AP Bio Unit 7 Test
1/177
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
178 Terms
Briefly describe how our solar system formed according to the Big Bang theory
- all matter and energy was in one spot and then boom
Describe what scientists believed early earth was like
- earth was a hot, rocky, and volcanic.
- the air was gaseous and smelly
- the gases present were: Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Phosphorous , Nitrogen, and Sulfur
Explain how Aristotle and Pasteur are involved in the theory of spontaneous generation
- Both of these scientists worked to disprove the theory of spontaneous generation
- Pasteur actually disproved the theory of spontaneous generation with his curved neck falsk
Describe the Miller-Urey experiment that tested Oparin's idea of how life formed on earth?
-Miller and Urey were proving that the first inorganic gases on earth created organic compounds
-How their experiment worked was that the CHOPNS were first struck by lightening
- then they were condensed (which created a condensed liquid substance)
- In that substance they found organic molecules such as amino acids, nitrogen bases, fatty acids, and hydrocarbon
- Finally the condensed liquid turned into a pure liquid which created the ocean
Explain the significance of the Miller and Urey's findings in regards to forming life on earth
- they proved that organic compounds came from the first inorganic compounds
Explain the role of hot rocks and in the first polymers
- when water containing organic compounds washed up on the hot rocks and clay, the heat could have caused the organic compounds to bond
- then liposomes form bubbles and the bubbles trap organic polymers called protobionts
Identify 3 characteristics of microspheres (protobionts) that are similar to the characteristics of cells
1.) both have a membrane to separate their internal environment from the external environment
2.) both reproduced by budding or binary fission
3.) both can grow
explain how microspheres might have become the first living cells
- a microshere/protobiont is not a cell because it has no nucleic acids, but the microsphere/protobionts could have taken in nitrogenous bases which may have formed RNA
- viola! Cells!
Explain why the first living cells were likely to be anaerobic
- they were likely anaerobic because there was no oxygen present
List 4 ways in which bacteria and archaea are different
1.) a bacteria's cell wall is made of peptidoglycan and an Archaea's isn't
2.) Bacteria only has 1 RNA polymerase and Archaea have several
3.) Bacteria do not have any Introns in their DNA and achaea have Introns in their DNA
4.) Bacteria do not have histones but Archaea do
Described groups of bacteria based on their shape
- coccus (pl=cocci)= spherical
- baccilus (pl=bacilli)= rod
- spirilus (pl=spirili)= corkscrew shape
photoautotroph
- energy:from light
- carbon source: carbon dioxide (CO2)
chemoautotrophs
- energy source: chemical (CH4, Nh3, Fe)
- carbon source: carbon dioxide (CO2)
photohertrophs
- energy source: light
- carbon source: organic compounds
chemoheterotrophs
- energy source: organic compounds
- carbon source: organic compounds
5 benefits of bacteria
- making yogurt and cheeses
- making wine and alcoholic beverages
- they keep the bad bacteria in check
- fixes nitrogen
- there are bacterium in the pit of your stomach
Name 3 groups of Archaea
- Halophiles
- Thermophiles
- Methanogens
Habits of Halophiles
- love salt
- their proteins and cell wall's function is improved in highly salty environments
- live in environments like The Great Salt Lake and The Dead Sea
Habits of Thermophiles
- thrive in hot environments
- their DNA and proteins adapt to make them stable at hot temperatures
- strain 121 survives at 121 degrees Celcius
- its DNA is used for PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction)
Habits of Methanogens
- Are poisoned by Oxygen
-produce Methane as a waste product
- live in swamps, marshes, guts of cattle, termites, and other herbivores
- compose "swamp gas" or "marsh gas"
What had to happen before organic compounds could move out of the ocean and onto land?
the ozone would have to form to create a protection from the harsh UV rays
Gram Positive Bacteria
- thick cell walls
- more affected by antibiotics
- can produce endotoxins and exotoxins
Gram Negative Bacteria
- thin cell wall
- outer layer of lypopolysaccharides
- not as affect by antibiotics
- produce endotoxins
Extotoxins
- Proteins
- releases by living bacteria
- only small amounts are required to cause disease
- affect specific cells
- symptoms are specific
- toxins damage cell memebrane; cause lysis
- toxins can disrupt intracellular functions
Endotoxins
- released by dead bacteria; caused by the lipopolysaccharides
- toxin in high doses
- General symptoms such as: nausea, fever, aches, diarrhea
Name the 2 theories of how eukaryotic cells formed?
- endosymbiosis
- infolding
Explain Lynn Margulis' theory of how the organelles mitochondria and chloroplasts were formed
- she believes the they were both formed by endocytosis because they both have 2 membranes, each has its own set of DNA, they both have proteins and carry out protein synthesis, and their oganelles can reproduce by binary fission
spontaneous generation
- the theory that non-living things can produce living things
biogenesis
- living things come from other living things
monomers
- one molecule that can be bonded to other identical molecules to make a chain
ploymers
- chain of multi-repeated parts
ribozymes
- an RNA molecule capable of acting as an enzyme
endospore
- hard casing, used for protection
pathogen
- a bacteria, virus, or other microorganism that can cause disease
strepto
- bacteria that form in a chain
staphlo
- bacteria that are clustered; grape-like
diplo
- bacteria that are in twos
peptidoglycan
- what the cell wall of bacteria is made of
6 biologically important elements
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Phosphorous, Nitrogen, Sulfur
Natural selection
A process in which individuals that have certain inherited traits tend to survive and reproduce at higher rates than other individuals because of those traits.
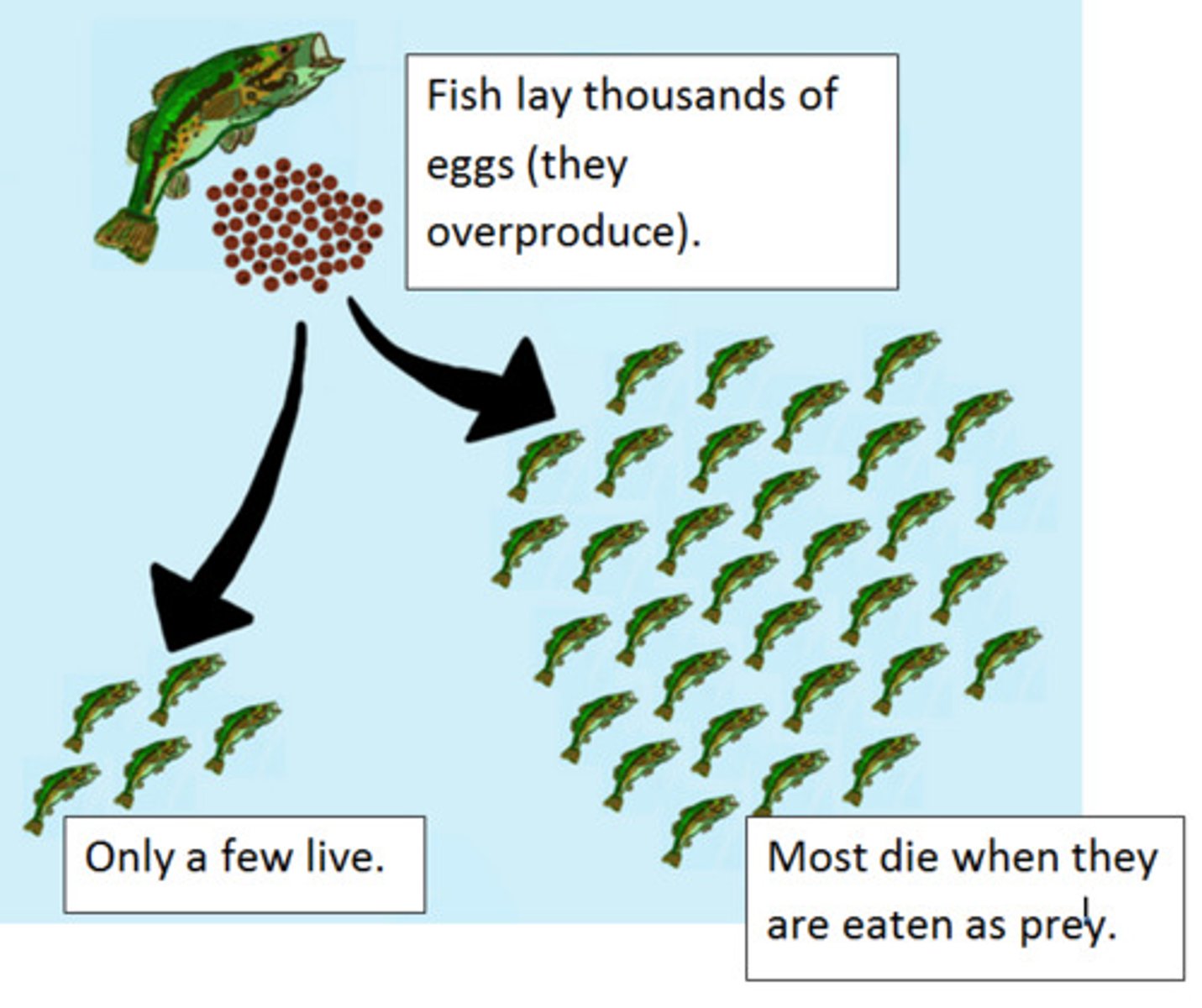
3 factors leading to natural selection
1. Organisms produce more offspring than can survive because there is a competition for resources.
2. Individuals in a population have variations in traits.
3. Beneficial traits are more likely to get passed down to offspring.
Speciation
the formation of new and distinct species in the course of evolution.
