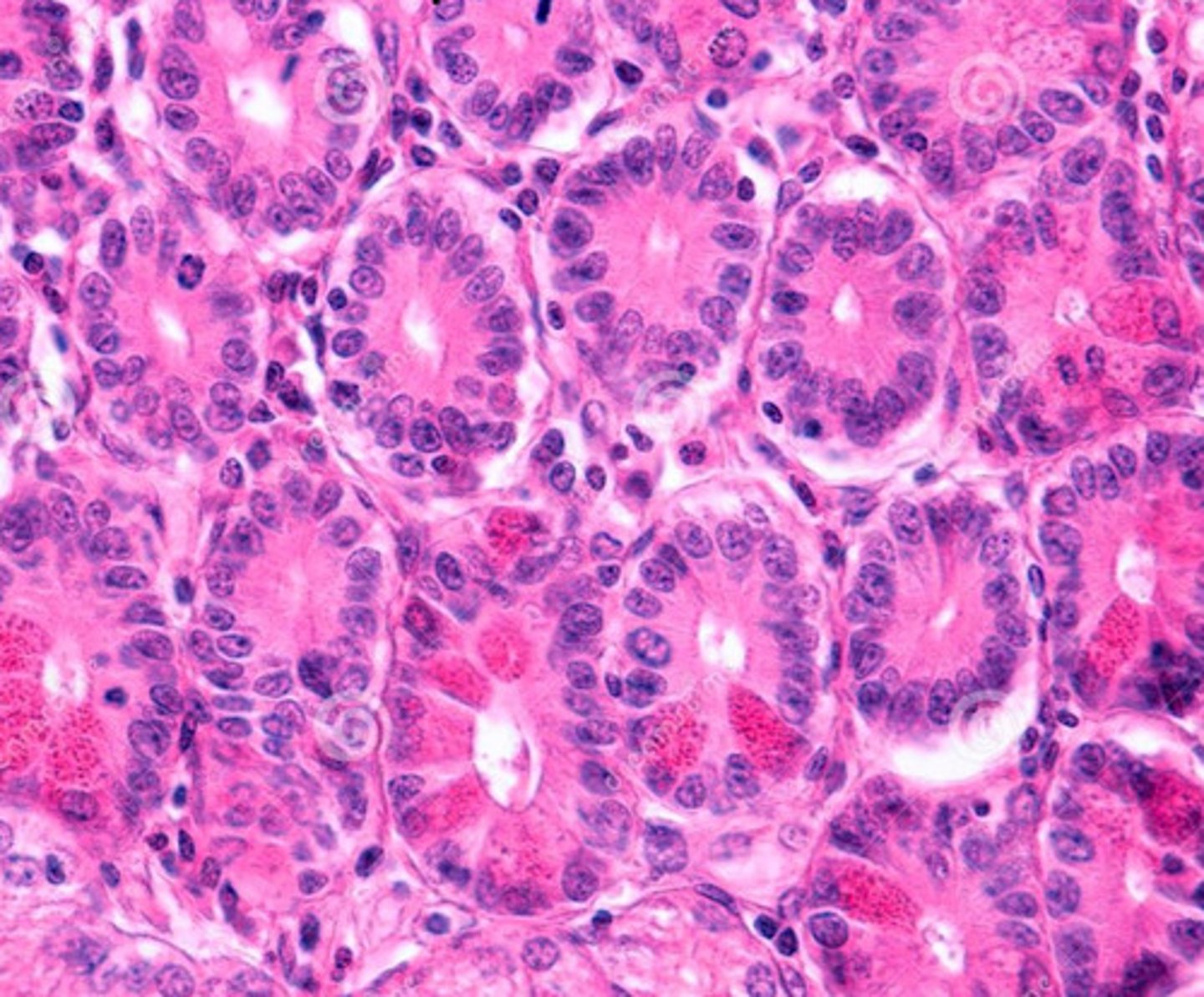
what is the function of these cells?
immune surveillance
secrete antimicrobial products:
- lysozyme
- alpha defensins
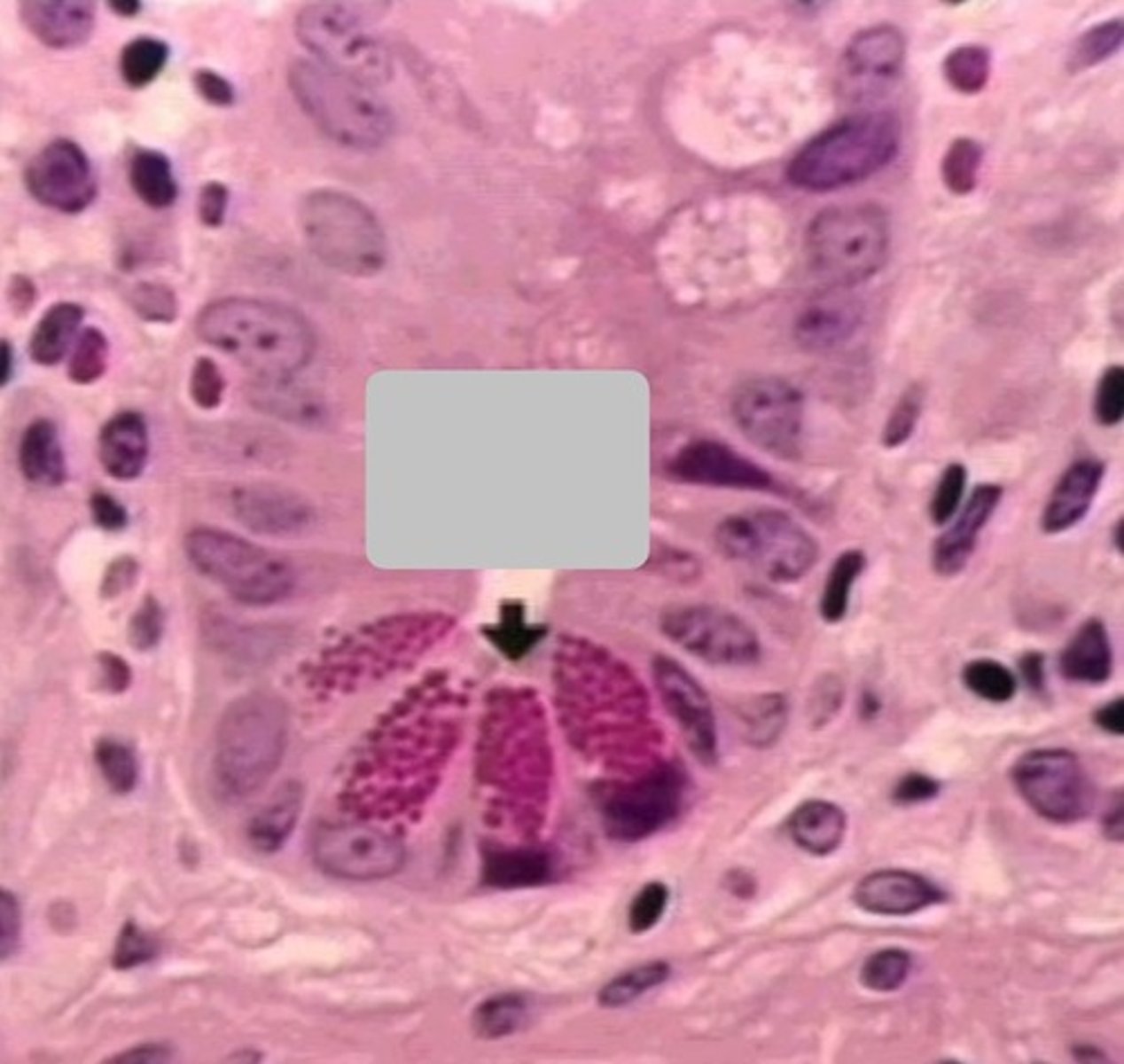
these are paneth cells found in crypts of the small intestine
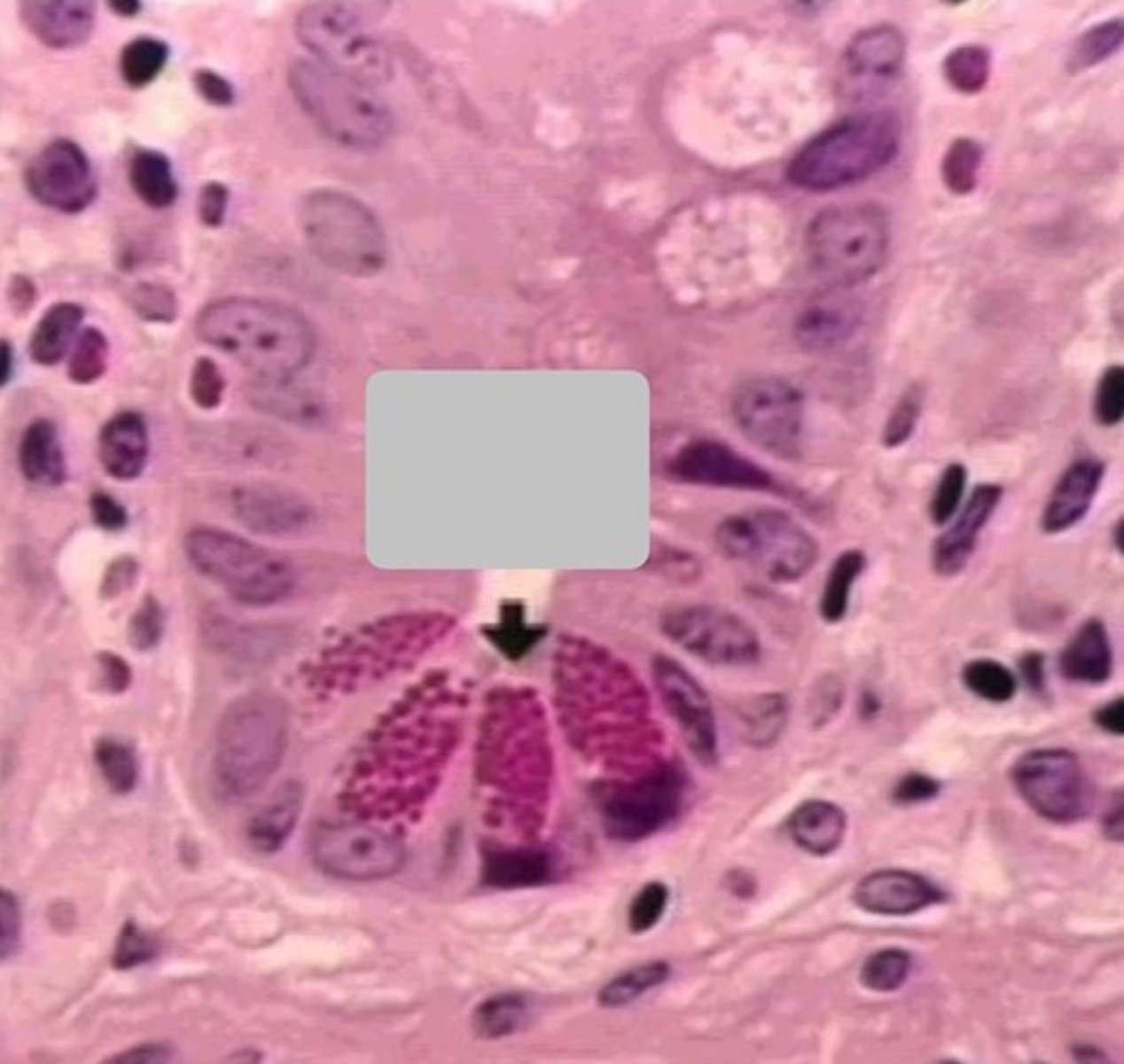
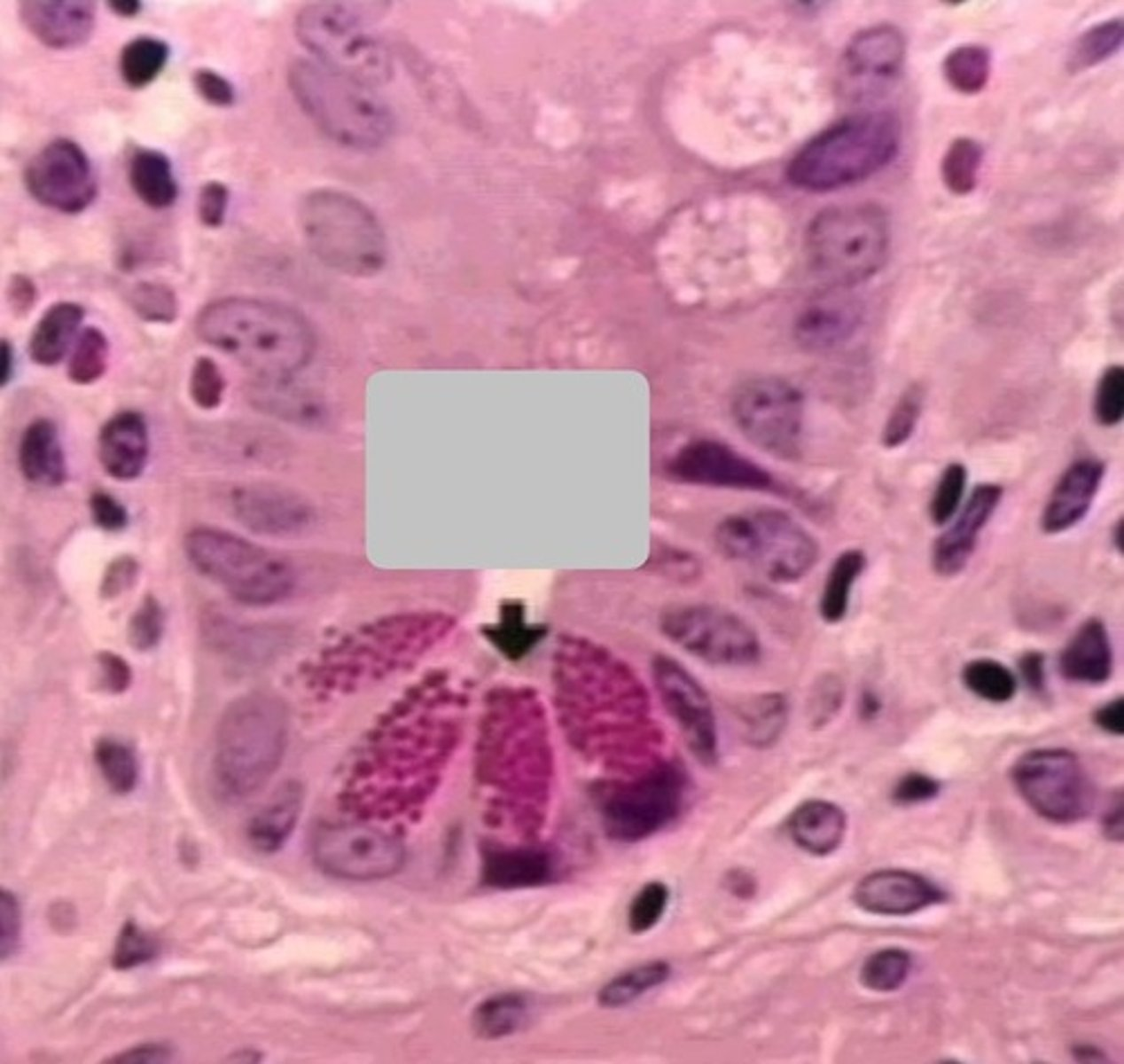
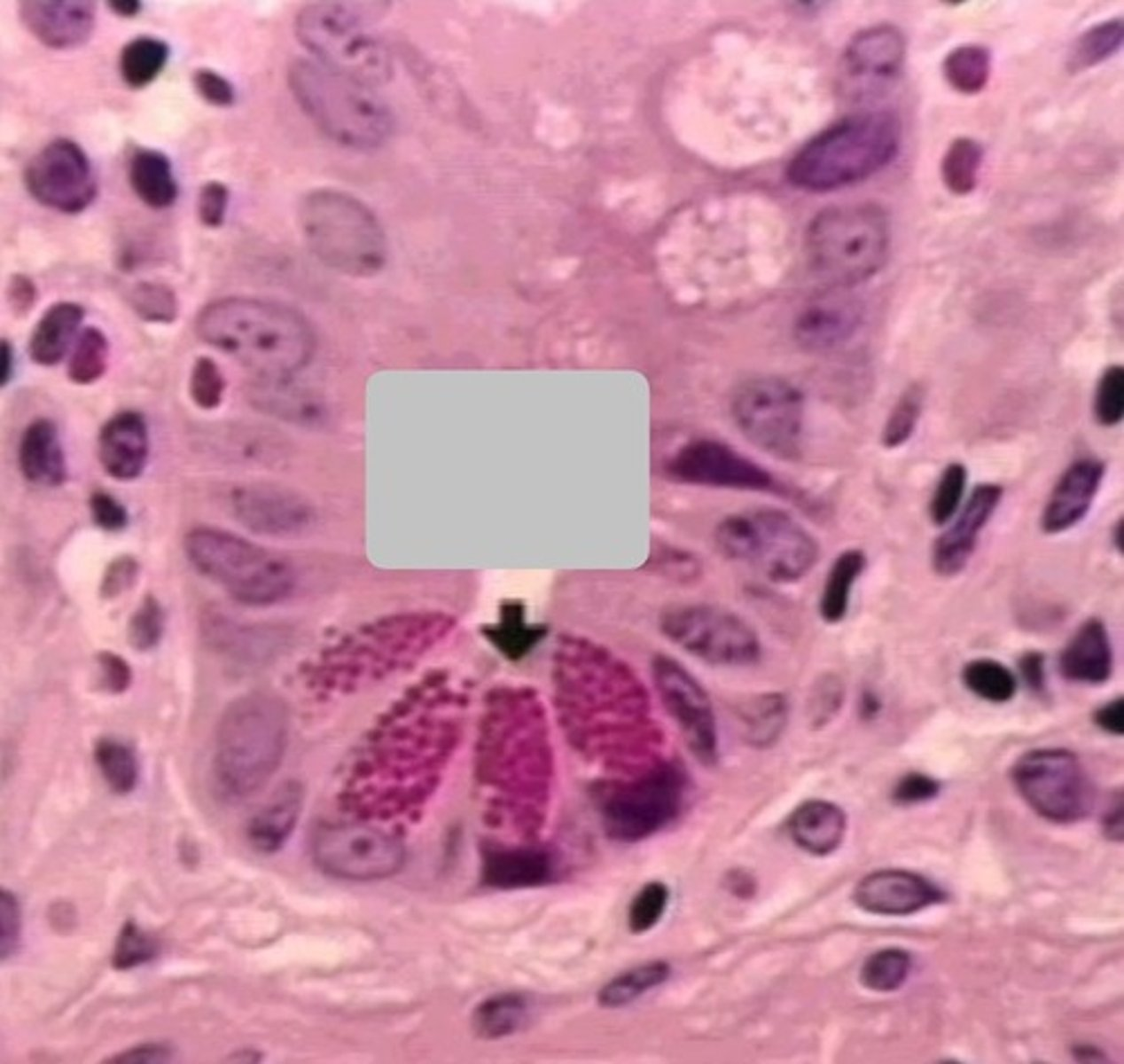
paneth cells
1
Peyer's patch in small intestine; the ilium, specifically
