3 Ortho (Midterm): Etiology of Malocclusion
1/108
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
109 Terms
malocclusion
Deviation from the desired form of occlusion:
- hereditary factors
- acquired/exogenous factors
what are the 2 etiologies of malocclusion?
- Class III
- Class II div 2
- Open bite
What are 3 examples of occlusal patterns that are inherited?
aggravation
a patient that has BOTH Class III malocclusion AND a pituitary adenoma that results in more growth in the mandible, this is an example of an _________ of the protrusive mandible
camouglage
a patient that has a Class III malocclusion, but experiences trauma to the mandibular condyles that stunts the growth of the mandible, this is an example of a _________ of the protrusive mandible
false
t/f: the majority of the population has a malocclusion from a cause that is known
true
t/f: the majority of the population has a malocclusion from unknown causes
malfunction
When a causal factor affects the neuromuscular tissue, it will primarily result in ________
malocclusion
When a causal factor affects the teeth, it will primarily result in ________
dysplasia
When a causal factor affects the bone tissue, it will primarily result in ________
local
ID if the following is a Local or General Factor:
- anomalies of number of teeth
local
ID if the following is a Local or General Factor:
- anomalies of tooth size
local
ID if the following is a Local or General Factor:
- anomalies of tooth shape
local
ID if the following is a Local or General Factor:
- mucosal barriers/ freni
local
ID if the following is a Local or General Factor:
- premature loss
local
ID if the following is a Local or General Factor:
- prolonged retention
local
ID if the following is a Local or General Factor:
- delayed eruption of permanent teeth
local
ID if the following is a Local or General Factor:
- abnormal eruptive path
local
ID if the following is a Local or General Factor:
- dental caries
local
ID if the following is a Local or General Factor:
- improper dental restorations
general
ID if the following is a Local or General Factor:
- heredity
general
ID if the following is a Local or General Factor:
- congenital
general
ID if the following is a Local or General Factor:
- environmental (prenatal/postnatal)
general
ID if the following is a Local or General Factor:
