Quiz #3: Maxillary Anesthesia
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
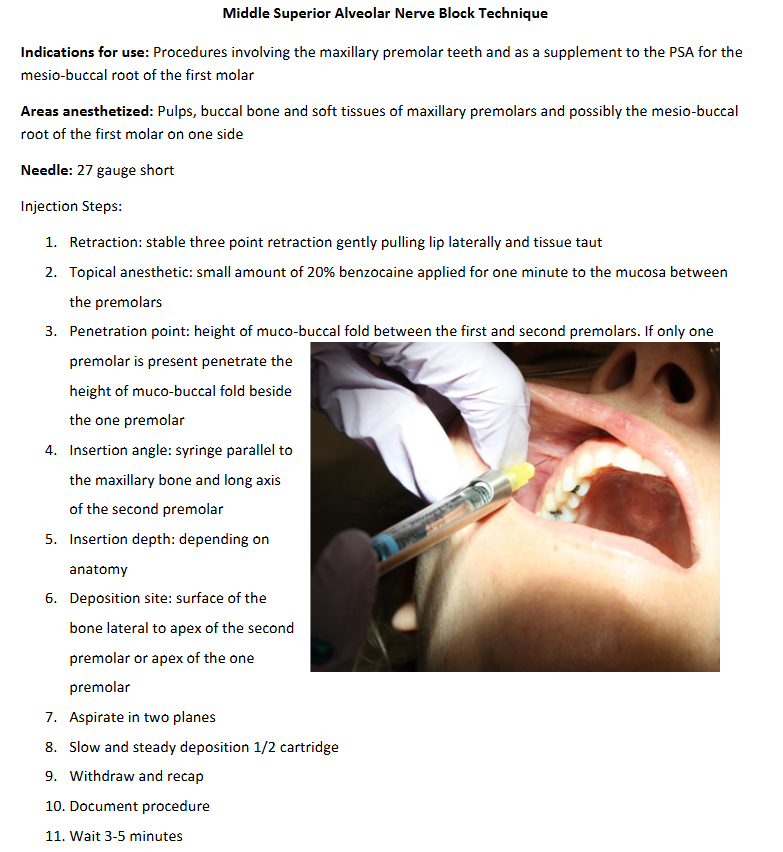
MSA Injection
Errors:
Deposition distal or mesial to apex of 2nd premolar
penetration depth too shallow (not near apex of 2nd premolar)
too lateral away from bone
scraping bevel along bone
not enough anesthetic
watch out for dense bone associated with the zygomatic process of the maxilla
Note:
may also innervate the maxillary sinus (4.28% of population)
may serve as a supplement to the PSA for anesthesia of the MB root of 1st molar
Penetration depth: 4-6mm (depends on anatomy)
may touch bone associated with the zygomatic process of the maxilla
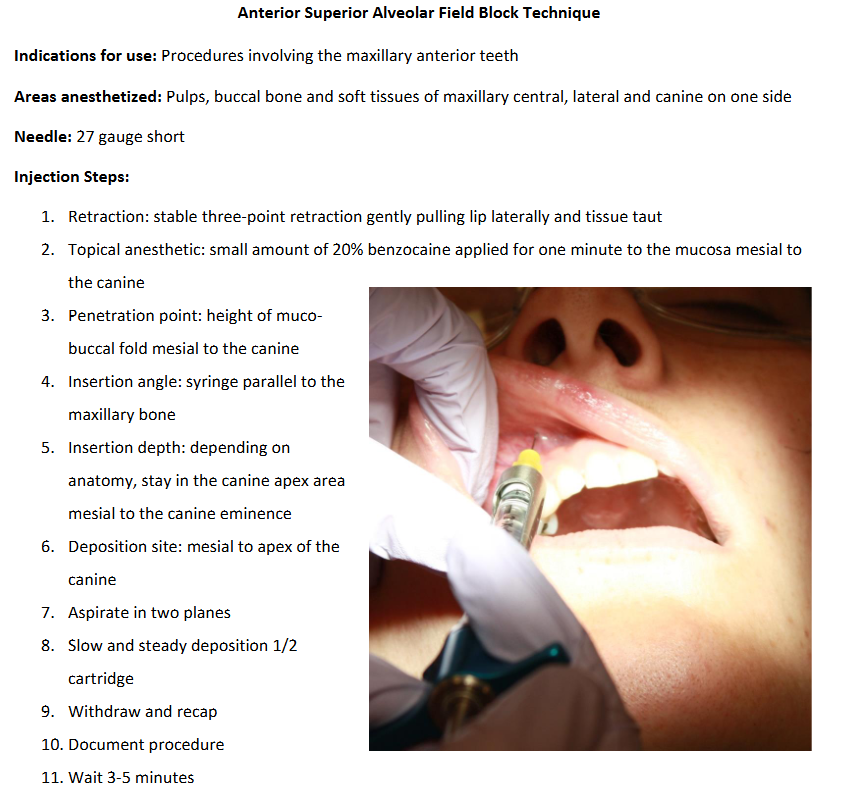
ASA Injection
Errors:
deposition distal to canine eminence
penetration depth too shallow (not near apex of canine)
too lateral away from bone
scraping bevel along bone
not enough anesthetic
midline cross-over: may need to inject above the central incisor on the opposite side
Note:
Penetration depth: 4-6+mm (depends on anatomy)
SP Injection
Contraindications:
tissue infection
dense bone
multiple teeth/large tissue area
Errors:
penetration depth too shallow (not at apex of target tooth)
too lateral away from bone
scraping bevel along bone
not enough anesthetic
Note:
The penetration point involves bisecting the long axis of the tooth!