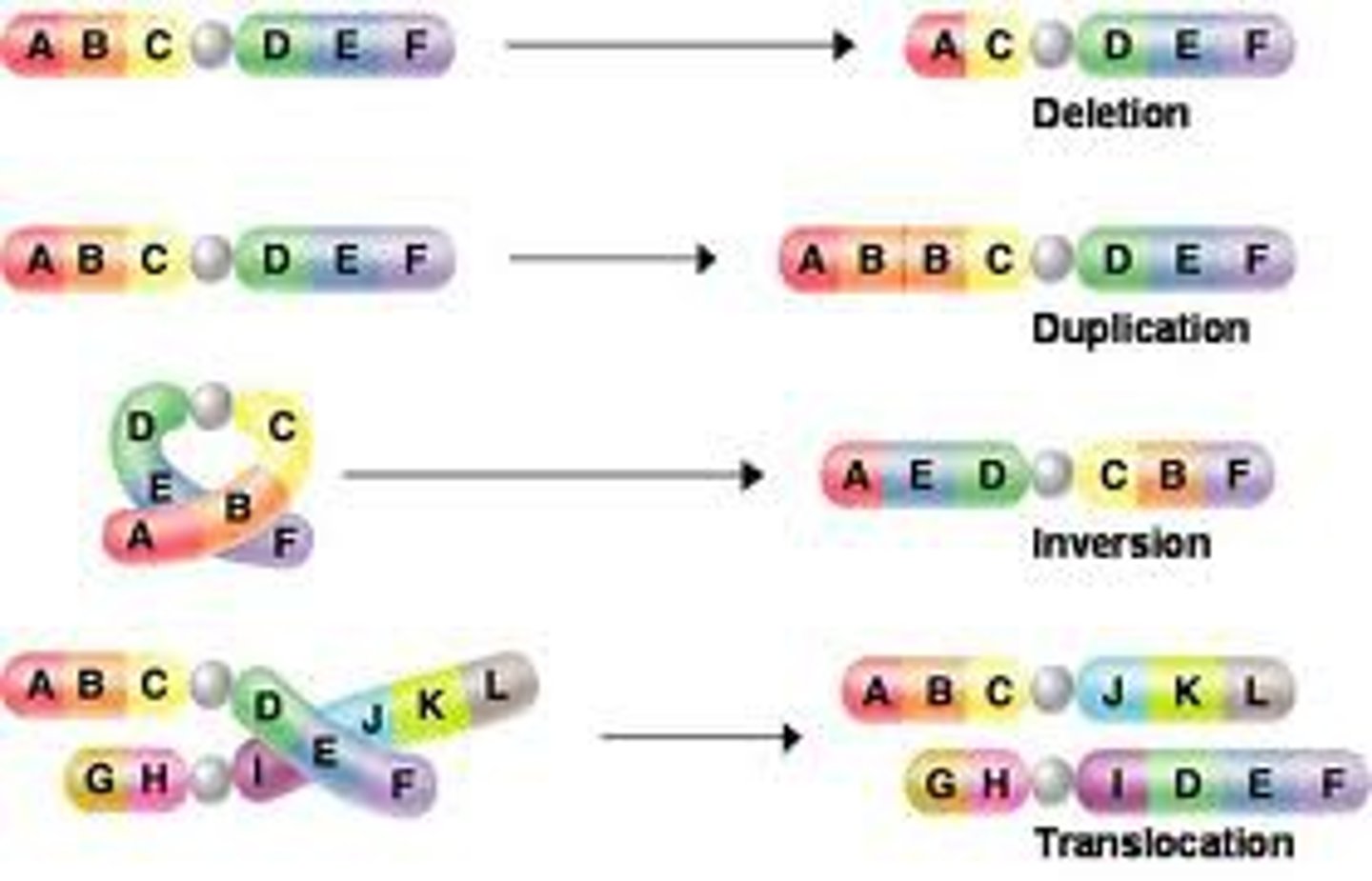
Mutation
spontaneous random change in DNA
Evidence for evolution
can be found in fossil records, geographical distribution (biogeography), homologous structures, similarities in early development (embryology)
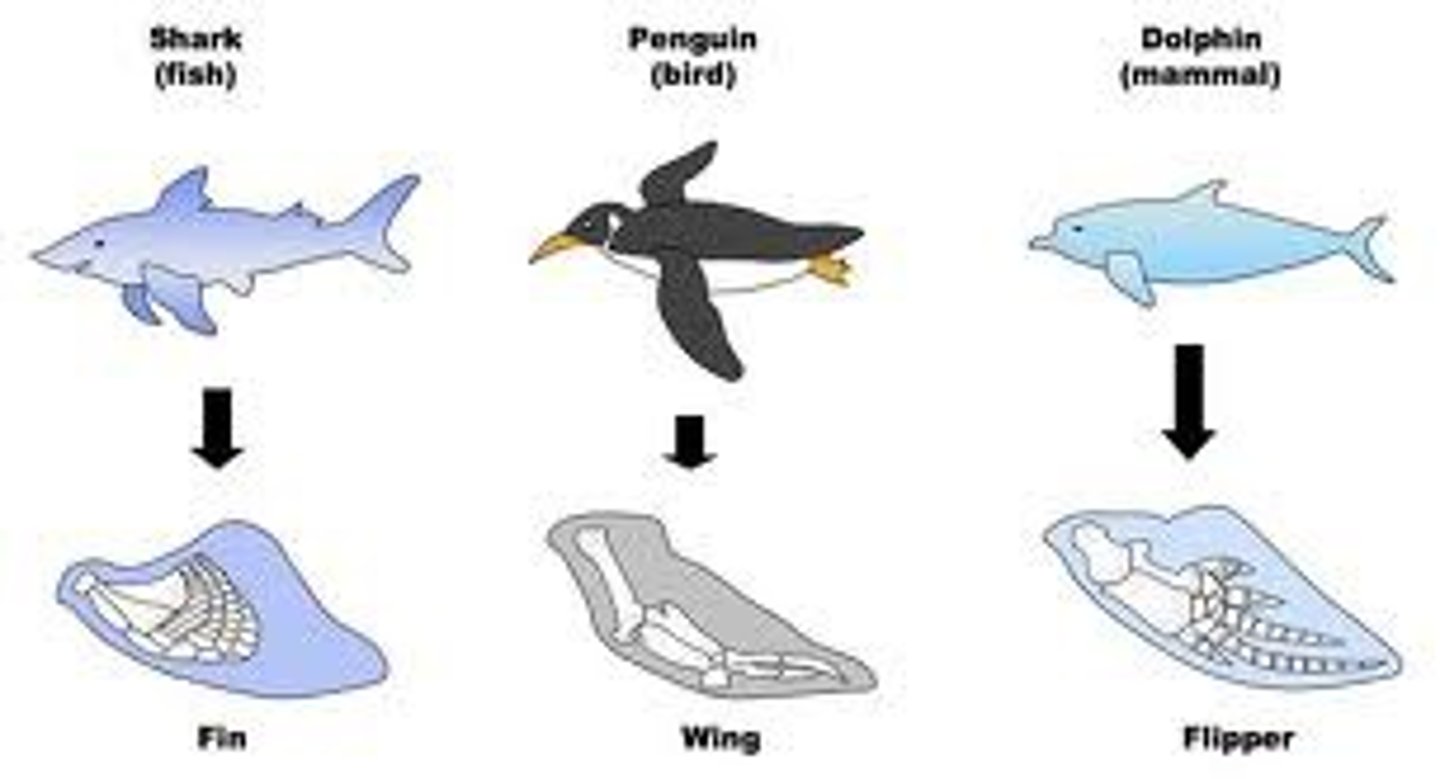
homologous structures
similarities in structures due to shared ancestry, such as the bones of a whale's flipper and a tiger's paw
convergent evolution
Process by which unrelated organisms independently evolve similarities when adapting to similar environments
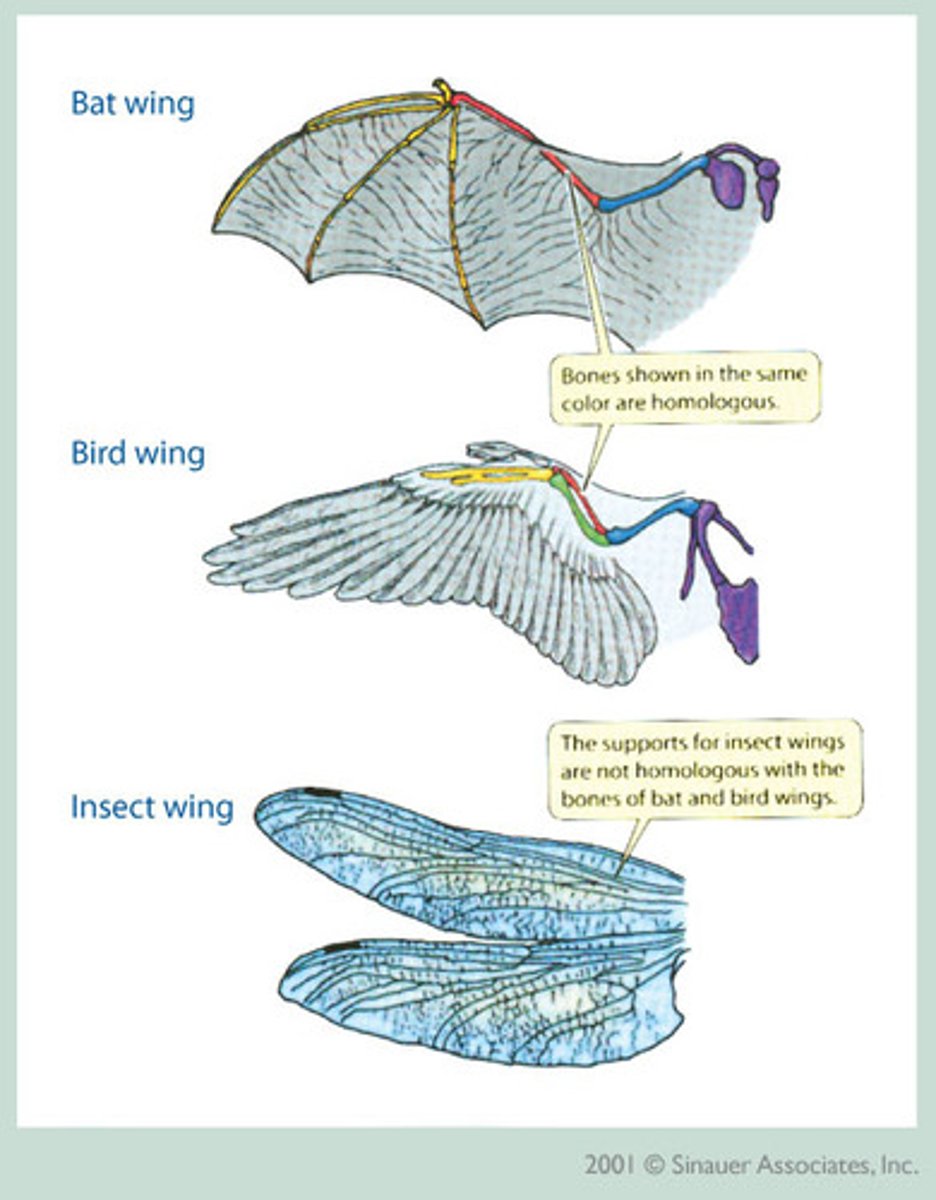
analogous structures
structures that do not have a common evolutionary origin but are similar in function; result from convergent evolution
parallel evolution
Two related species that have made similar evolutionary adaptations after their divergence from a common ancestor
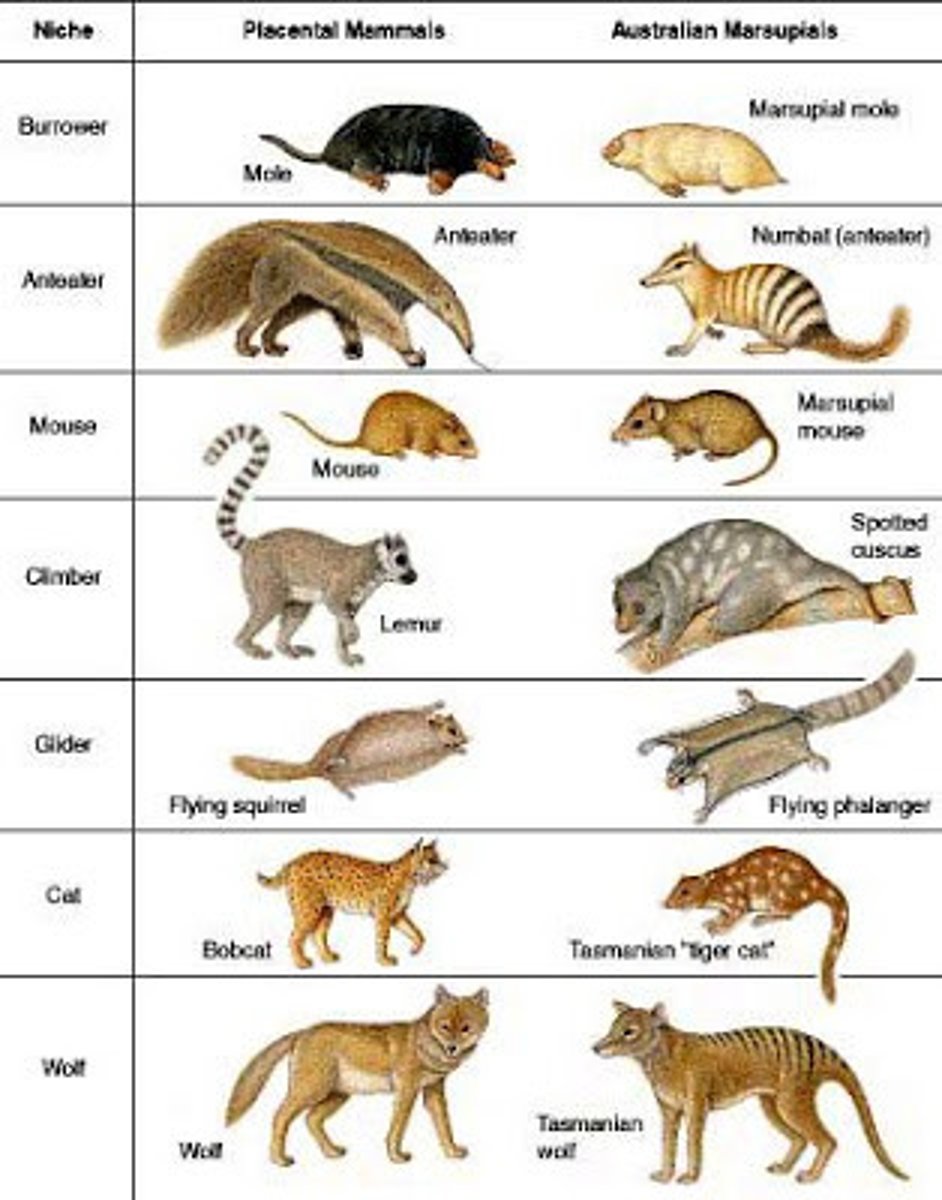
vestigial structures
remnant of a structure that may have had an important function in a species' ancestors, but has no clear function in the modern species.
