Digestive System
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
What is the purpose of the digestive system?
breakdown of food and absorption of nutrients
Absorption of nutrients
What are the Digestive processes
ingestion
peristalsis
Mechanical Breakdown
Digestion
Absorption
Defecation
Ingestion
Taking food into the mouth (eating)
Peristalsis
Movement of food through the alimentary canal (one way flow)
Mechanical Breakdown
Breaking down big pieces and making them smaller without altering their chemical form. Done by our teeth.
Digestion
Chemical breakdown of food via enzymes. Specific enzymes break down specific food.
Absorption
Transport of nutrients into blood stream
Defecation
Elimination of indigestible waste, this is anything we cannot absorb or something we took all the nutrients from.
Peritoneal Cavity
Potential space in the abdomen with fluid. between the visceral and parietal peritoneum.
Serous Membrane
Two layers, Parietal (first layer) which is the lining of the cavities and Visceral (inner layer) which covers the surface of organs (attaches to organs)
Retroperitoneal Structures
Organs and vessels located in the space behind the peritoneum abdomen. Includes: kidneys, aorta, Inferior vena cava, and blood vessels
Mesenteries
Serves to anchor alimentary canal to the body. Lesser omentum, Greater omentum, and Mesentary
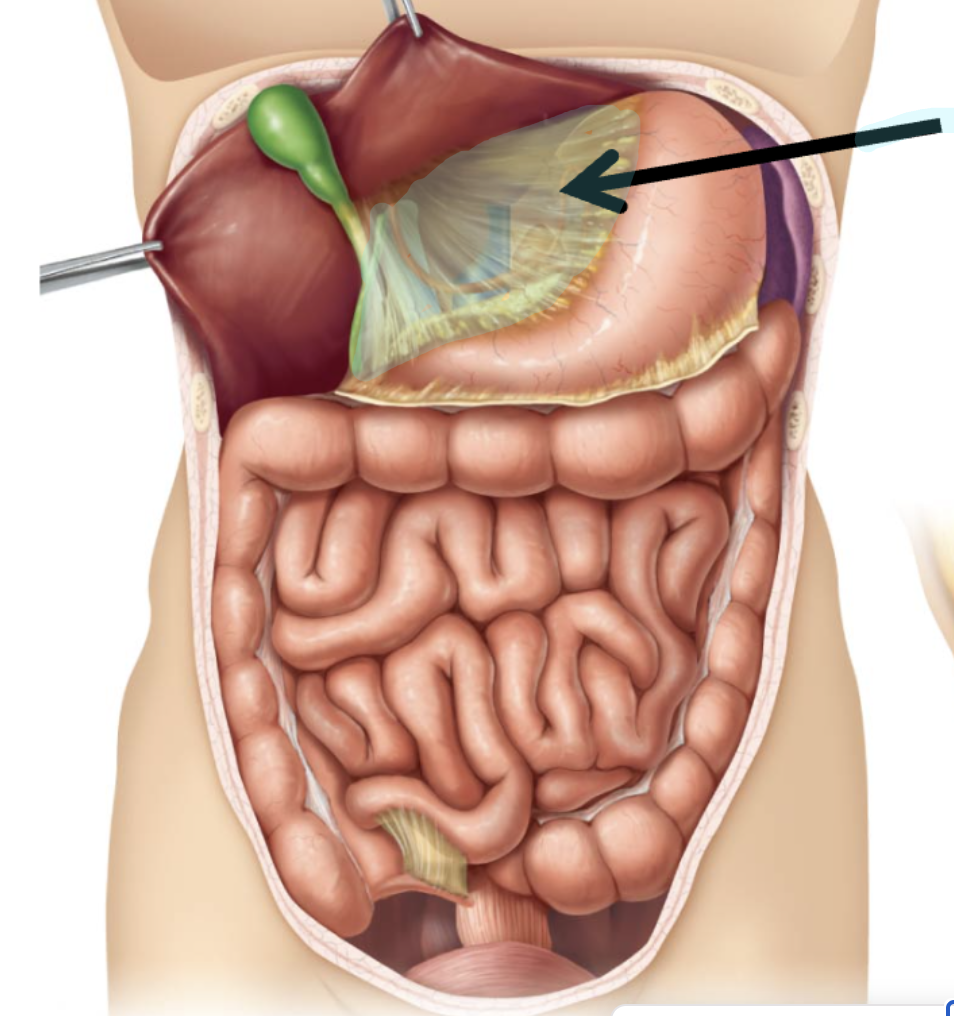
Lesser Omentum
Connect between liver and stomach
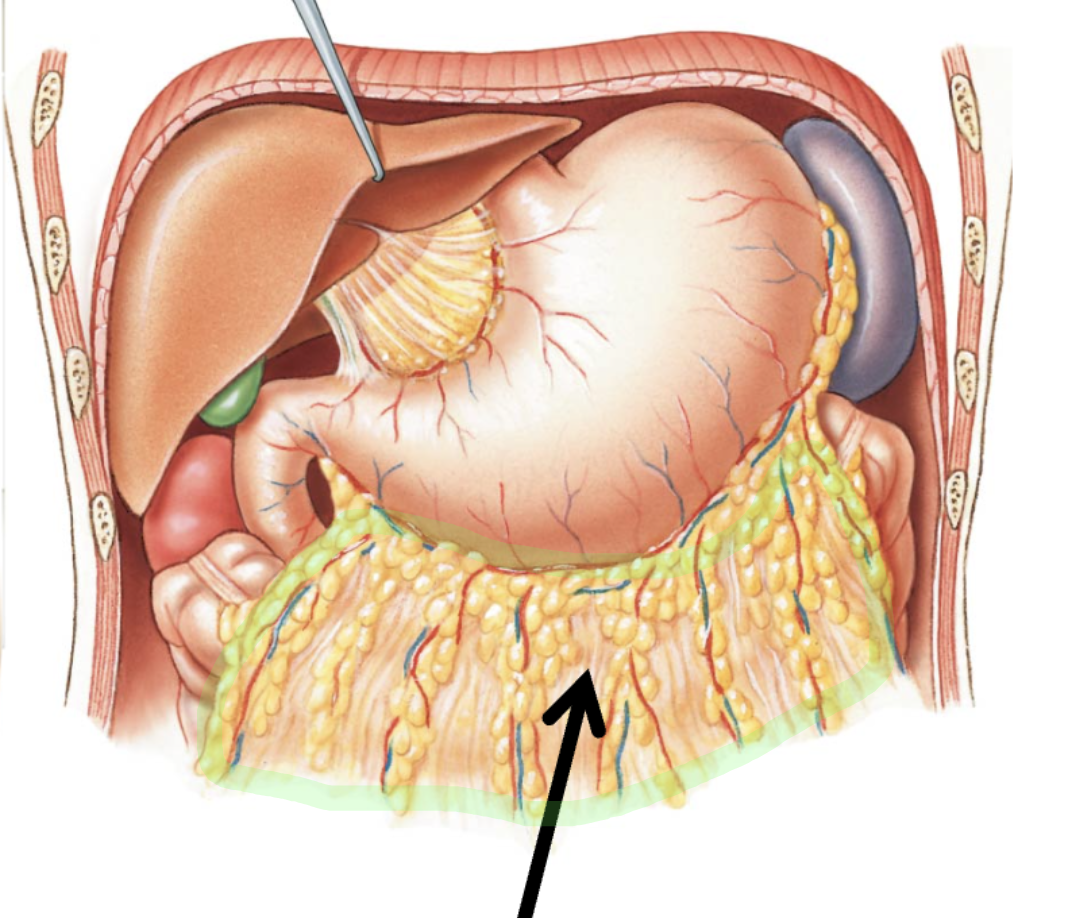
Greater Omentum
Connects stomach and colon, covers small intestines (hanfs like a flap that you can pull up)
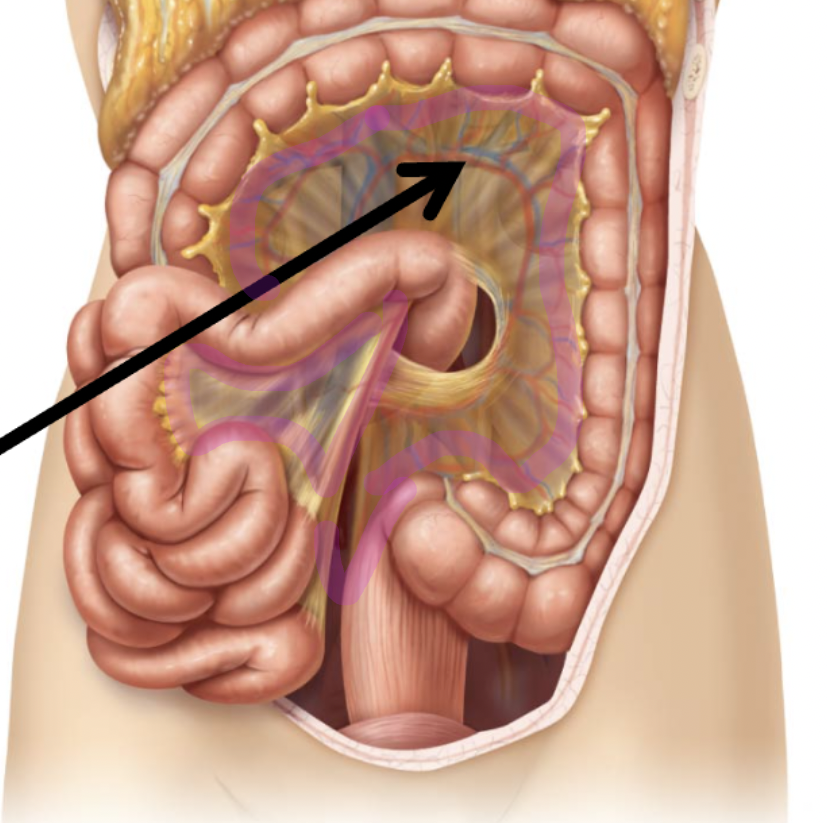
Mesentery
Connects intestines large and small to the posterior wall of our abdomen
Alimentary canal
Muscular tube connecting the mouth to the anus
Muscularis externa