Penetration depth: 3-5mm (depends on anatomy)

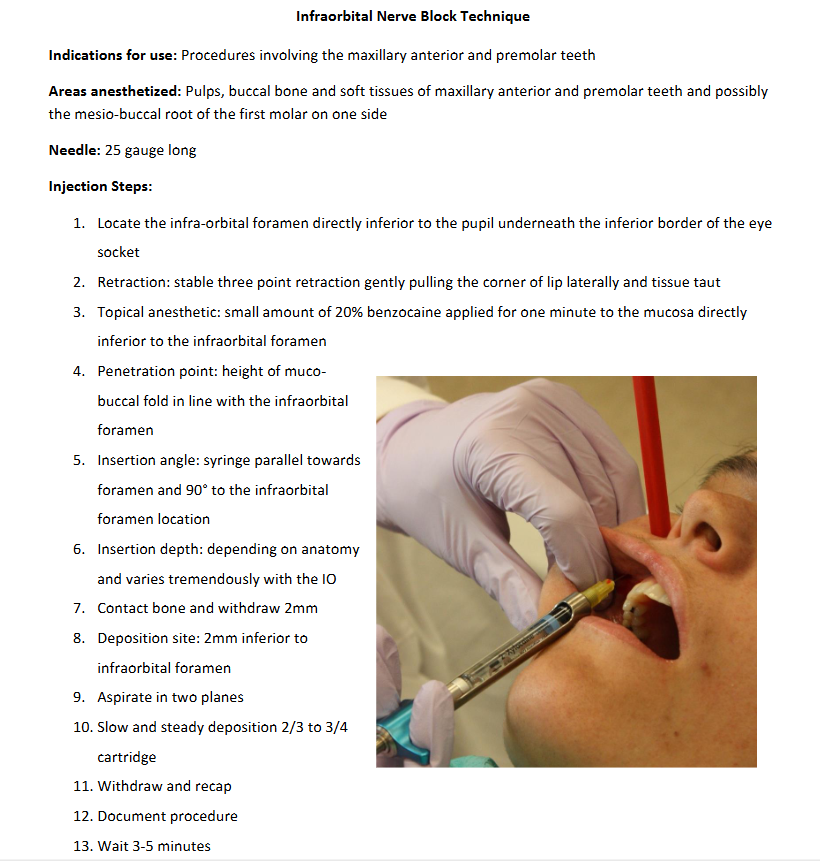
IO Injection
Errors:
penetration site too lateral or too medial (aim in line with pupil!)
deposition site too inferior to infraorbital foramen (you MUST contact bone and use a LONG needle!)