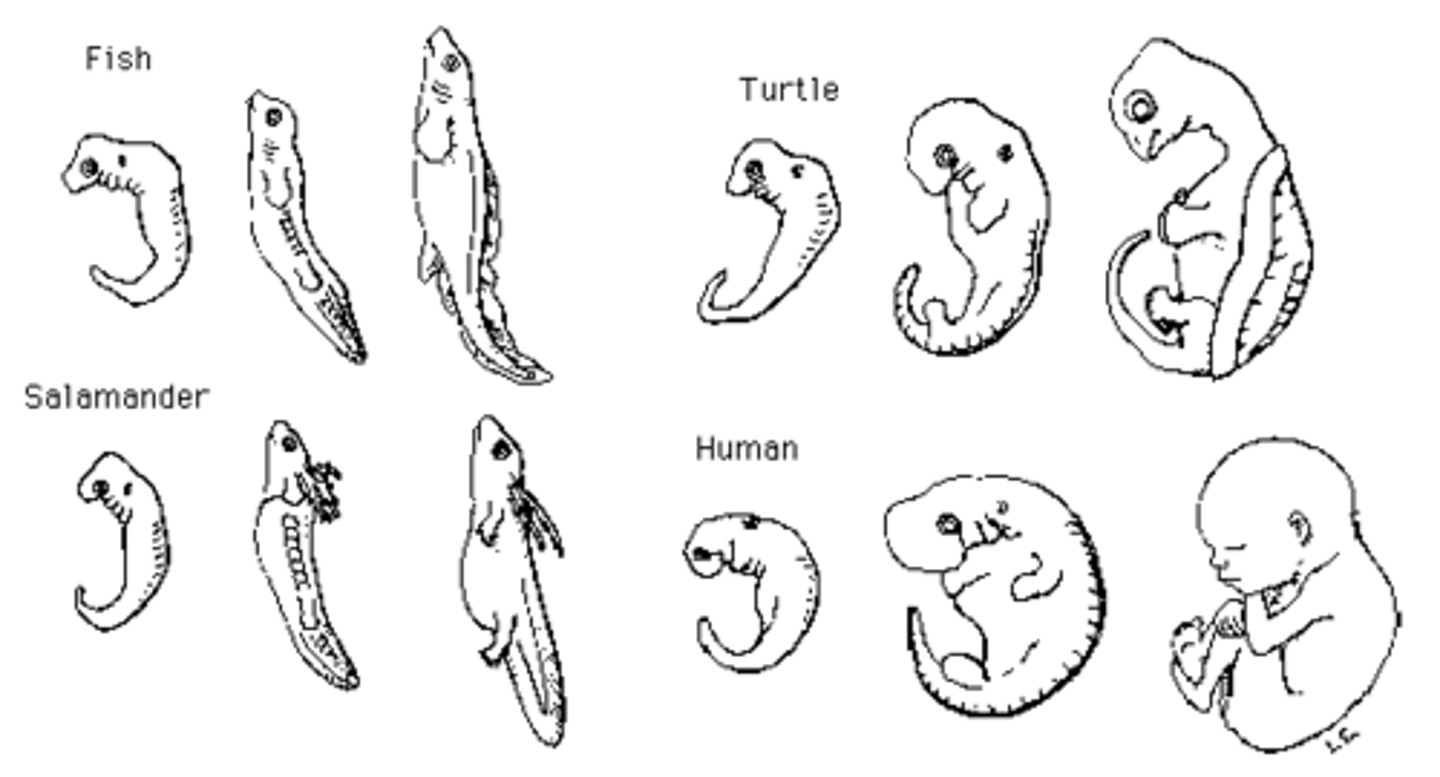
embryology
Embryos of vertebrates share many anatomical homologies.
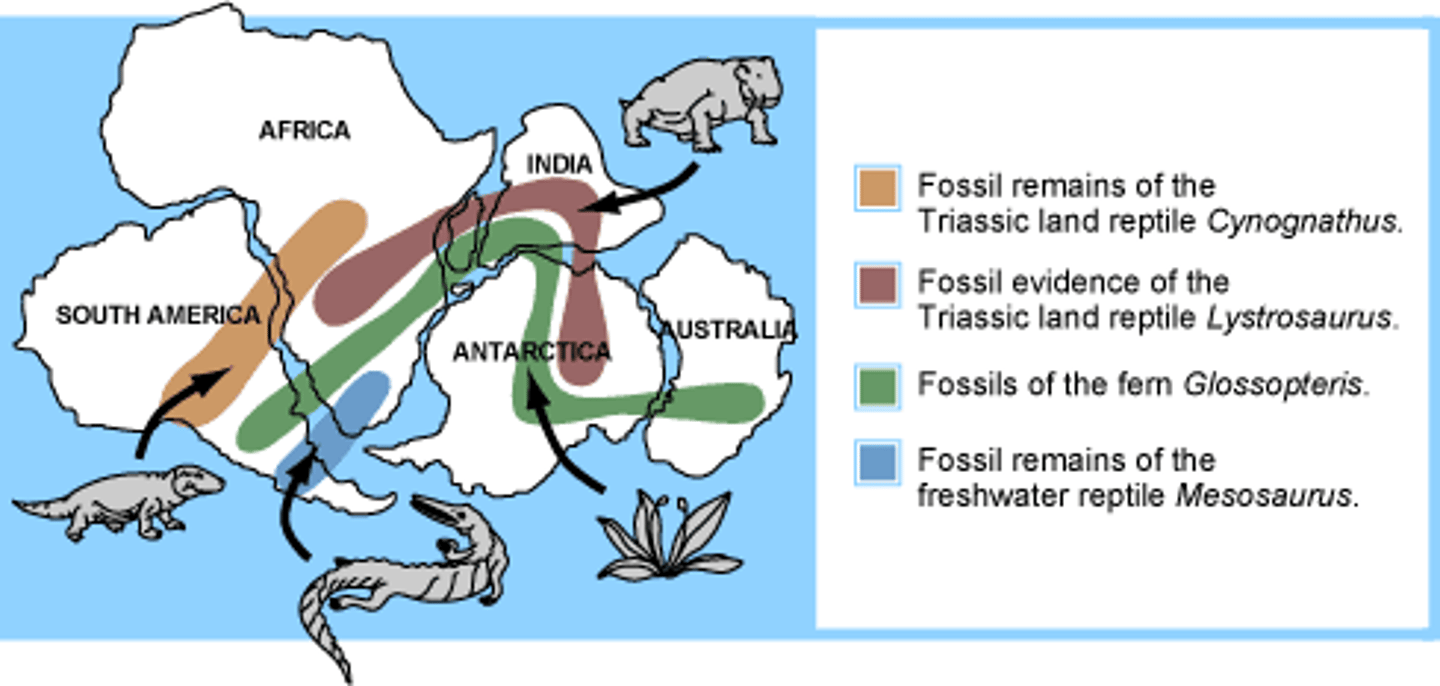
Biogeography
study of the distribution of organisms around the world
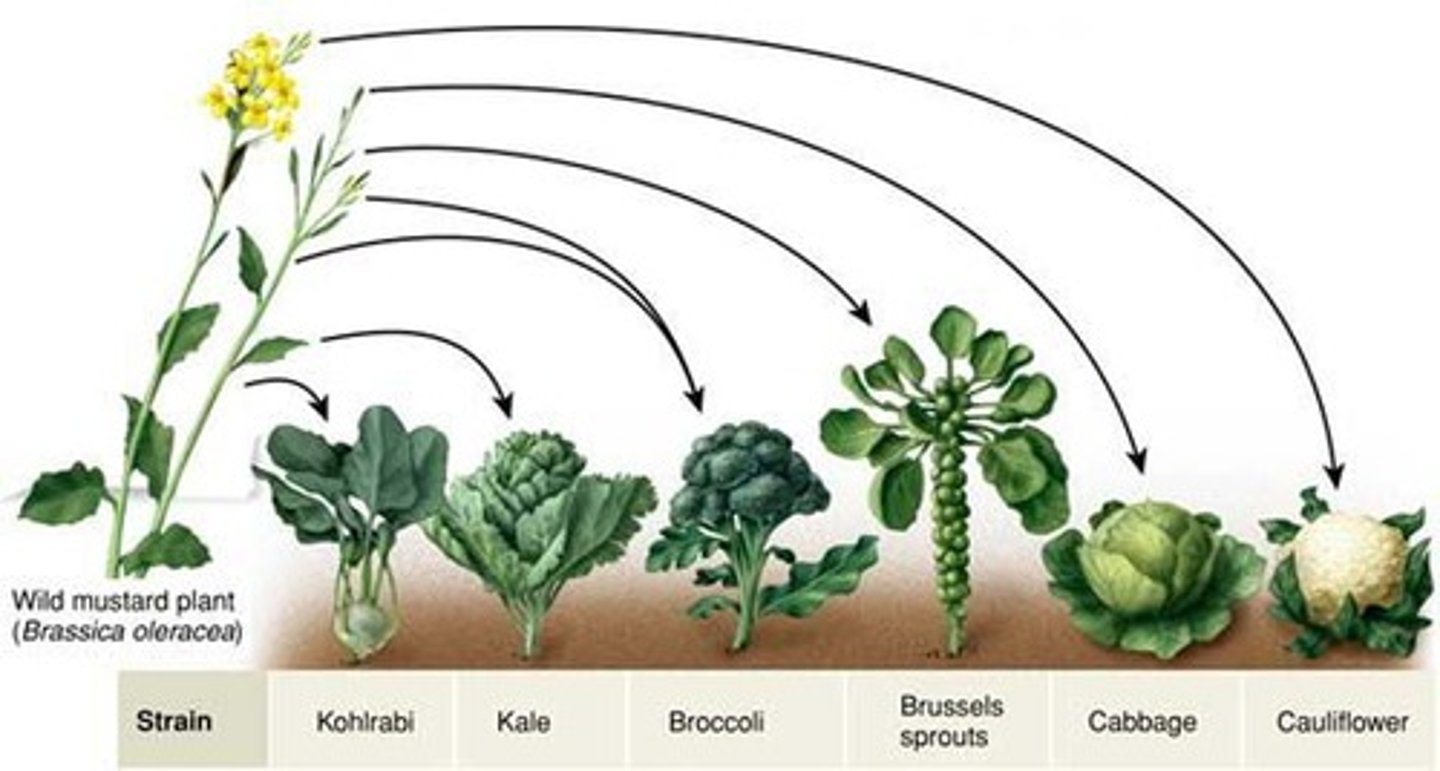
artificial selection
Breeding organisms with specific traits in order to produce offspring with identical traits.