- predisposing metabolic climate and disease
general
ID if the following is a Local or General Factor:
- dietary problems
general
ID if the following is a Local or General Factor:
- abnormal pressure habits and functional aberrations
general
ID if the following is a Local or General Factor:
- posture
general
ID if the following is a Local or General Factor:
- trauma and accidents
initiation and proliferation
if a patient presents with an anomaly of the number of teeth present, this deviation occurred at the ____________ stage of tooth development
morphodifferentiation and histodifferentiation
if a patient presents with an anomaly of the size and shape of teeth present, this deviation occurred at the ____________ stage of tooth development
apposition or mineralization
if a patient presents with an anomaly of the enamel and/or dentin of teeth present, this deviation occurred at the ____________ stage of tooth development
- Esthetics
- Arch-perimeter (spacing/crowding)
- Occlusion (TSALD)
Anomalies of tooth size and shape can cause what type of orthodontic problems?
tooth size arch length discrepancy
What does TSALD stand for?
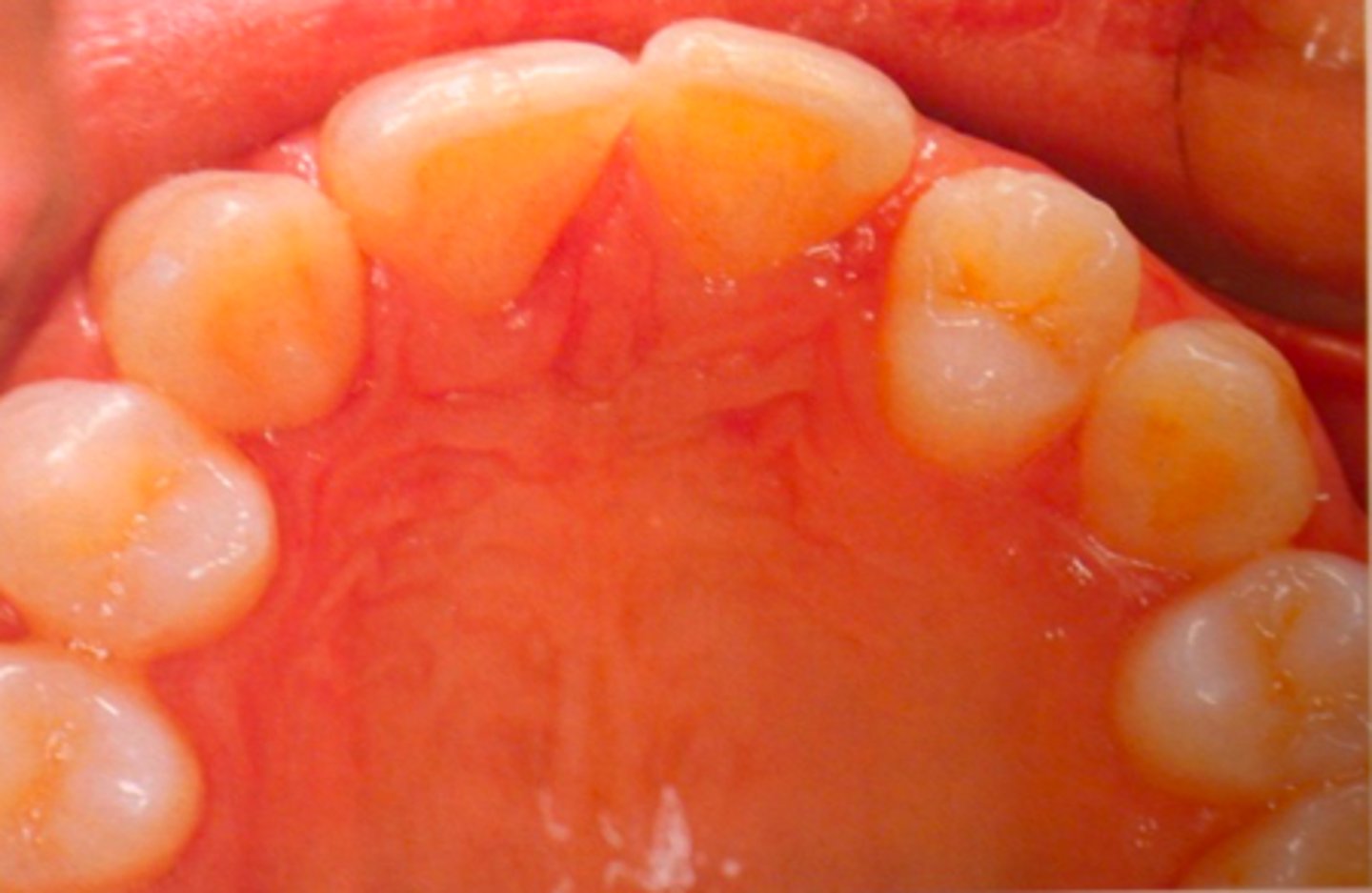
generalized microdontia
ID the anomaly:
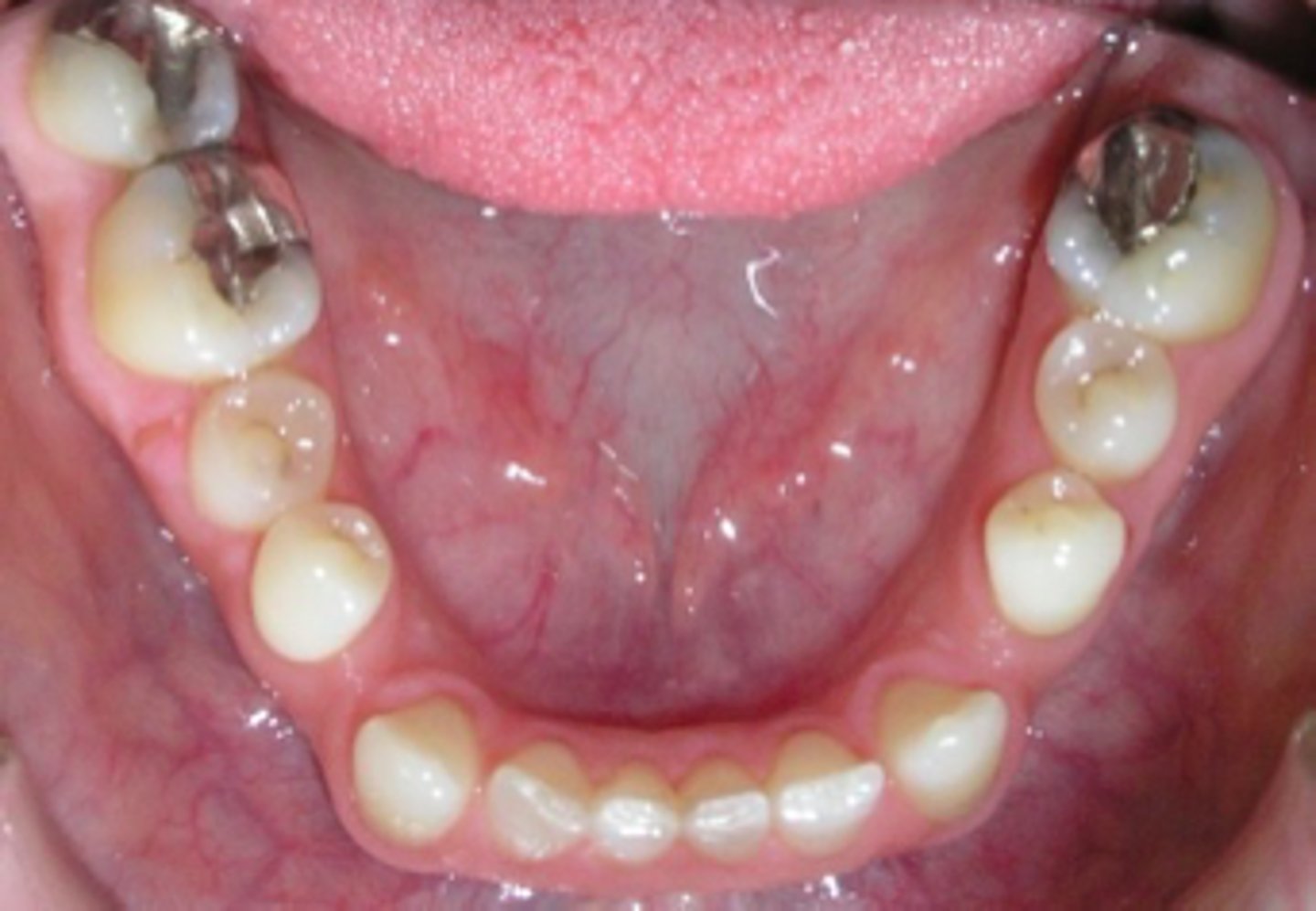
localized microdontia
ID the anomaly:
- MSX-1
- PAX-9
- AXIN
What are 3 genes that have been identified for causing missing teeth:
Anodontia
Complete Lack of tooth development:
Oligodontia
Missing 6 or more teeth:
Hypodontia
few missing teeth (less than 6):
Hyperdontia
supernumerary teeth; teeth that appear in addition to the regular number of teeth:
mesiodens
What is the most common presentation of supernumerary teeth?
maxillary 4th molar/ distomolar
What is the 2nd most common presentation of supernumerary teeth?
false
t/f: it is more common to see supernumerary teeth in the primary dentition vs the permanent dentition
true
t/f: it is more common to see supernumerary teeth in the permanent dentition vs the primary dentition
true
t/f: it is more common to for teeth to be missing in the permanent dentition vs seeing extra teeth
false
t/f: it is more common to see extra teeth in the permanent dentition vs seeing teeth missing
arch perimeter problems
What orthodontic problems do congenitally missing teeth cause?