not enough anesthetic
Indications:
pulpal anesthesia on the mx anterior and premolar teeth
pulpal anesthesia on more than two teeth
inflammation which contraindicates an SP injection
SP injection is ineffective due to dense cortical bone
Contraindications:
treatment of one/two teeth only
need for hemostasis
Note:
if the needle buzzes the nerve bundle, stop advancing, pull back 2mm, aspirate, and inject
penetration depth: 12-25mm depending on anatomy
alternatives: ASA & MSA; SP
PSA Injection
Errors:
penetration depth is too lateral, distal, or shallow
scraping the bevel along the bone
not enough anesthetic
deposited anesthesia too far laterally and anesthetized the mandibular nerve instead
Indications:
pulpal anesthesia for more than one tooth
bone too dense for SP
periodontal/surgical procedures requiring anesthesia of buccal tissue and bone adjacent to the molar teeth
Contraindications:
hemophiliacs at risk of hemorrhage
infection/inflammation
Note:
may also numb the mucous membrane of the maxillary sinus
positive aspiration ≠ hematoma
PSA has the HIGHEST risk of post-injection hematoma
hematomas can happen when you enter the pterygoid plexus and nick the maxillary artery
you are entering the pterygomaxillary fossa
insertion depth: 13-16 mm depending on anatomy (“hubba-hubba” = stop penetrating when the hub is parallel with the CEJ of the 2nd molar)

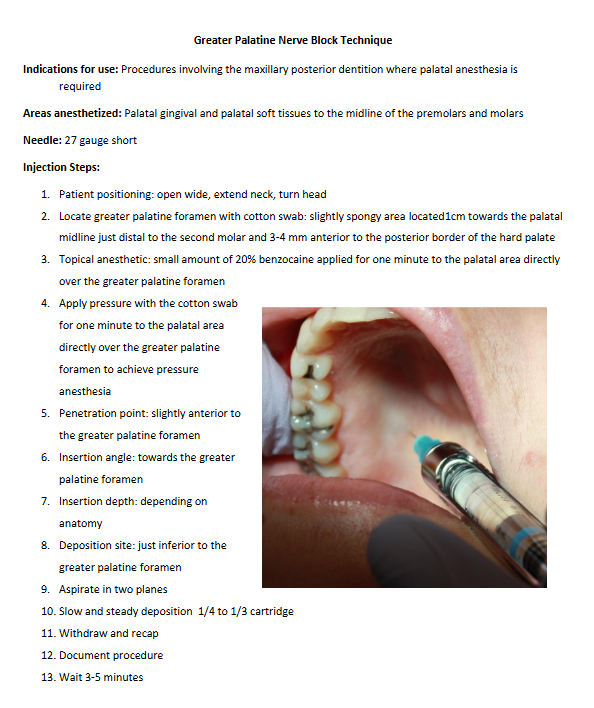
GP Injection
Errors:
too fast/too much deposited: ischemia and necrosis
too fast deposit: sloughing
soft palate anesthetized
Contraindications:
inflammation/infection at injection site
Note:
insertion depth: 5-6mm depending on anatomy
hematomas are rare
deposit 0.4-0.6 mL (1/4-1/3 cart) over 30 sec
NP Injection
Errors:
too fast/too much deposited: ischemia and necrosis
sterile abscess
too fast deposit: sloughing
soft palate anesthetized
inserted directly into incisive papilla/penetrated foramen
Contraindications:
inflammation/infection at injection site
Note:
you will see tissue blanching
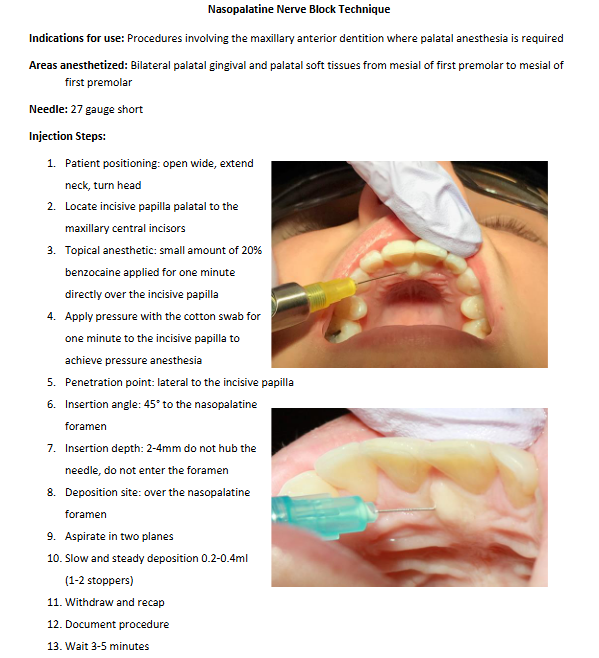
Local Infiltration
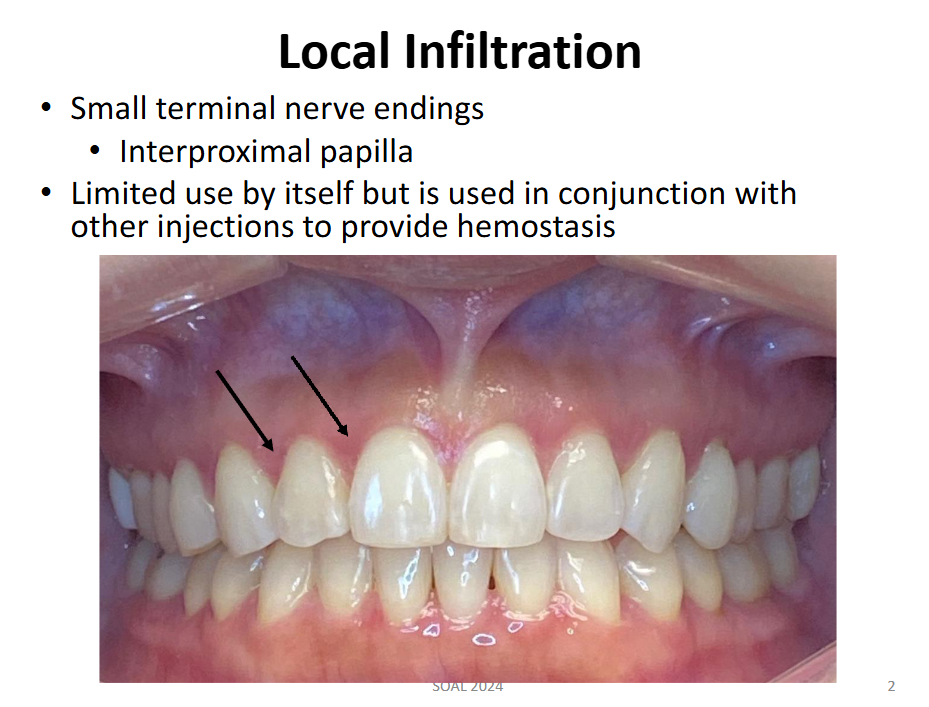
Field Block
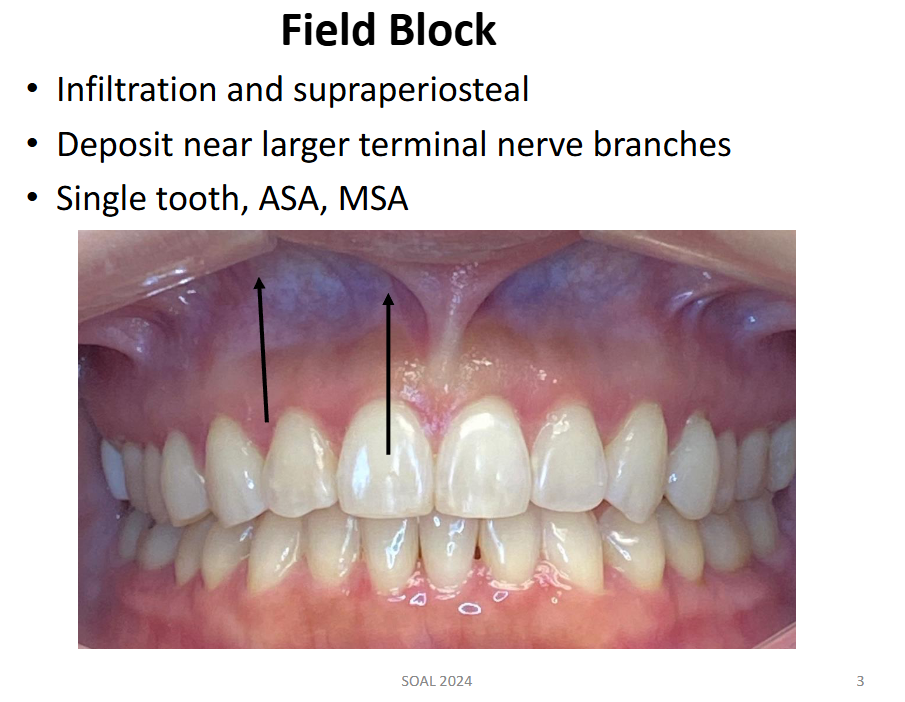
Nerve Block
1.) GP means __________________
Greater Palatine
2.) NP means __________________
Nasopalatine
3.) PSA means __________________
Posterior Superior Alveolar
4.) Which type of needle is used for the following injections?
