Planetary Geology Quest 1
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
Mercury
0.39 AU
Venus
0.72 AU
Earth
1 AU
Mars
1.52 AU
Jupiter
5.20 AU
Saturn
9.54 AU
Uranus
19.19
Neptune
30.07
Pluto
Dwarf Planets
the formal definition of a planet
A planet is a celestial body that is in orbit around the sun, has a round shape, and has cleared the neighborhood around its orbit
Nicholas Copernicus
1473 - 1543
The Center of the earth is not the center is not the center of the universe
Tycho Brahe
1546 - 1601
o Observed a supernova, and periodic comets, proof that the stars and planets are not fixed and constant, meticulously determined position and motion of planets
Galileo Galilei
1564 - 1642
o Systemically used telescope and recorded his observations, satellites orbiting Jupiter, phases of Venus, Saturn Rings, Craters and mountains on the moon, sunspots
Johannes Kepler
1571 - 1630 Tycho Brahe students, deduced 3 laws of planetary motion
Daniel Kirkwood
1866 ~ noticed depleted gaps in the asteroid belt
Kepler’s laws
1st: orbits are ellipses not circles
• 2nd: equal areas in equal time
• 3rd: semi-major axis cubed equals period squared for all planets orbiting the sun)
Newtonian gravity
N2: F=ma = F(gravity) = G(universal gravitional constant) M(mass of sun) m(mass of planet)) / r(distance between sun and planet)^2, Mass of earth = 5.9E24
Reflectance
measure the amount of light reflected from a surface across different wavelengths
absoption spectra
measure the amount of light absorbed by a material, usually by detecting the light transmitted
multi - spectra
3-50 "wider" band
hyper - spectral
hundreds of narrow band
Temporal
how often is the same location imaged
spatial
how much "ground" is being imaged and can be resolved, spatial resolution determines what can be
resolved in an image or data file
Spectral
number and width of bands
radiometric
8 vs 16 bit (# of tones/colors); 256 (2^8), 65,536(2^16)
Stars
Sunspots, Sun outer layer consist of chromosphere, transition region, and the corona,
Sunspots
temporary, dark, cooler region on the sun surface that develop where magnetic fields are really strong, blocking heat from reaching the surfaces
Supernova
generate elements heavier than iron, then scattered to the cosmos
Radioactivity
Neutron disintegrate into positron and electron
proto-planetary disc
dense clumps in a collapsing molecular cloud form a disc (a disk of gas and dust around a young star), Protostar
o Central Region
o Soot Line
o Snow/Frost Line
Central Region
only metals and minerals condense into planets
Snow/frost line
The boundary in a protoplanetary disk beyond which the temperature is cold enough for gases like water vapor to condense into solid ice grains forming small planets like Earth, creating Solar System
Disk instability Model
Clumps of gas collapse in circumstantial
Core Accretion Model
Planet agglomerates from dust and attract gas envelop
Refractory
chemical precipitates arranged by distance from the protosun
Asteroids
rocky, airless remnants left over from the early formation of our solar system
Comets
cosmic snowballs of frozen gases, rock, and dust that orbit the Sun, The dust and gases form a tail that stretches away from the Sun for millions of miles
o Tails ~ Ion & Dust
o Nucleus & Coma ~ Solid body of comet, gas and dust
o Trails ~ Large solid debris left behind on orbital path
Meteors
When meteoroids enter Earth’s atmosphere, or that of another planet, at high speed and burn up, they’re called meteors
Meteorites
space rocks that range in size from dust grains to small asteroids, Most meteoroids are pieces of other, larger bodies that have been broken or blasted off like comet, asteroids, moon
Asteroid Belts
a ring-shaped region of space located between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter, populated by asteroids
Trojan Asteroids
celestial bodies that share a planet's orbit and are located at stable gravitational points, called Lagrange points, ahead of and behind the planet
Near-Earth Asteroids
Amors
Orbit outside 1 AU
Mars Crossing
o Appolos
Semi-major axis > 1 AU
Earth & Mars Crossing
o Atens
Semi-major axis < 1 AU
Venus and earth crossing
Heliosphere
the cavern carved out of the interstellar gas by the solar wind
The Oort cloud
contains billions of comet nuclei in a spherical distribution that extends out up to 50,000 AU from the Sun
Celestial Line/equator
The celestial equator is an imaginary line on the celestial sphere that lies directly over Earth's equator
Ecliptic line
represents the plane in which the planets orbit, seen from our position within the plane itself
ecliptic line vs celestial line
The ecliptic line is based on earth's motion around the sun while the celestial line is based on earth rotational axis, there is a 23.5 degree difference which is the earth axial tilt
alpha process
carbon, oxygen, neon, magnesium, silicon, sulfur, argon, and calcium, which are produced in stars and supernovae through nuclear fusion reactions that build upon the alpha particle
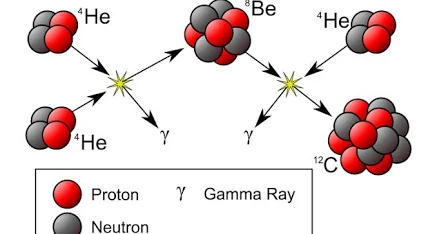
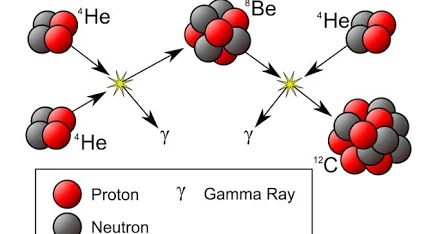
Triple alpha process
The triple-alpha process is a set of nuclear fusion reactions where three helium nuclei (alpha particles) fuse to create a carbon-12 nucleus. This process begins with two alpha particles combining to form an unstable beryllium-8 nucleus, which then captures a third alpha particle before it can decay. The creation of carbon through this process requires specific stellar conditions, including high temperatures and densities, and the existence of a resonant energy state in carbon-12 known as the Hoyle state.
CNO Process
a process of nuclear fusion in stars where hydrogen is converted into helium using carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen as catalysts, which are regenerated at the end of the cycle. This cycle produces energy and is the dominant source of energy in stars more massive than the Sun

Iron Peak
a group of chemical elements from Scandium (Sc) to Germanium (Ge) that are characterized by having high binding energy per nucleon, making them the most stable nuclei formed during stellar nucleosynthesis
Gamma Rays
1E-12 meters
o water equivalent hydrogen abundance
o Spatial Resolution
X-rays
1E-10 meters
Ultraviolet Rays
1E-8, Venus Blue
Visible Light
4E-7 ~ 7E-7
o Albedo ~ reflecting power of a surface
o Morphology ~ Dunes on Earth and Mars
Infrared Rays
1E-6
o Measures a material’s resistance to change in temperature, Meridiani Planum
Micro-wave
1E-3
o Morphology and Stratigraphy, Polar ice caps on Mars, Dunes and Lakes on Titan
Radio
1E1
o Morphology and Stratigraphy, Polar ice caps on Mars, Dunes and Lakes on Titan