- barriers in tooth eruption
- displacement of tooth gems
What orthodontic problems do supernumerary teeth cause?
true
t/f: it is common for siblings to experience the same patterns of hypodontia
- canine impaction/directional change of canine
- ectopic eruption of canine
- premolar-canine transposition
What are 3 sequelae of discrepancies or missing of the maxillary lateral incisiors:
maxillary lateral incisors
What tooth is responsible for guiding the maxillary canines into position?
3rd molars
What is the 1st most common tooth to be missing in the dentition?
mandibular second premolar
What is the 2nd most common tooth to be missing in the dentition?
maxillary lateral incisors
What is the 3rd most common tooth to be missing in the dentition?
- Aperts syndrome
- Cleidocranial Dysostosis
- Gardners syndrome
- Crouzons syndrome
What are 4 syndromes that present with supernumerary teeth?
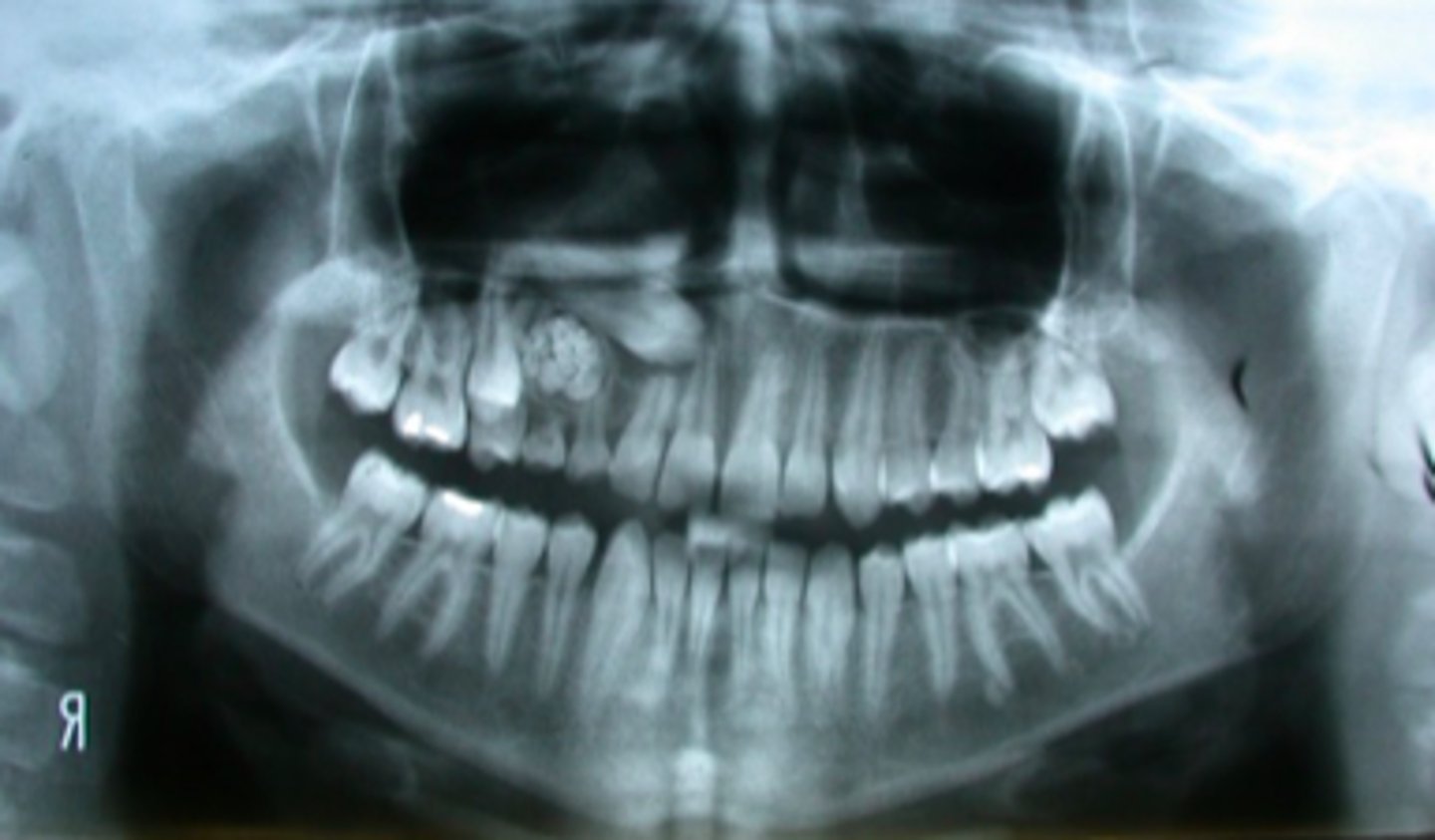
odontoma
What is the cause of the tooth displacement/impaction in this patient?
age 7
at what age is it recommended that all children receive an orthodontic evaluation by?
preventative orthodontics
What type of orthodontic intervention is it when a patient has sever interproximal caries, so you quickly restore the tooth to prevent loss of space and mesial migration?
interceptive orthodontics
What type of orthodontic intervention is it when a primary 2nd molar has advanced caries, you extract the tooth and provide a space maintainer?
corrective orthodontics
What type of orthodontic intervention is it when a patient already lost a primary tooth to caries and mesial migration has already occurred, so you prescribe a space regainer device?
- wear problem
- arch-perimeter problem
- occlusion
Hypoplasia of dental structures can cause what type of problems?
