10. Social Thinking (10%)
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
Golden Ratio
Social Behavior
Humans are attracted to individuals with body proportions approximating 1.618:1.
Relates to innate human preferences for beauty, harmony, and balance, suggesting we find proportions matching it—found in nature and art (like faces, shells)—inherently pleasing, triggering subconscious comfort and familiarity
Self-Disclosure
Social Behavior
The sharing of one’s fears, thoughts, and goals with another person and being met with non-judgmental empathy
A component of attraction
Reciprocal Liking
Social Behavior
The phenomenon whereby people are usually attracted to people who like them back.
Mere Exposure Effect (aka Familiarity Effect)
Social Behavior
The tendency for people to prefer stimuli to which they have already been exposed to more frequently
amygdala
Social Behavior
The part of the brain responsible for telling us whether or not something is a threat
If activated, this increases aggression
Cognitive Neoassociation Model
Social Behavior
Model stating that we are most likely to respond aggressively to others when we are feeling negative emotions, such as being tired, sick, frustrated, or in pain
Attachment
Social Behavior
An emotional bond between a caregiver and a child that beings to develop during infancy
Secure Attachment
Social Behavior - Secure vs. Avoidant vs. Ambivalent vs. Disorganized Attachment
Attachment style seen when a child has a consistent caregiver and is able to go out an explore, knowing that they have a base to return to
The child will be upset at the departure of the caregiver and will be comforted by the return of the caregiver
Avoidant Attachment
Social Behavior - Secure vs. Avoidant vs. Ambivalent vs. Disorganized Attachment
Attachment style that results when a caregiver has little to no response to a distressed child
Given the choice, these children will show no preference between a stranger and the caregiver
They show little or no distress when the caregiver leaves and little or no relief when the caregiver returns
Ambivalent Attachment
Social Behavior - Secure vs. Avoidant vs. Ambivalent vs. Disorganized Attachment
Attachment style that occurs when a caregiver sometimes responds appropriately to a distressed child, but also sometimes responds neglectfully
The child will be very distressed on separation from the caregiver but has a mixed response when the caregiver returns
The child is always anxious about the reliability of the caregiver
Disorganized Attachment
Social Behavior - Secure vs. Avoidant vs. Ambivalent vs. Disorganized Attachment
Attachment style wherein children show no clear pattern of behavior in response to the caregiver's absence or presence
Often associated with erratic behavior and social withdrawal by the caregiver
May also be a red flag for abuse
Social Support
Social Behavior
The perception or reality that one is cared for by a social network
Can be divided into many different categories such as emotional, esteem, material, informational, and network
Hypothalamus
Social Behavior
The part of the brain that controls hunger and drives the biological part of foraging.
Mating System
Social Behavior
Describes the organization of a group's sexual behavior.
Mate Choice (aka Intersexual Selection)
Social Behavior
The selection of a mate based on attraction.
Mate Bias
Social Behavior
Describes how selective an individual is when choosing a mate
An evolutionary mechanism aimed at increasing the fitness of the species
May carry direct or indirect benefits
Direct Benefits
Social Behavior - Direct vs. Indirect Benefits
Benefits carried by mate bias that include providing material advantages, emotional support, or protection.
Indirect Benefits
Social Behavior - Direct vs. Indirect Benefits
Benefits provided by mate bias that include promoting better survival of offspring.
Phenotypic Benefits
Social Behavior - The 5 Mechanisms of Mate Choice
Observable traits that make a potential mate more attractive to the opposite sex
Usually these traits indicate increased production and survival of offspring
EX: choosing a male with a good nest
Sensory Bias
Social Behavior - The 5 Mechanisms of Mate Choice
The development of a trait to match a preexisting preference in the population.