a. ASA
b. MSA
c. IO
d. PSA
e. GP
f. NP
a. ASA: 27 gauge short
b. MSA: 27 gauge short
c. IO: 25 gauge long
d. PSA: 27 gauge short
e. GP: 27 gauge short
f. NP: 27 gauge short
5.) The teeth anesthetized for the ASA are:
a) Maxillary central incisors
b) Maxillary central and lateral incisors
c) Maxillary central incisor to the canine
d) Maxillary central incisor to the MB root of the 1st molar
a) Maxillary central incisors
b) Maxillary central and lateral incisors
c) Maxillary central incisor to the canine
d) Maxillary central incisor to the MB root of the 1st molar
6.) The deposition site for the ASA is the:
a) Apex of the central incisor
b) Medial to the apex of the lateral incisor
c) Distal to the apex of the canine
d) Mesial to the apex of the canine
a) Apex of the central incisor
b) Medial to the apex of the lateral incisor
c) Distal to the apex of the canine
d) Mesial to the apex of the canine
7.) The deposition site for the MSA is the:
a) Above the apex of the 2nd premolar
b) distal of the canine
c) above the apex of the MB root of the 1st molar
d) infraorbital foramen
a) above the apex of the 2nd premolar
b) distal of the canine
c) above the apex of the MB root of the 1st molar
d) infraorbital foramen
8.) The teeth anesthetized for the MSA are:
a) maxillary 1st and 2nd premolars and MB root of the 1st molar
b) maxillary 1st and 2nd premolars and mesial of the canine
c) maxillary 1st, 2nd, and 3rd molars
d) maxillary 1st, 2nd, and 3rd molars except for the MB root of the 1st molar
a) maxillary 1st and 2nd premolars and MB root of the 1st molar
b) maxillary 1st and 2nd premolars and mesial of the canine
c) maxillary 1st, 2nd, and 3rd molars
d) maxillary 1st, 2nd, and 3rd molars except for the MB root of the 1st molar
9.) The deposition site for the IO is:
a) inside the infraorbital foramen
b) above the apex of the 1st premolar
c) 2mm superior to the infraorbital foramen
d) 2mm inferior to the infraorbital foramen
a) inside the infraorbital foramen
b) above the apex of the 1st premolar
c) 2mm superior to the infraorbital foramen
d) 2mm inferior to the infraorbital foramen
10.) The teeth anesthetized for the IO are the:
a) maxillary central incisor to the MB root of the 1st molar
b) maxillary 1st and 2nd premolars and MB root of the 1st molar
c) maxillary 1st, 2nd, and 3rd molars
d) maxillary central incisor to the canine
a) maxillary central incisor to the MB root of the 1st molar
b) maxillary 1st and 2nd premolars and MB root of the 1st molar
c) maxillary 1st, 2nd, and 3rd molars
d) maxillary central incisor to the canine
11.) The deposition site for the nasopalatine nerve block is:
a) behind the canine
b) 2mm inferior to the greater palatine foramen
c) over the nasopalatine foramen
d) inside the nasopalatine foramen
a) behind the canine
b) 2mm inferior to the greater palatine foramen
c) over the nasopalatine foramen
d) inside the nasopalatine foramen
12.) The nasopalatine nerve block anesthetizes the:
a) central incisor to canine
b) anterior palatal tissues from canine to canine
c) palatal soft tissues distal to canine
d) palatal soft tissues in the molar region only
a) central incisor to canine
b) anterior palatal tissues from canine to canine
c) palatal soft tissues distal to canine
d) palatal soft tissues in the molar region only
13.) The greater palatine nerve block anesthetizes the:
a) canine to MB root of the 1st molar
b) anterior hard palate from canine to canine
c) palatal tissues distal to the canine
d) palatal tissues in the molar region only
a) canine to MB root of the 1st molar
b) anterior hard palate from canine to canine
c) palatal tissues distal to the canine
d) palatal tissues in the molar region only
14.) The deposition site for the greater palatine nerve block is:
a) behind the 3rd molar
b) 2mm inferior to the greater palatine foramen
c) over the nasopalatine foramen
d) inside the greater palatine foramen
a) behind the 3rd molar
b) 2mm inferior to the greater palatine foramen
c) over the nasopalatine foramen
d) inside the greater palatine foramen
15.) What is a potential but rare complication while administering the PSA injection?