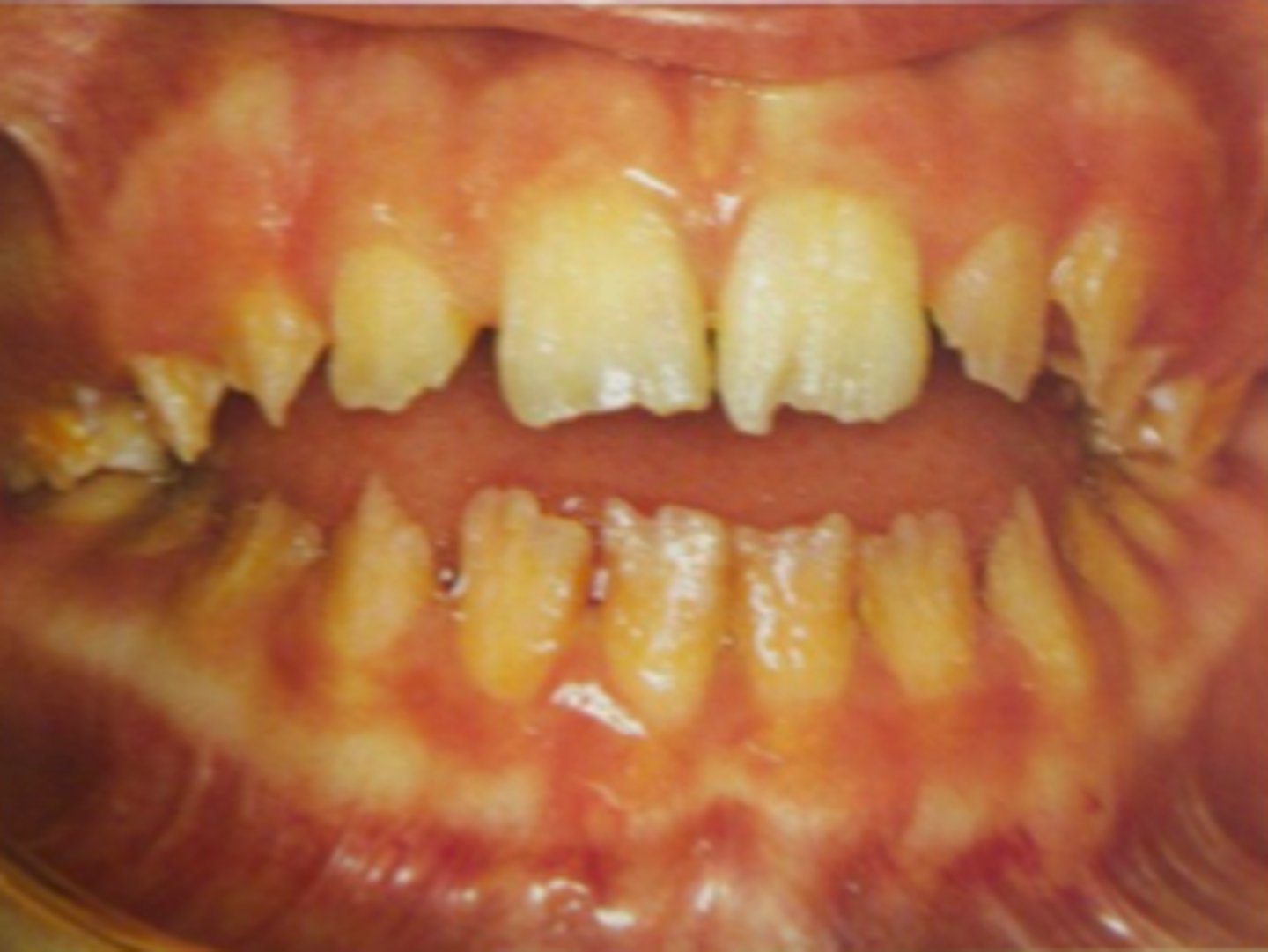
- orthodontics
- endodontic
- restorative
Regional odontodysplasia can cause what type of problems?
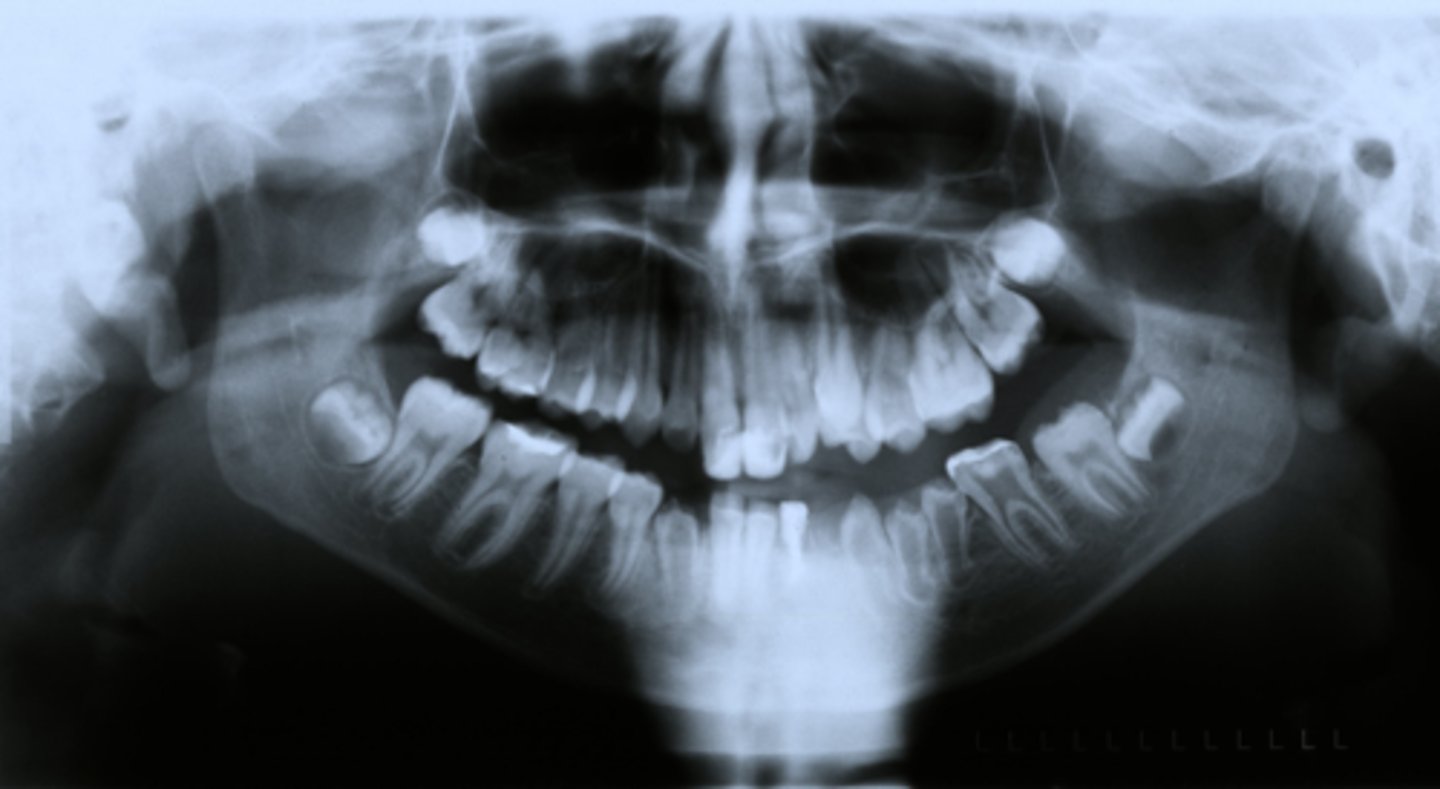
- Facial clefts
- Microstomia
- Anomalies of the frena
- Ankyloglossia
What are some soft tissue anomalies?