EX: liking red berries leads to liking red males
Fisherian/Runaway Selection
Social Behavior - The 5 Mechanisms of Mate Choice
How a particular trait with no negative effect on survival becomes more and more exaggerated over time
In this model, a trait is deemed sexually desirable and thus is more likely to be passed on
A positive feedback loop where a preference for a trait (like long tails) and the trait itself become genetically linked
Females prefer it, males with it survive to mate, and the trait/preference rapidly escalates, even if it harms survival (e.g., peacock's tail).
Indicator Traits
Social Behavior - The 5 Mechanisms of Mate Choice
Females choose males with costly, elaborate traits (like bright feathers or large antlers) that signal underlying genetic quality, health, and vigor, ensuring good genes for offspring.
Notably, these traits may or may not be genetic in origin
Genetic Compatibility
Social Behavior - The 5 Mechanisms of Mate Choice
The creation of mate pairs that, when combined, have complementary genetics
Provides a mechanism for the reduced frequency of recessive genetic disorders in the population
Altruism
Social Behavior
A form of helping behavior in which the person's intent is to benefit someone else at some cost to themselves.
Empathy
Social Behavior
The ability to vicariously experience the emotions of another.
Empathy-Altruism Hypothesis
Social Behavior
Hypothesis stating that one individual helps another person when feeling empathy for the other person, regardless of the cost
Game Theory
Social Behavior
Theory attempting to explain decision-making behavior.
A game is defined by the players, information, and actions available to each player at the time of decision, and the payoffs associated with each outcome.
Evolutionary Stable Strategy (ESS)
Social Behavior
Strategy that when adopted by a given population in a specific environment, natural selection will prevent alternative strategies from arising.
The strategies are thus inherited traits passed along with the population, with the object of the game being becoming more fit than competitors.
Hawk-Dove Game
Social Behavior
A game that represents pure competition between individuals
Focuses on access to shared food resources, with 3 potential outcomes based on both the value of the reward and the cost of fighting
Hawk
Social Behavior - Hawk vs. Dove
Exhibits a fighter strategy, displaying aggression and fighting until he wins or is injured.
Dove
Social Behavior - Hawk vs. Dove
Exhibits a fight avoidance strategy, displaying aggression at first but retreating if the fight escalates.
Hawk-Hawk
Social Behavior - Hawk-Hawk vs. Hawk-Dove vs. Dove-Dove
Hawk-Dove Game outcome where one wins and one loses.
Hawk-Dove
Social Behavior - Hawk-Hawk vs. Hawk-Dove vs. Dove-Dove
Hawk-Dove Game outcome where the hawk will definitely win.
Dove-Dove
Social Behavior - Hawk-Hawk vs. Hawk-Dove vs. Dove-Dove
Hawk-Dove Game outcome where they will share the food resources.
Inclusive Fitness
Social Behavior
A measure of an organism's success in the population
Based on the number of offspring, success in supporting offspring, and the ability of the offspring to then support others
Social Perception (aka Social Cognition)
Social Perception & Behavior
How we form impressions about the characteristics of individuals and groups of people
Provides the tools to make judgments and impressions regarding other people
Perceiver, Target, Situation
Social Perception & Behavior
3 components of social perception.
Perceiver
Social Perception & Behavior - Perceiver vs. Target vs. Situation
The component of social perception that is influenced by experience, motives, and emotional state.
Target
Social Perception & Behavior - Perceiver vs. Target vs. Situation
The component of social perception that refers to the person about which the perception is made.
Situation
Social Perception & Behavior - Perceiver vs. Target vs. Situation
The component of social perception associated with how the social context can determine what information is available to the perceiver.
Primacy Effect
Social Perception & Behavior - Primacy vs. Recency Effect
The idea that our first impression is the most important impression.
Recency Effect
Social Perception & Behavior - Primacy vs. Recency Effect
The idea that our most recent experience with an individual is the most important impression.
Reliance on Central Traits
Social Perception & Behavior
The idea where individuals tend to organize the perception of others based on traits and personal characteristics of the target that are most relevant to the perceiver.
Implicit Personality Theory
Social Perception & Behavior
The category that we place others in during impression formation is reliant on this.