Peristalsis and segmentation
Submucosa
Connective tissue, elastic and allows for organ to return to original shape.
Mucosa
Epithelium for absorption of nutrients (deepest layer)
Accessory digestive organs
Secondary organs, not part of alimentary canal, sit outside however they provide breakdown of food (chemical and mechanical).
Oral cavity
Where mechanical breakdown mostly occurs
Palate
Hard palate and Soft palate ( uvula, soft tissue)
Dentation
Mastication via teeth, teeth occlude to break down food
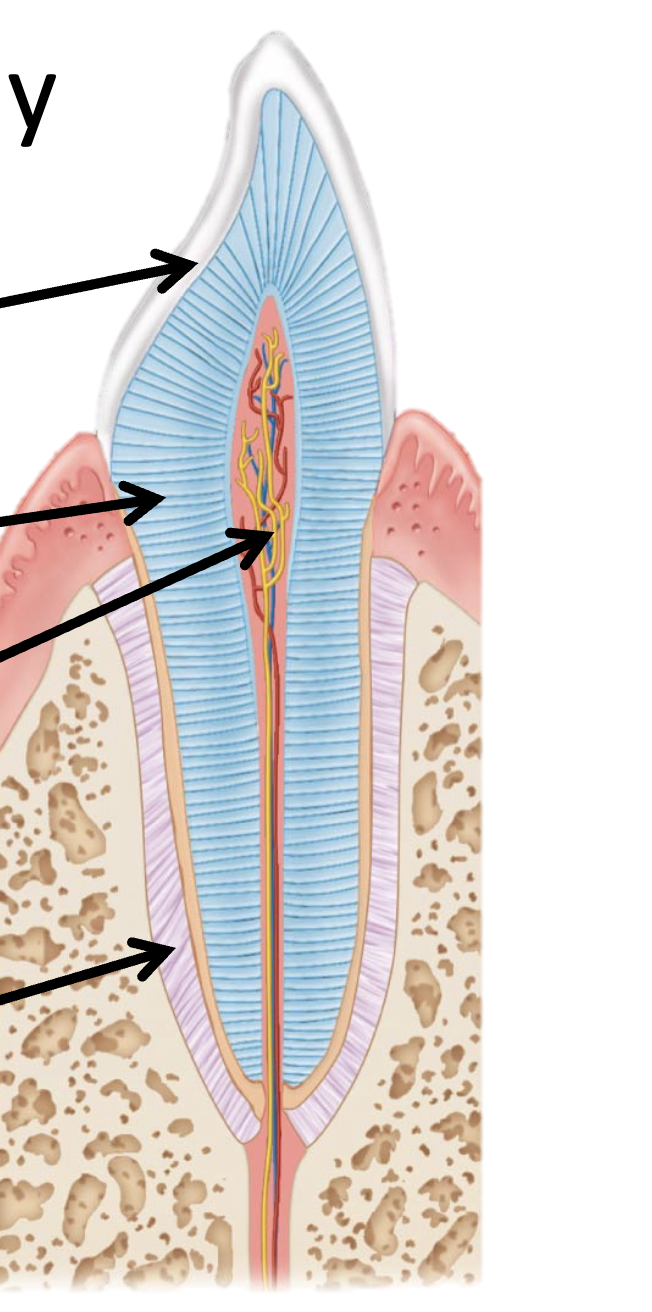
Tooth anatomy
enamel: hardest substance
Dentin: replaced throughout life (living tissue)
Pulp Cavity: Blood supply and innervation
Periodontal ligament: anchors tooth to bone
Tongue
Manipulation of food and creations of bolus
Salivary Glands
where digestion begins, produces saliva
Mostens mouth/food
Enzymes begin digestion
What are the three salivary glands?