- we are getting close to the external environment so we needs stronger immune surveillance
2
lumen of small intestine
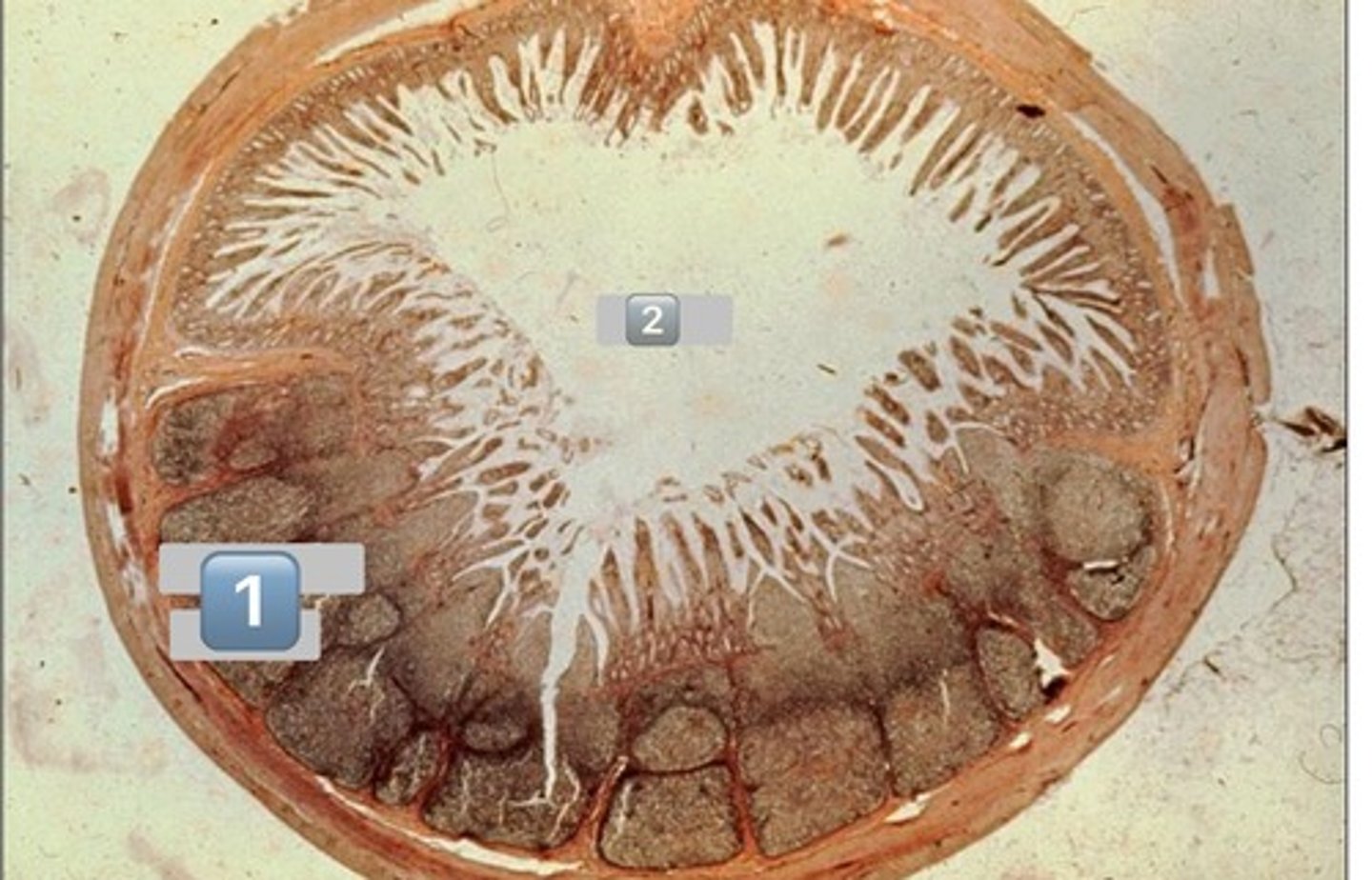
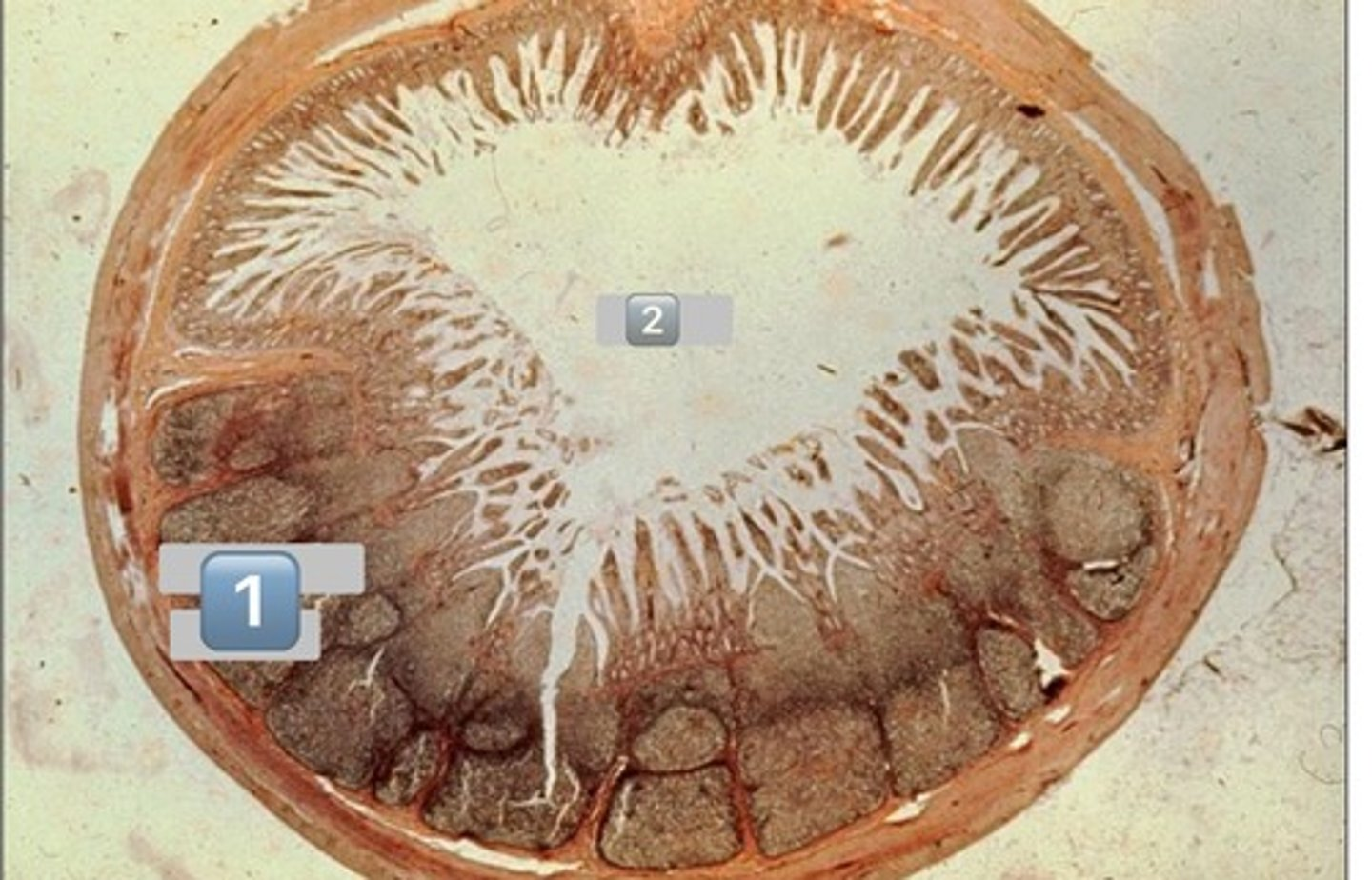
small intestine-duodenum
Brunner's glands
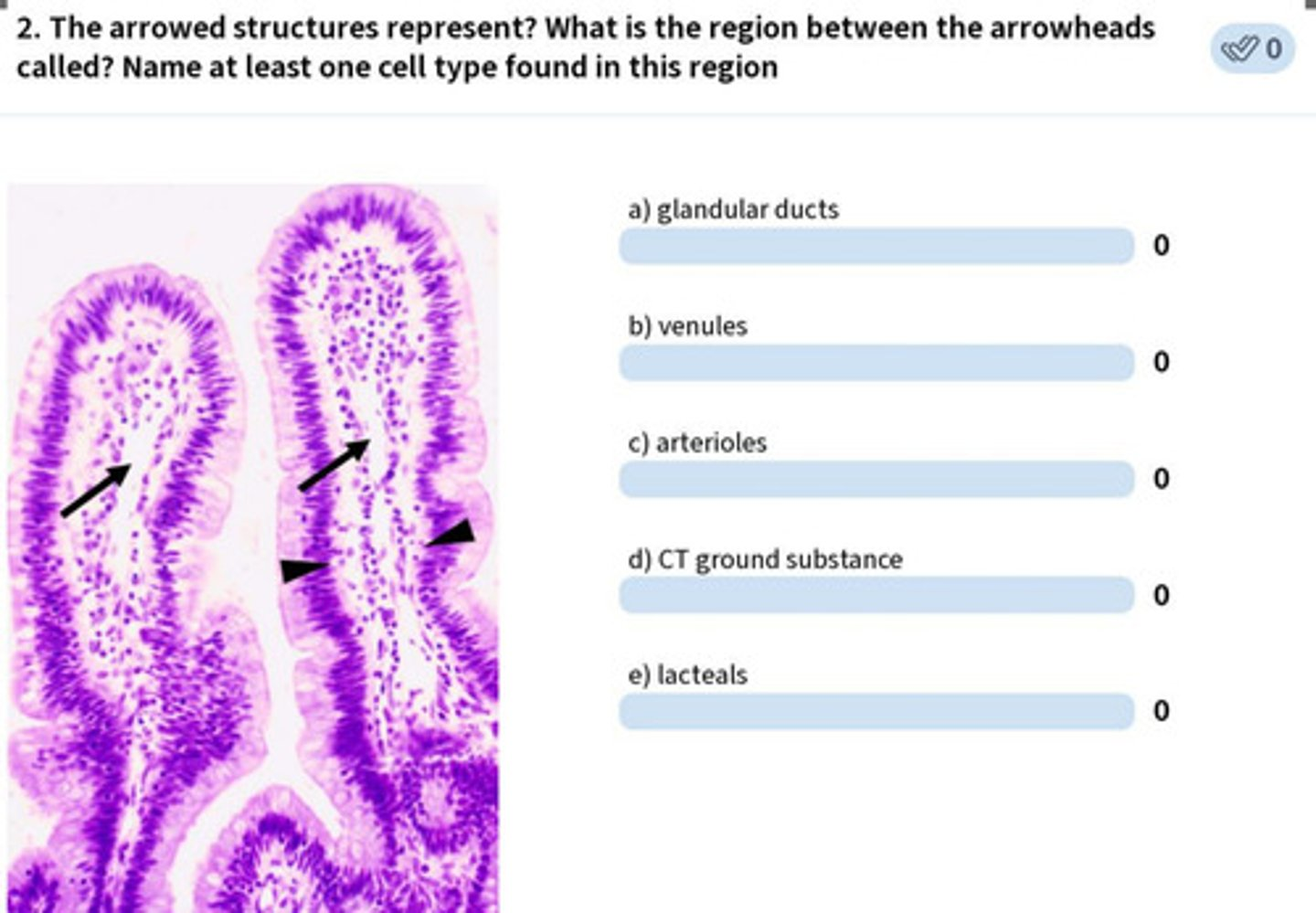
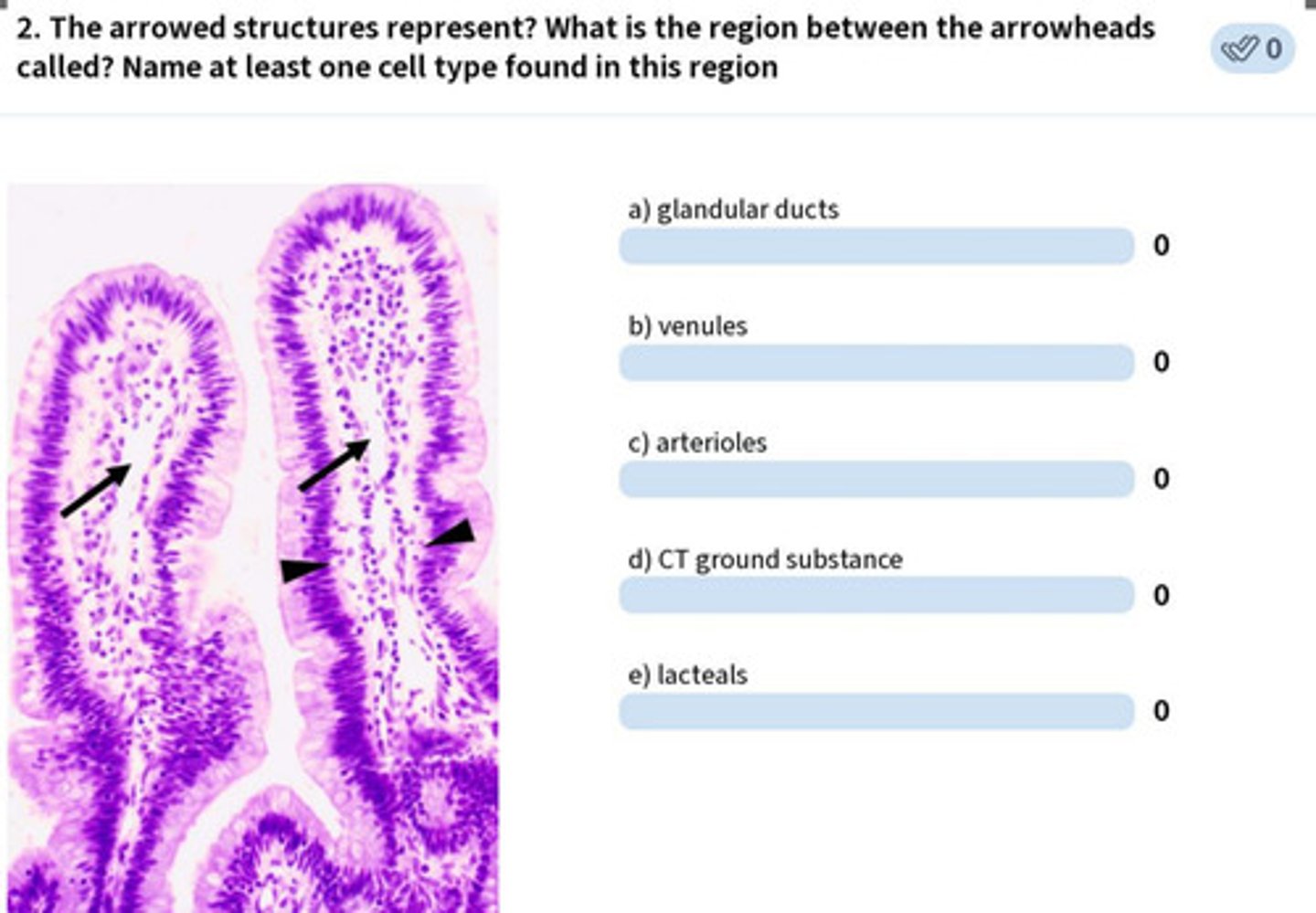
arrow: lacteals
arrowhead: lamina propria
fibroblasts, blood, connective tissue, etc.