males
The presentation of cleft lip WITH cleft palate is more common in ________
females
The presentation of isolated cleft palate is more common in ________
females
Clefting anomalies tend to be more severe in ____
left
Clefting anomalties tend to affect which side of the face more?
cleft lip/palate
ID the anomaly:
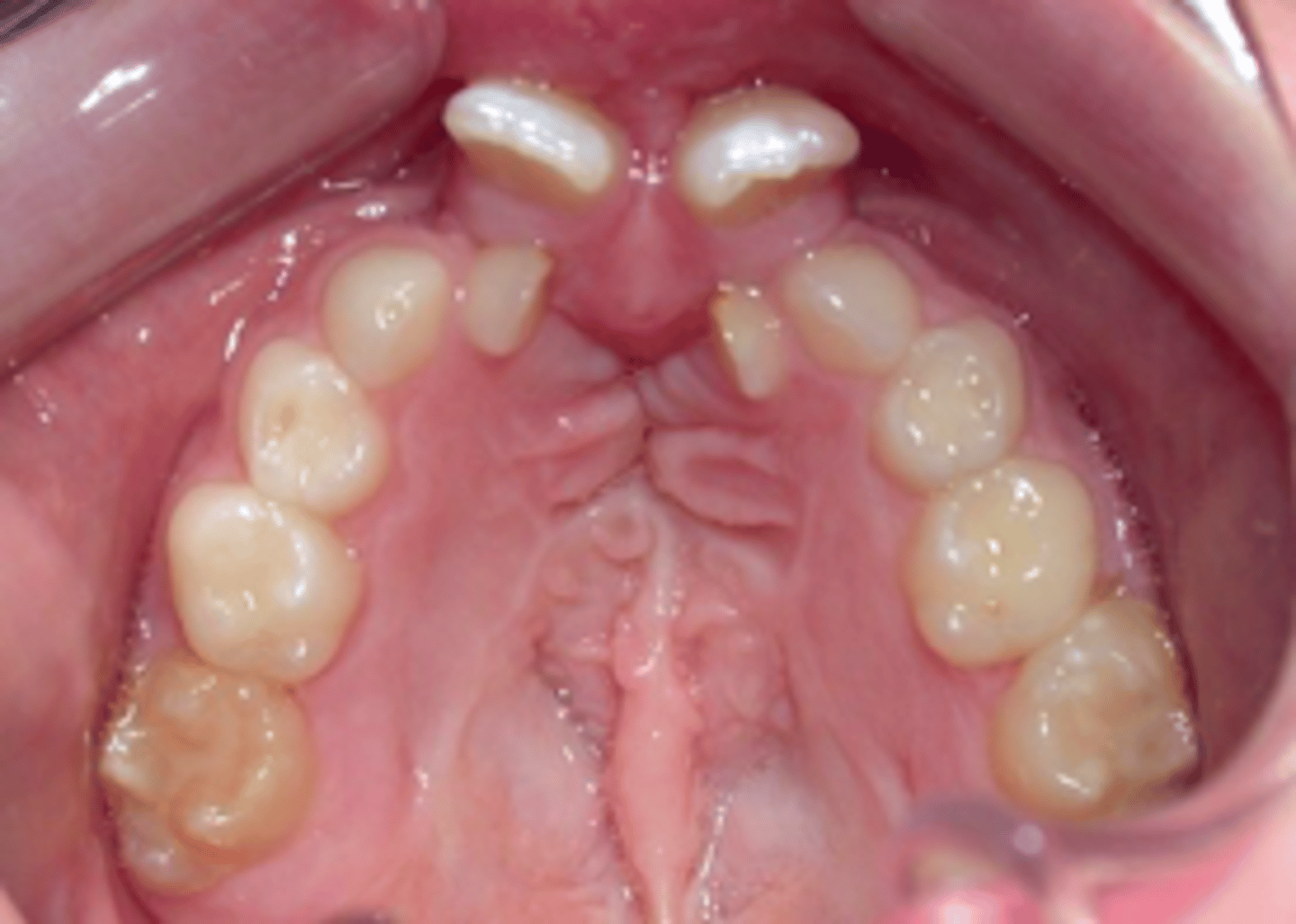
large freni attachment
ID the anomaly:
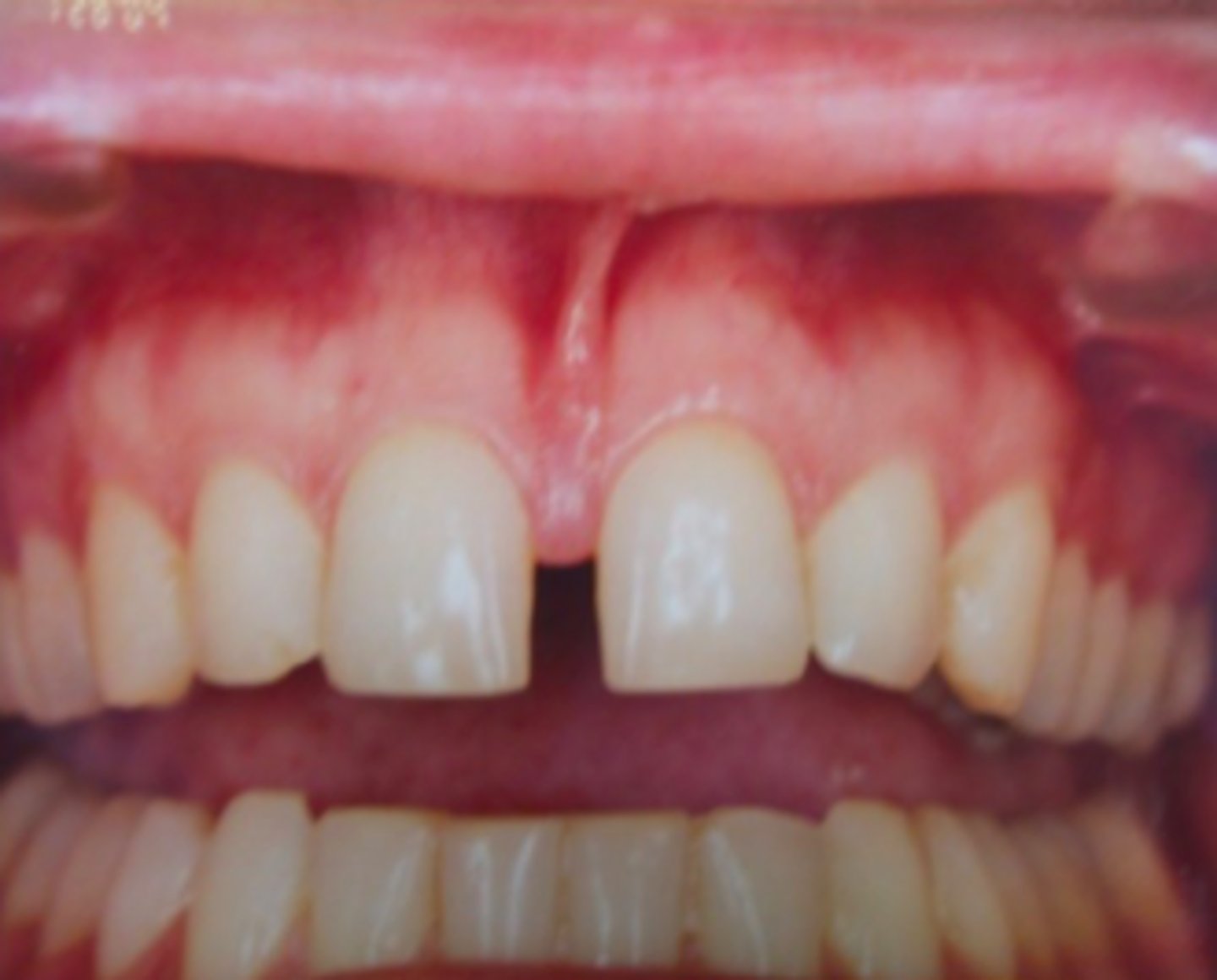
ankyloglossia
ID the anomaly:
cleft lip/palate
Aspirin has what teratogenic affect?
cleft lip/palate
Smoking cigarettes has what teratogenic affect?
cleft lip/palate
Dilantin has what teratogenic affect?
mid-face deficiency
Alcohol consumption has what teratogenic affect?
premature suture closure
Vitamin D excess has what teratogenic affect?
teratogens
Chemical or other agents capable of producing embryologic defects if given at a critical time:
true
t/f: cleft lip/palate can be both hereditary and acquired
- Mandibular prognathism
- Bimaxillary protrusion
- Skeletal open bites
what are 3 skeletal malocclusions that are hereditary?
- extent and localization of the trauma
- at what point in development phase it occurs
The influence of trauma depends on 2 things:
PDL
