SciRev. X102 Exam 3 wk. 9 astronomy with expert curated questions and answers
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
what was an instrument for discovering marvels in the heavens (17th century)?
-the telescope
-new stars, satellites around jupiter and saturn, saturn's rings, features on the moon and sun
telescope in the 18th century
-largely became an instrument for postitional astronomy, to accurately measure the positions of stars and other celestial bodies, such as the moon
3 tests of Newton's universal gravity
-shape of the earth
-observed motion of the moon
-periodicity of comets
shape of the earth
-had to be determined whether it is flattened at the poles as predicted by newton (he was right)
-Maupertuis
Maupertuis
-polar expedition
-w/ Clairaut and Ander Celsius
-measured earth's meridian at different latitudes
-measured their arc in the winter month below the Arctic circle
-found that the earth was slightly flattened at the poles
-"the man who flattened the earth"
observed motion of the moon
-involved perturbations that seemed double what newton had predicted relying on universal gravity
-clairaut
Clairaut and the moon
-announced that newton's laws didn't account for the moon
-calculating the moon's motion required three bodies mutually attracting each other
-found the moon differed month to month from the predicted value by 2
-moon is attracted strongly by two bodies, the earth and the sun, pulling at different angles to one another
-clairaut announced that newton was right all along nd that all perturbations relied on the inverse-square law
periodicity of comets
-had never been proved and had to be established observationally
-looked at Halley's comet bc it came around every 75 years or so so more observations could be done on it
-Halley predicted the return of the comet
-newton predicted that comets moved along conic sections (Halley and clairaut proved him right)
James Bradley
-discovered two major phenomena: aberration of light and nutation of the earth's axis
-both were tiny effects requiring extremely accurate and long-term observations
aberration of light
-we tilt our telescopes forward by an angle related to the ratio btw the speeds of light and of the earth
-implicitly proves the earth's motion
-was discovered when he noticed that the "fixed" stars would reach as much as 20 arc seconds