paneth cells

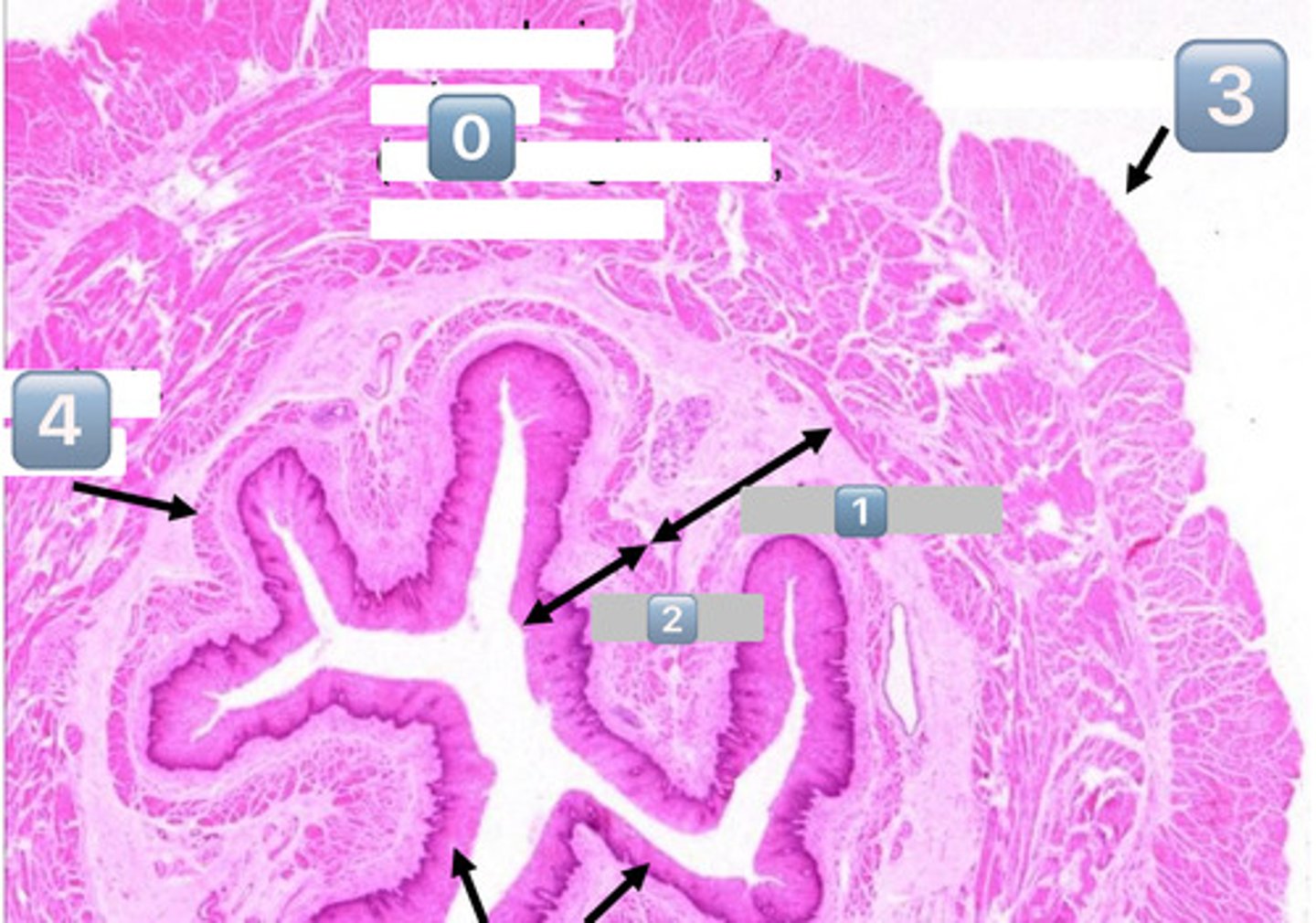
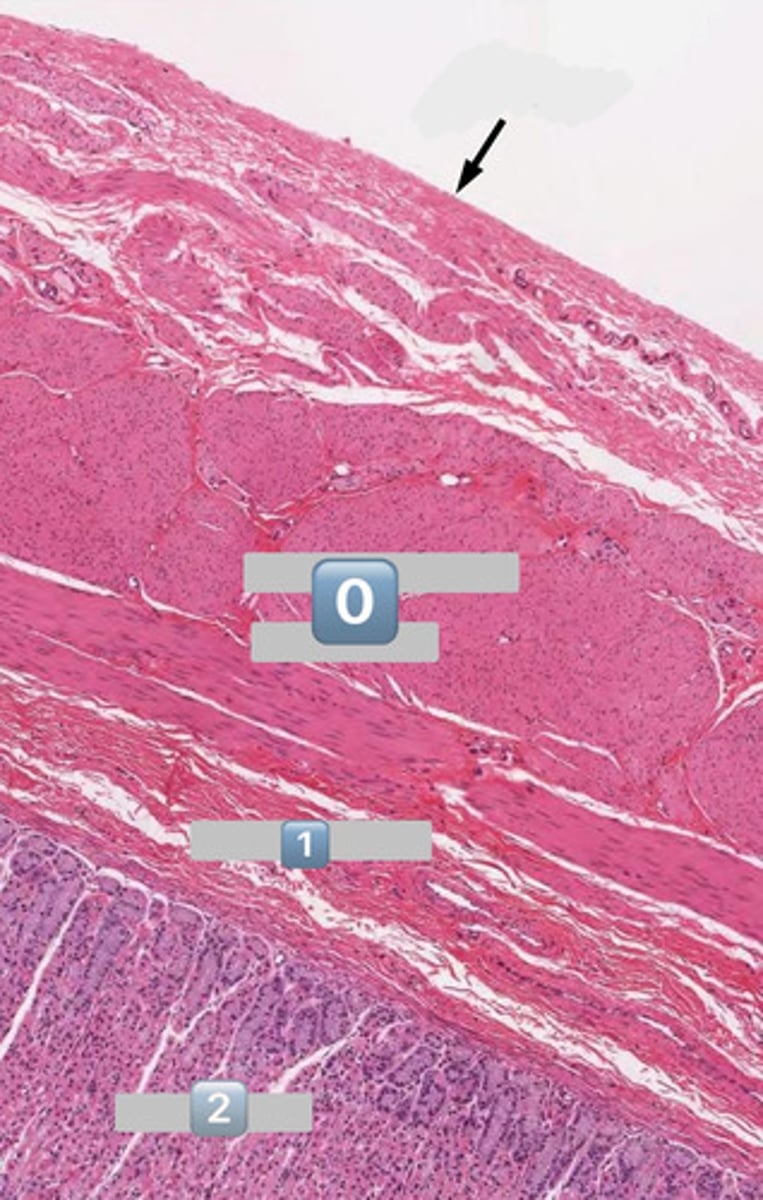
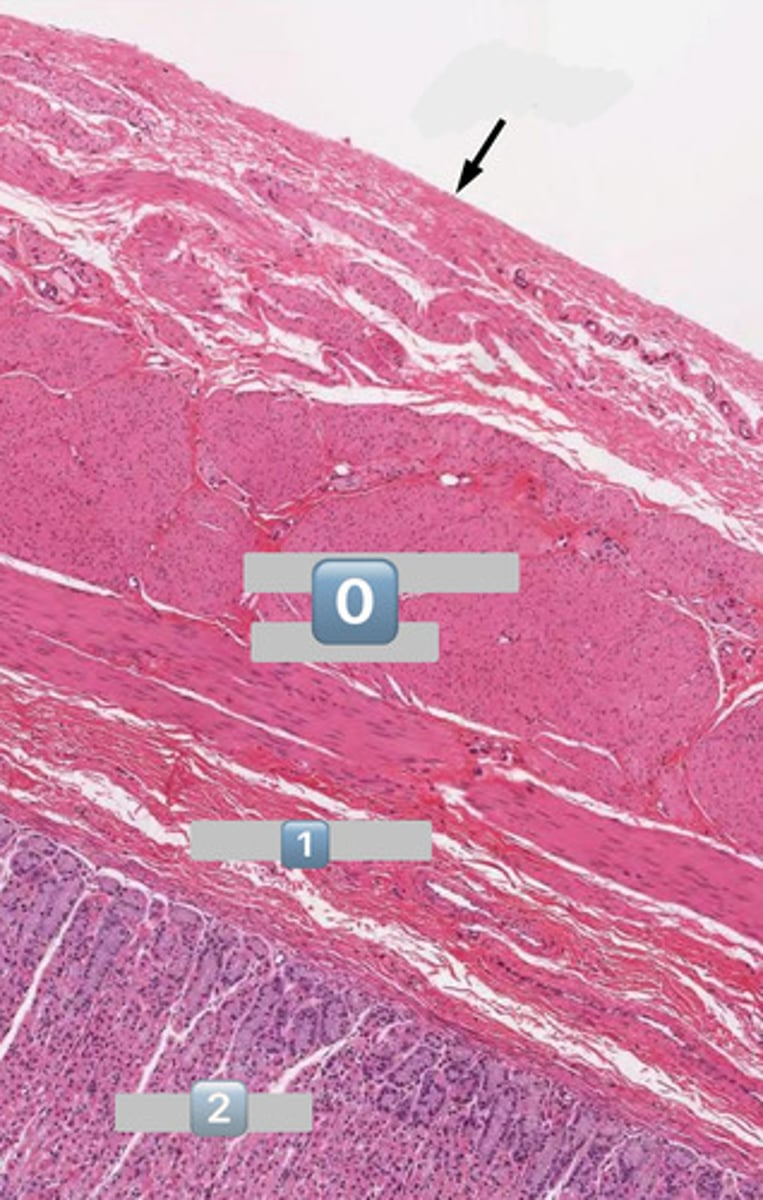
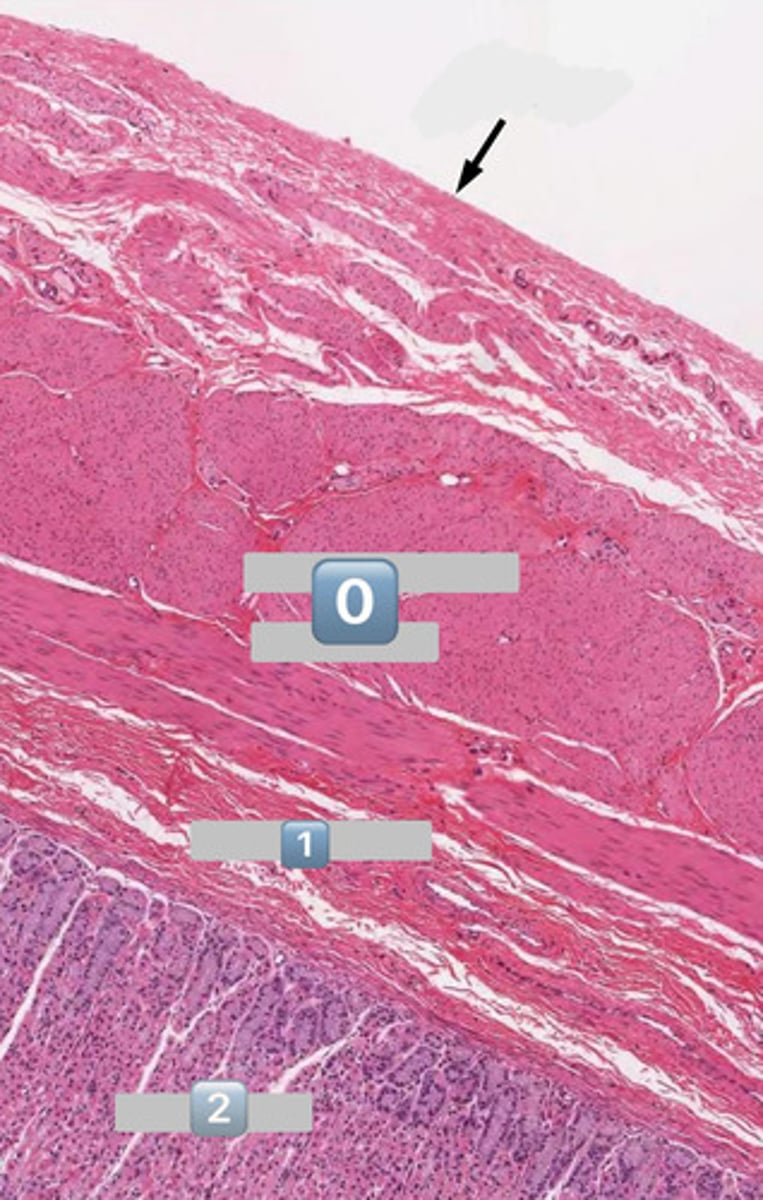
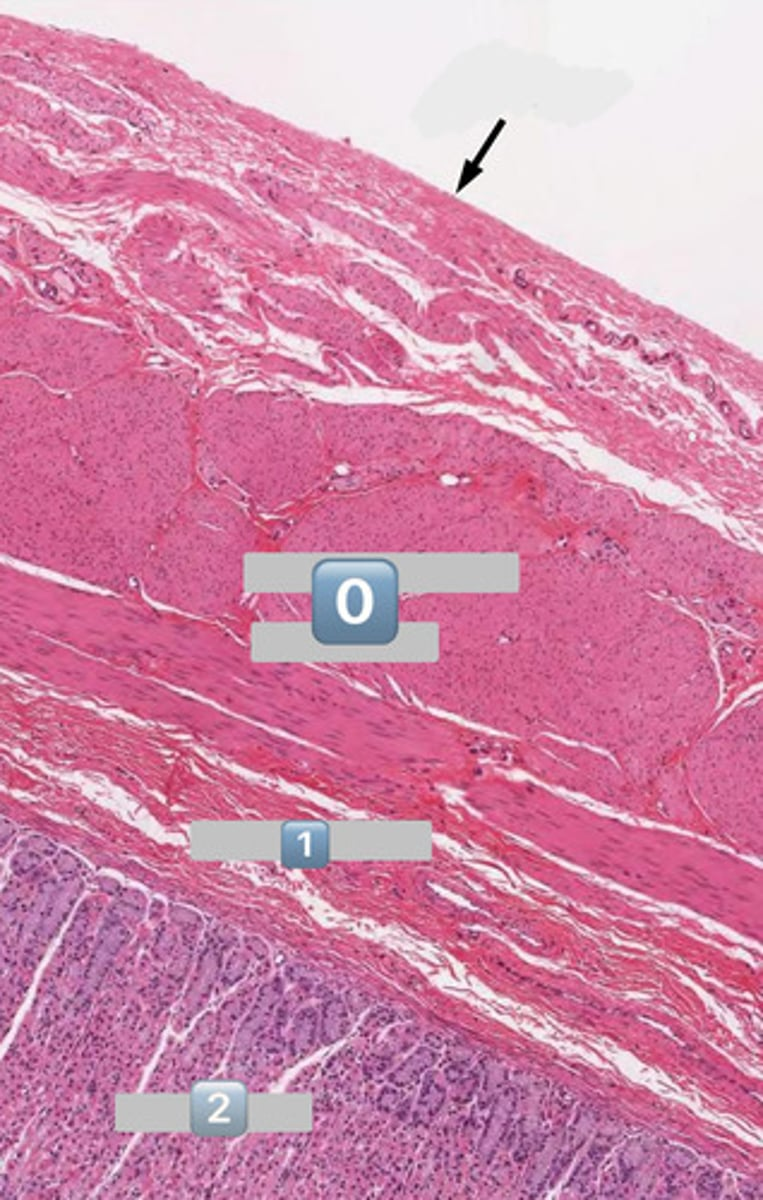
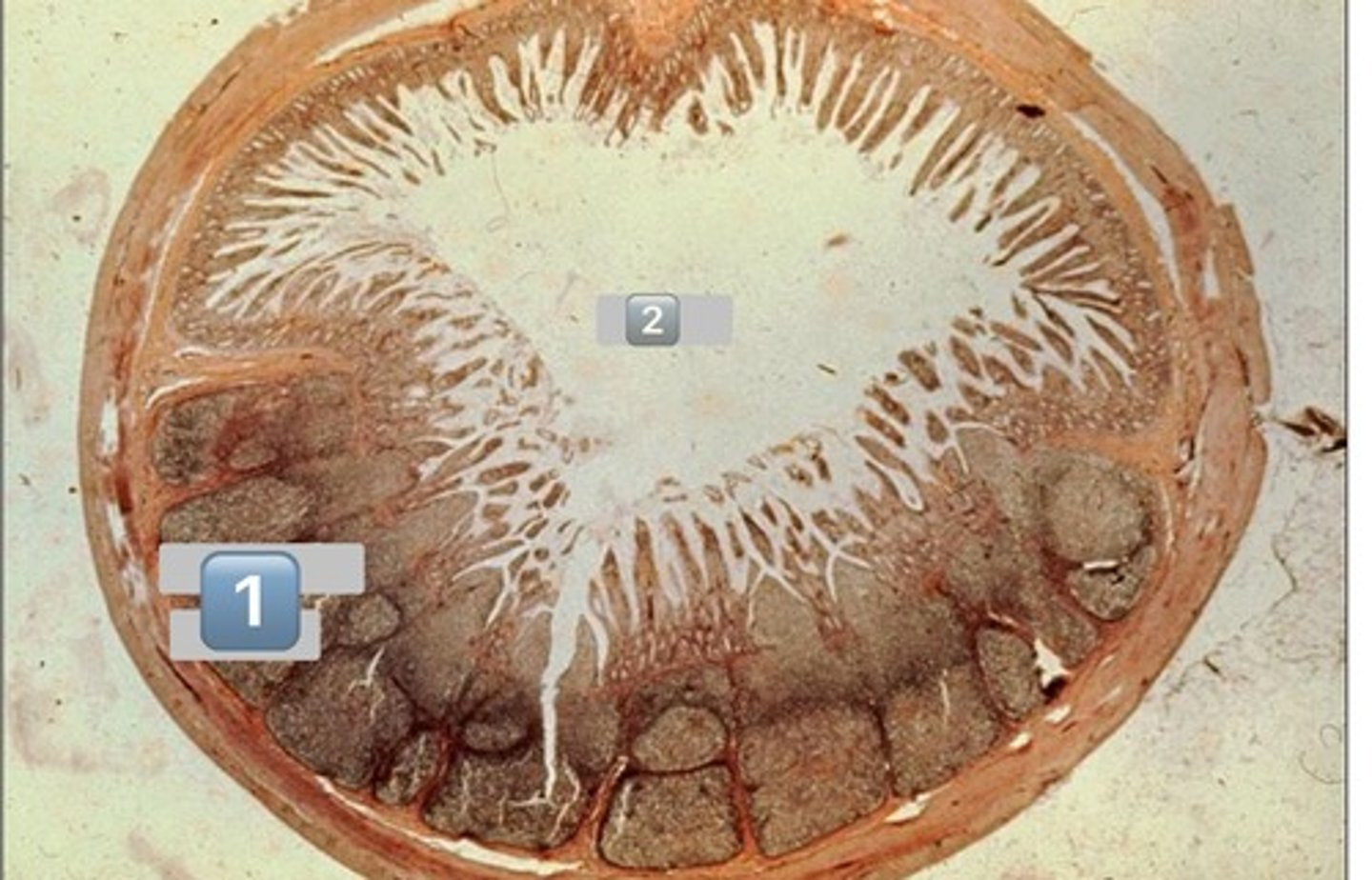
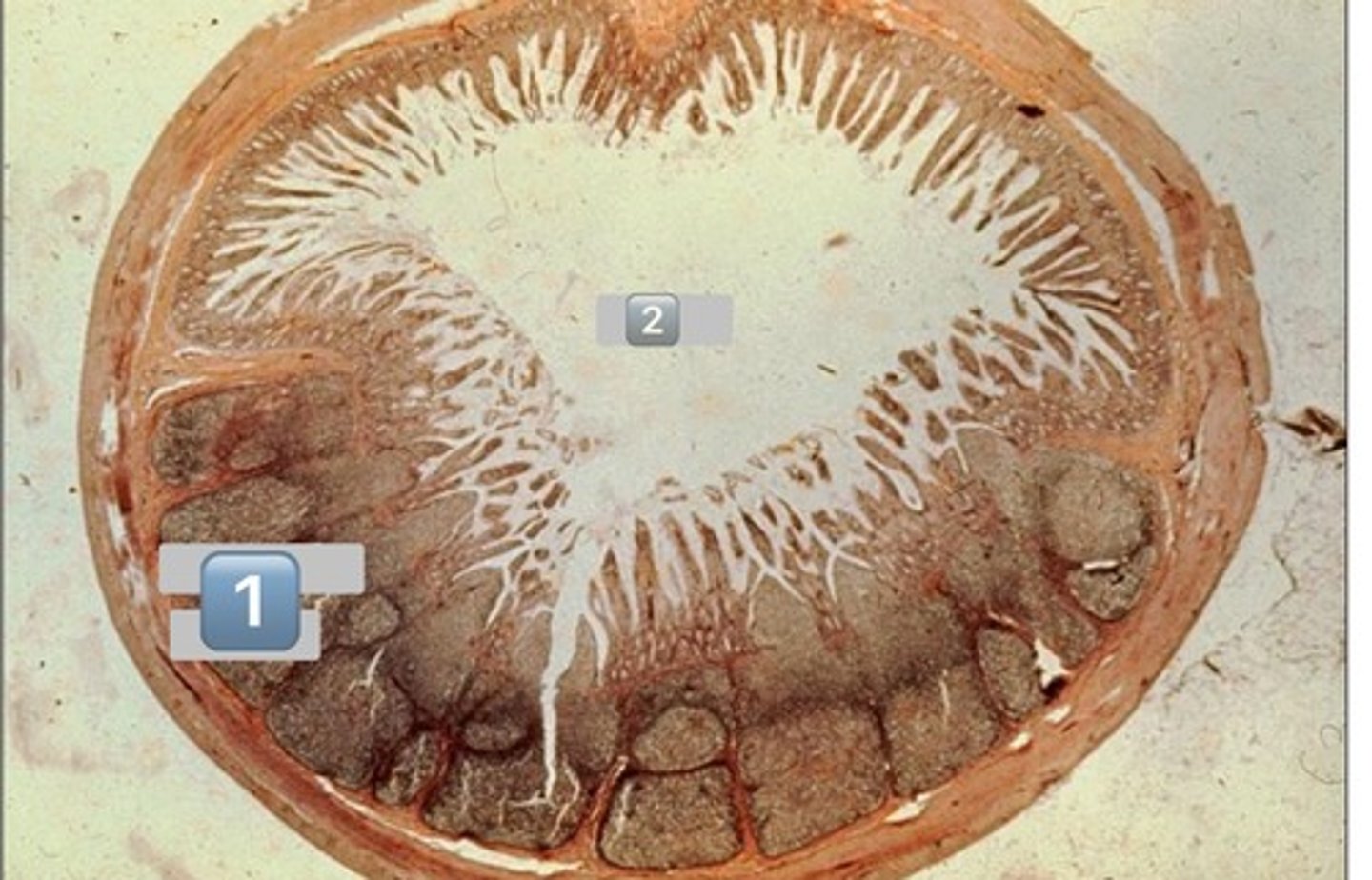
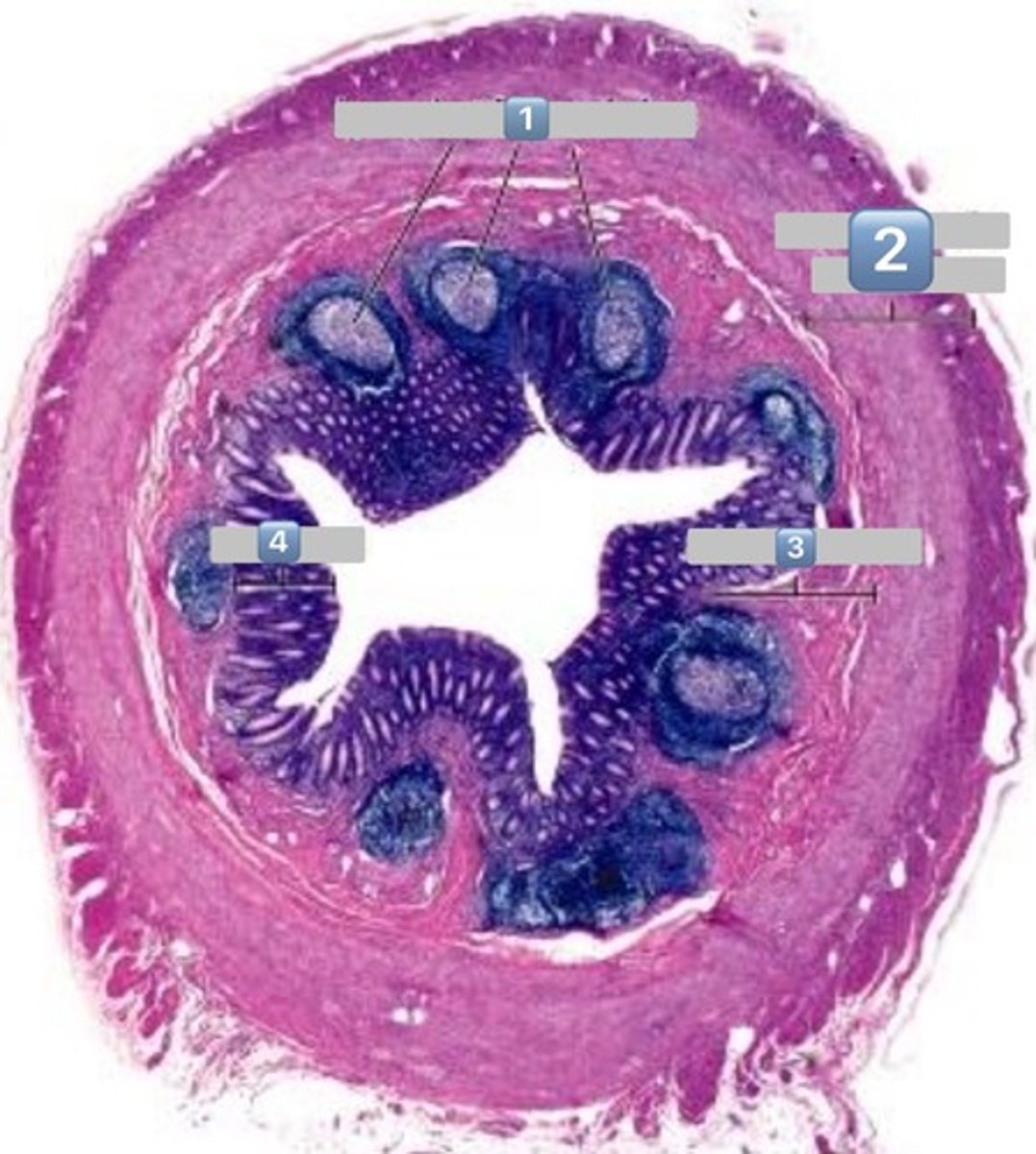