once a tooth has been ankylosed, it is impossible to move orthodontically because it no longer has a _______
lingual
permanent tooth buds develop _____ to the roots of primary teeth
- Intensity
- Duration
- Type of habit
The Relationship between orofacial dysfunction and malocclusion depends on:
10th week
thumb sucking has been observed to start as early as the ____ in utero
- Open bite
- Protraction of maxillary anterior teeth
- Mandibular retrusion
- Maxillary constriction
- Narrow nasal floor and high palatal vault
- Compensatory tongue thrust
what are 6 Sequelae of Digit/ Thumb sucking:
- Humped up tongue/Higher tongue position
- Shallow central furrow of tongue
- Momentary incisor contact
- No mandibular thrust
- reduced peri-oral sphincter activity (no lip movement)
What are the characteristics of the Mature (Somatic) Swallow:
- Elongated tongue
- Depressed central furrow of tongue
- Narrow tongue
- lower tongue position
- Pursed lips
- Mandibular thrust
What are the characteristics of the Infantile (Visceral) swallow:
CN 5
Which cranial nerve is mostly in control during the Mature (Somatic) Swallow:
CN 7
Which cranial nerve is mostly in control during the Infantile (Visceral) swallow:
Class II div 1
what malocclusion class will present with the continuation of the Infantile (Visceral) swallow?