Fitness
Ability of an organism to survive and reproduce in its environment
genetic variation
Differences among individuals in the composition of their genes or other DNA segments. Needed for evolution to occur.
Where does variation come from?
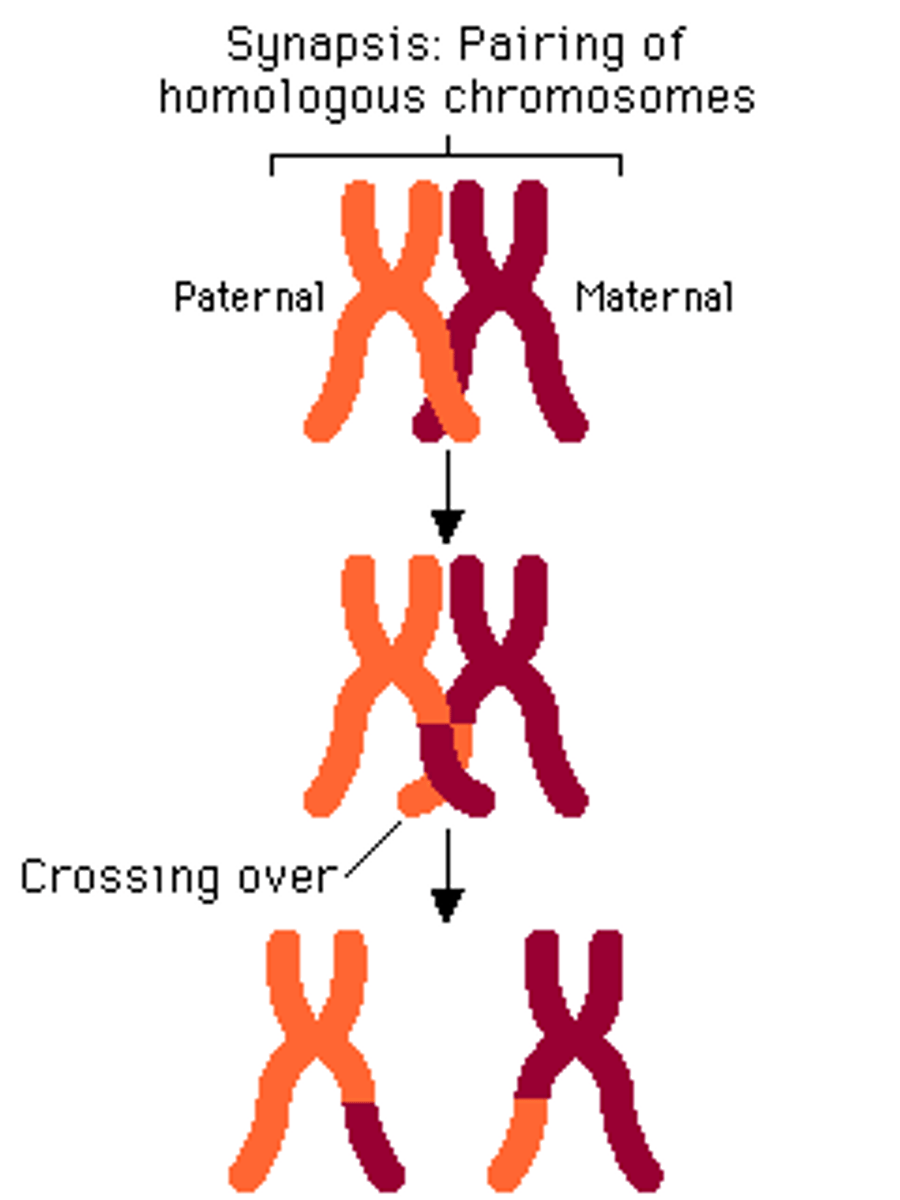
mutations and sexual reproduction (crossing over, recombination of alleles in fertilization)
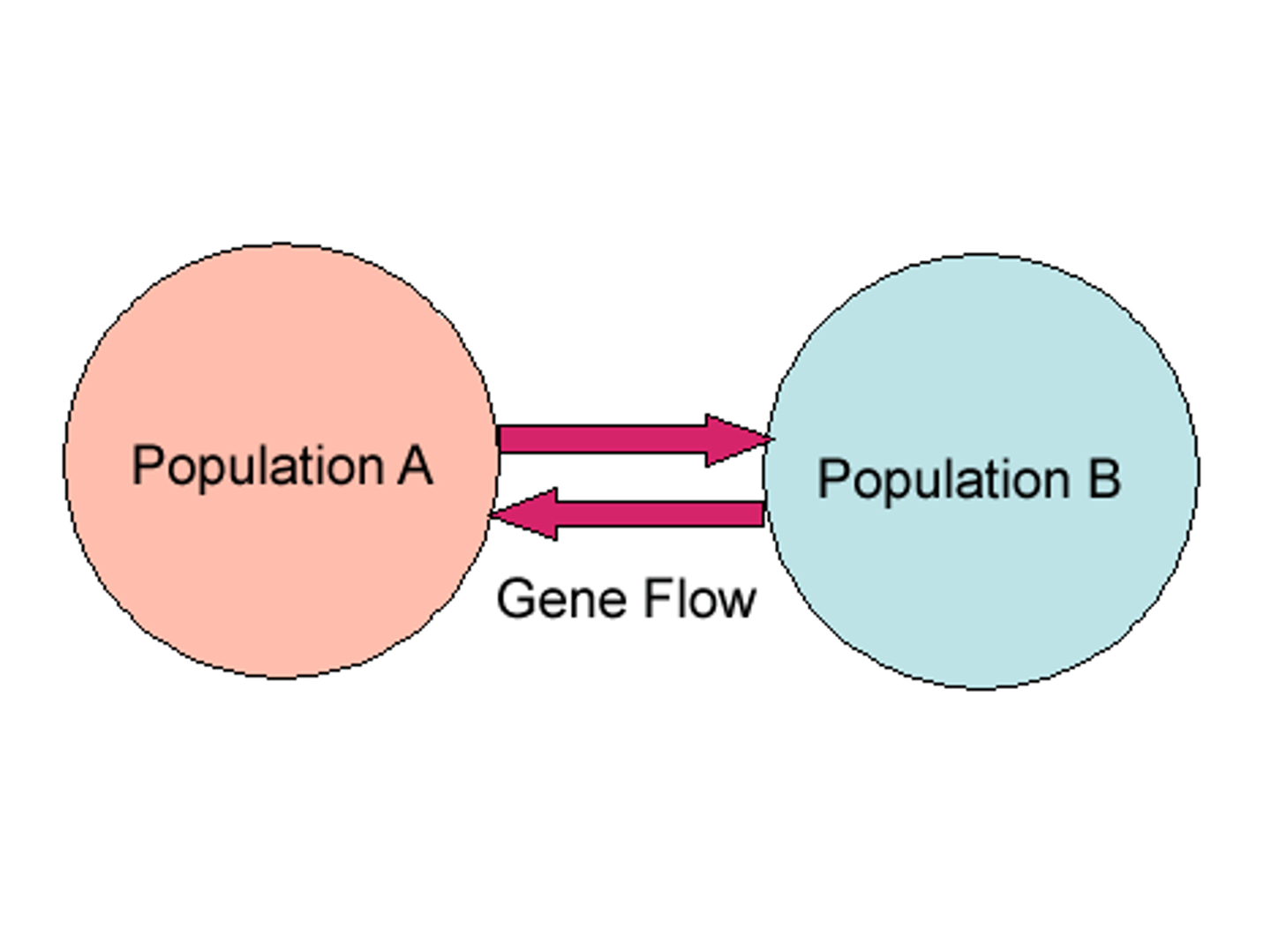
gene flow (migration)
Movement of genes in or out of a population due to interbreeding after migration.
sexual selection
when individuals select mates based on heritable traits (non-random mating)
genetic drift
A change in the allele frequency of a population as a result of chance events rather than natural selection.

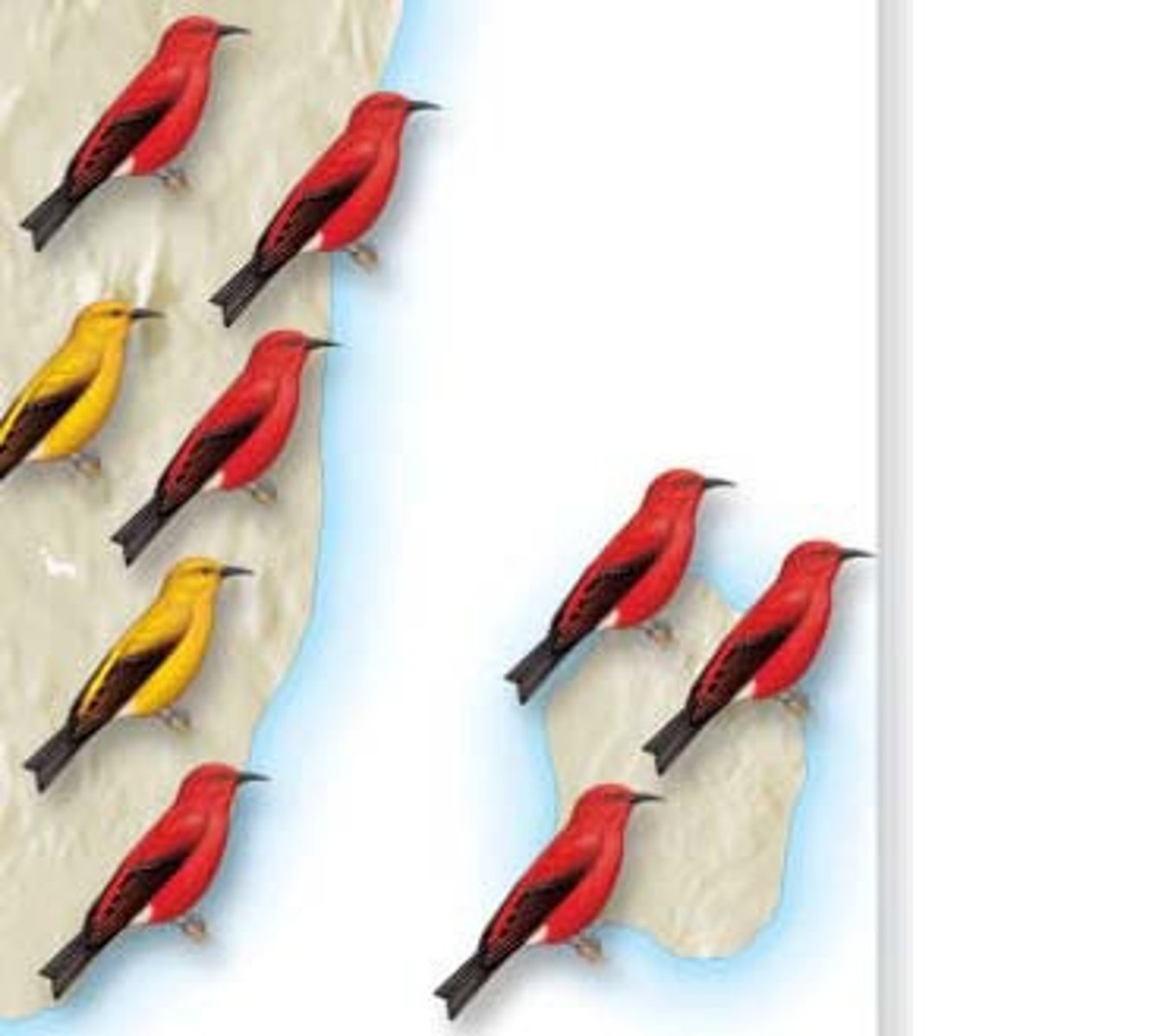
founder effect
Genetic drift that occurs when a few individuals become isolated from a larger population and form a new population whose gene pool composition is not reflective of that of the original population.