taenia coli
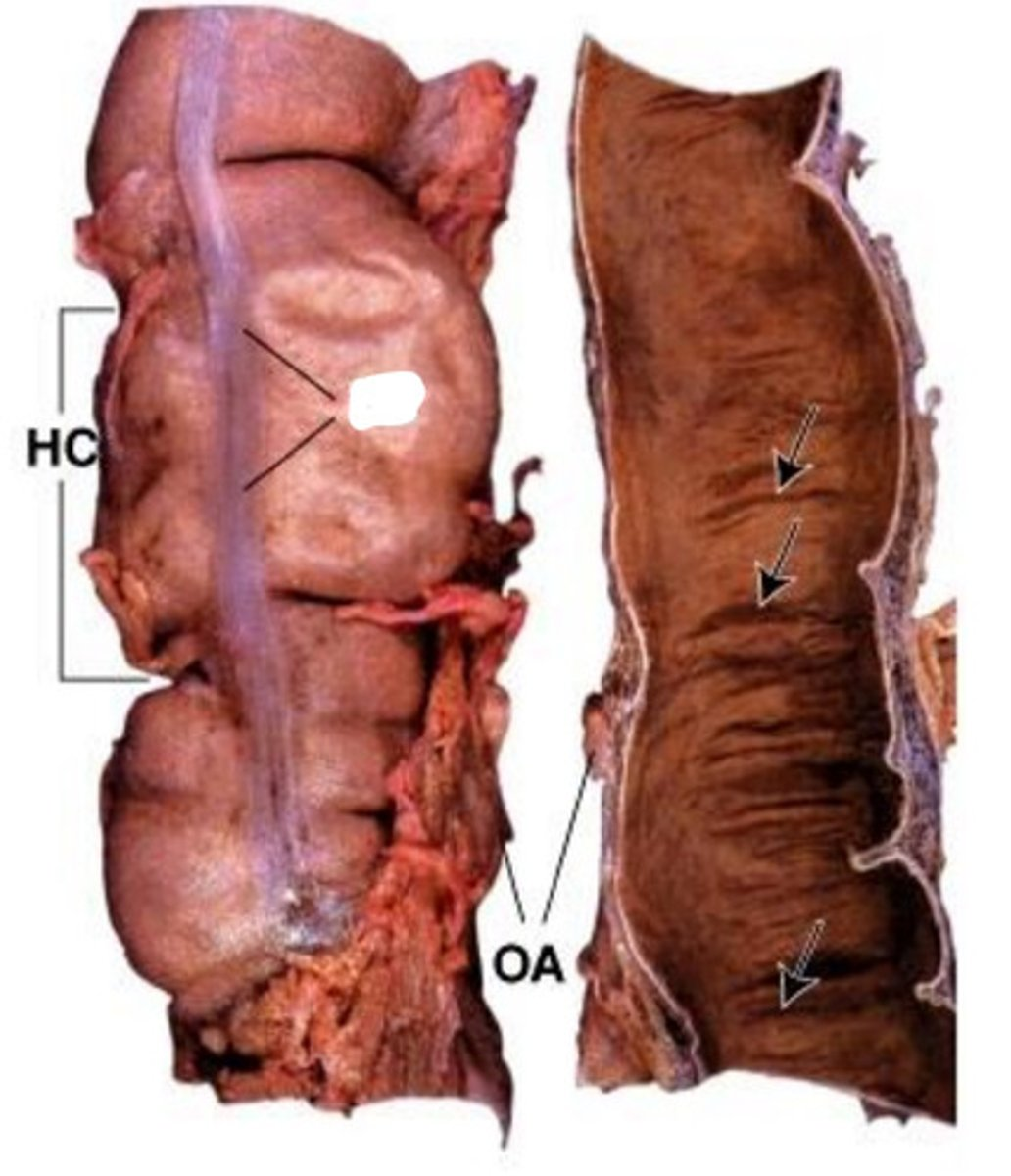
taenia coli
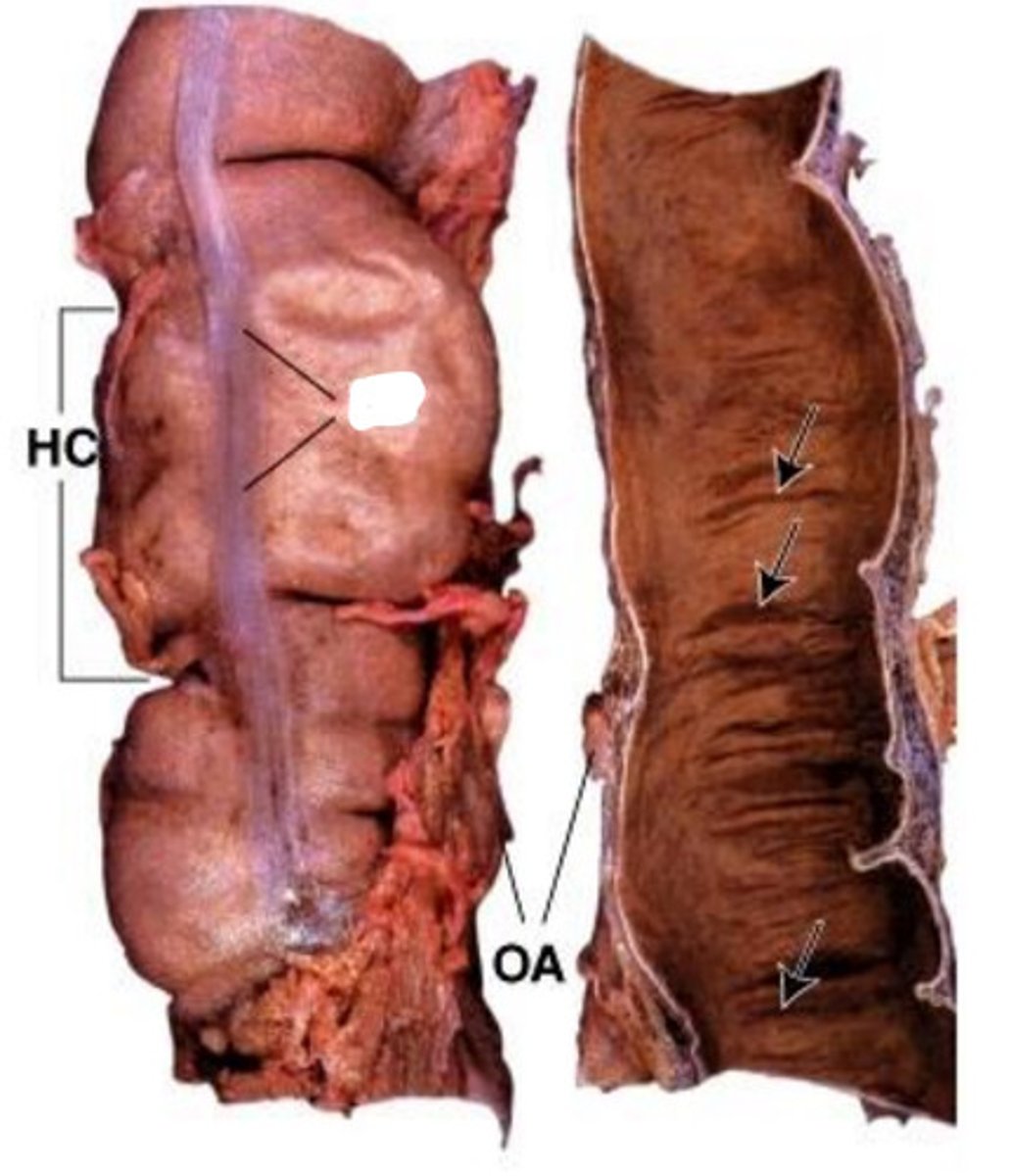
1
lymphatic
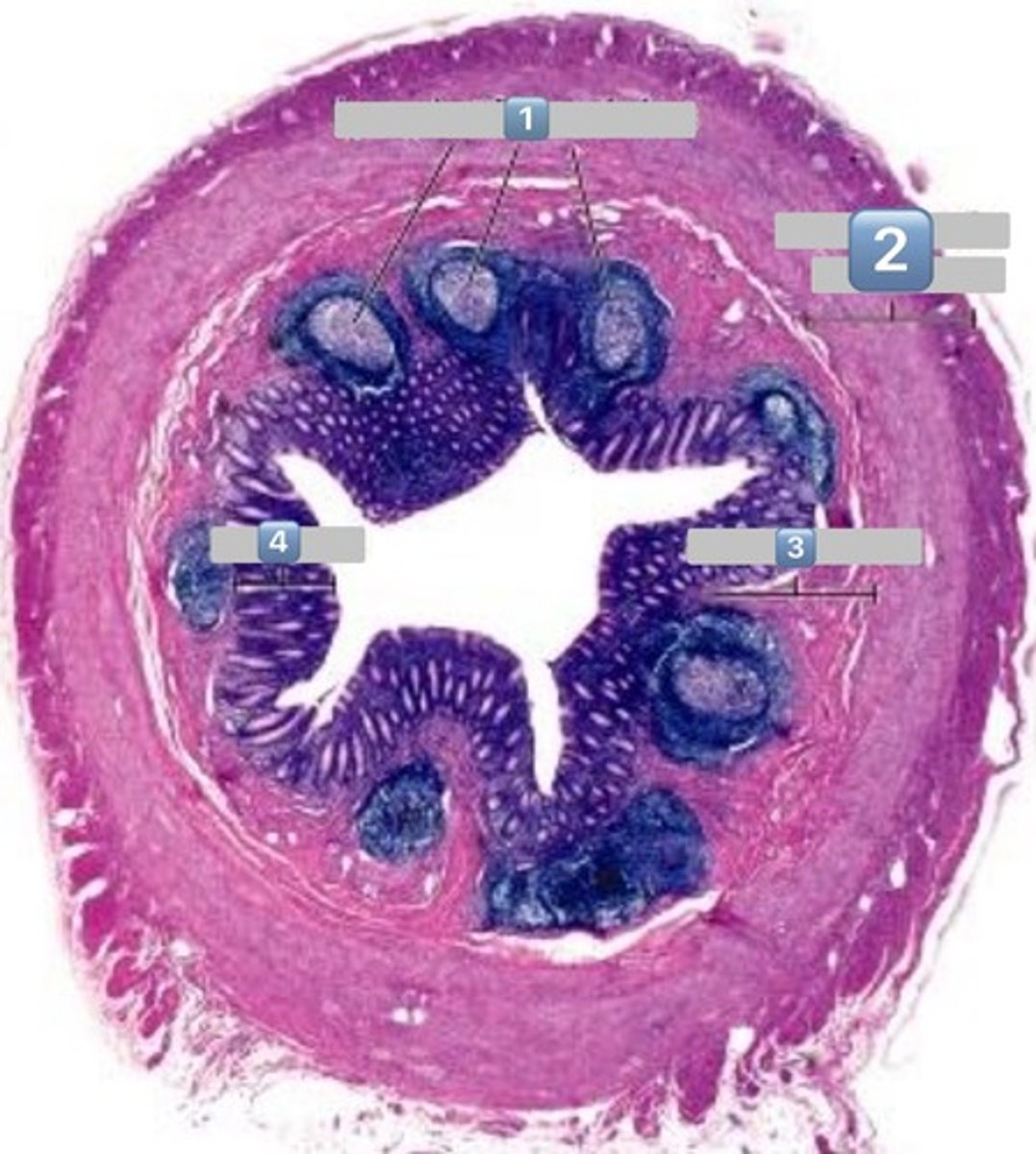
2
muscularis externa
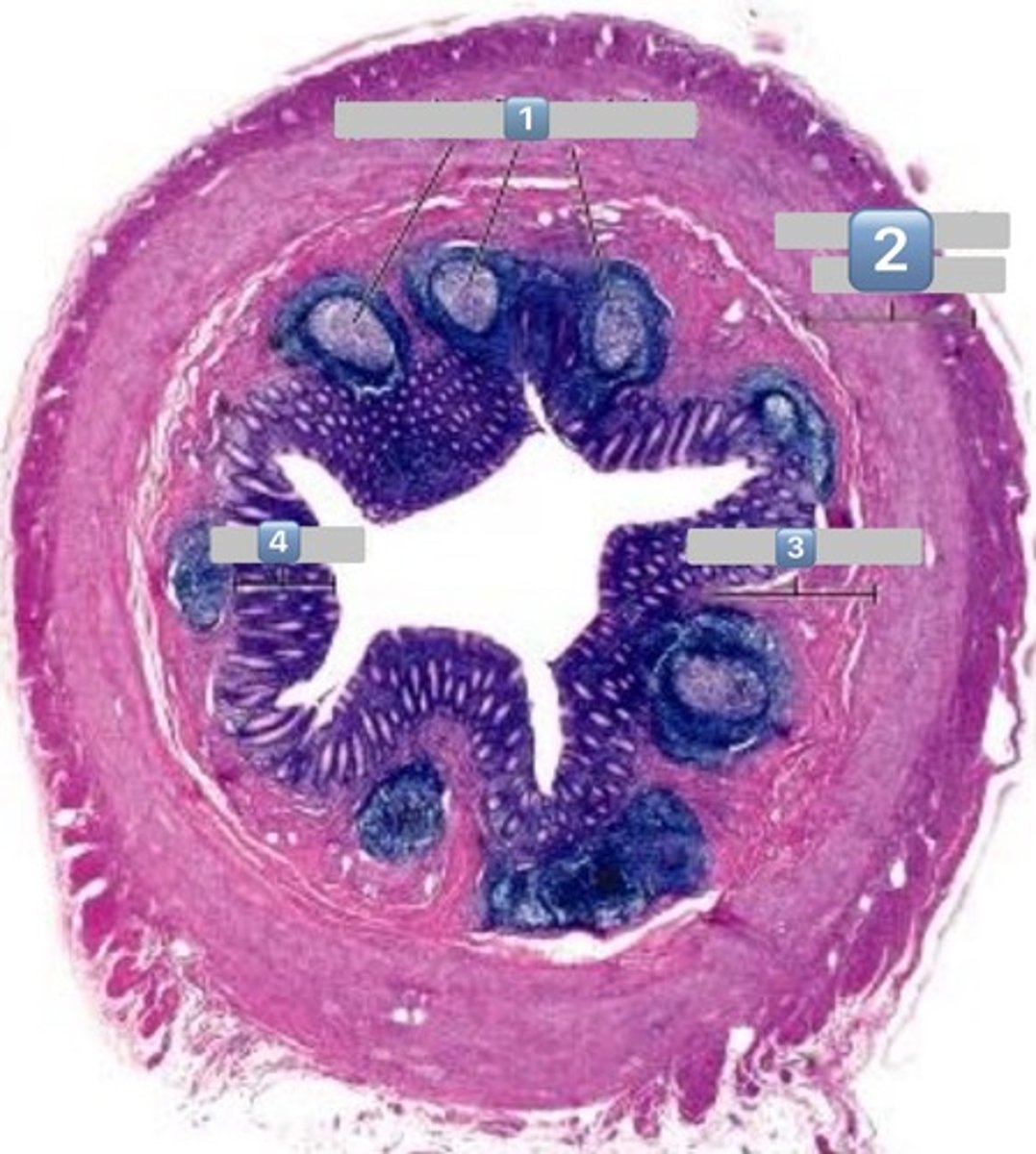
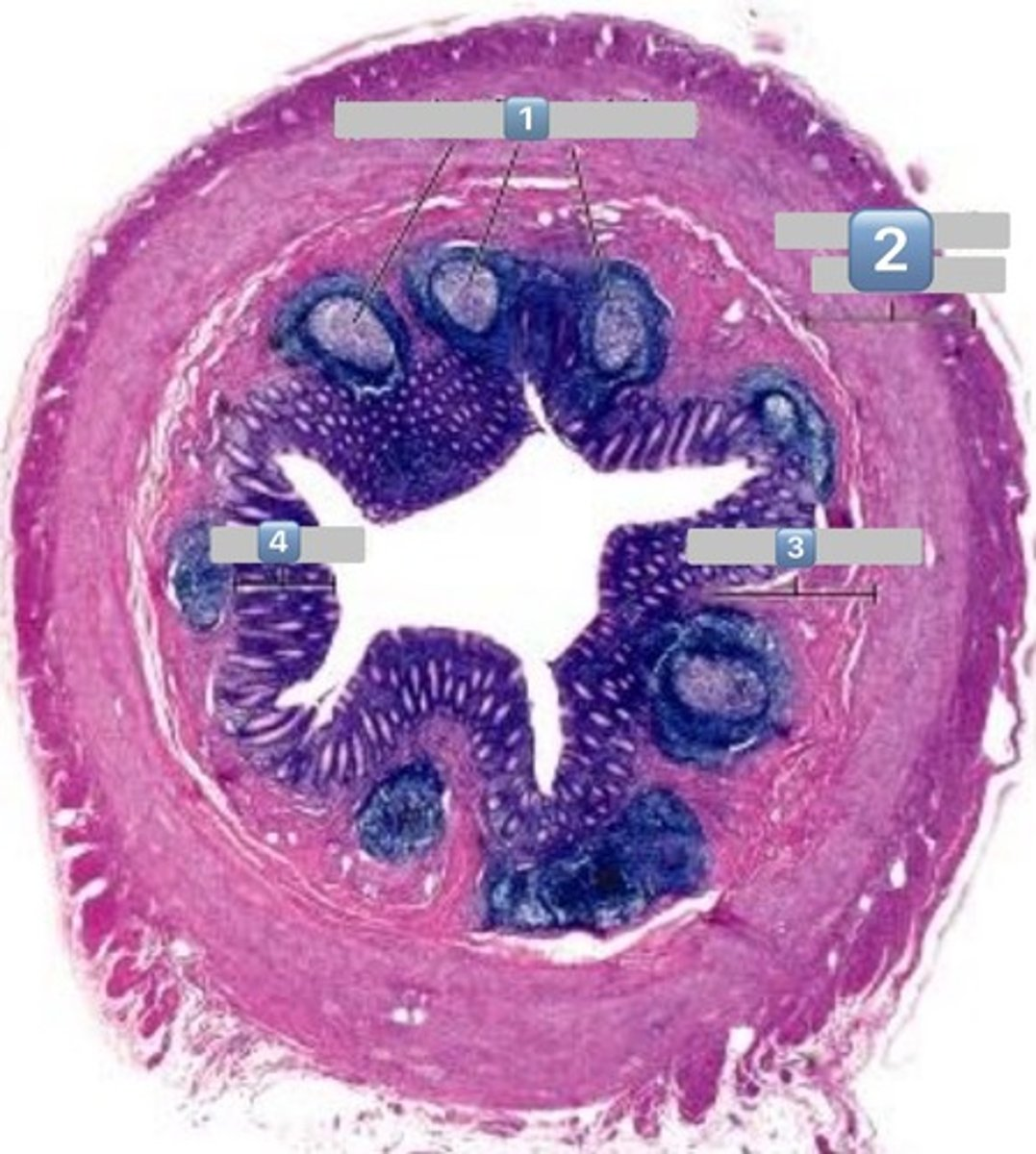
3
submucosa
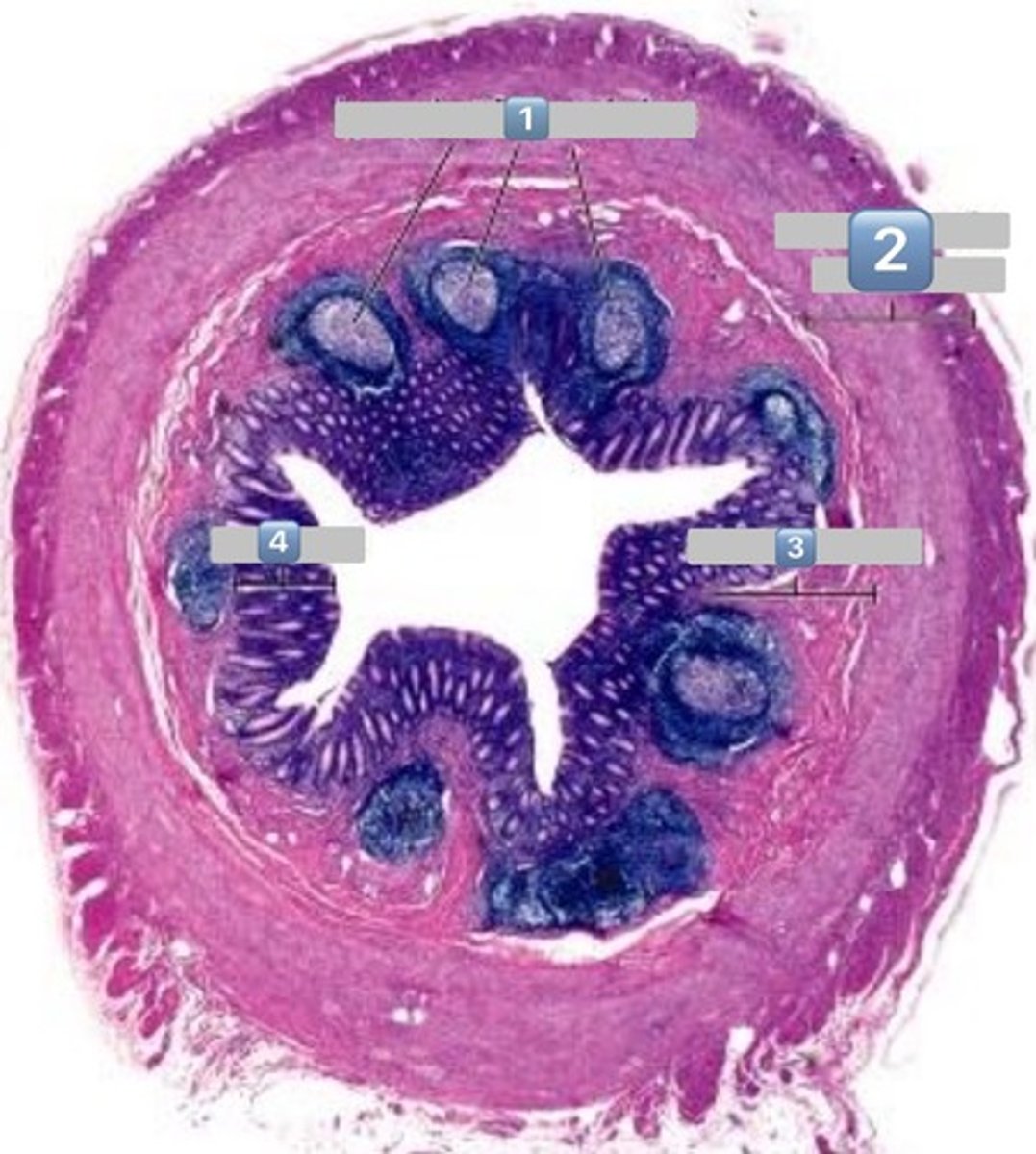
