nuclear reactions/radioactivity/half life
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
what is evidence for the strong nuclear force
in order to overcome the Coulomb repulsion force there must be a powerful force that prevents the nucleus from splitting (SNF)
long range force
a force that keeps its strength as distance increases, only slightly dropping in strength (ex. electromagnetic coulomb force)
short range force
force that is only effective over short distances and loses strength as its applied over a greater distance (ex. strong nuclear force)
effects of the strong nuclear force
allows for the material world
allows for the existence of all elements that make u our natural word and our bodies
what does the “e” in e=mc² say
that mass is energy (that they are not separate things)
rest energy
different from other types (KE or PE) matter has rest energy even if its not moving, or high above the ground or electrically charged
what does e=mc² show
that a small amount of matter is equivalent to a very large amount of energy
mass definicicy
mass differences between expected mass and actual mass - “missing mass” is released as energy
binding energy
the energy it takes to break apart a nucleus
E(binding) = mass definicicy x c²
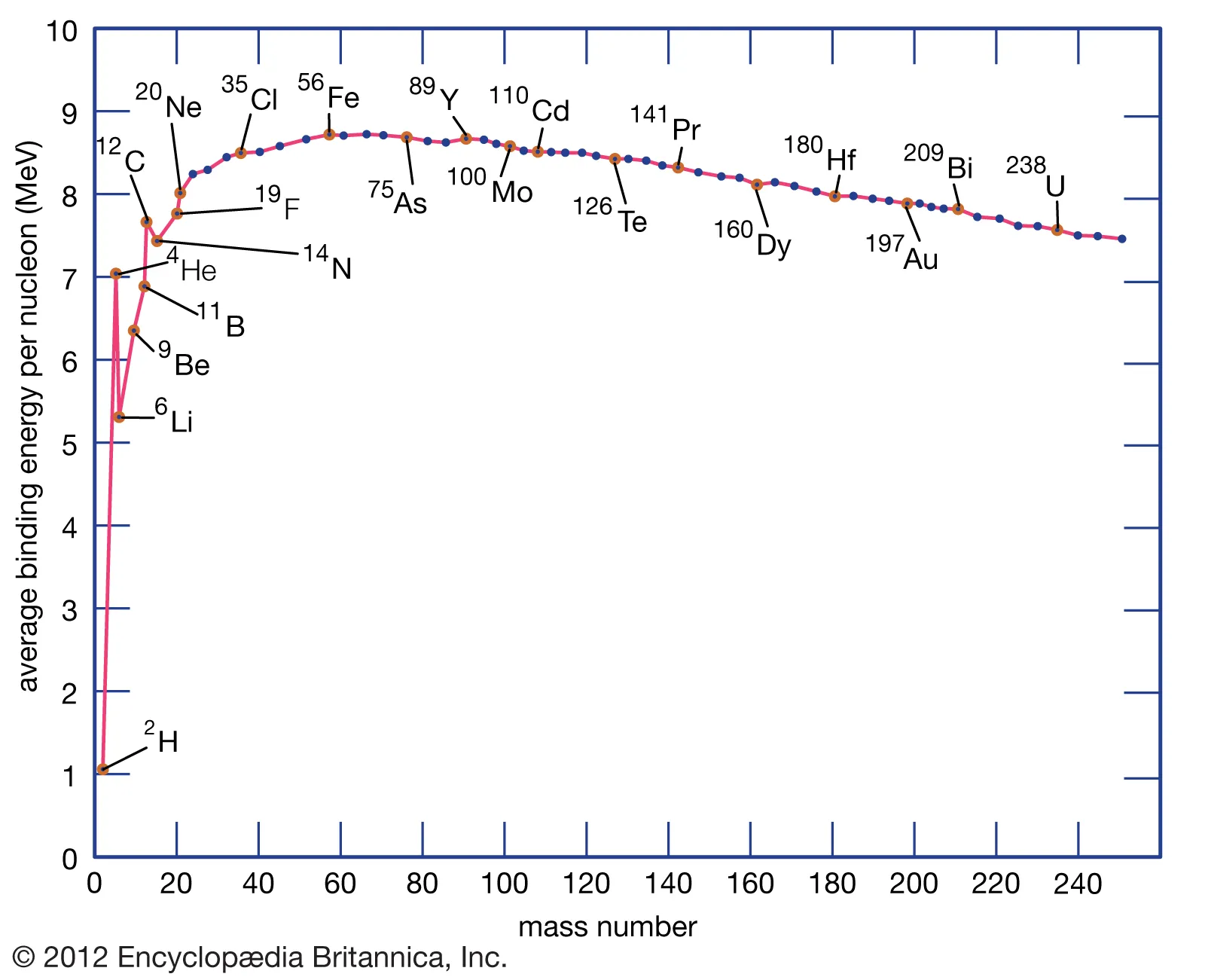
whats unique about iron
its has the lowest energy - before iron the elements pack the nucleus causing the strong force and binding energy to go up but after iron the binding energy goes down
when does radioactivity get released
when a nucleus undergoes radioactive decay
what will an unstable nucleus do
will spontaneously decay into a more stable nucleus (new nucleus will have less mass, more mass deficiency - “missing mass” is released as energy)
what are types of radioactive decay
alpha
beta
gamma
alpha decay
a nucleus splits into an alpha particle and new nucleus (atomic # goes down by 2, mass down by 4)
alpha radiation can be stopped by a couple inches of air
beta decay
a neutron decays into a proton and electron (atomic number goes up by 1)
electrons emitted during neutron decay = beta particles
beta radiation can be stopped by a piece of paper
is evidence for a presence of a 4th force of nature - weak nuclear force
gamma decay
the excited nucleus emits a gamma ray (high energy photon) - doesn’t change the number of protons or neutrons in the nucleus
only blocked by a lead shield (dangerous)
what do nuclear reactions involve
involve lots of energy - either forming or breaking the strong nuclear force
what two things can occur during nuclear reactions
energy is released - new nucleus is formed with lower energy - (fusion reactions)
energy input - new nucleus is formed with higher energy (fission reactions)
fusion reaction
2 nuclei fuse together to form a heavier nucleus
massive amount of energy is released
how can nuclear fusion happen
you need to smash the nuclei into each other at such a fast speed that they overcome to coulomb law
give the nuclei massive amounts of KE by heating them
nuclear fission
nucleus is split
if new nucleus has less energy then large amounts are released
can only happen with elements heavier than iron
how can nuclear fission happen
we fire a high speed neutron at a nucleus, this destabilizes the nuclei causing a chain reaction, than an explosion
what two things are needed to generate a lot of usable energy
temp > 10,000,000 degrees celsius
an extreme amount of fusion reactions
is a large nucleus very stable
no, the SNF is a short range force (will get weaker as nucleus gets bigger) + the mass would be large and using e=mc² it shows how there would be a lot of energy meaning its more unstable
half-life
the time it takes for half of the atoms in a smaller to decay
radiation
the emission or transmission of energy in the form of waves or particles through space