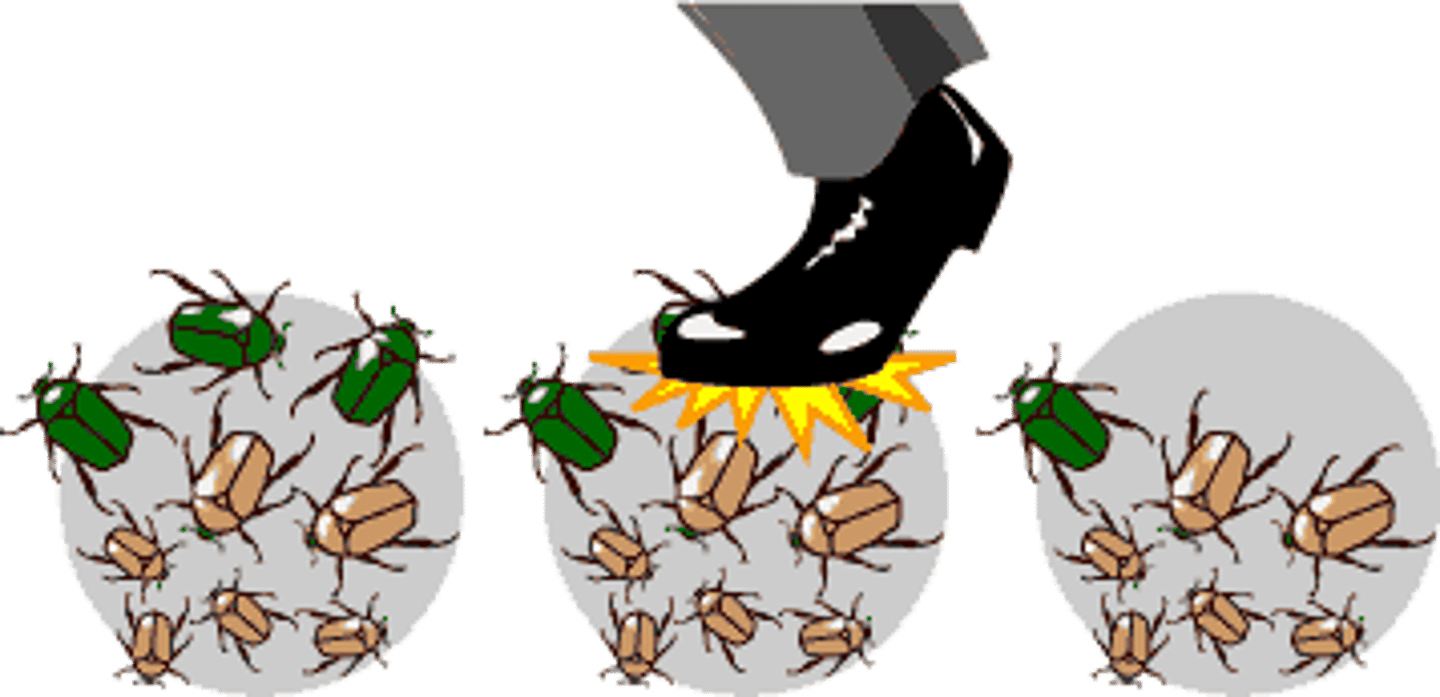
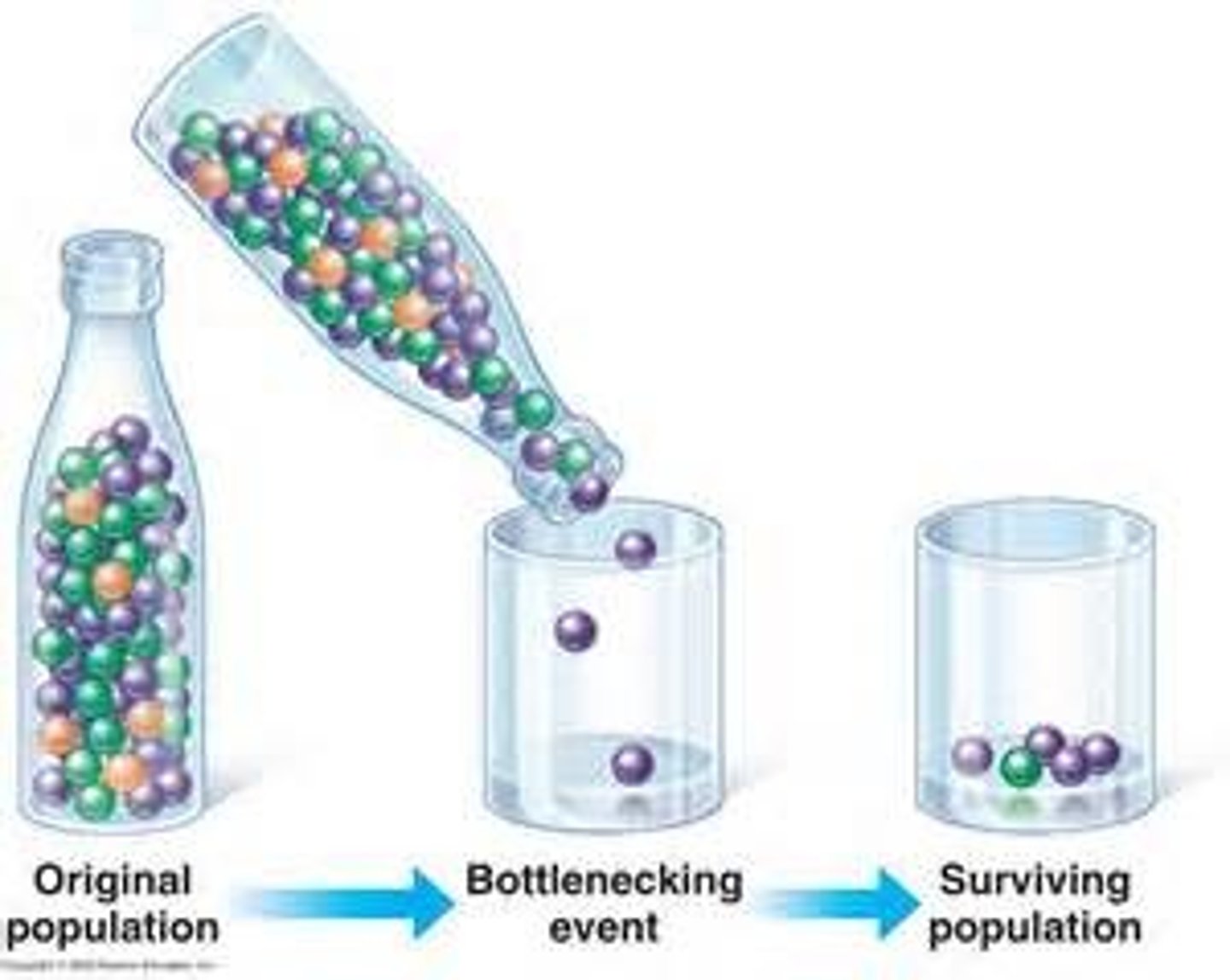
bottleneck effect
A change in allele frequency following a dramatic reduction in the size of a population
Microevolution
Evolutionary change below the species level; change in the allele frequencies in a population over generations.
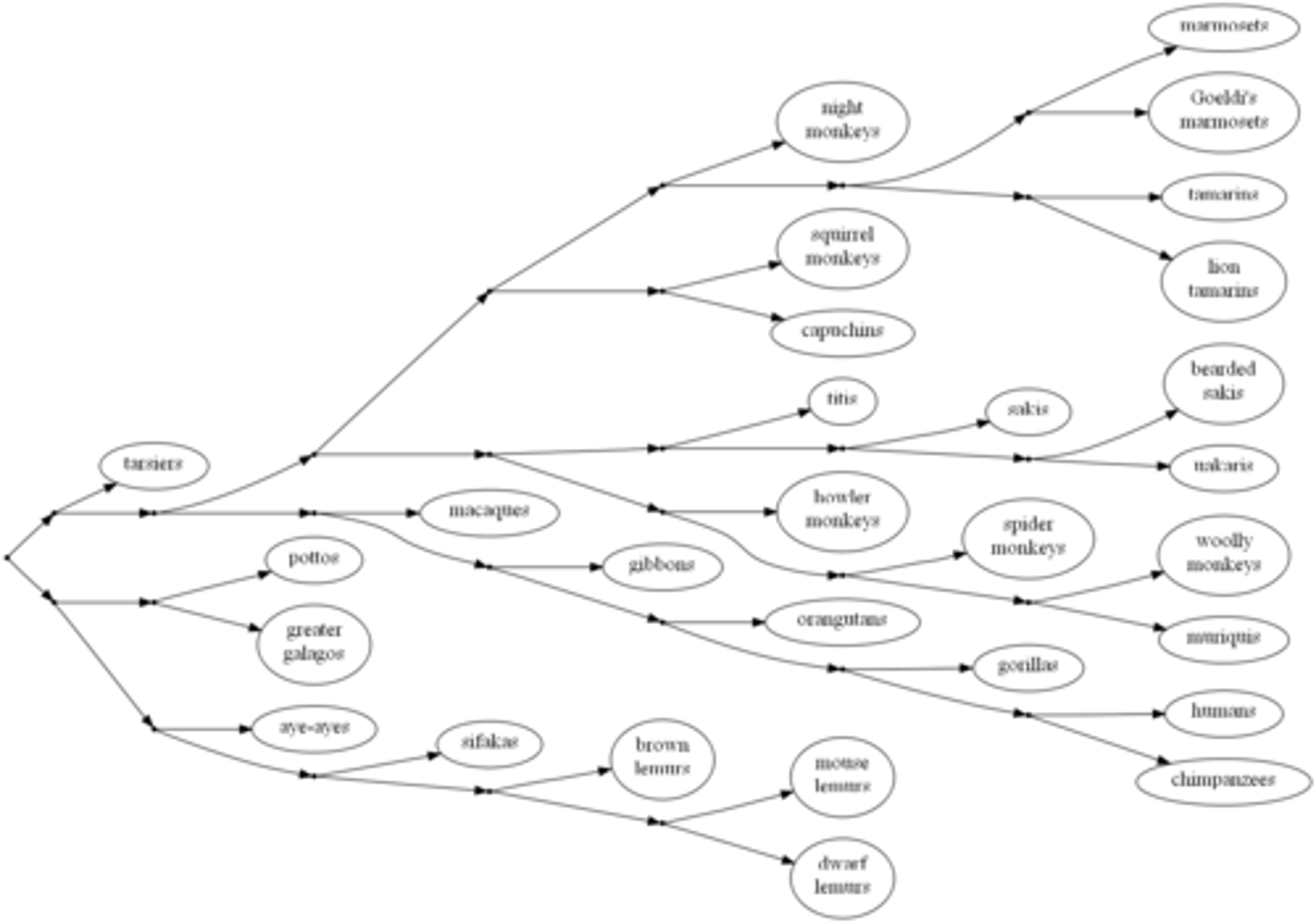
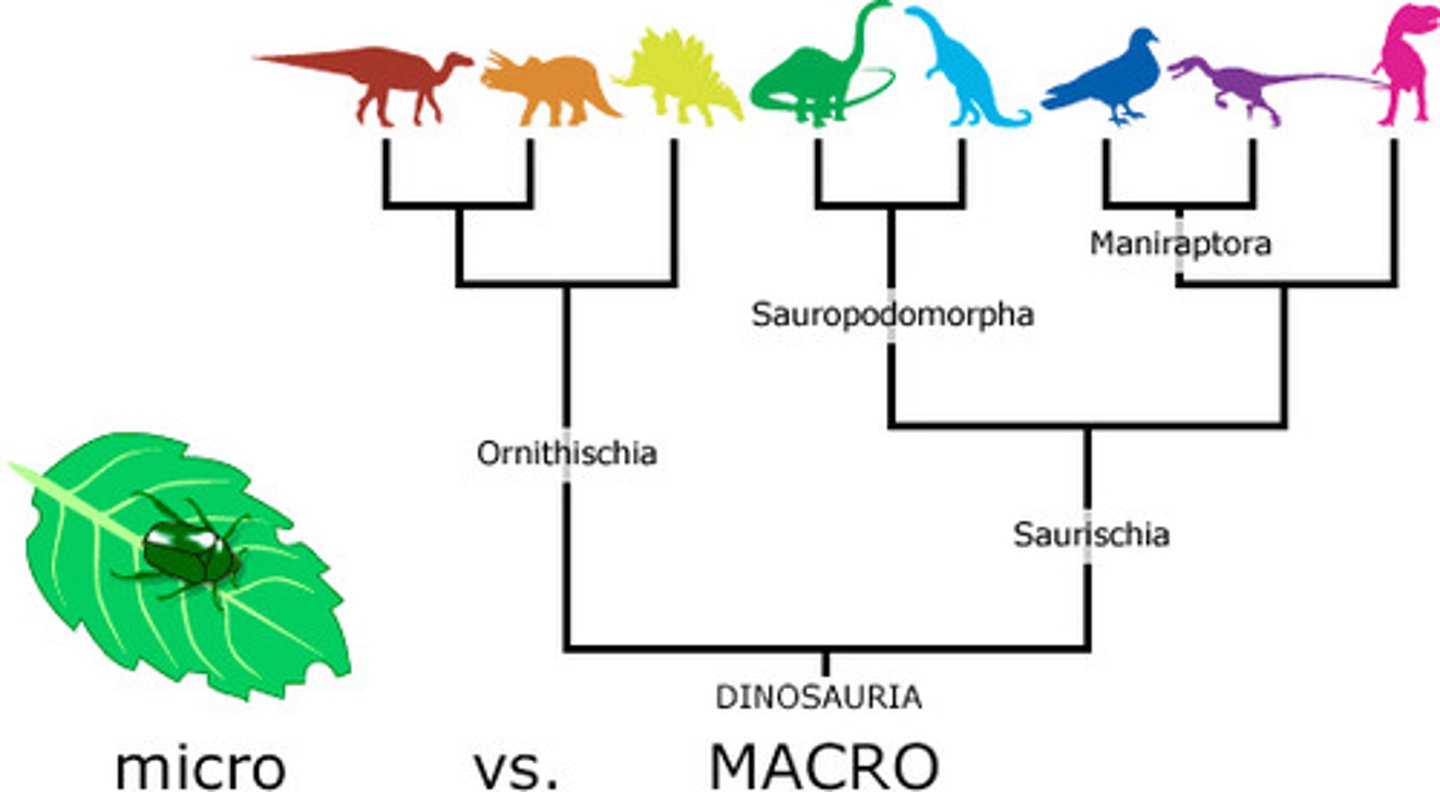
Phylogeny
Evolutionary history of a species or group of species.