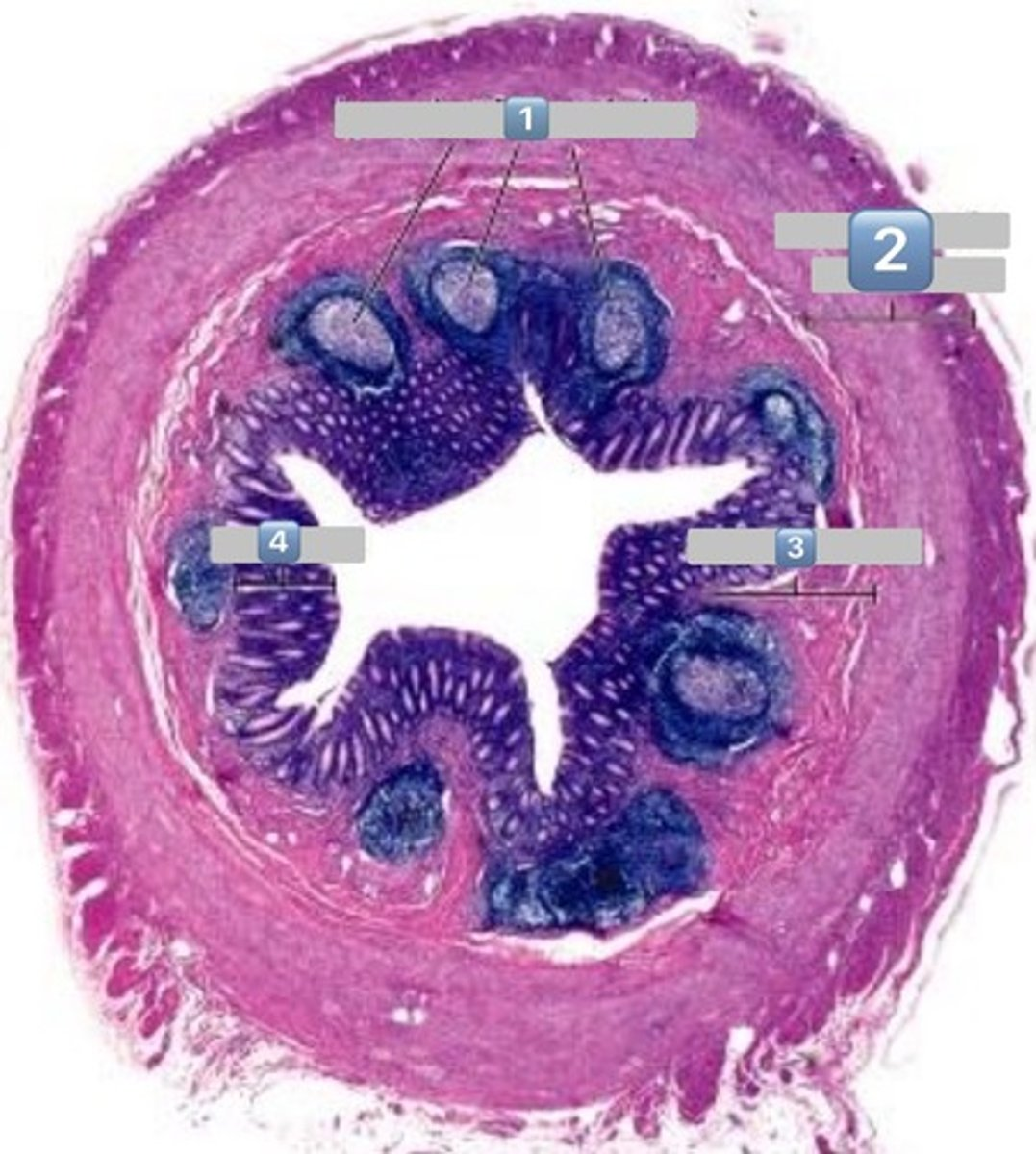
4
mucosa
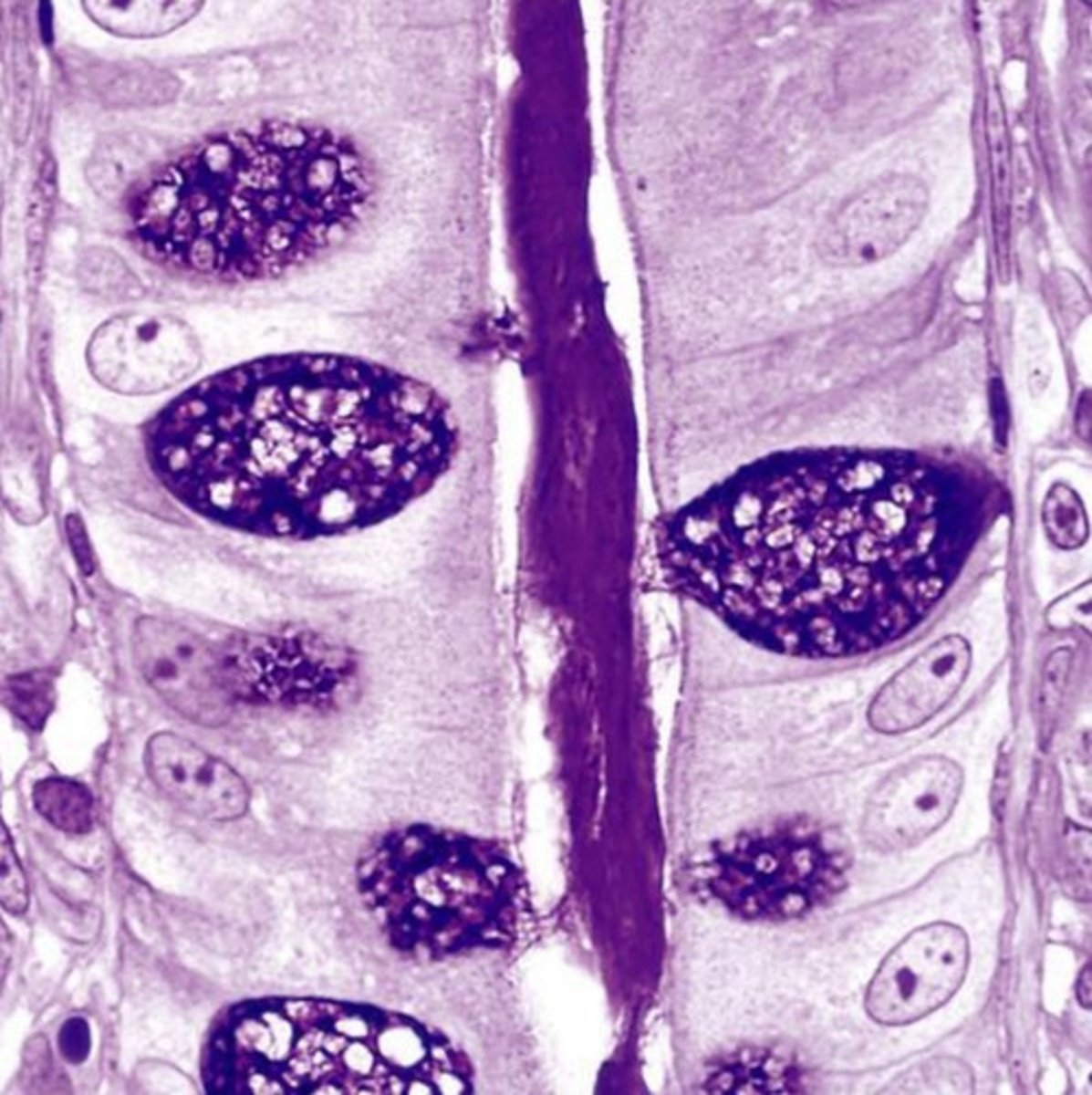
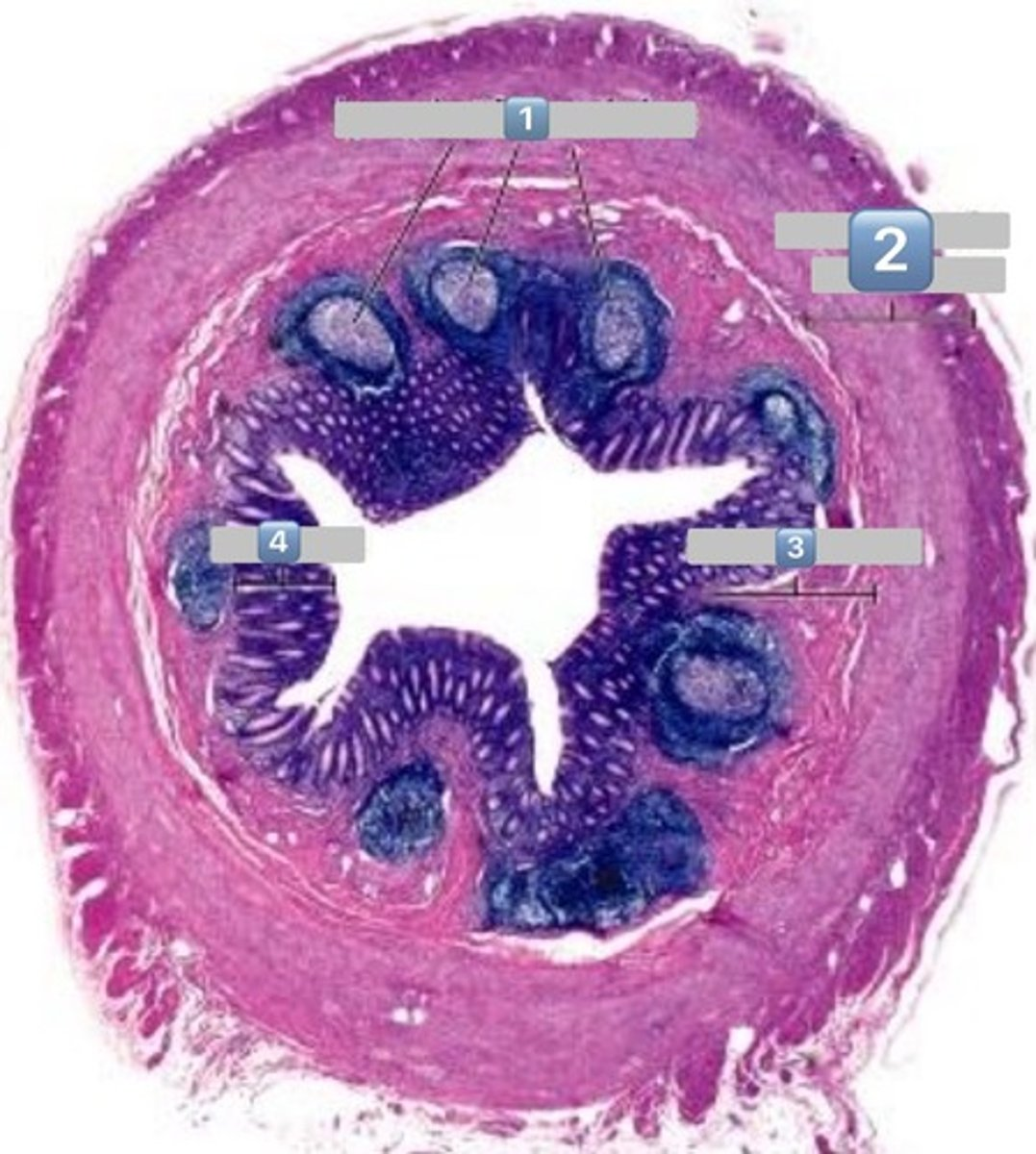
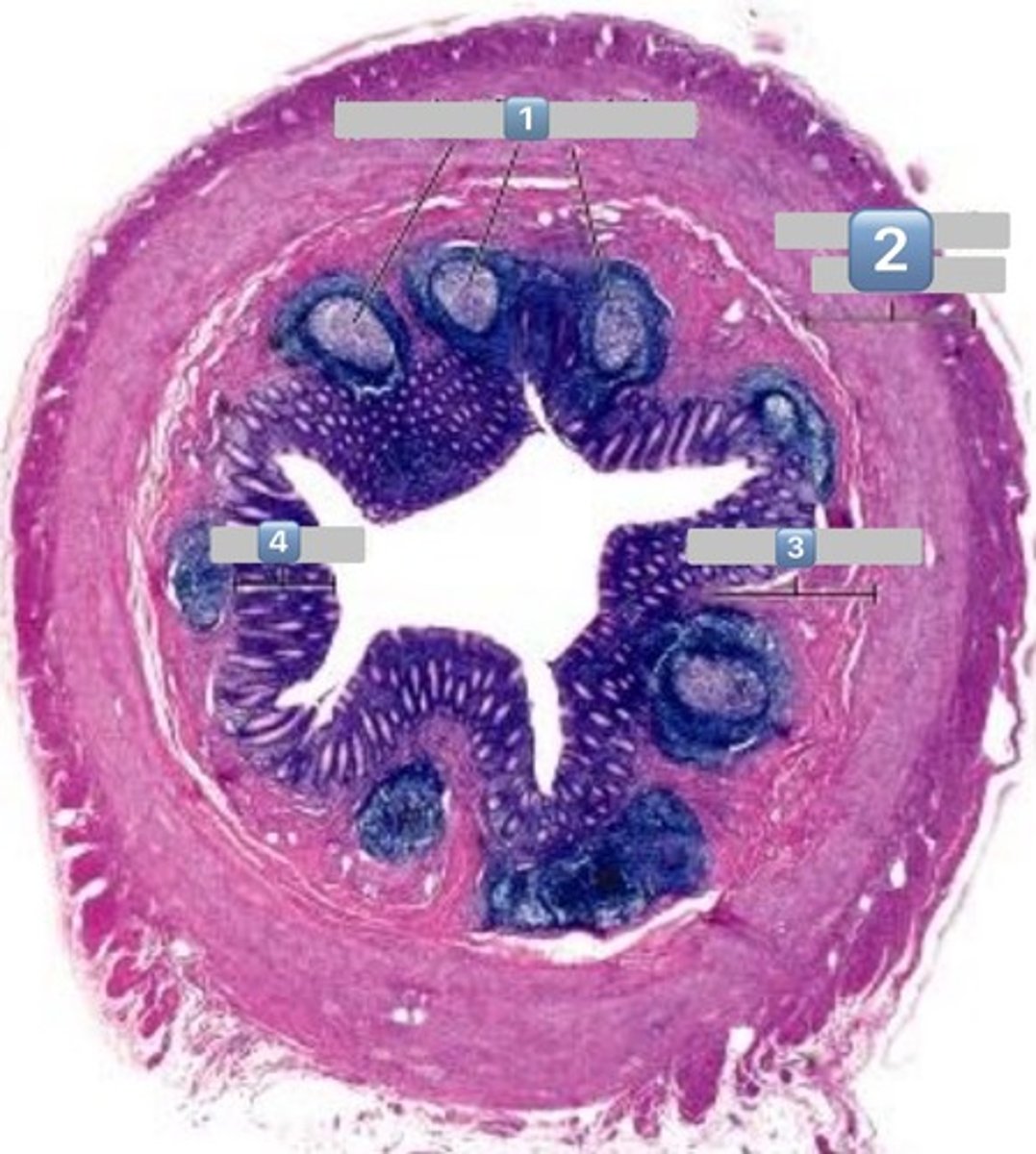
colonocytes (dark staining)
- absorptive
goblet cells (light staining)
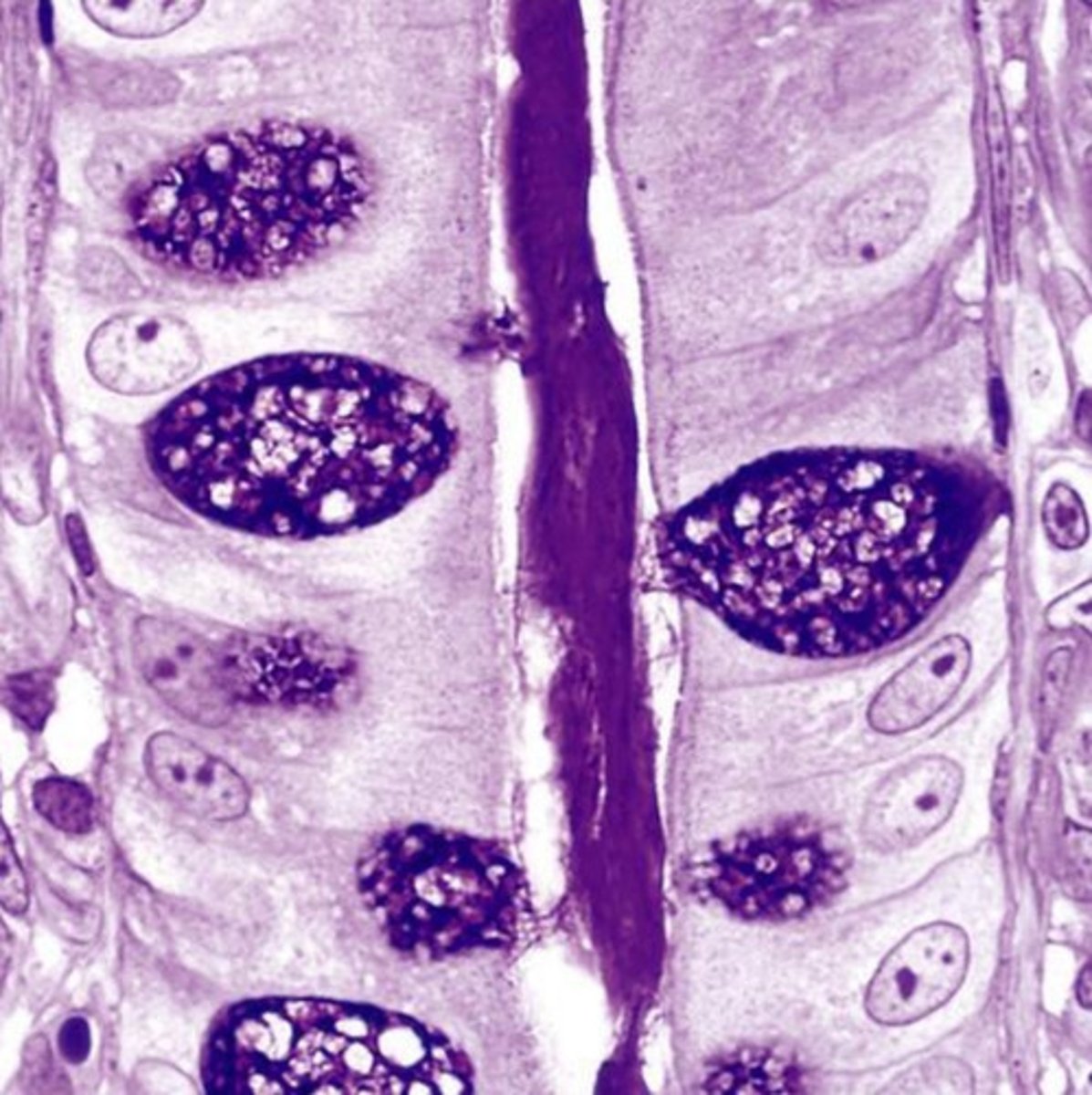
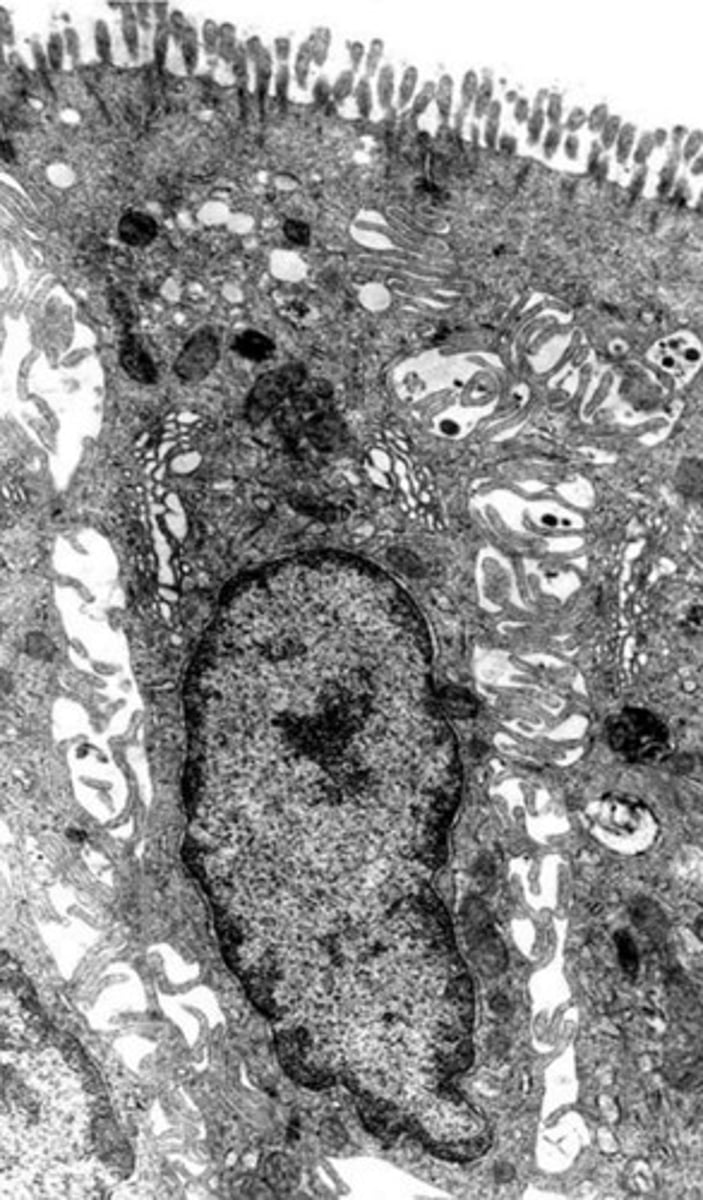
what is the role of this cell?