Parotid gland
Sublingual glands
Submandibular gland
Peristaltic wave
Contractions of smooth muscles from superior to inferior. Involuntary wave.
Stomach
Muscular bag of many functions. widest part of alimentary canal. Highly acidic. Made up of many enzymes to protect itself from autodigestion.
Why do we need multiple muscle layers in the stomach
muscles do mechanical breakdowns (contract and mix food). mixes with gastric enzymes for chemical breakdown.
Stomach Functions
storage of food usually last 4 hours, produce chyme, and digest proteins
Chyme
Paste resulting from churning food some absorption.
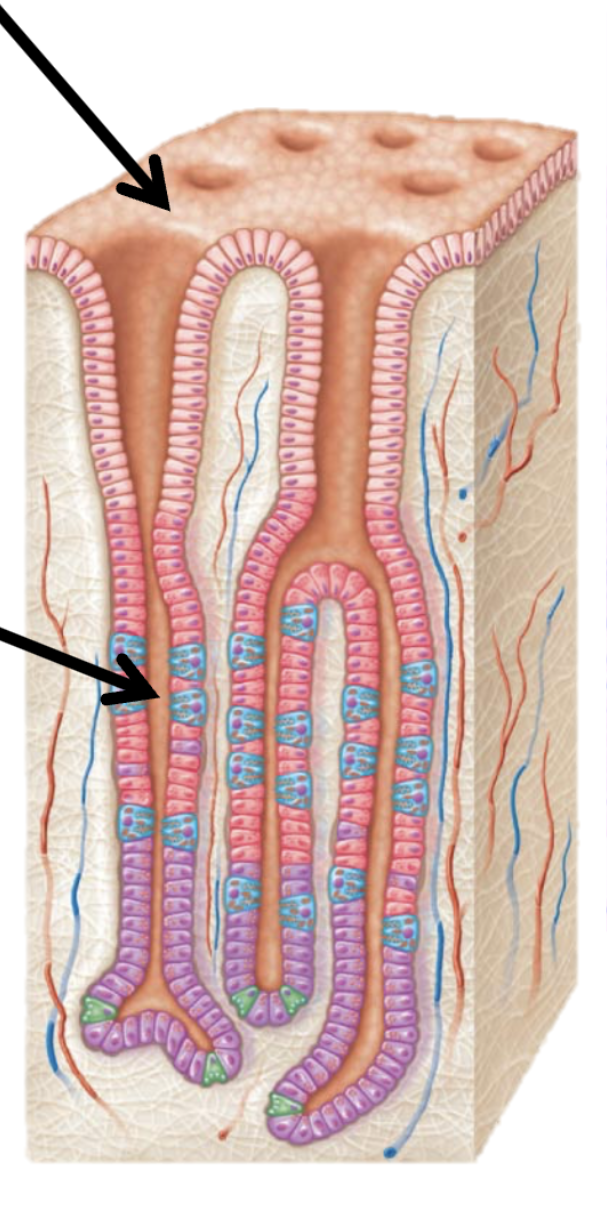
Stomach lining
Surface epithelium: secrete acid buffering mucus
Gastric pit: secretion of pepsin and HCL
Mucous Neck cells
Produce mucus, clear white/substance to cover inner lining of stomach
Gastric glands
Parietal cells and chief cells
Gastric Ulcer
damage to surface epithelium, HCL and pepsin released into the body. A hole in stomach, mucus lining gets damaged or thin, so HCL and pepsin start to autodigest
Gastroesophageal reflux
Due to weakened cardiac sphincter, HCL and pepsin enter the esophagus and get burning sensation.