outgroup
the organism in a cladogram that has the least in common with the other organisms
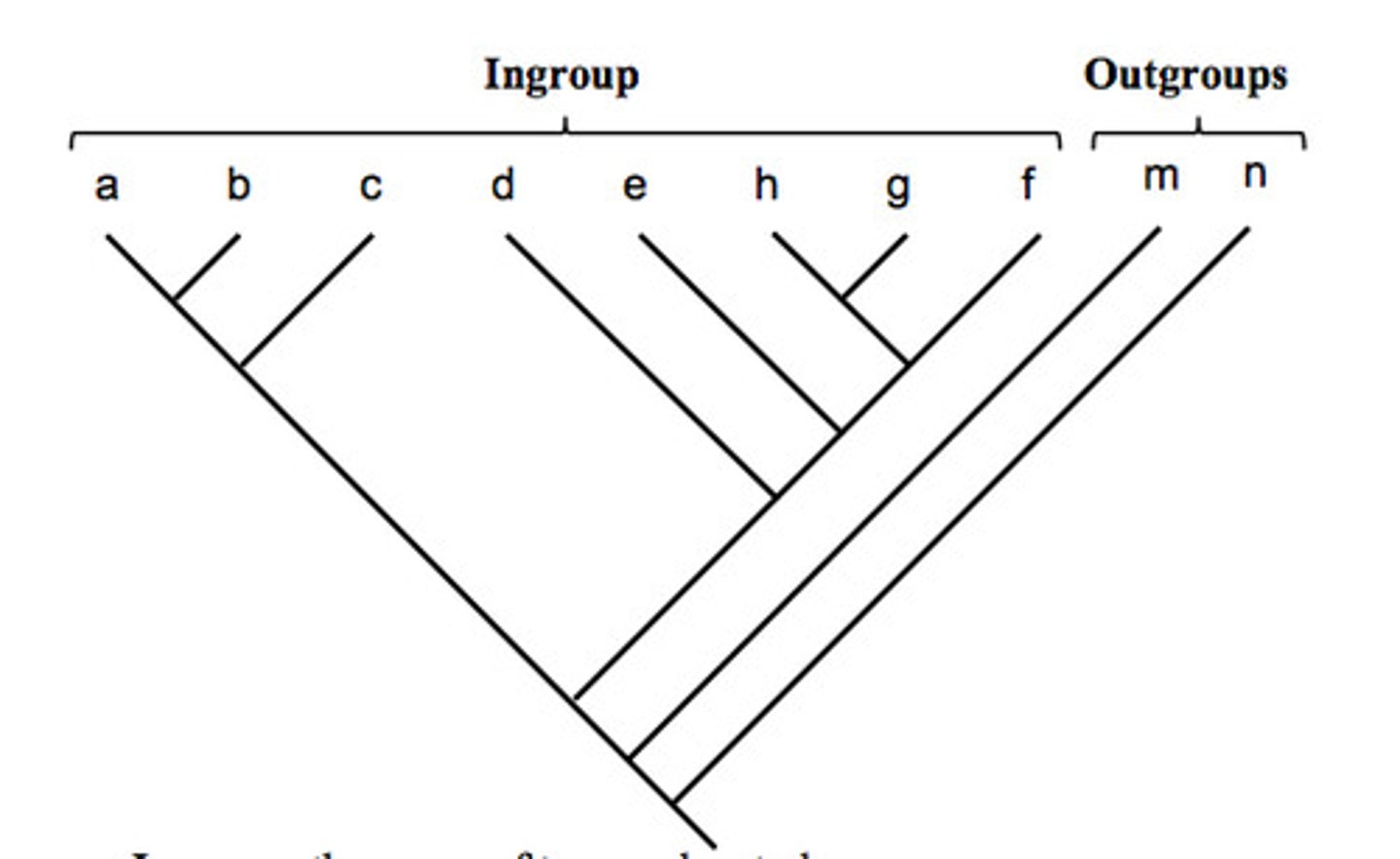
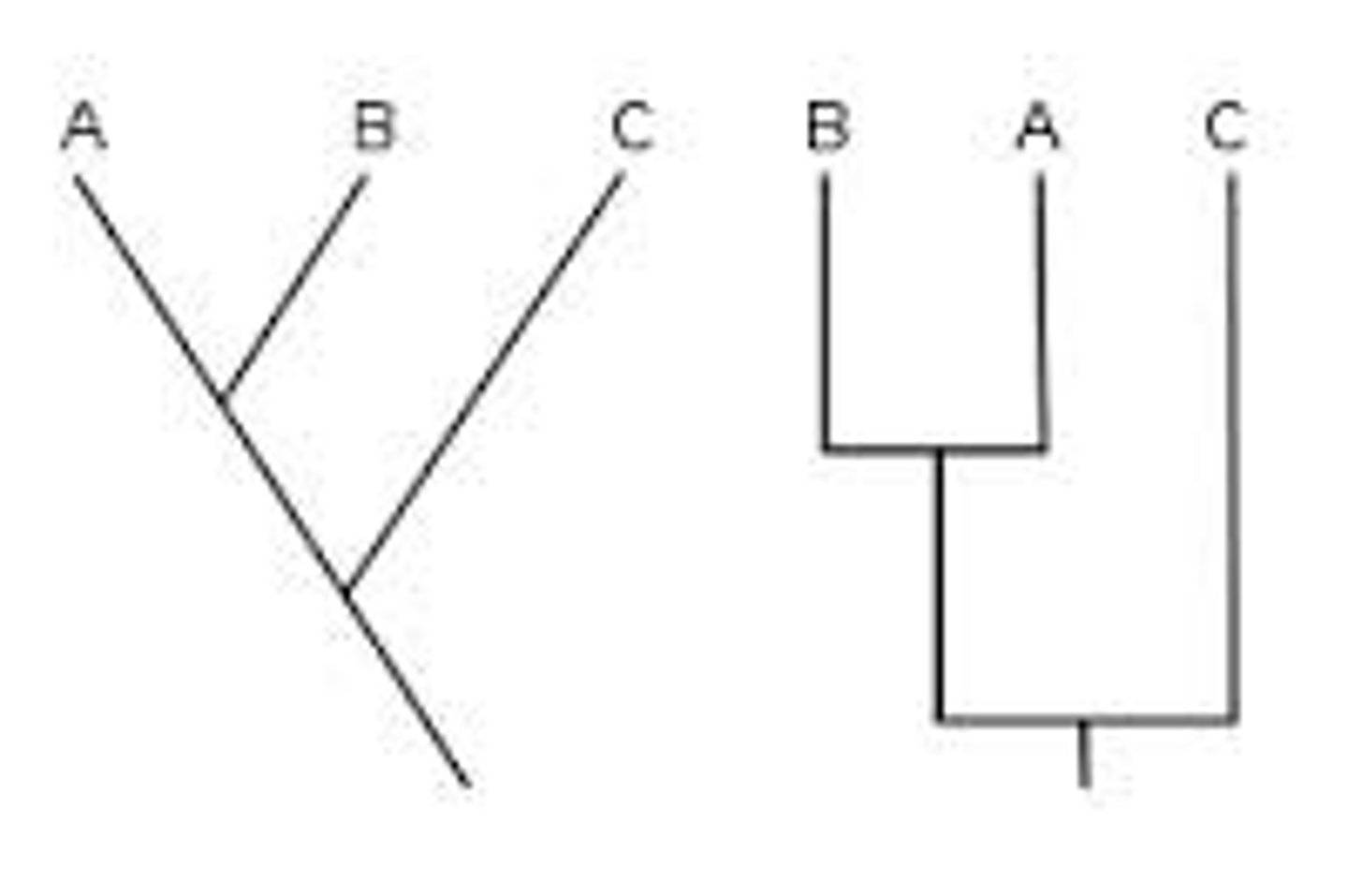
Cladogram
Diagram that shows the evolutionary relationships among a group of organisms
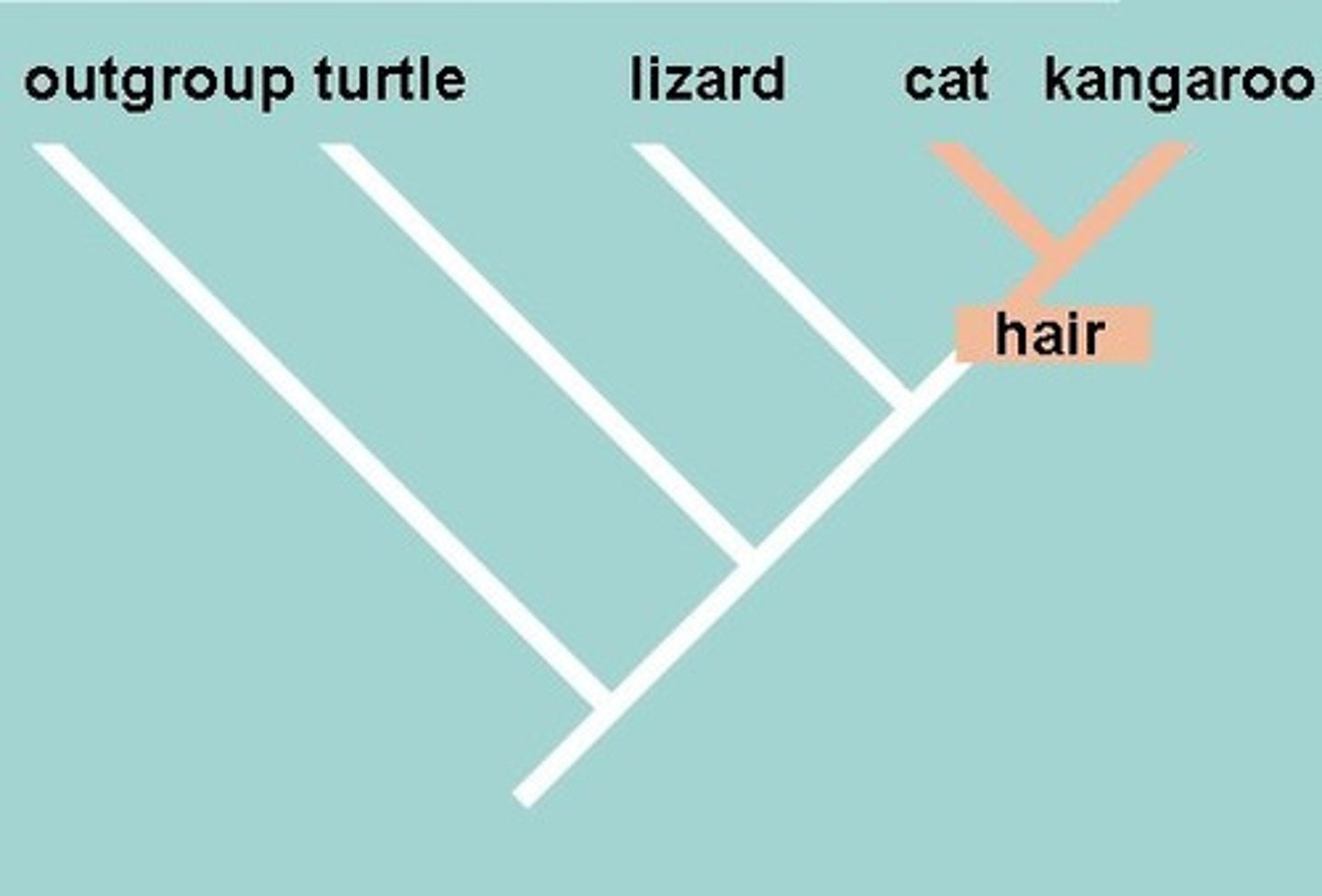
shared derived characteristic
A characteristic or trait, such as fur, that the common ancestor of a group had and passed on to its descendants.