Theory stating that there are sets of assumptions people make about how different types of people, their traits, and their behavior are related.
Halo Effect
Social Perception & Behavior
A cognitive bias in which judgments about a specific aspect of an individual can be affected by one's overall impression of the individual
It is the tendency to allow a general impression about a person to influence other, more specific evaluations about a person
Explains why people are often inaccurate when evaluating people that they either believe to be generally good or those that they believe to be generally bad
Can be produced by an individual’s attractiveness
Just-World Hypothesis
Social Perception & Behavior
Cognitive bias during impression formation.
Hypothesis stating that in a so-called just world, good things happen to good people, and bad things happen to bad people
Noble actions are rewarded and evil actions are punished
A strong belief in this increases the likelihood of victim-blaming
Self-Serving Bias
Social Perception & Behavior
Describes how individuals will view their own success based on internal factors while viewing their failures based on external factors.
Influenced by cognitive processes (locus of control) and motivational processes (self-enhancement).
Locus of Control
Social Perception & Behavior
The cognitive process that influences self-serving bias.
It is a person's tendency to perceive the control of rewards as internal to the self or external in the environment.
Self-Enhancement
Social Perception & Behavior
The motivational process that influences self-serving bias.
It focuses on the need to maintain self-worth and can be done through internal attribution of successes and external attribution of failures.
Self-Verification
Social Perception & Behavior
Suggests that people will seek the companionship of others who see them as they see themselves, thereby validating a person’s self-serving bias
Attribution Theory
Social Perception & Behavior
Theory that describes how individuals infer the causes of other people's behavior
Founded by Fritz Heider
Dispositional Attributions
Social Perception & Behavior - Dispositional vs. Situational Attributions
½ causes of attribution according to Fritz Heider’s Attribution Theory
Internal attributions which relate to the person whose behavior is being considered.
EX: beliefs, attitudes, personality characteristics.
Situational Attributions
Social Perception & Behavior - Dispositional vs. Situational Attributions
½ causes of attribution according to Fritz Heider’s Attribution Theory
External attributions which relate to features of the surroundings.
EX: threats, norms, money, peer pressure
Consider the characteristics of the social context rather than the characteristics of the individual as the primary cause
Consistency Cues
Social Perception & Behavior - Consistency vs. Consensus vs. Distinctiveness Cues
Cues that refer to the behavior of a person over time
The more regular the behavior, the more we associate that behavior with the motives of the person
Consensus Cues
Social Perception & Behavior - Consistency vs. Consensus vs. Distinctiveness Cues
Cues that relate to the extent to which a person’s behavior differs from others
If a person deviates from socially expected behavior, we are likely to form a dispositional attribution about the person’s behavior
Distinctiveness Cues
Social Perception & Behavior - Consistency vs. Consensus vs. Distinctiveness Cues
Cues that refer to the extent to which a person engages in similar behavior across a series of scenarios
If a person’s behavior varies in different scenarios, we are more likely to form a situational attribution to explain it
Correspondent Interference Theory
Social Perception & Behavior
Theory that takes the concepts of cues one step further by focusing on the intentionality of others' behavior.
States that when an individual unexpectedly does something that helps or hurts us, we tend to attribute it to their personality through dispositional attribution.
Thus, we may correlate these unexpected actions with the person’s personality.
Fundamental Attribution Error
Social Perception & Behavior
Posits that we are generally biased toward making dispositional attributions rather than situational attributions when judging the actions of others, especially in negative context
Assuming that a person’s behaviors accurately portray who they are as a person is easier than speculating about what circumstances may have caused the observed behavior
Attribute Substitution
Social Perception & Behavior
Occurs when individuals must make judgments that are complex, but instead, they substitute a simpler solution or apply a heuristic
This process is common when dealing with size and color in optical illusions
Cognitive
Stereotypes, Prejudice, & Discrimination - Affective vs. Behavioral vs. Cognitive
The component of attitude applied to stereotypes
Affective
Stereotypes, Prejudice, & Discrimination - Affective vs. Behavioral vs. Cognitive
The component of attitude applied to prejudice
Behavioral
Stereotypes, Prejudice, & Discrimination - Affective vs. Behavioral vs. Cognitive
The component of attitude applied to discrimination
Stereotypes
Stereotypes, Prejudice, & Discrimination
Occur when attitudes and impressions are based on limited and superficial information about a person or group.