Small Intestine
Connects to stomach with the large intestine, its purpose is to digest and absorb nutrients
Subdivisions of the small Intestines
Duodenum
jejunum
ileum
Duodenum
First and shortest section, C-shaped. Receives chyme, bile, and enzymes. Final phase of digestion, Neutralizes stomach acid
Liver
Storage of glucose, bile (gallbladder), Vitamins. etc. Detoxifies poisons and drugs. makes blood proteins
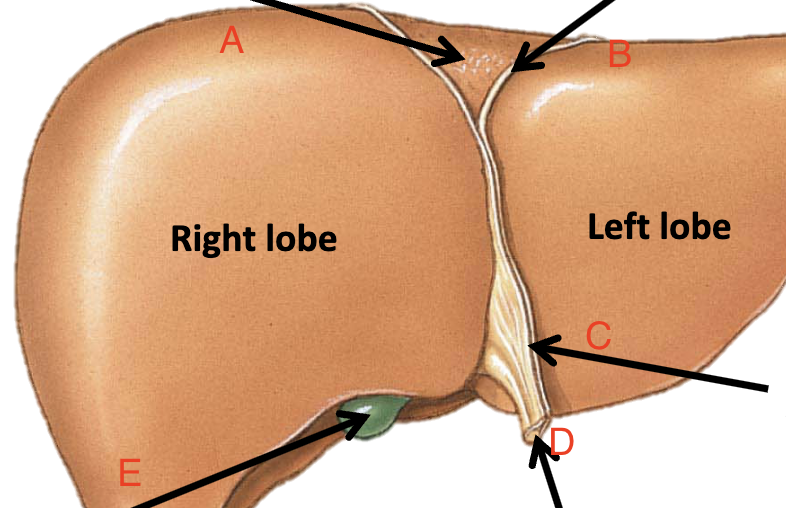
A
Bare area
B
Coronary ligament
C
Falciform ligament
D
Ligamentum teres
E
Gallbladder
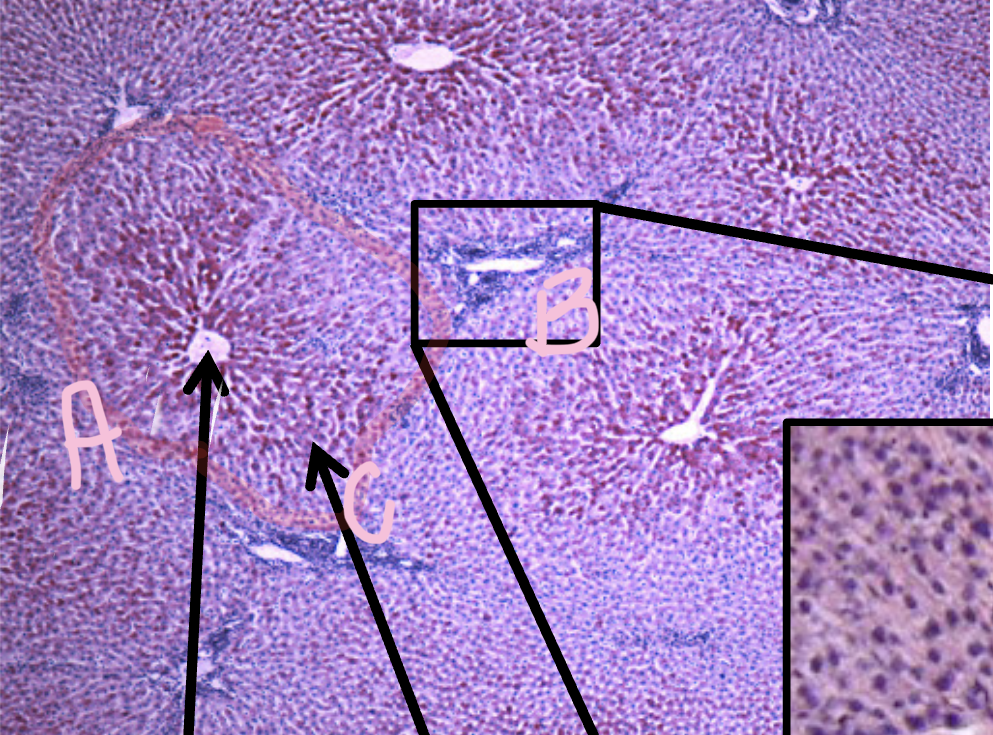
A
Central Vein
B
Portal triad
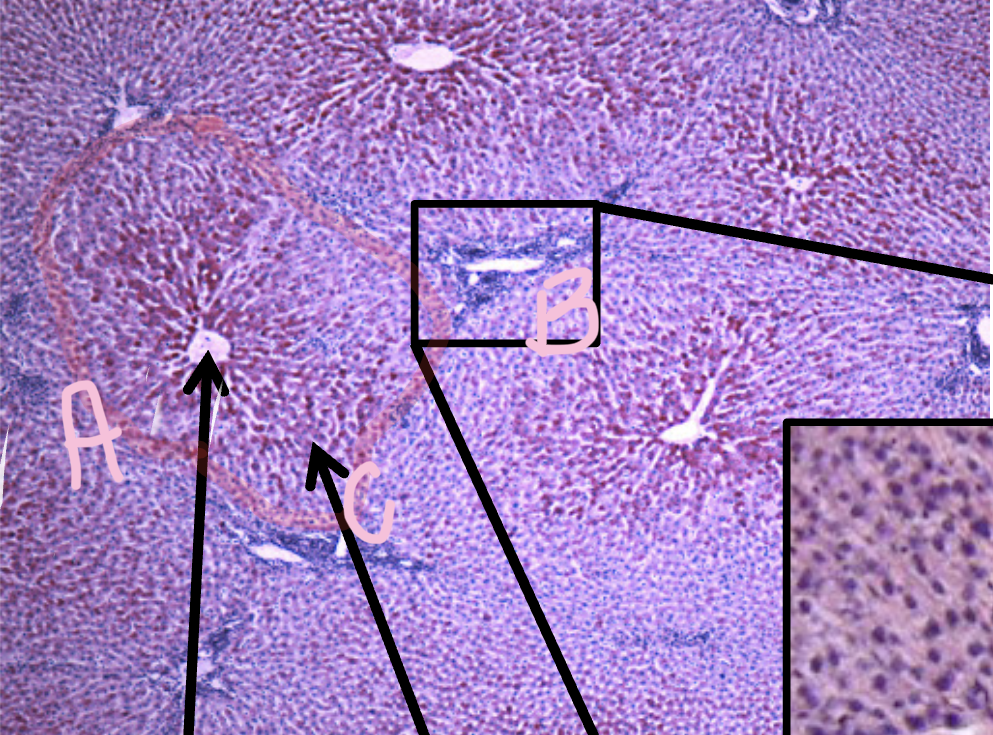
C
Lobule
Portal triad ( three things)
Interlobular bile duct
Interlobular duct
Interlobular artery
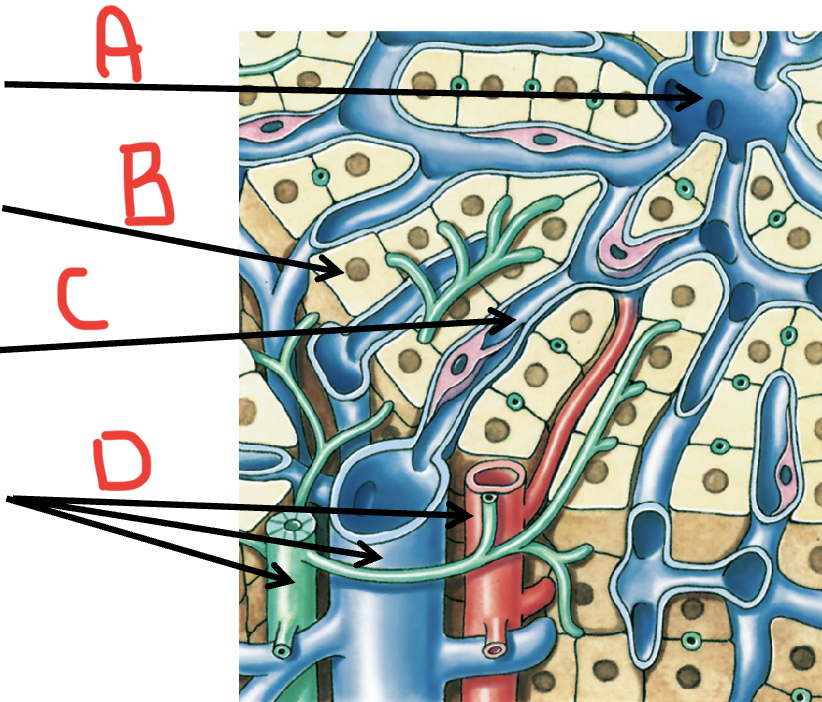
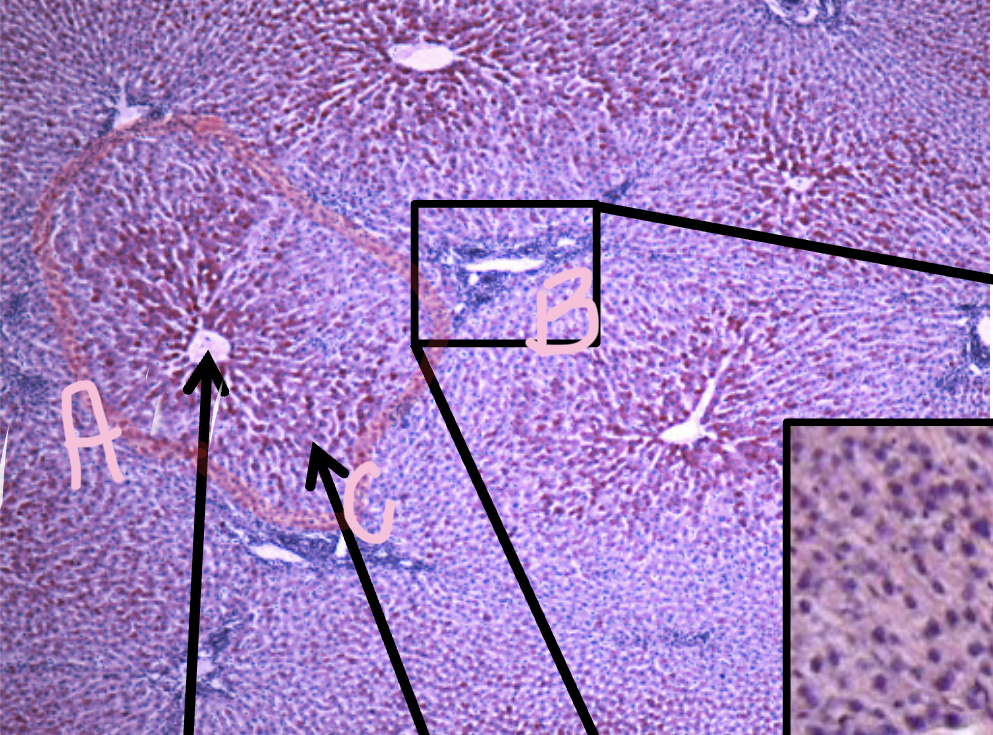
A
Central vein
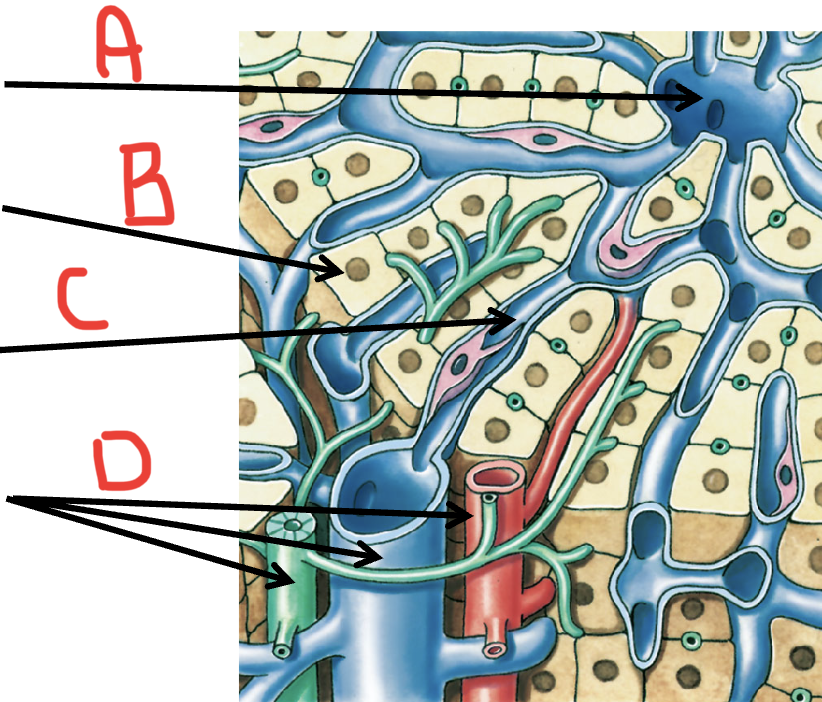
B
Hepatocyte
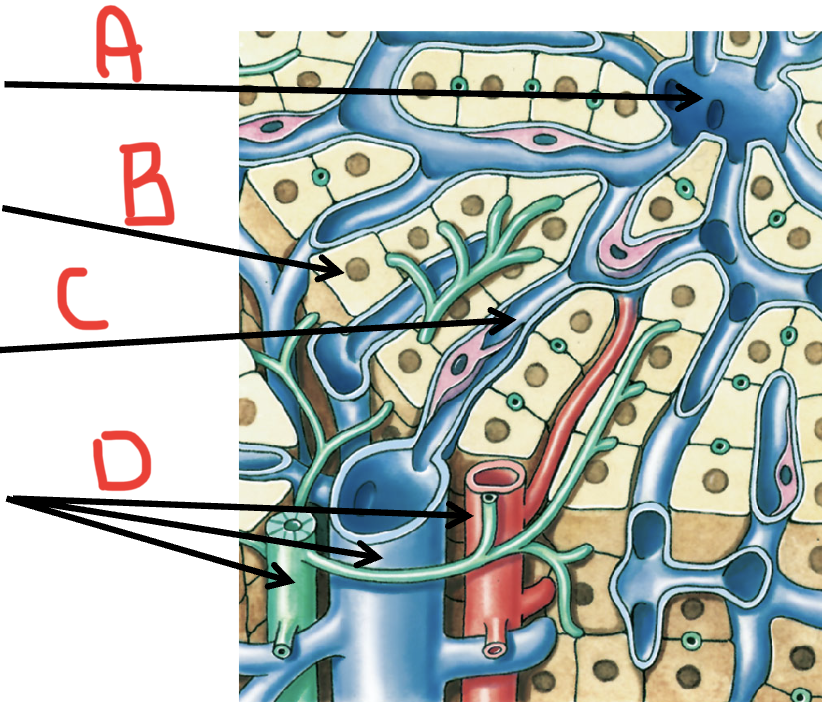
C
Sinusoid
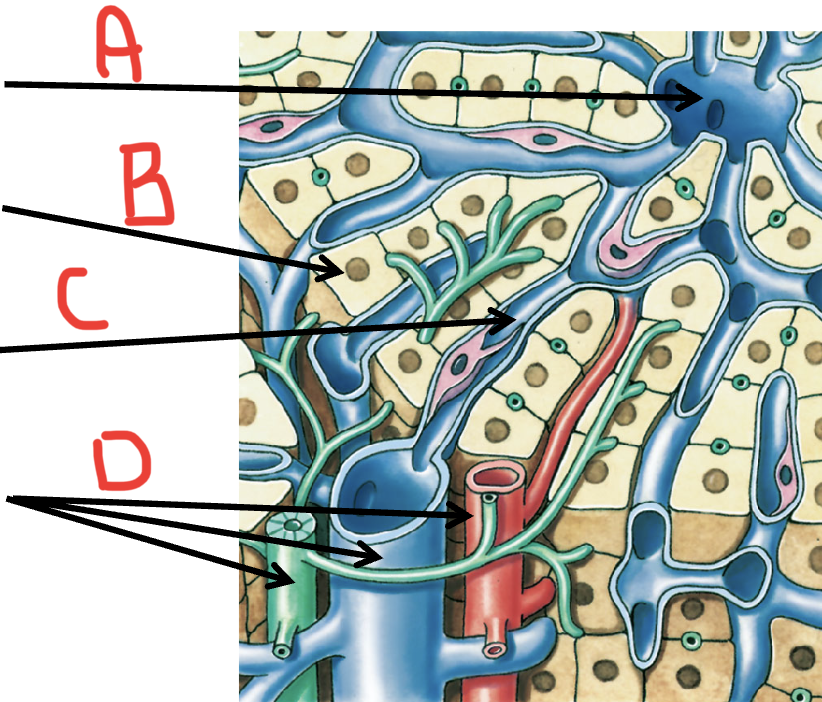
D
portal triad