absorption of water from the apical surface to the basal surface
- these are colonocytes
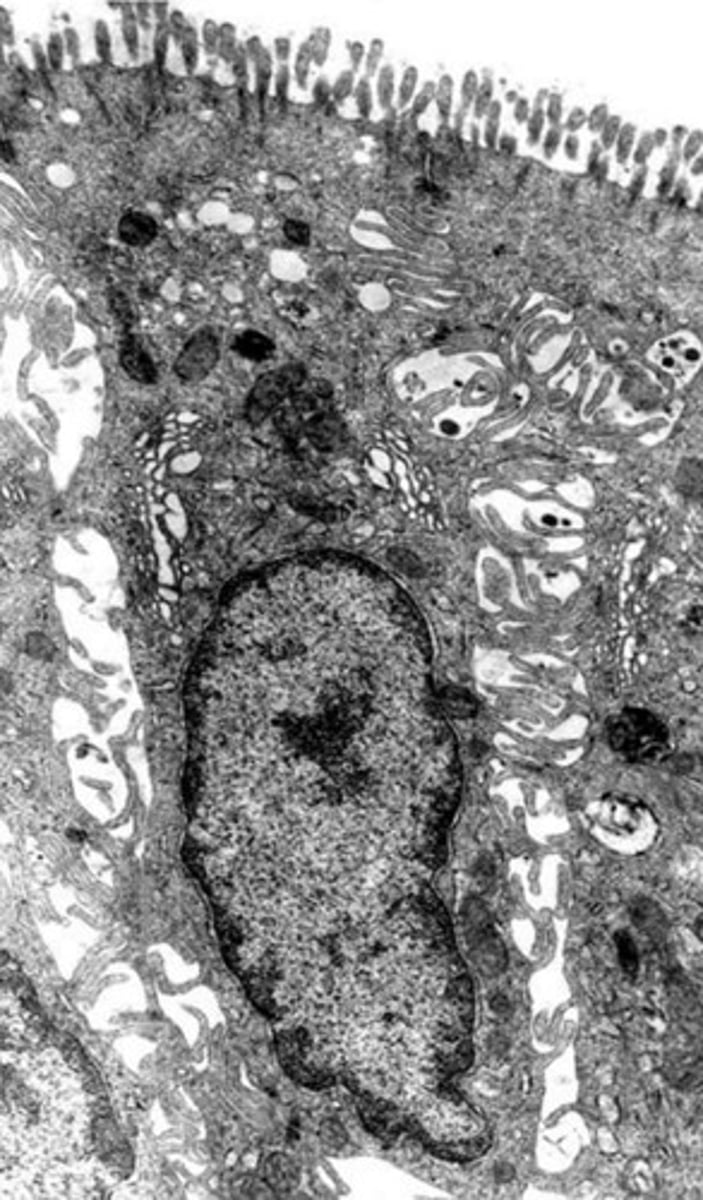
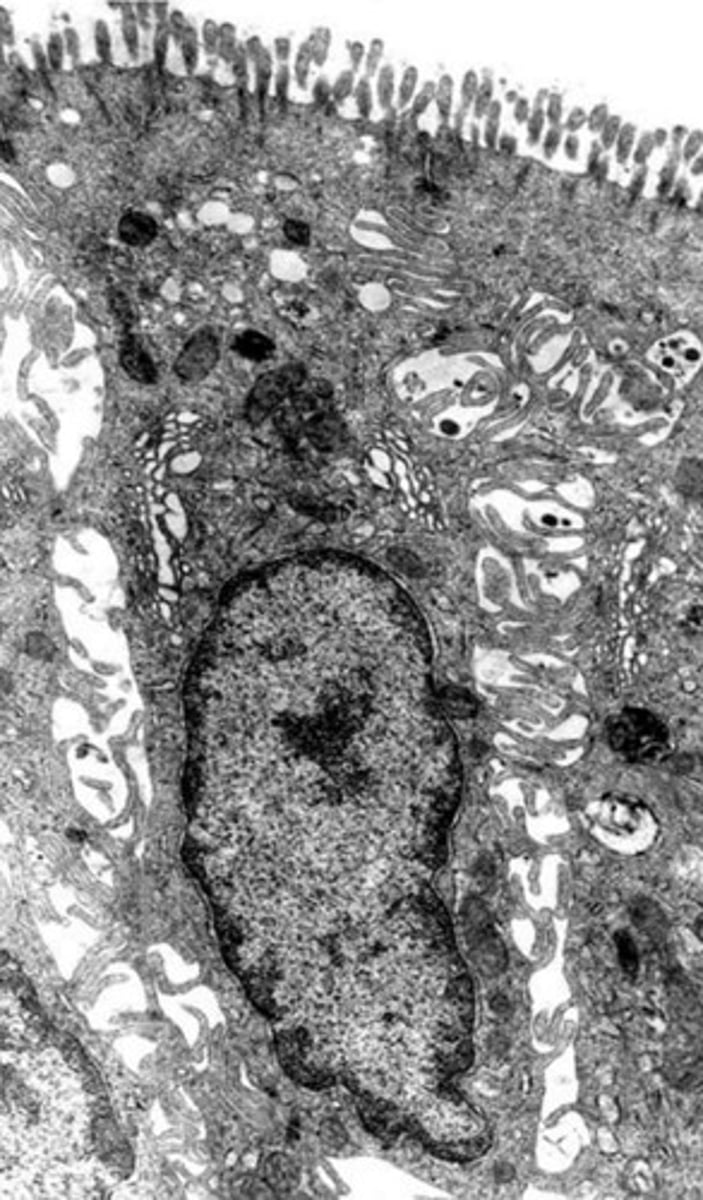
colonocytes
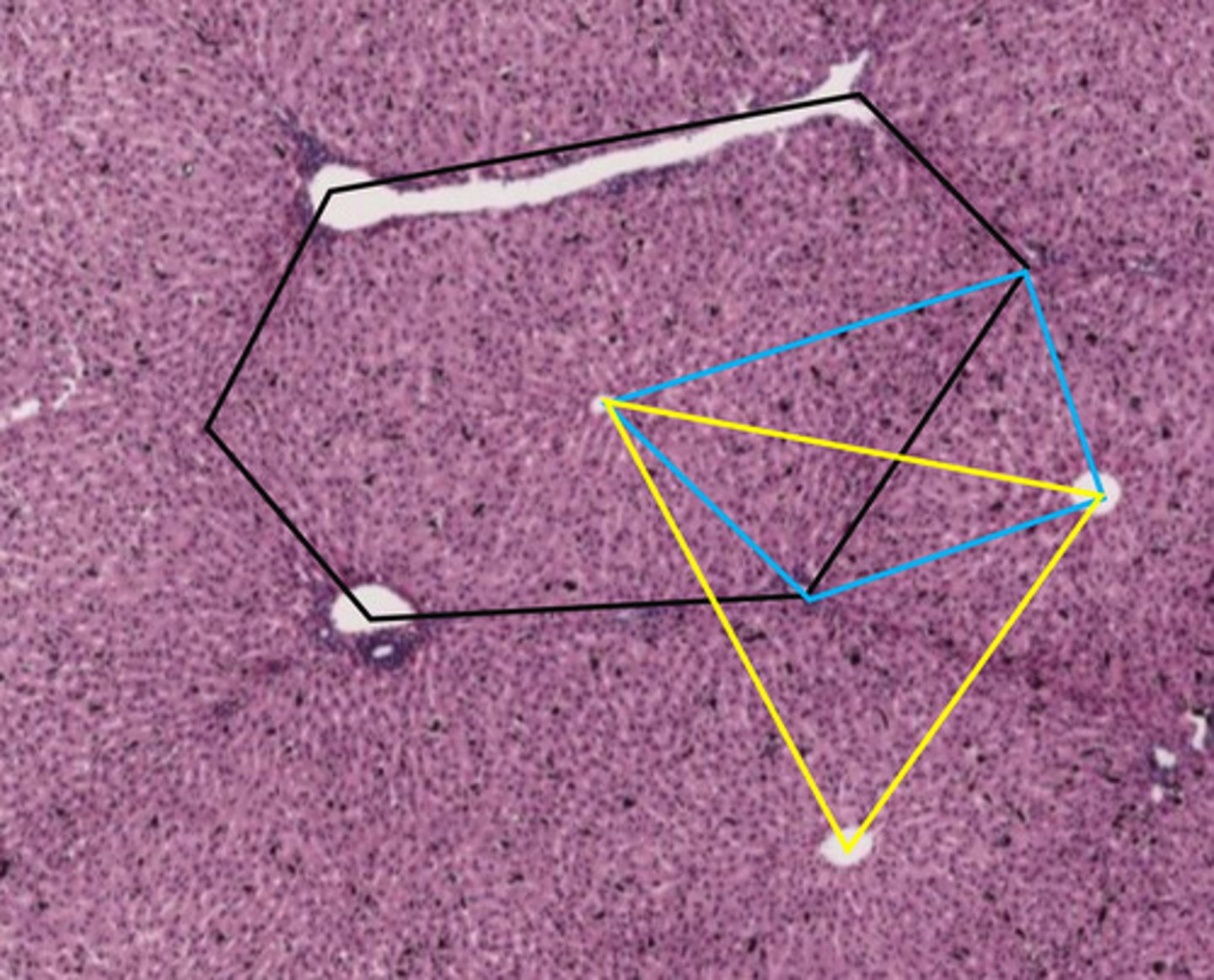
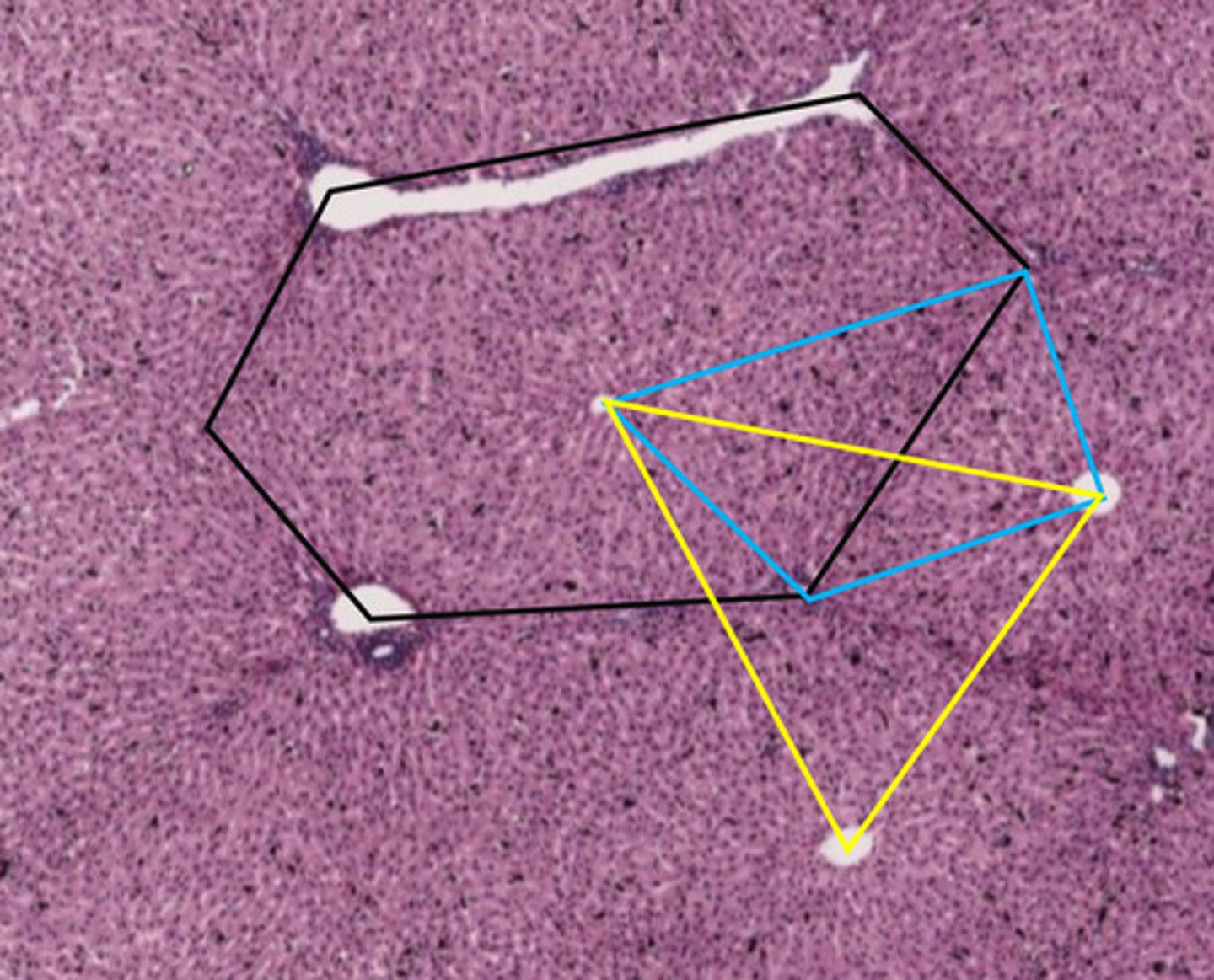
black hexagon
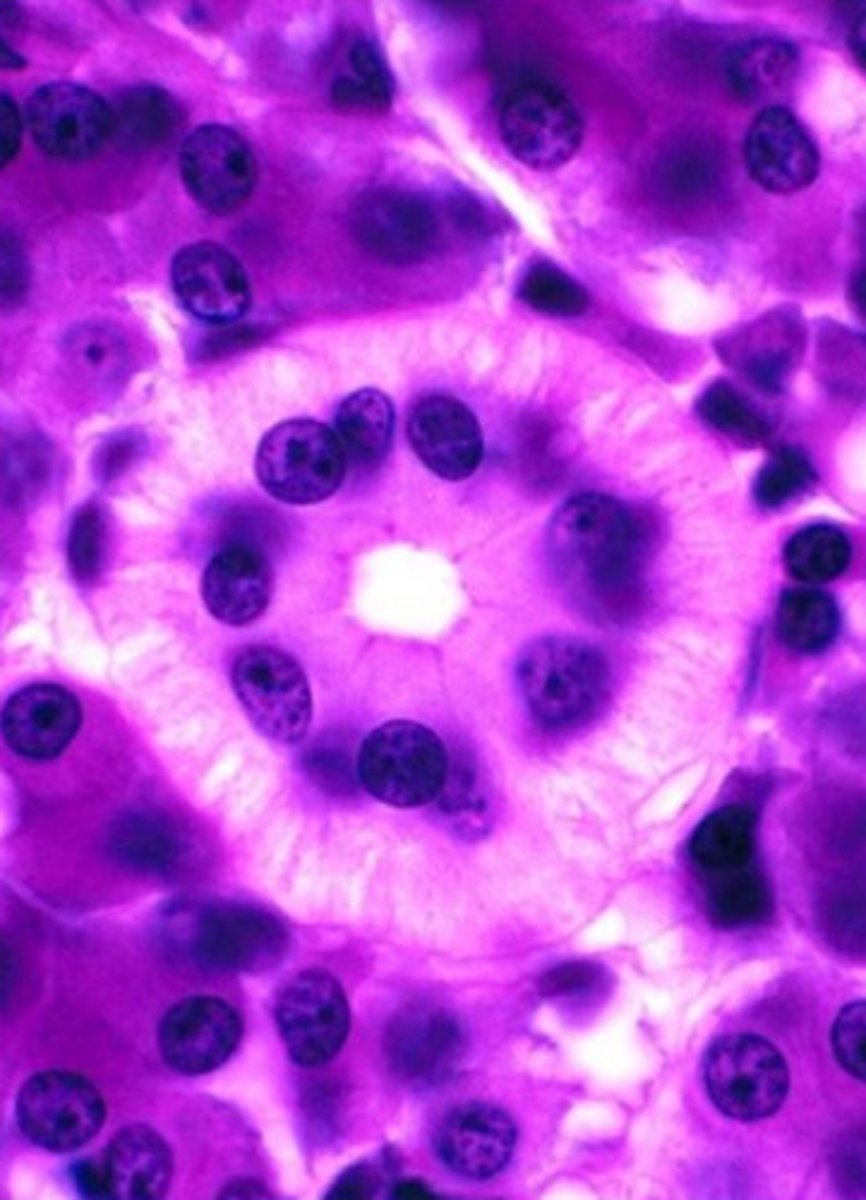
classic liver lobule
- centered around a central vein
- endocrine and metabolic functions