Macroevolution
Evolutionary change that results in the formation of a new species.
biological species concept
Species is a group of populations whose members have the potential to produce fertile offspring.
reproductive isolation
Separation of species or populations so that they cannot interbreed and produce fertile offspring
prezygotic barriers
Barriers that impede mating or hinder fertilization.
habitat isolation
When two species encounter each other only rarely.
behavioral isolation
Form of reproductive isolation in which two populations have differences in courtship rituals or other types of behavior that prevent them from interbreeding
example: blue footed boobies

temporal isolation
form of reproductive isolation in which two populations reproduce at different times
example: skunks

mechanical isolation
mating is attempted, but morphological differences prevent its successful completion
example: damsel fly
gametic isolation
Sperm of one species may not be able to fertilize eggs of another species
example: sea urchins
postzygotic barriers
prevent the hybrid zygote from developing into a viable, fertile adult
reduced hybrid viability
When the genes of different species interact and impair hybrid development.
example: sheep and goats
reduced hybrid fertility
Even if hybrids are viable, they may be sterile
example: mules
hybrid breakdown
Hybrid is fertile, but when they breed the next generation is sterile.
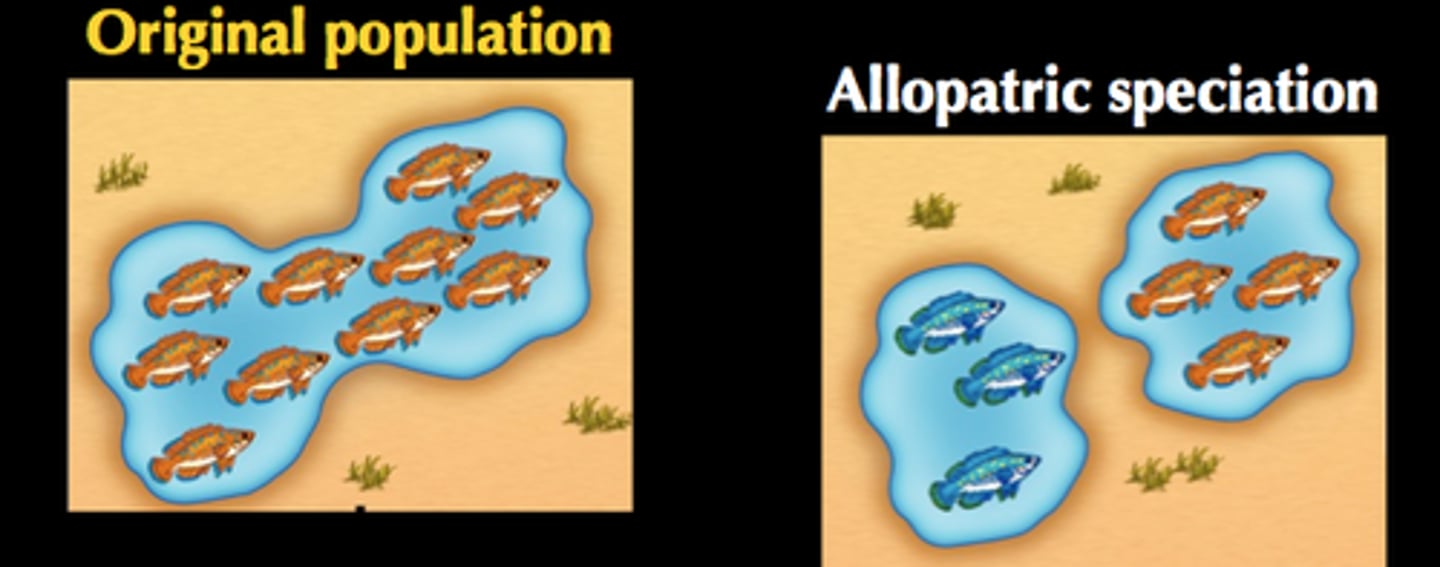
allopatric speciation
The formation of new species in populations that are geographically isolated from one another.
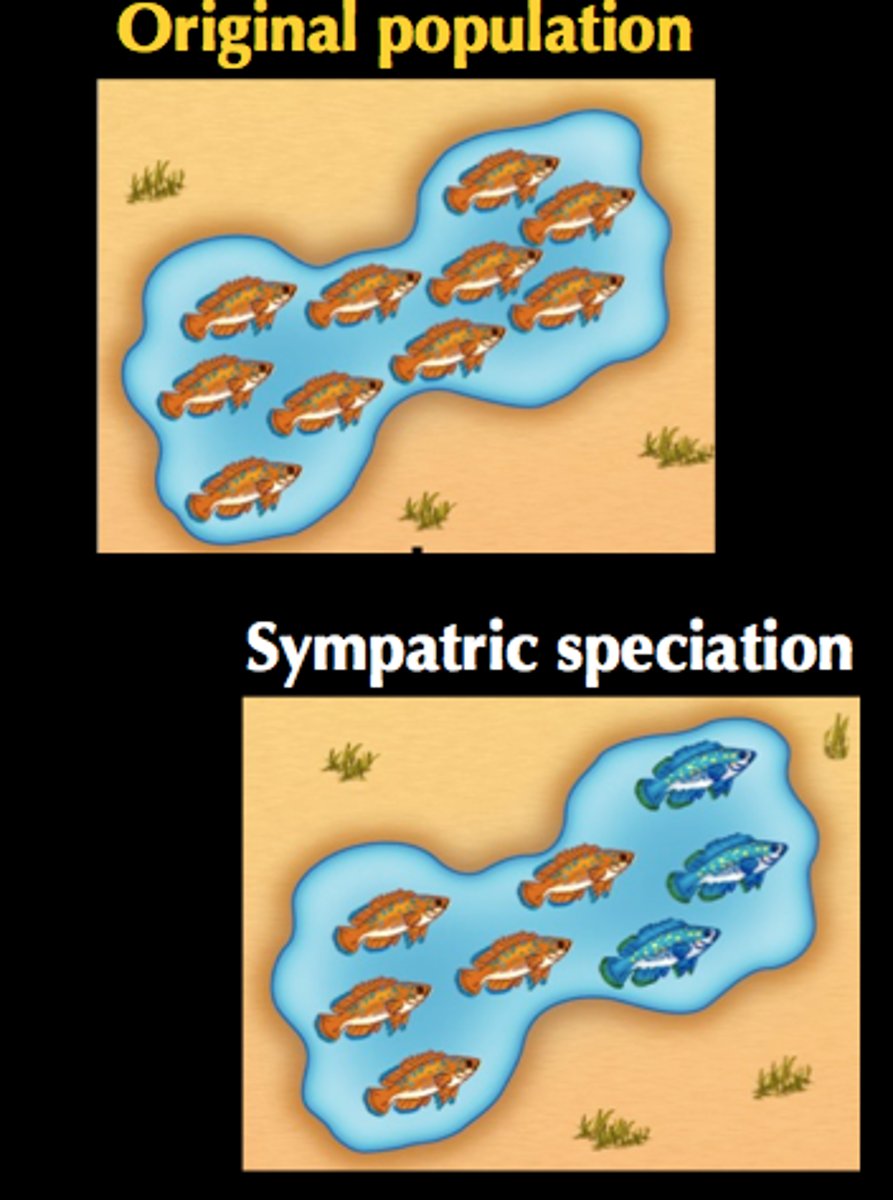
sympatric speciation
The formation of new species in populations that live in the same geographic area
adaptive radiation
An evolutionary pattern in which many species evolve from a single ancestral species as individuals fill new niches
Gradualism
The theory that evolution occurs slowly but steadily
punctuated equilibrium
Pattern of evolution in which long stable periods are interrupted by brief periods of more rapid change
disruptive selection
extreme values for a trait are favored over intermediate values
stabilizing selection
form of natural selection by which the center of the curve remains in its current position; occurs when individuals near the center of a distribution curve have higher fitness than individuals at either end, example: birthweight
directional selection
occurs when natural selection favors one of the extreme variations of a trait
sexual dimorphism
Differences in physical characteristics between males and females of the same species.