These generalizations lead to the formation of prejudice.
Stereotype Content Model
Stereotypes, Prejudice, & Discrimination
Attempts to classify stereotypes with respect to hypothetical in-group using two dimensions: warmth and competence.
Warm groups are those that are not in direct competition with the in-group for resources.
Competent groups are those that have high status within society.
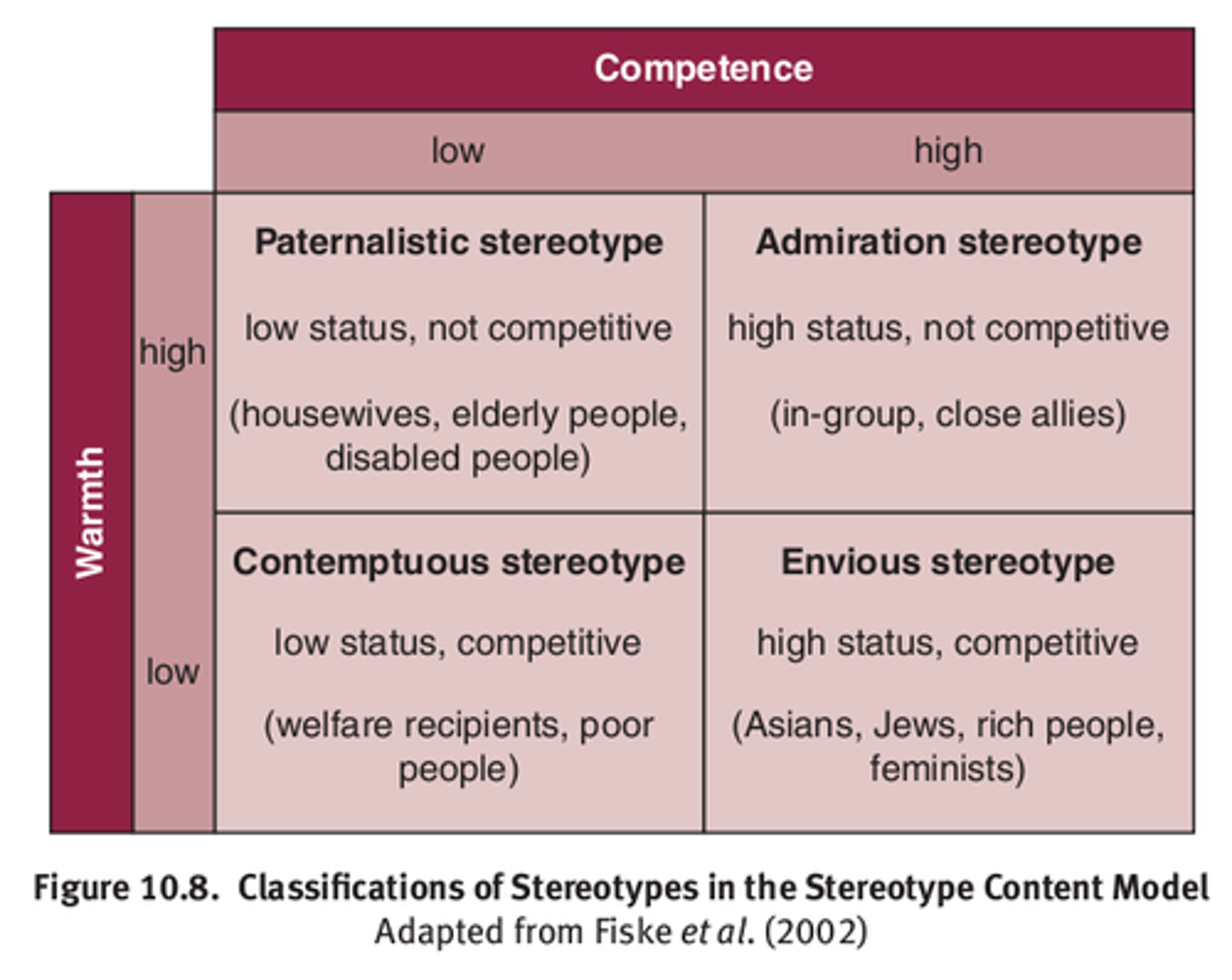
Paternalistic, Contemptuous, Envious, Admiration
Stereotypes, Prejudice, & Discrimination
The 4 classifications of stereotypes in the stereotype content model.