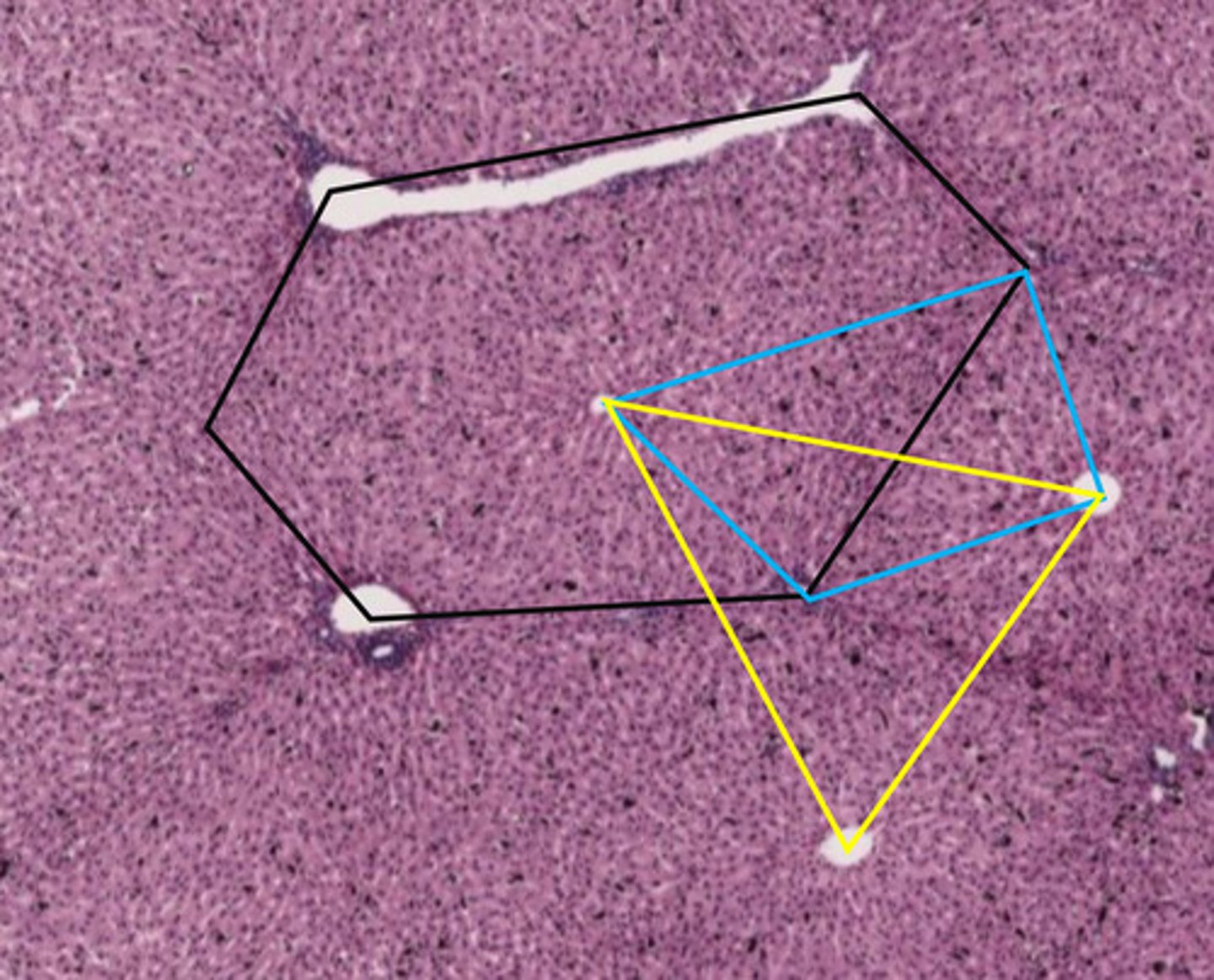
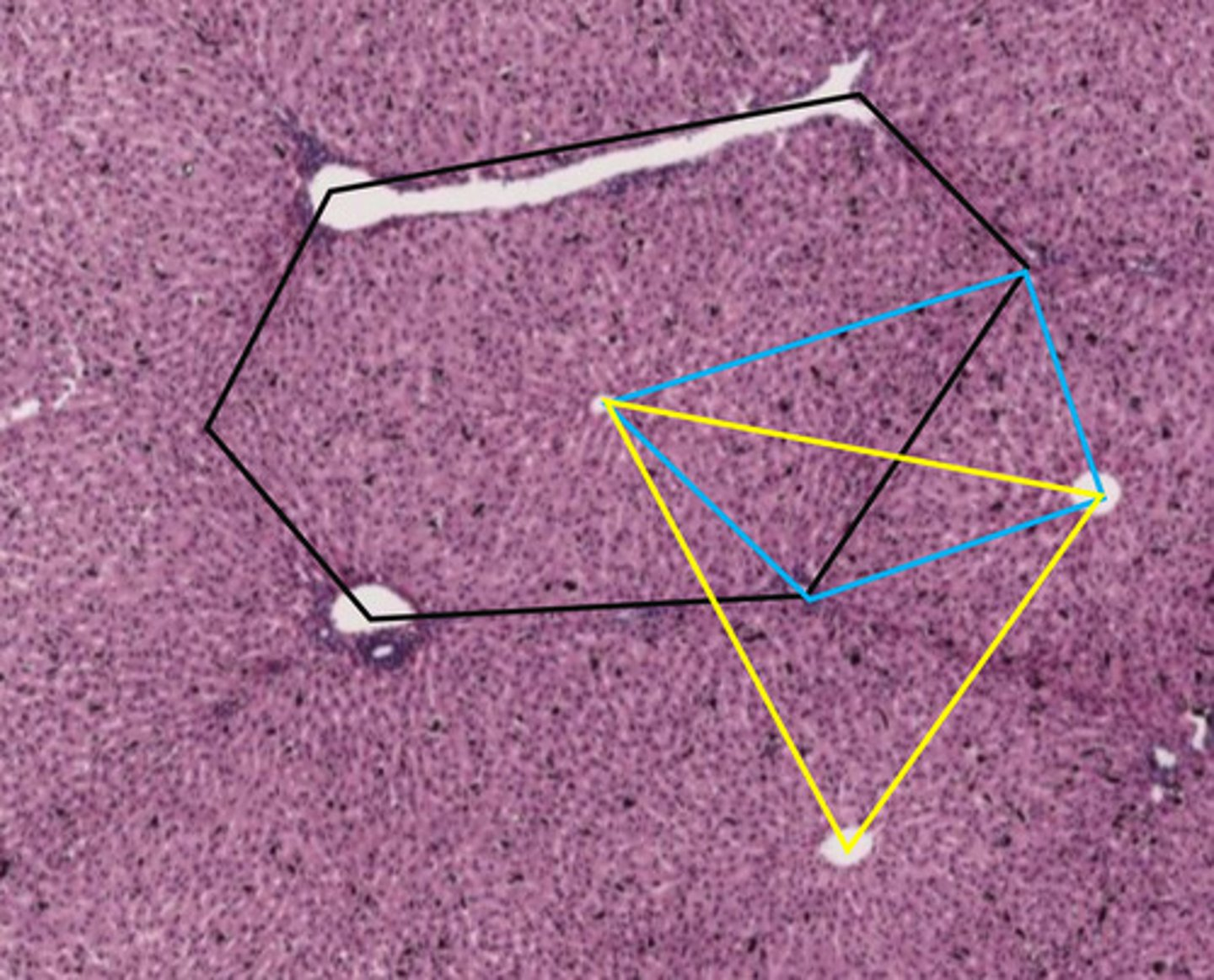
the black hexagon describes what function of the liver?
endocrine/metabolic functions
- this is a classic lobule
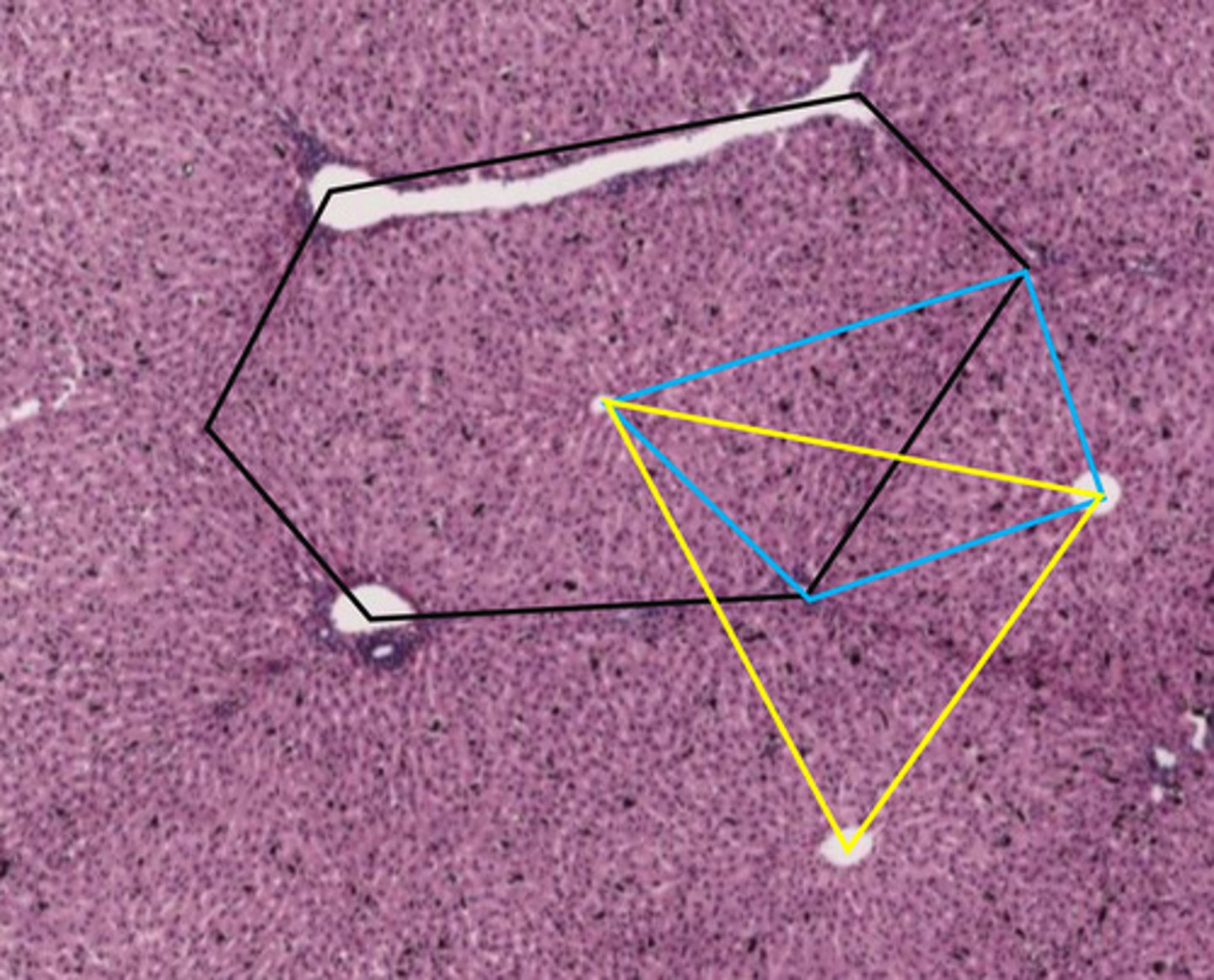
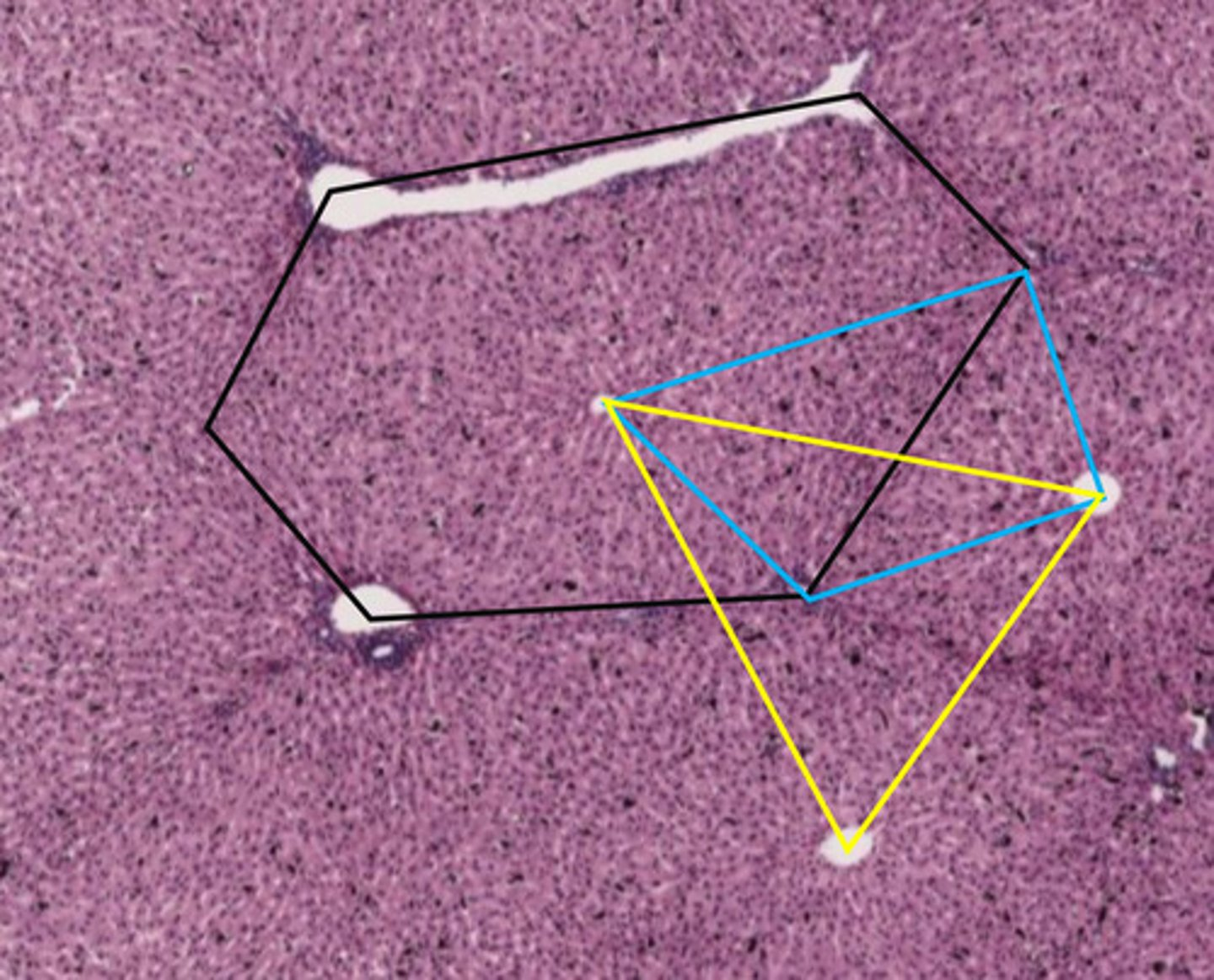
blue shape
liver acinus
- centered around incoming blood
- metabolic functions
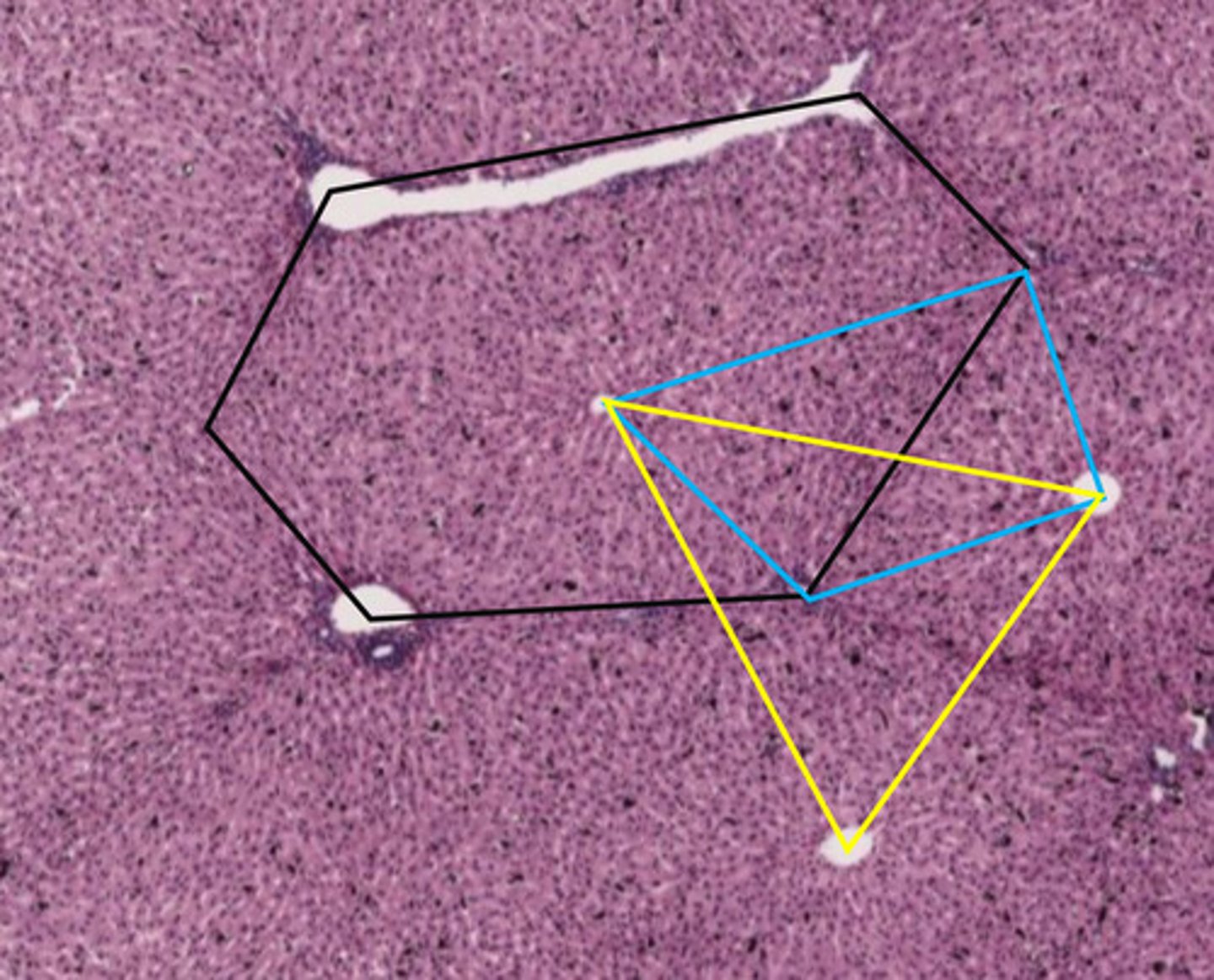
the blue shape describes what function of the liver?