6124
-537 (most common)
-357
-573
What is the maxillary sequence of eruption:
61234578
What is the mandibular sequence of eruption:
maxillary 1st molar
What tooth most commonly experiences ectopic eruption?
false
t/f: in most cases, the ectopic eruption of the maxillary 1st molars will require surgical intervention
- crowding
- transposition
- altered position of teeth
What are the sequelae of an ectopic eruption:
maxillary lateral incisors
during eruption, if the permanent maxillary canine goes past the midline of the ________ the likelyhood that it will fully erupt on its own is significantly decreased, and it will be impacted
ectopic eruption
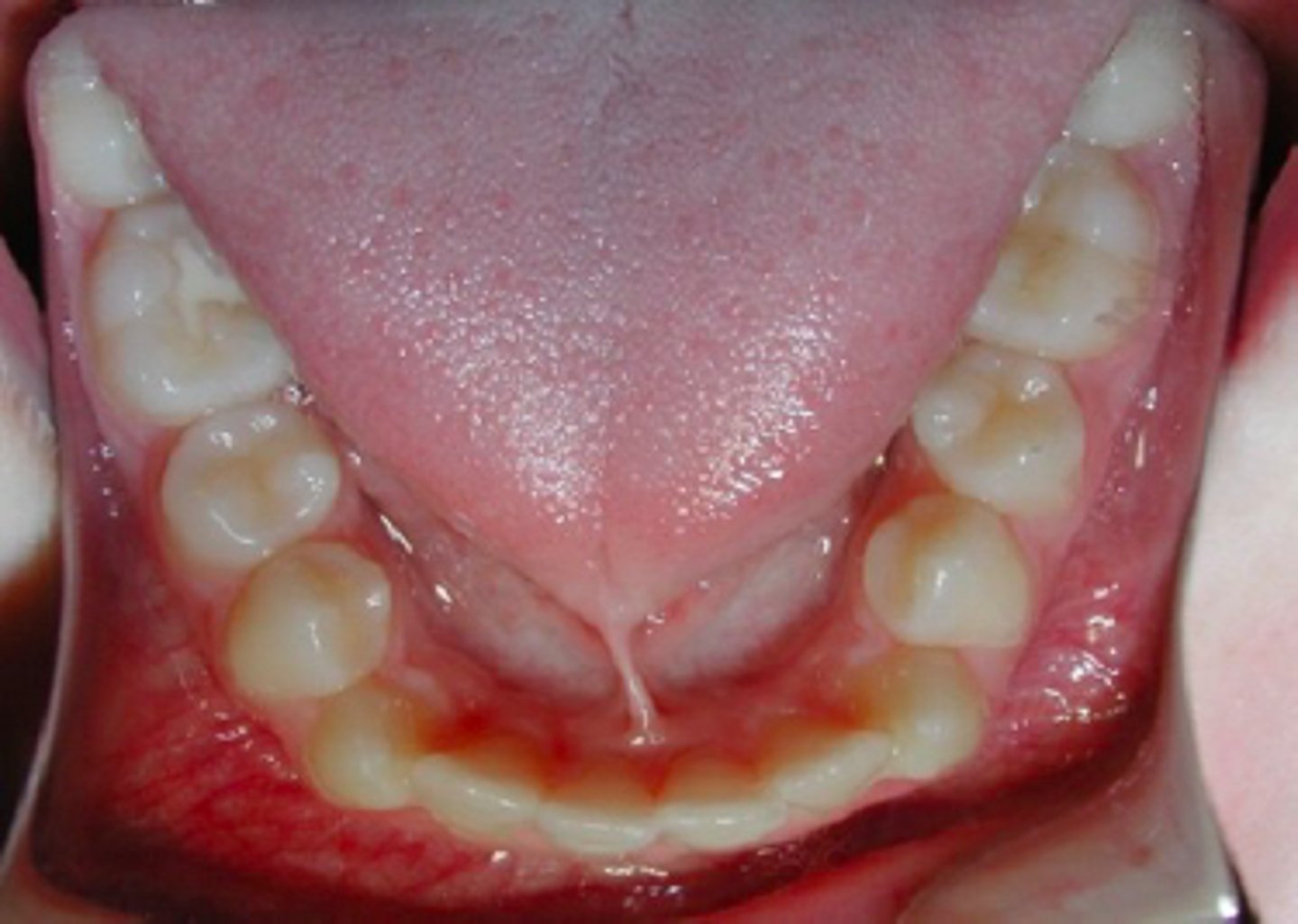
ID the developmental disturbance:
ectopic eruption
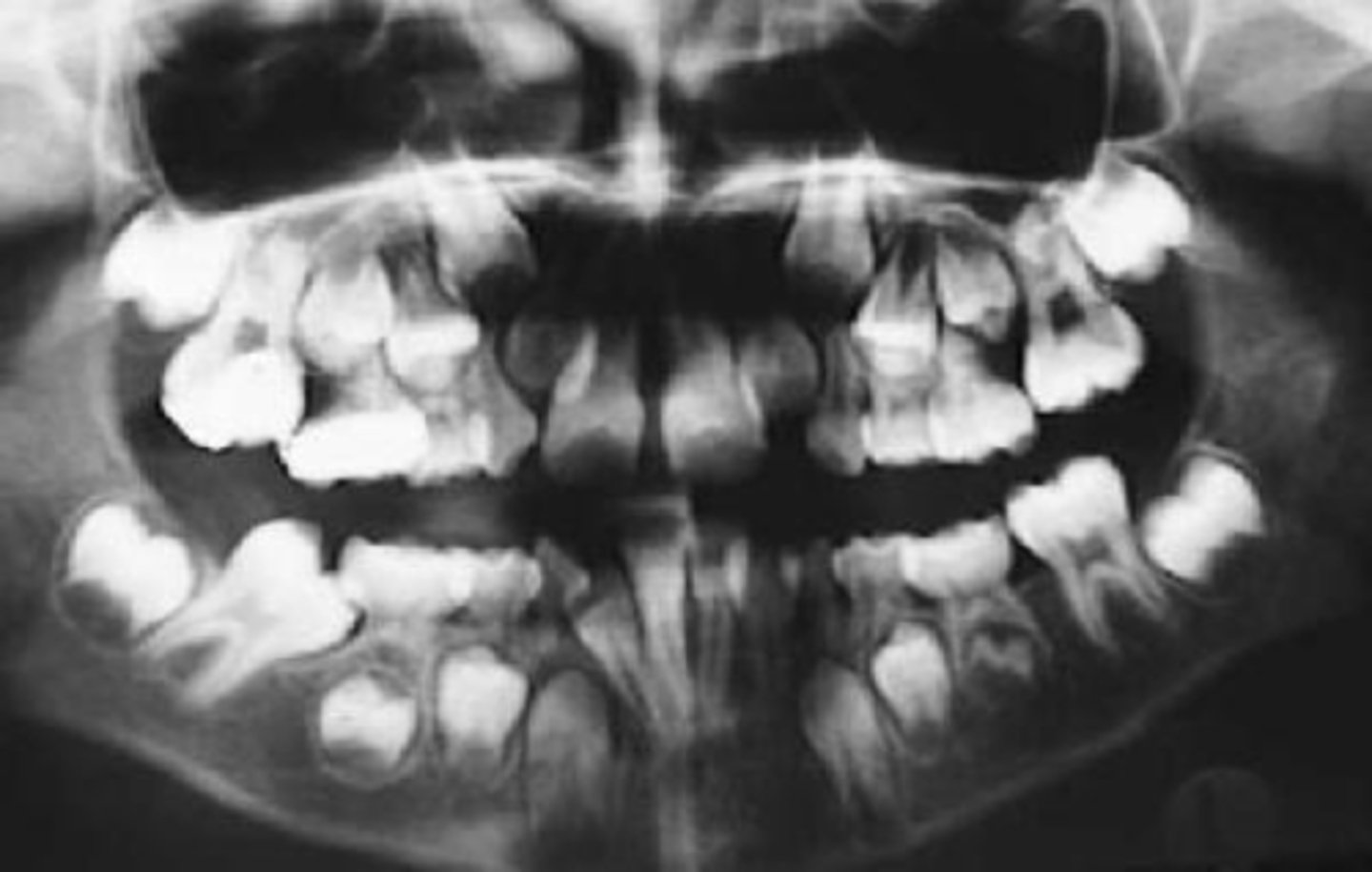
ID the developmental disturbance:
abnormal sequence of eruption
ID the developmental disturbance:
- crowding
- midline deviation
What are the sequelae of an abnormal sequence of eruption:
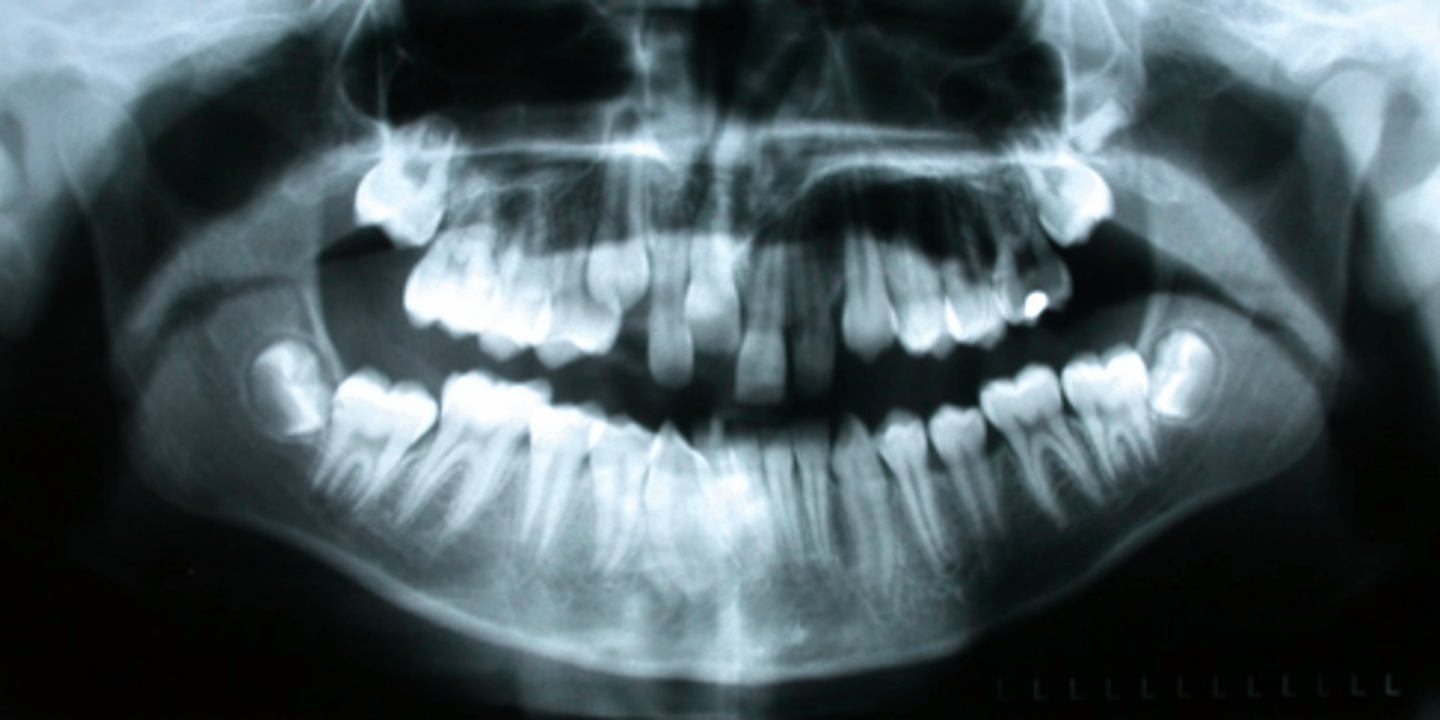
transposition of teeth
ID the developmental disturbance: