APES LAST MINUTE REVIEW
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Carbon sequestration
a process by which carbon dioxide (CO2) is captured from the atmosphere or emitted sources and stored long-term instead of being released into the atmosphere
Provisioning services
goods taken directly from ecosystems made from natural resources
Regulating services
natural ecosystems regulate and stabilize climate, water, air quality, soil, biodiversity
Supporting services
natural ecosystem processes that sustain ecosystems and allow them to support life
Cultural services
money generated by recreation (parks, camping, tours) or scientific knowledge
"Every Thing Must Stay Together"
Exosphere
Thermosphere
Mesosphere
Stratosphere
Troposphere
Exosphere
outermost layers, merges into space
Thermosphere
where auroras happen; very hot
Mesosphere
coldest layer; middle
Stratosphere
contains the ozone layer
Troposphere
where the weather happens; closest to Earth
El Nino
-el is like elevated temperatures
-warm waters in the pacific
La Nina
-la is like lowered temperatures
-cool waters in the pacific
Rain shadow effect
occurs when a mountain range blocks prevailing moisture-laden winds, causing one side of the mountain to be relatively dry while the other side receives abundant rainfall
Albedo effect
measure of how much sunlight is reflected by a surface compares to how much is absorbed
O layer (soil horizon)
top layer, organic material, decomposing organisms, humus
A layer (soil horizon)
zone of leaching, made of weathered rock/organic material, second layer, topsoil
B layer (soil horizon)
subsoil, deposited minerals and metal salts
C layer (soil horizon)
bottom of soil, composed of mainly unweathered rock
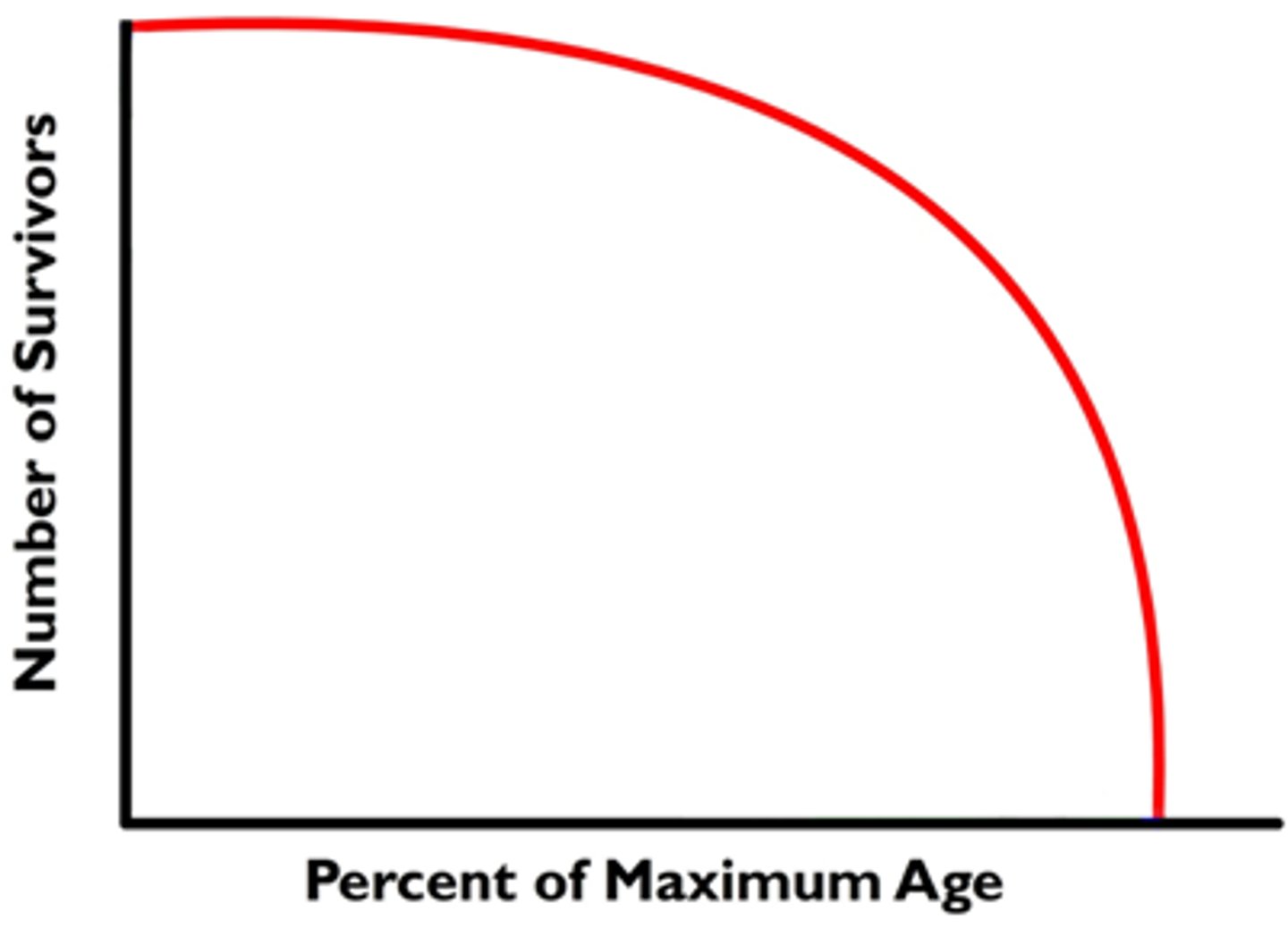
Type 1 survivorship curve
a pattern of survival over time in which there is high survival throughout most of the life span, but then individuals start to die in large numbers as they approach old age
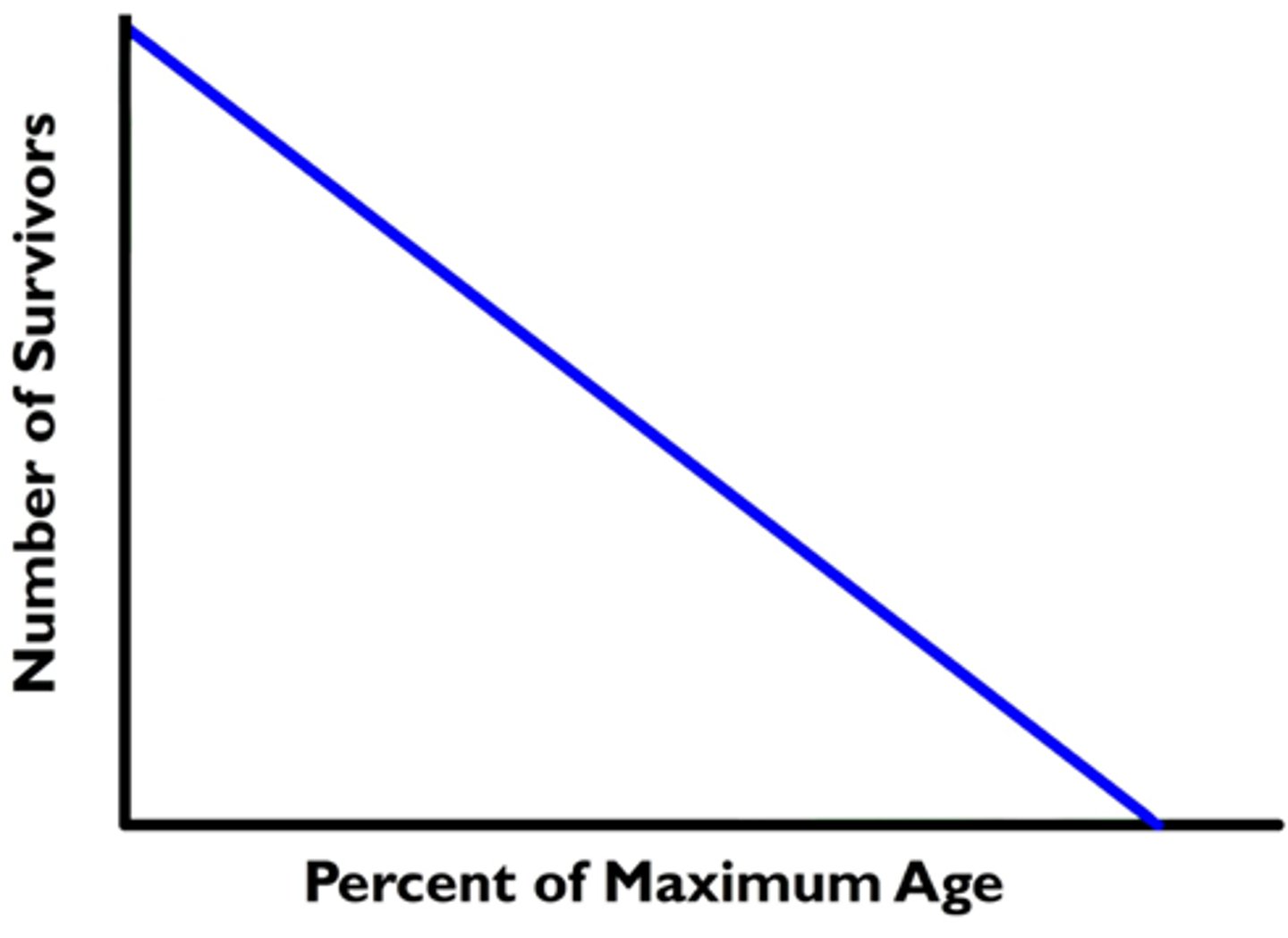
Type 2 survivorship curve
a pattern of survival over time in which there is a relatively constant decline in survivorship throughout most of the life span
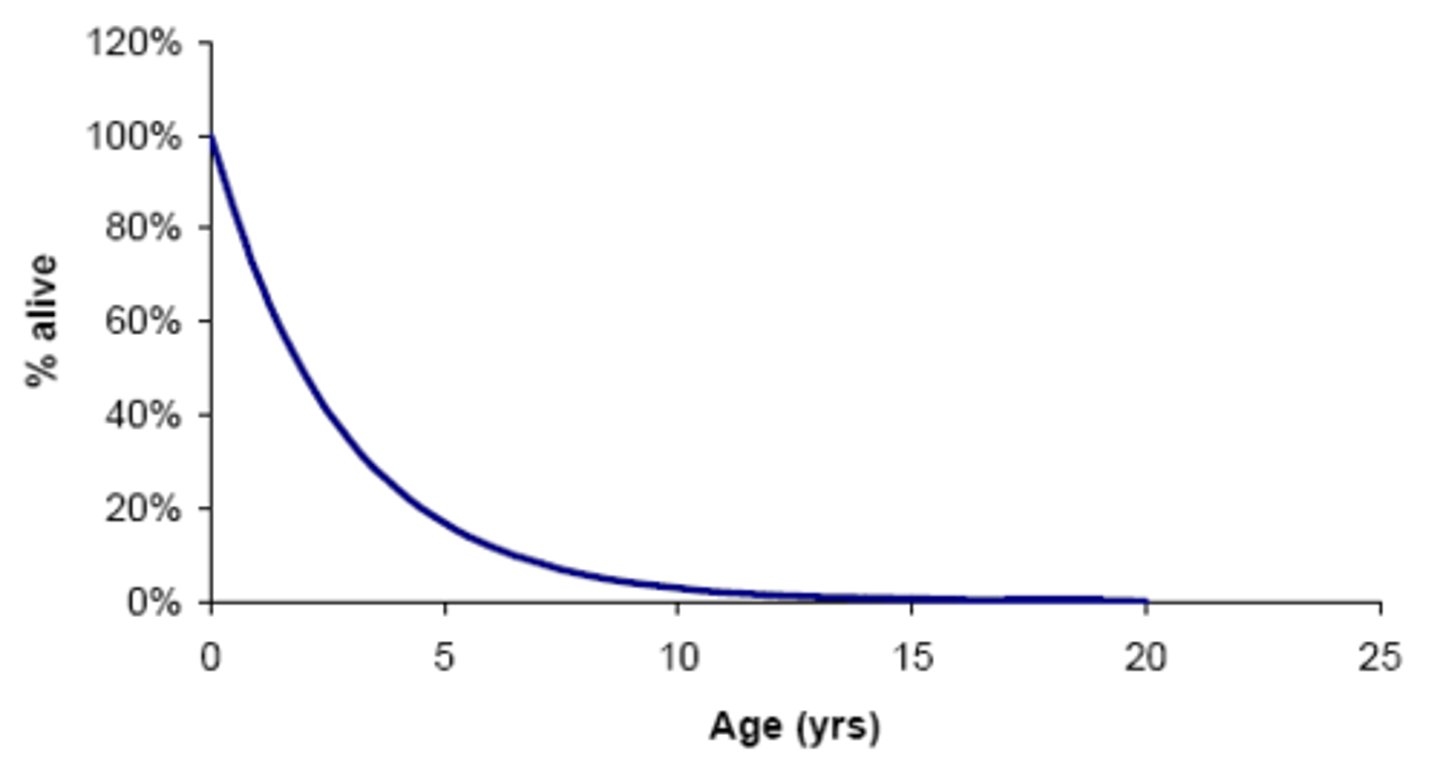
Type 3 survivorship curve
a pattern of survival over time in which there is low survivorship early in life with few individuals reaching adulthood
r-selected species
species that reproduce early in their life span and produce large numbers of usually small and short-lived offspring in a short period.
k-selected species
species that produce a few, often fairly large offspring but invest a great deal of time and energy to ensure that most of those offspring reach reproductive age.
Reducing emissions =
reducing air pollutants
Ways to reduce emissions
-drive less, walk/bike/bus more
-conserve electricity
-eat more plants and less meat
-more renewable NRG sources
CAFE vehicle standards
(Corporate Average Fuel Economy). require all US vehicles to meet certain average fuel mileage (makes manufacturers make more efficient vehicles). raising these standards leads to a decrease in the amount of gasoline burned and pollutants released
Vapor recovery nozzle
an air pollution control device on a gasoline pump that prevents fumes from escaping into the atmosphere when fueling a motor vehicle
Catalytic converter
a device that reduces carbon monoxide emissions from vehicles.
Crushed limestone
used to reduce SO2 from coal power plants
Fluidized bed combustion
a clean-coal technology in which crushed coal is mixed with limestone to neutralize the acidic sulfur compounds produced during combustion
Dry scrubber
a column filled with chemical agents that trap and neutralize SO2, VOCs, and NOx in emissions from coal power plants. Calcium oxide is a common chemical agent that traps and neutralizes these pollutants.
Wet scrubbers
remove particulates by passing the stack gases through water
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)
a family of organic compounds whose properties make them ideal for use in refrigeration and air-conditioning.
Effects of ocean warming on marine species
-disruption of migratory patterns or mating seasons
-habitat loss
-toxic algal blooms
Coral bleaching
occurs when a coral becomes stressed and expels most of its colorful algae, leaving an underlying ghostly white skeleton of calcium carbonate