PSA injections can result in an extraoral hematoma.
16.) What is the correct sequence for managing a PSA hematoma?
a) rest, ice, compression
b) nothing as it will go away on its own
c) administer more anesthetic
d) compression, ice, analgesics, time
a) rest, ice, compression
b) nothing as it will go away on its own
c) administer more anesthetic
d) compression, ice, analgesics, time
17.) Give reasons related to the clinician as to why PSA hematomas may happen.
inexperience
probing with needle
inappropriate needle length/using long needles in highly vascular areas
multiple penetrations into the same site
rough handling of pt
18.) Give reasons related to the patient as to why PSA hematomas may happen.
bleeding disorders (e.g. hemophilia)
Blood Thinners
Fragile tissues from inflammation / age (loss of fat pads)
19.) TRUE or FALSE: All positive PSA aspirations result in extensive hematomas.
FALSE
20.) Describe the deposition site for the PSA injection.
posterior, superior, and medial to the maxillary tuberosity
21.) What structures are innervated by the PSA?
pulps, buccal bone, and buccal soft tissues of the maxillary molars on one side (possible exception: MB root of 1st molar)
22.) Upon aspiration, you see a worm of blood enter the cartridge. Your next step is to:
pull back a few mm, reposition the needle, then reaspirate in two planes
23.) Upon aspiration, you see a cloud of blood entering the cartridge. Your next step is to:
completely remove the needle from the tissues, change the needle and cartridge, then reinsert the needle and reaspirate in two planes
24.) Topical anesthetic for palatal injections should last for:
a) 1 minute of topical and pressure together
b) 1 minute of pressure followed by 1 minute of topical
c) 1 minute of topical followed by pressure
d) 1 minute of topical only
a) 1 minute of topical and pressure together
b) 1 minute of pressure followed by 1 minute of topical
c) 1 minute of topical followed by pressure
d) 1 minute of topical only
25.) Topical anesthetic should stay on the injection site for how long before an injection is administered?
1 minute
26.) Aspiration must be done:
a) as the needle advances
b) in two planes
c) at the penetration site
d) after withdrawal
a) as the needle advances
b) in two planes
c) at the penetration site
d) after withdrawal
27.) A blue needle is _____ gauge.
A blue needle is 30 gauge.
28.) A red needle is _____ gauge.
A red needle is 25 gauge.
29.) A yellow needle is _____ gauge.
A yellow needle is 27 gauge.
30.) 1.5 cartridges of 3% mepivacaine contains _____mg of mepivacaine.
1.5 cartridges of 3% mepivacaine contains 76.5 mg of mepivacaine.
.
1.5 cart × 51mg/cart = 76.5mg mepivacaine
31.) 1.75 cartridges of 2% lidocaine with 1:100,000 epinephrine contains _____mg lidocaine and _____mg epinephrine.
1.75 cartridges of 2% lidocaine with 1:100,000 epinephrine contains 59.5 mg lidocaine and 0.02975 mg epinephrine.
.
1.75 cart x 34mg/cart = 59.5mg lidocaine
1.75 cart x 0.017mg/cart = 0.02975mg epi
32.) 1.25 cartridges of 4% prilocaine with 1:200,000 epinephrine contains _____mg prilocaine and _____mg epinephrine.
1.25 cartridges of 4% prilocaine with 1:200,000 epinephrine contains 85 mg prilocaine and 0.010625 mg epinephrine.
.
1.25 cart x 68mg/cart = 85mg prilo
1.25 cart x 0.0085mg/cart = 0.010625mg epi
33.) 2.5 cartridges of 4% articaine with 1:100,000 epinephrine contains _____mg articaine and _____mg epinephrine.
2.5 cartridges of 4% articaine with 1:100,000 epinephrine contains 170 mg articaine and 0.0425 mg epinephrine.
.
2.5 cart x 68mg/cart = 170mg art
2.5 cart x 0.017mg/cart = 0.0425mg epi
34.) 3 cartridges of 0.5% bupivacaine with 1:200,000 epinephrine contains _____mg bupivacaine and _____mg epinephrine.
3 cartridges of 0.5% bupivacaine with 1:200,000 epinephrine contains 25.5 mg bupivacaine and 0.0255 mg epinephrine.
.
3 cart x 8.5mg/cart = 25.5mg bup
3 cart x 0.0085mg/cart = 0.0255mg epi