Paternalistic Stereotypes
Stereotypes, Prejudice, & Discrimination - Paternalistic vs. Contemptuous vs. Envious vs. Admiration Stereotypes
Stereotypes in which the group is looked down upon as inferior, dismissed, or ignored
Seen as low-status and not competitive
HIGH warmth, LOW competence
EX: housewives, elderly people, disabled people
Contemptuous Stereotypes
Stereotypes, Prejudice, & Discrimination - Paternalistic vs. Contemptuous vs. Envious vs. Admiration Stereotypes
Stereotypes in which the group is viewed with resentment, annoyance, or anger
Seen as low status and competitive
LOW warmth, LOW competence
EX: welfare recipients, poor people
Envious Stereotypes
Stereotypes, Prejudice, & Discrimination - Paternalistic vs. Contemptuous vs. Envious vs. Admiration Stereotypes
Stereotypes in which the group is viewed with jealousy, bitterness, or distrust
Seen as high status and competitive
LOW warmth, HIGH competence
EX: rich people, feminists
Admiration Stereotypes
Stereotypes, Prejudice, & Discrimination - Paternalistic vs. Contemptuous vs. Envious vs. Admiration Stereotypes
Stereotypes in which the group is viewed with pride and other positive feelings
Seen as high status and not competitive
HIGH warmth, HIGH competence
EX: in-group, close allies
Self-Fulfilling Prophecy
Stereotypes, Prejudice, & Discrimination
The idea that stereotypes lead to expectations of people, and those expectations can lead to confirmation of those expectations.
Stereotype Threat
Stereotypes, Prejudice, & Discrimination
The concept of people being concerned or anxious about confirming a negative stereotype about one's social group
This may hinder performance, which may actually create a self-fulfilling prophecy
Prejudice
Stereotypes, Prejudice, & Discrimination
An irrational positive or negative attitude toward a person, group, or thing, prior to an actual experience with that entity
Can be kept internally or shared with the larger community such as through propaganda
Power, Prestige, Class
Stereotypes, Prejudice, & Discrimination
3 social factors that influence prejudice
Ethnocentrism
Stereotypes, Prejudice, & Discrimination
The practice of making judgments about other cultures based on the values and beliefs of one's own culture, especially when it comes to language, customs, and religion
Cultural Relativism
Stereotypes, Prejudice, & Discrimination
The recognition that social groups and cultures should be studied on their own terms
Acknowledges that the values, mores, and rules make sense in the context of that culture and should not be judged against the norms of another culture
Discrimination
Stereotypes, Prejudice, & Discrimination
Occurs when prejudicial attitudes cause individuals of a particular group to be treated differently from others.
Individual Discrimination
Stereotypes, Prejudice, & Discrimination - Individual vs. Institutional Discrimination
One person discriminating against a particular person or group.
Institutional Discrimination
Stereotypes, Prejudice, & Discrimination - Individual vs. Institutional Discrimination
The discrimination against a particular person or group by an entire institution.