Bradley's nutation
-is a wobble of the earth's axis w/ a period of 18.6 years due to the perturbation of the moon
-noticed there were fluctuations of about 7 arc seconds which was caused from the wobble
precession of the equinoxes
change in orientation of a rotational axis w/ respect to a reference plane
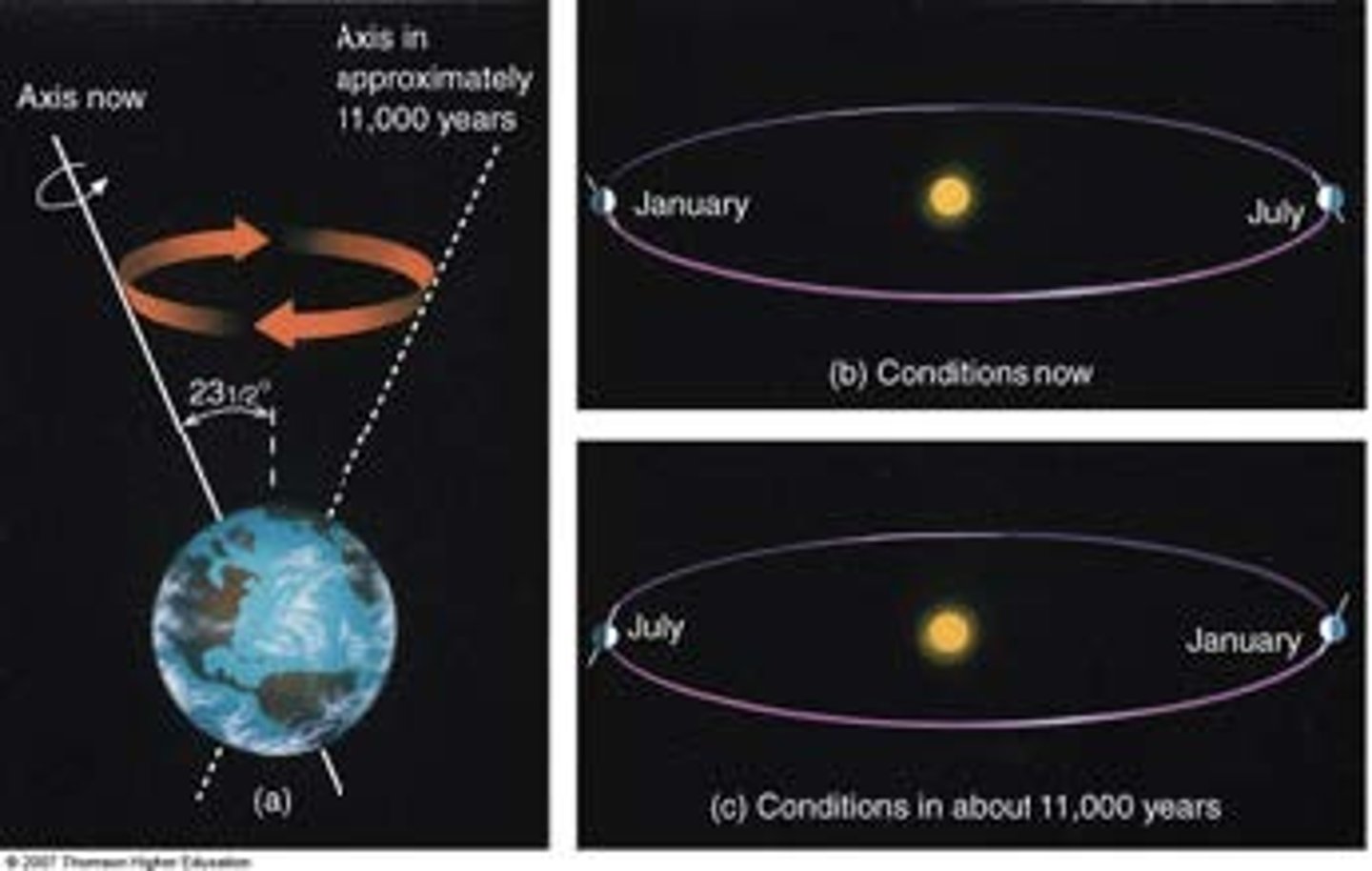
Tobais Meyer
-produced the best lunar map and lunar tables of the time (to w/in 1 degree)
-lunar motion was crucial for determining the longitude at sea, using the moon's motino as a clock against the background of the stars
-after he died, his wife received 3,000 from the british admiralty
John Harrison
-built many superior chronometers that won him 20,000
-helps find the longitude at sea through acurate time keeping
-one problem was that each watch had its 'own rate of going' in which it would steadily gain o lose small amount each week. (once this was fixed, longitude could be calculated)
Captain James Cook
-3 journeys to the pacific led to hugely improved maps from australia to new zealand to the bering straight and hawaii
Cook's first journey
-sent to find the elusive continent (australia)
-when they were repairing 'the endeavor' they sketched a kangaroo
-ran into eastern shore of austrlia and called it new south whales
-used the lunar method to determine longitude
-angular distance btw the moon and celestial objects
cook's second voyage
-he carried three chronometers (made by Arnold) and one made by Kendall
-also had the nautical almanac
-was to seek the southern continent
-got below 71 S
-circumnavigated Antarctica w/out seeing it (as ice was blocking it) ('resolution' ship)
nautical almanc
-Maskelyne
-method of finding longitude by accurately observing the distance btw the sun and the moon and then consulting tables
Cook's third voyage
-died in hawaii
-showed an extreme example of unfortunate cross-cultural contact
-carried a replica of harrison's chronometer to determine latitude
Frederick William Herschel
-and his sister Caroline
-relied on a giant reflecting telescope w/ a mirror
-discovered a new planet, uranus, moving beyond the orbit of saturn
-was the first scovery of a new planet since antiquity
-mapped the milky way and discovered a huge number of non-stellar objects tht he called nebulae