metabolic functions
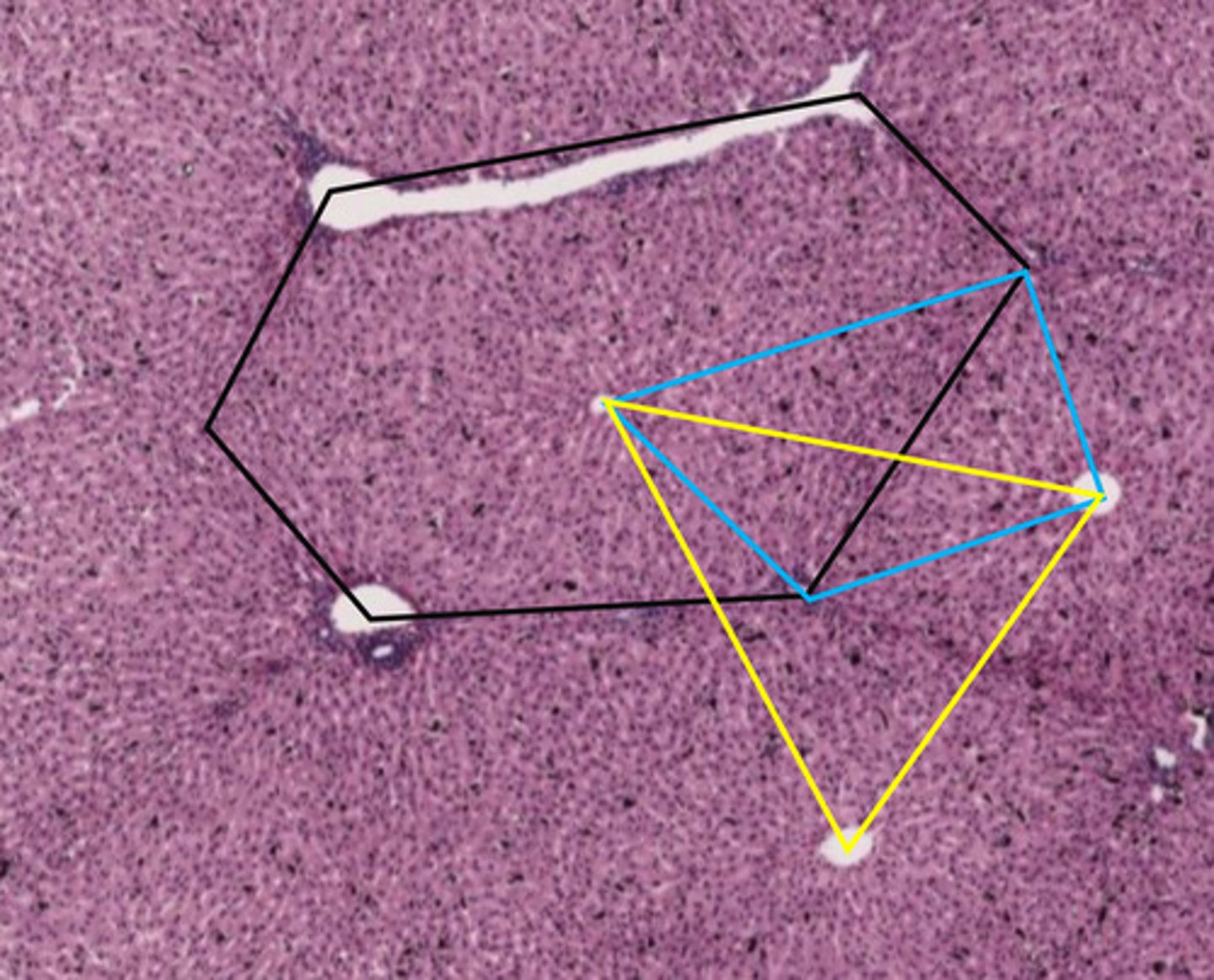
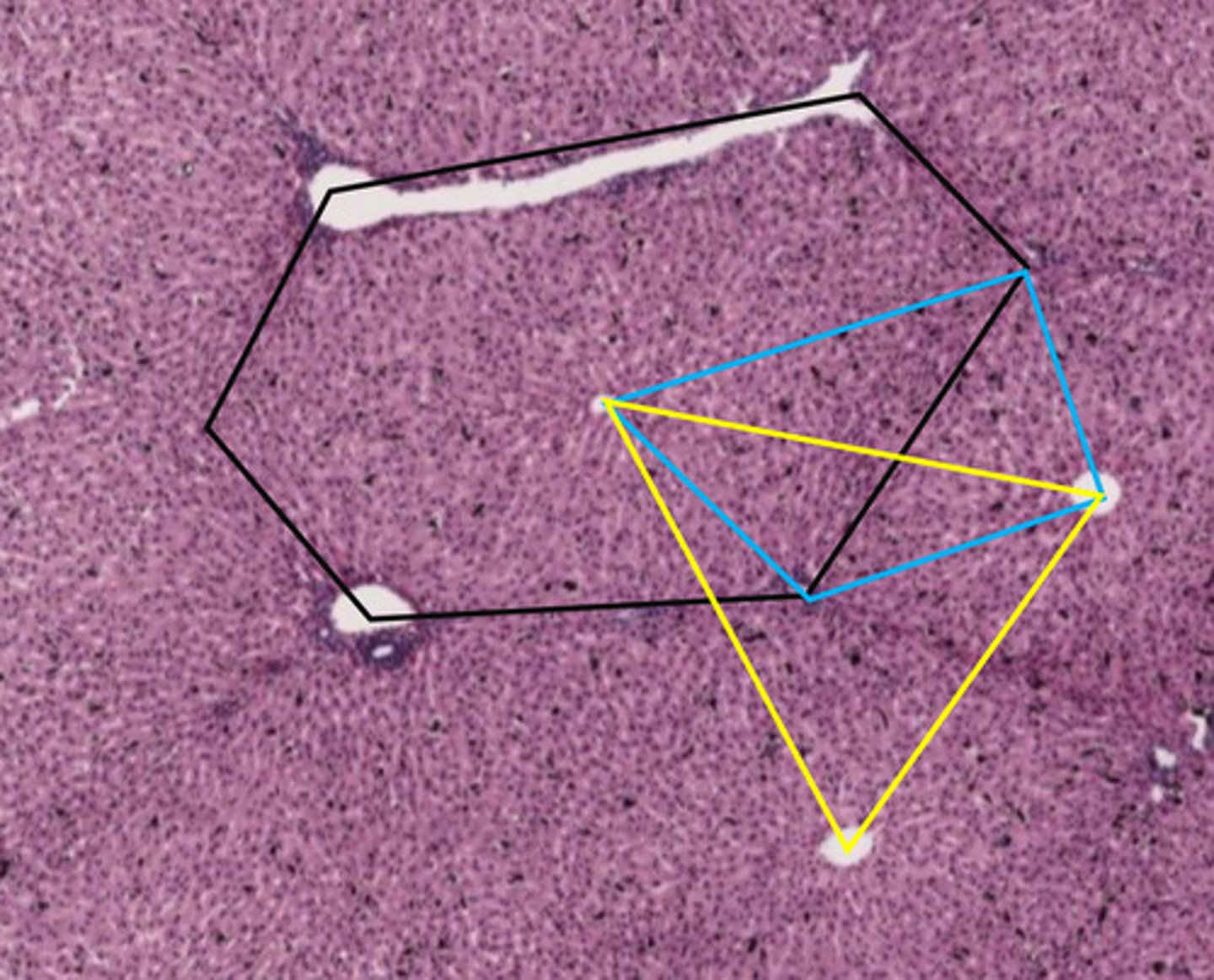
yellow triangle
portal lobule
- centered around bile duct
- exocrine/waste removal functions
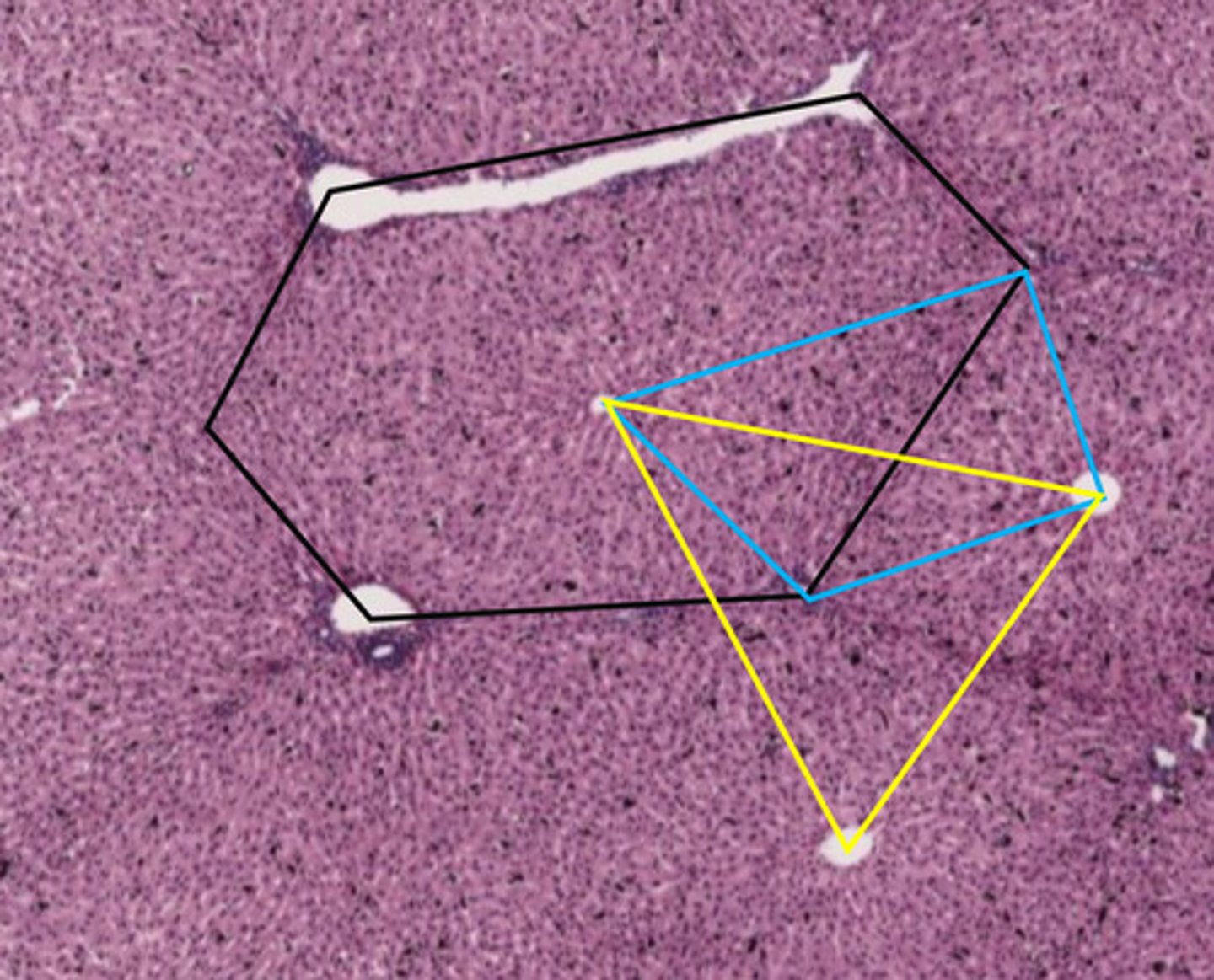
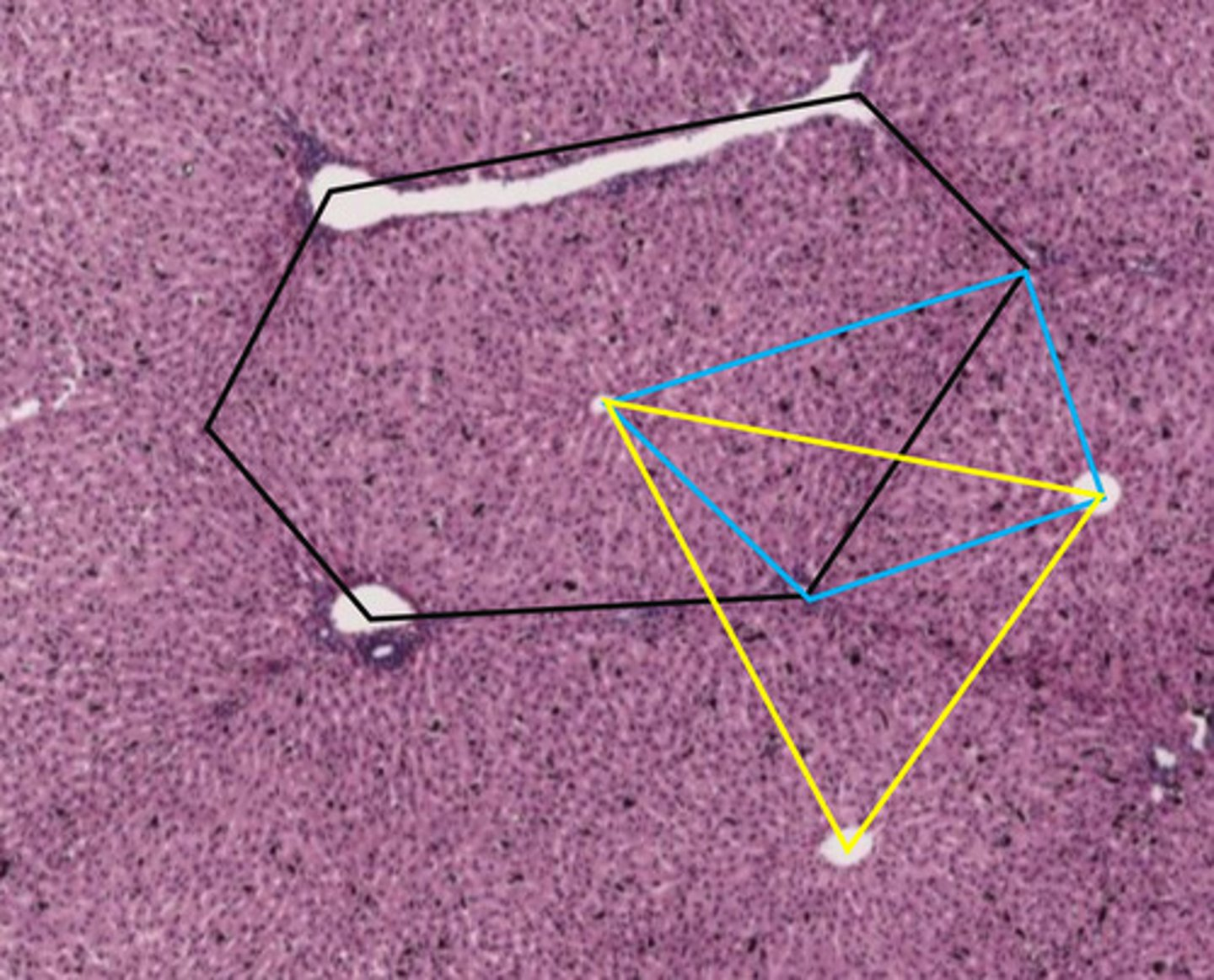
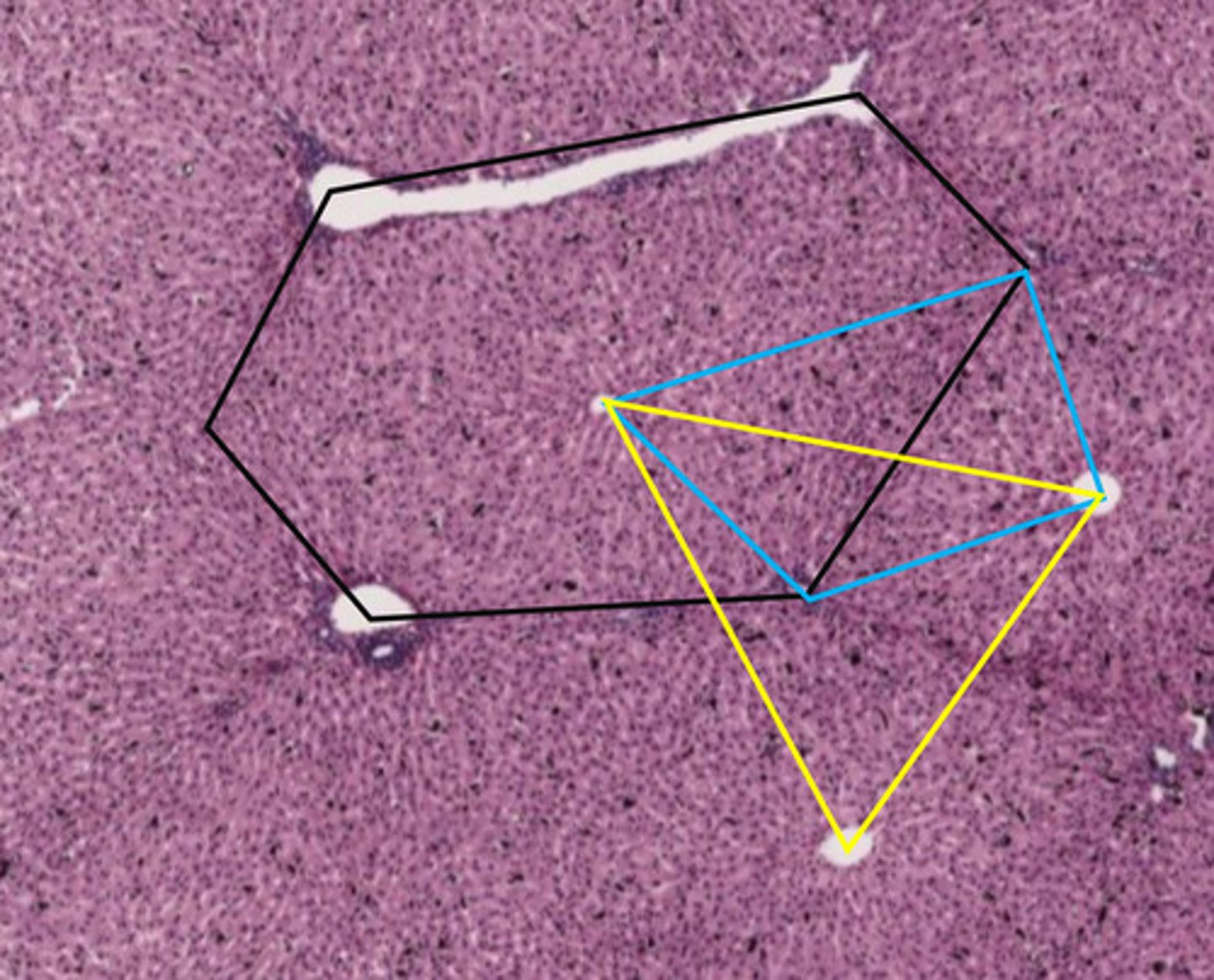
the yellow triangle describes what function of the liver?
exocrine/waste removal functions