geographic isolation
isolation between populations due to physical barriers
example: squirrels on opposite sides of grand canyon
fossil record
Chronological collection of life's remains in sedimentary rock layers
RNA world hypothesis
hypothesis that RNA served as the genetic information of early life
endosymbiotic theory
theory that eukaryotic cells formed from a symbiosis among several different prokaryotic organisms
evidence of endosymbiosis
1) Inner membrane of chloroplast/mitochondria has enzymes and transport systems similar to bacterial ones
2) They reproduce by splitting into 2 (binary fission)
3) Contain circular DNA like bacteria
4) Have own ribosomes that are more similar to bacterial ribosomes
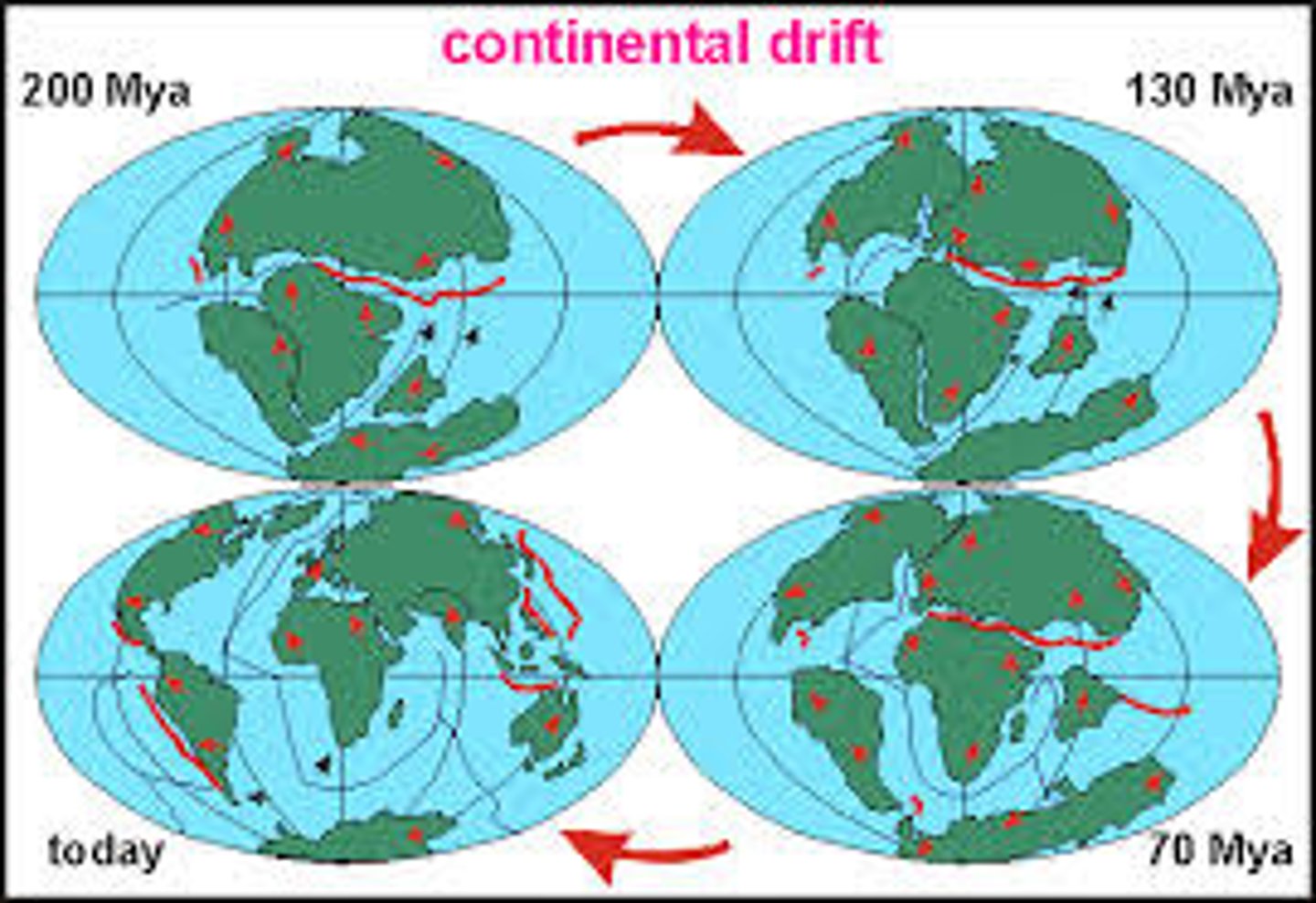
continental drift
The hypothesis that states that the continents once formed a single landmass, broke up, and drifted to their present locations. Explains geographic distribution of species
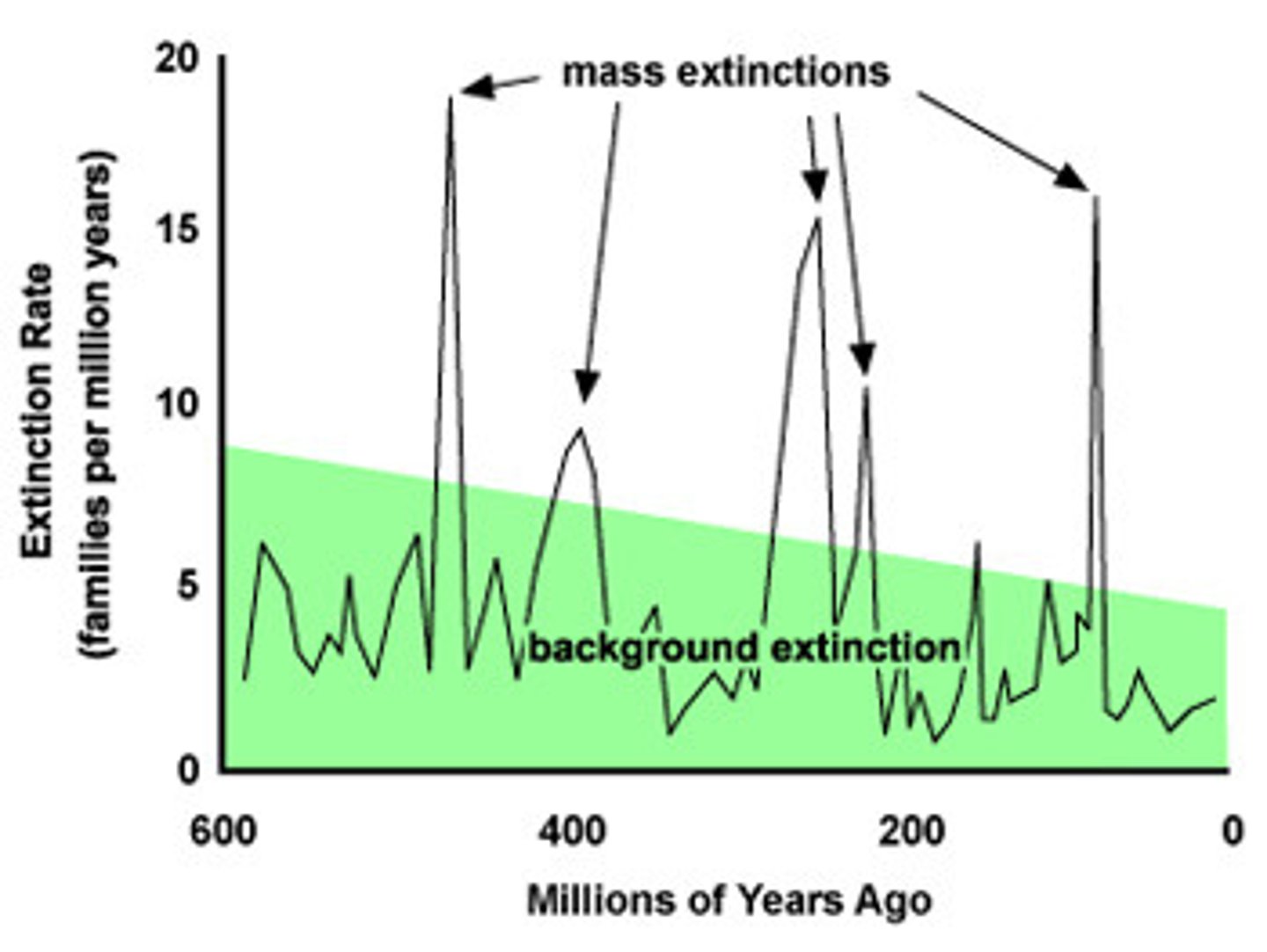
mass extinctions
The extinction of a large number of species within a relatively short period of geological time, thought to be due to factors such as a catastrophic global event or widespread environmental change that occurs too rapidly for most species to adapt.
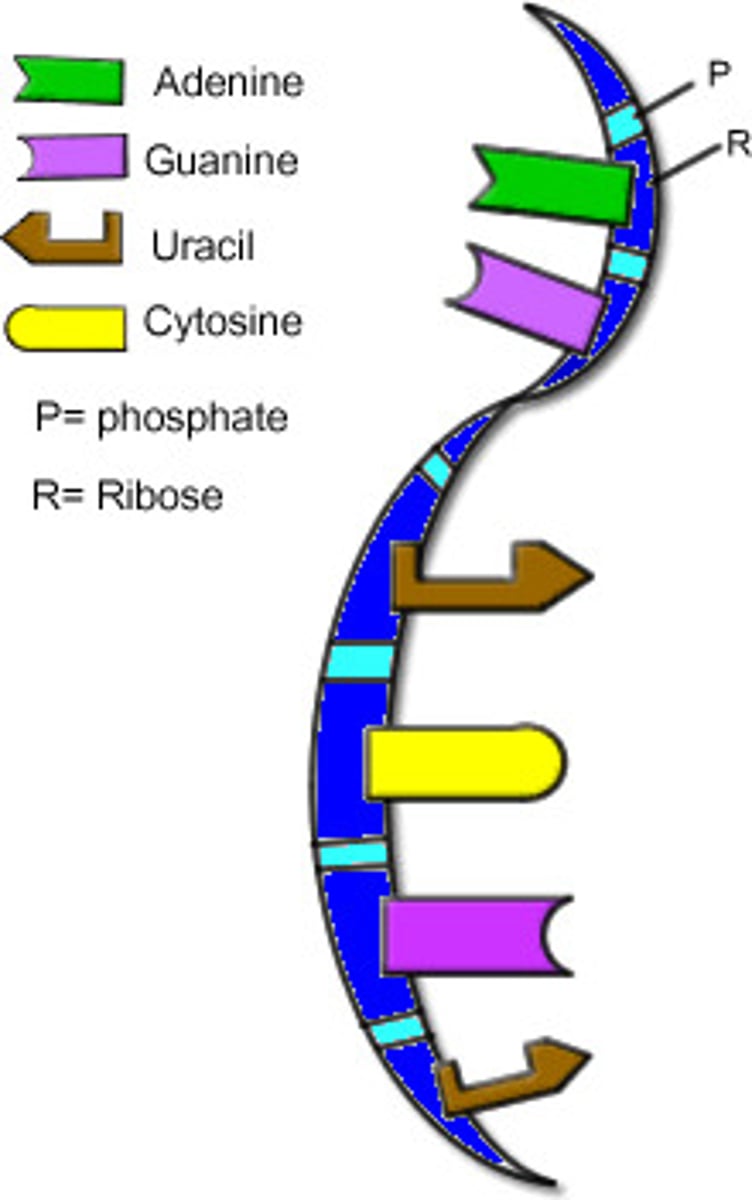
Origin of cells
spontaneous assembly of small organic molecules into macromolecules
rna
multifuncional
codes information
enzyme functions
regulatory molecule
transport molecule
structural adaptation
a physical feature of an organism's body having a specific function that contributes to the survival of the organism
behavioral adaptation
an inherited behavior that helps an organism survive
divergent evolution
when two or more species sharing a common ancestor become more different over time
co-evolution
Process by which two species evolve in response to changes in each other